theme 2
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
hematopoiesis → what is it + what does it make + regulated by
formation of blood cells from HSC in BM
produces erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets
regulated by cytokines and growth factors → epo, tpo, g-csf
HSC = hematopoietic cell (character, act by?)
self renewing, multipotent
activated by stress or injury
myeloid lineage → produces (4) + controlled by
produces:
erythrocytes
megakaryocytes → platelets
monocytes
granulocytes
controlled by mainly cytokines → epo, tpo, gm-csf
lymphoid lineage produces (3) + controlled by
produces:
B cell
T cell
NK cell
regulated by IL7 and antigenic stimulation in lymhoid organs
cytokines in hematopoiesis
EPO: stimulates RBC production.
TPO: regulates platelet production.
G-CSF/GM-CSF: stimulate granulocyte/monocyte formation.
IL-3, IL-6, SCF: early progenitor stimulation.
stress hematopoiesis (HT) (what happens, driven by, might do to compensate)
enhanced HT activity during infection, bleeding or hypoxia
driven by incr cytokine release
may activate extramedullary HT (spleen, liver)
dysregulated HT
disruption of normal diff/prolif of progenitors
leads to cytopenia (underproduction) or cytosis (overproduction)
seen in BM failure, leukemia or myeloproliferatative disorders
cytopenia (what is it + causes 4 + what to check 3)
low blood cell count of one or more lineages
causes → BM failure, infiltration, immune destruction, nutrient deficiency
check CBC, reticulocytes, BM
cytosis (what is it + causes)
elevated cell count → erythrocytosis, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis
causes
reactive → infection, inflamma
neoplastic → myeloproliferative
myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN)
clonal prolif of mature myeloid cells
myelodysplastic syndromes = MDS (what, dysplasia, can become?)
ineffective HT → cytopenias despite hypercellular marrow
dysplasia in 1 or more lineage
can progress to AML
acute leukemia → what + kinds + symptoms + what is a hint
rapid prolif of immature blast cells in BM
2 kinds
AML → myeloid blasts
ALL → lymphoid blasts
symptoms → anemia, infections, bleeding, bone pain
cytopenia + leukocytosis → hint!
chronic leukemia → what + types
accum of more mature but dysfunctional cells
2 types
CML → myeloid lineage, BCR-ABL fusion (philadelphia chr)
CLL → B cell accum, common in elderly
lymphoma
malignancy of lymp tissue → nodes or extranodal
two major types → hodgkin or non-hodgekin
classified by
cell of origin → B or T cell
clinical behavior
approach to cytopenia
confirm with repeat CRC
evaluate BM morphology + cellularity
assess for nutrional, autoimmune (AI), drug-induced or malignant cause
approach to cytosis (if persistent? evaluate what?)
rule out reactive cause
if persistent test for clonal markers → JAK2 or BCR-ABL1
evaluate splenomegaly and thrombosis esp in MPN
lab tests for hematologic malignancies 4
cytology/histology → morphology of blood and marrow cells
immunophenotypin (FACS) → surface markers (CD antigens)
cytogenetics/FISH → chromosomal abnormalities
mol testing → mutation analysis, gene expression prolif
flow cytometry (FACS) → measures what, identifies what, for which diseases
measures cell surface + intracellular markers w/ fluor antibodies
identifies lineage (+ clonality) of blasts or lymphocytes
mye vs lym
if lymp → B or T cells
Essential for diagnosing leukemia and lymphoma.
Cytogenetic analysis (karyotyping) + examples
Detects large chromosomal abnormalities and translocations.
Examples
t(9;22) BCR-ABL in CML
t(15;17) PML-RARA in APL.
FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) in hematology
Detects specific chromosomal rearrangements in interphase nuclei.
Faster than conventional karyotyping.
Used for confirming known fusions (BCR-ABL1, MYC, etc.).
Gene expression profiling
Measures mRNA levels to classify malignancies by molecular subtype.
Connection hematologic malignancy and cell development → when does a mutation occur?
mutations during specific diff atages determine disease type
early progenitor → acute leukemia
mature lymp cell → lymphoma
Leukemia vs lymphoma distinction
leukemia → primarily in BM and blood
lymphoma → primarily in lymph nodes or tissues
Overlap exists (e.g., lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma).
chronic mye leukemia = CML (what?, causes what kind of prolif? how treated?)
BCR-ABL1 fusion → constitutively active TK
causes granulocytic prolif
treated with imatinib = TKI
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia = APL (what?, causes what? how treated?)
t(15;17) → PML-RARA fusion
blocks myeloid diff
treated with ATRA + arsenic trioxide
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) → what kind of cells
reed-sternberg cells → cd15, cd30
typically arises in one nodal region → contigouos spread
often curable with combined chemo-radiotherapy
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
diverse group of B/T cell malignancies
examples
DLBCL
foll lymphoma
burkitt lymphoma
mantle cell lymphoma
Multiple myeloma (what, leads to, diagnosed by)
plasma-cell malignancy producing monoclonal Ig (M protein)
causes CRAB features → hypercalcemia, renal failure, anemia, bone lesions
diagnosed by serum electrophoresis + BM biopsy
burkitt lymphoma → gene, cell, what infection
t(8;14) → MYC activation
extremely fast-growing B cell lymphoma
associated with EBV infection
treatment of hematologic malignancies
chemo → backbone for most leukemias lymphomas
targeted therapy
if CML → TKI
CLL → BTK inhibi
or anti-cd20 (rituximab)
stem cell transplantation → for high risk or relapse
Autologous vs allogeneic stem-cell transplant
auto → pt own stem cells
lower rejection
higher relapse risk
allogeneic → donor
potential graft vs tumor effect, but risk of GVHD
Minimal residual disease (MRD)
small number of malignant cells remaining after therapy
detected by flow cytometry or mol methods (PCR/NGS)
Prognostic markers in hematologic malignancies
cytogenix/mol abnormalities
MRD status after therapy
environment in BM that protect HSC → stromal cells
fibroblasts → produces ECM + growth factors
fat cells → regulate metabolism + cytokine signaling
environment in BM that protect HSC → specialized cells
CAR cells = CXCL12 (SDF1)abundant reticular cells
-NES+ MSC = Nestin+ MSC
erythropoiesis (ery = RBC) → start + 3 phases
hemocytoblast → pro-erythroblast
= stemcell → committed cell
phase 1 = ribosome synthesis → early erythroblast
phase 2 = Hb accum → late eryblast → normoblast
phase 3 = ejection of nucleus → normoblast → reticulocyte
thrombopoiesis
platelet (=thrombocyte) formation from megakaryocytes in BM
coagulation
damaged blood vessel → release of clotting factors (CF)
CF makes prothrombin → thrombin
left shift of neutrophil granulocytes
presence of more immature forms of neutrophil in blood
due to increased production
eg = during infection
hematopoietic growth factors + cytokines INFLUENCE
HGF → directly influence → inhib/stim HSC or progenitor cells
cytokines → indirectly influ → inhib/stim prod of hematopoietic GF
HGF (4 + IL’s)
SCF → stem cell factor
TPO → thrombopoietin
EPO → erythopoietin
G/M-CSF → gran/monocolony stim factor
IL 2, 3, 7
TPO → what does it do and where is it made
stim platelet production
produced by liver
EPO (source + job)
source → kidney
stim prod of ery in BM
G/M-CSF (source (3) + job)
G-CSF made by → endo cells, fibroblasts, macrohphages
G-CSF incr granulocyte prod in BM → leukocytosis = WBC high
myeloperoxidase (MPO) staining
to distinguish AML from ALL
MPO + → myeloid origin → AML
MPO - → lymphoid blasts → ALL
acute + myeloid
AML
chronic + myeloid
MPN = myeloproliferative neoplasmata
eg → CML
acute + lymp = 2
ALL/LBL
acute lym leukemia
lymfoblastic lymphoma
chronic + lymfoid
lymphomas → B or T/NK cell
passenger mutations
not harmful
copied during cell division
driver mutations
muta in genes that regulate prolif or diff
can cause clonal expansion
class I mutation in AML
GF receptors → Flt3 or KIT
signal transduction molecules → TK, NRAS
class II mutation in AML
cell cycle → cyclin dependent kinase inhib
gene transcription
gene splicing
malignant lymphoma classification
AgR - = TdT + → precursor neoplasia
AgR + → mature neoplasia
proto-oncogene activation by VDJ recombination
dna segments in B and T cell precursors are cut + joint → error prone process
somtimes recom machinary mistakenly joins POG next to strong Ig or TCR promoter/enhancer
results in overexpression of POG
follicular lymphoma → translocation, Ig, gene
t14→18
IgH - BCL2
mantle cell lymphoma → transloca, ig, gene
t11 → 14
IgH - CCND1
burkitt lymphoma which gene
t8 → 14,8,22
IgH/IgL → MYC
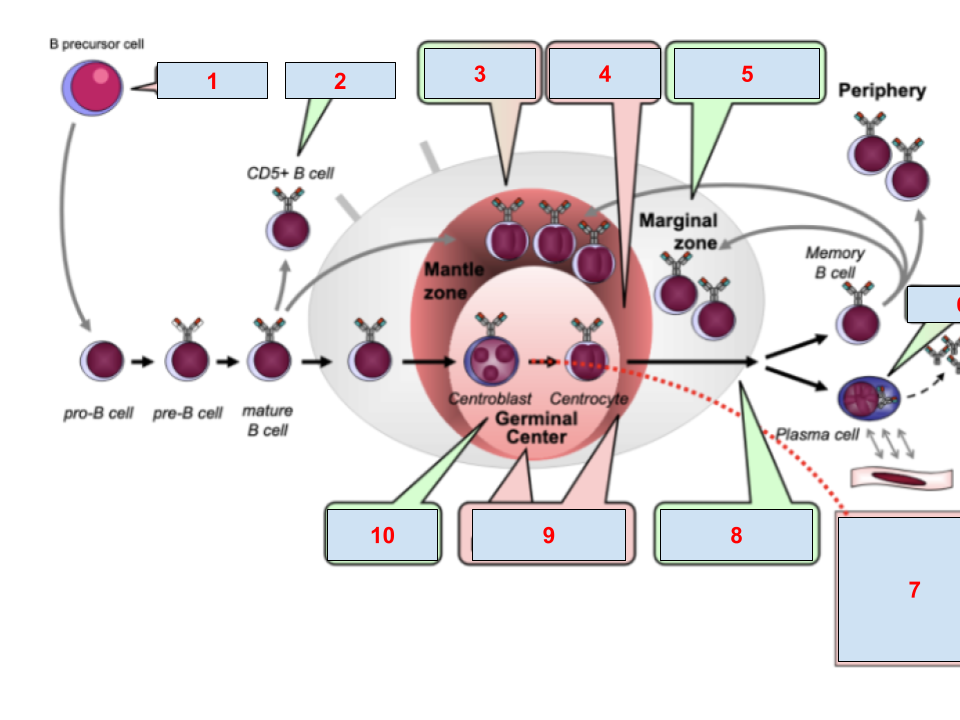
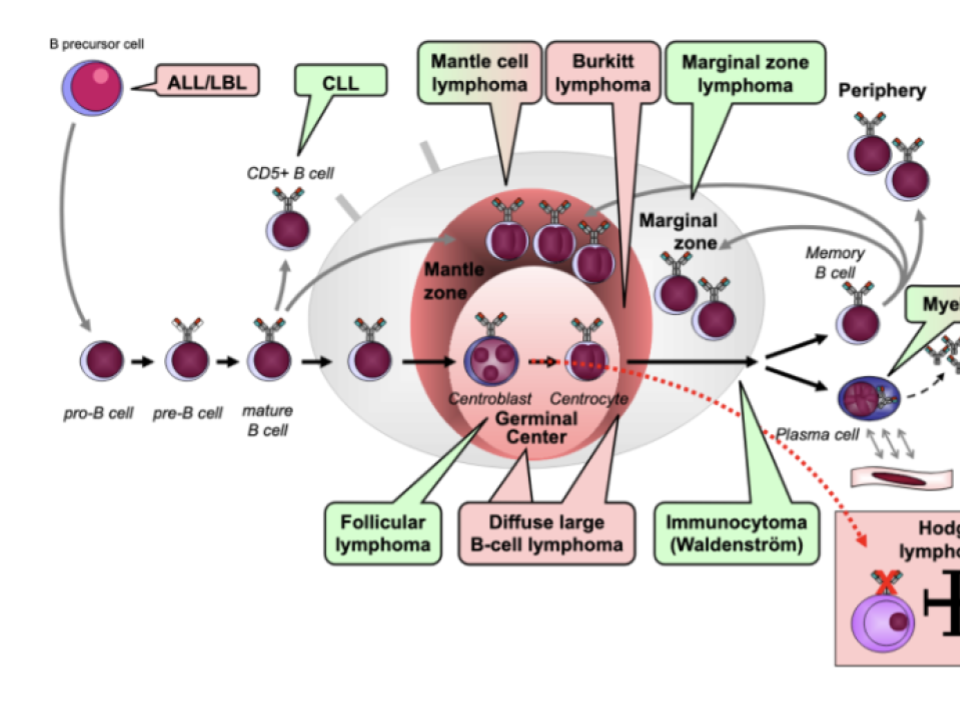
mantle cell lymphoma, follicuar, ALL/LBL, myeloma, hodgkin, CLL, burkitt, maginal zone, immunocytoma, diffuse large B cell lymphoma
ALL/LBL
CLL
mantle
burkitt
marginal
myeloma
hodgkin
immunocytoma
diffuse large b cell lymphoma
follicular lymphoma
extra nodal marginal zone lymphoma of MALT
chronic ag stimulation like h. pylori → act T helper cells → cytokines that stimulate B cell prolif
clonal B cell expansion → MALT lymphoma h pylori dependent
genetic changes → MALT lymphoma h pylori independent
follicular lymphoma → gene, when does mistake occur + leads to what
derived from germinal center B cells
VDJ + VJ recomb
transloca IgM-BCL2 → anti-apop BCL2 gene under control of Ig
overexpression of BCL2 → resistance to apoptosis
B cell survives abnormally long
diffuse large B cell lymphoma → where, when mistake+ where mutation, which gene
derived from (post)germinal center B cells
SHM
act mutation in BCR → contstituve sig → prolif
BCL6 act → block diff + promotes survival
buffy coat
platelets
leukocytes
plasma apheresis
donors blood processed by machine
plasma is collected → non collected cells back to donor
when RBC transfusion (2)
anemia
blood loss
when platelet transfusion
thrombocytopenia
when plasma transfusion
coag factor deficiencies
classification anemia
cell size → micro-, macro-, normocytic
Hb content → hypo-, hyper-, normochromic
small cells = microcytes characteristics → what MCV + 4 reasons
low MCV <80
iron def
thalassa
anemia of chronic disease
sideroblastic anemia
large cells = macrocytes → MCV, 2 kinds, 2/4 reasons
high MCV > 96
megaloblastic
vit B12 or folate def
MDS
normoblastic
alcohol
high reticulocytes → hemolysis, heamorrhage
liver disease
drug therapy
normal sized cells → how is MCV + 6 causes
normal MCV
acute blood loss
anemia of chronic disease
chronic kidney disease
marrow infiltration/fibrosis
AI rheuma
hemalytic anemias
inherited corpuscular hemolysis
thalassemia = mi
sickle cell disease = N
combi of both = m
thalass beta soorten = 3
minor → carrier = trait
intermedia → moderate anemia
major → severe anemia = Cooley anemia
thalass alpha deletion of genes
deletion of 1-4 alpha genes
1 gene → mild or no anemia = carrier
2 → mild anemia = minor
3 → moderatley severe = int
4 → hydrops fetalis = major/Hb Bart
mutation in thala → 0
leads to absent production
mutation in thala → +
leads to reduced production
beta thalasemia major → what possible mut combi/what happens
welke hemolyse
hoezo geen beta thal → leidt tot en waarom
b0/b0 of b+/b0
normal erythroblast → insoluble alpha-globin aggregate → no beta-thal and this leads to:
ineffective erythropoies → hypochromic RBC only in circulation
extravascular hemolysis bc aggr-containing RBCs are destructed in spleen
alpha thala (AT) inheritance → 4 and name disease
auto rec disorder
3 normal copies = aa/a- → AT minima → asymp
2 normal copies = a-/a- OR aa/-- → trait → minimal anemia
1 normal copy = a-/-- → HbH disease → mod to severe
0 normal copies = --/-- → Hb Bart → incomp extra-ut life
BT minor or trait
b+/b OR b0/b
usually asymp
BT intermedia
b+/b+
only reduced prod
not dependent of transfusions
sickle cell disease = SCD → 4 kinds
SC trait = HbS → inheri of 1 abnormal sickle
SC anemia = HbSS → inheri of 2 abnormal sickle genes
SCD = HbSC → inheri of 1 abnormal sickle gene + 2nd Hb variant of beta-chain that causes sickling
sickle-thalassamia = BbSB0 → inheri of 1 abnormal SG and thala gene
anemia through increased destruc of ery → hemolysis due to extracorp factors → 2 causes that have each 2 categories
auto immune
warm → IgG
cold → IgM
alloimmune
ABO
Rh
AI IgG → what happens at temp, what does it, which test
warm temperature → IgG attaches at RBC
extravasc hemolysis → removal of IgG + complement coated ery
Coombs detects C + IgG → strong positive
AI IgM
cold temp → IgM attaches
intravas hemolysis → C acti by IgM bound to RBC
MAC
coombs light positive
spherocytosis
loss of RBC membrane bc of scission
scission = partial phagocytosis
storage of filt RBC, thrombocytes and plasma → what temp and how long
RBC → 2-6 graden → 35 dagen
thrombocytes → 20 graden → 5-7 dagen
plasma → -30 graden → 1 jaar