Veterinary Anatomy
1/235
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
236 Terms
Renal Cortex; Renal Medulla; Calyx; Renal Pelvis; Renal Hilus; Ureter; Bladder; Urethra
Flow of Urine
Testicles; Epididymus; Spermatic Cord; Inguinal Canal; Vas Deferens; Urethra
Flow of Sperm
Olecranon
Elbow bone
Osteoblast
Bone-forming cell
Osteoclast
Bone-destroying cells
Kidney
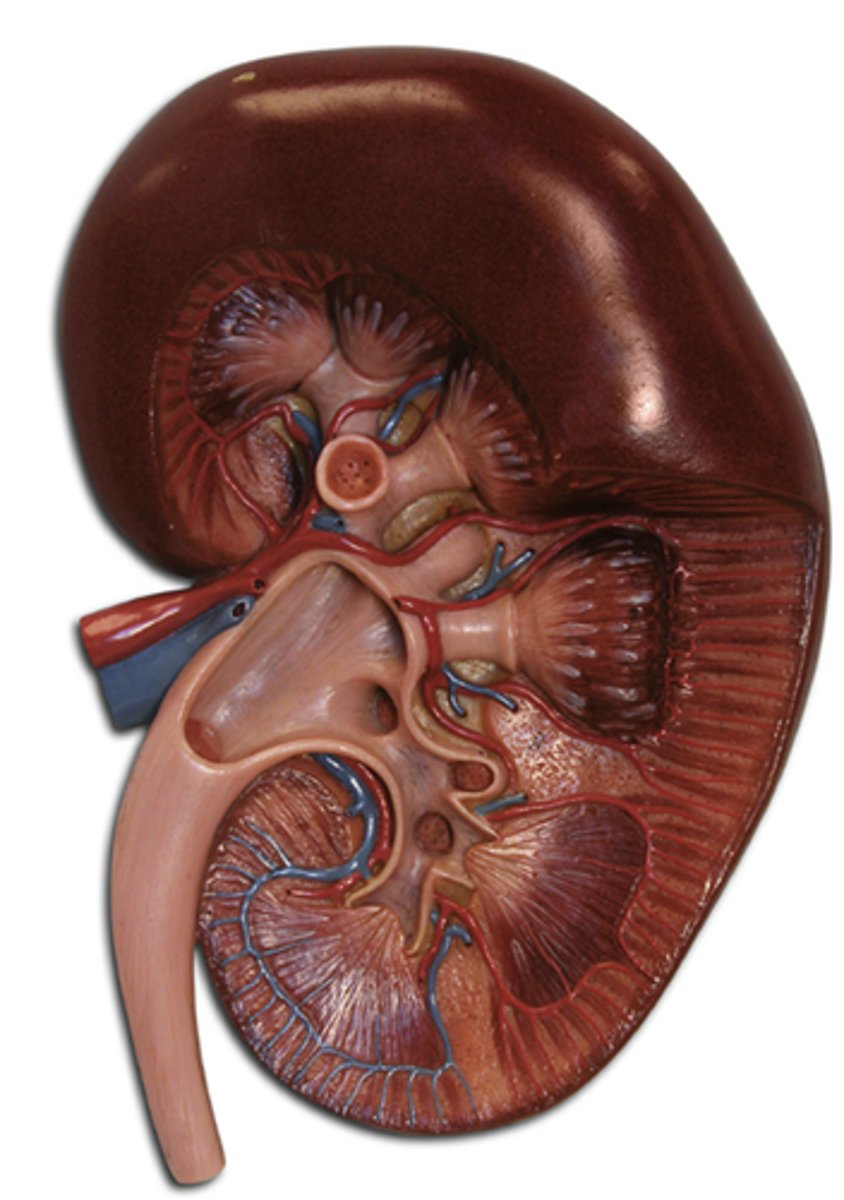
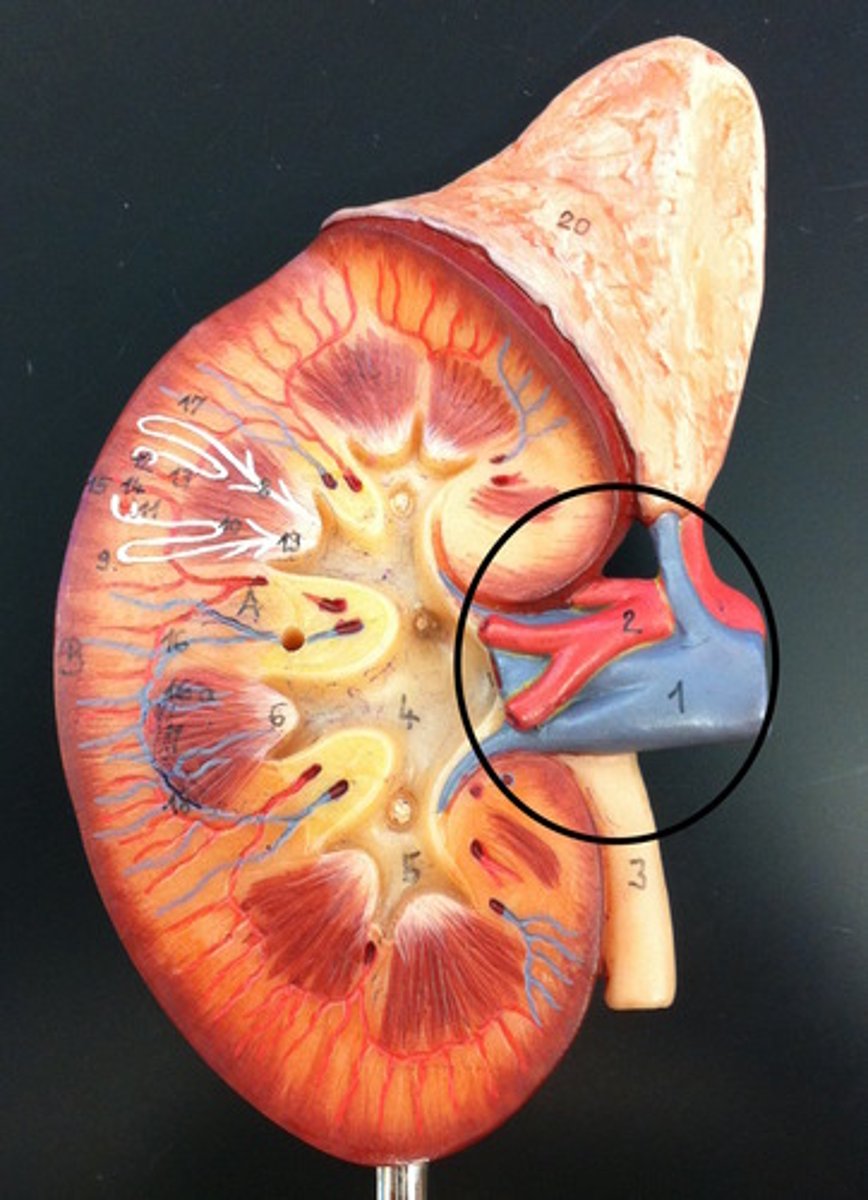
Renal Hilus
Indentation of kidneys where the blood vessels, lymphatic tissues, nerves and ureter pass through.
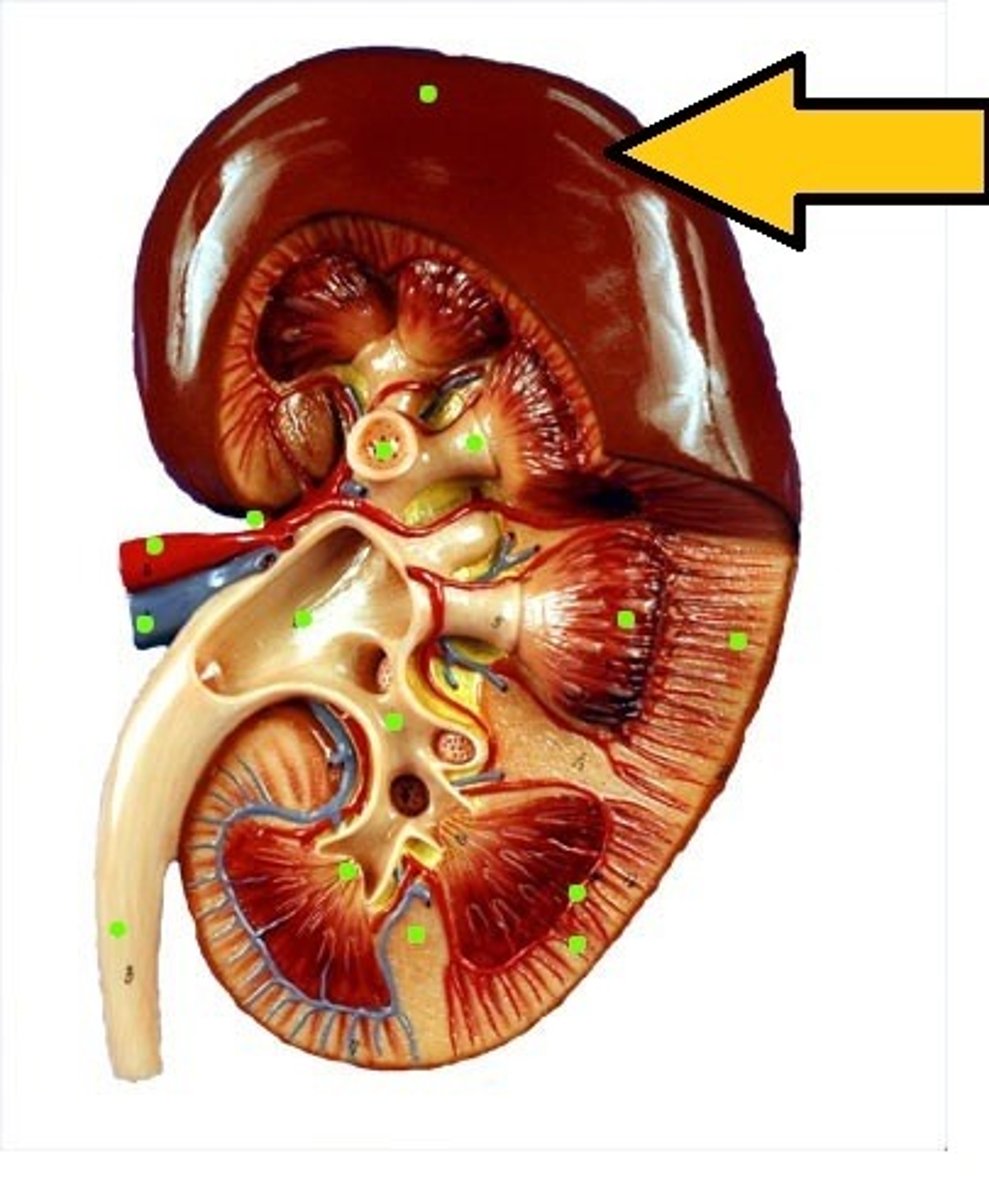
Renal Capsule
The connective tissue covering the external surface of the kidney.
Renal Cortex
Outer region of the kidney.
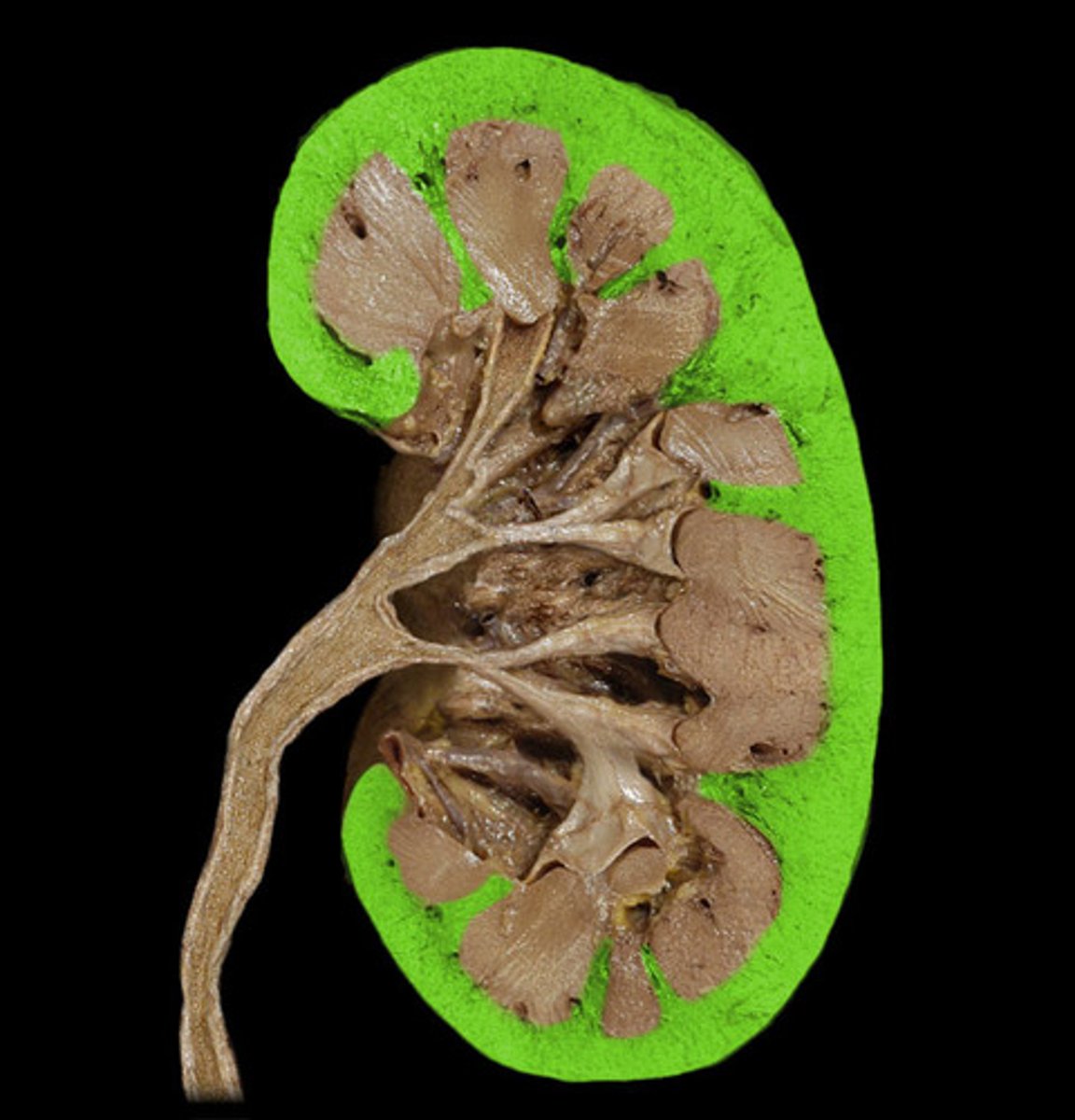
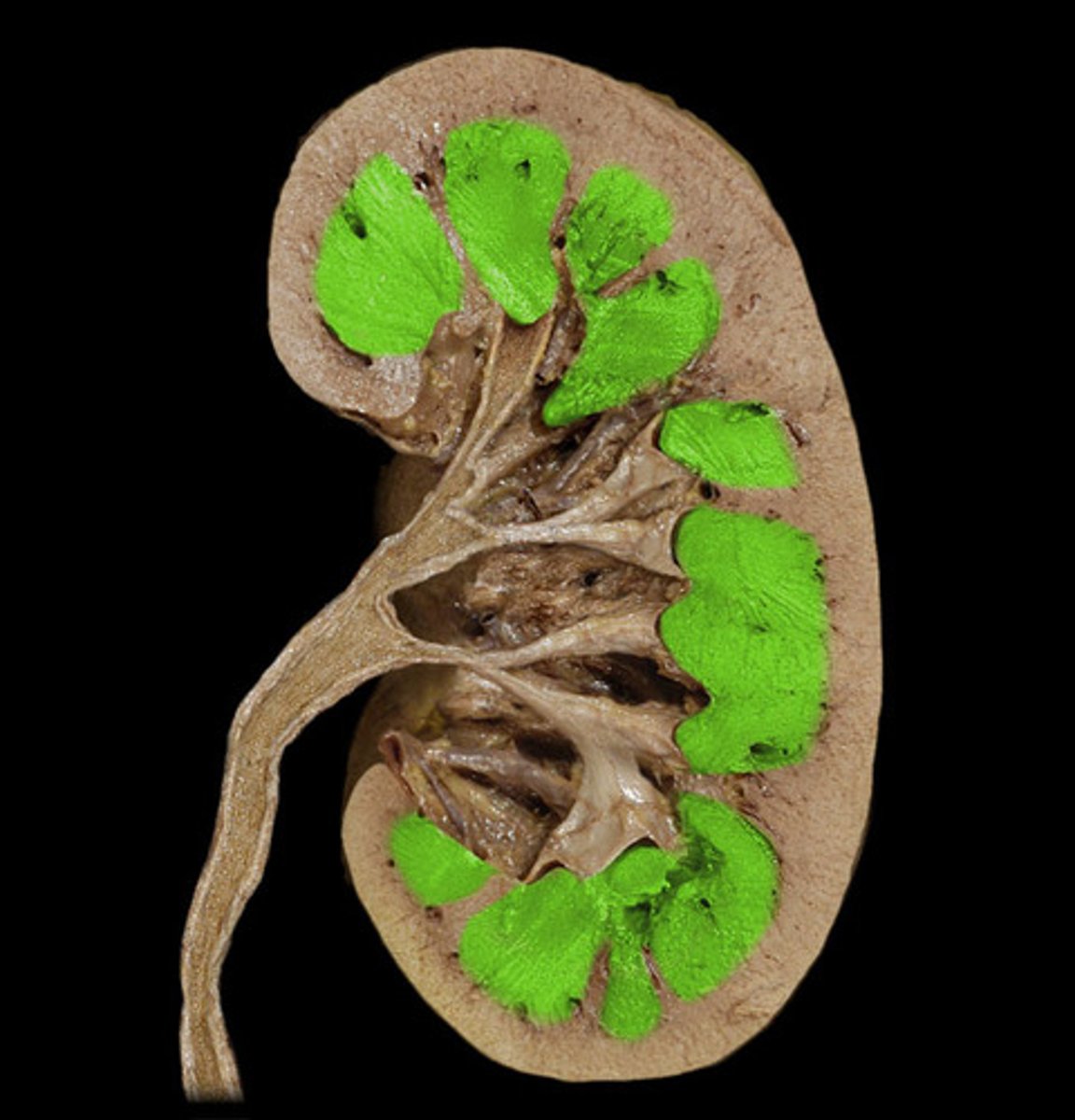
Renal Medulla
Inner region of the kidney.
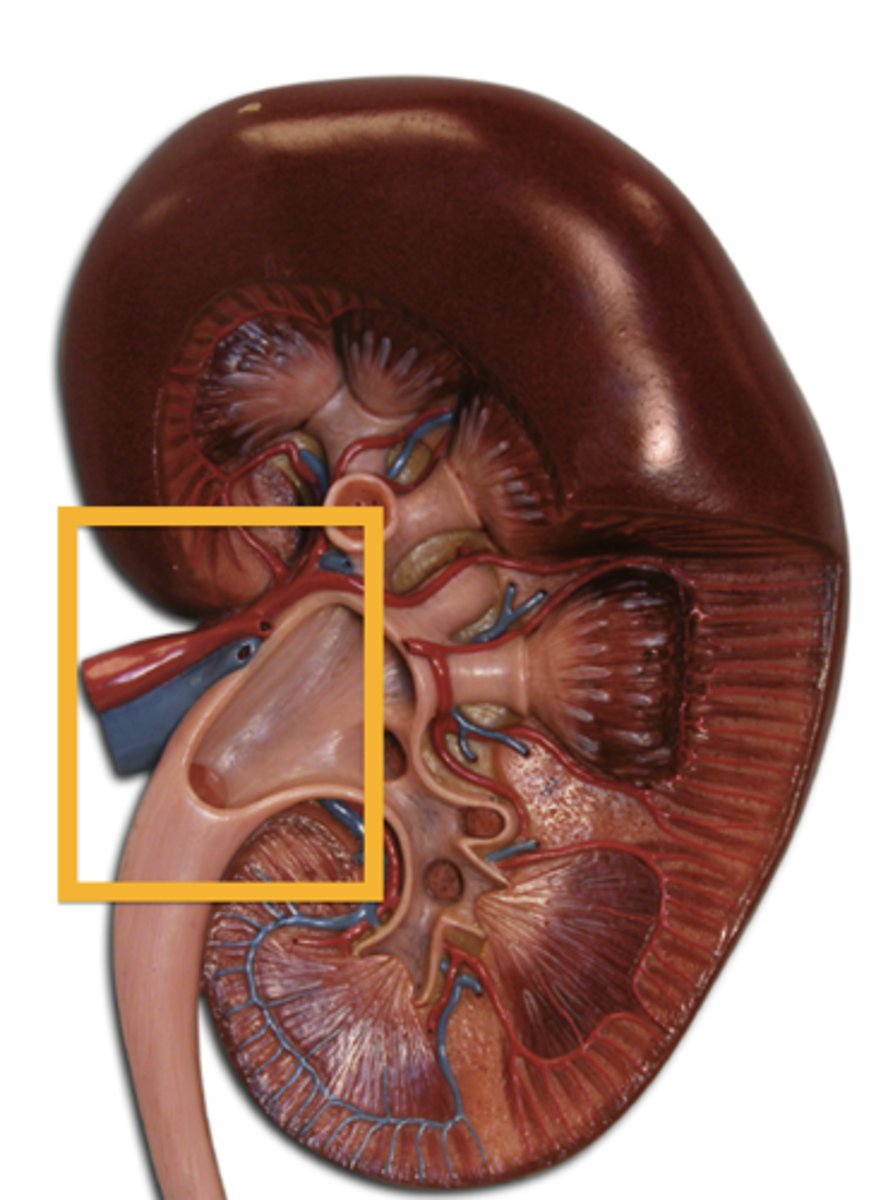
Renal Artery and Vein
Blood supply to and from the kidneys.
Ureters
The tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
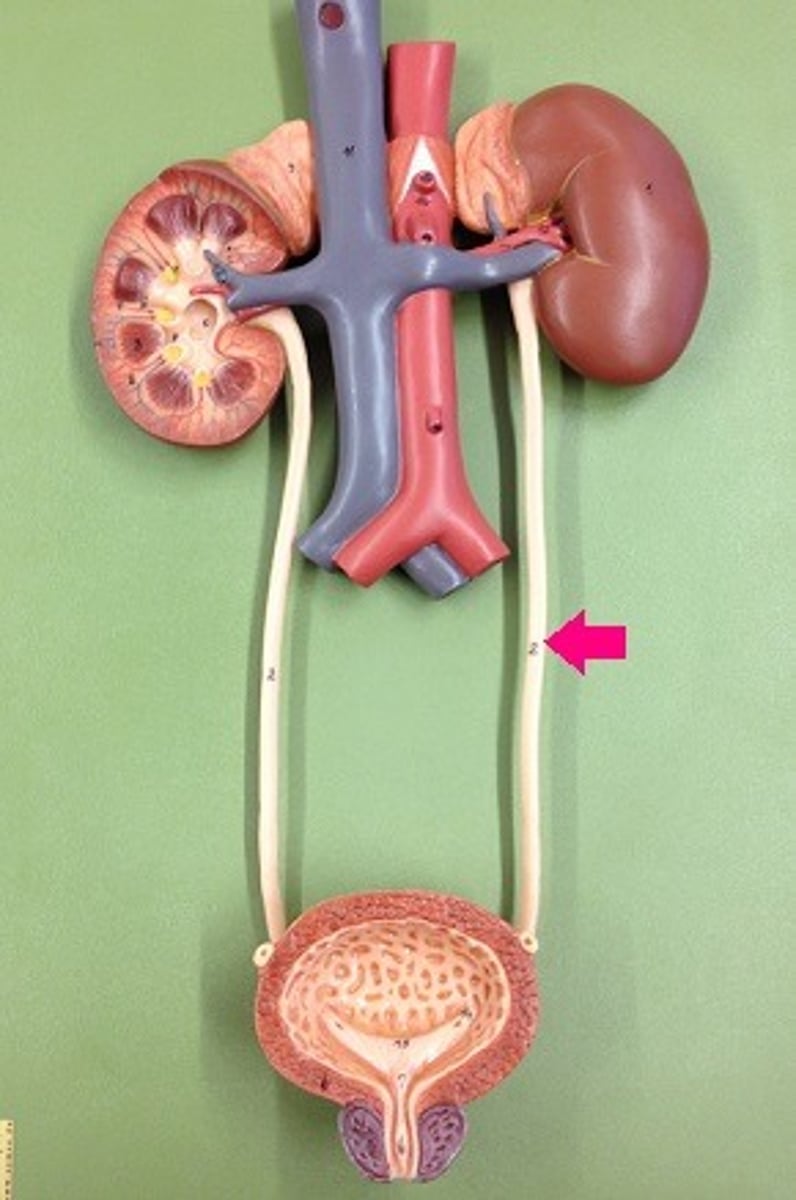
Urinary Bladder
Saclike organ in which urine is stored before being excreted.
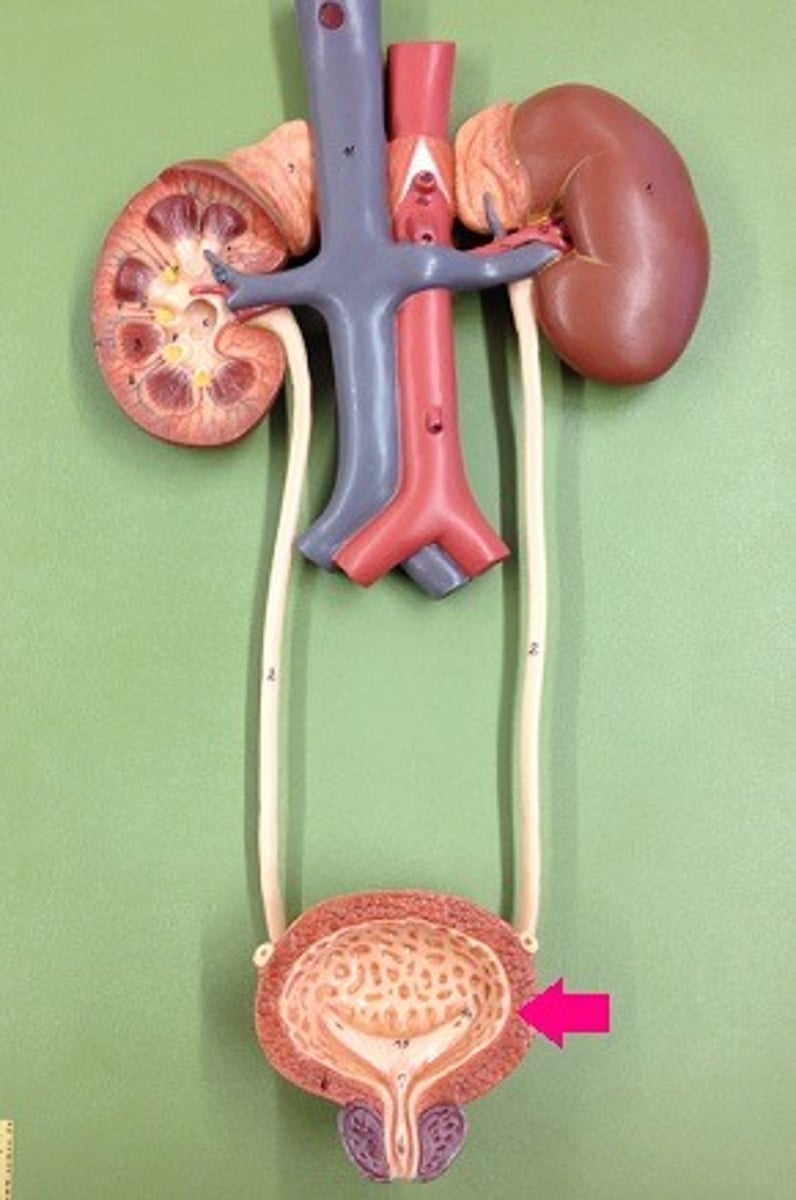
Urethra
Tube leading from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body.
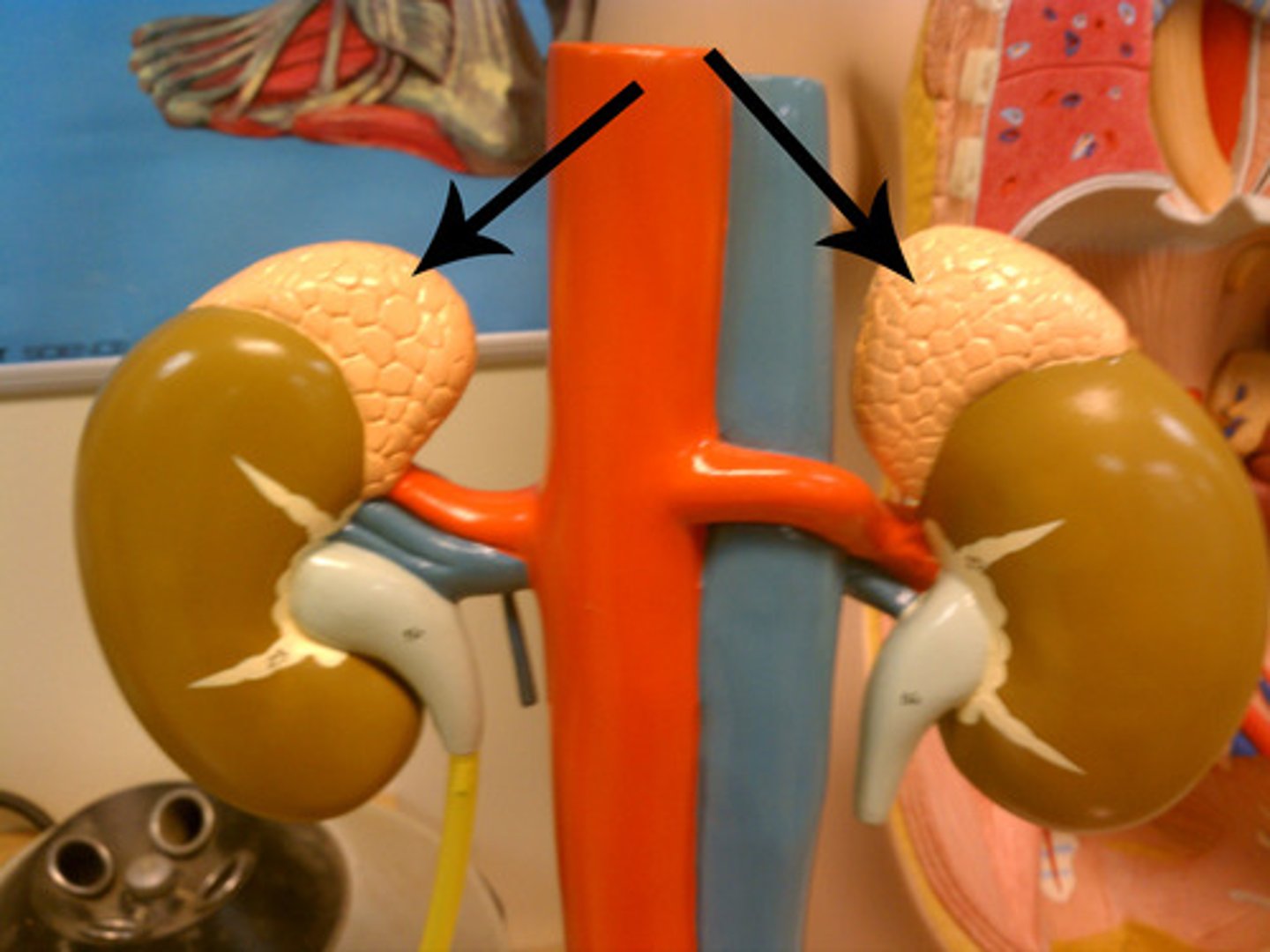
Adrenal Glands
A pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
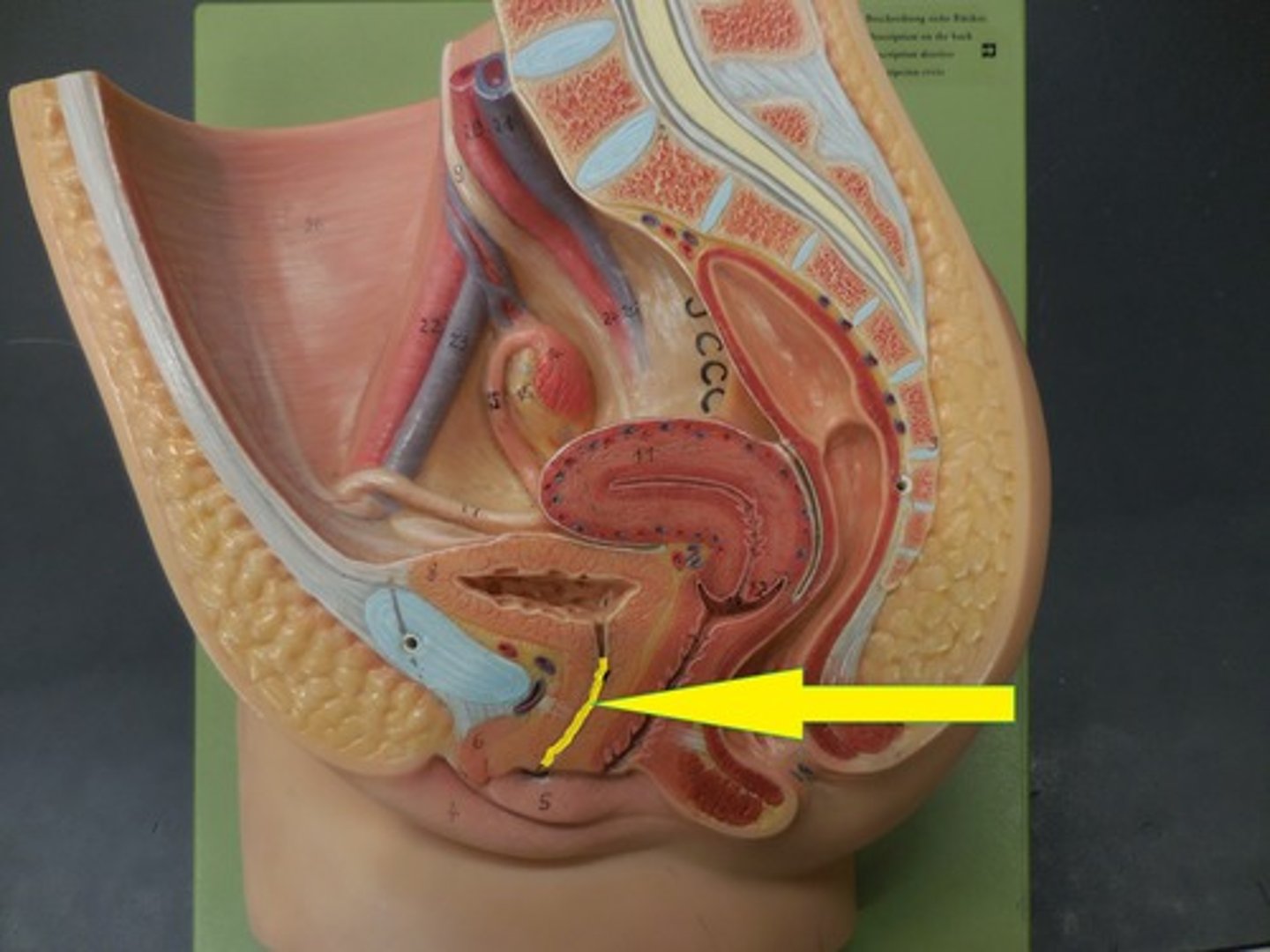
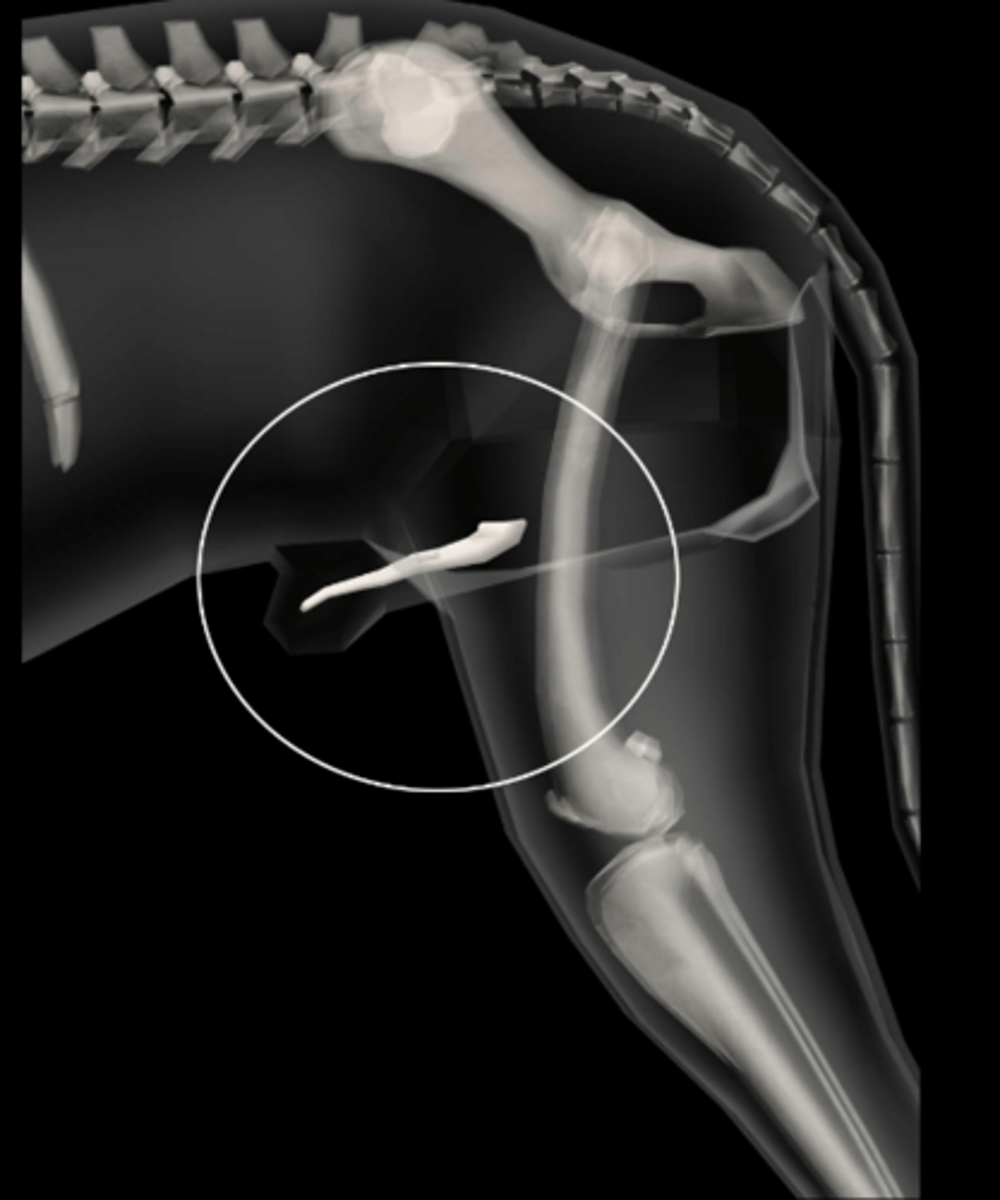
OS penis
Bone within the urethra of male dogs.
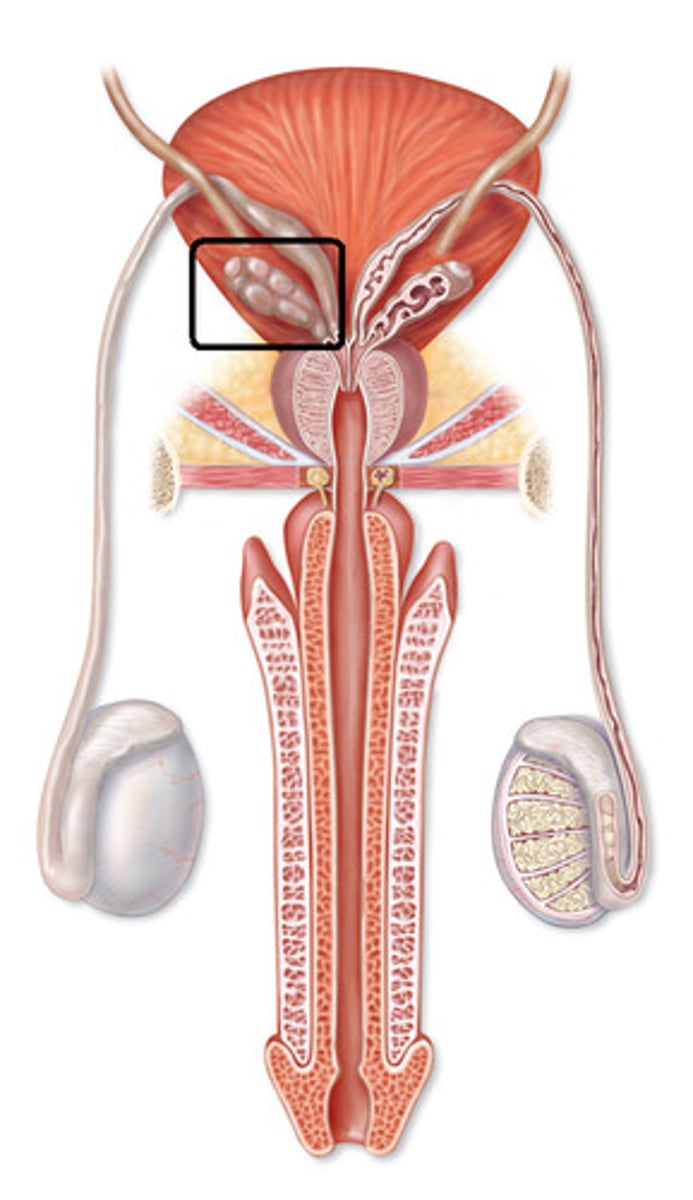
Prostate Gland
Accessory sex gland that secretes the largest share of the fluid in semen
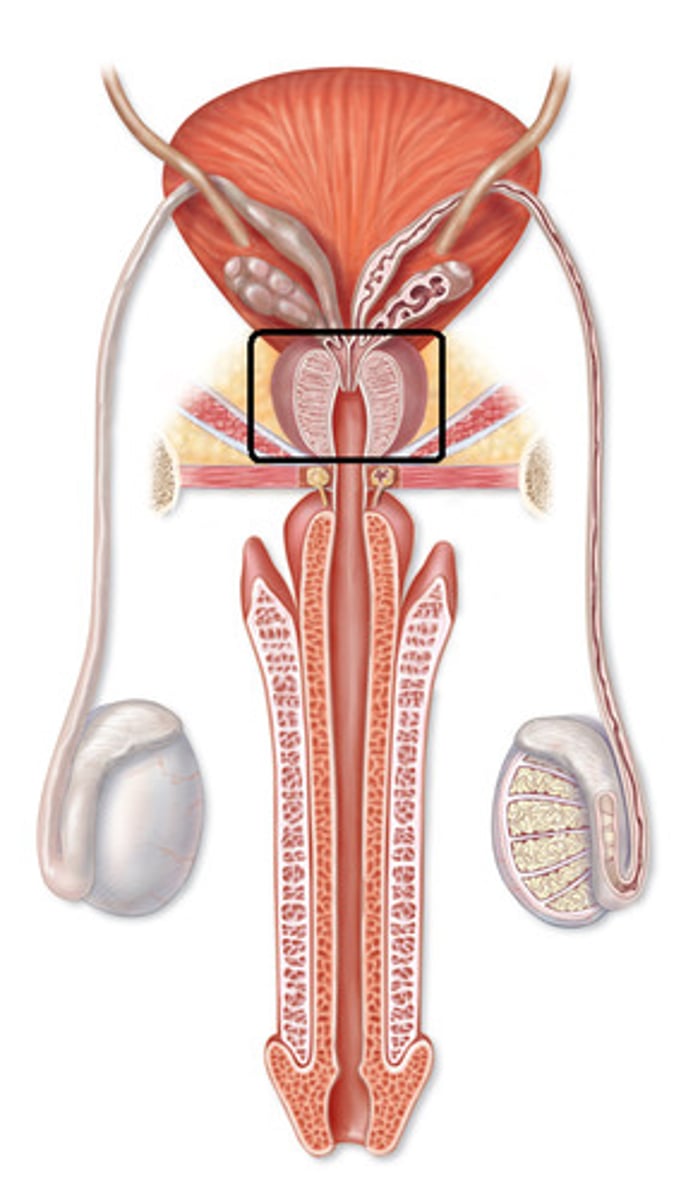
Bulbourethral glands
A pair of exocrine glands near the male urethra. They secrete fluid into the urethra. Also called Cowper glands
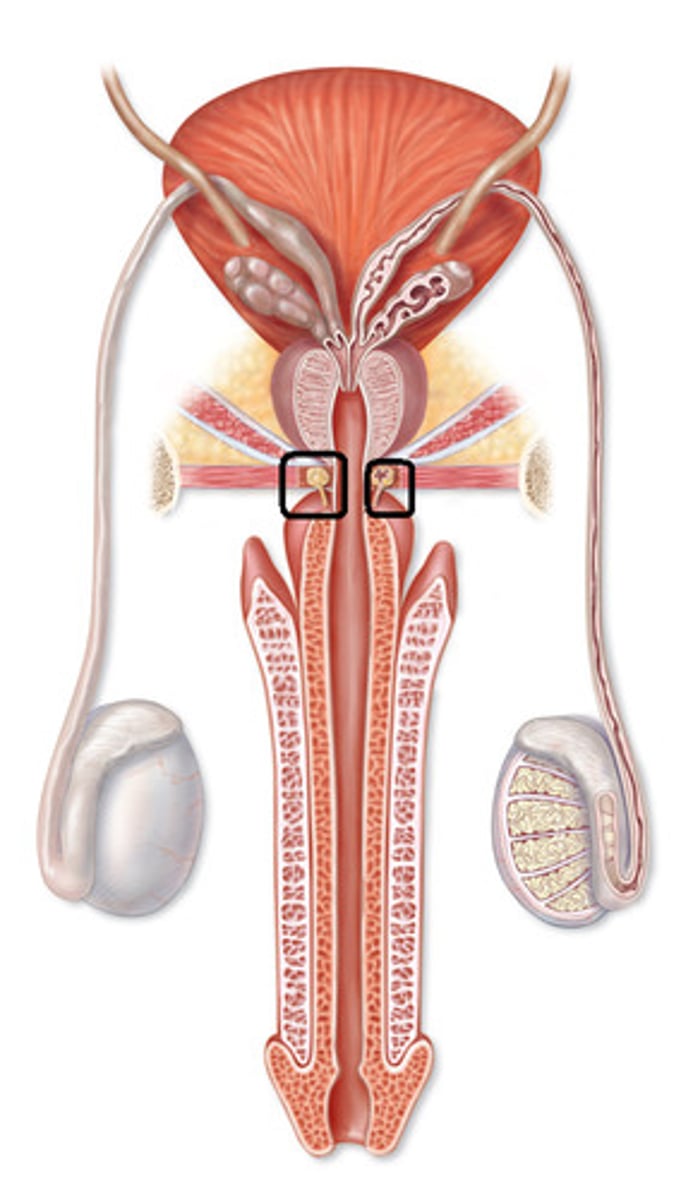
Seminal Vesicles
Two small glands that secrete a fluid rich in sugar that nourishes and helps sperm move
Scrotum
External sac that contains the testes
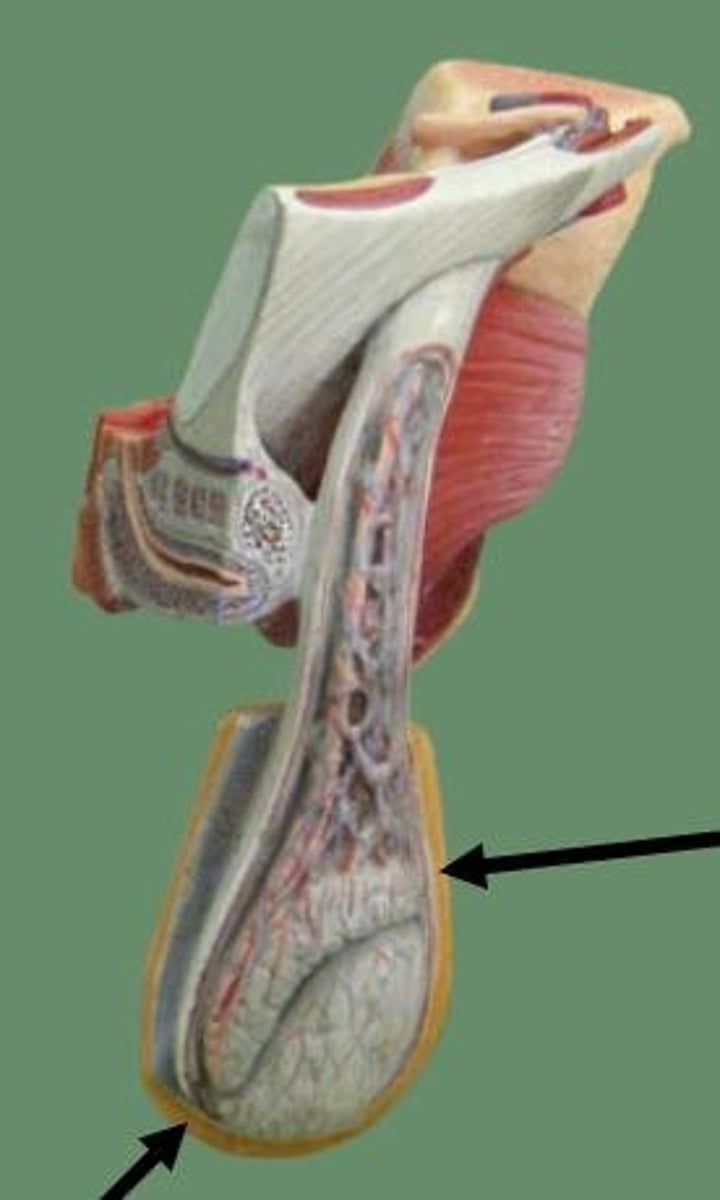
Testicles
The two small, egg-shaped glands that produce the sperm
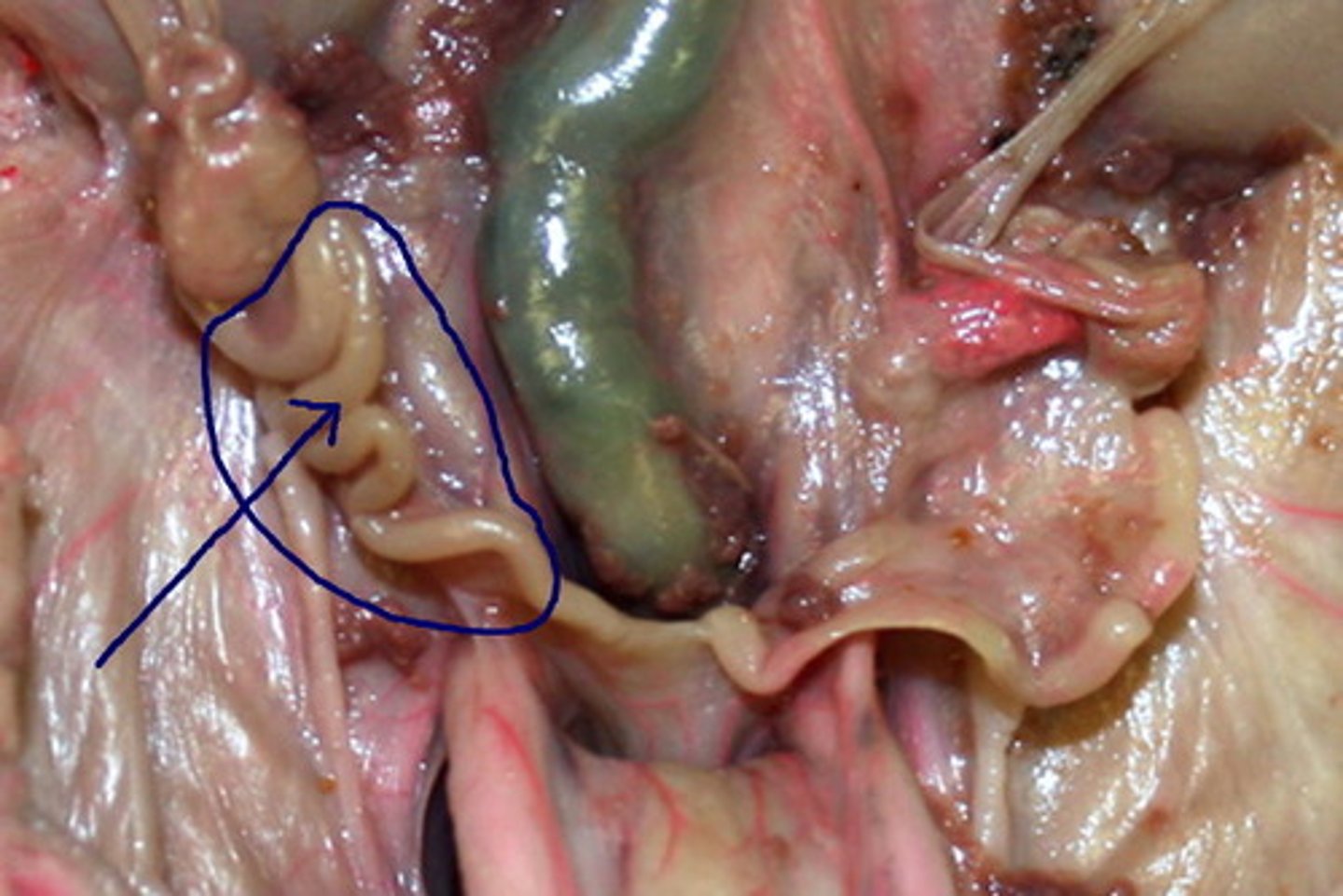
Epididymis
A long, coiled duct on the outside of the testis in which sperm mature.
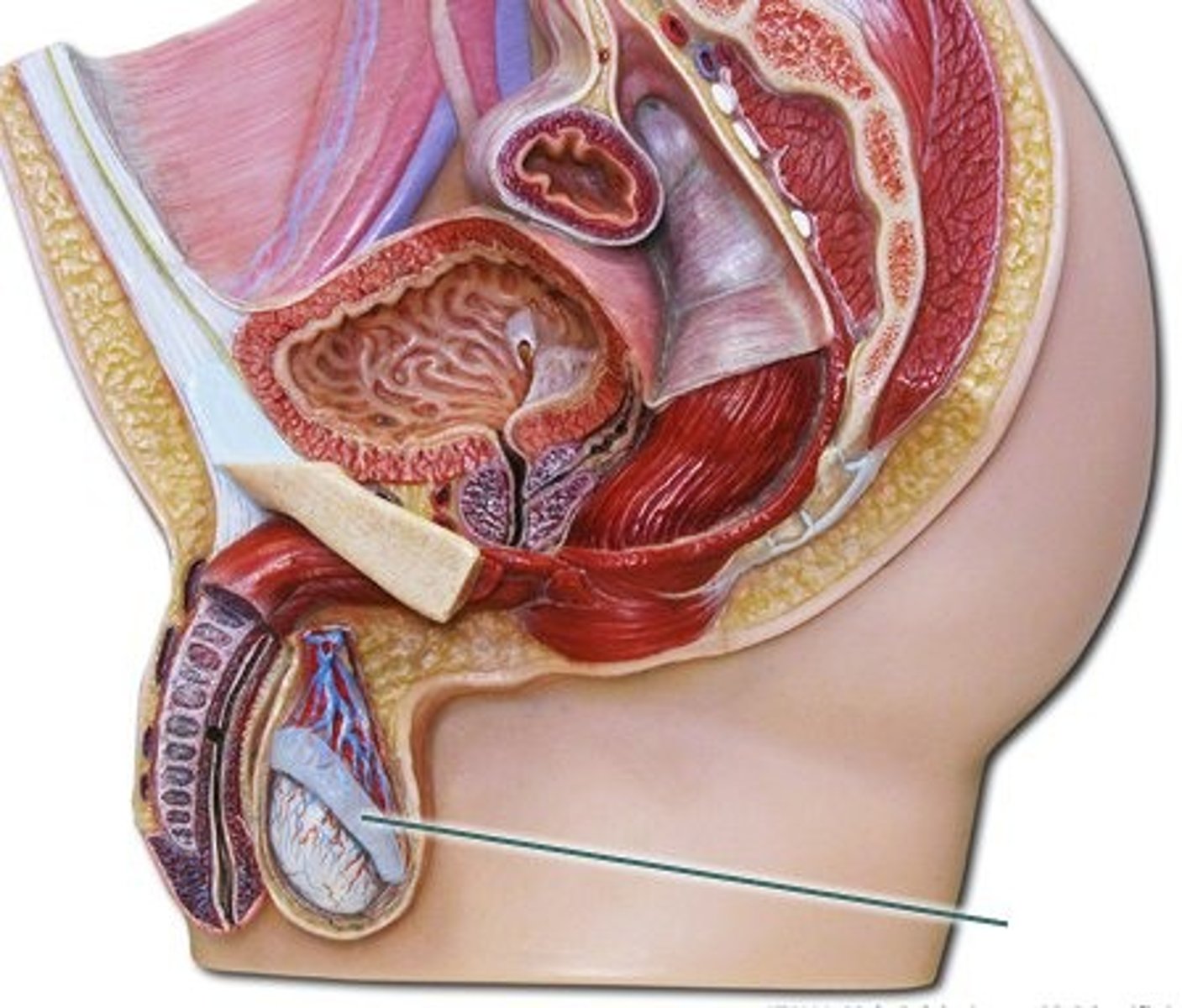
Tunica vaginalis
The delicate layer of serous membrane that covers the testis.
Spermatic Chord
Made up of blood vessels and nerves that reach the testis through the inguinal canal
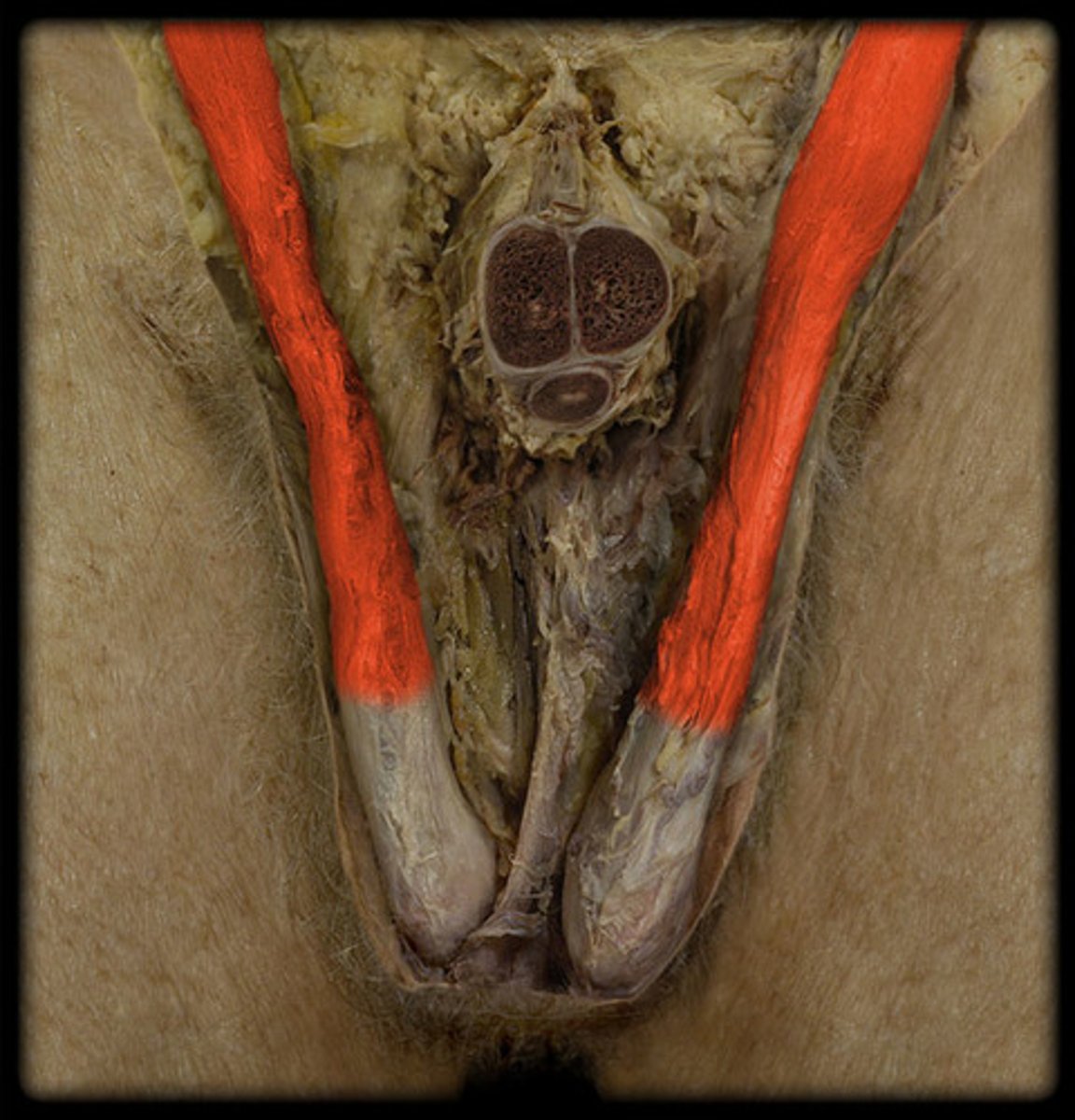
Inguinal Canal
The channel through which the testis descends into the scrotum in the male
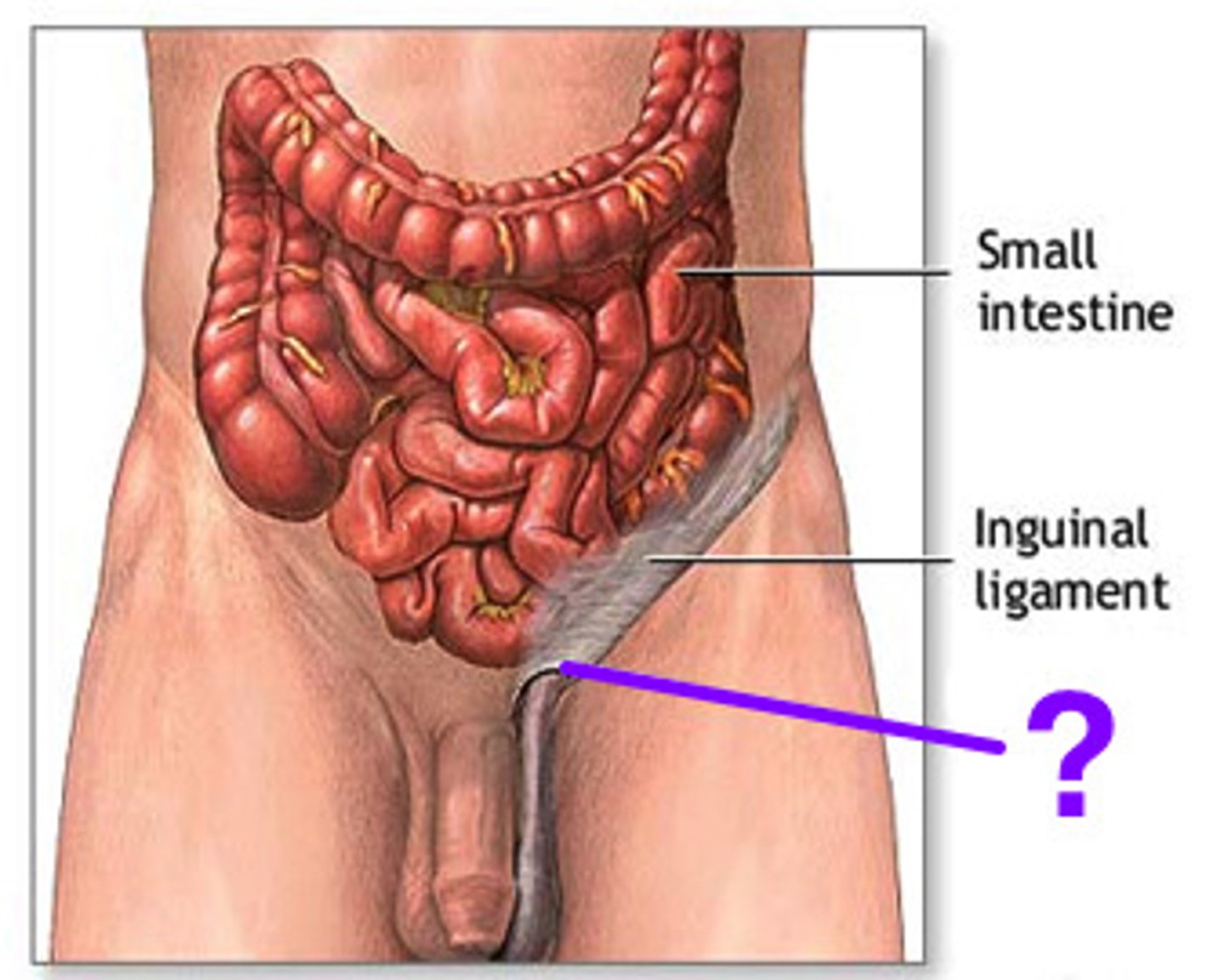
Vas Deferens
Long, narrow tube carrying sperm from epididymis to ejaculatory duct
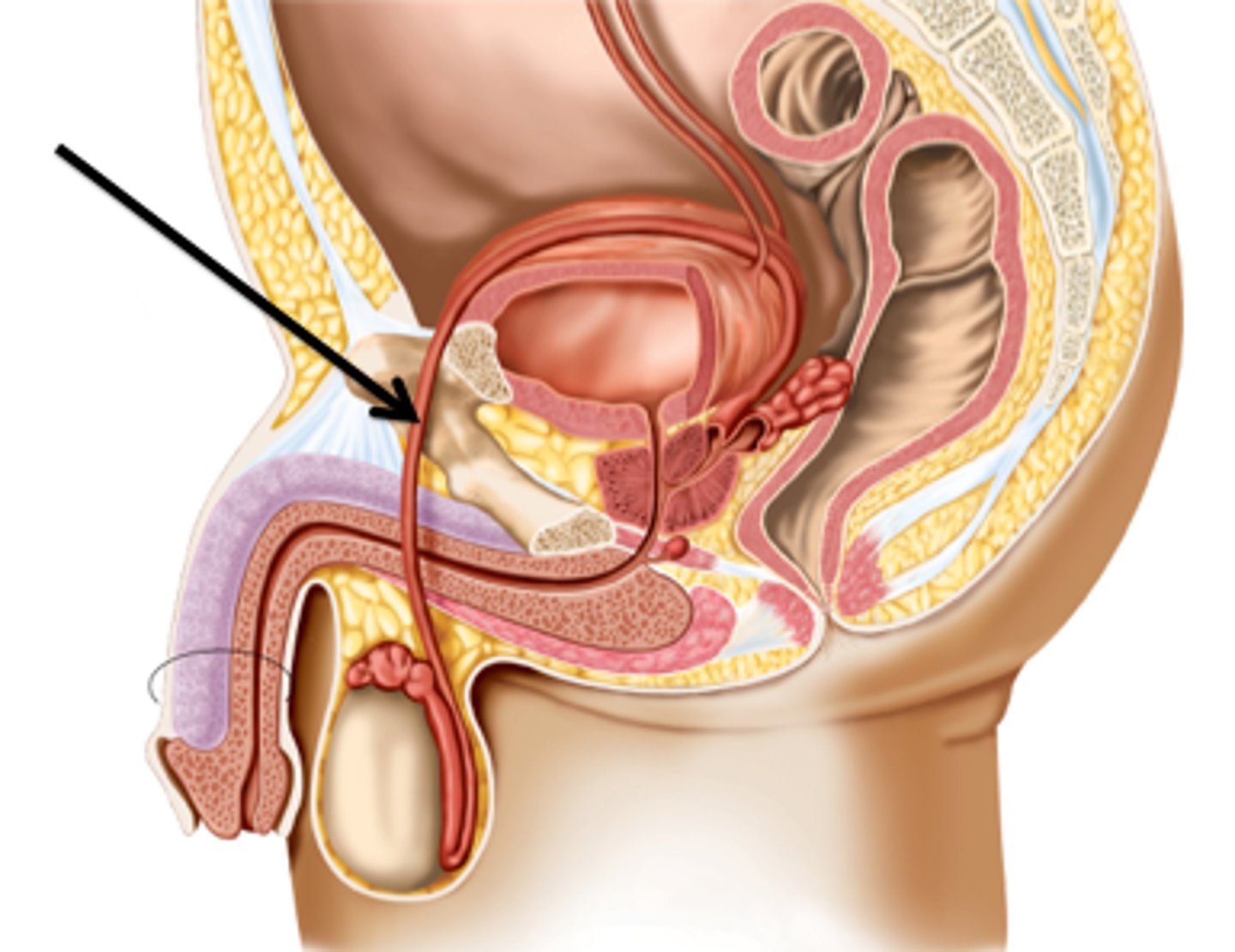
Vulva
external female genitalia; includes the labia, hymen, clitoris, and vaginal orifice
Vagina
A muscular, elastic passageway that extends from the uterus to the outside of the body
Cervix
The opening to the uterus
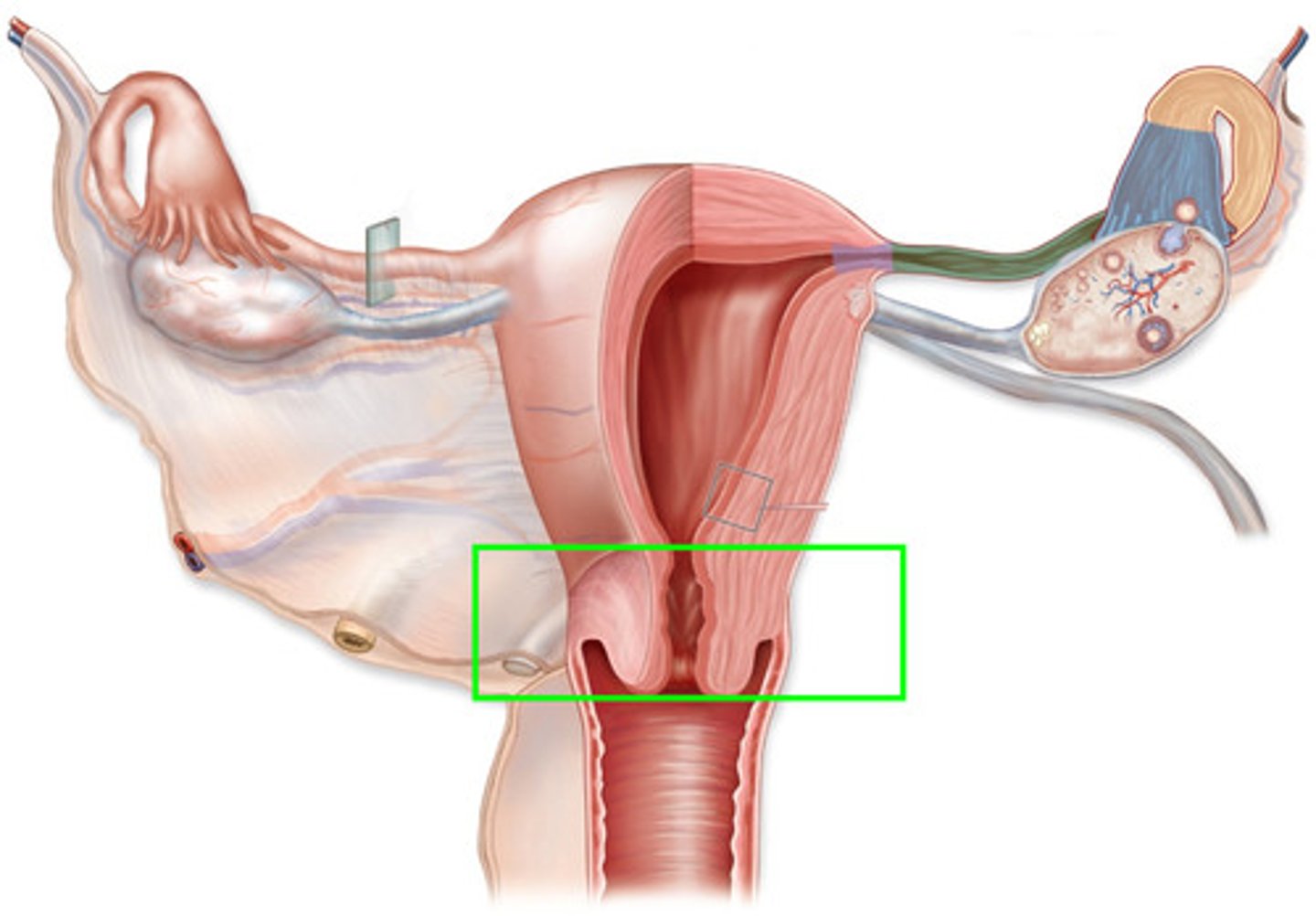
Uterine Body
This is the single, wider tube formed by the union of the two uterine horns. The cervix is at its posterior end.
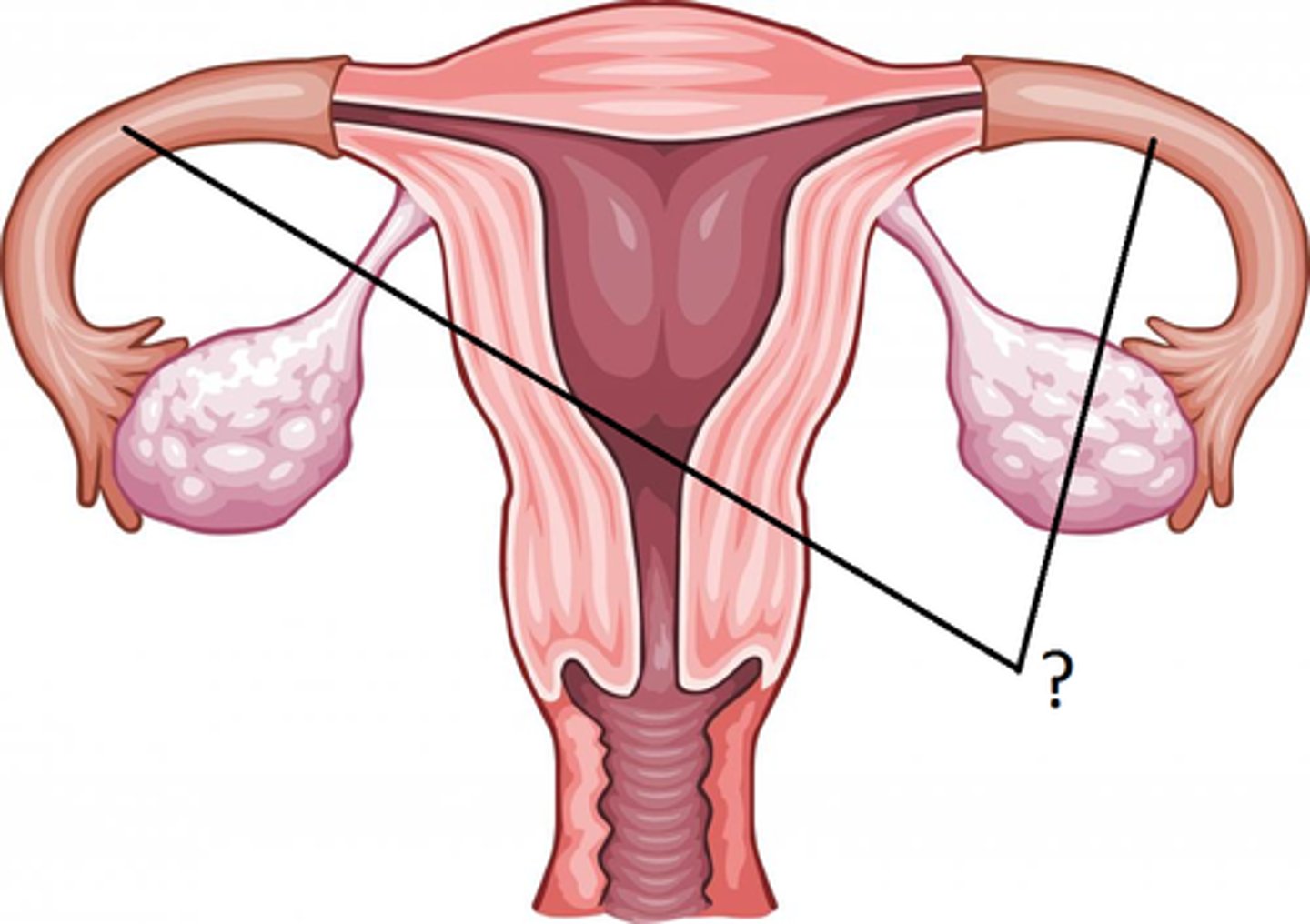
Uterine Horns
point where uterus & uterine tubes meet; connect body of uterus & ovaries; in the pig, fetus develops here
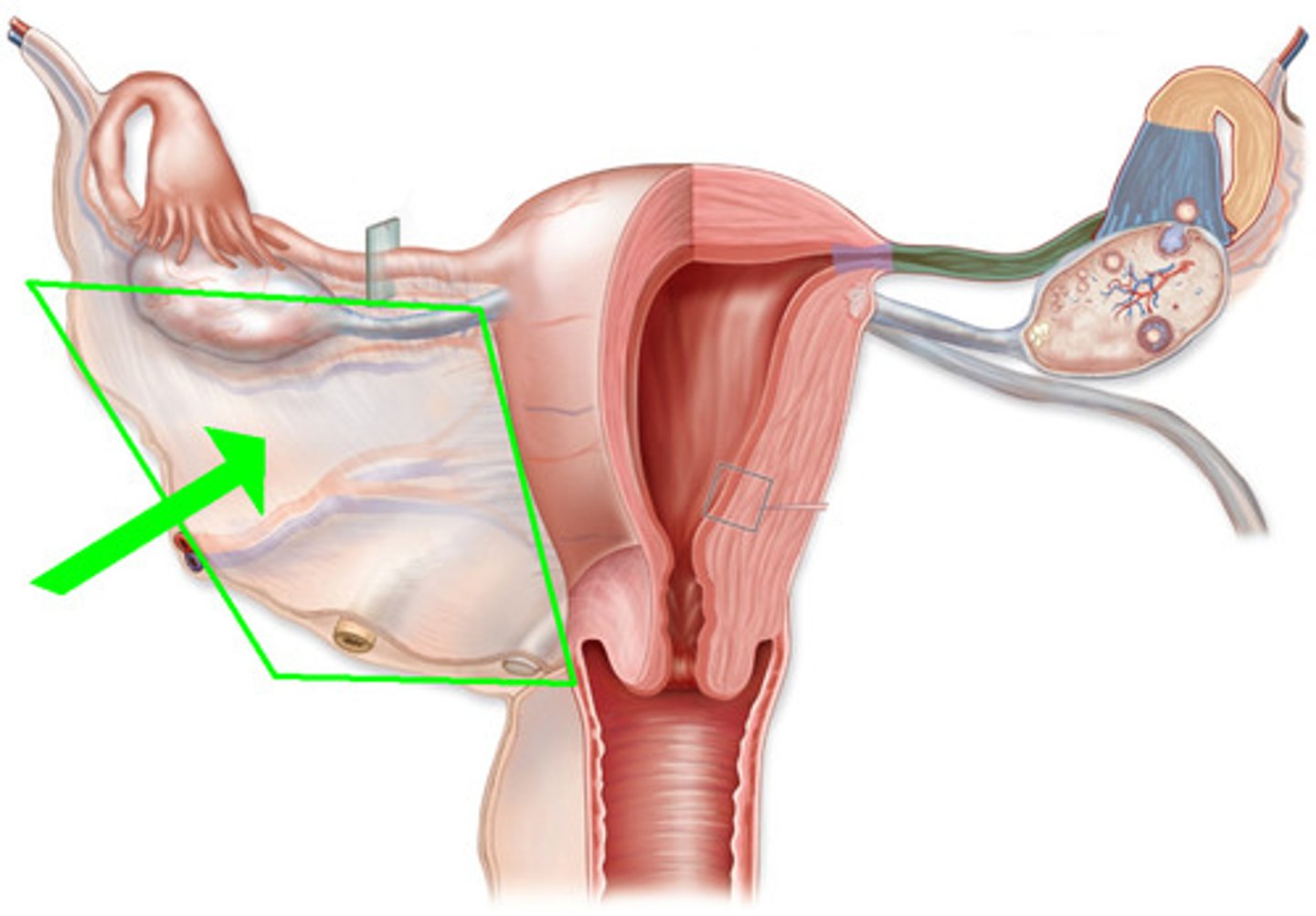
Broad Ligament
The ligament extending from the lateral margins of the uterus to the pelvic wall; keeps the uterus centrally placed and provides stability within the pelvic cavity.
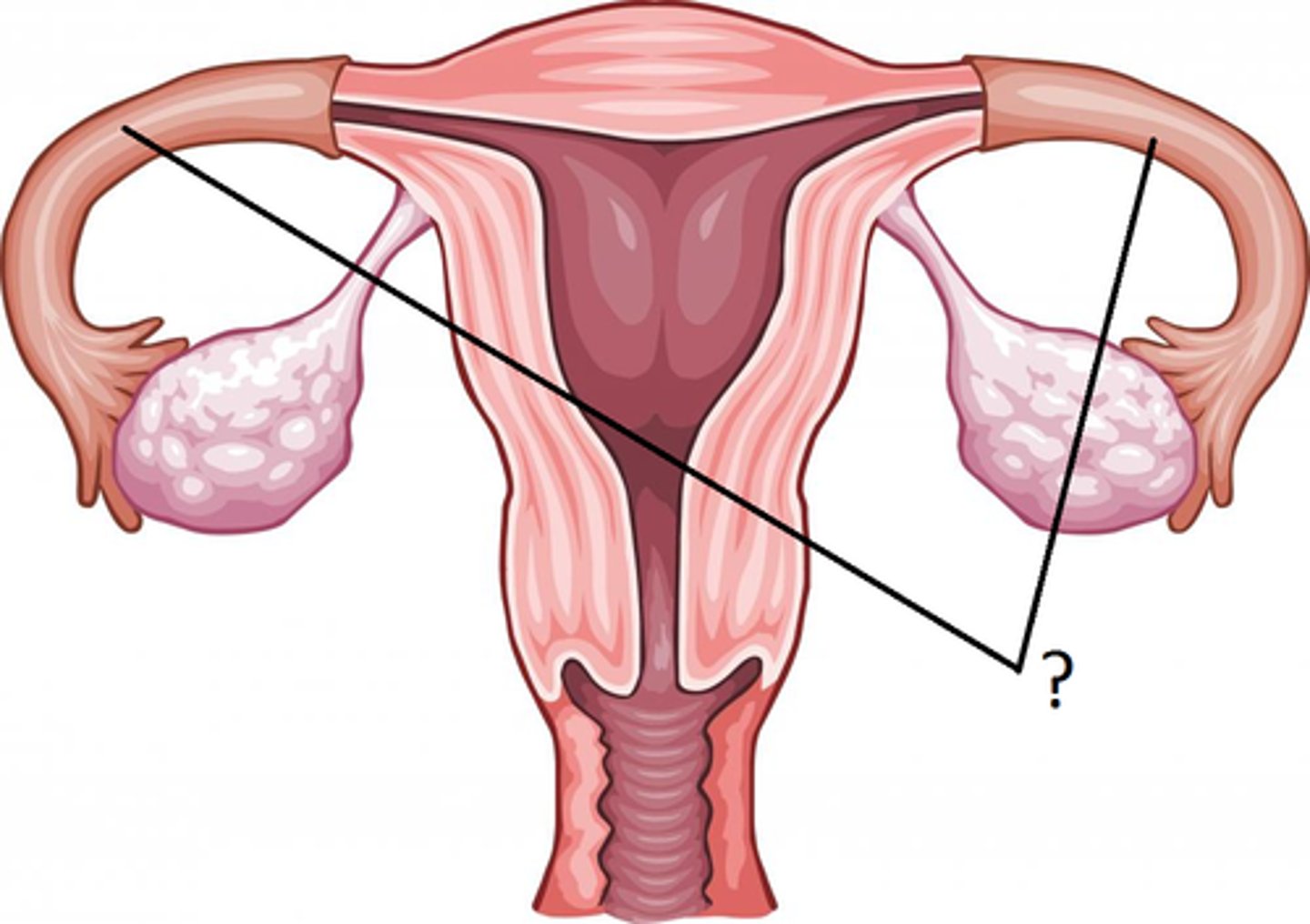
Ovary
A flower structure that encloses and protects ovules and seeds as they develop.
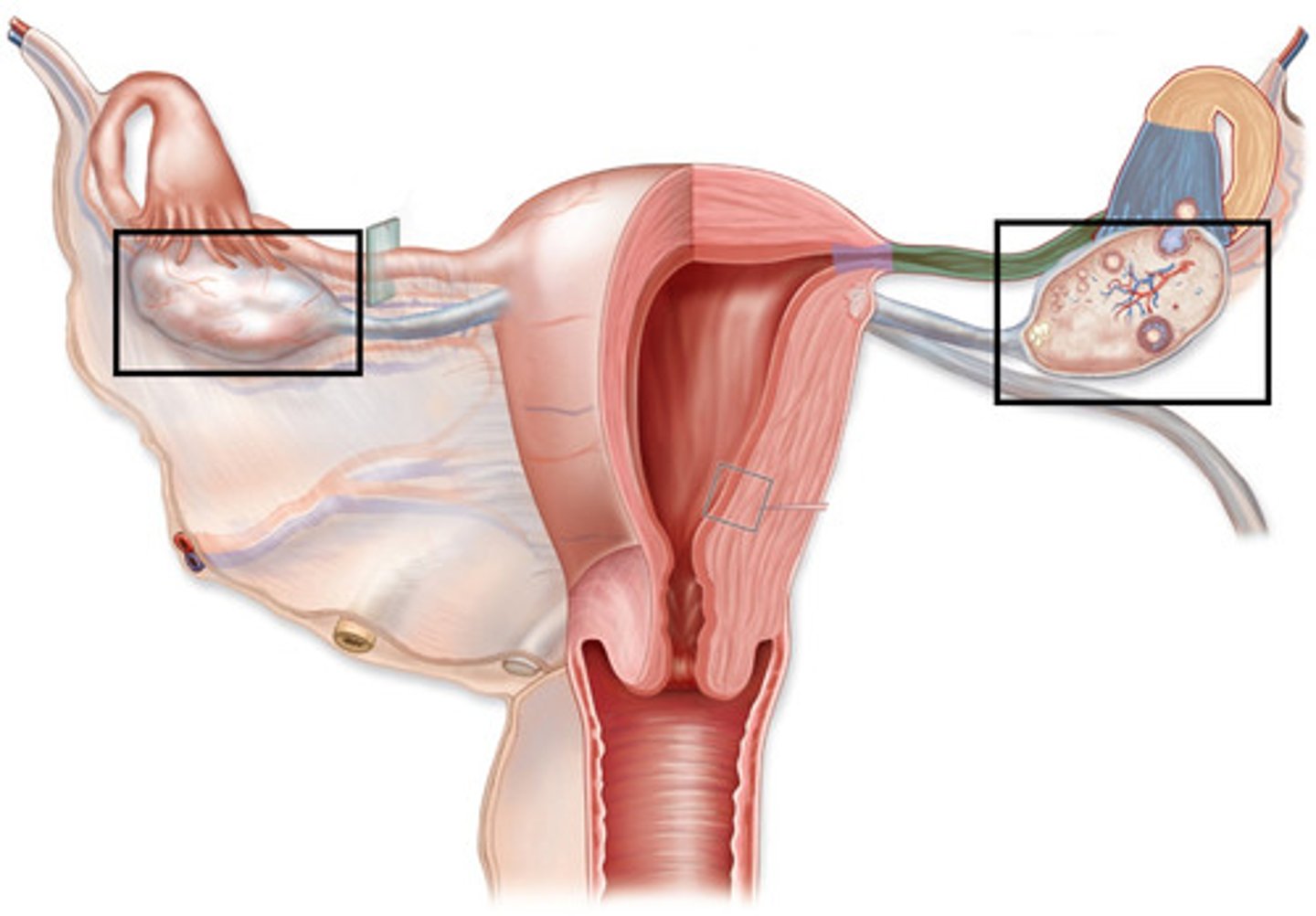
Suspensory Ligament
anchors ovary laterally to pelvic wall
Ovarian Vessels
Blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to and drain deoxygenated blood away from the ovaries
Oviducts
fallopian tubes
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
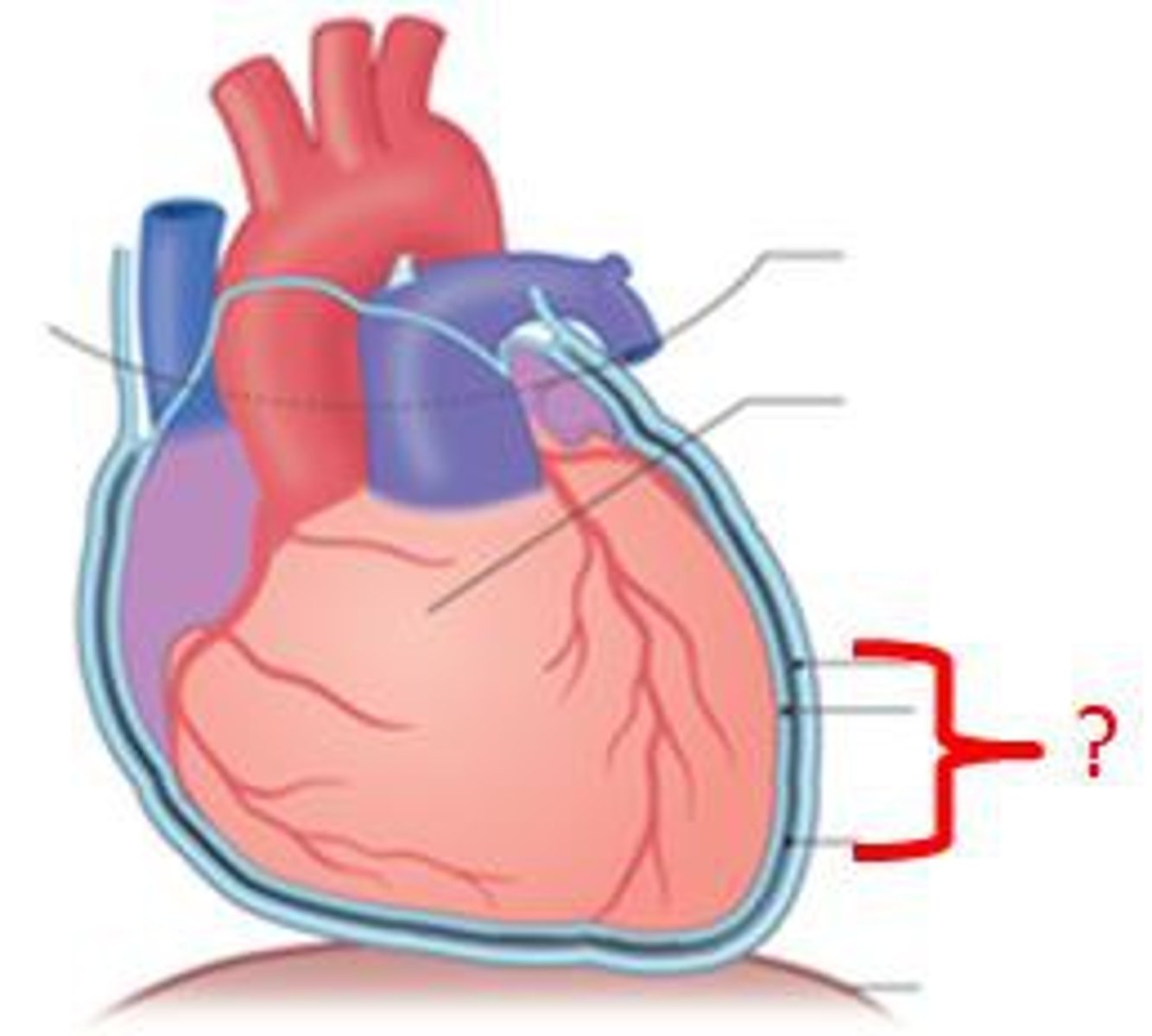
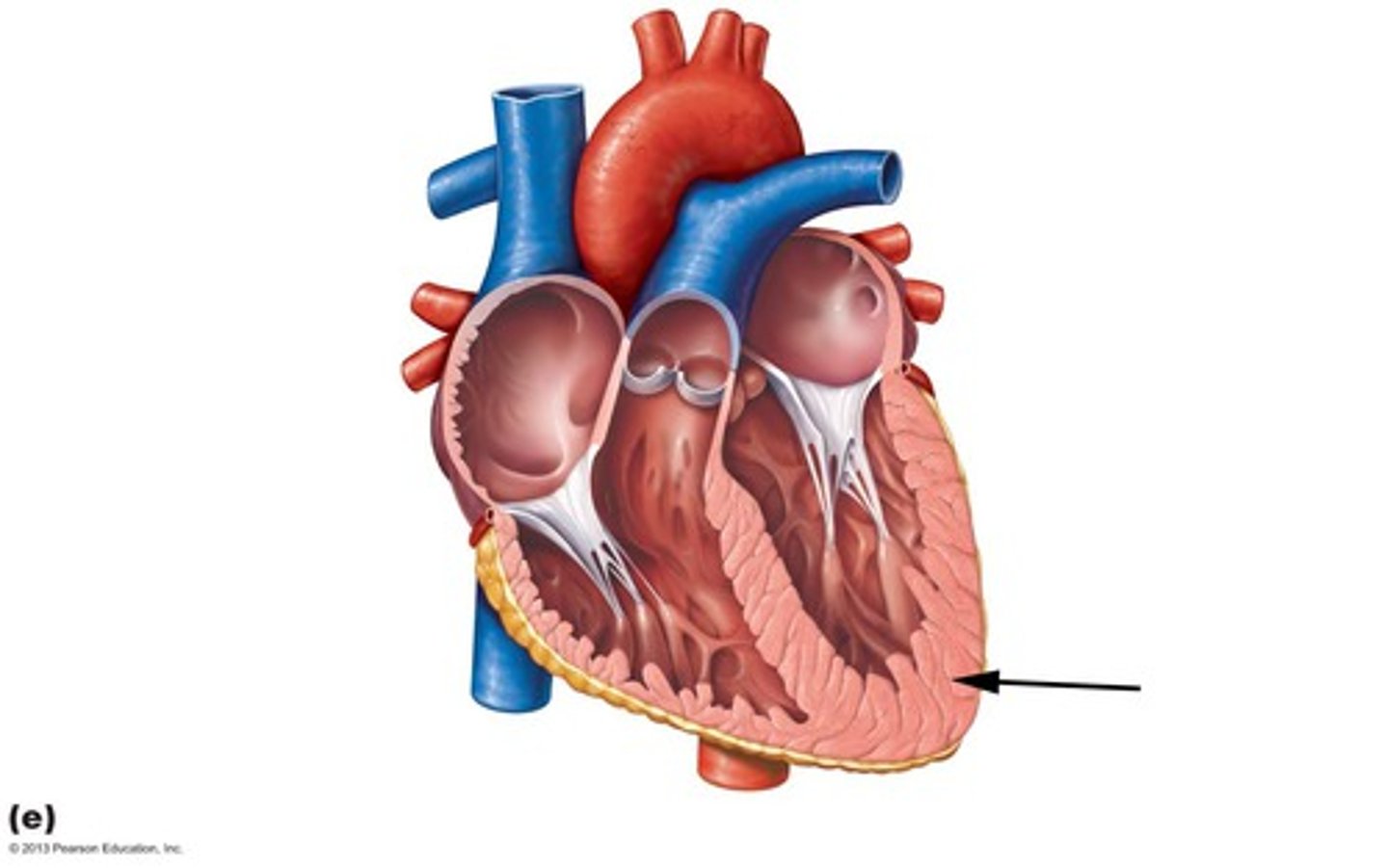
Myocardium
Muscular, middle layer of the heart
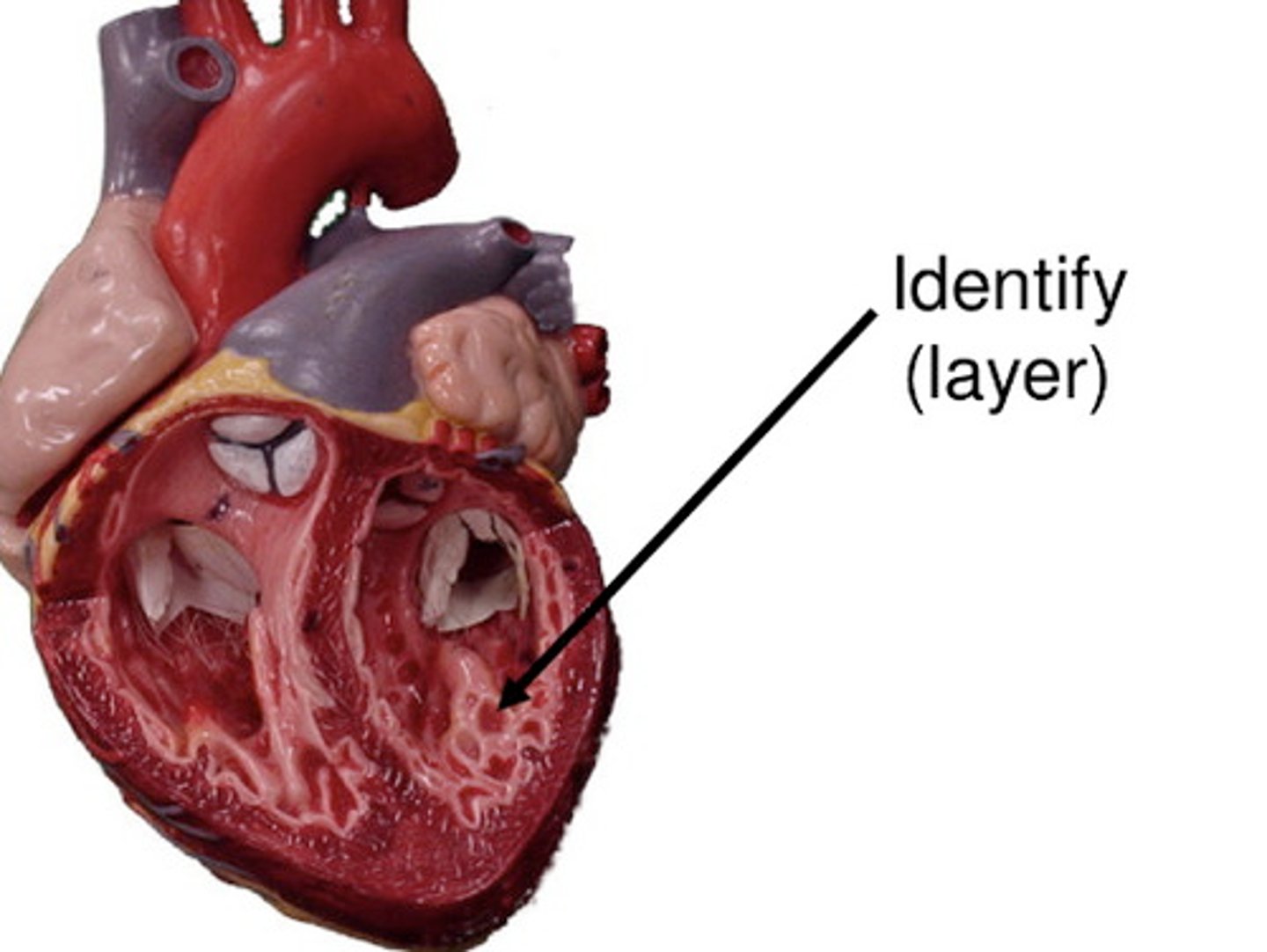
Endocardium
Membrane lining the cavities of the heart
Superior & inferior vena cava;
Right atrium;
Tricuspid valve;
Right ventricle;
Pulmonary semilunar valve;
Pulmonary artery;
Lungs;
Pulmonary veins;
Left atrium;
Bicuspid valve;
Left ventricle;
Aortic semilunar valve;
Aorta;
Route of Blood Flow Through Heart
Right Atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body
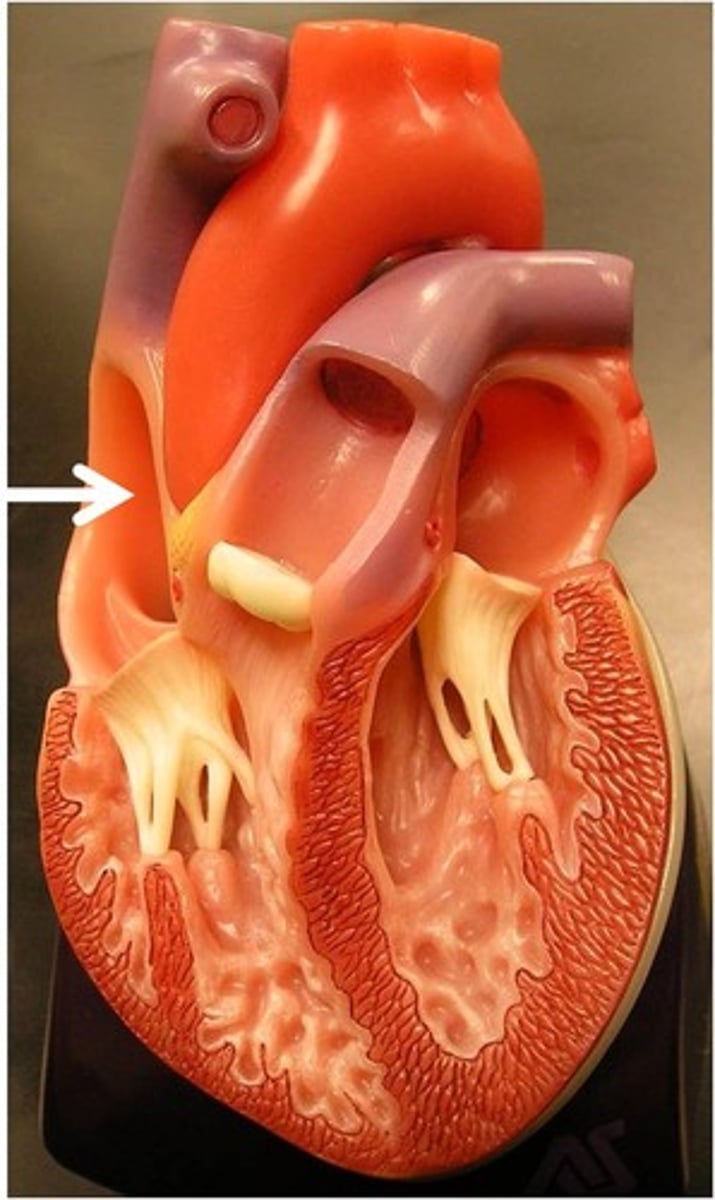
Right Ventricle
pumps blood to the lungs
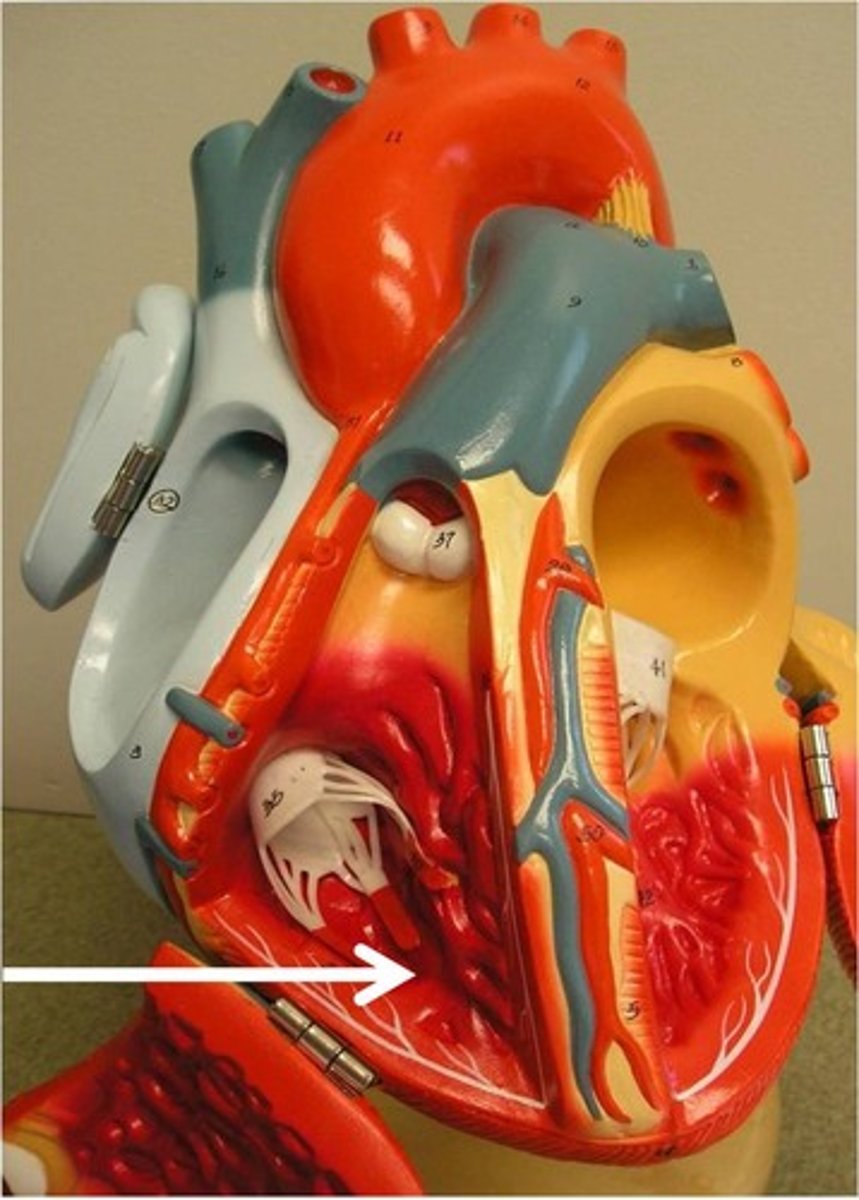
Right Auricle
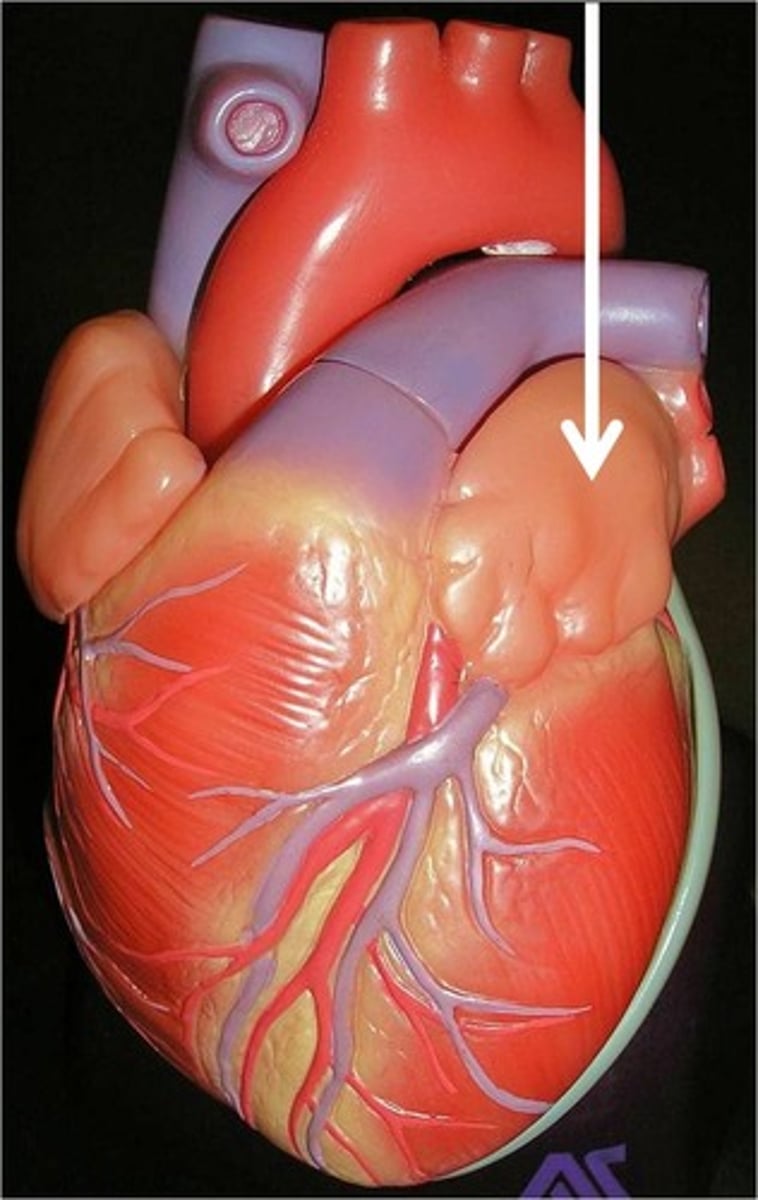
Left Atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
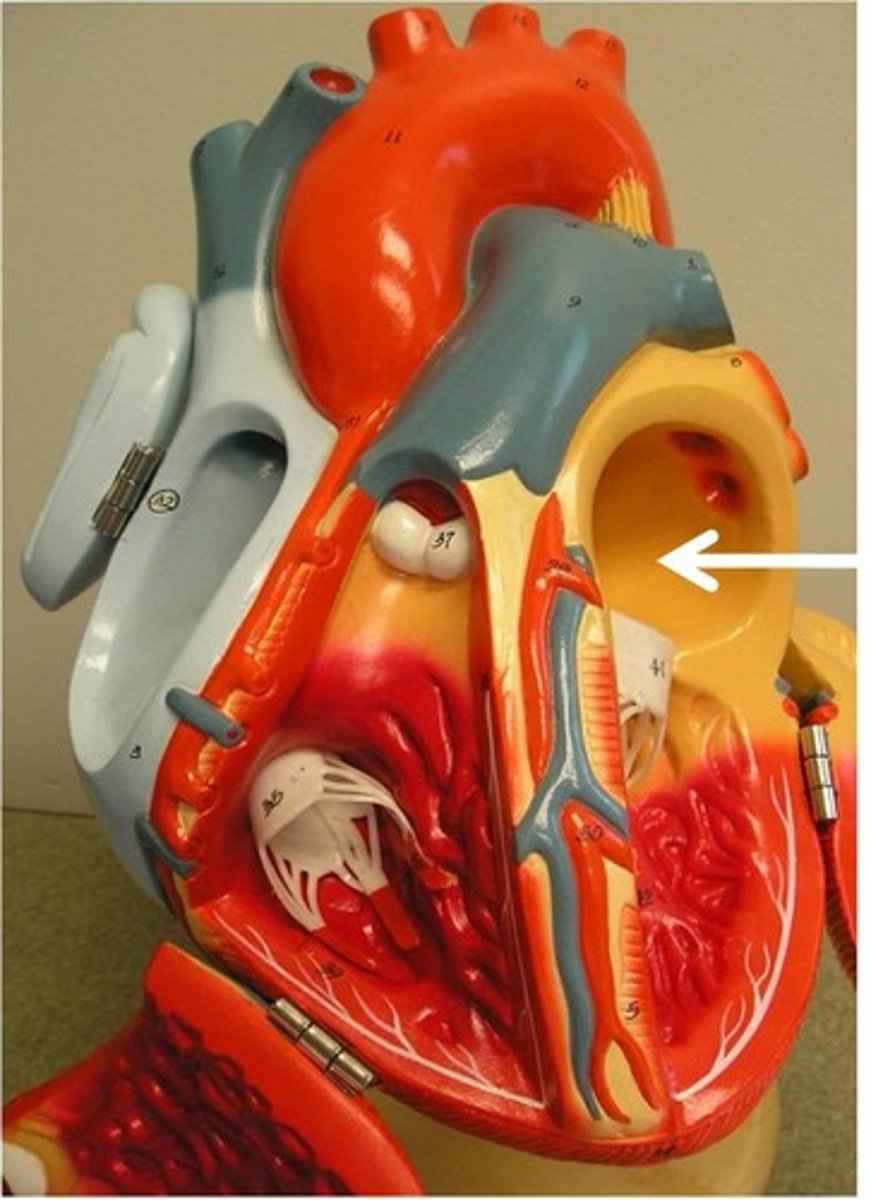
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body
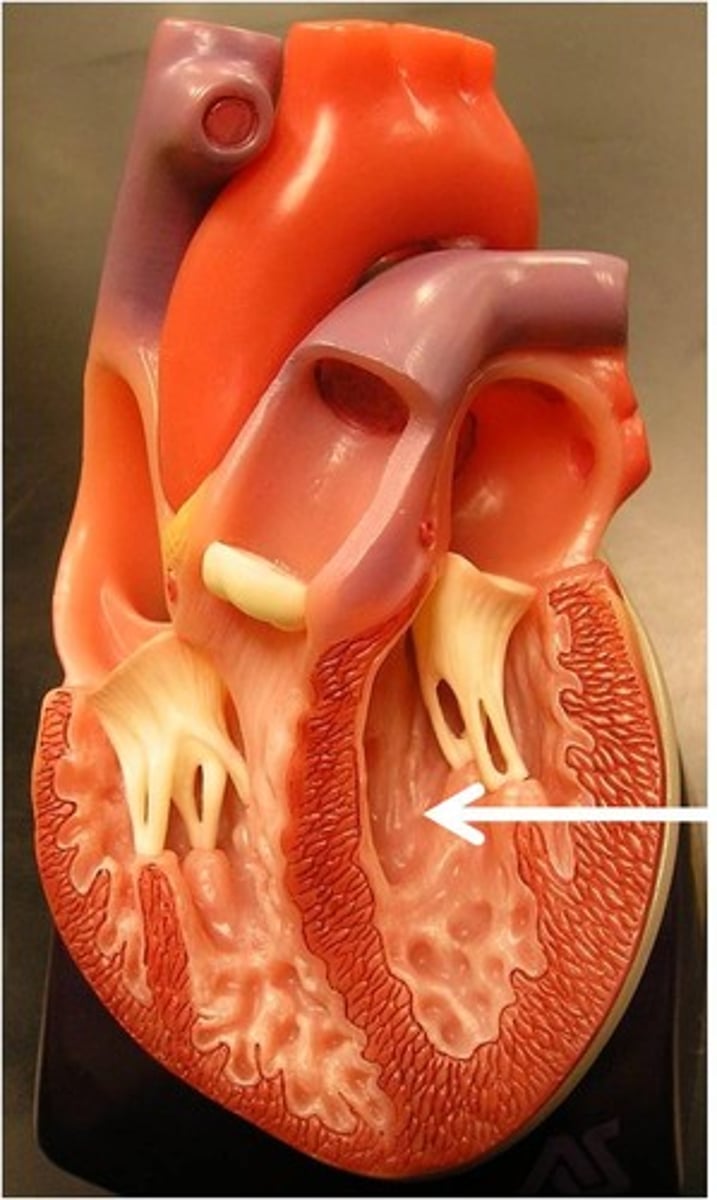
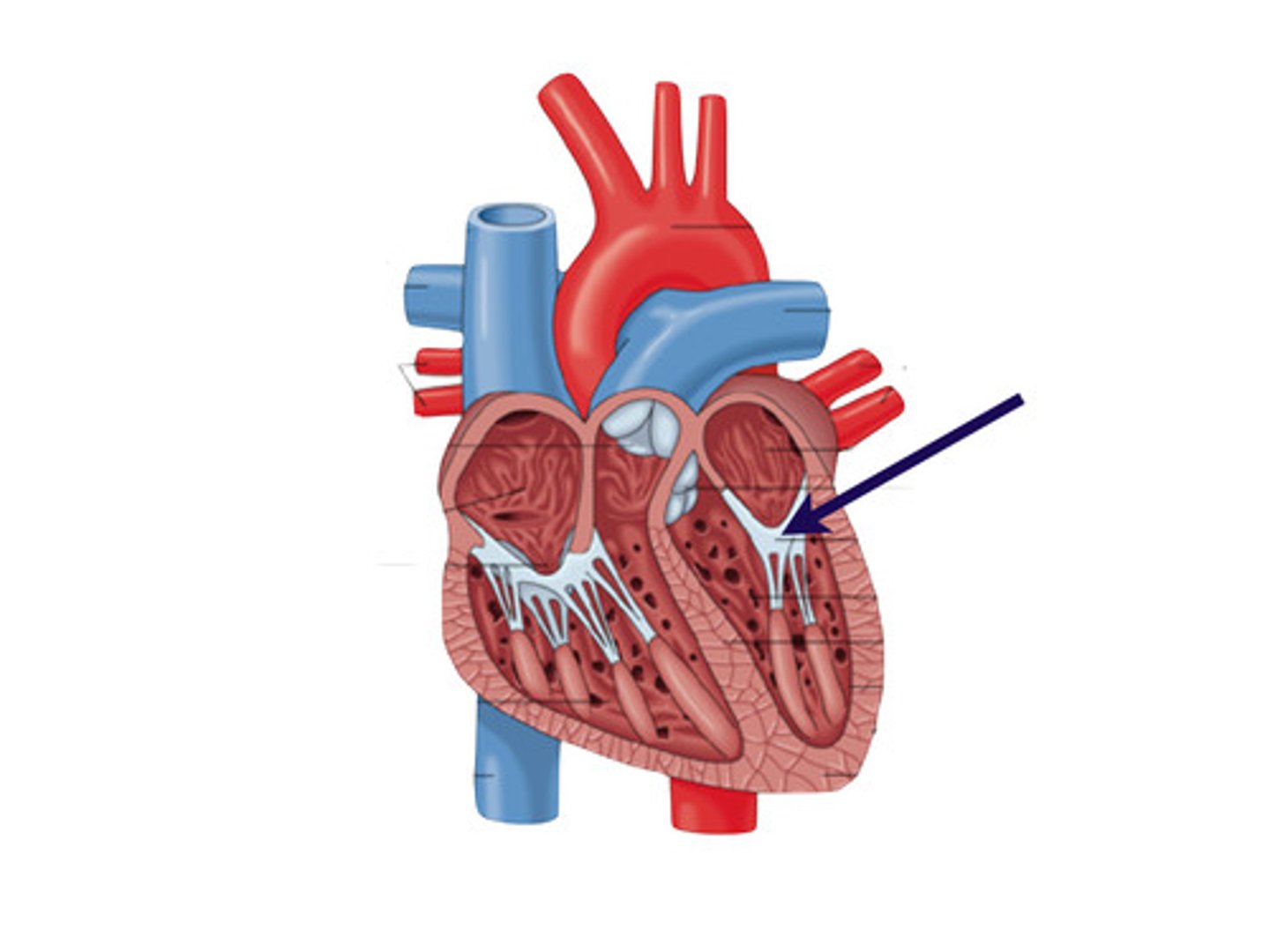
Right AV valve
The valve between the right atrium and right ventricle; the tricuspid valve
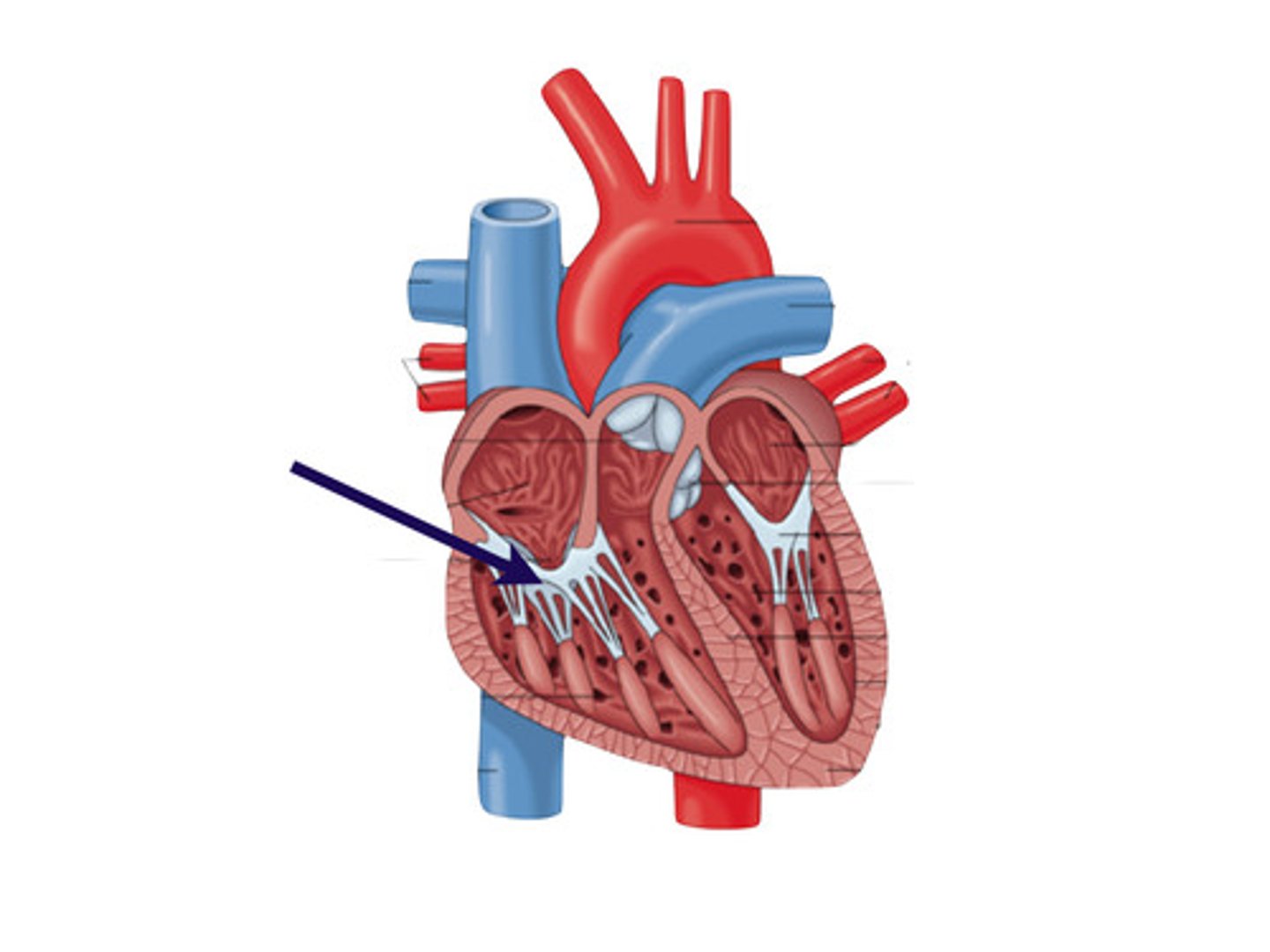
Left AV valve
the valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle; the mitral valve or bicuspid valve
Sternomastoid
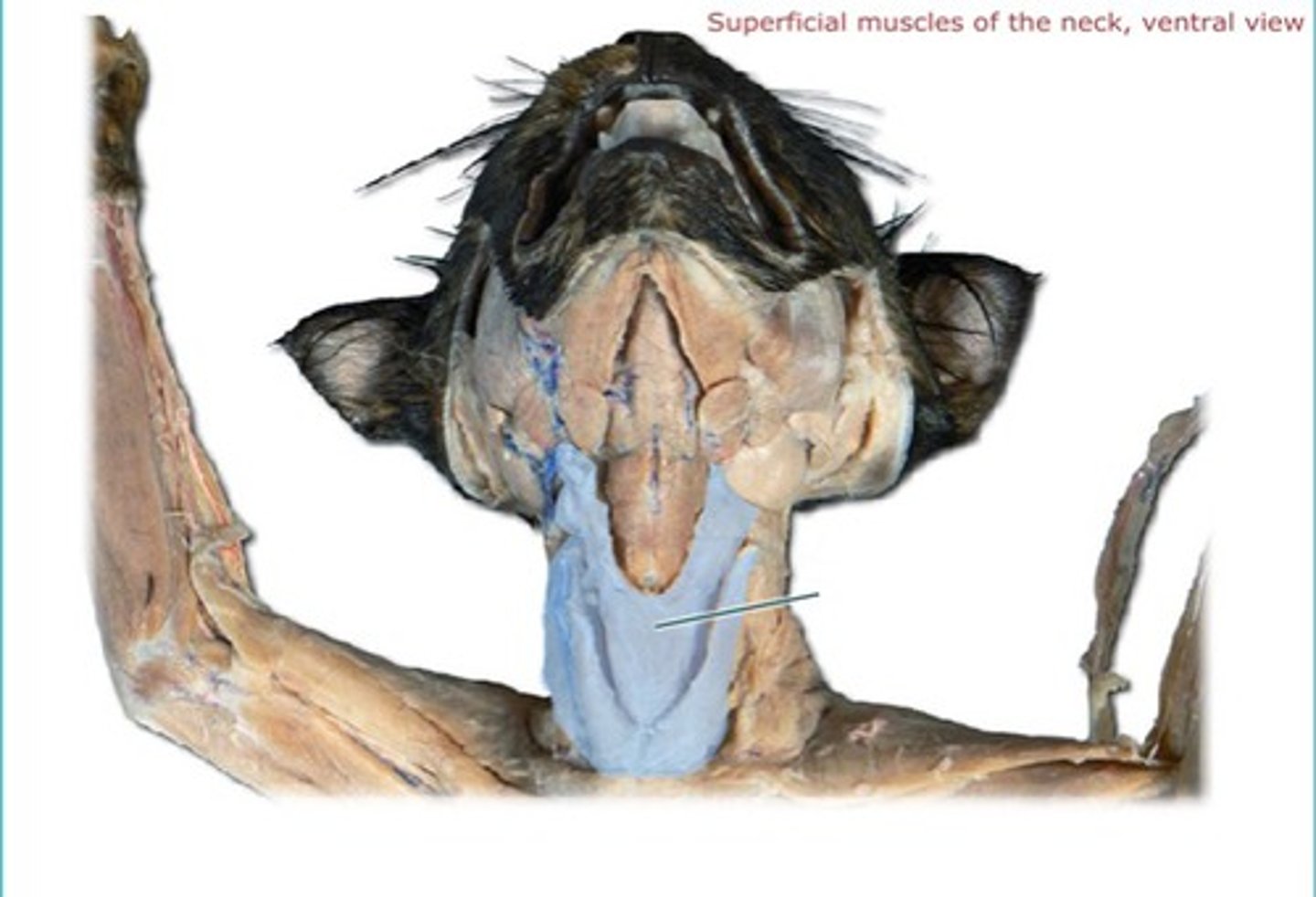
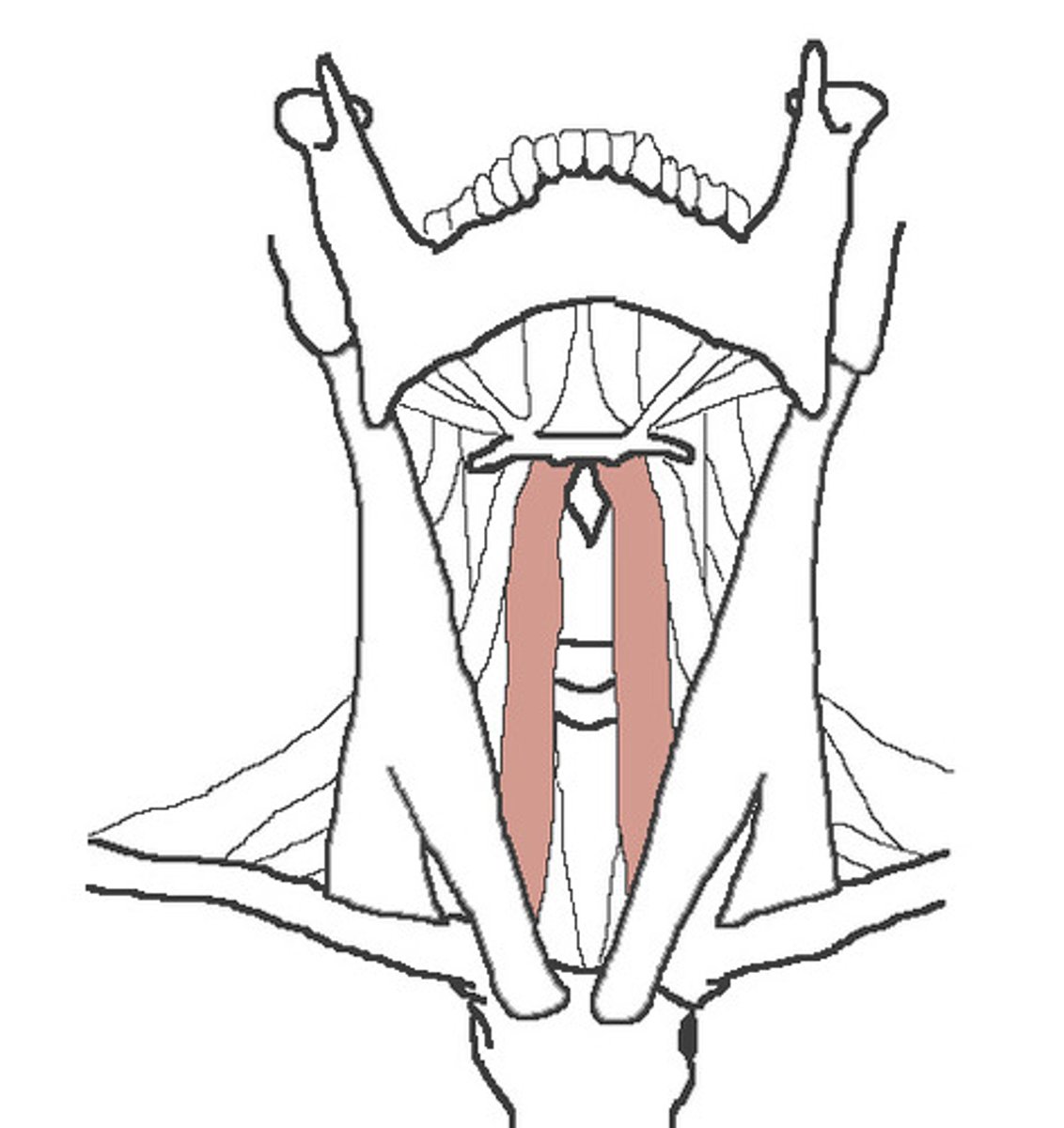
Sternohyoid
intercostal
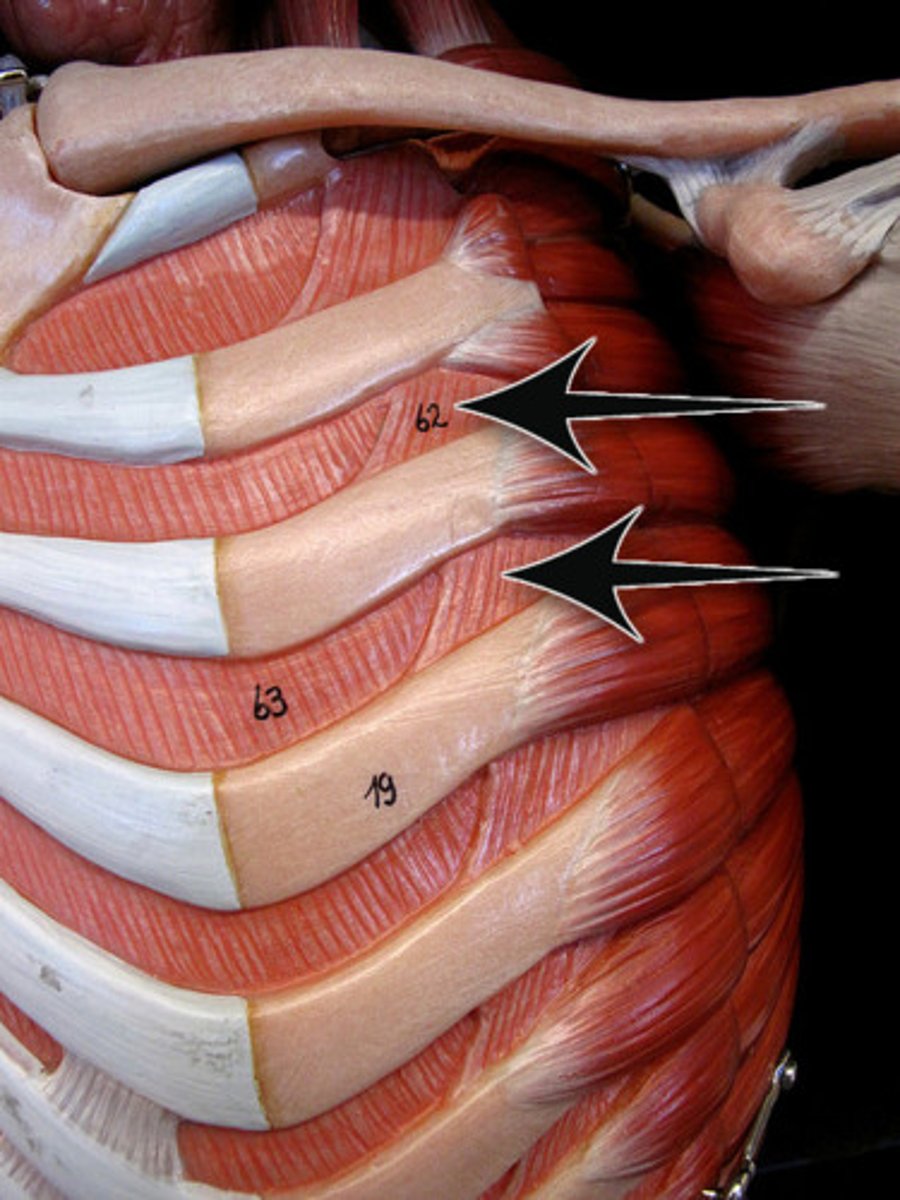
Diaphragm
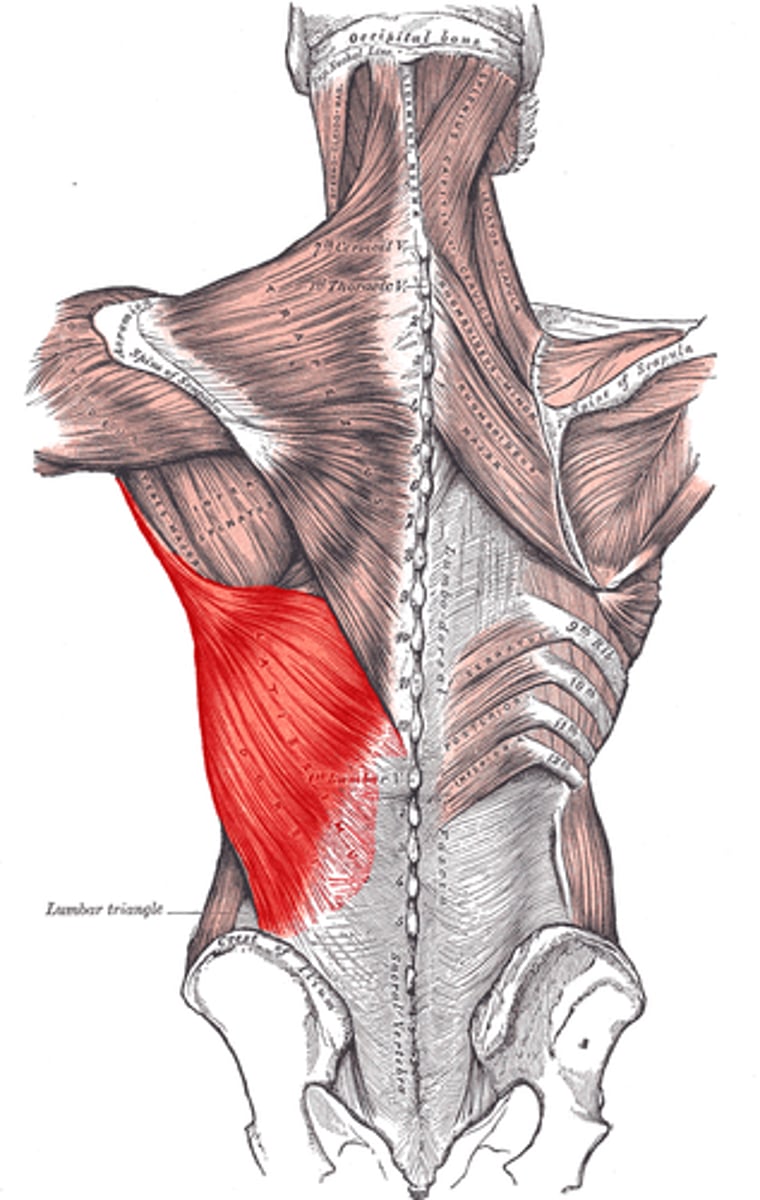
Latissimus Dorsi
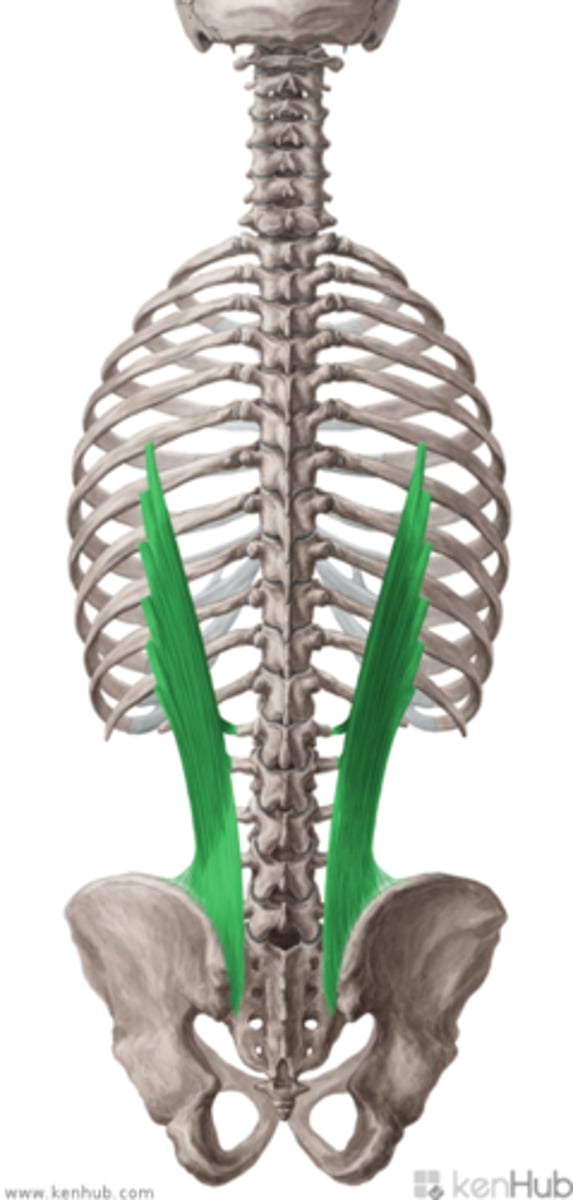
Iliocostalis
External Abdominal Oblique
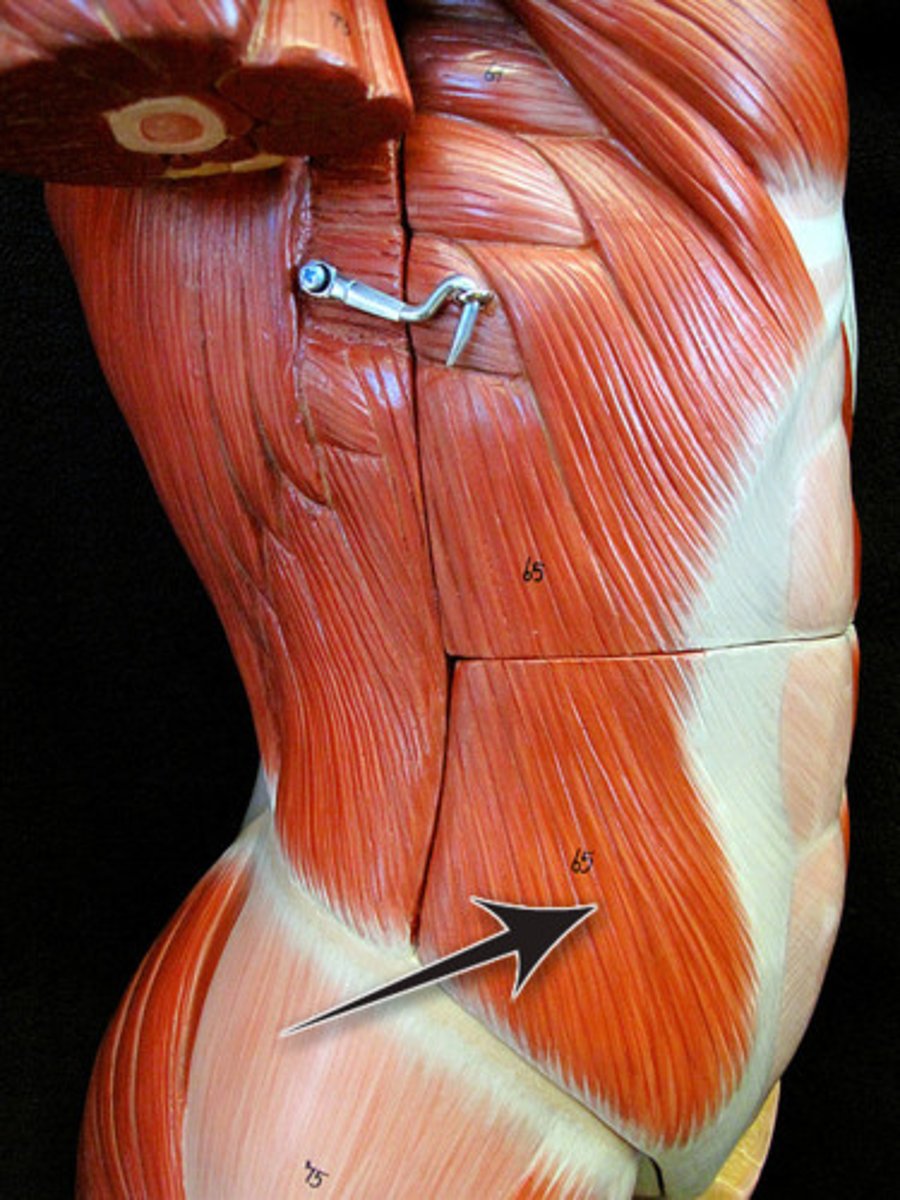
Internal Abdominal Oblique
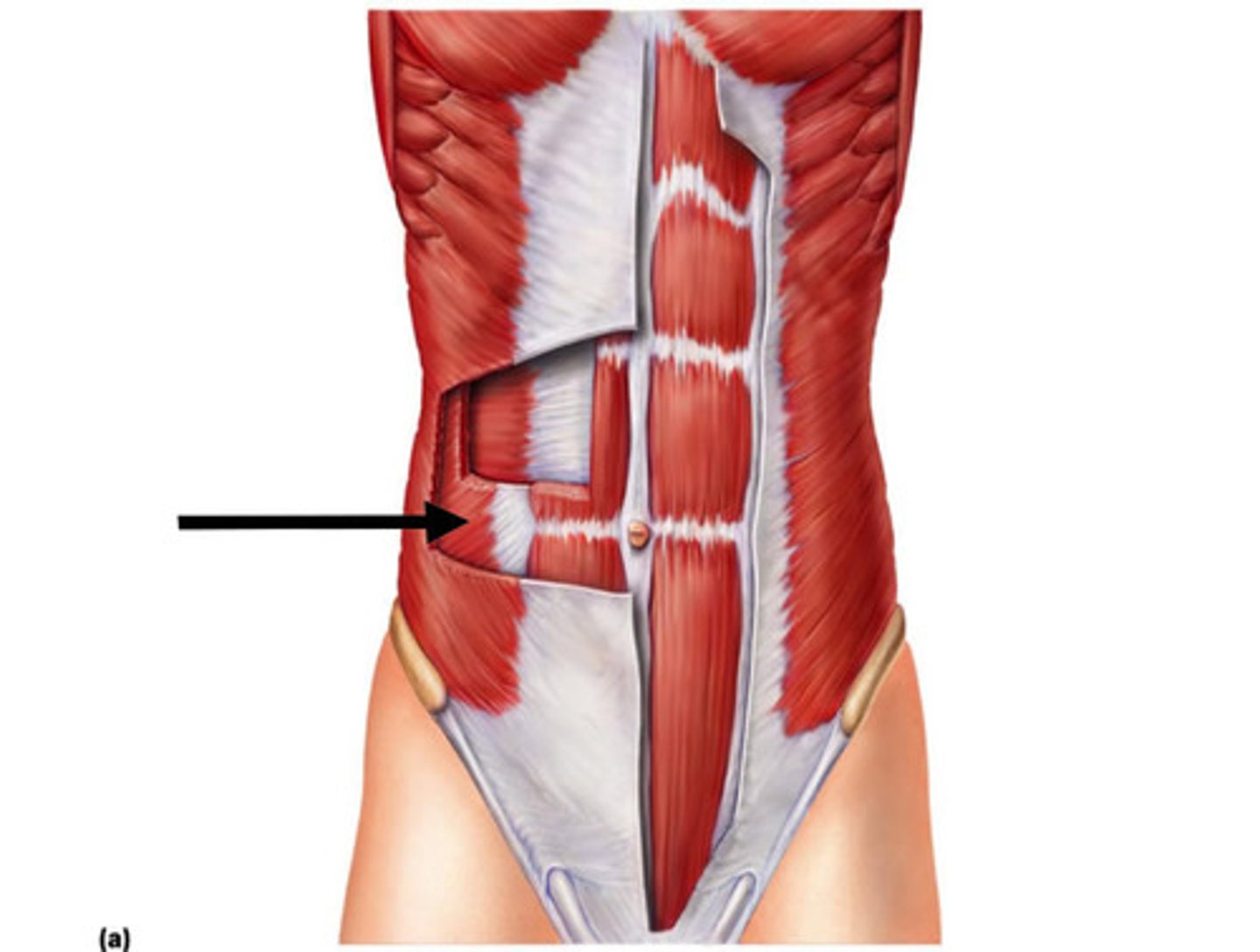
Transverse Abdominal Oblique
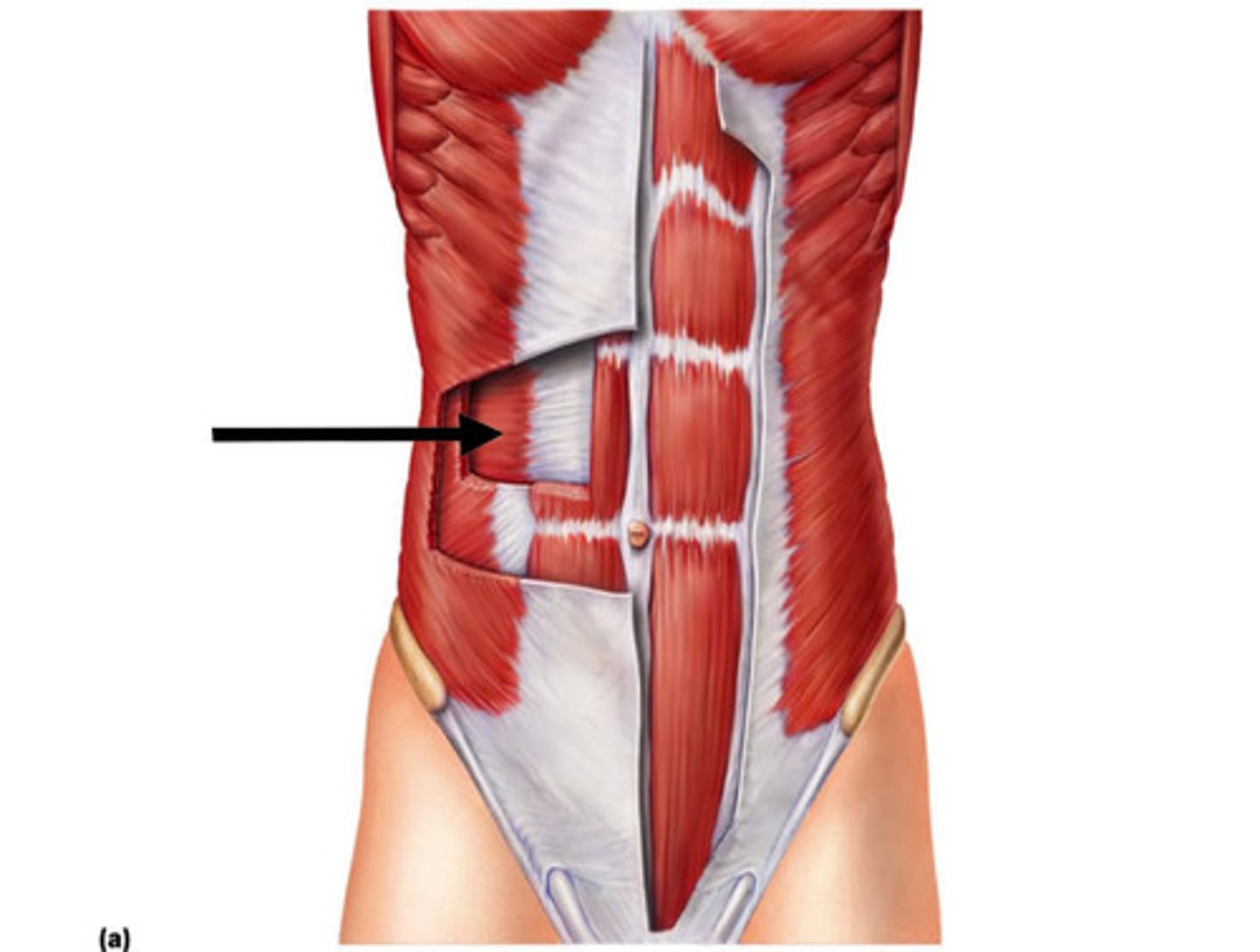
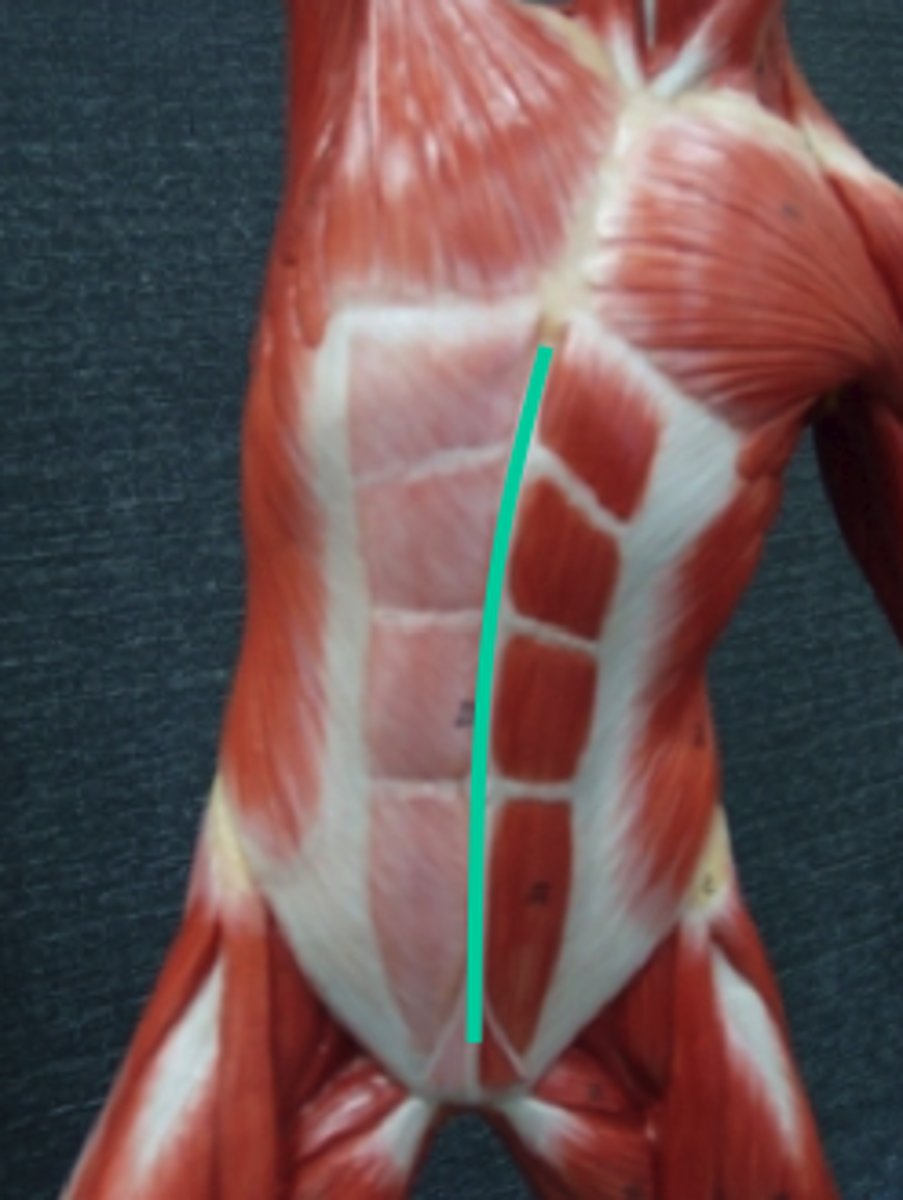
Rectus Abdominis
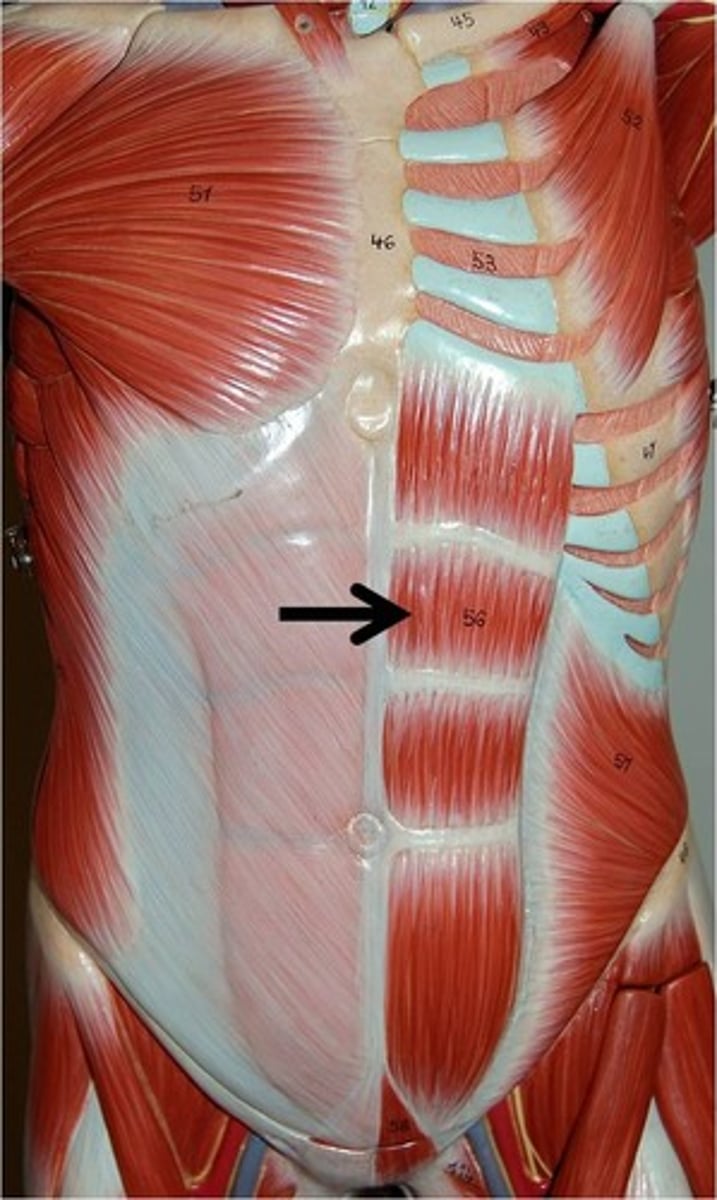
Linea Alba
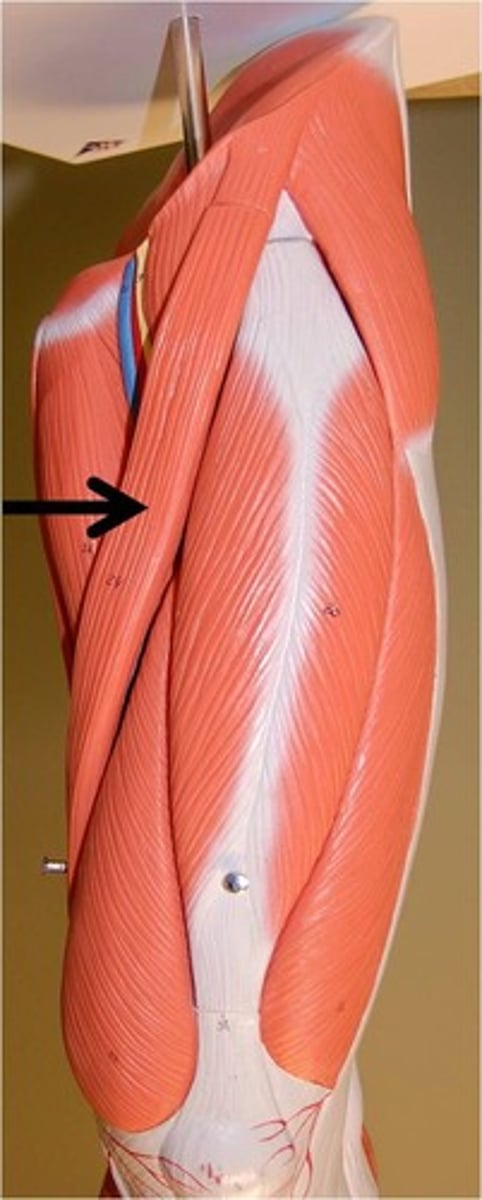
Sartorius
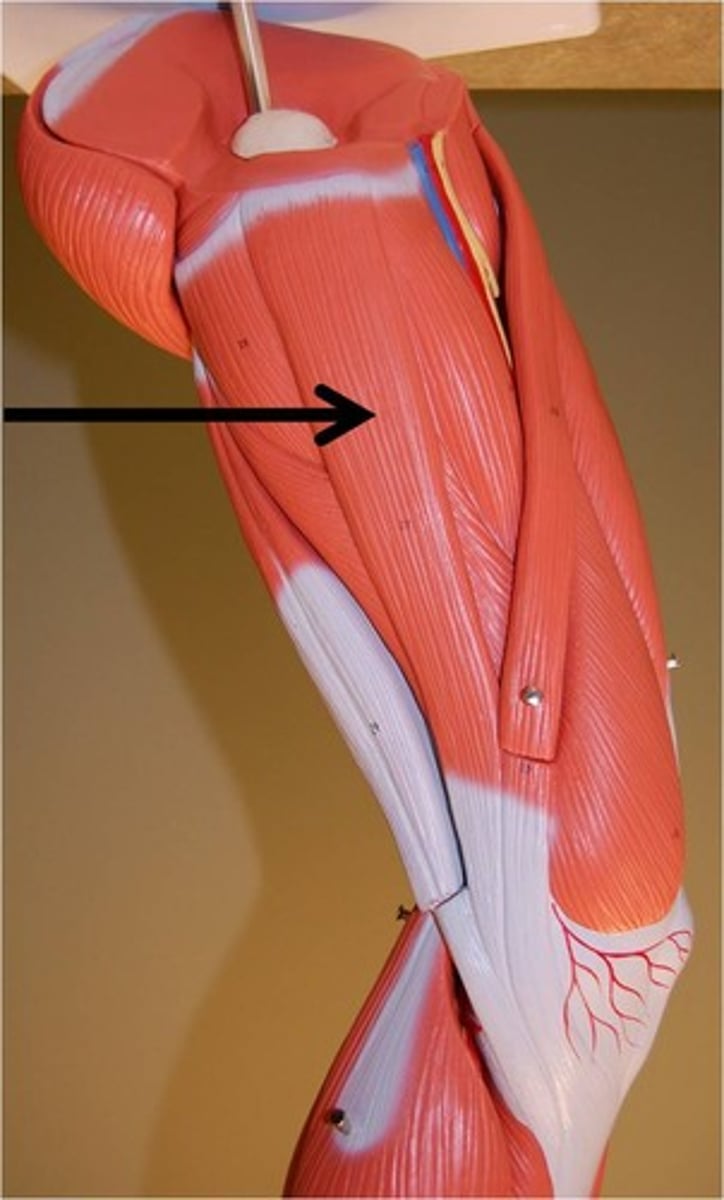
Gracillis
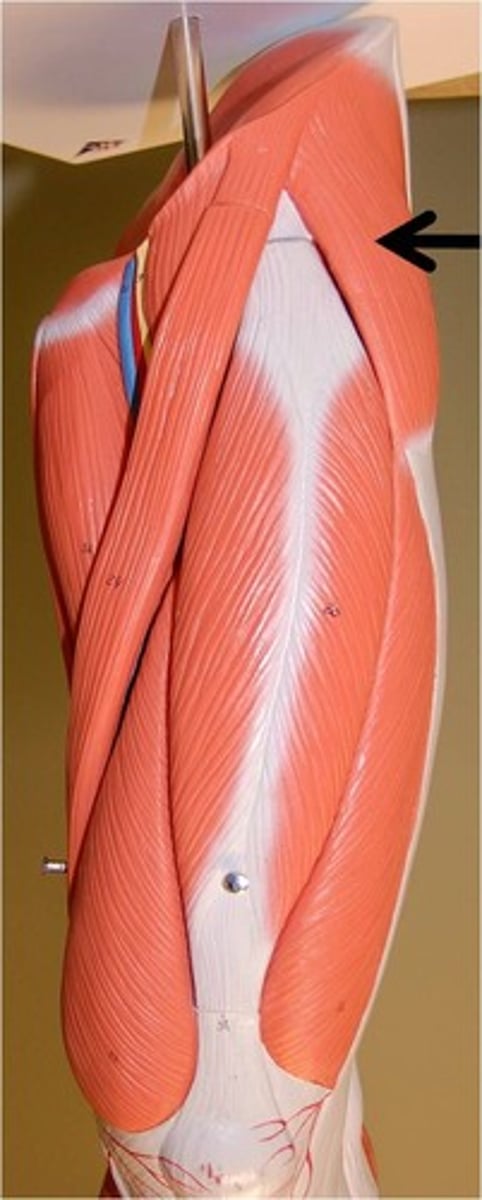
Tensor Fascia Latae
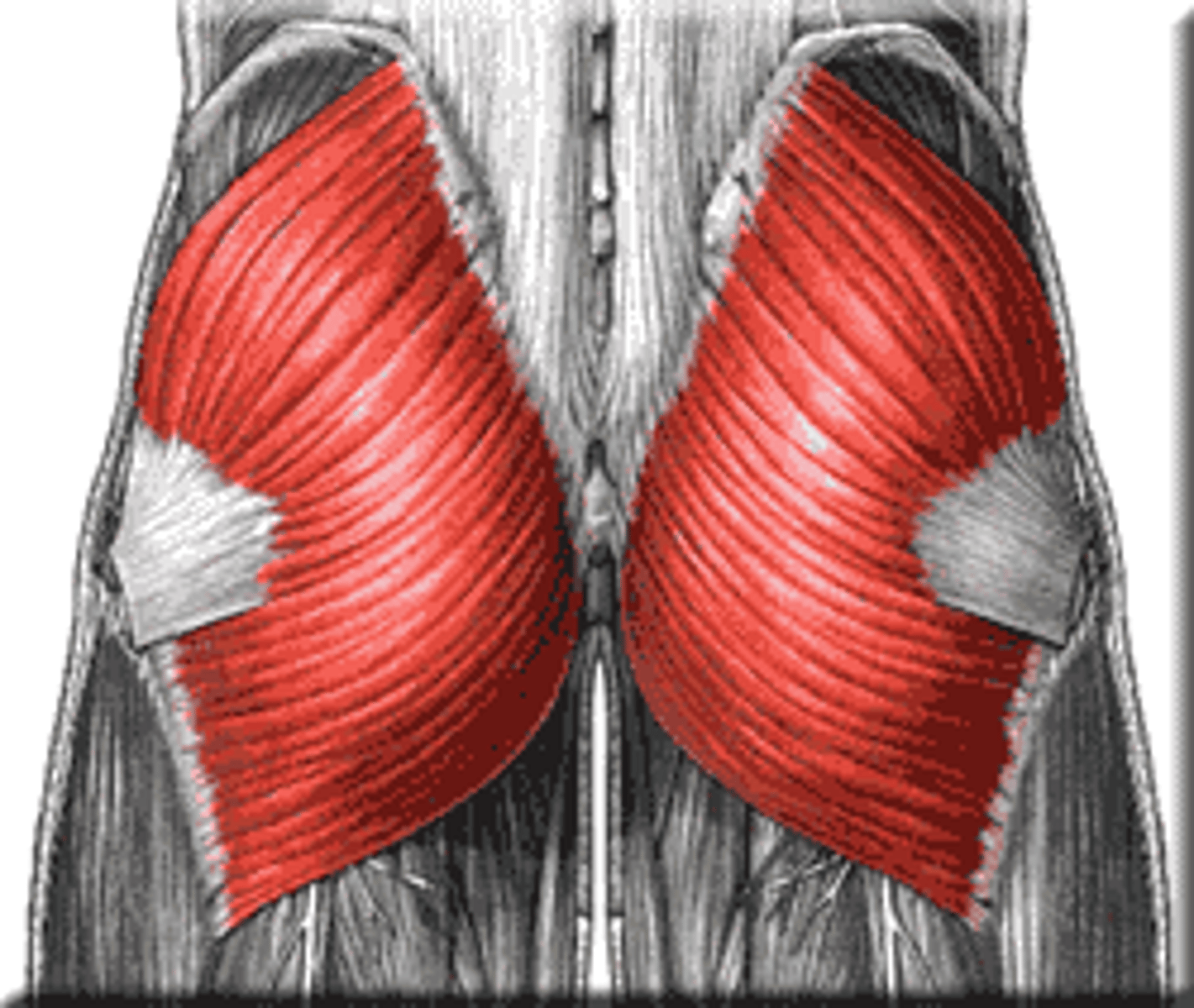
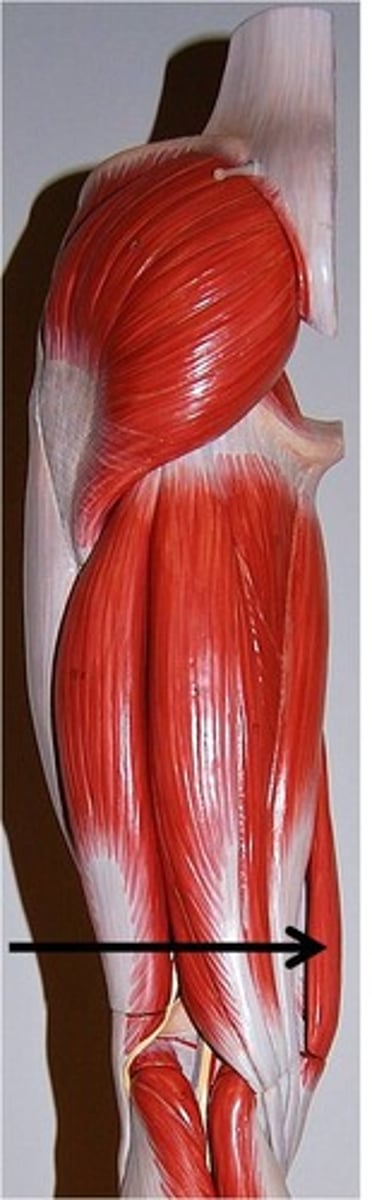
Superficial Gluteal Muscle
Middle Gluteal Muscle
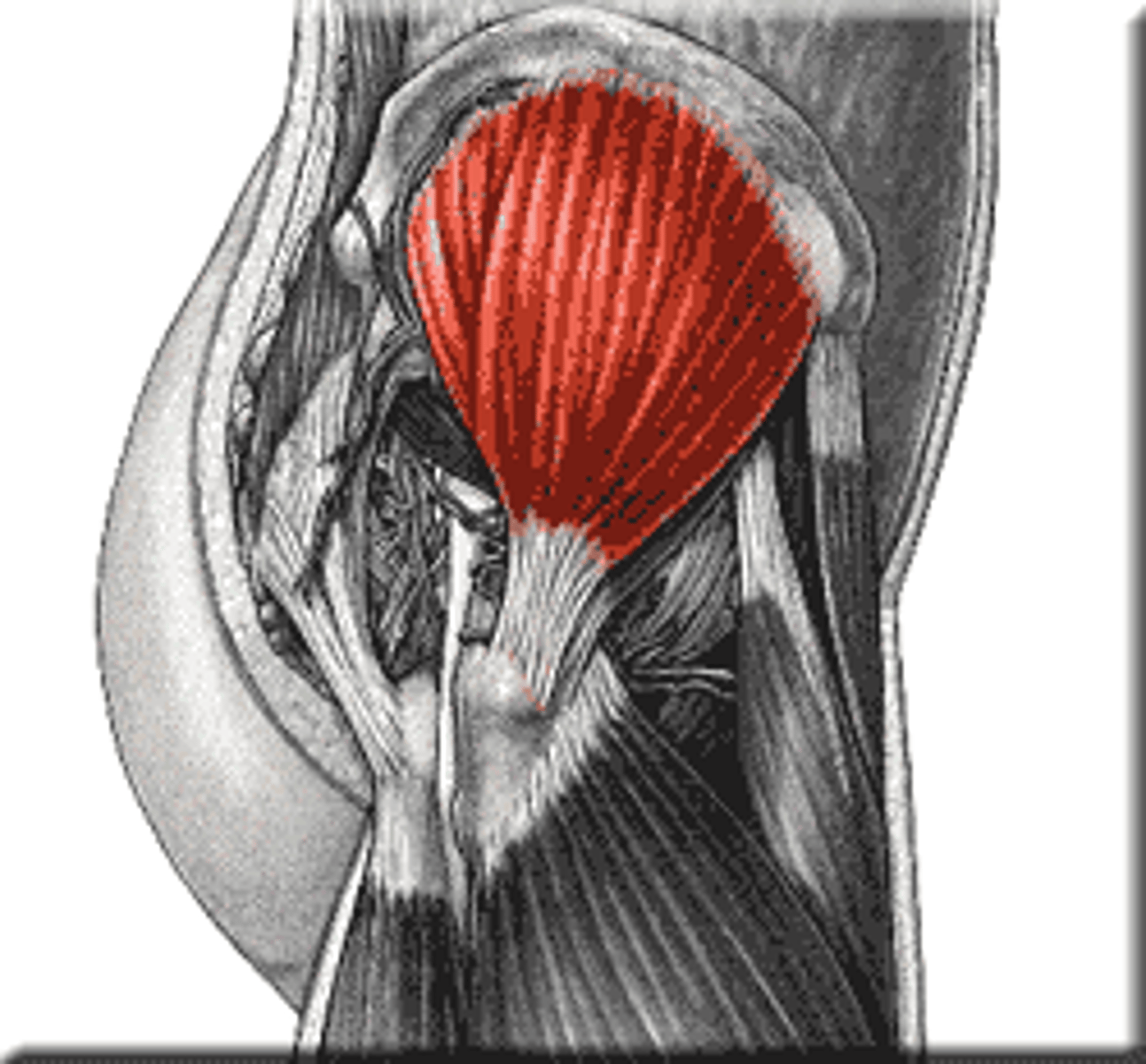
Deep Gluteal Muscle
Rectus Femoris; Vastus Lateralis; Vastus Medialis; Vastus Intermedius
The 4 quad muscles
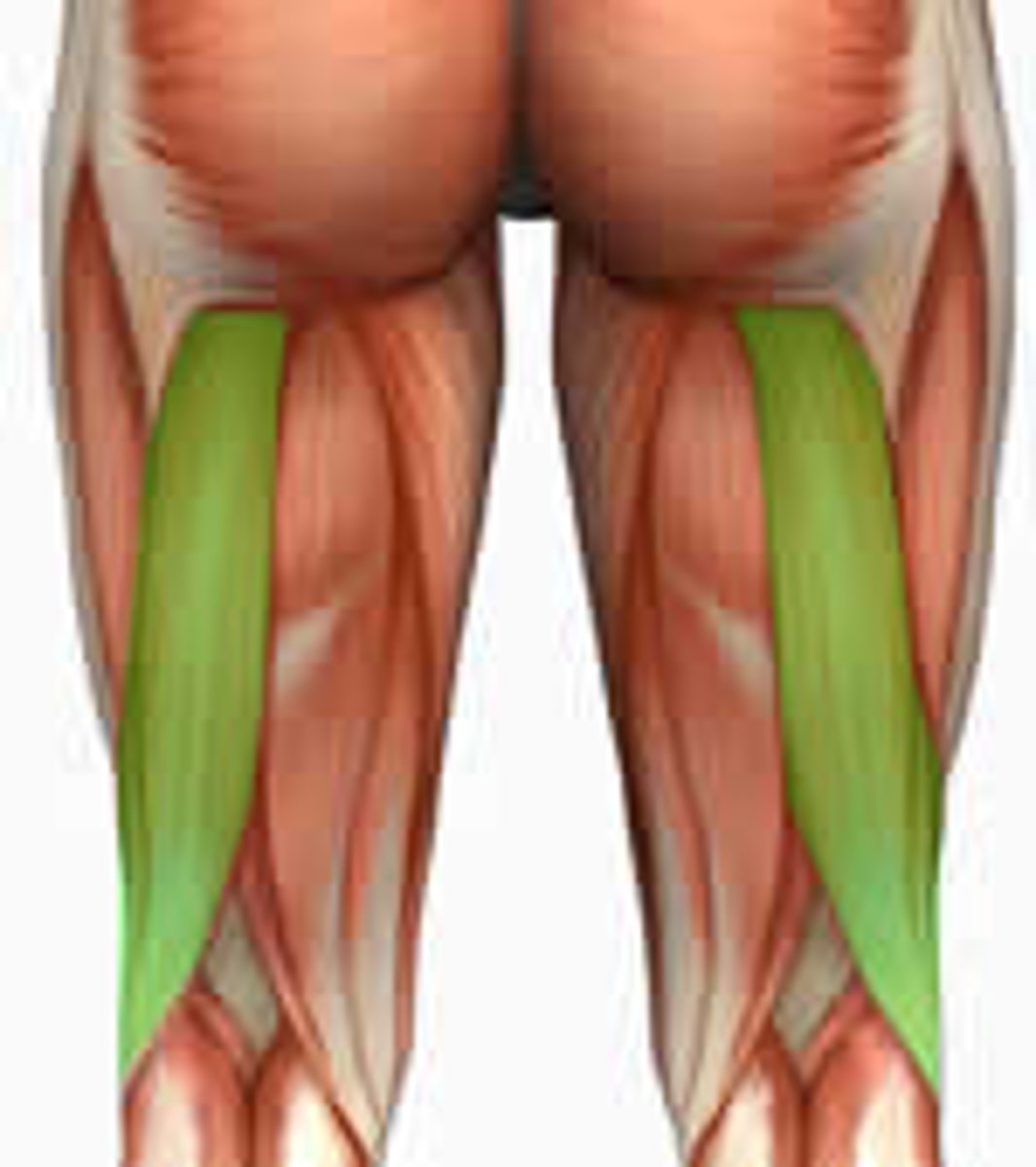
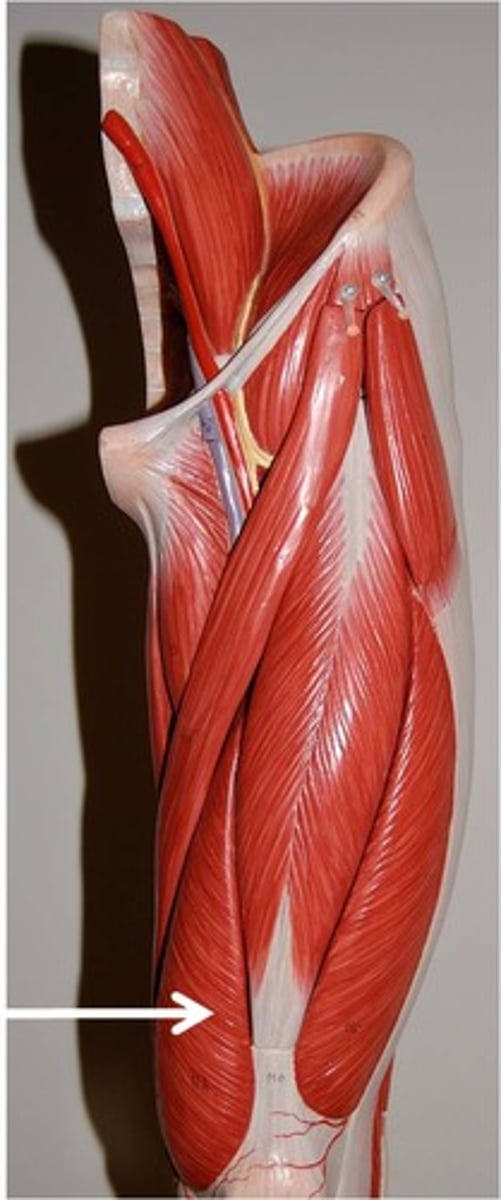
Hamstring Muscle Group
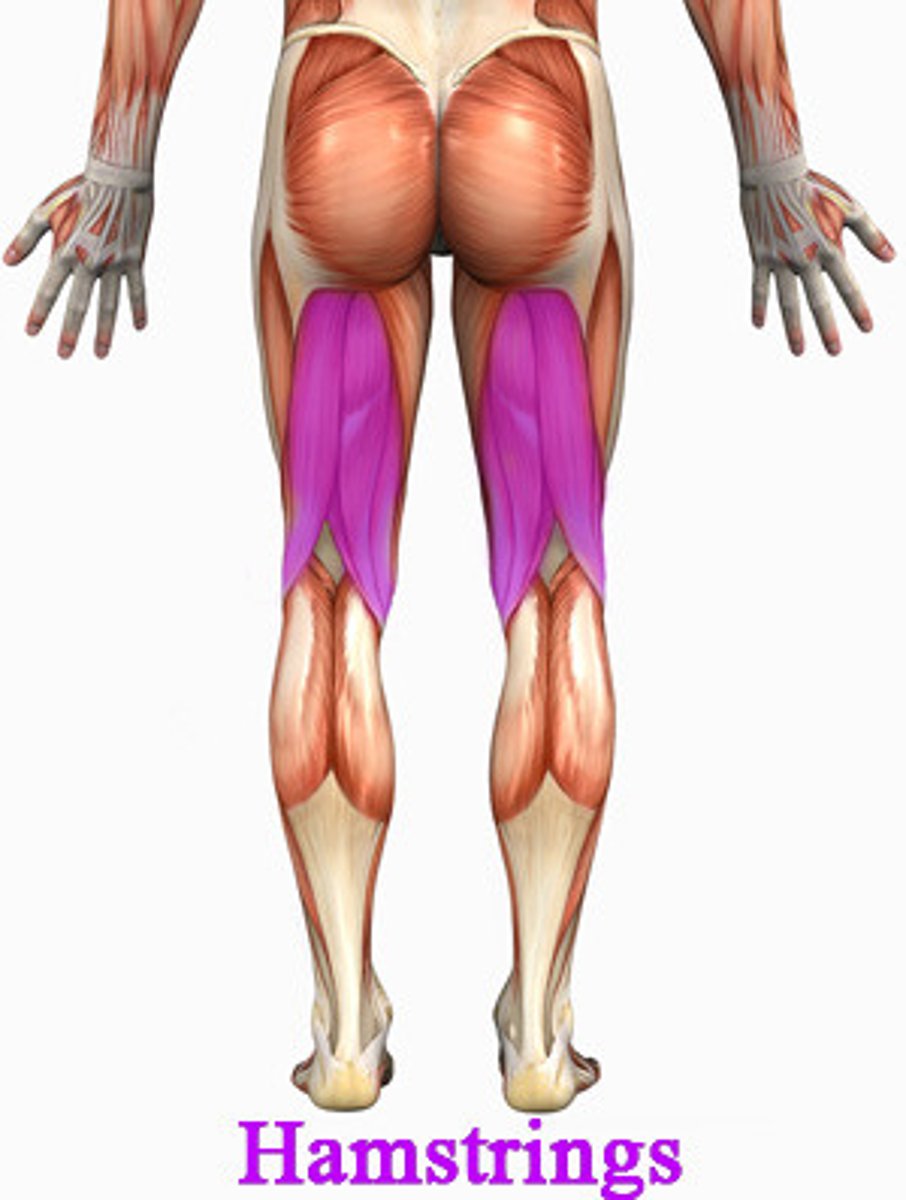
Semitendinosus
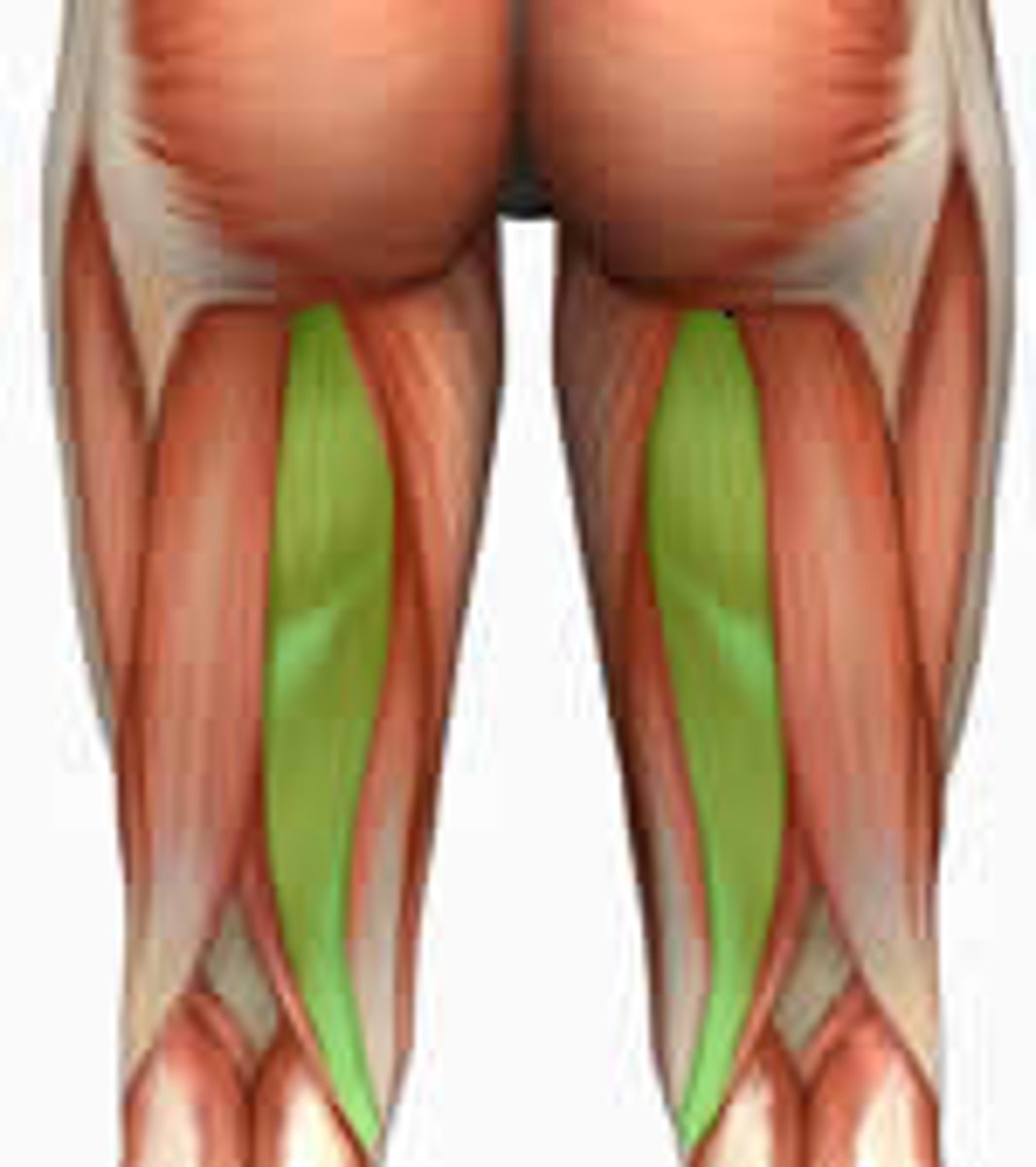
Semimembranosus
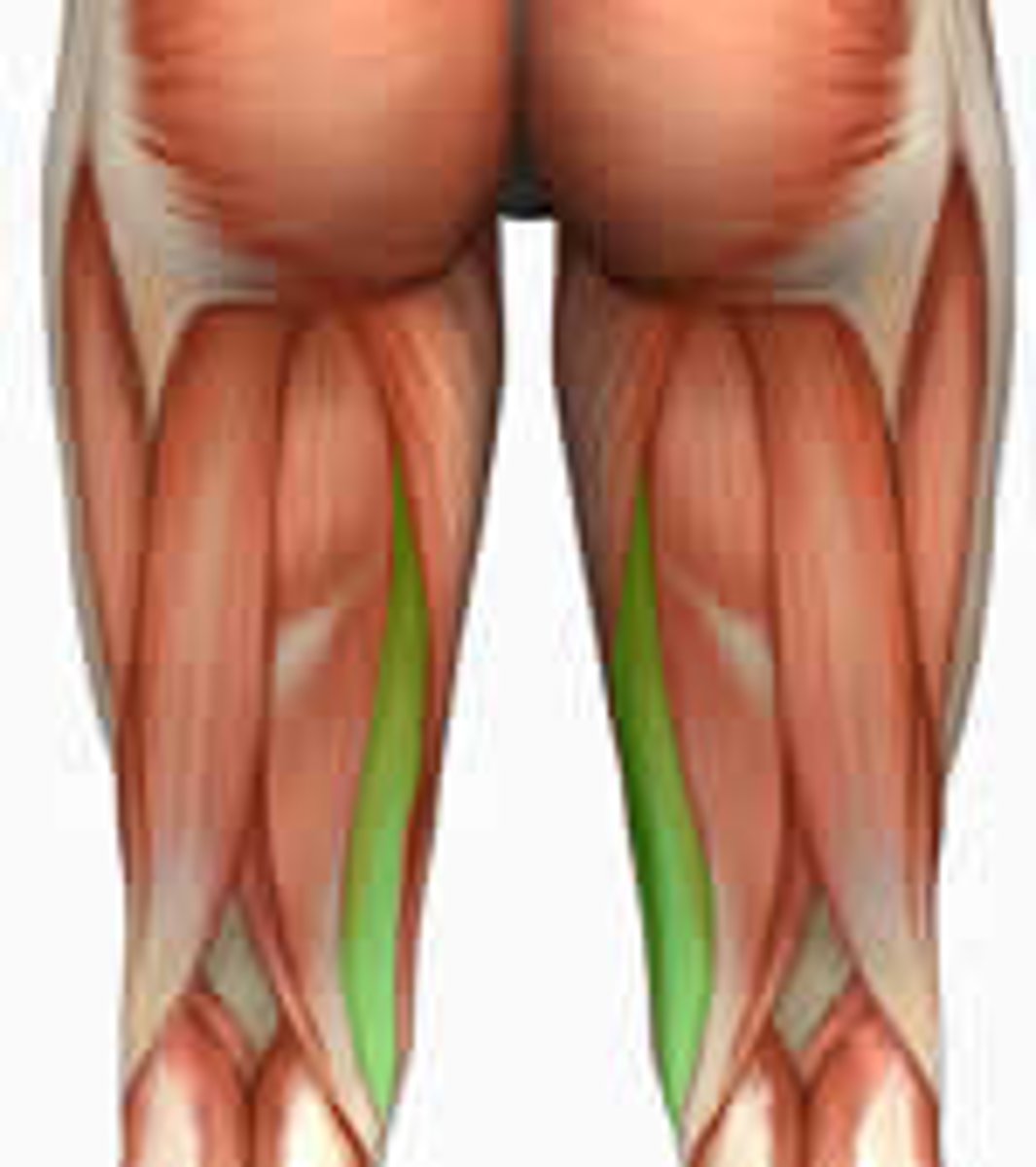
Biceps Femoris Muscle
Rectus Femoris
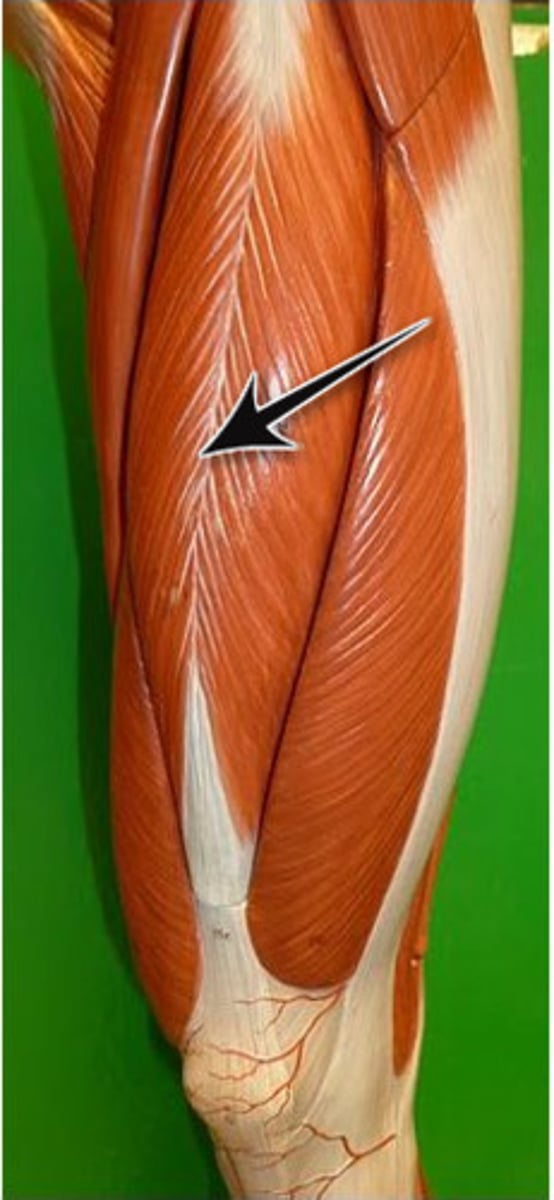
Vastus Lateralis
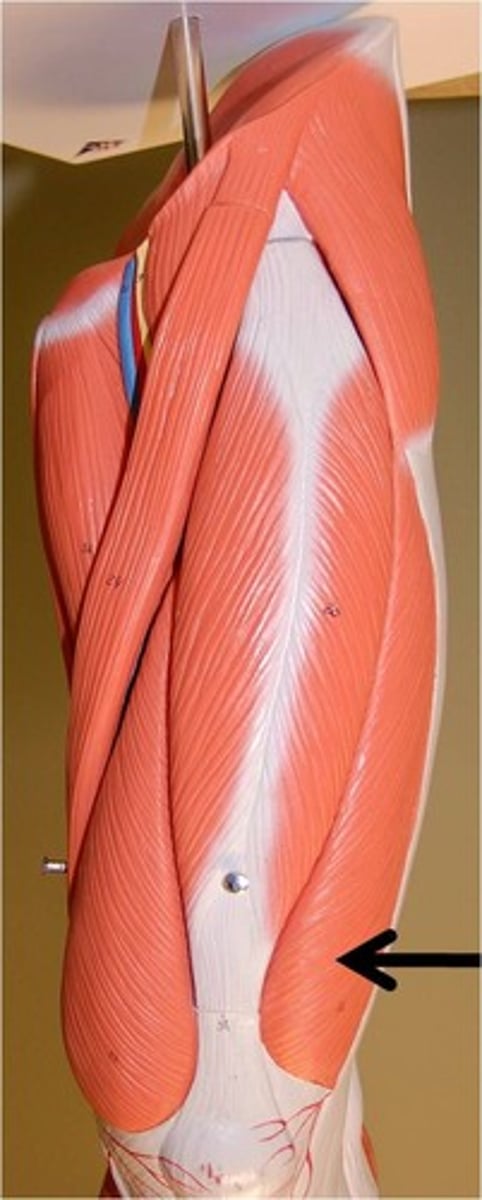
Vastus Medialis
Vastus Intermedius
Pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygentated blood from the heart to the lungs
Pulmonary veins
carry the oxygenated blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart
aorta
The large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body.
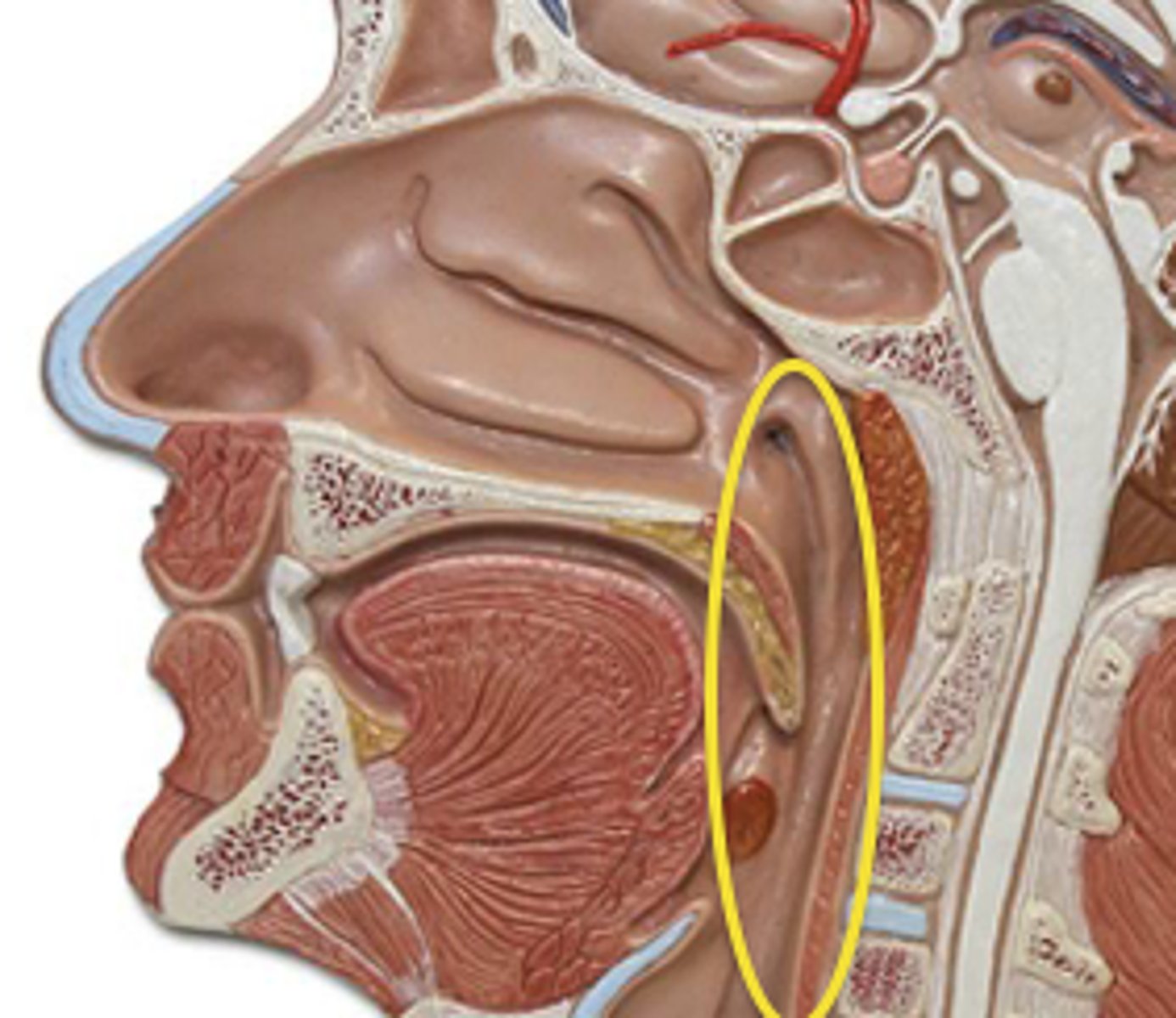
Pharynx
the membrane-lined cavity behind the nose and mouth, connecting them to the esophagus.
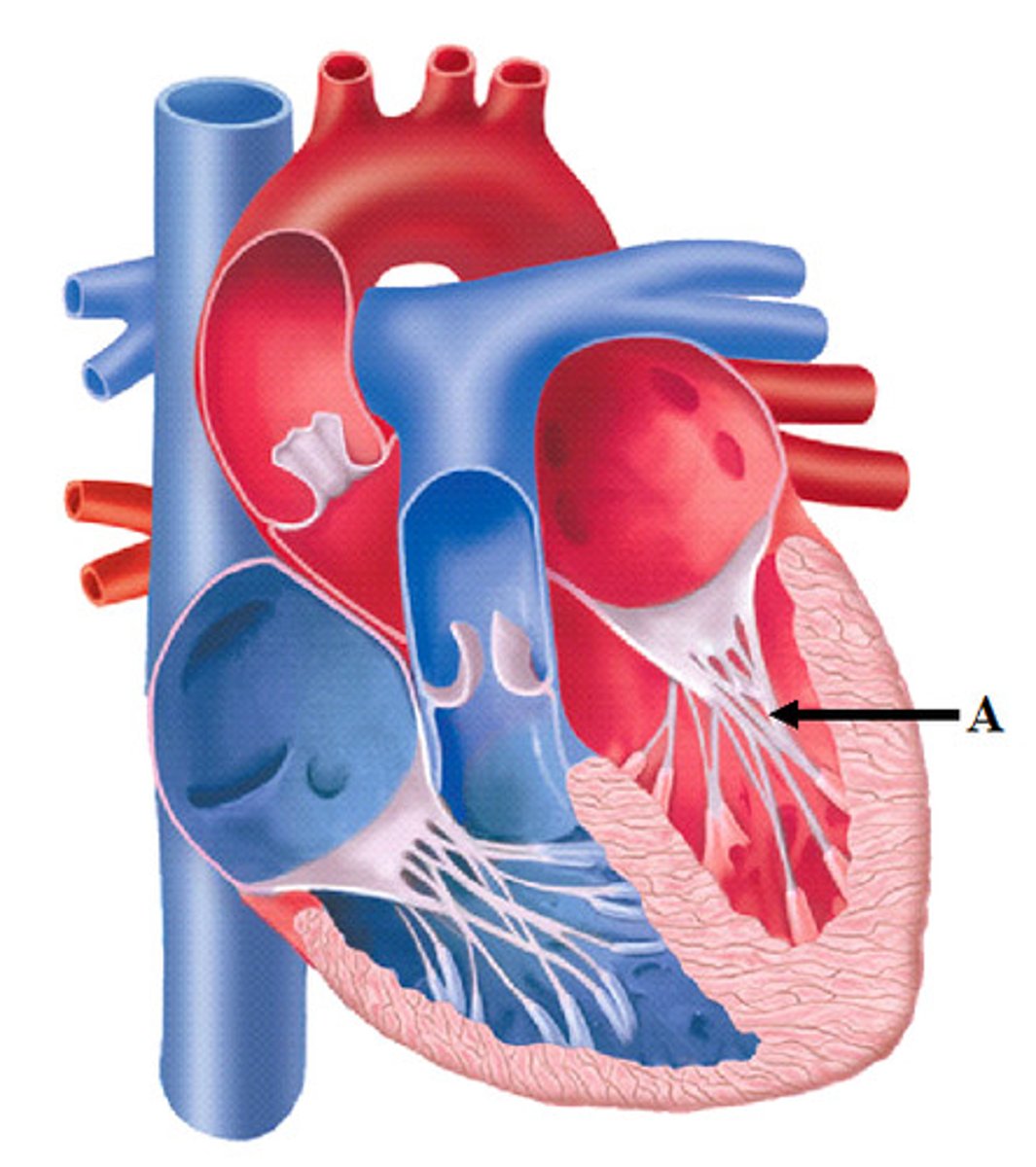
chordae tendinae
Fibers (heart strings) attatched to the tricuspid and mitral valve which pull it closed when papillary muscles contract, preventing back flow of blood
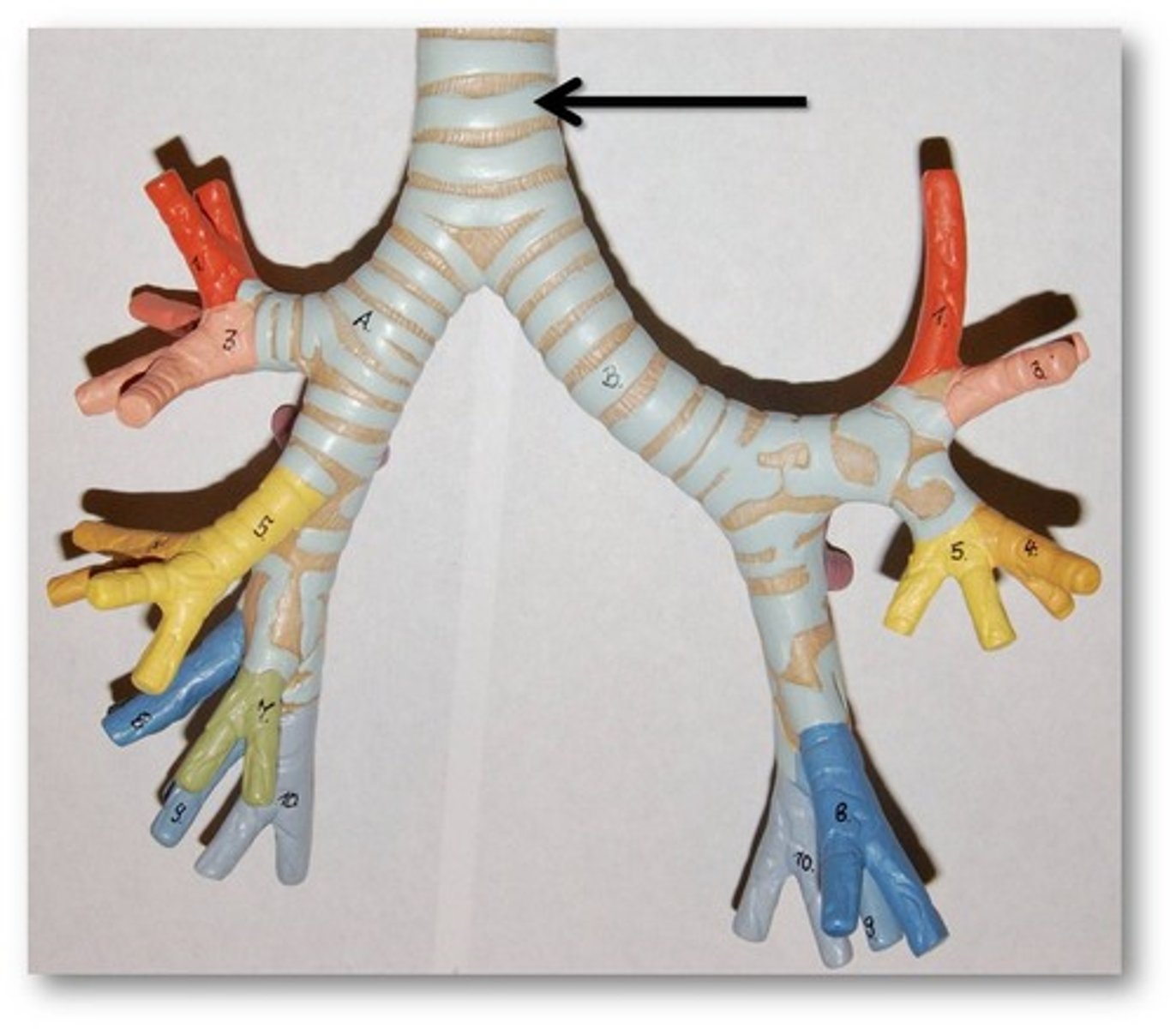
Larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
trachea
a large membranous tube reinforced by rings of cartilage, extending from the larynx to the bronchial tubes and conveying air to and from the lungs; the windpipe.
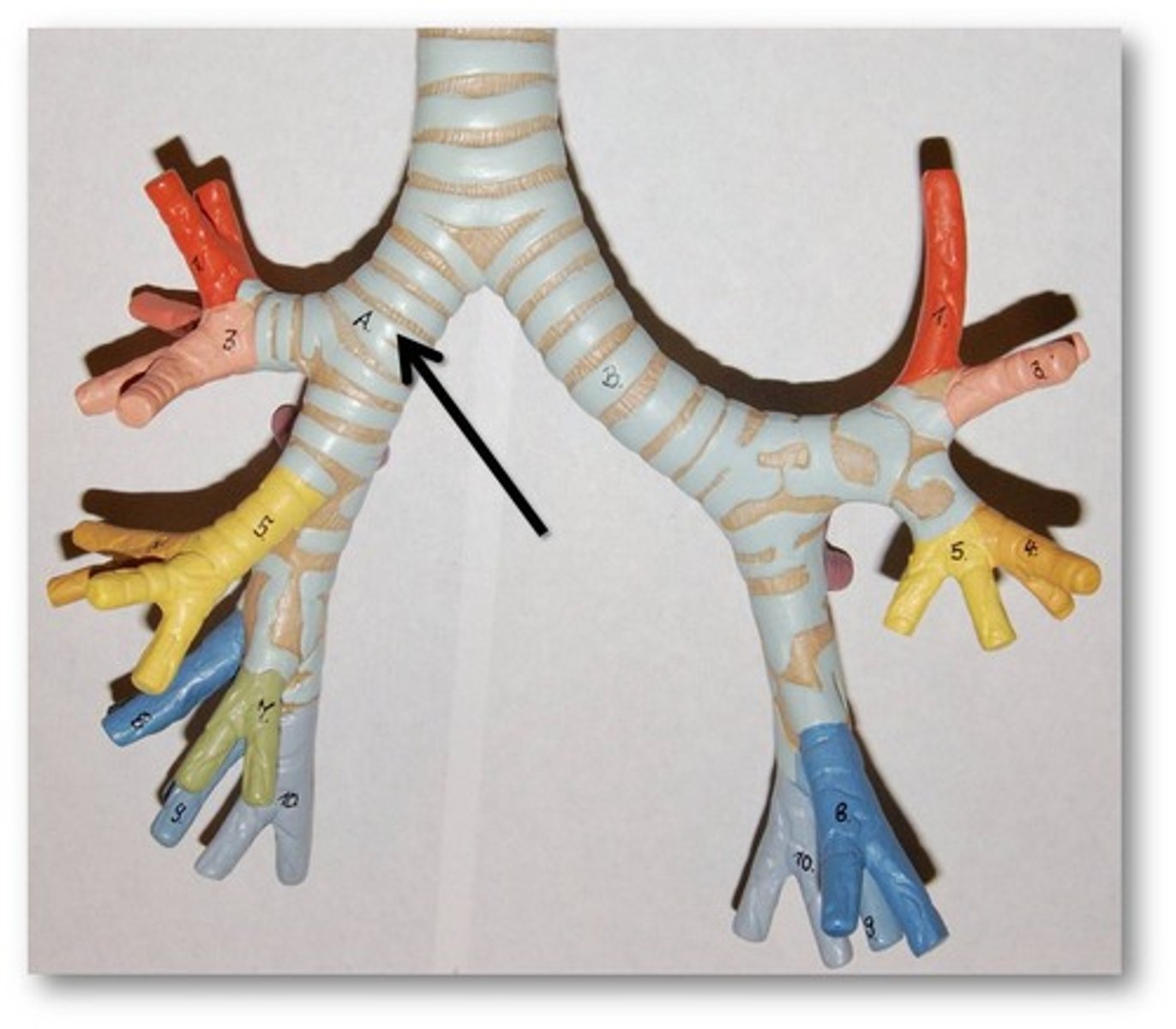
bronchi
two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs.
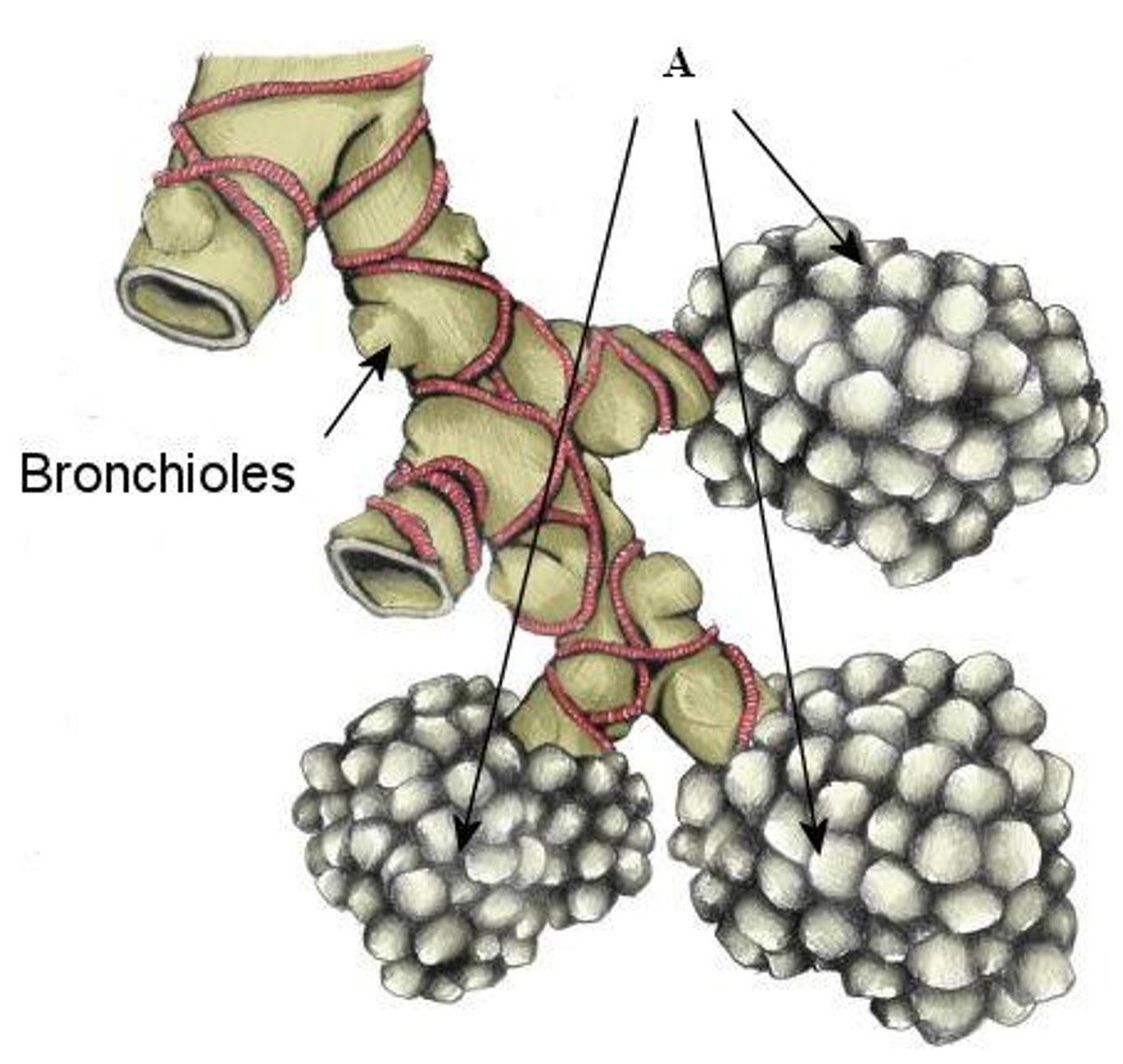
bronchioles
Airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
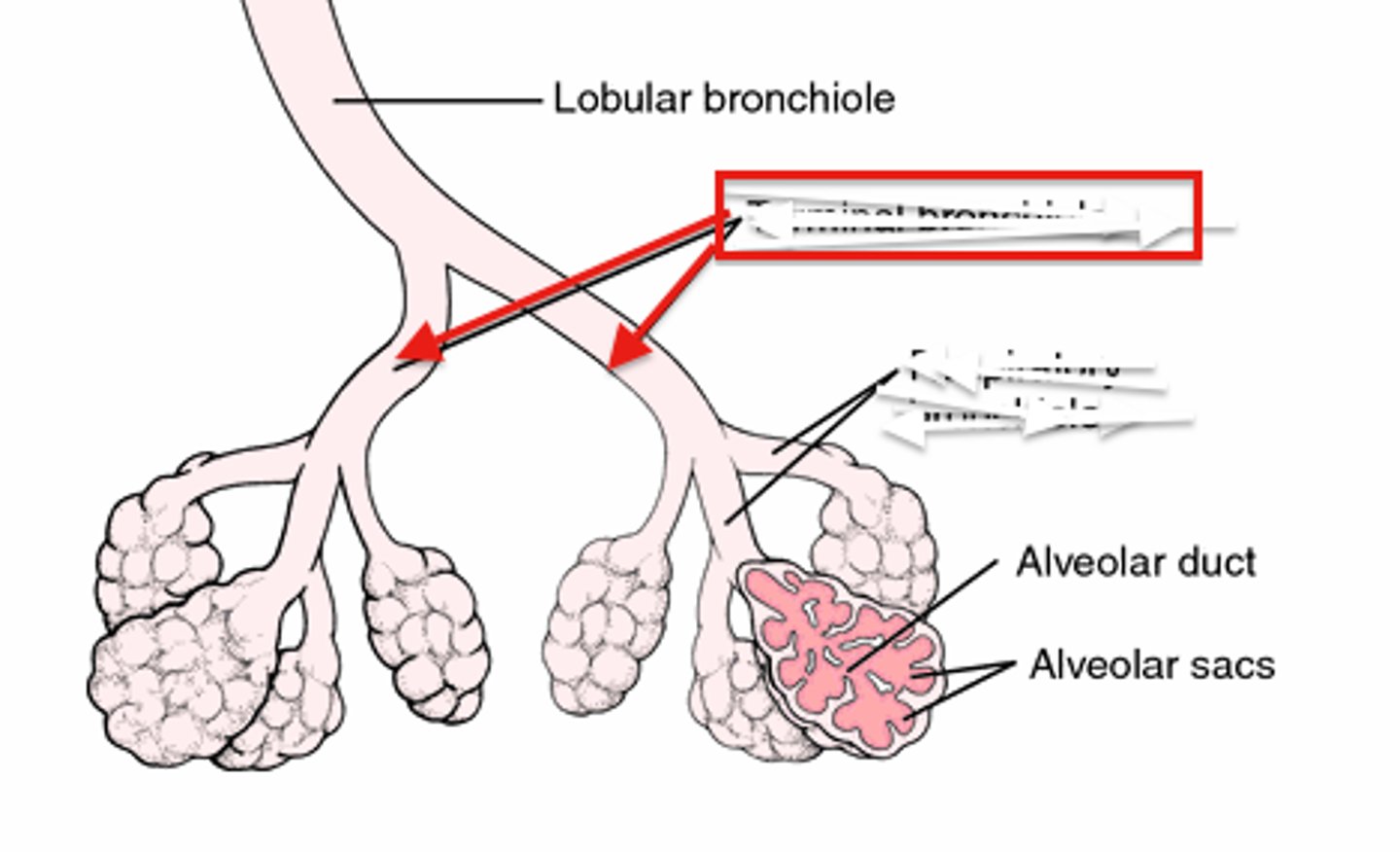
Alveolar ducts
Small passages connecting the respiratory bronchioles and the alveolar sacs.
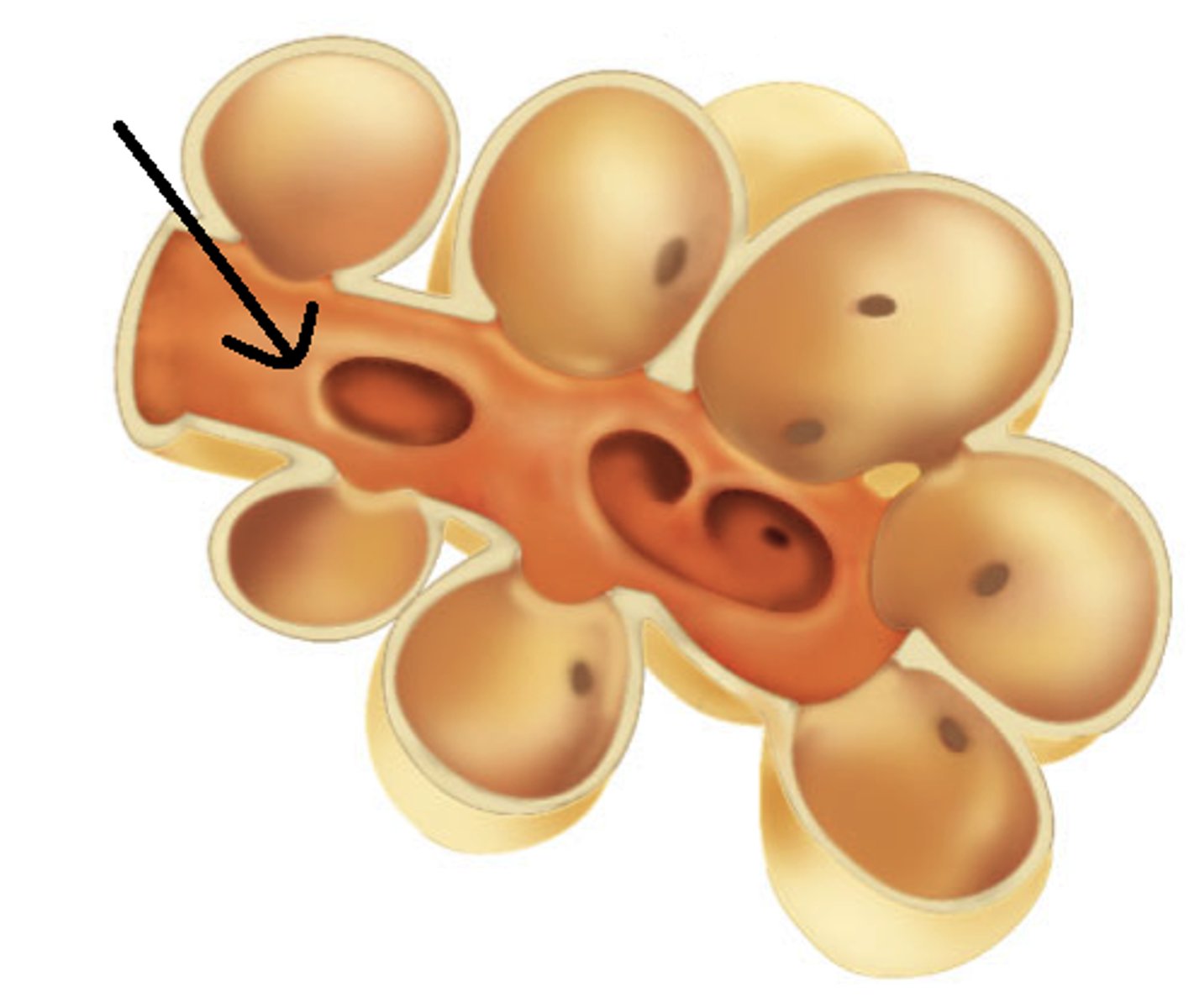
Alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
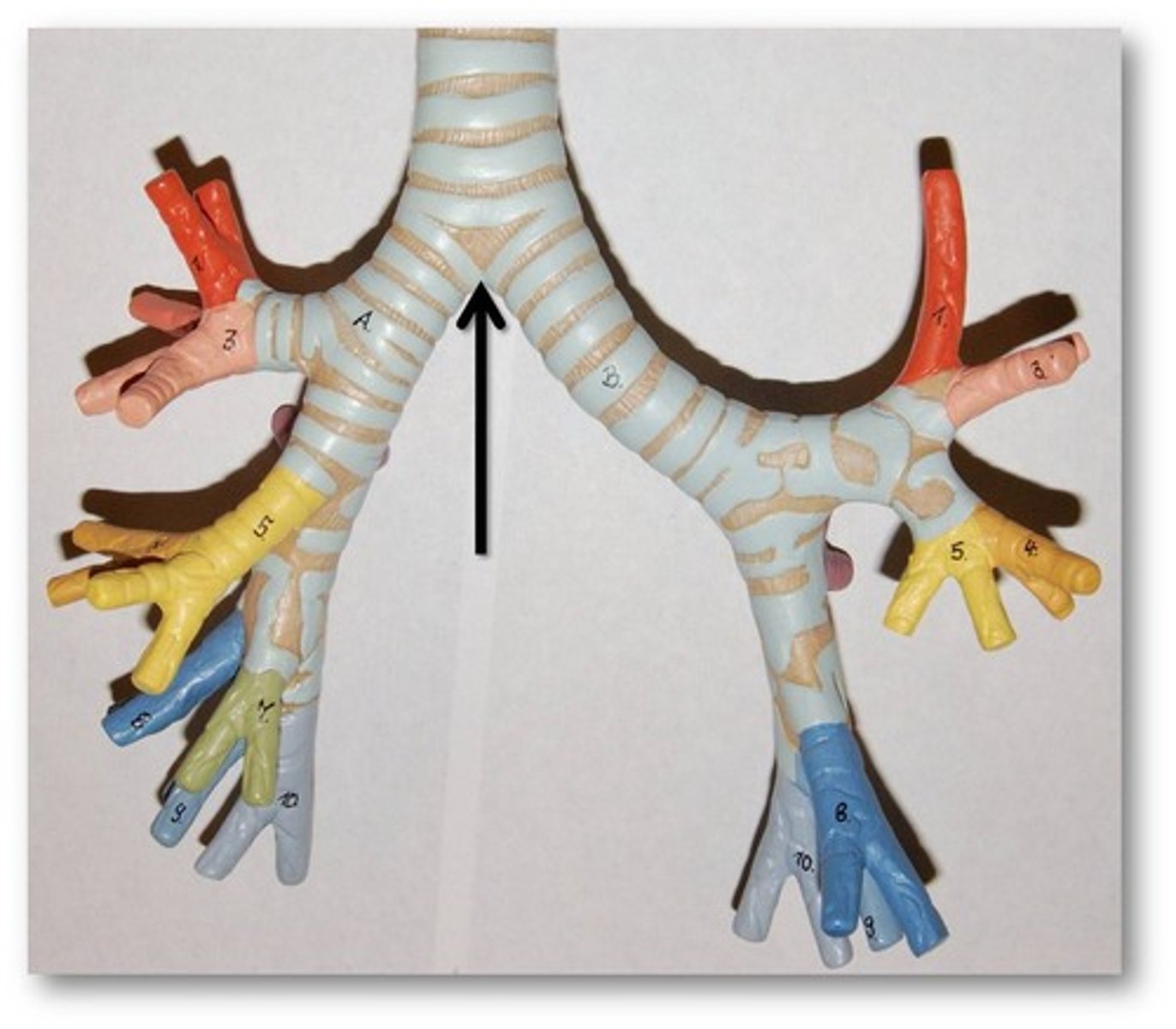
Tracheal bifurcation
the division of the trachea into the right and left main bronchi
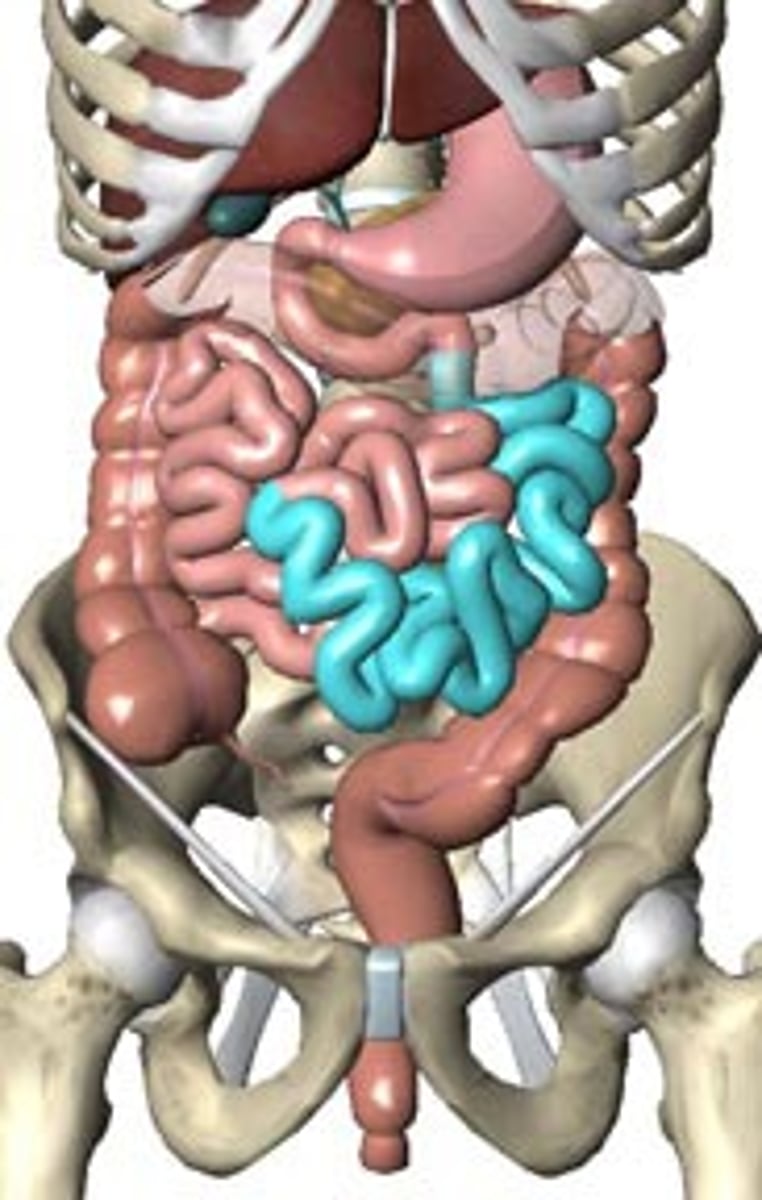
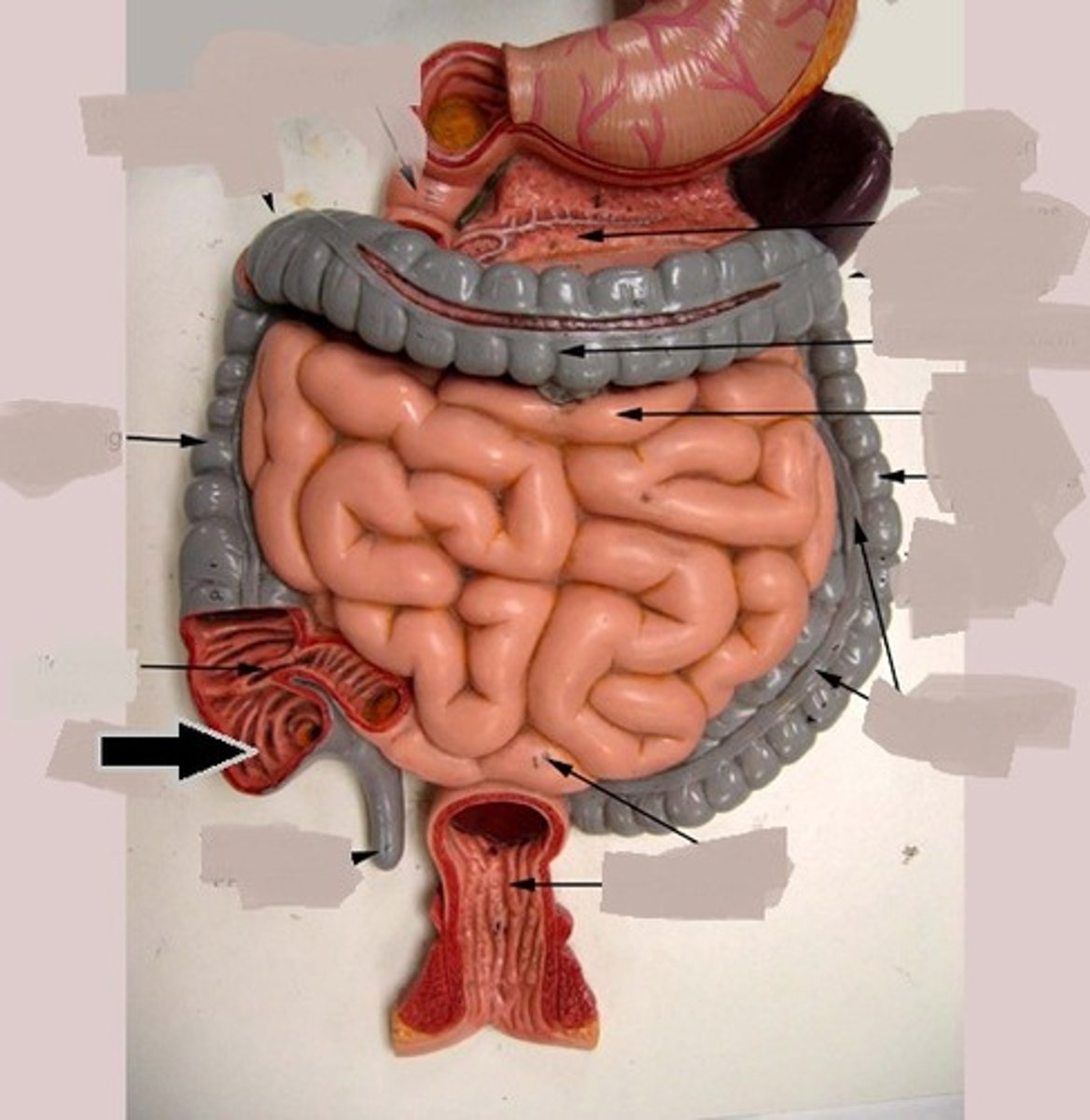
duodenum
first part of the small intestine
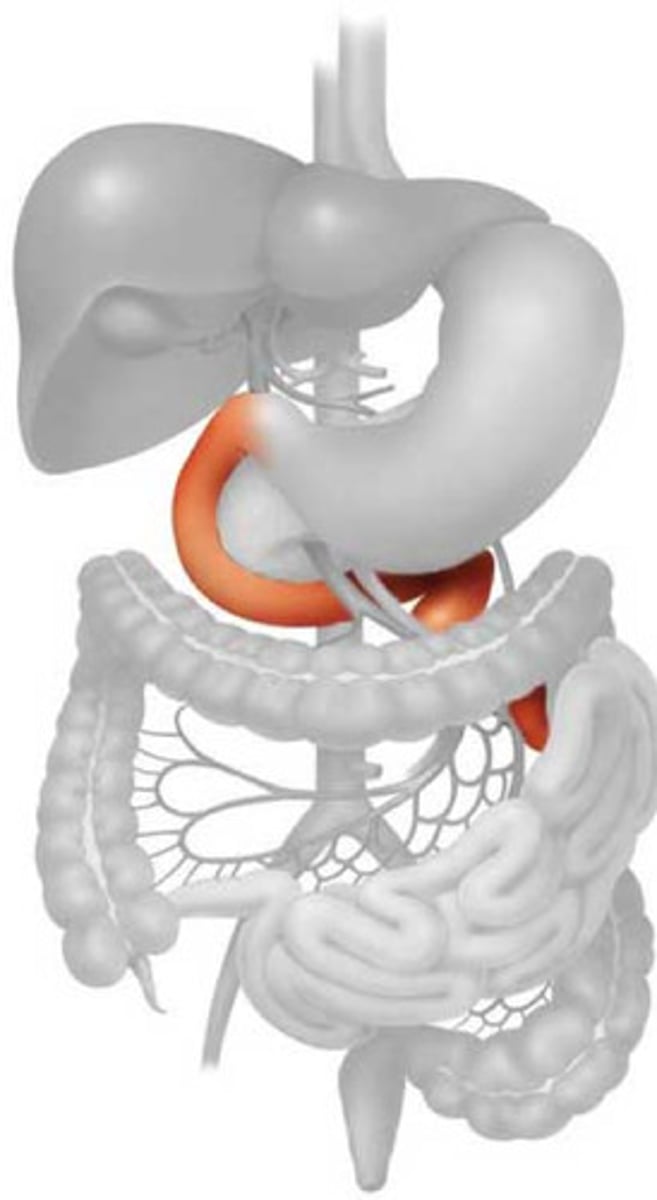
jejunum
second part of the small intestine
ileum
third part of the small intestine
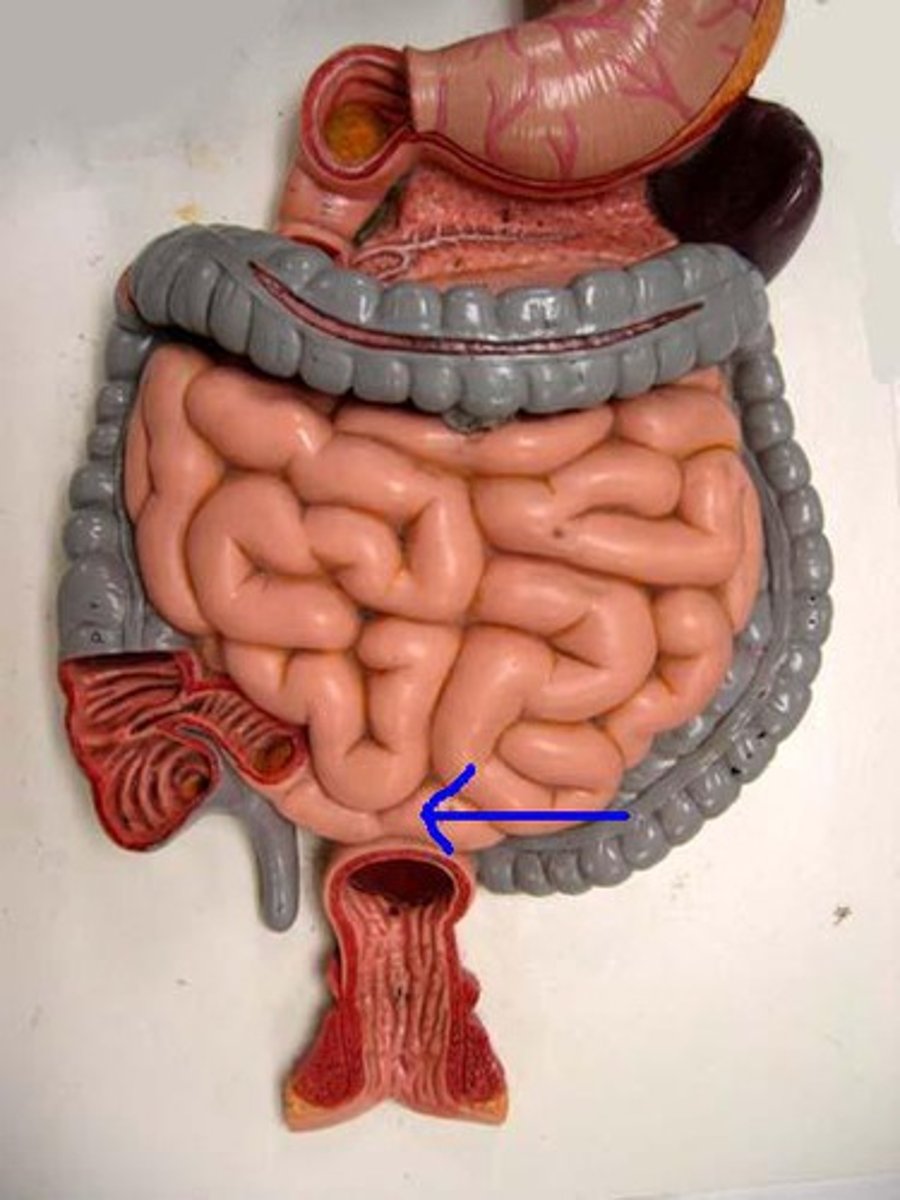
ileocolic junction
valve between the ileum of the small intestine and the cecum of the large intestine; prevents material from flowing back from the large to the small intestine
mesentary
supportive membrane surrounding internal organs and attaching to the body wall
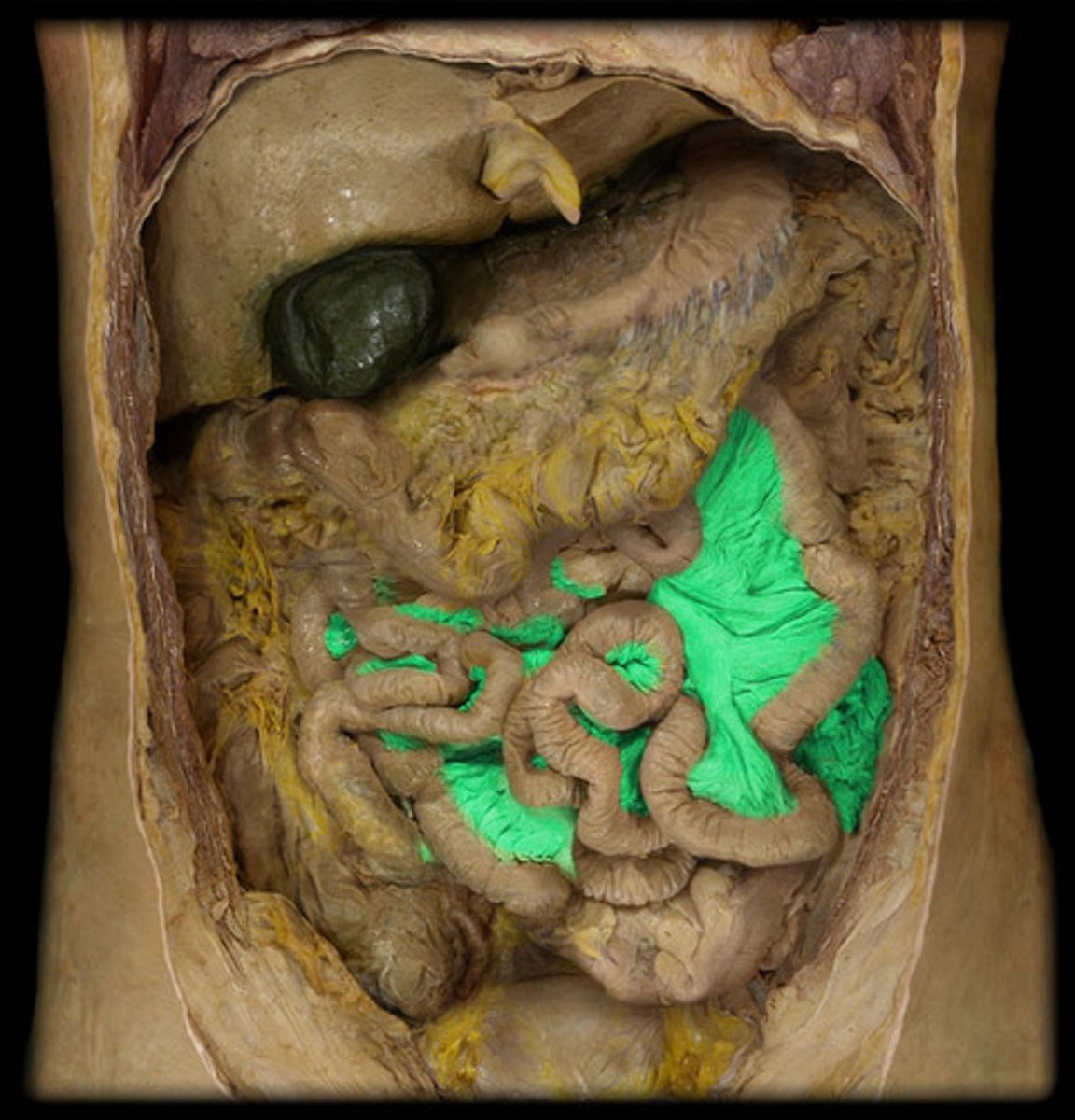
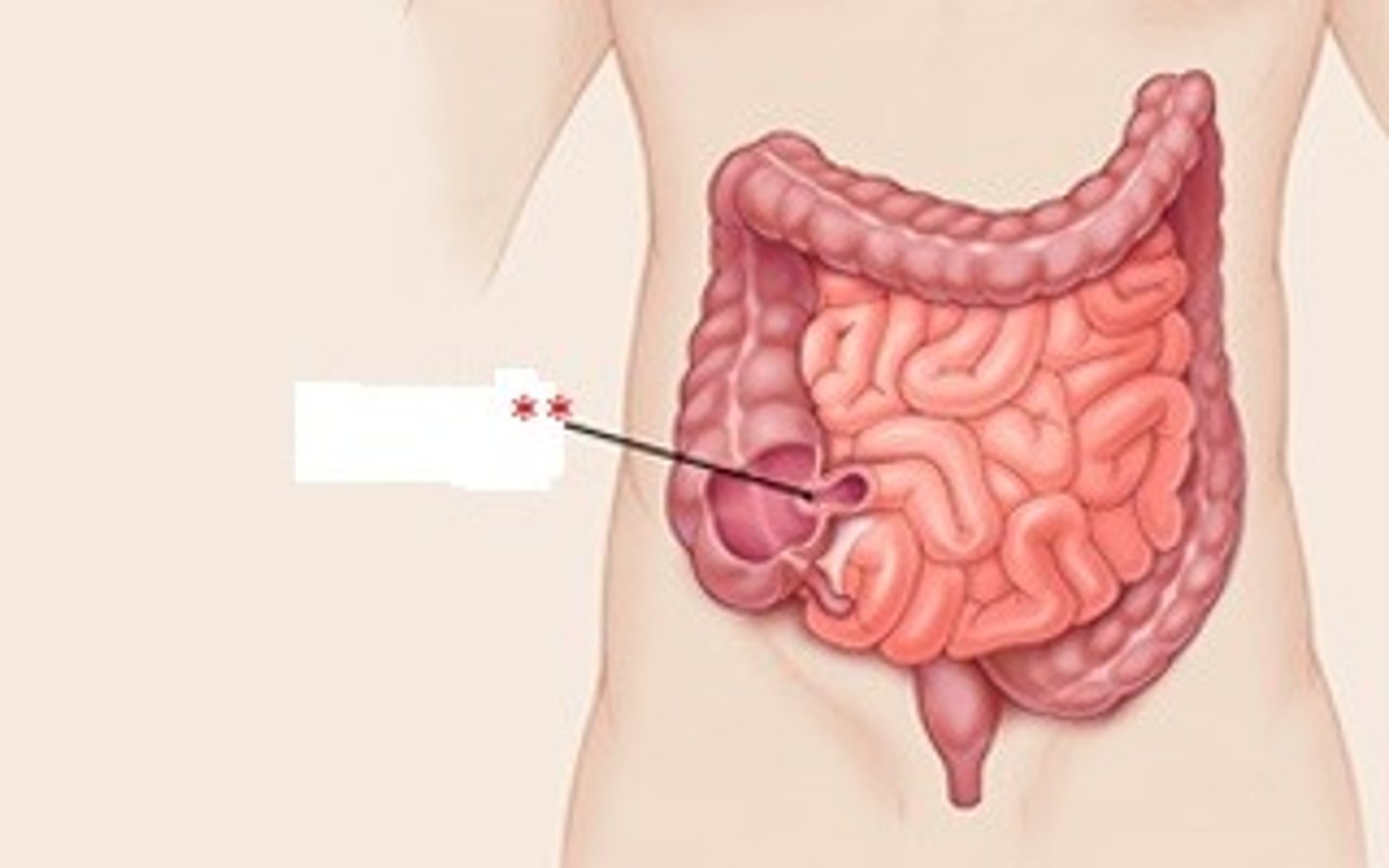
cecum
the cavity in which the large intestine begins and into which the ileum opens
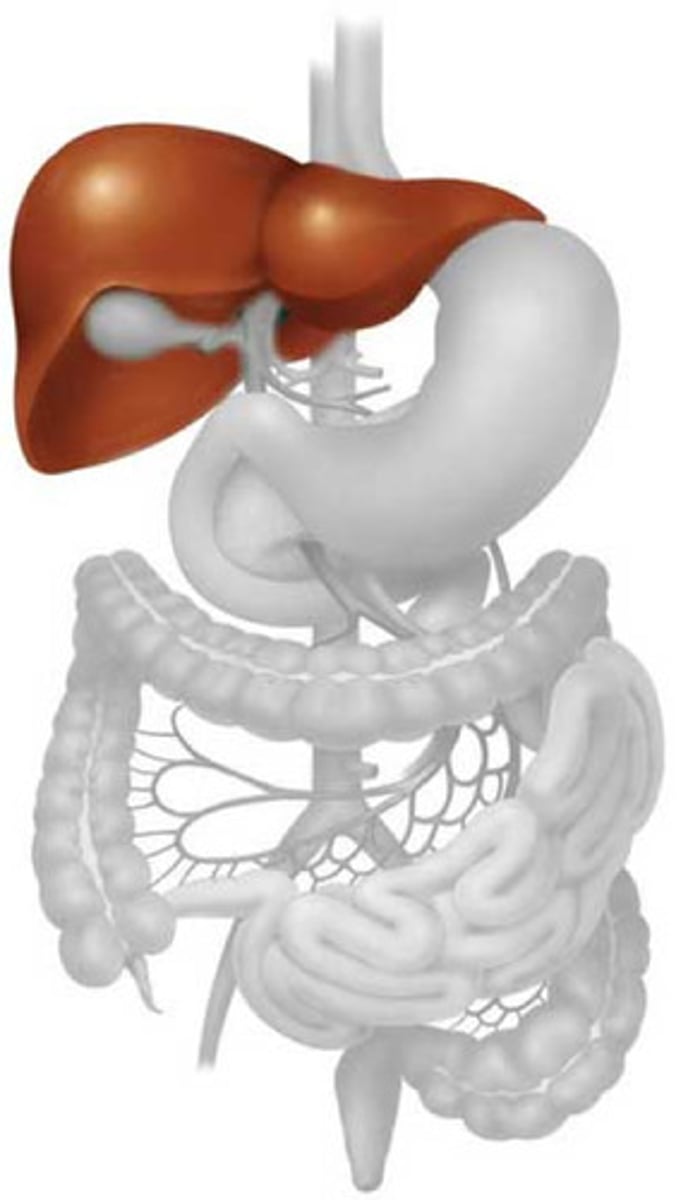
liver
produces bile
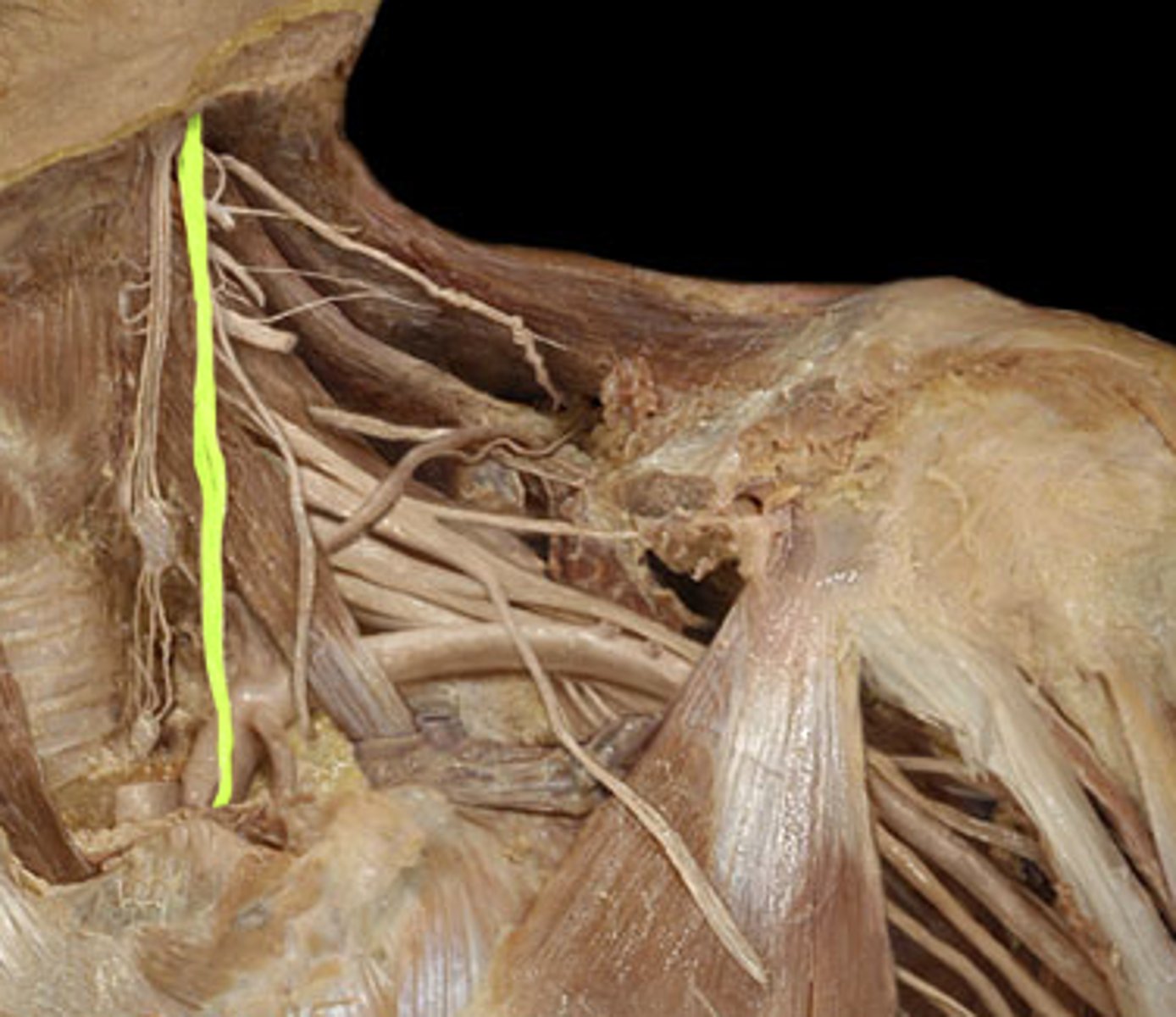
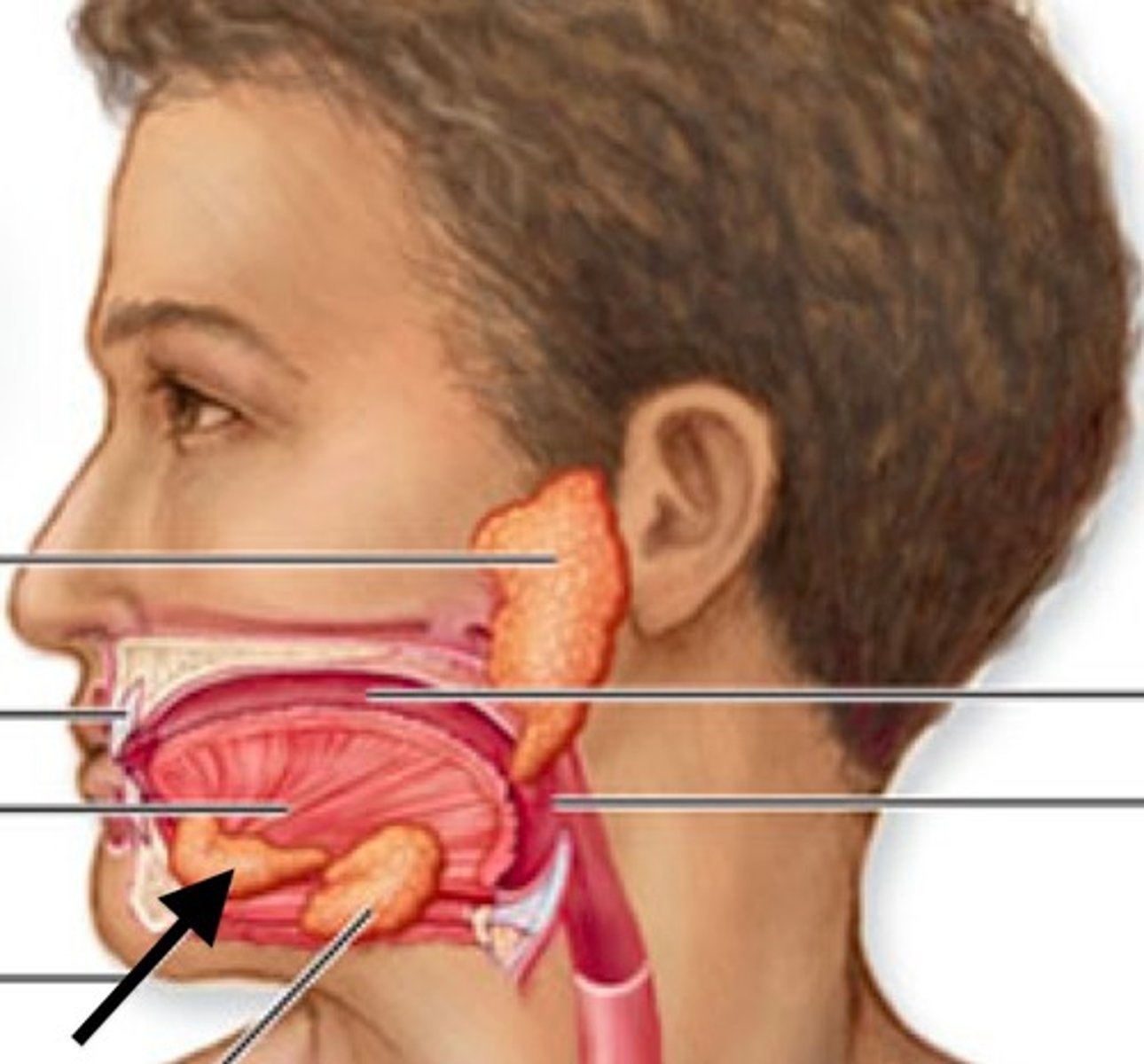
Sublingual veins
drains the floor of the mouth
external jugular veins
The second set of vessels to emerge from the cranial vena cava, medially. These veins carry blood from the head to the brachiocephalic veins.
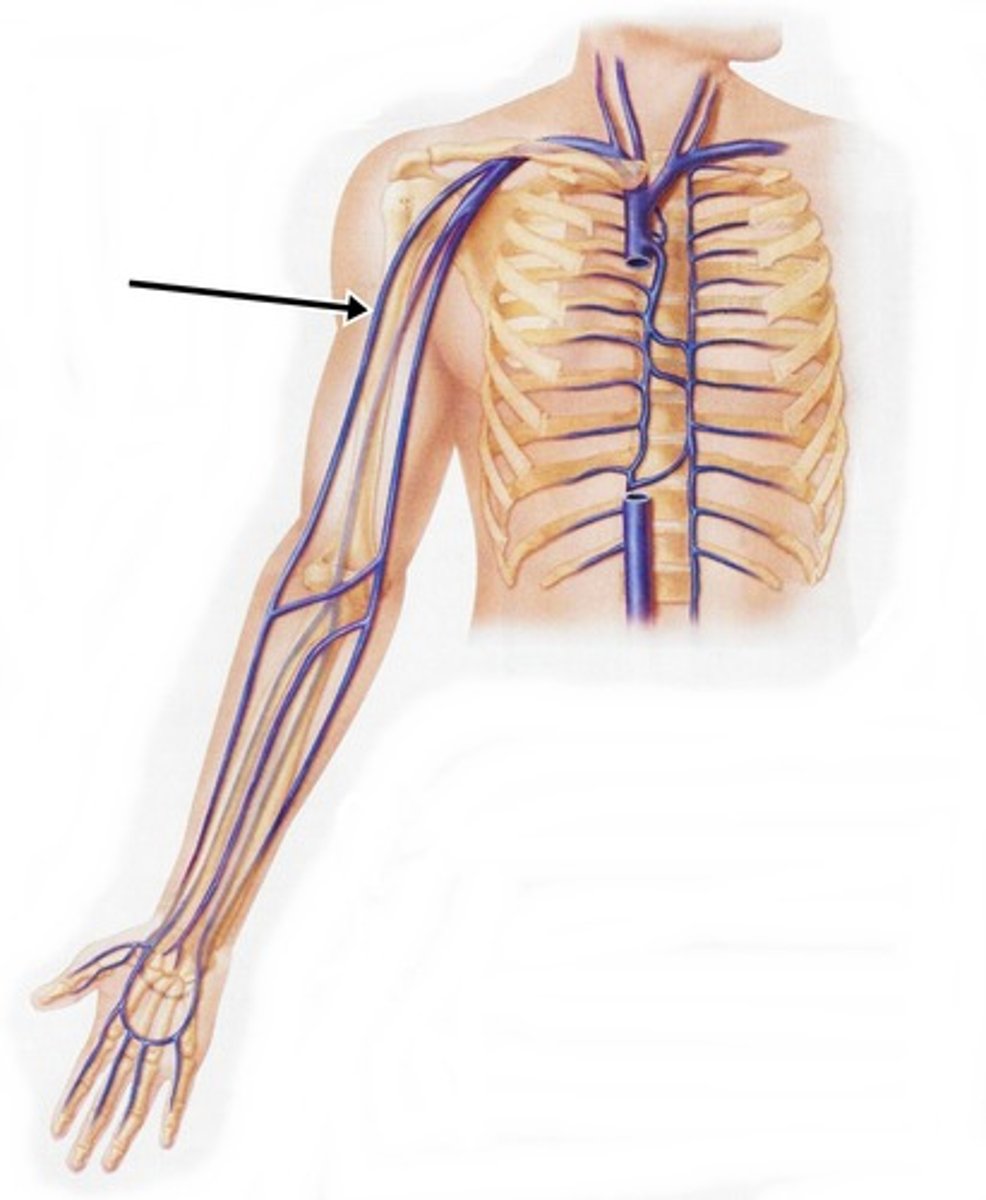
cephalic veins
The third vessels to emerge from the cranial vena cava, medially. These veins carry blood from the forelimb to the brachiocephalic veins.
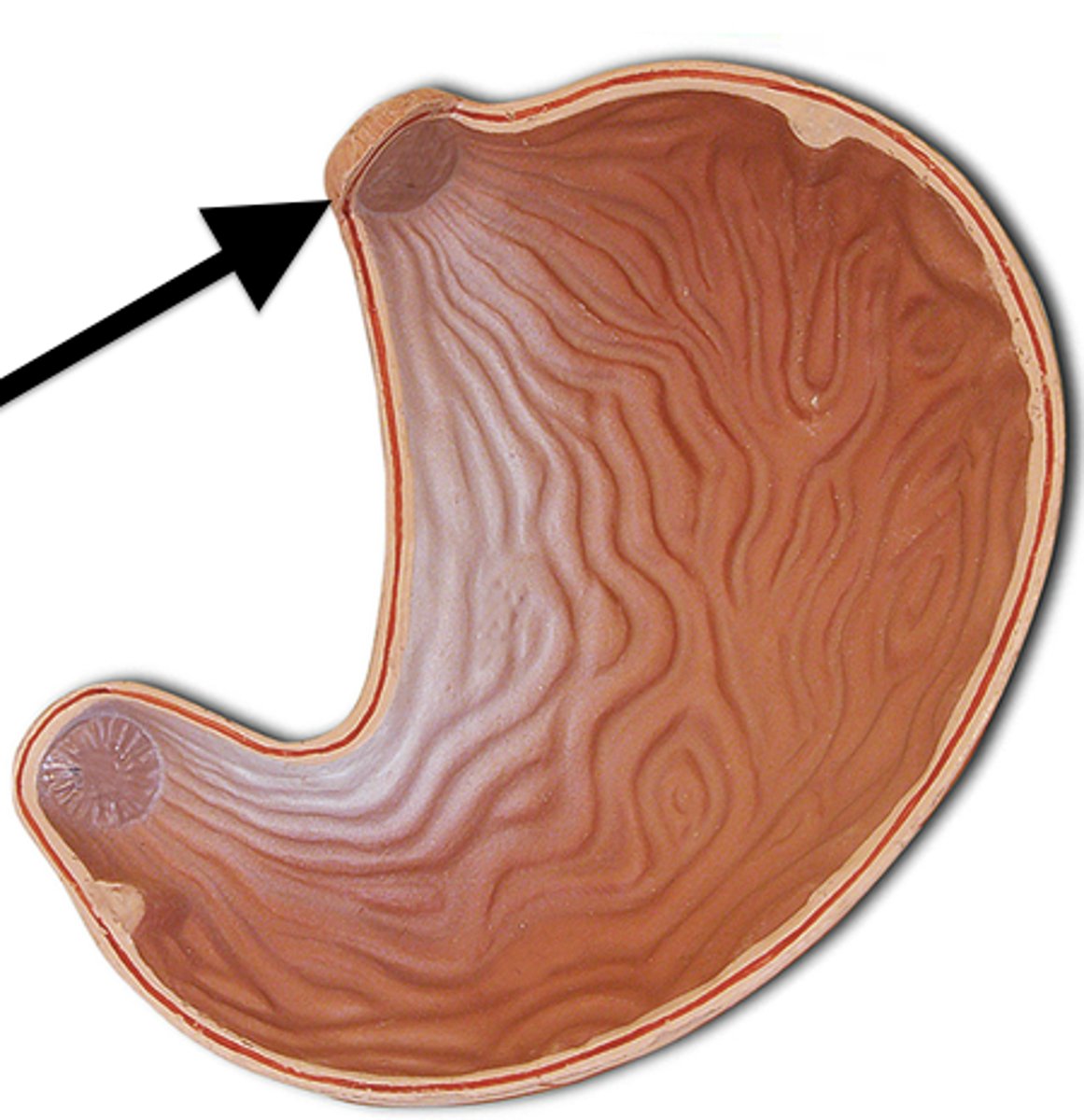
Cardiac sphincter
A circular muscle located between the esophagus and the stomach
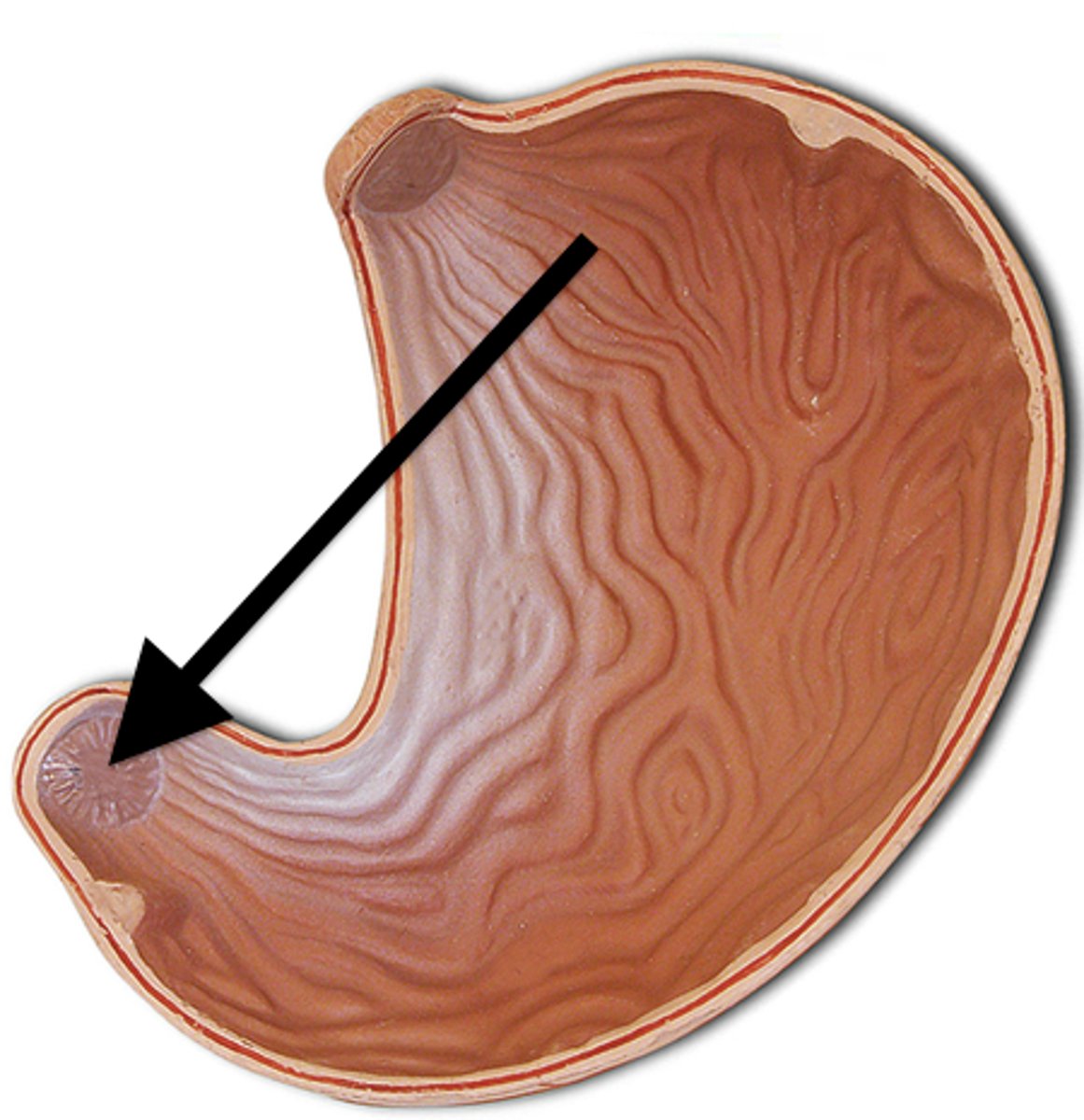
Pyloric sphincter
ring of muscle that guards the opening between the stomach and the duodenum
Greater Curvature
convex lateral surface of the stomach
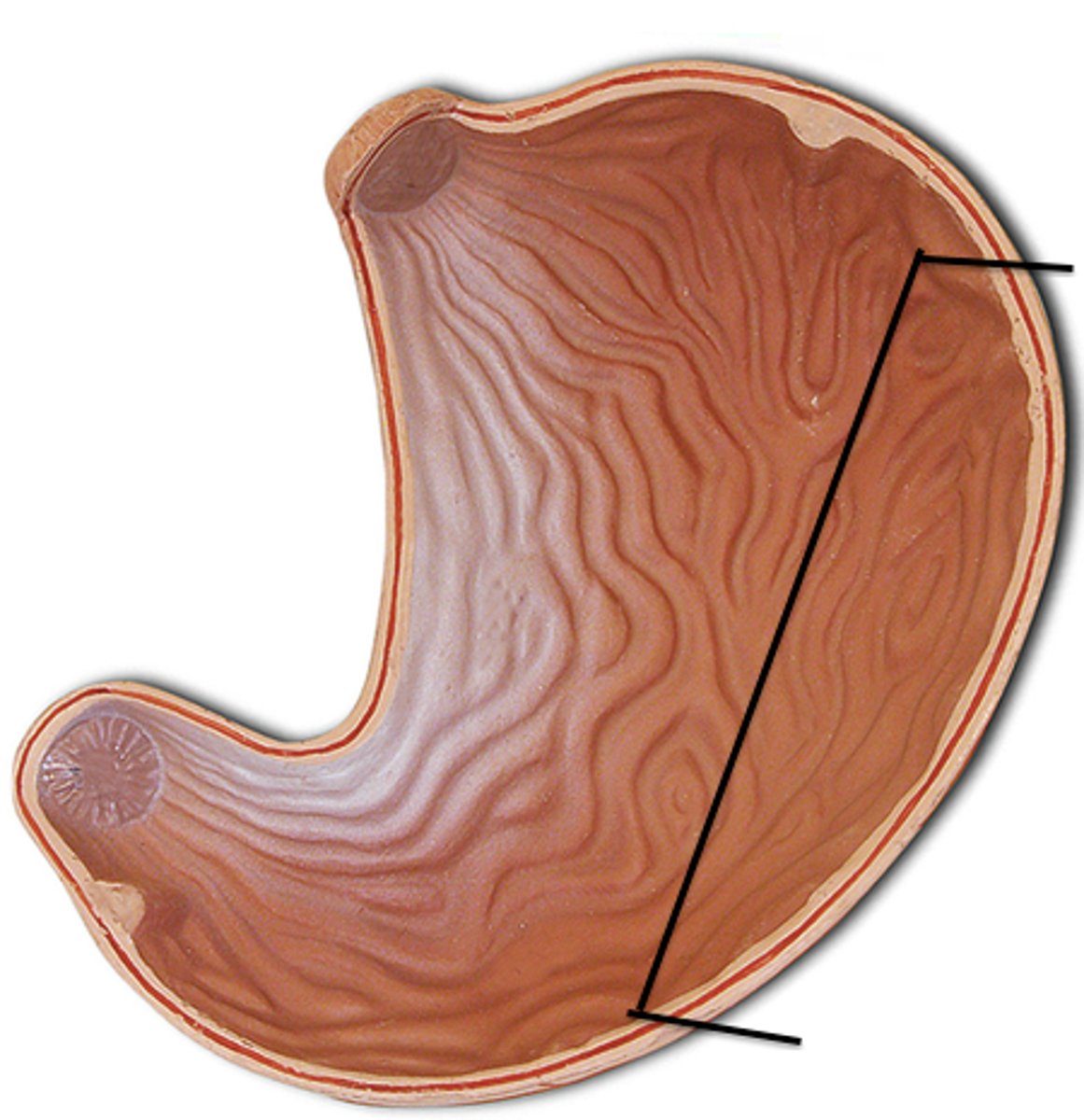
Lesser Curvature
concave medial surface of the stomach
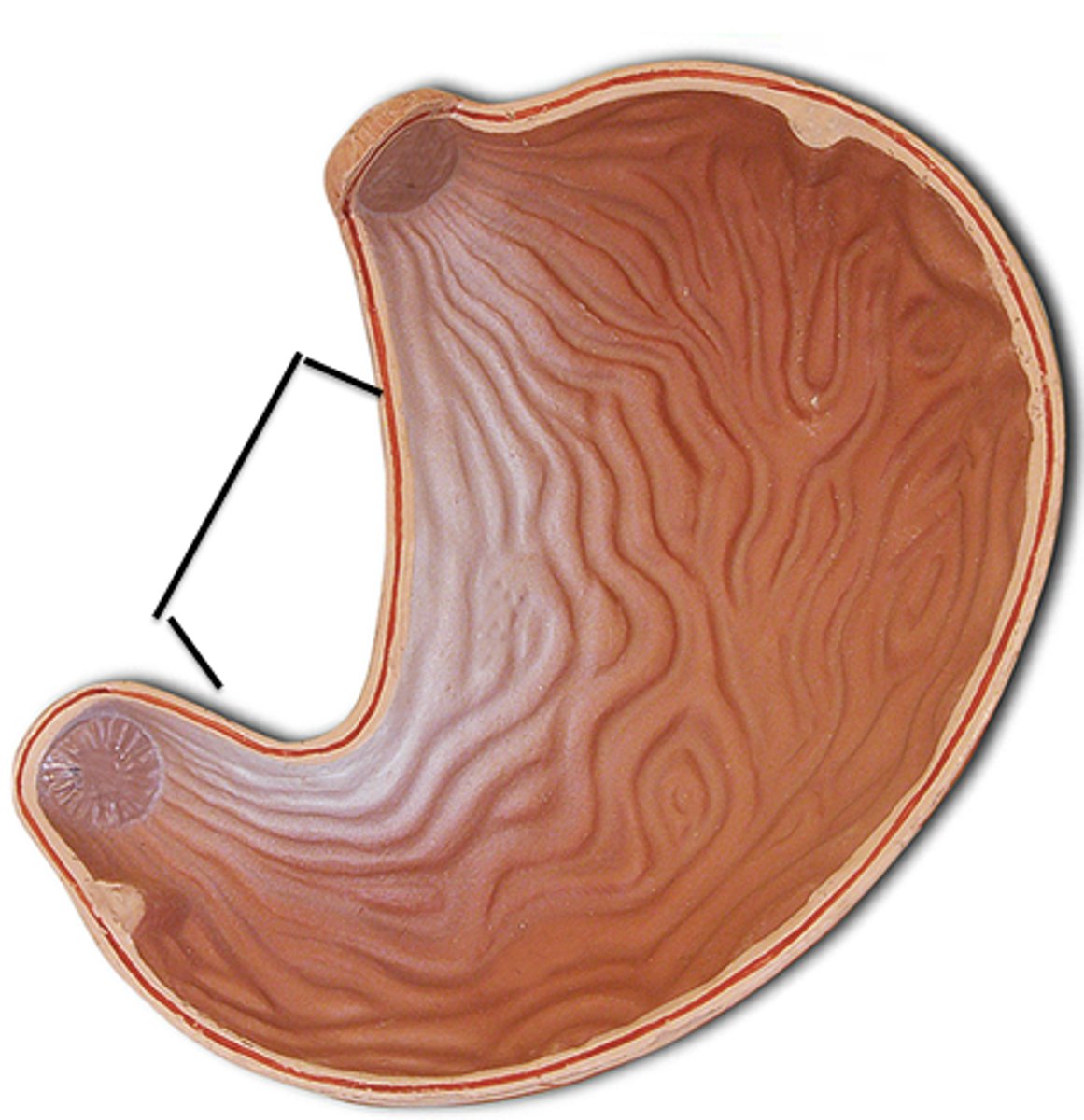
Vagus Nerve
the tenth cranial nerve that innervates digestive organs, heart and other areas