Maternity and Neonatology Mark K lecture 10
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Naegele’s Rule
Take the first day of the LMP, add 7 days and subtract 3 months from it.
Edit year if passed December 31st.
Weight Gained During Pregnancy 1st trimester and 2nd and 3rd trimester
1st Trimester (12 weeks)
1lb per month = Today 3lbs
2nd and 3rd trimester
Add 1lb every week
Ideal Weight Gained During Pregnancy
28 lbs plus or minus 3
Between 25lbs to 31 lbs
If weight gain during pregnancy is within +/- 1 to 2lbs of the ideal weight for the gestation week
Patient is WDL
If weight is gained +/- 3 lbs
Assess patient
If weight gained is within +4lbs or -4lbs
There is trouble
Perform a Biophysical Profile (BPP)
Quick way to come up with the ideal weight gained during pregnancy is to?
Take the number of weeks gestation and minus 9.
When can the fundus be palpated at the umbilicus?
Between 20 and 22 weeks
Fundal Height
Measurement from the top of the symphysis pubis to the top of the fundus.
Fundus height cannot be palpated until the second trimester true or false?
TRUE
Fundus cannot be palpated until the second trimester
Positive Signs of Pregnancy
Fetal skeleton on X-ray
Presence of fetus on ultrasound
Auscultation of fetus on ultrasound
EXAMINER palpates fetal movement (outline) NOT THE MOTHER.
In OB there are 3 types of questions regarding range values.
When would you first? (Pick EARLIEST range)
When would you most likely? (Pick MID range)
When should you by? (Pick END range)
When can a fetal heart rate be heard?
Fetal Heart rate can be heard first between 8 to 12 weeks of gestation
When would you first hear the fetal heart rate?
8 weeks
When would you most likely hear the fetal HR?
10 weeks
When should you hear the fetal heart beat?
12 weeks
When should quickening ( baby kicks) be first felt between?
16 to 20 weeks
First 16 weeks
Most likely 18 weeks
By 20 weeks
Maybe signs of pregnancy
Positive urine/blood hCG tests
A positive pregnancy test may result from other conditions for instance, cancer.
Chadwick sign- Cervical color change to cyanosis (Cs)
Goodell sign- good and soft. Softening of the cervix.
Hegar sign- uterine softening. Softening of the lower uterine segment.
Chadwick Sign
Cervical Color Change to Cyanosis (Cs)
Goodell Sign
Good and Soft
Softening of the cervix
Hegar sign
Uterine softening
Softening of the lower uterine segment
Patient teaching for Prenatal visits during the first 28 weeks?
Once a month until week 28
Prenatal Visits between week 28- week 36?
Every other week between week 28-week 36.
Prenatal visits after week 36?
Once a week after week 36 until delivery or week 42
At week 42 delivery can be induced or by C-section.
Hemoglobin levels WILL FALL during pregancy. A pregnant woman can tolerate lower levels of hemoglobin.
Normal hemoglobin Hb in females is 12-16
First Trimester Hemoglobin normal drop
Hemoglobin can fall to 11 and be perfectly normal.
Second Trimester Hemoglobin normal drop
Hb can fall to 11.5 and be perfectly normal.
Third trimester hemoglobin drop.
Hb can fall to 10 and be perfectly normal
If Hemoglobin is < 9
Anemia
Evaluation
How do you treat morning sickness?
Morning sickness usually seen during the 1st trimester.
Treatment: Dry Carbohydrates- not before breakfast but BEFORE PATIENT GETS OUT OF BED.
How do you deal with urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontince is seen in the first and 3rd trimesters.
Patient needs to void every 2 hours from the day she gets pregnant until 6 weeks postpartum.
Patient complains of difficulty breathing. What should you advise her to do?
Difficulty breathing is a problem during the 2nd and 3rd trimesters
Advise patient to assume TRIPOD position
Tripod position is a physical stance often assumed by people experiencing respiratory distress.
The patient will be leaning forward with hands on knees or the surface of a desk or table.

A pregnant patient complains of back pain. What should you advise her to do?
Back pain is seen during 2nd and 3rd trimester
Advise PELVIC TILT exercises to patient.

What is the truest most valid sign that she is in labor?
The truest most valid sign of labor is the onset of regular/progressive contractions.
Dilation
opening of the cervix from 0cm to 10cm
Effacement
Thinning of the cervix. It goes from thick to 100% efface ( thin like paper)
Station
Relation between fetal presenting part and the mother’s ischial spine.
Ischial Spine
the narrowest part of the pelvis
Positive numbers mean the baby has made it through the tight squeeze and is good to go.
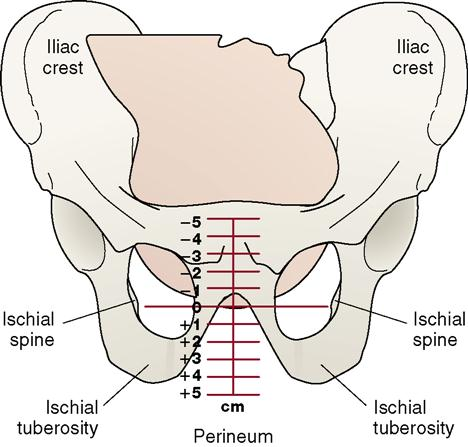
What does it mean if the baby stays at -3, -2, -1?
It can’t get through vaginally.
It needs a C-section
What intervention needs to be done if the baby stays at +4, +2, +4, +2
Vacuum/ Forceps
Engagement
station zero this means the presenting part is at ischial spines.
Lie
relationship between the spine of the mother and spine of the baby.
Vertical lie
Compatible with vaginal birth
Parallel
The mother’s spine and the baby’s spine is parallel- we got a baby.
Lie is Perpendicular
Tranverse lie = Trouble… C-section
If we got them perpendicular, we’ve got trouble T.
Most common presentations is ROA or LOA
That’s the guess don’t bother memorizing.
Pick ROA FIRST!
How many stages of labor are there?
4 stages
How many phases are there in labor?
3 phases in the first stage of labor
LAT
Latent, Active, Transitioning
Stage 1 of labor
Onset of labor it has 3 stages.
Latent
Phase 1 in stage 1
Cervcal dilation from 0 to 4cm
Contractions are 5 to 30 minutes apart, lasting 15-30 seconds
Mild Intensity
Active
Phase 2 of Stage 1
Cervical dilation from 5-7 cm
contractions are 3 to 5 minutes apart
Lasting 30-60 seconds
Moderate Intensity
Transition
Phase 3 of Stage 1
Cervical dilation from 8 to 10cm
Contractions are 2 to 3 minutes apart, lasting 60 to 90 seconds.
Strong Intensity.
A pregnant woman comes into L&D. She is 5cm dilated, with contractions 5 minutes apart, lasting 45 seconds. What PHASE of labor is the patient in?
Active Phase
She is in the First STAGE.
Pay careful attention to wording phase vs stage!
Stage 1
Onset of labor- Cervical Dilation and Effacement
3 Phases in Stage 1
Phase 1 Latent
Phase 2 Active
Phase 3 Transition
Stage 2
Delivery of the Baby
Stage 3
Delivery of the placenta
Stage 4
Recovery: 2 hours until bleeding stops
What is the purpose of the uterine contraction in 1st stage?
Dilation and Effacement
What is the purpose of the contactions in the 2nd stage?
Delivery of the baby
What is the purpose of contractions in the 3rd stage?
Delivery of the placenta
What is the purpose of contractions in the 4th stage?
Stop Bleeding
When does postpartum technically begin?
2 hours after delivery of the placenta
What is the #1 priority of the 2nd phase?
Pain Management
2nd phase the Active Phase is in the first stage of labor.
What is the #1 priority of second stage?
Second Stage is the Delivery of the Baby so it would be
Clearing Baby’s airway
What is the number one priority of the third phase?
Third phase is in the first stage of Labor
Checking Cervical Dilation, Helping Pregnant mother with breathing and pain management.
What is the #1 priority of the third stage?
Third Stage is Delivery of the Placenta
Assess the placenta for smoothness and intactness, and for 3-vessel (not 2) umbilical cord.
Uterine Contractions should be no longer than how many seconds and minutes?
No longer than 90 seconds and no closer than 2 minutes
What is a sign of Uterine Tetany?
No longer than 90 seconds and no closer than 2 minutes.
What parameters regarding uterine contraction would make you stop pitocin?
No longer than 90 seconds and no closer than 2 minutes.
What is uterine hyperstimulation?
No longer than 90 seconds and no closer than 2 minutes.
Frequency
The beginning of one contraction and the beginning of the next.
A,C
Duration
Beginning to End of one contraction.
A to B
C to D
How do you teach a pregnant mom to palpate?
Palpate with one hand over the fundus with the pads of the fingers.
Painful Back pain- OP = Oh Pain. What do you do?
Position - Push
What position?
KNEE -CHEST POSITION
Then PUSH fist into sacrum to use counter pressure
Low priority

Fist into sacrum to relieve back pain in pregnant client
Position Knee to Chest then push fist into sacrum to relieve back pain.

Prolapsed Cord
PUSH - POSITION
PUSH HEAD off cord and position KNEE- Chest or Trendelenburg
Prep for C-section
THINK PUSH/POSITION
Push head off the cord of the fetus and position mother to knee-chest.
HIGH PRIORITY
Interventions for all other complications including
Tetany
Maternal Hypertension
Vena Cava Syndrome
Toxemia
Uterine Rupture
All treated with LION
LION
Left side ( place mother on left side)
IV
Oxygen
Notify HCP
STOP PITOCIN (PIT) IF IT WAS RUNNING- FIRST THING YOU DO!!!
IN A OB CRISIS IF PITOCIN IS RUNNING YOU STOP IT BEFORE IMPLEMENTING LION.**
LION
LEFT side
IV
Oxygen
Notify HCP
When to administer systemic pain medication?
DO NOT ADMINISTER a systemic pain medication if the baby is likely to be born when the med is at its peak.
You have a primigravida at 5cm dilated who wants her IV push pain med. What is the nursing intervention?
Would give it because the patient is a primigravida and not likely to deliver in about 15-30 minutes when the medication PEAKS.
You have a multigravida at 8cm and she wants her IM pain med. What is the nursing intervention?
Do not administer the pain medication because the client is likely to deliver when the medication would be at its peak.