A1 - Food production and processing
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Three types of food industry
Fresh food production
Ingredient production
Product assembly
What is Fresh Food production?
The converting of freshly harvested products into consumer products
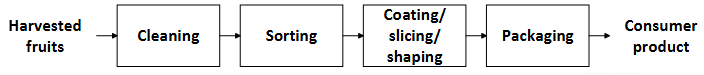
Steps of fresh food production
Harvested fruits
Cleaning
Sorting
Coating/slicing/shaping
Coating with wax for example. This prevents moisture from diffusing out of the apple.
Also relevant for amount of Kg in supermarkets.
Packaging
Consumer product
Steps of fresh food production (canning)
Fruits
Cutting
Packaging
Heating
Canned product
Can be kept for a long time
What is ingredient production?
The converting of freshly harvested products into ingredients.
Ingredients = not directly consumed
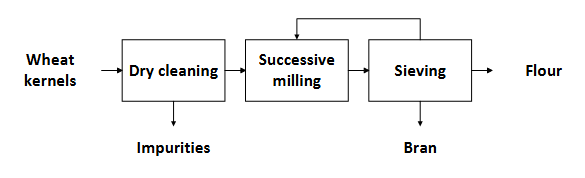
Steps of ingredient production
Example of wheat kernels → flour
Milling is for separating bran (hard part of wheat) from the rest.
General steps of ingredient production
Cleaning or purification of raw material
Preparation for fractionation (e.g. peeling)
Fractionation (sometimes by using sifting, often by dissolution)
Purification (separation from contaminants) and concentration)
Stabilization
Waste steam/side stream
Waste that is not used for further production. Often used for cattle feed.
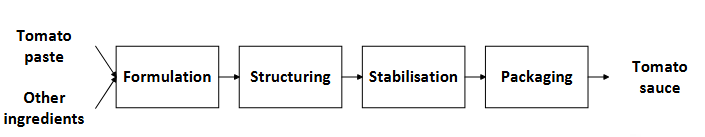
What is product assembly?
Purchasing ingredients to assemble it into consumer products
Example steps of product assembly
The four types of unit operations
Separation - into 2 or more streams
Conversion - changing the composition
Structuring - changing the way that ingredients are positioned
Stabilization - preservation and packaging
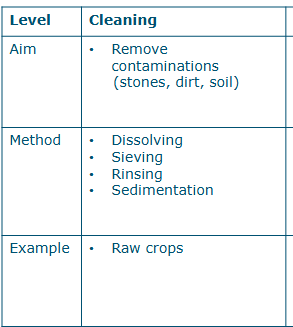
Aim, method and example of cleaning in separation (unit operations)
Aim, method and example of fractionation in separation (unit operations)

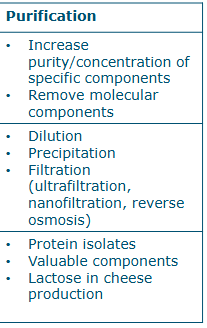
Aim, method and example of purification in separation (unit operations)
Conversion (unit operations)
Changing molecular composition
Fermentation
Acidification/neutralization (pH change)
Reactions (enzyme, heating, gelatinization)
Inactivation (microbial, enzyme)
Structuring (unit operations)
Changing the way that ingredients are positioned
mixing ingredients to the right formulation
Baking bread, cake, cookies
Emulsification (homogenization)
Crystallization
Freezing
Drying
Lots of phase changes
Don’t have to remember all this, just recognize that it has something to do with structure
Food stabilization/food preservation (unit operations)
Reduction of water activity, antimicrobial composition
salting, sugar addition
Drying
Fermentation, acidulation, causticity
Hurdle technology
Thermal preservation
Heating: pasteurization, sterilization, UHP
Cooling: chilling, chilled chain
Freezing: related to lower aw
Non-thermal preservation
high hydrostatic pressure
Pulsed electric fields
Magnetic fields, UV, light pulses
Block chart
Process: rectangle represents a process
Arrow: line that connects material flows between processes
Text: Shows input and output material
Blanching
When fruits and vegetables are heated to 100C for a few minutes. This will inactivate enzymes and micro-organisms on the outside of the product.
Production chain of meat
Animals are slaughtered
Meat is aged for a few days at lower temperature allowing glycogen to be metabolized into lactic acid.
Proteolytic enzymes partially break down the cellular structure, which allows the meat to become tender.
Waste meat is turned into sausages, canned meat or processed into ground meat
Bones are used for broths
Meat is frozen after processing