UNIT 1 REVIEW HUMAN GEOGRAPHY
4.4(5)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Shoutout to Conner Sisemore for writing all of these questions. Created in 2022 for P. Hammond's AP Human Geography course.
Last updated 4:28 PM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
How does a large scale map compare to a small scale map?
A large scale map has MORE detail, but shows less. (1:190,000,000) A small scale map has LESS detail, but shows more. (1:16,000)
2
New cards
Compare reference maps and thematic maps.
Reference maps include locations/names of features. Thematic maps have special topics, and include spatial data or patterns, and stats.
3
New cards
Absolute vs relative location
Quantitive/countable (fixed point, single address.) vs where something is relative to something else (w. of raymore)
4
New cards
Absolute vs relative distance
Physical unit of measurement (km) vs time, effort, cost
5
New cards
Absolute vs relative direction
Fixed fram of reference (N, E, S, W) vs left, right, up, down, etc.
6
New cards
Geography vs history
Where vs when
7
New cards
The science of map making?
Cartography
8
New cards
Define SCALE
the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole
9
New cards
The 3 c's
Check title, key, and spatial info.
10
New cards
Scale of analysis
a scale that determines what is being studied based on the size of the area being examined (GLOBAL, REGIONAL (Latin America), NATIONAL (State/country), SUB-NATIONAL , LOCAL.)
11
New cards
Latitude
UP TO DOWN, prime meridian
12
New cards
Longitude
Side to side, longitude
13
New cards
ESPen
Economic, Social, Politics, Environmental
14
New cards
Toponym
The name given to a place ex. Missouri ("People with canons")
15
New cards
Site
The physical character of a place, climate, water, etc.
16
New cards
Situation
Where something is, physical, cultural, emotional.
17
New cards
Space
The physical gap or interval between distribution
18
New cards
Spatial
Adjective for space
19
New cards
Distance decay
the effects of distance on interaction, generally the greater the distance the less interaction. Less important further you get.
20
New cards
Space Time Compression
The reduction in the time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place, as a result of improved communications and transportation systems
21
New cards
Human Environment Interaction
the study of the interrelationship between people and their physical environment

22
New cards
Environmental determinism vs possibilism
Human capability relies strictly on the environment vs IT CAN rely on the environment in some circumstances.
23
New cards
Map projection
a way of representing the spherical Earth on a flat surface
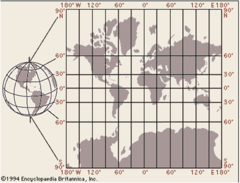
24
New cards
Map distortion
a change in the shape, size, distance, or position of a place when it is shown on a map
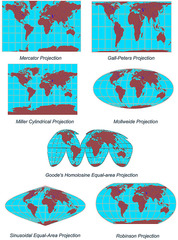
25
New cards
Mercator Projection
A true conformal cylindrical map projection, the Mercator projection is particularly useful for navigation because it maintains accurate direction. Mercator projections are famous for their distortion in area that makes landmasses at the poles appear oversized. TOO SMALL AFRICA?
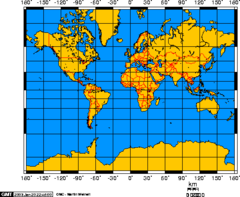
26
New cards
Gall-Peters Projection
equal area projection that distorts the shape of land masses (looks stretched out). what we're used to.
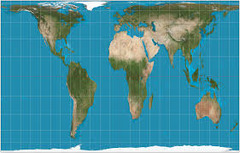
27
New cards
Polar/Azimuthal Projection
-Accurate distance
-Size and shape of land are distorted
-Bodies of water are also distorted
-Size and shape of land are distorted
-Bodies of water are also distorted
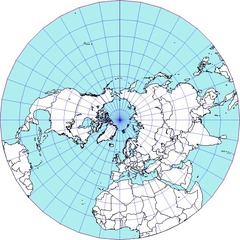
28
New cards
Region
An area distinguished by a unique combination of trends or features.
29
New cards
Formal Region
An area in which everyone shares in one or more distinctive characteristics
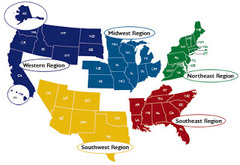
30
New cards
Functional Region
An area organized around a node or focal point. WATER HOLE.
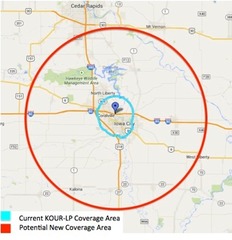
31
New cards
Vernacular Region
an area that people believe exists as part of their cultural identity
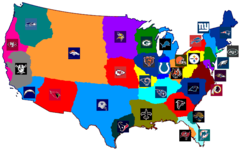
32
New cards
GIS
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
33
New cards
GPS satellite
monitor changes in elevation (vertical) as well as horizontal movement along faults. Network of satellites and receiving devices.
34
New cards
Remote Sensing
A method of collecting data or information through the use of instruments that are physically distant from the area or object of study.
35
New cards
Online Mapping
Websites that provide graphical information in the form of maps and databases
36
New cards
Sources of spatial data
Hard copy maps, aerial photos, remotely-sensed imagery; point data, sample from surveys, existing digital data files, etc.
37
New cards
How is geospatial data used and applied?
Analyze soil, asses seismic info, create 3D displays of geo features.
38
New cards
Define density
the frequency with which something occurs in space
39
New cards
Concentration
extent of a feature spread over space.
40
New cards
Clustered vs dispersed
clustered- close together
dispersed- far apart
dispersed- far apart
41
New cards
Pattern
Geographic arrangement or placement.
42
New cards
Mental Maps
image or picture of the way space is organized as determined by an individual's perception, impression, and knowledge of that space
43
New cards
Isoline map
A thematic map with lines that connect points of equal value.
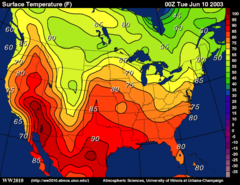
44
New cards
Chloropleth Map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit area.
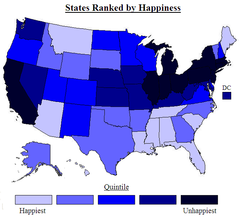
45
New cards
Proportional map
Uses size of shapes or symbols to show how serious a theme is in the area
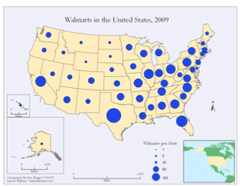
46
New cards
Dot Density map
Thematic map that uses dots to represent the frequency of a variable in a given area
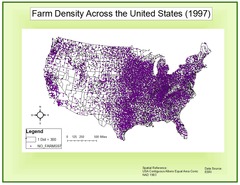
47
New cards
Cartogram map
A map in which the shape or size is distorted in order to demonstrate a variable such as travel, population or economic production
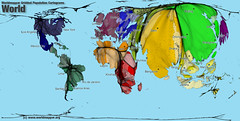
48
New cards
Topographic map
A map that shows the surface features of an area.
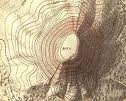
49
New cards
Flow Line Map
Shows movement with arrows of different size
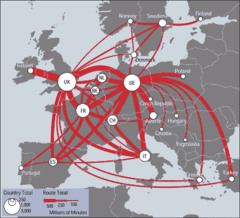
50
New cards
Wallenstein's World Systems Theory
Countries which exhibit core characteristics have consistently higher levels of education, higher salaries, and more technology. Makes things seem permanent.
51
New cards
Core country
countries that dominate trade, control the most advanced technologies, and have high levels of productivity within diversified economies.
52
New cards
Periphery country
Country that incorporates lower levels of education, salaries, and technology.
53
New cards
Brandt Line
divides the more developed north from the less developed south
54
New cards
BRICS
Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa. "Movin' on up!"