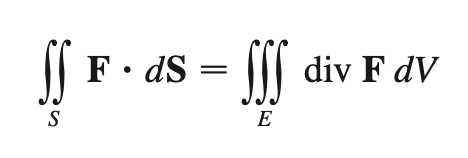Calc III - ultimate review
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
sphere eqn
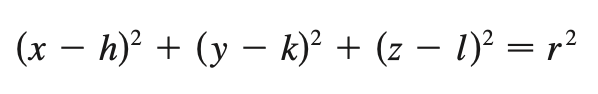
direction angles
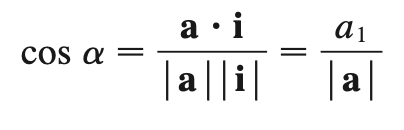
v = <a, b, c>
a → α
scalar projection (b onto a)
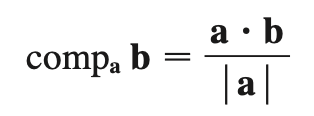
*magnitude of b that falls over a
vector projection (b onto a)
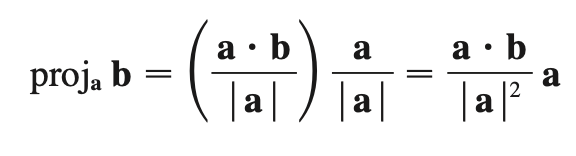
*captures scalar projection as well as direction
limit of a vector
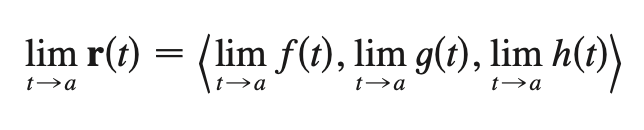
dot product
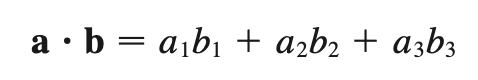
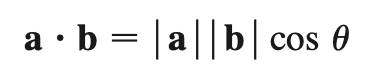
cross product
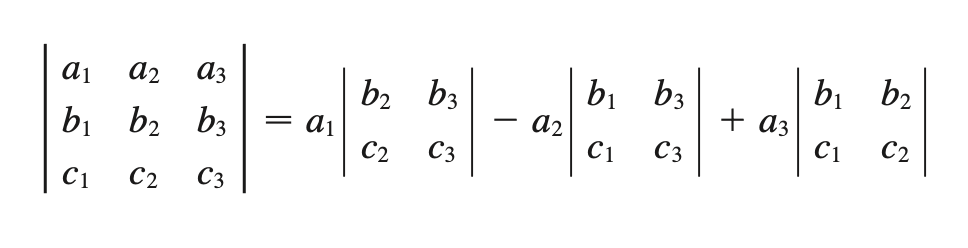
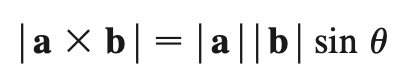
a x b = area of parallelogram
|a • (b x c)| = area of parallelepiped
vector eqn
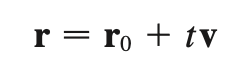
parametric eqns (vector)
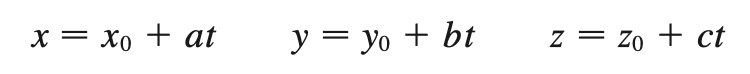
v = <a, b, c>
v: parallel to actual vector, defines direction
symmetric eqns (vector)
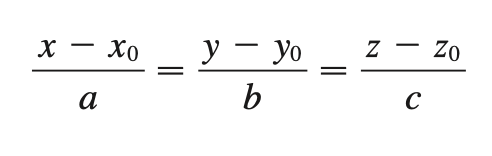
2-point vector eqn
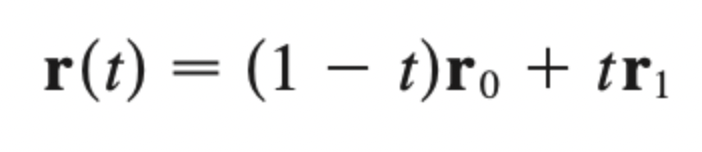
r0 + v = r1
v: vector connecting points r0 & r1
scalar plane eqn
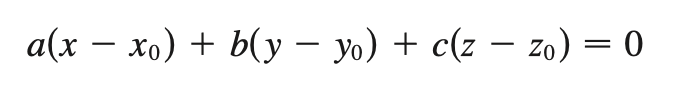
P0 = <x0, y0, z0>
n = <a, b, c>
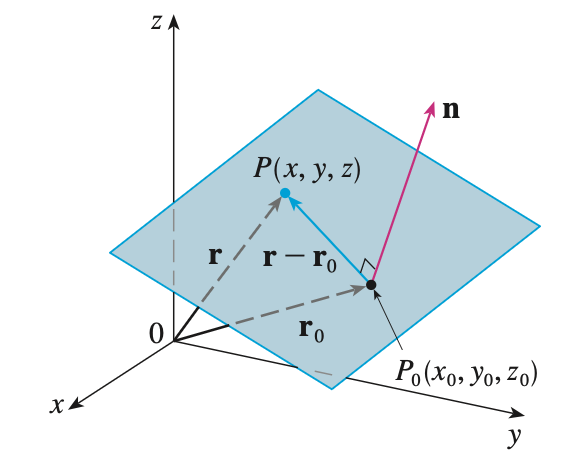
linear plane eqn
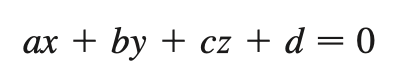
d = -(ax0 + by0 + cz0)
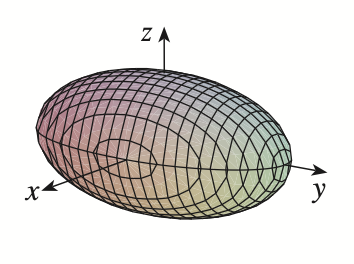
ellipsoid
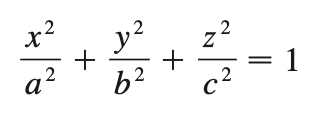
cone
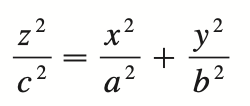
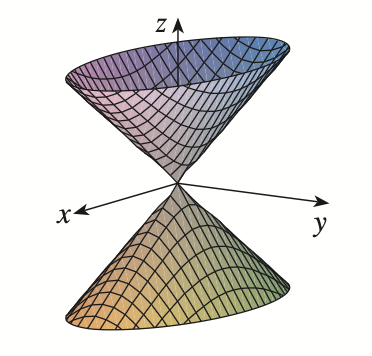
elliptic paraboloid
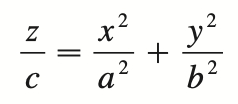
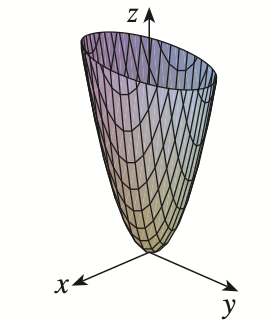
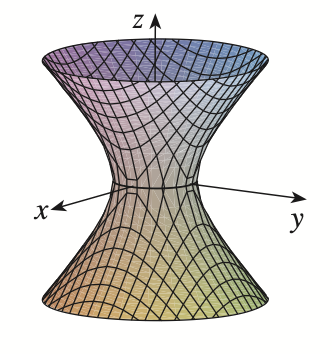
hyperbolic of one sheet
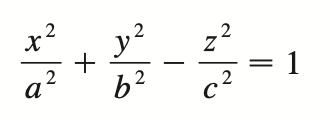
hyperbolic paraboloid
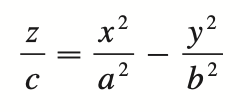
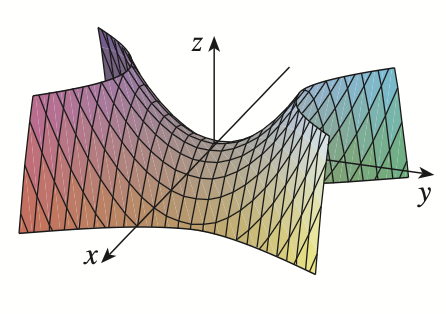
hyperboloid of two sheets
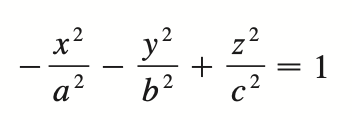
unit tangent vector
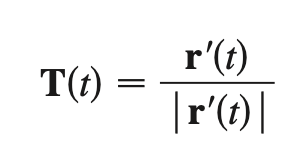
derivative of a vector
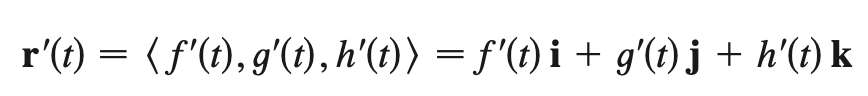
derivative of cross & dot product
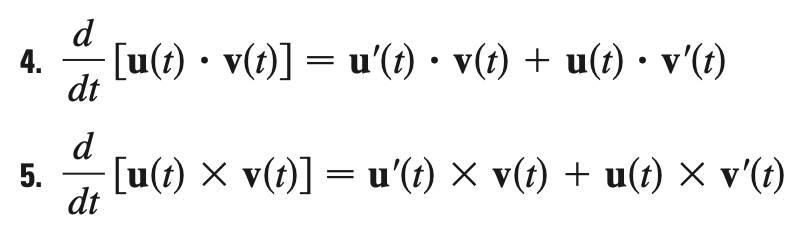
integral of a vector
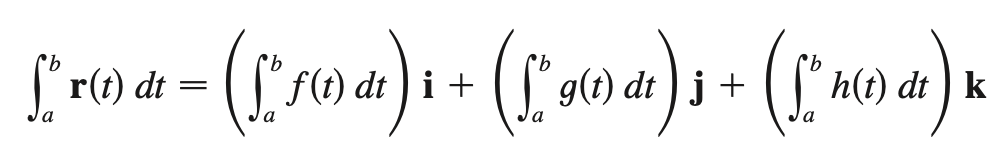
arc length
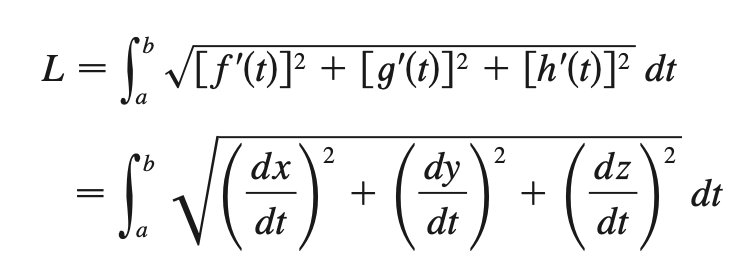
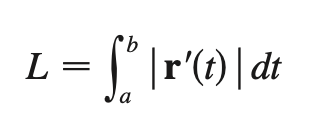
curvature
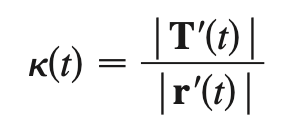
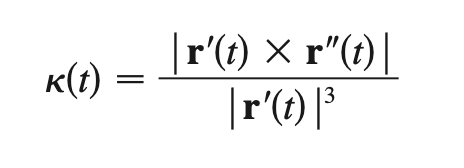
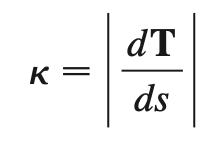
unit normal
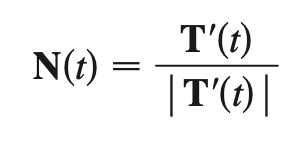
unit binormal
B(t) = T(t) x N(t)
acceleration (tangent & normal)
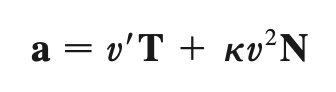
partial derivative
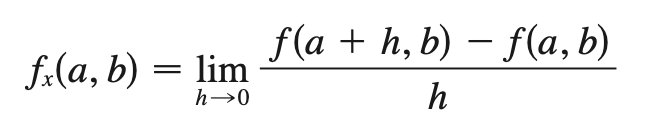
b = constant
derivative notation
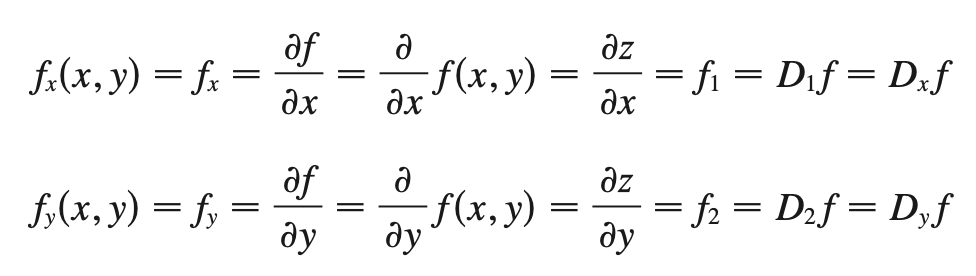
Clairaut’s thm
If fxy & fyx are continuous on D
fxy(a, b) = fyx(a, b)
True for most functions
plane eqn
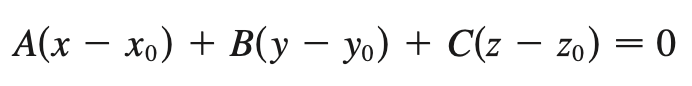
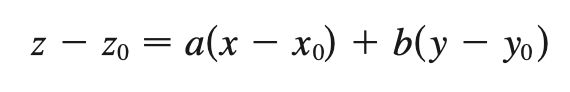
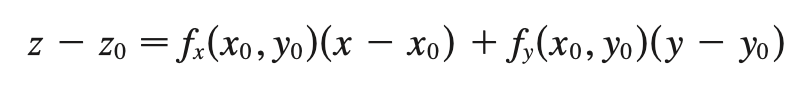
a = -A/C
b = -B/C
total differential
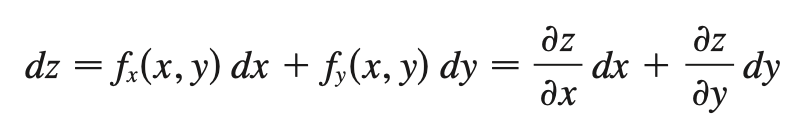
chain rule (multivariable)
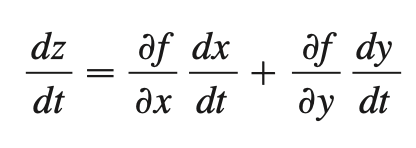
intermediate variables: ???
implicit differentiation??? (multivariable)
implicit function theorem?
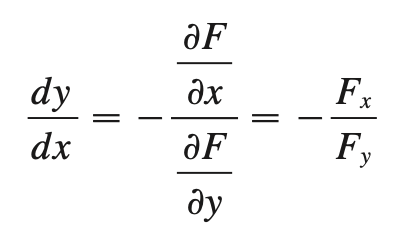
directional derivative
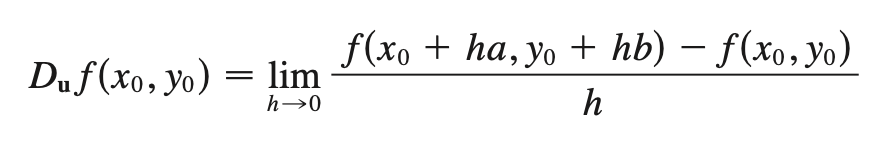
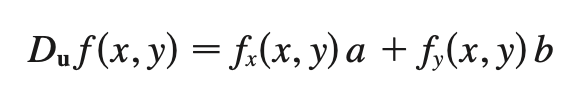
rate of change of a multivariable function along some unit vector u
u = <a, b>
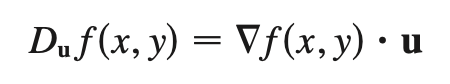
gradient vector
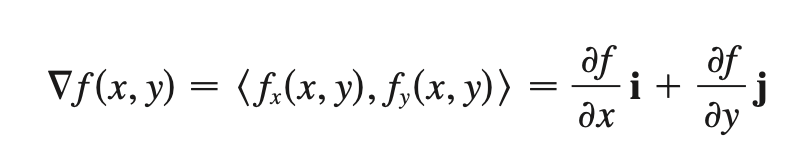
shows direction of fastest increase
tangent plane (symmetric eqns)
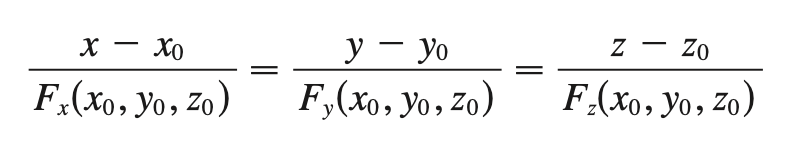
critical point (multivariable)
fx and fy = 0
fx or fy DNE
SDT
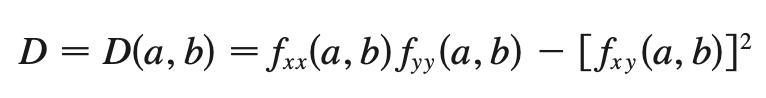
D > 0:
fxx(a, b) > 0
Local minimum
fxx(a, b) < 0
Local maximum
D < 0:
no max/min
EVT (multivariable)
if f is continuous on closed, bounded D:
Both an absolute max & min exist within D
lagrange multiplier
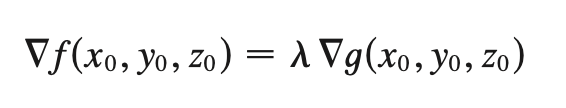
Find all values of lambda satisfying:
∇f(x0, y0, z0) = λ∇g(x0, y0, z0)
g(x, y, z) = k
Evaluate f @ all points
Greatest f is maximum, smallest is minimum
average value (multivariable)
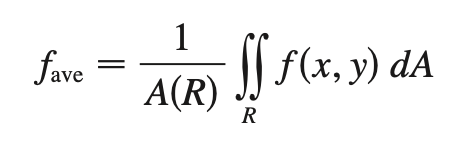
double integral
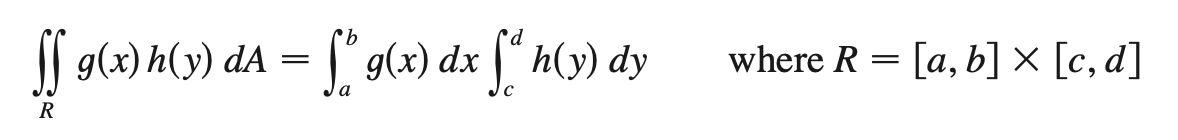
general regions (double integral)
type 1: between 2 continuous functions of x
type 2: between 2 continuous functions of y
double integral (polar)
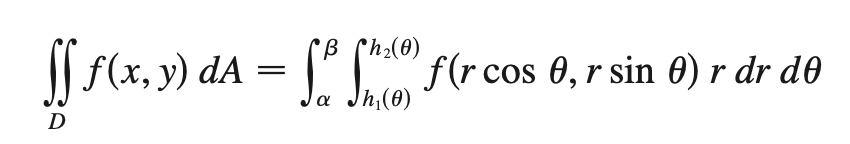
*similarity: r dθ = arc length → “area” dA = r dr dθ
lamina mass
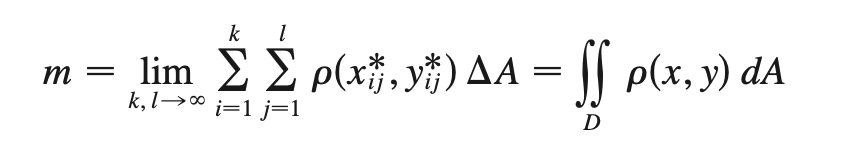
COM (multivariable)
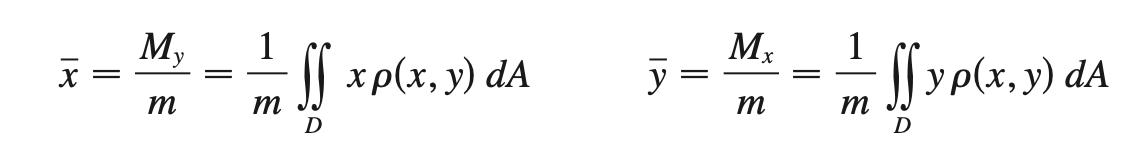
moment of inertia (Ix, Iy, I0)
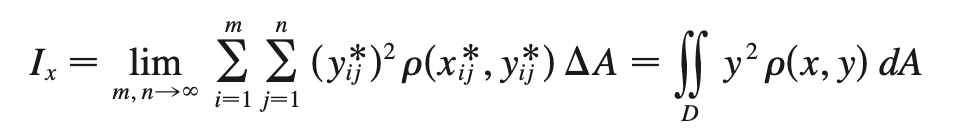
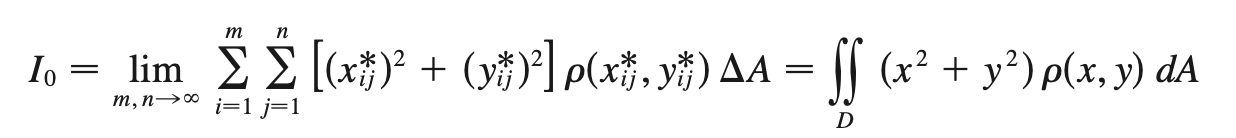
I0 + Ix + Iy
radius of gyration
average distance from the axis of rotation (R)
R = sqrt(I/m)
If all mass was concentrated R distance from the axis, I = mR2 regardless of shape/distribution
surface area (multivariable)
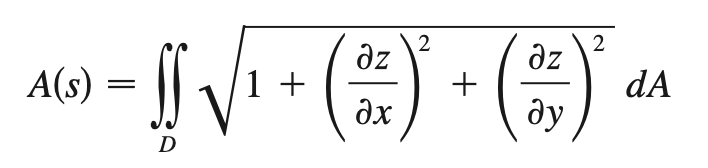
triple integral
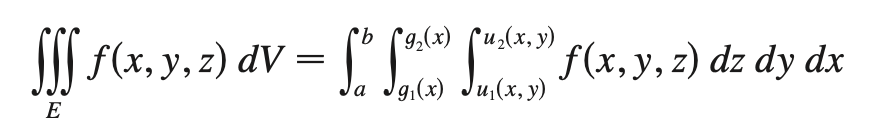
yields bound volume if f(x, y, z) = 1
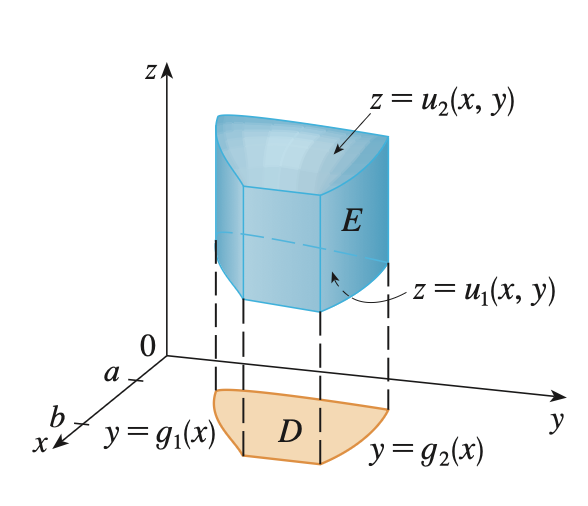
general regions (triple integral)
type 1:
between graphs of 2 continuous f(x, y) functions
region D projected from xy-plane
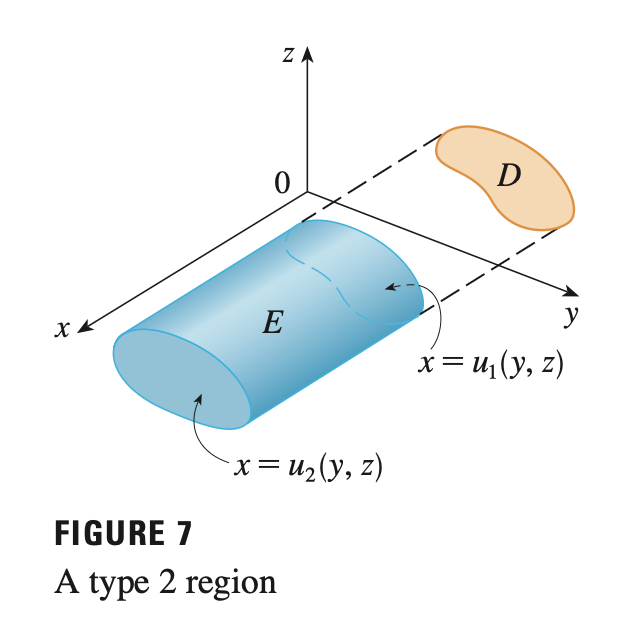
type 2:
between graphs of 2 continuous f(y, z) functions
region D projected from yz-plane
type 3:
between graphs of 2 continuous f(x, z) functions
region D projected from xz-plane
moments of inertia (3 axes)
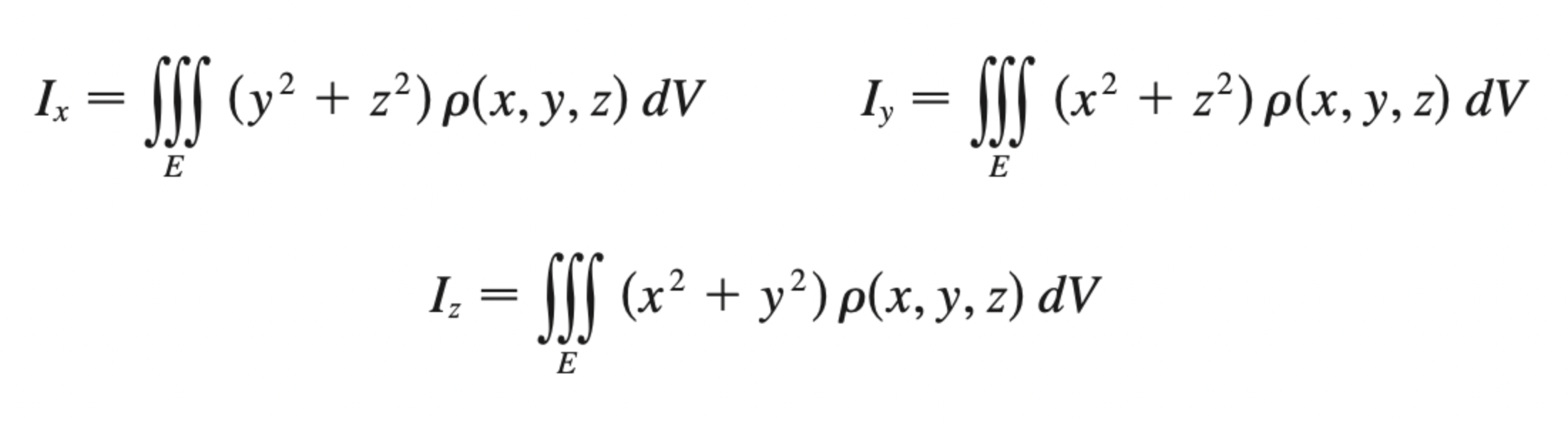
moments (3 axes)
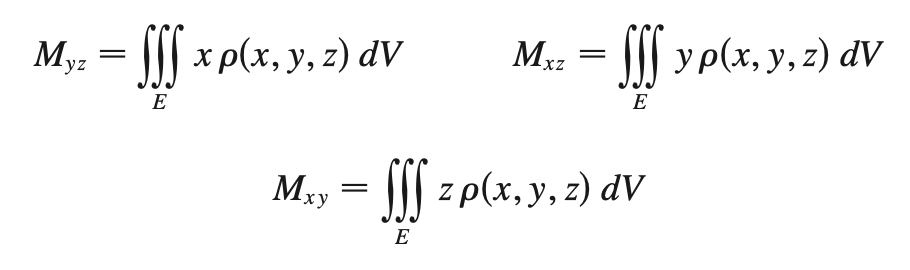
x̄ = Myz/m
ȳ = Mxz/m
z̄ = Mxy/m
cylindrical coords
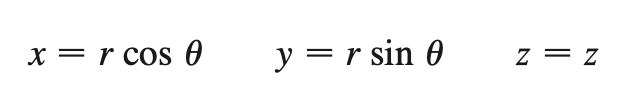
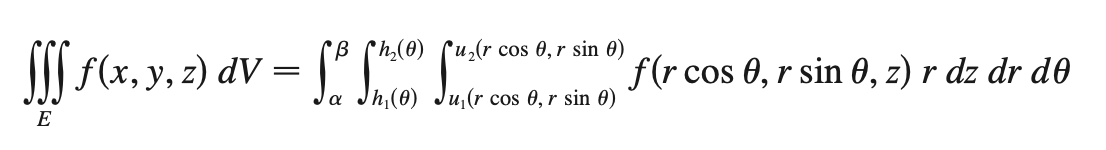
(θ, r, z)
spherical coords
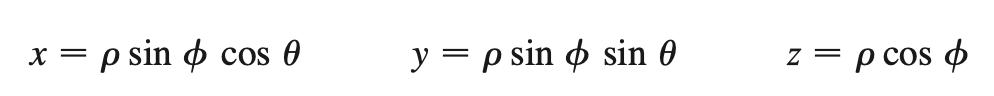
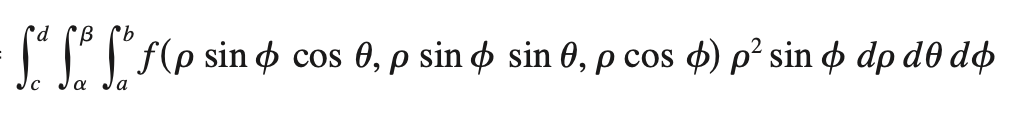
(ρ, θ, Φ)
Jacobian
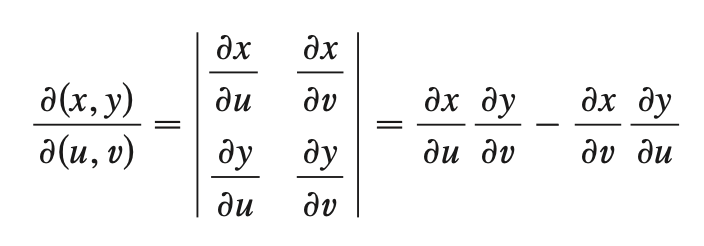
x = g(u, v)
y = h(u, v)
vector fields
assigns each point on the coordinate plane with a vector F(x, y) or F(x, y, z)
conservative vector field
F is conservative if some f exists where:
F = ∇f
line integral (standard)
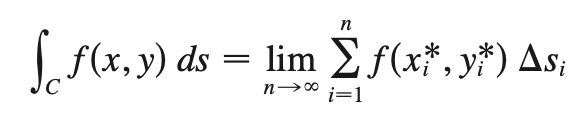
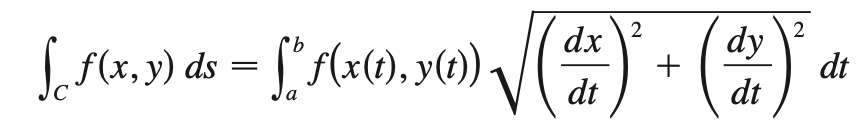
line integral (x’(t))
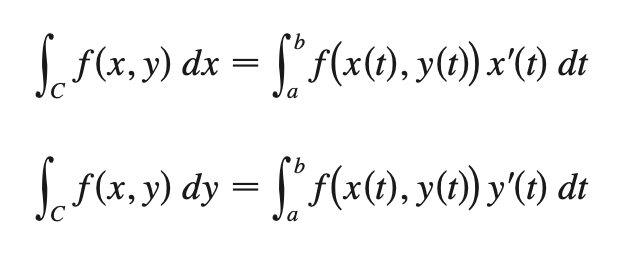
line integral (short form)
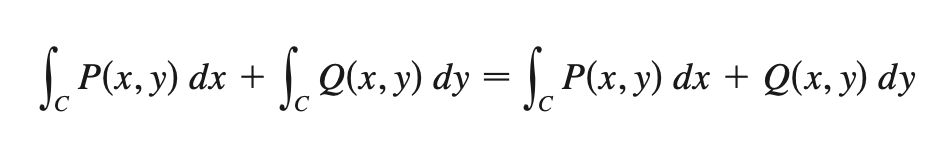
P integration only considers value change over changes in x
Q integration only considers value change over changes in y
work done (line integral)
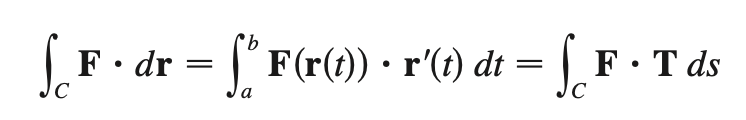
T = unit tangent on C
Fundamental theorem for line integrals
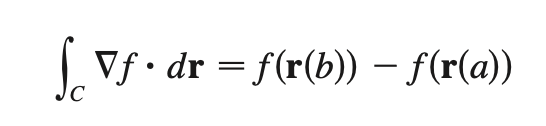
line integrals of conservative vector fields only require values of f @ C’s endpoints!
test for conservative vector field
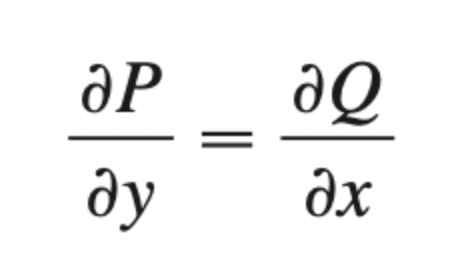
F(x, y) = P(x, y)i + Q(x, y)j
ONLY true in a simple region
Green’s thm
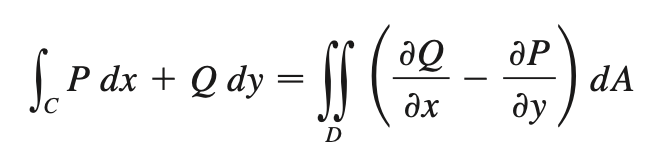
true if P & Q have continuous partial derivatives on D
Area (region D around closed line integral)
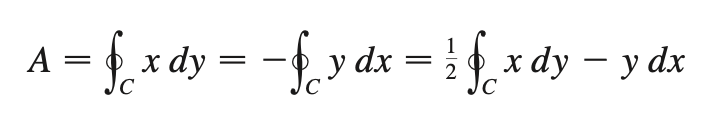
curl
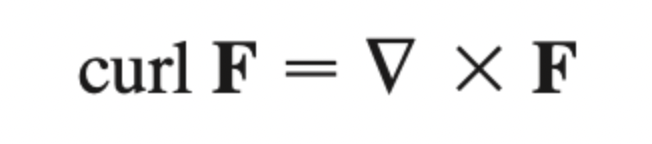
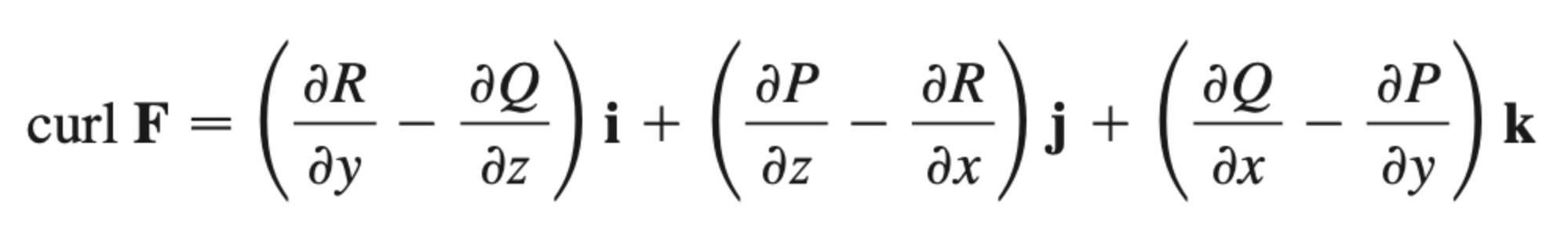
F = Pi + Qj + Rk
measures rotation in a vector field
curl(∇f)
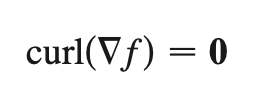
implies conservative vector fields also have no curl
true if second-order partial derivatives are continuous
divergence
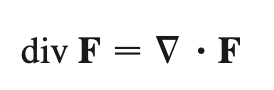
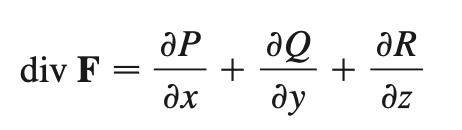
measures the rate at which vectors move away from a point
div curl
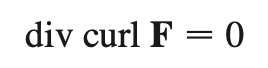
true if F has continuous second-order partial derivatives
second vector form of green’s thm
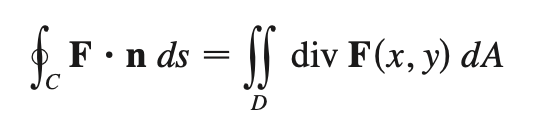
parametric equations of surface S
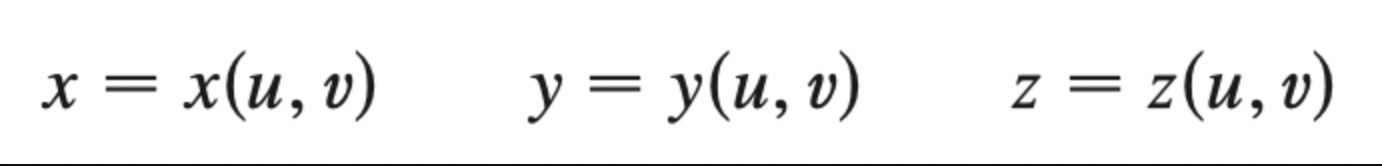
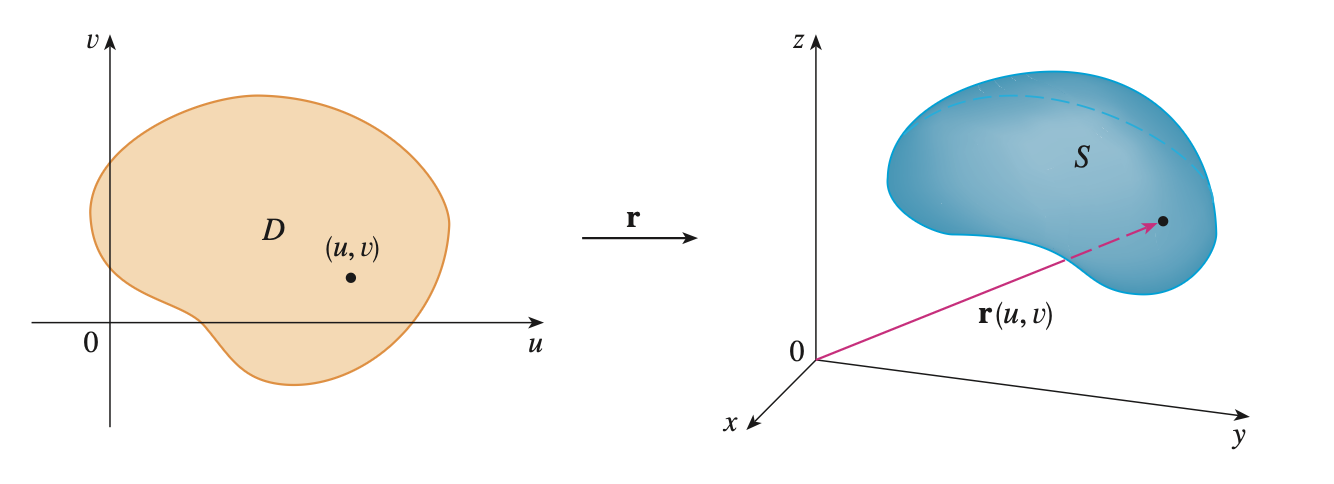
surface of revolution
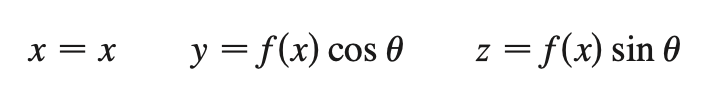
surface area/ surface integral
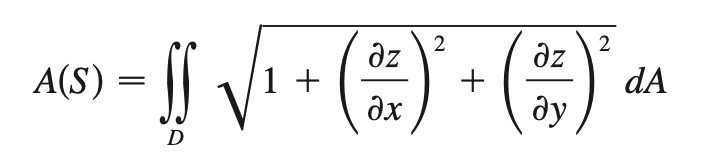
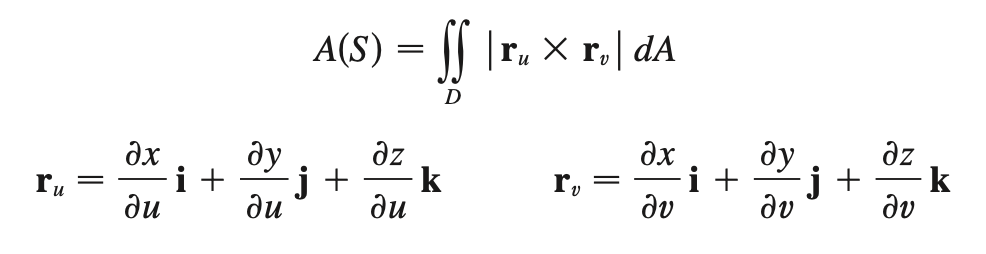
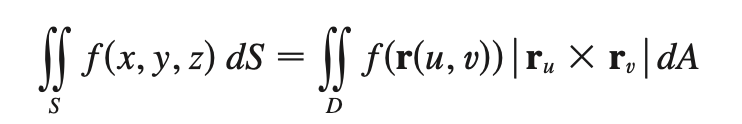
can be used for COM or moments of inertia
vector surface integrals
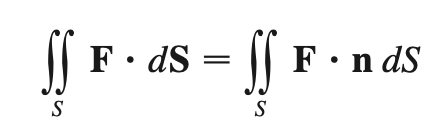
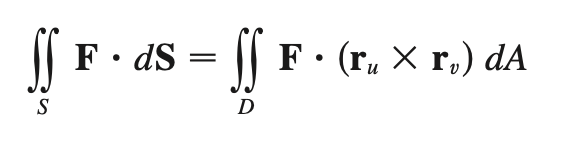
Stokes’ thm
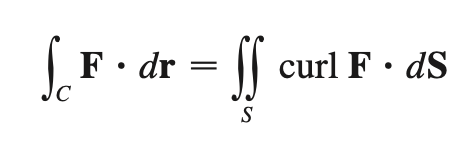
Divergence thm