Campbell Biology- Chapter 2
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Atom
The basic unit of an element that retains the properties of the element.
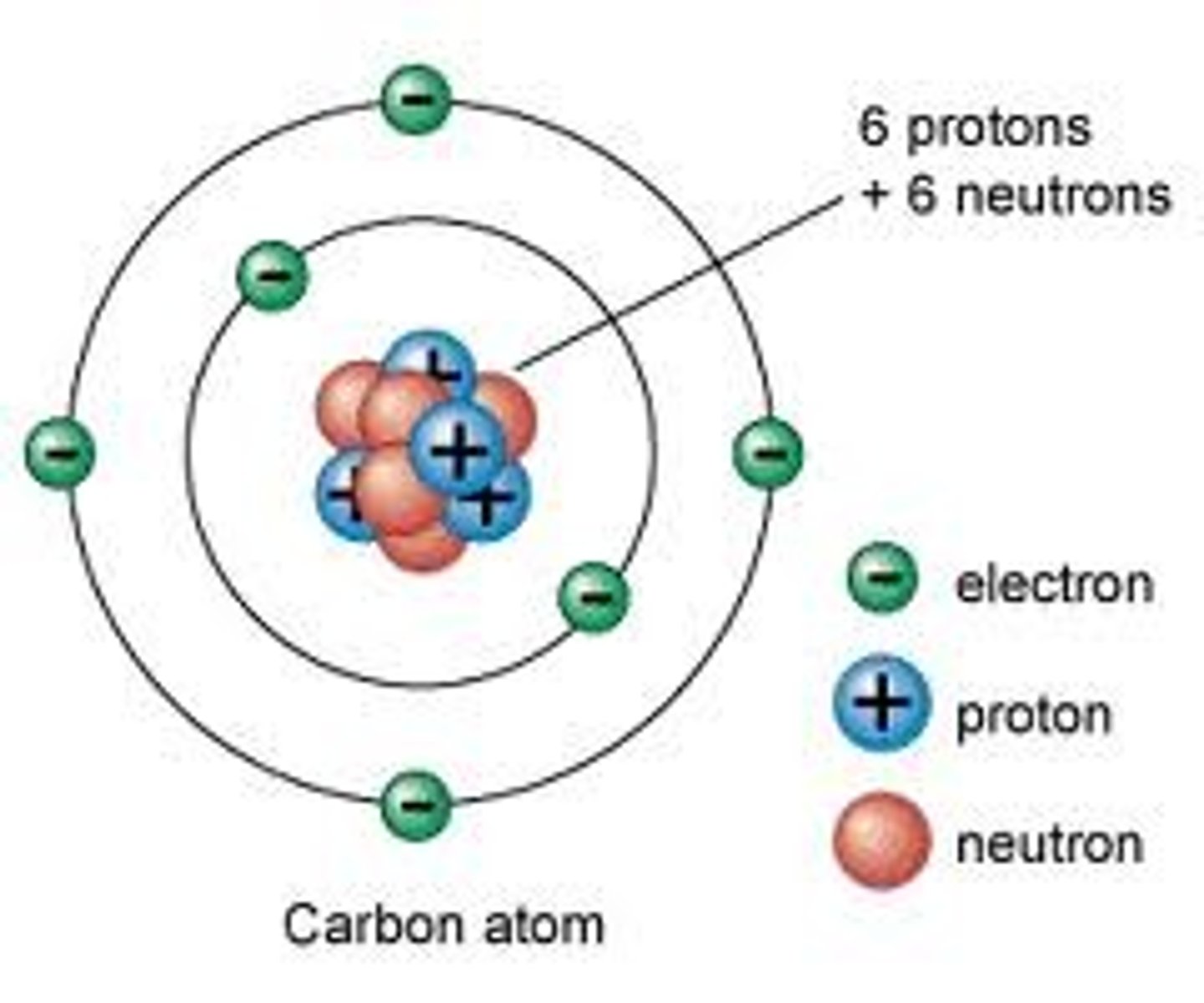
Proton
Positively charged subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom; equal to the number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom.
Neutron
A neutrally charged subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
Electron
A negatively charged subatomic particle found orbiting the nucleus of an atom; equal to the number of protons in an electrically neutral atom.
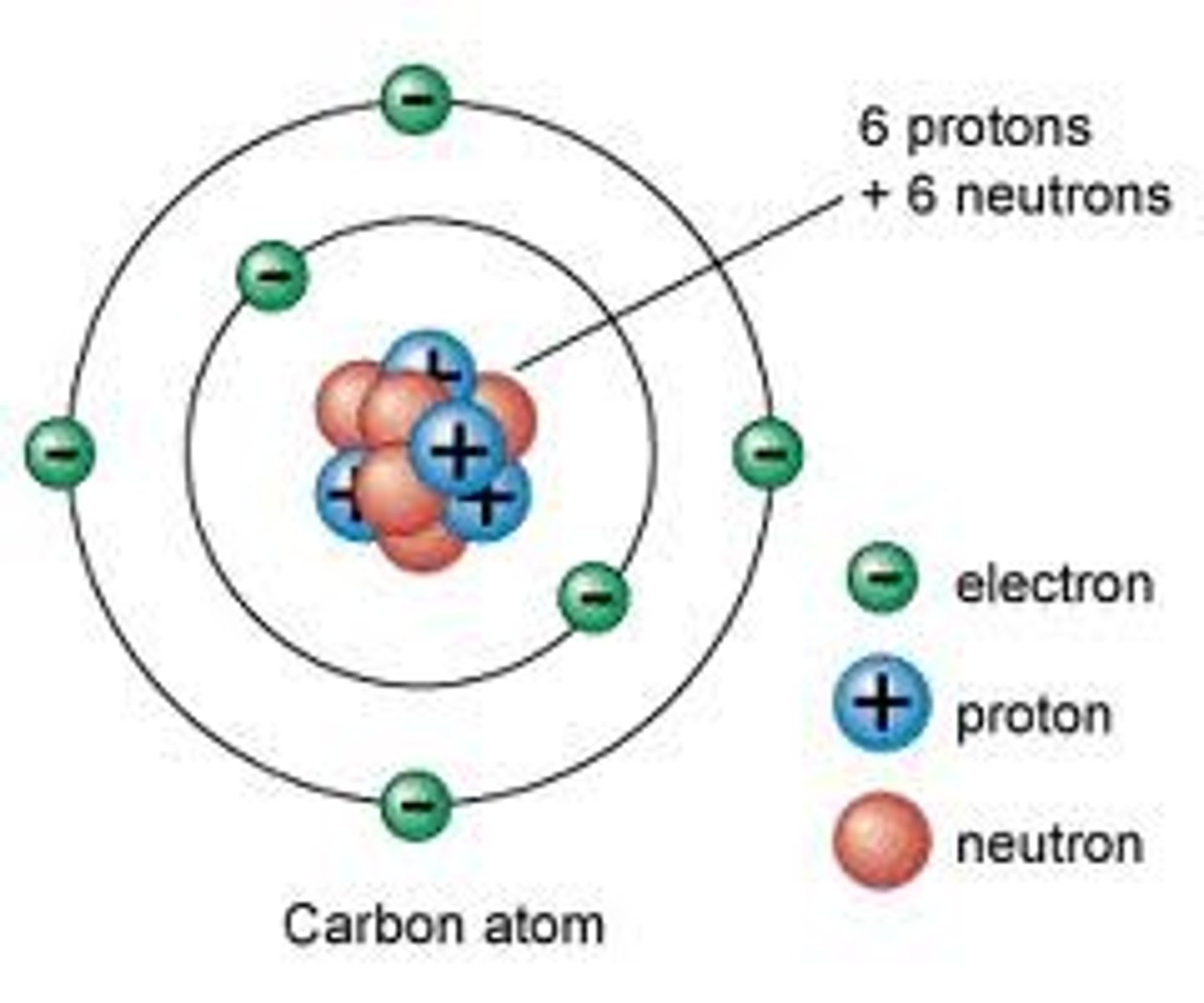
Atomic Weight
Measured in daltons, and consists of the weight of protons and neutrons together, each of which weighs about one dalton.

Atomic Nucleus
The portion of an atom which contains protons and neutrons.
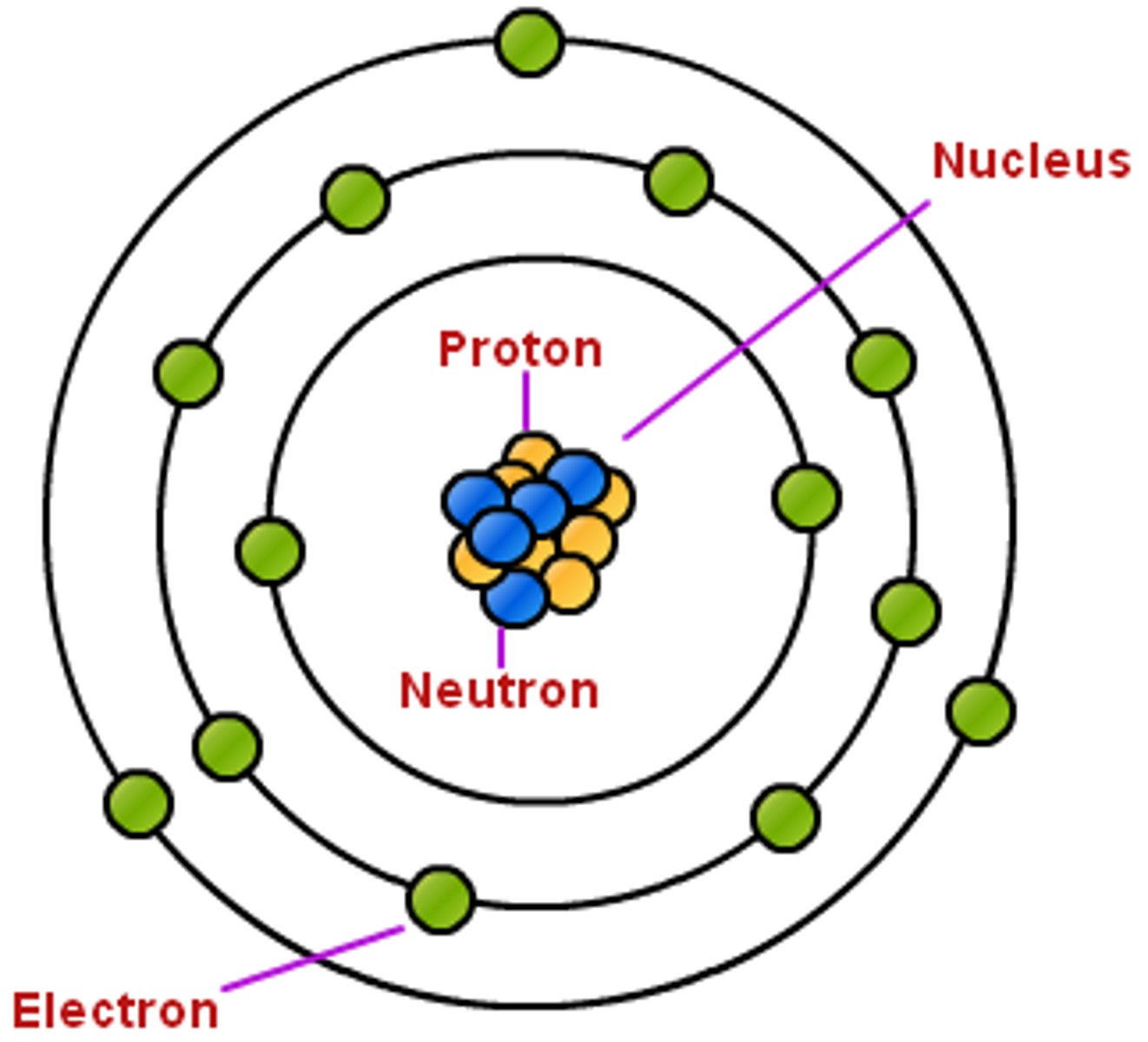
Orbital
The volume of space an electron occupies.
Energy Shells
Represent the state of potential energy of an electron. Those closer to the nucleus have the least amount of energy.
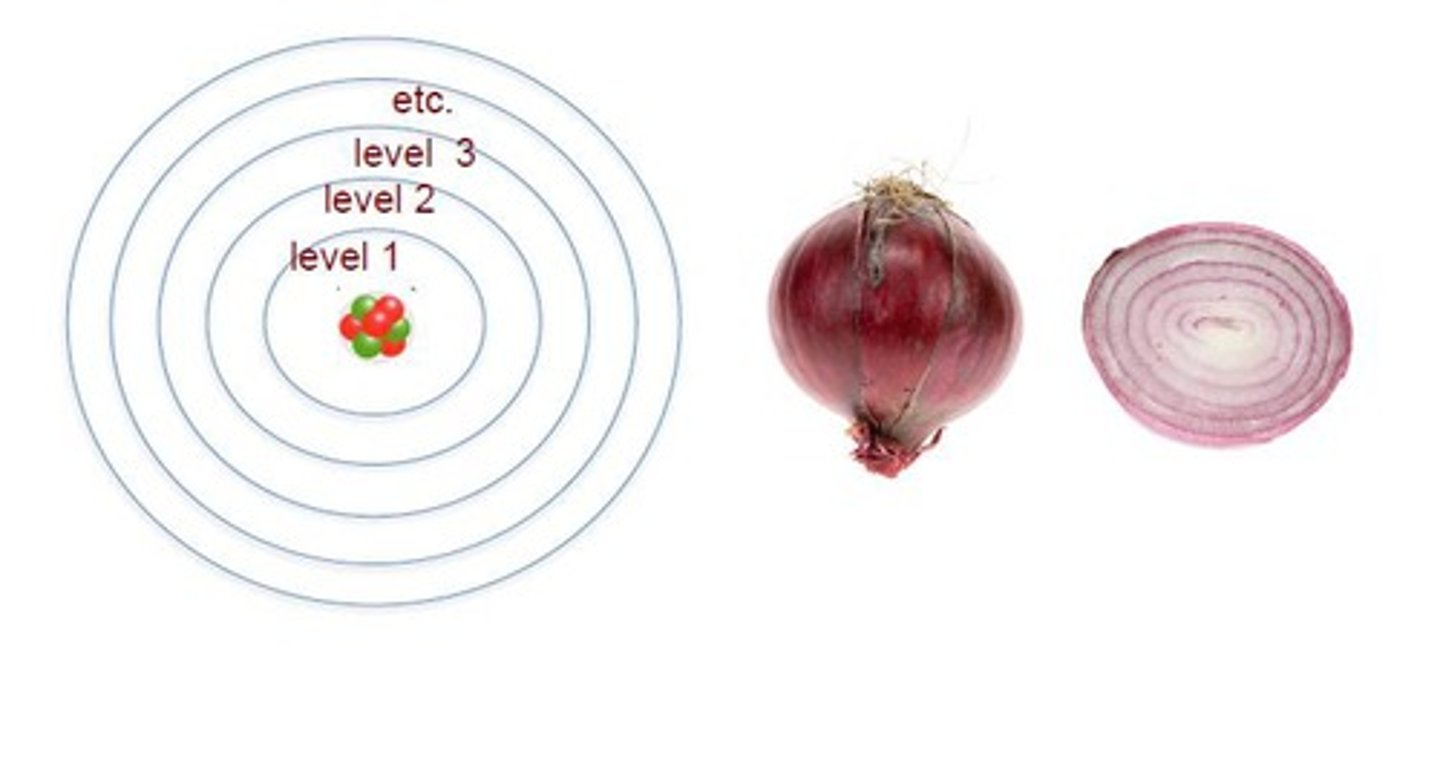
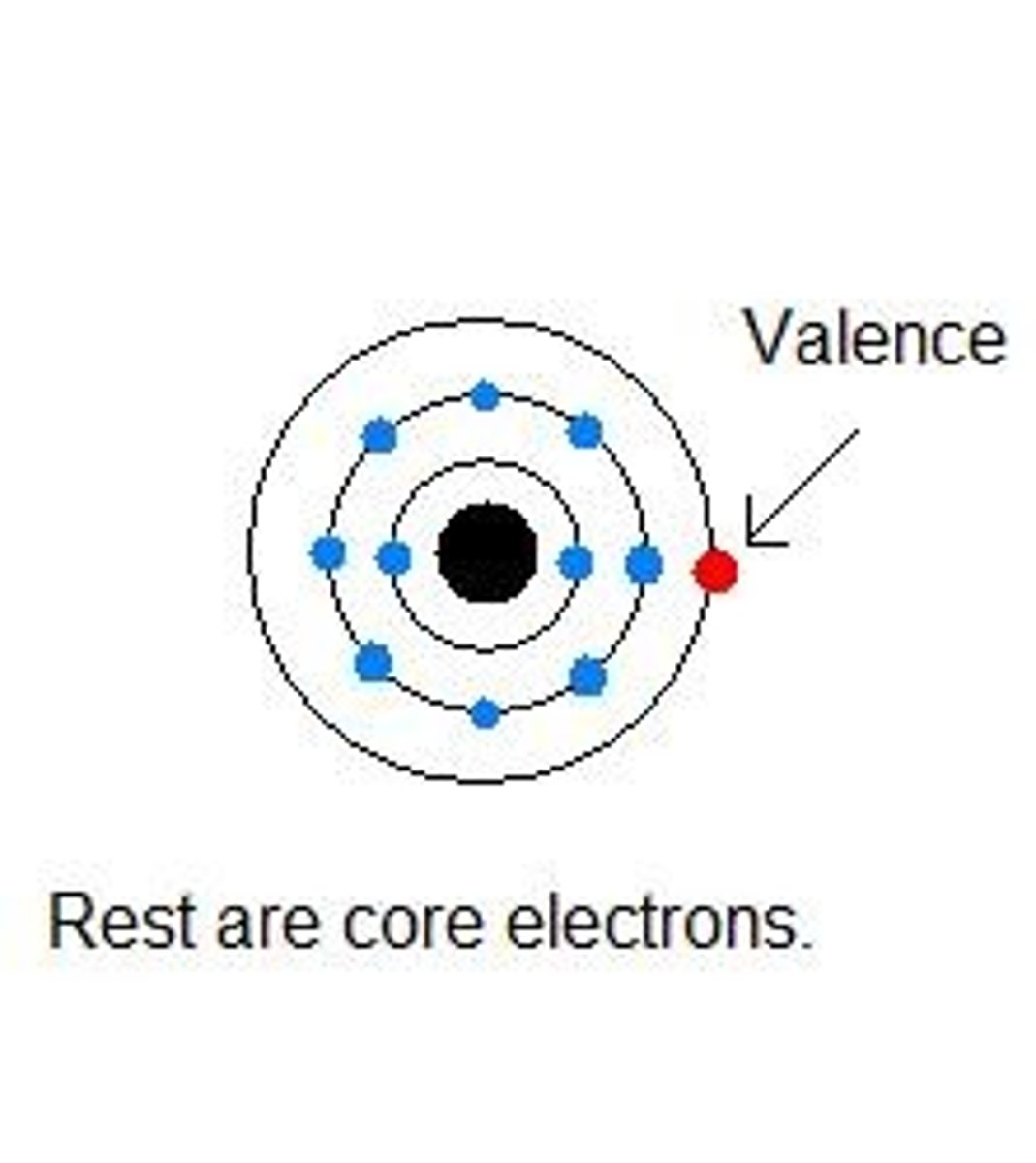
Valence Shell
The outermost shell of an atom which has the most potential energy.
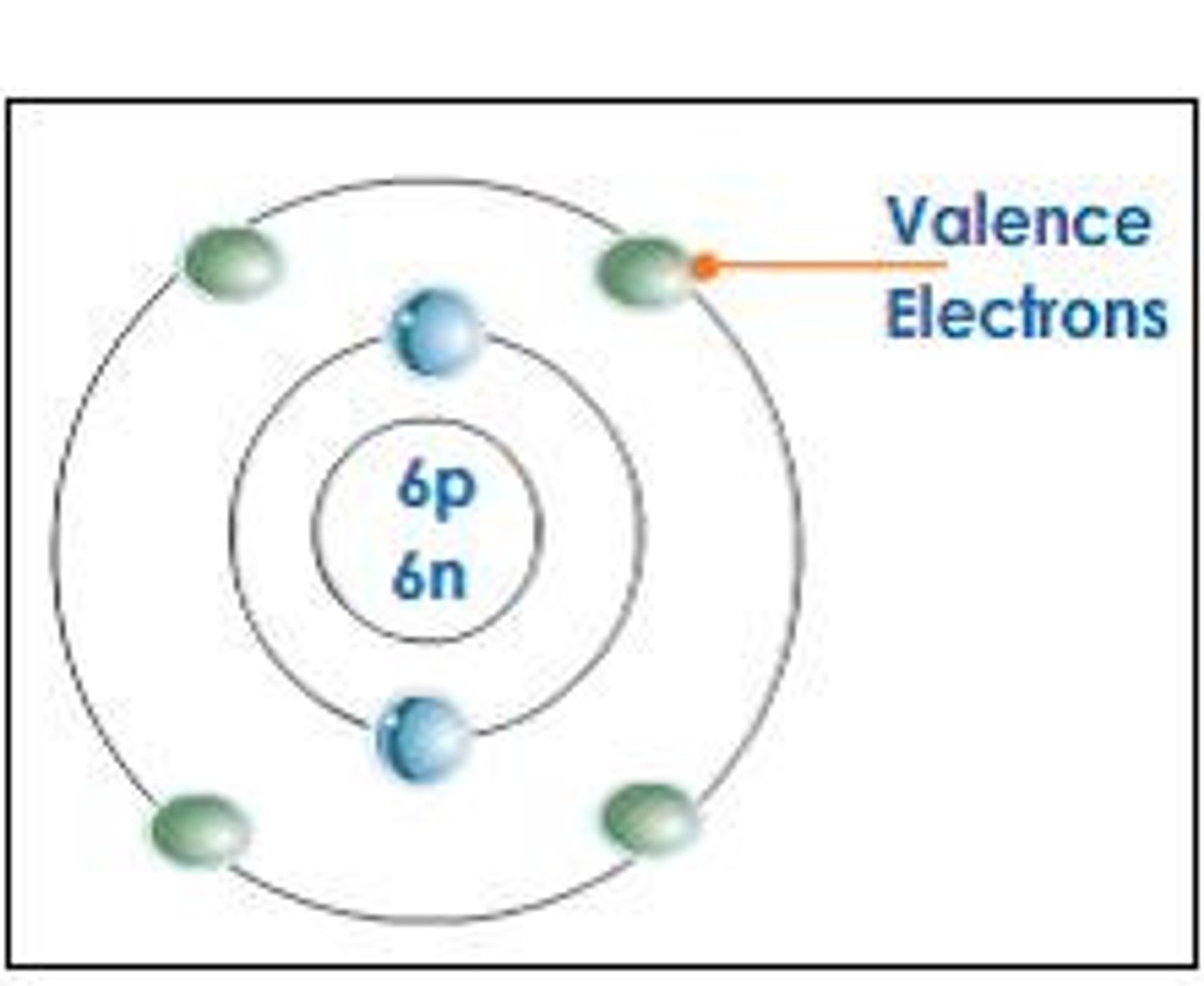
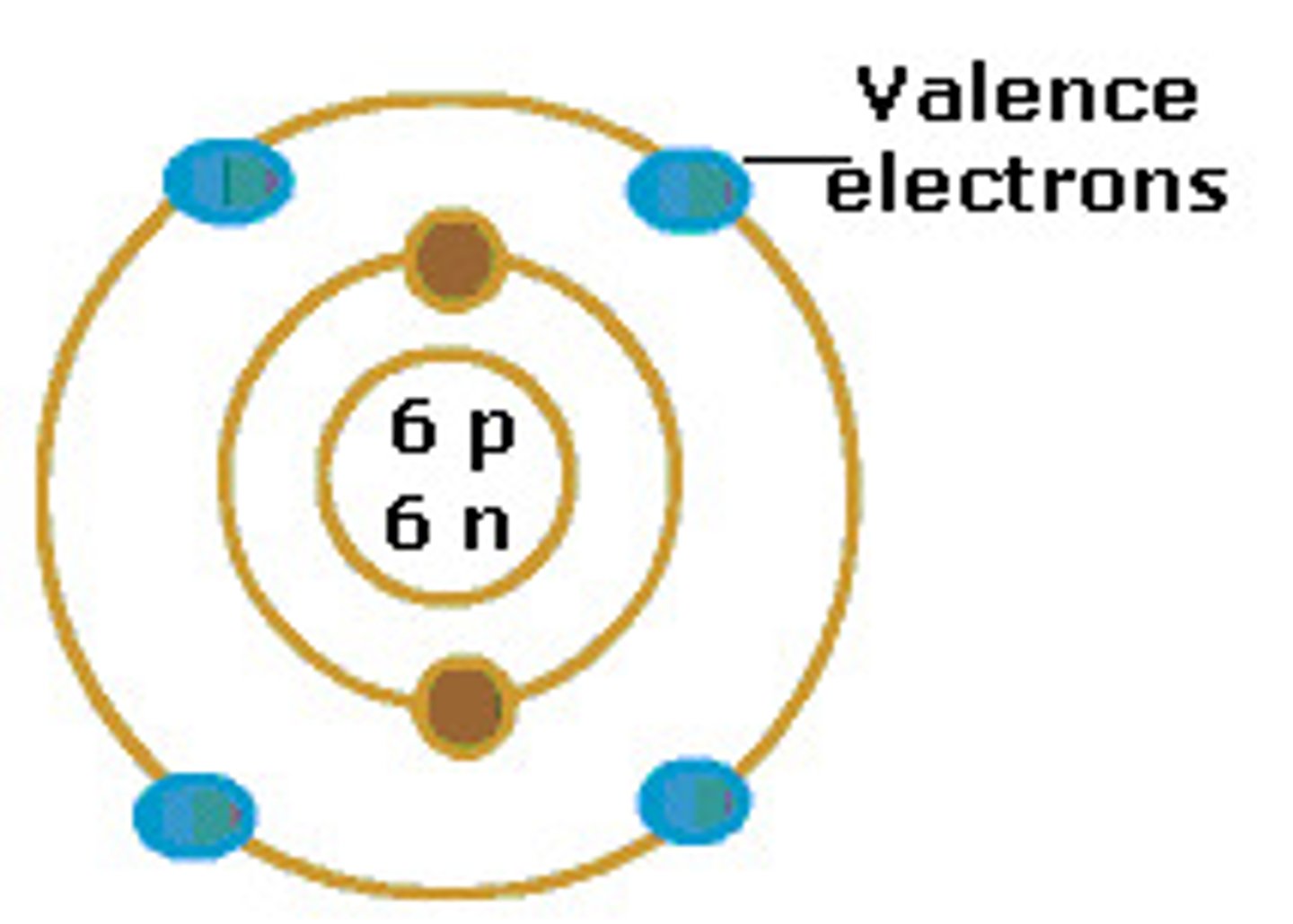
Valence electrons
Electrons in the valence, or outermost, energy shell of an atom, which have the most potential energy and which can form bonds with other atoms.
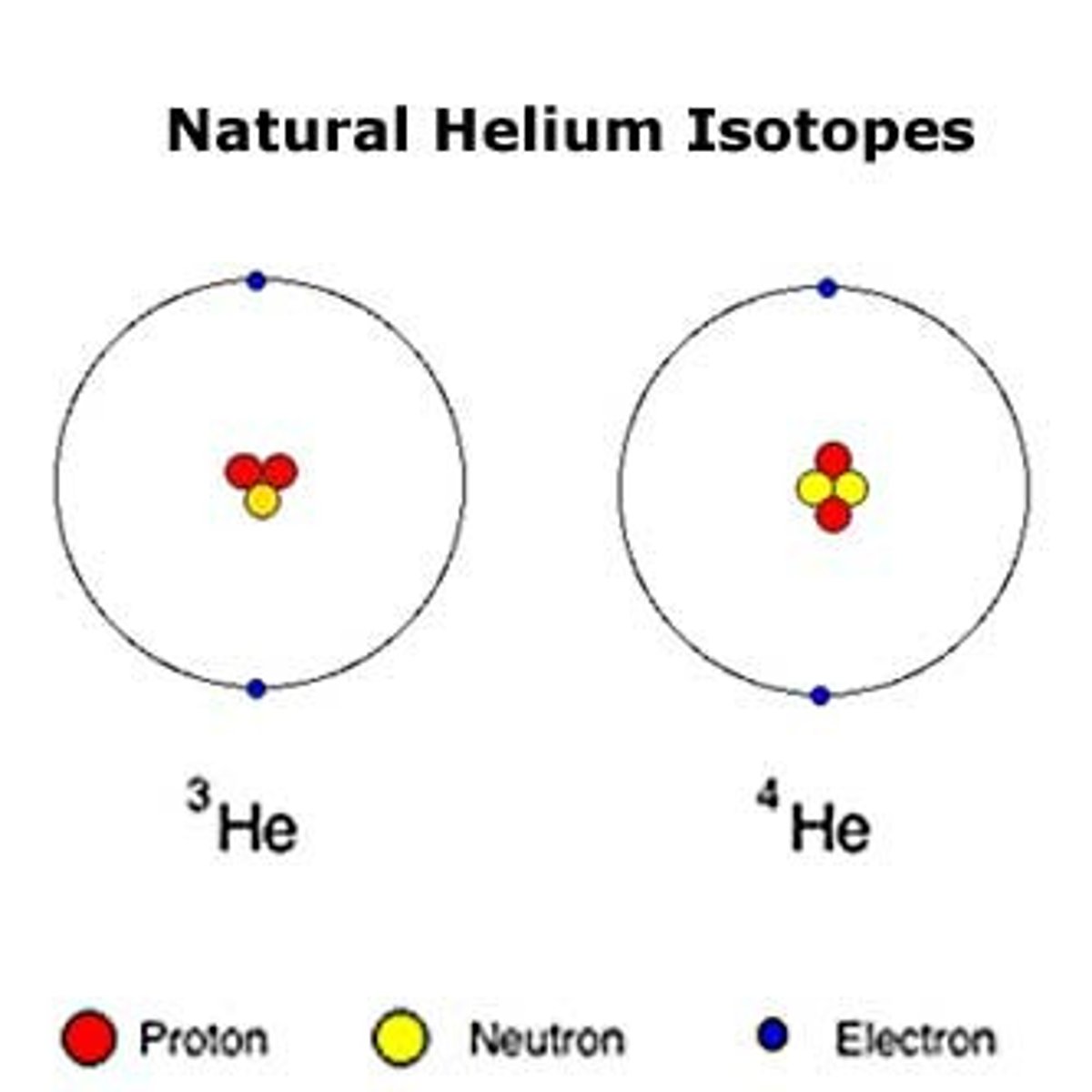
Isotopes
Varying atomic forms of an element which vary from an electrically neutral atom in the number of neutrons, causing the atomic weight to vary. Radioactive isotopes have medical imaging and other applications.
Chemical Bonds
Attractions between atoms resulting from a sharing of valence electrons or the presence of opposite charges on the atoms. The bonded atoms gain complete valence shells.
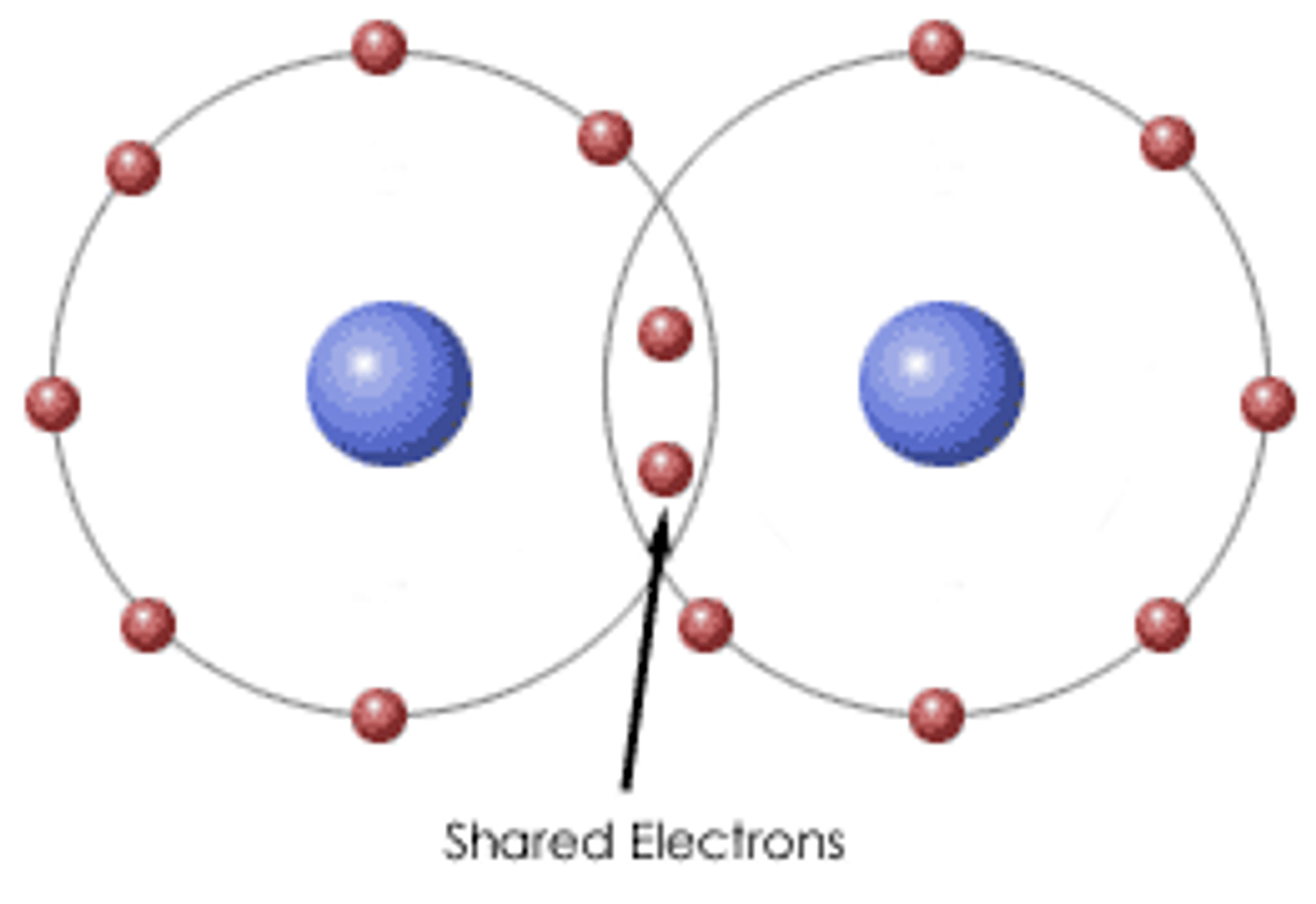
Covalent Bond
The sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms.
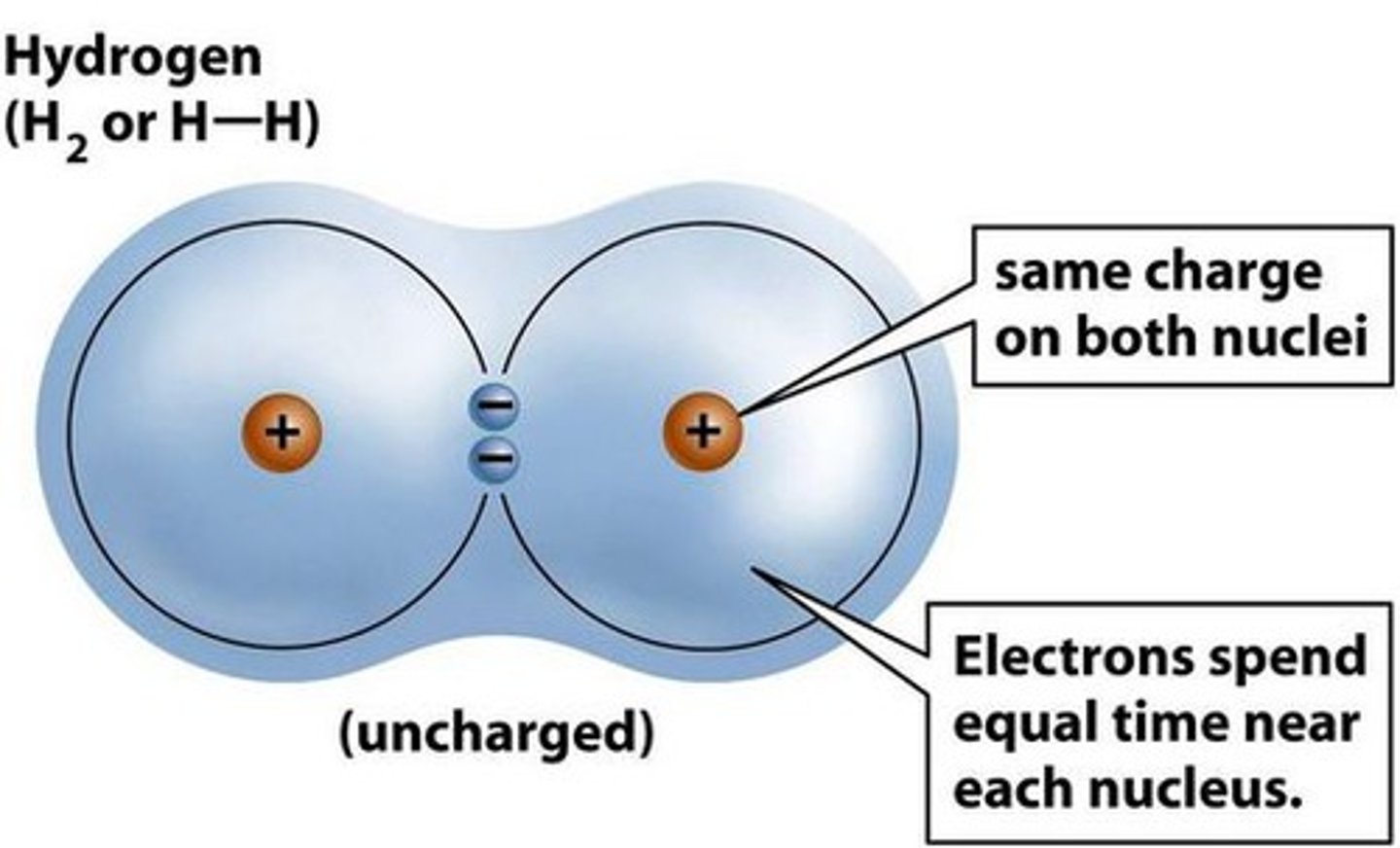
Molecule
Two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds.
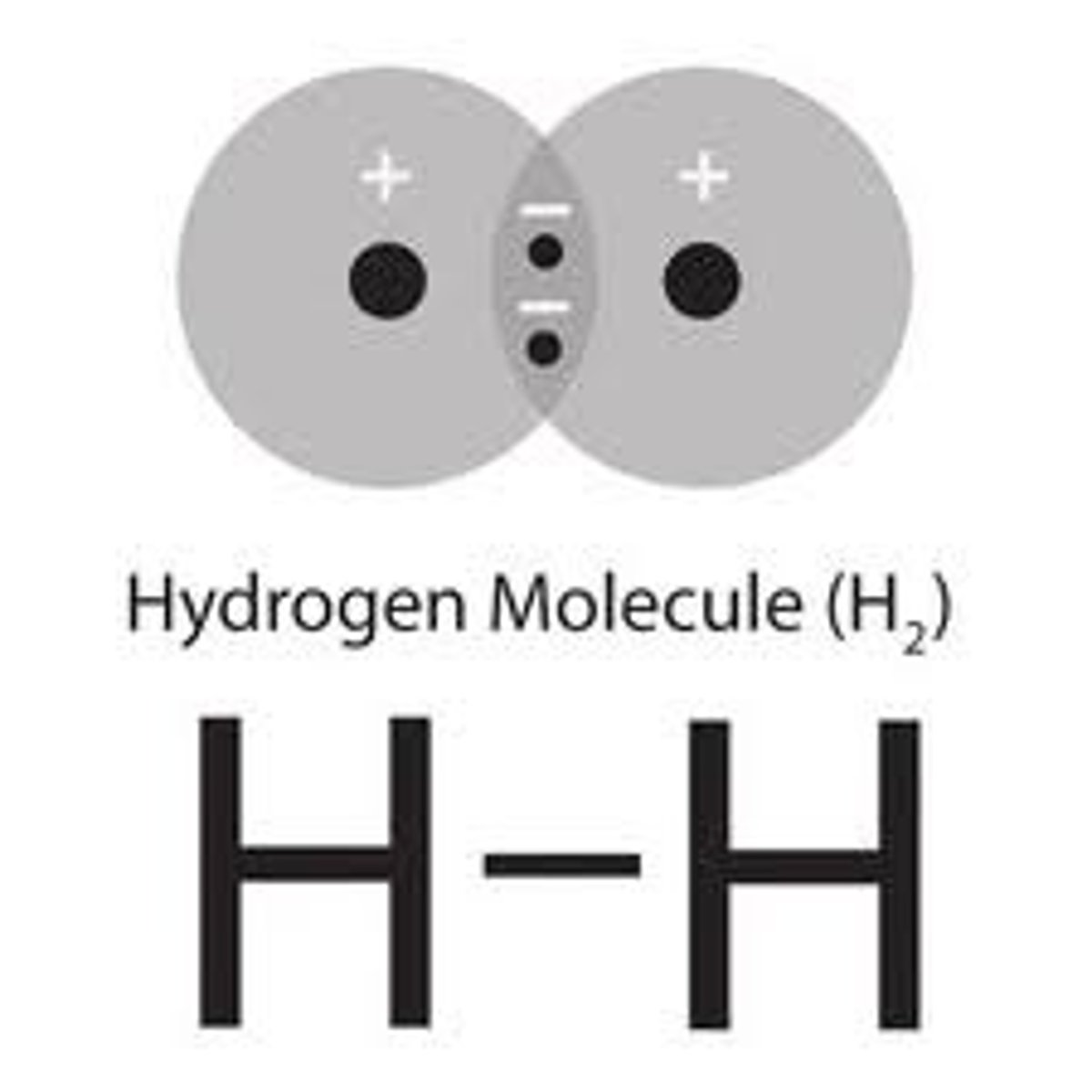
Single Bond
One pair of shared electrons. Example: hydrogen.
Double Bond
Two pairs of shared electrons. Example: Oxygen has 6 electrons in its valence shell, which can hold 8. Each atom shares 2 electrons for a total of 4.
Valence
An atom's bonding capacity, or the number of covalent bonds the atom can form to give the atom a full complement of electrons in the valence shell. Usually equals the number of unpaired electrons required to complete the valence shell.
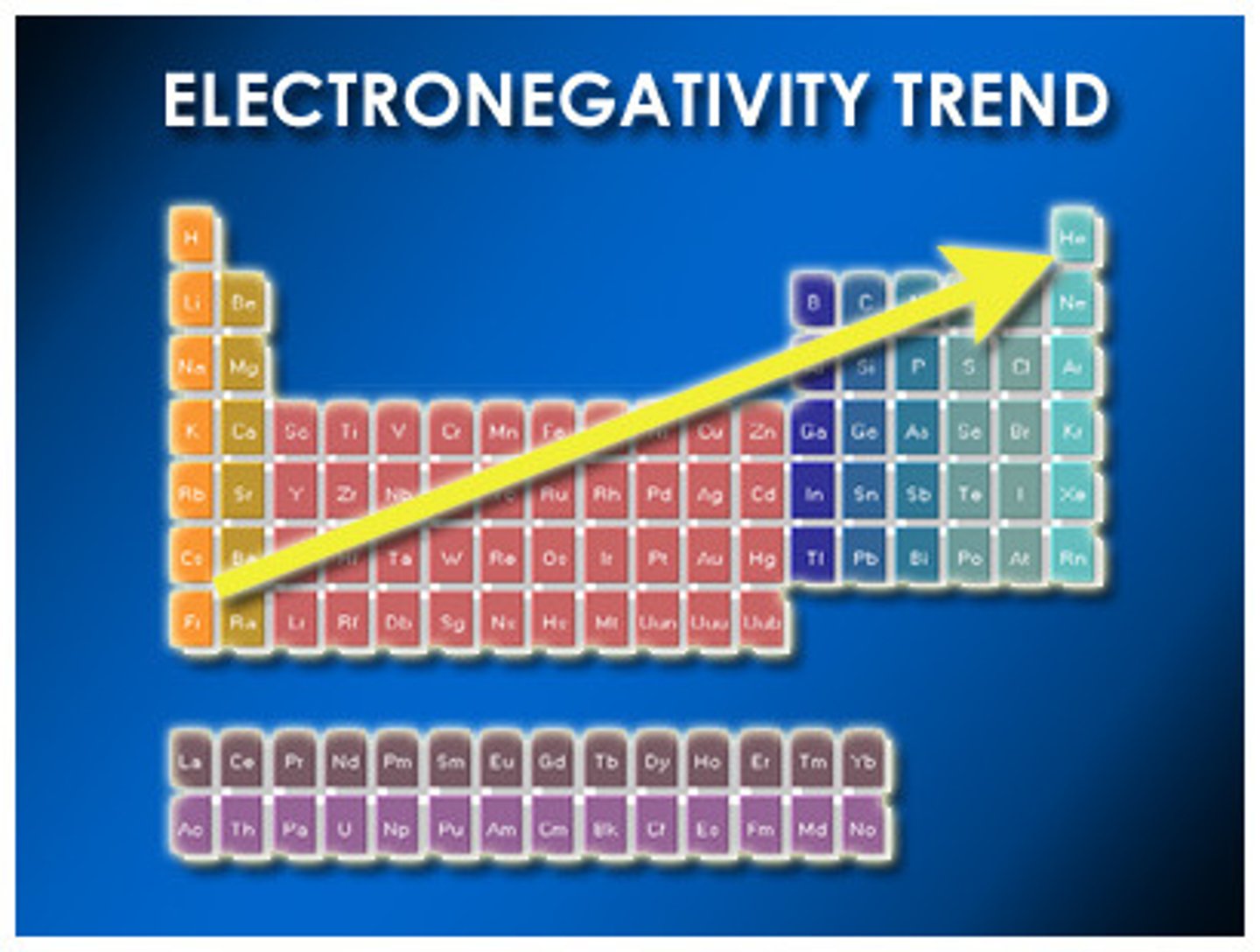
Electronegativity
The attraction of a particular atom for the electrons of a covalent bond. Atoms in a molecule attract shared bonding electrons to varying degrees. This degree is _________.
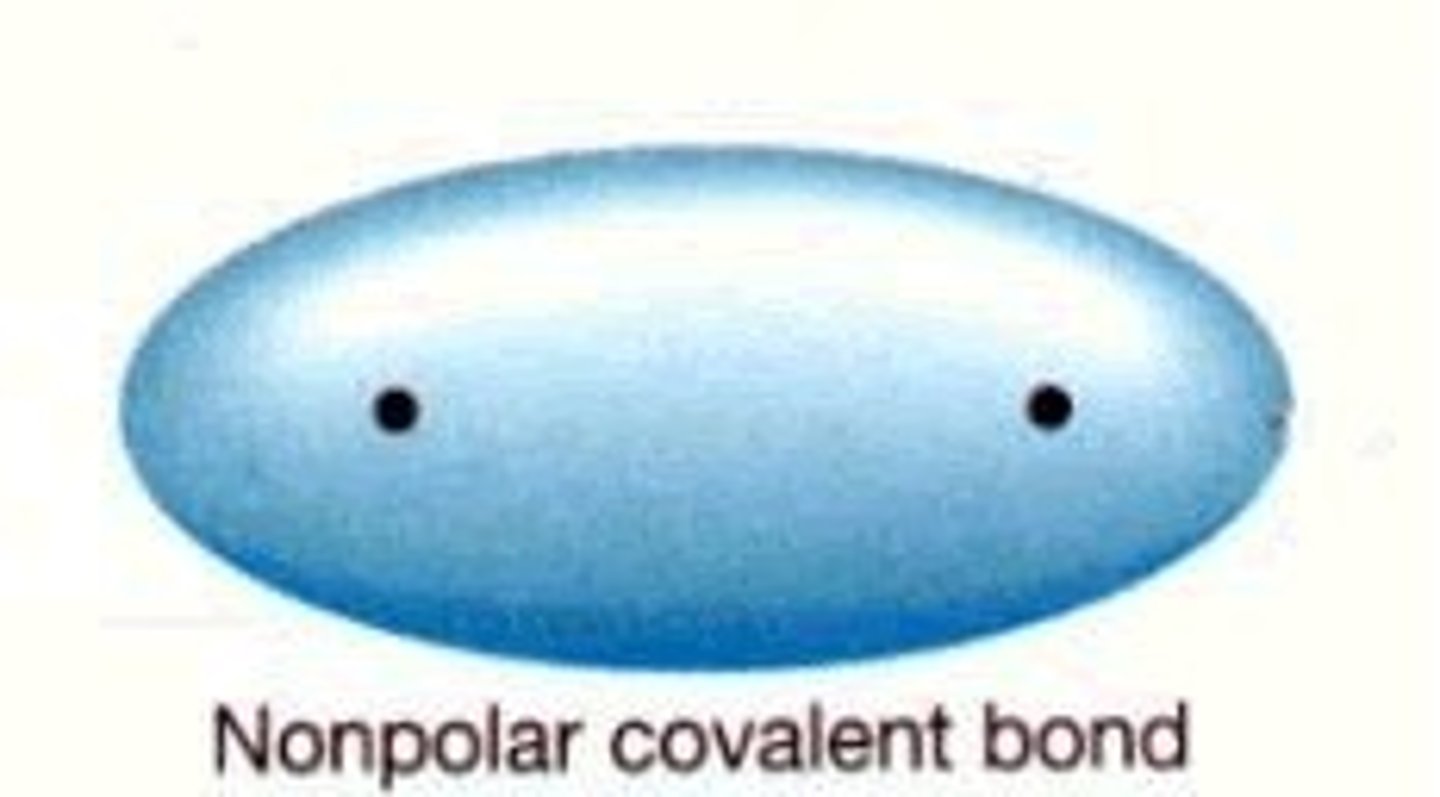
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
A covalent bond between 2 atoms of the same element in which the electrons are shared equally because the two atoms have the same electronegativity.
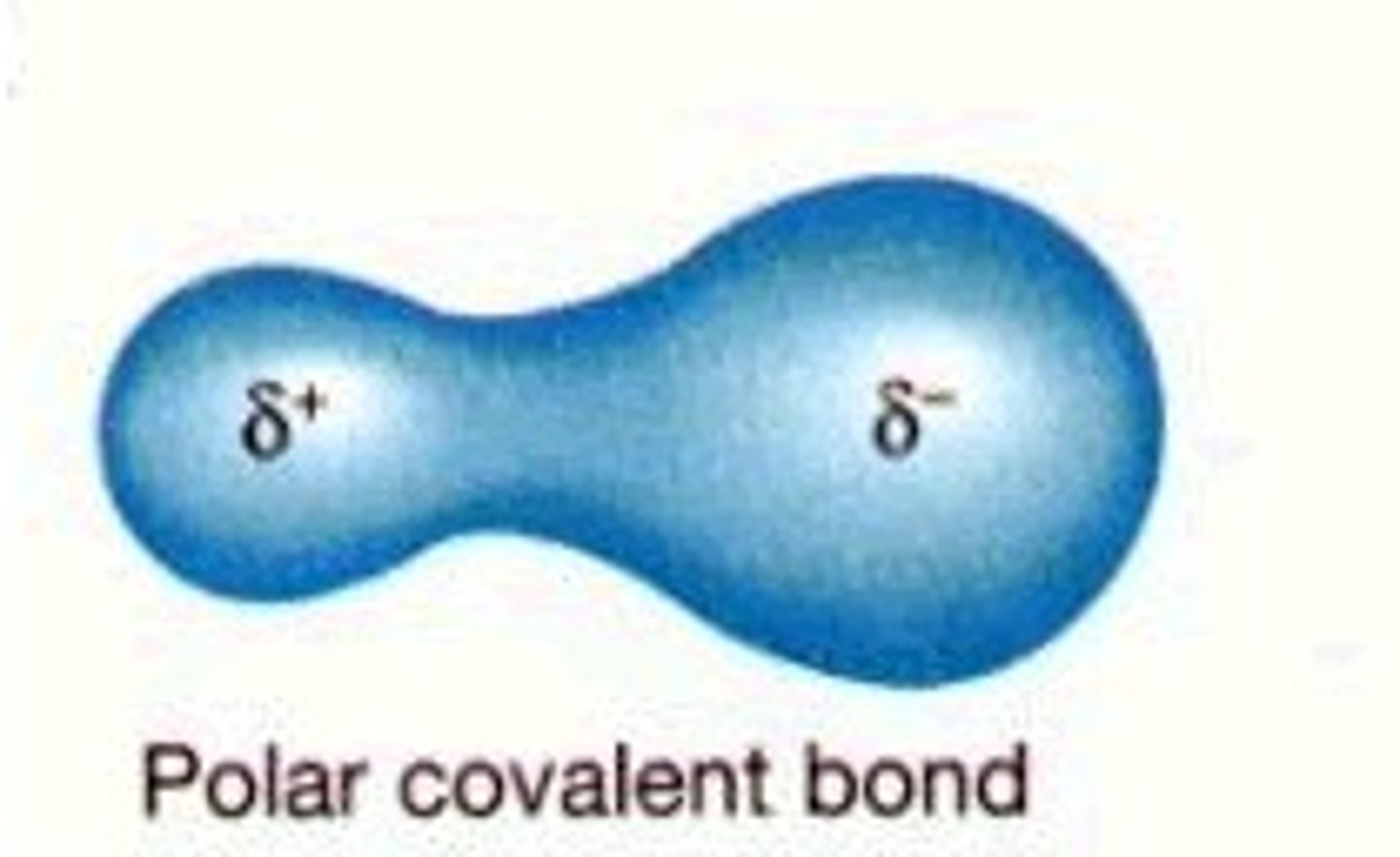
Polar Covalent Bond
An atom bonded to a more electronegative atom.
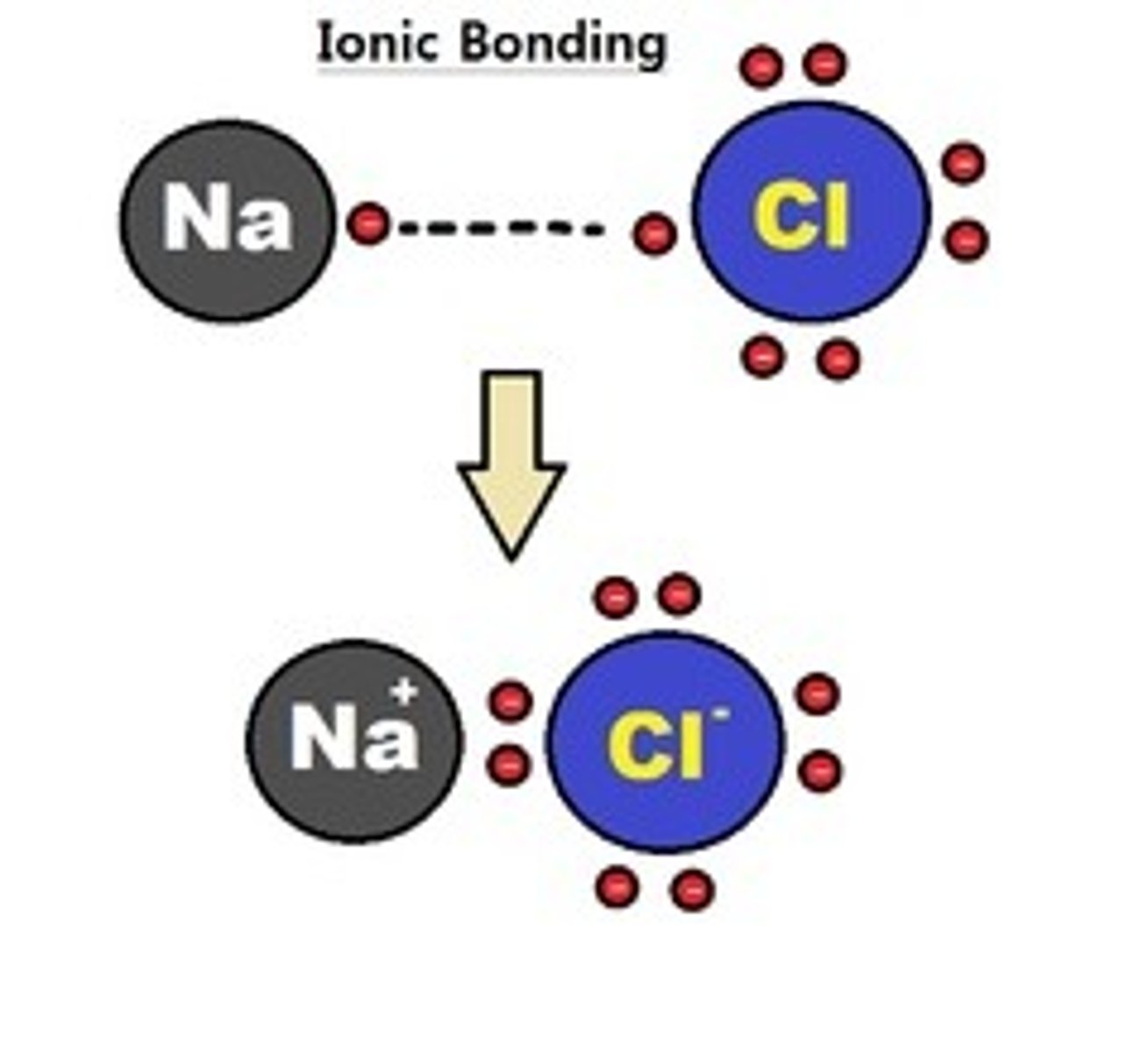
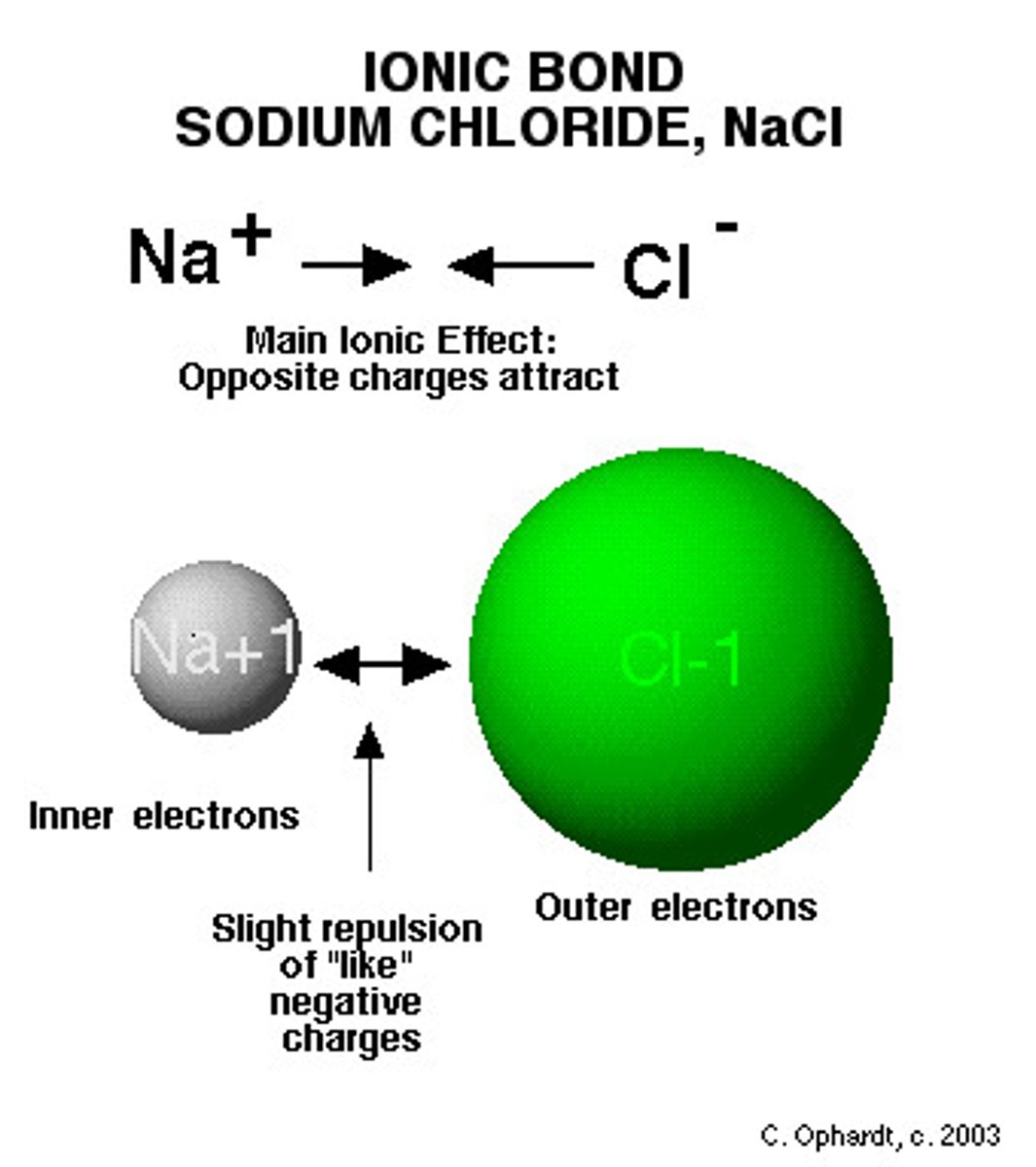
Ionic Bonds
Bonds between two atoms so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner.
Ion
One of two charged atoms resulting from an ionic bond.
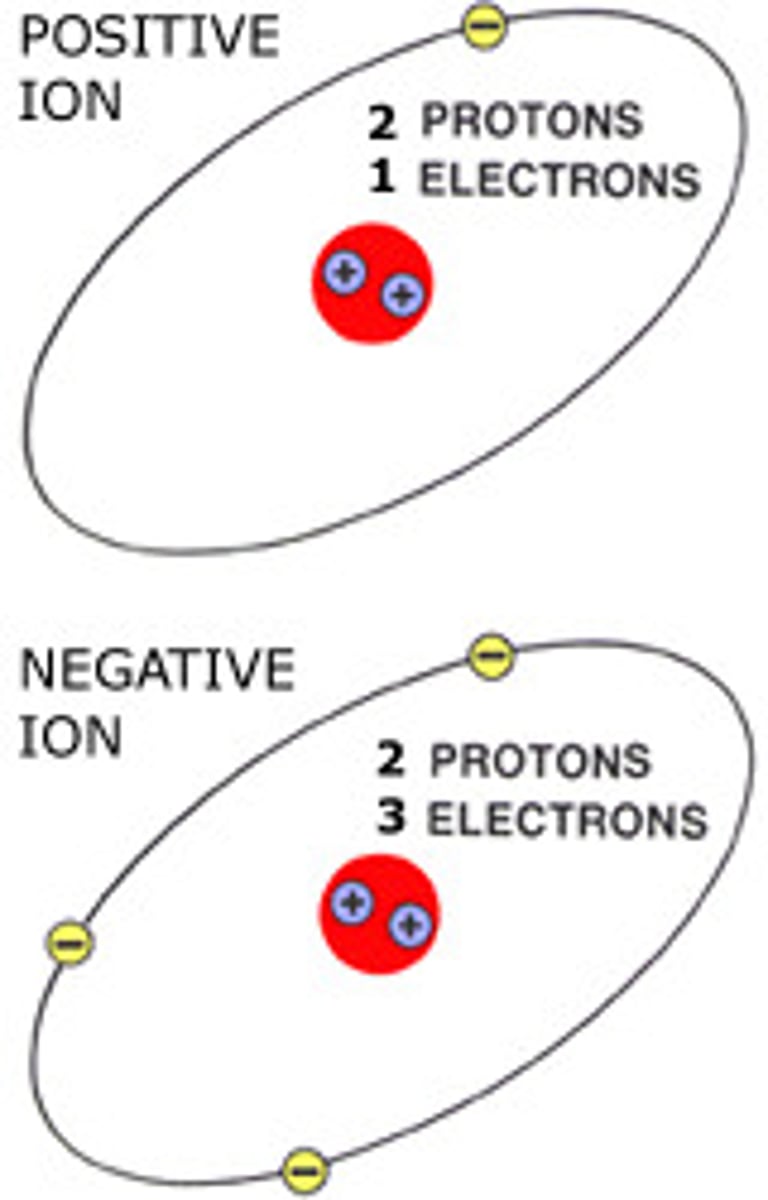
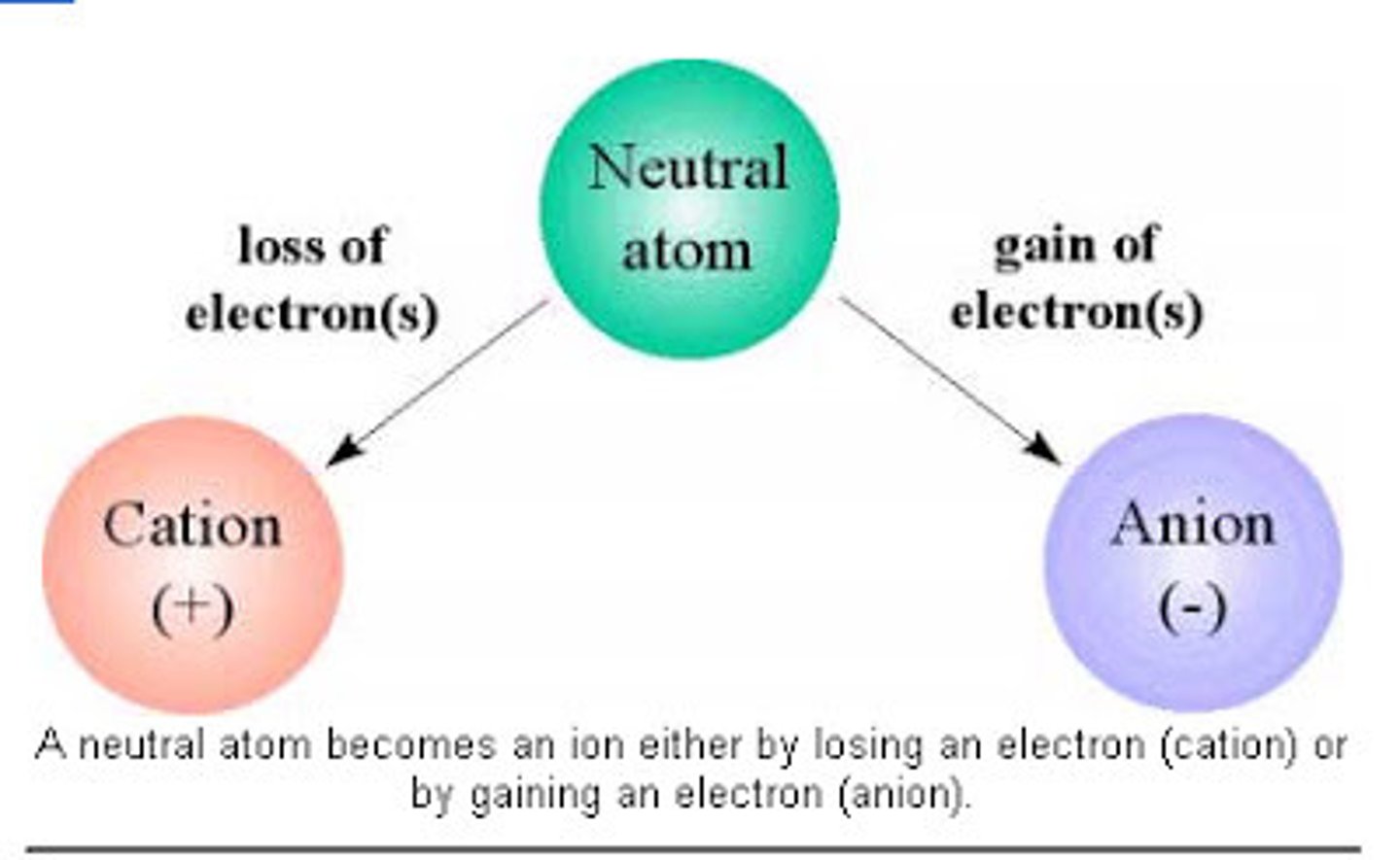
Cation
A positively charged ion

Anion
A negatively charged ion
Ionic compounds
Compounds formed by ionic bonds.
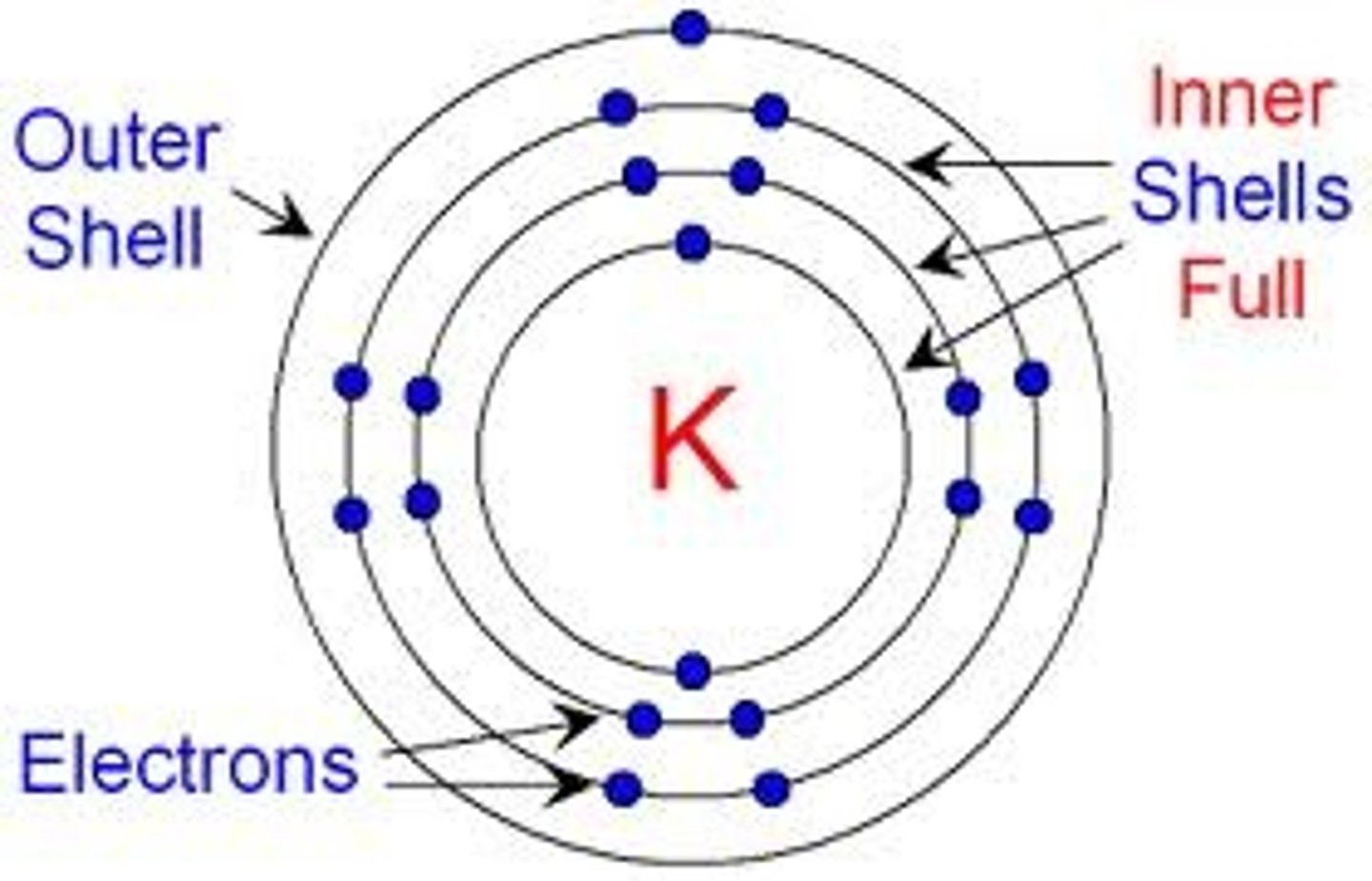
Stable or Inert Atom
An atom with a full valence shell
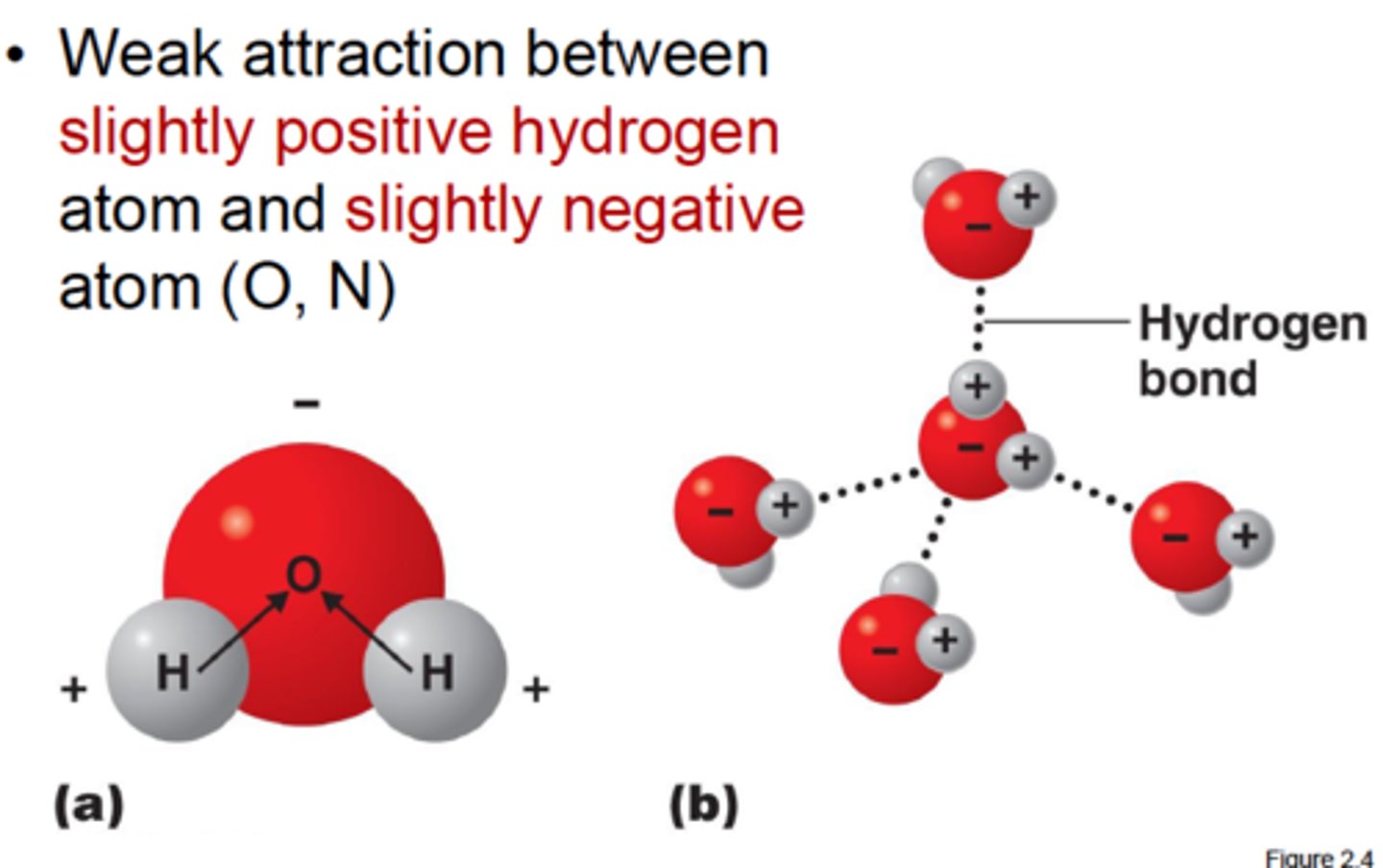
Hydrogen Bonds
Relatively weak bonds formed due to the mutual attraction of two electronegative atoms to hydrogen.
Compound
A substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio.
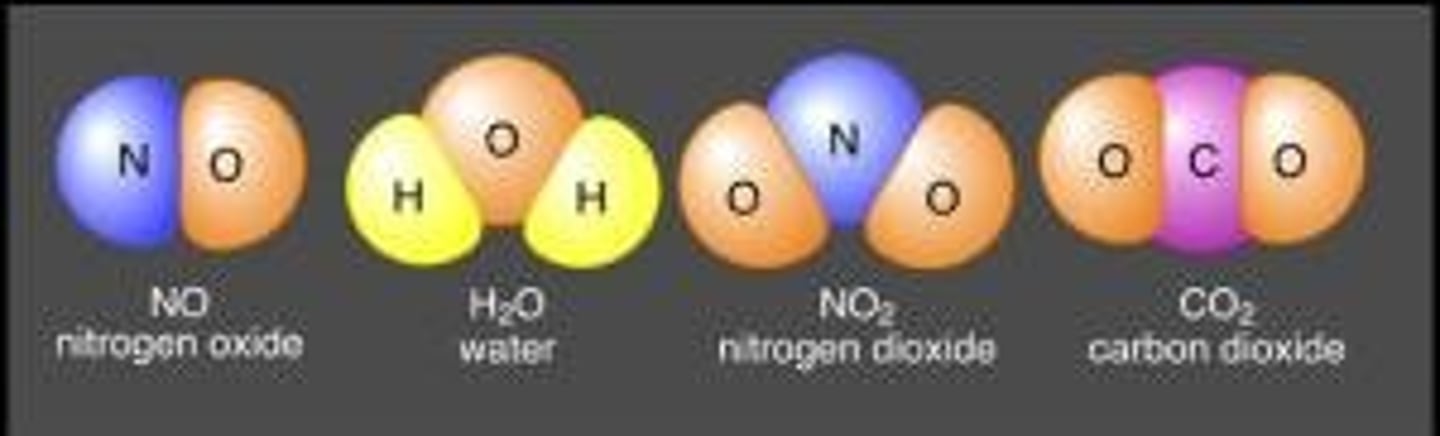
Element
A substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions.
Trace Elements
Elements required by organisms but only in minute quantities.

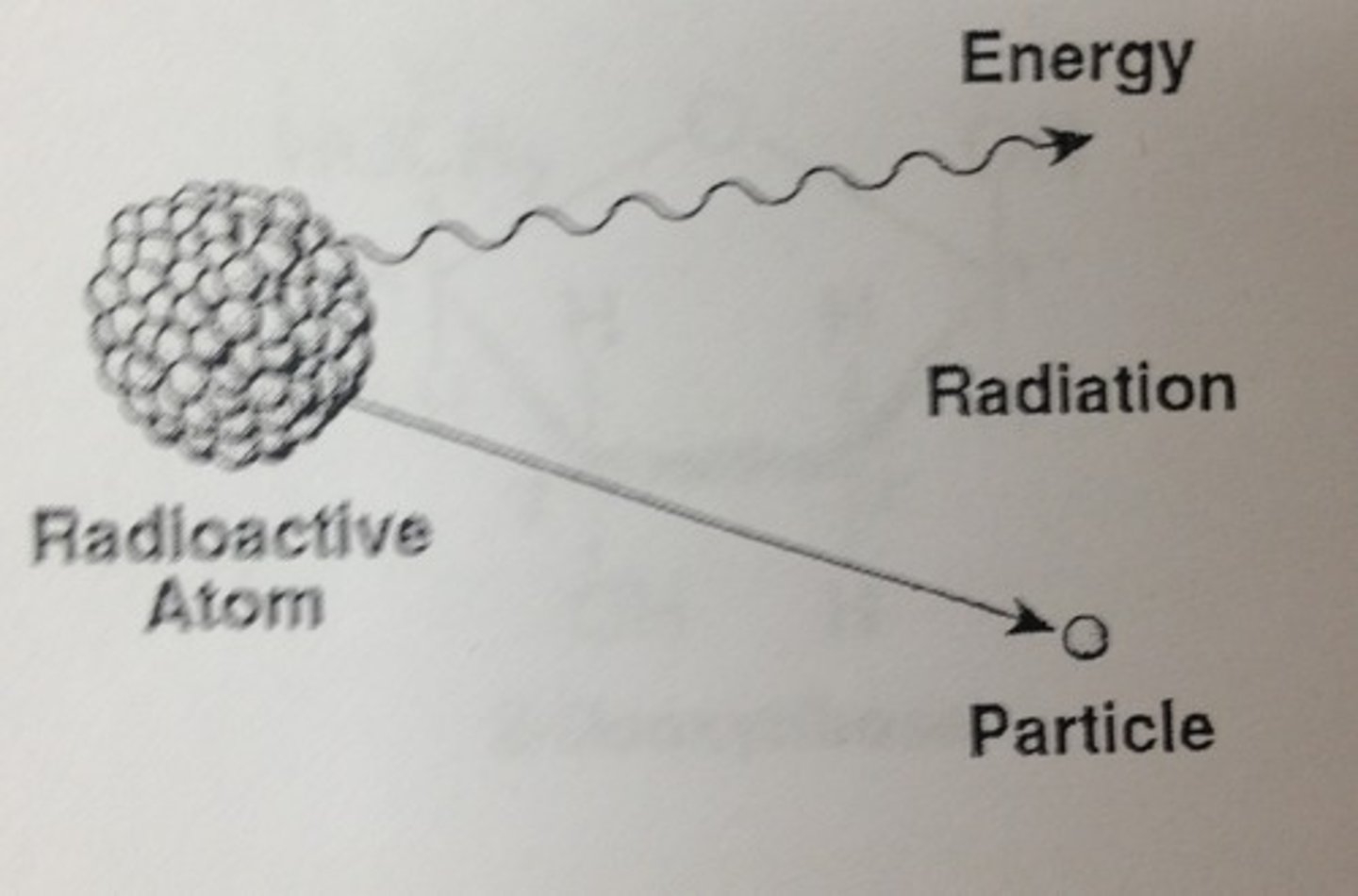
Radioactive Isotopes
An unstable isotope with a nucleus that decays spontaneously, emitting particles and energy. Have many applications in biological research, including fossil dating (Carbon-14 or 14C), tracing atoms through metabolic processes, and diagnosing medical disorders.
Two or more atoms held together by a covalent bond consistute a _________.
Molecule
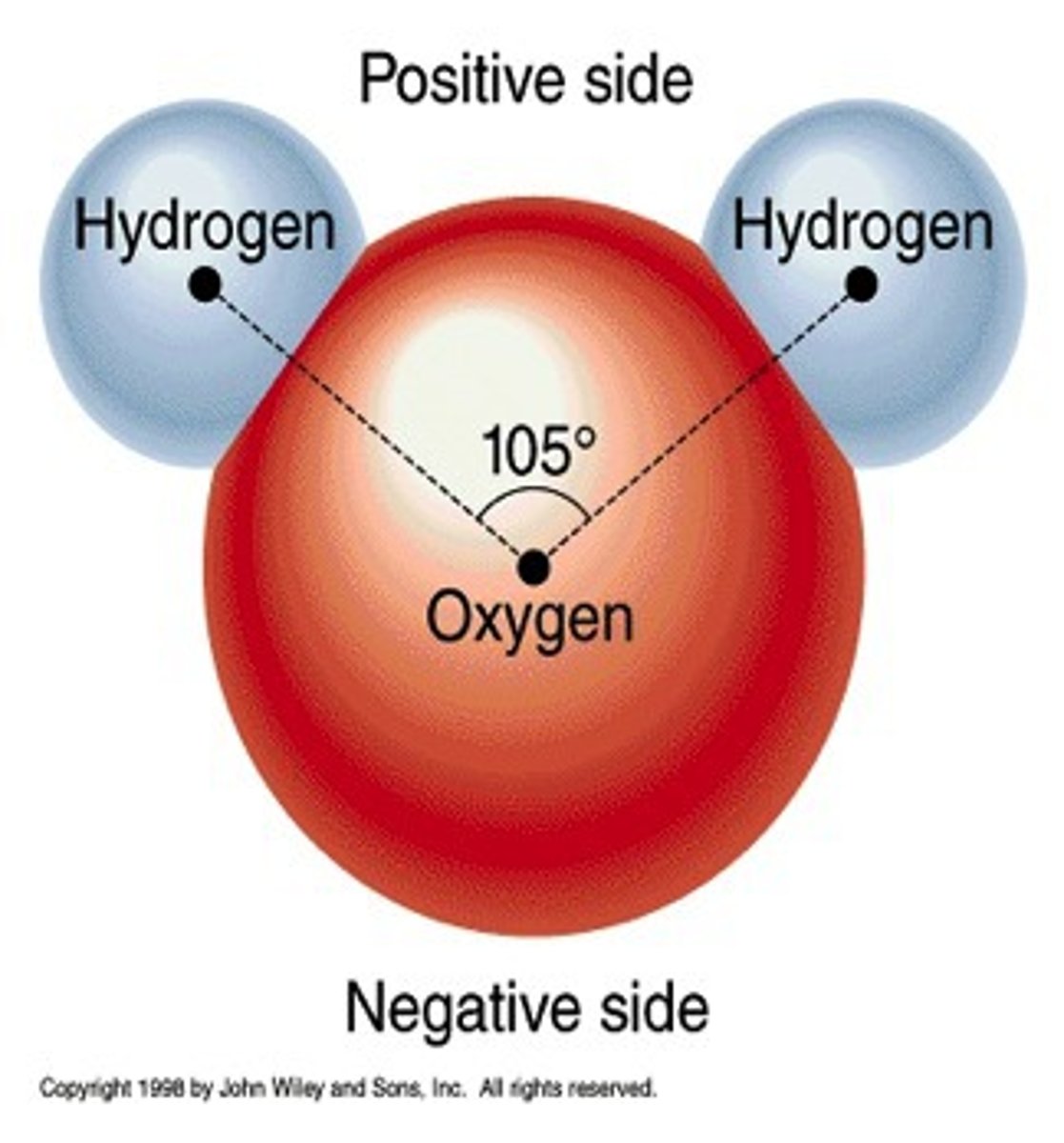
Octet Rule
An atom with more than 1 energy shell is most biologically
stable with 8 electrons in the valence shell.
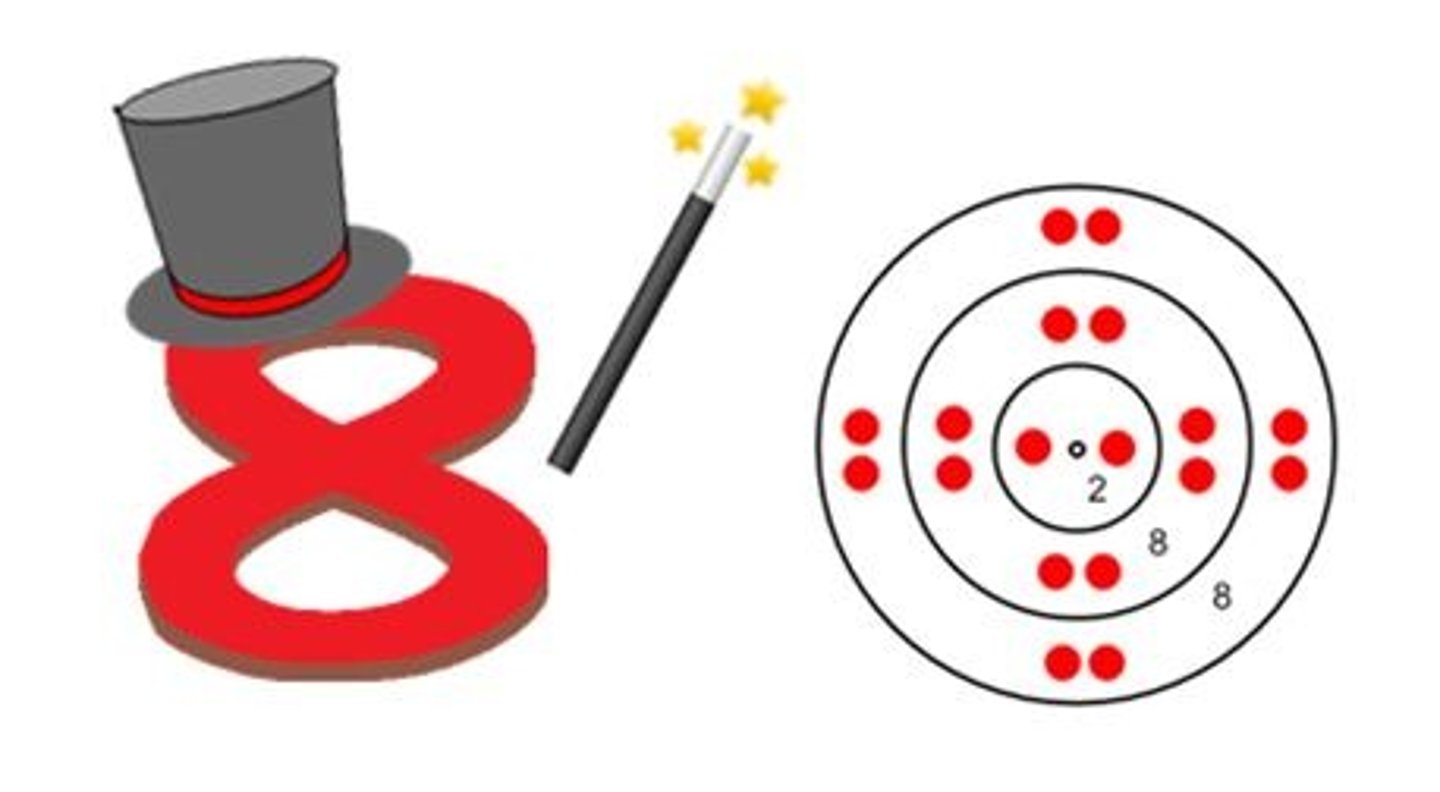
Structural Formula
Uses bond symbols to show shared electrons between atoms. Example: H-H shows a hydrogen molecule sharing one pair of valence electrons. O=O shows two oxygen atoms sharing two pairs of valence electrons.
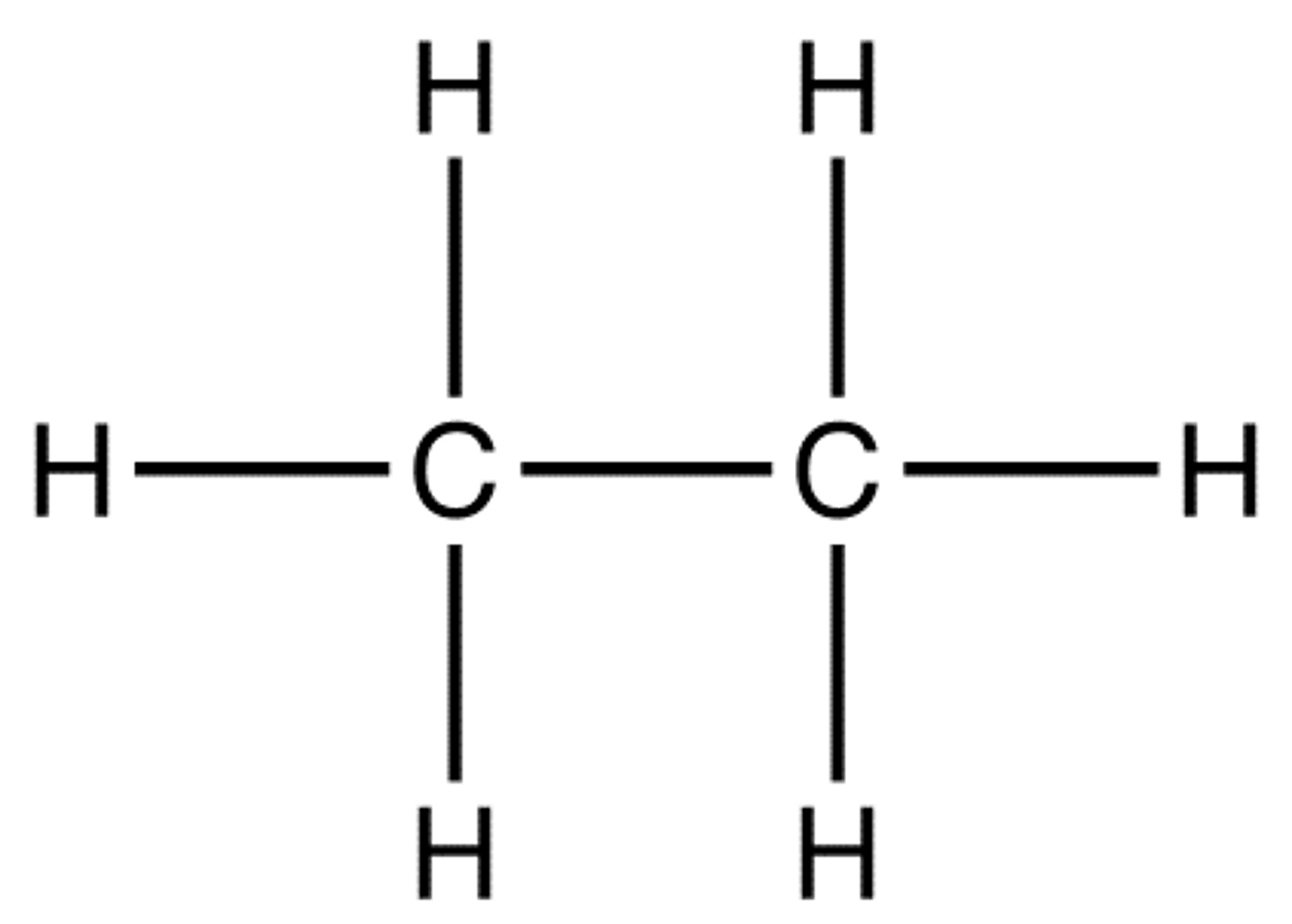
Molecular Formula
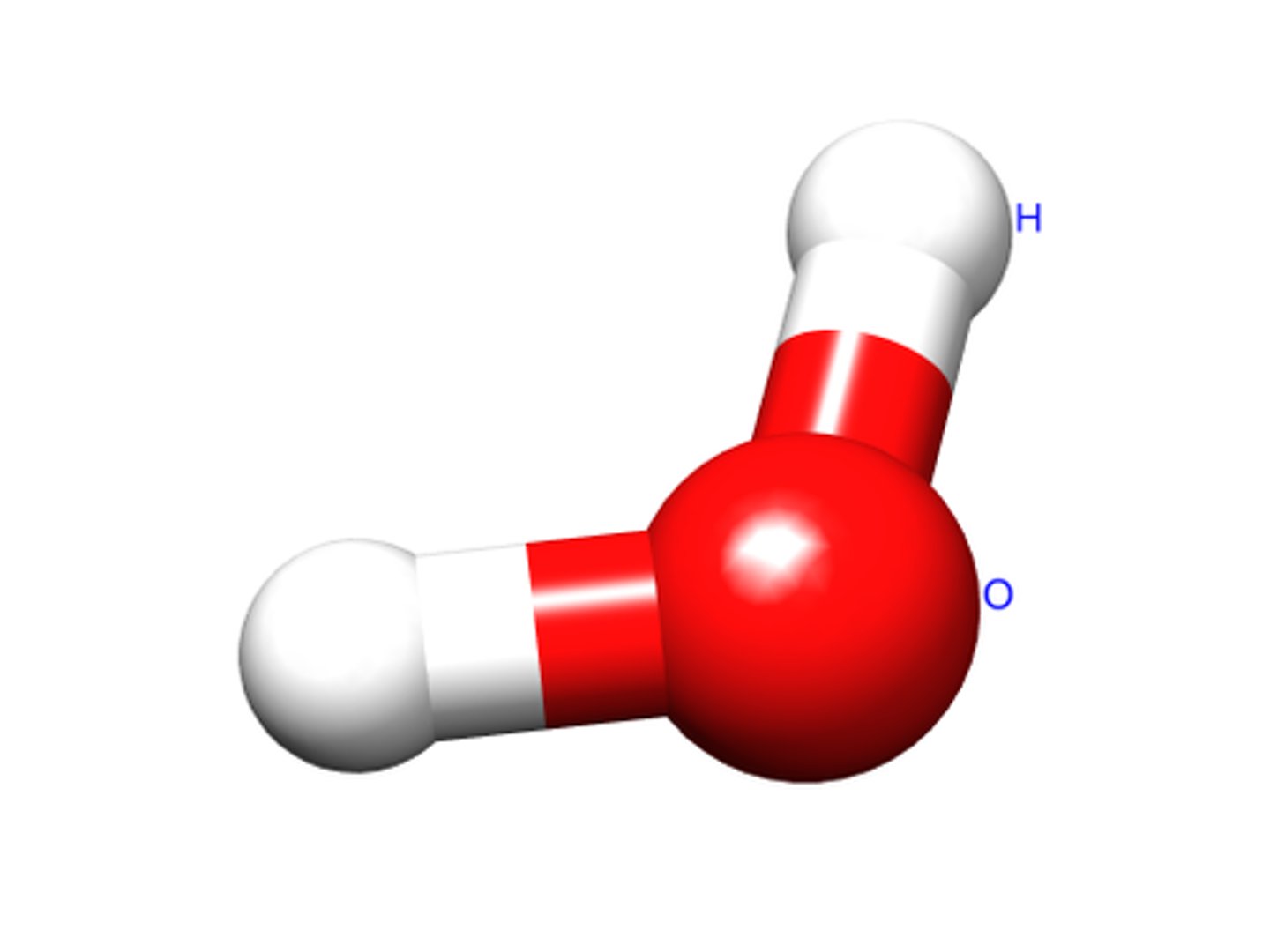
A formula showing the type of element and number of atoms only. Example: H2O
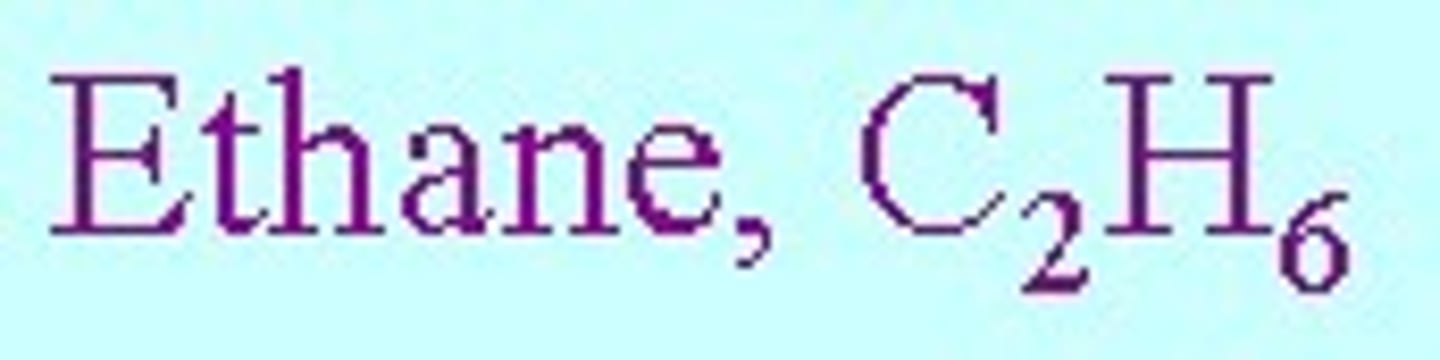
van der Waals interactions
Weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that result from transient local partial charges.

Chemical Reactions
The making and breaking of chemical bonds, leading to changes in the composition of matter.
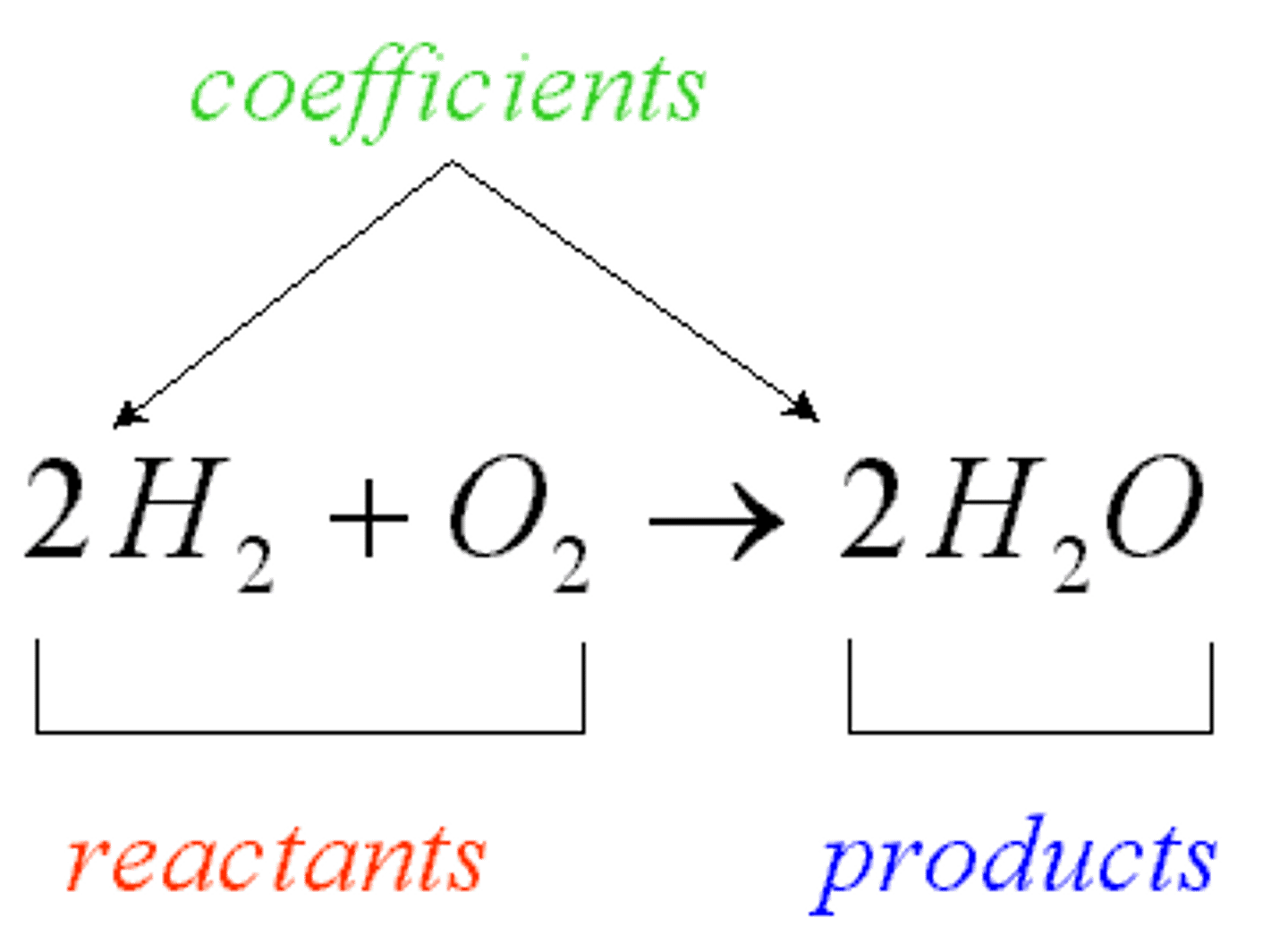
Reactants
The starting materials in a chemical reaction.
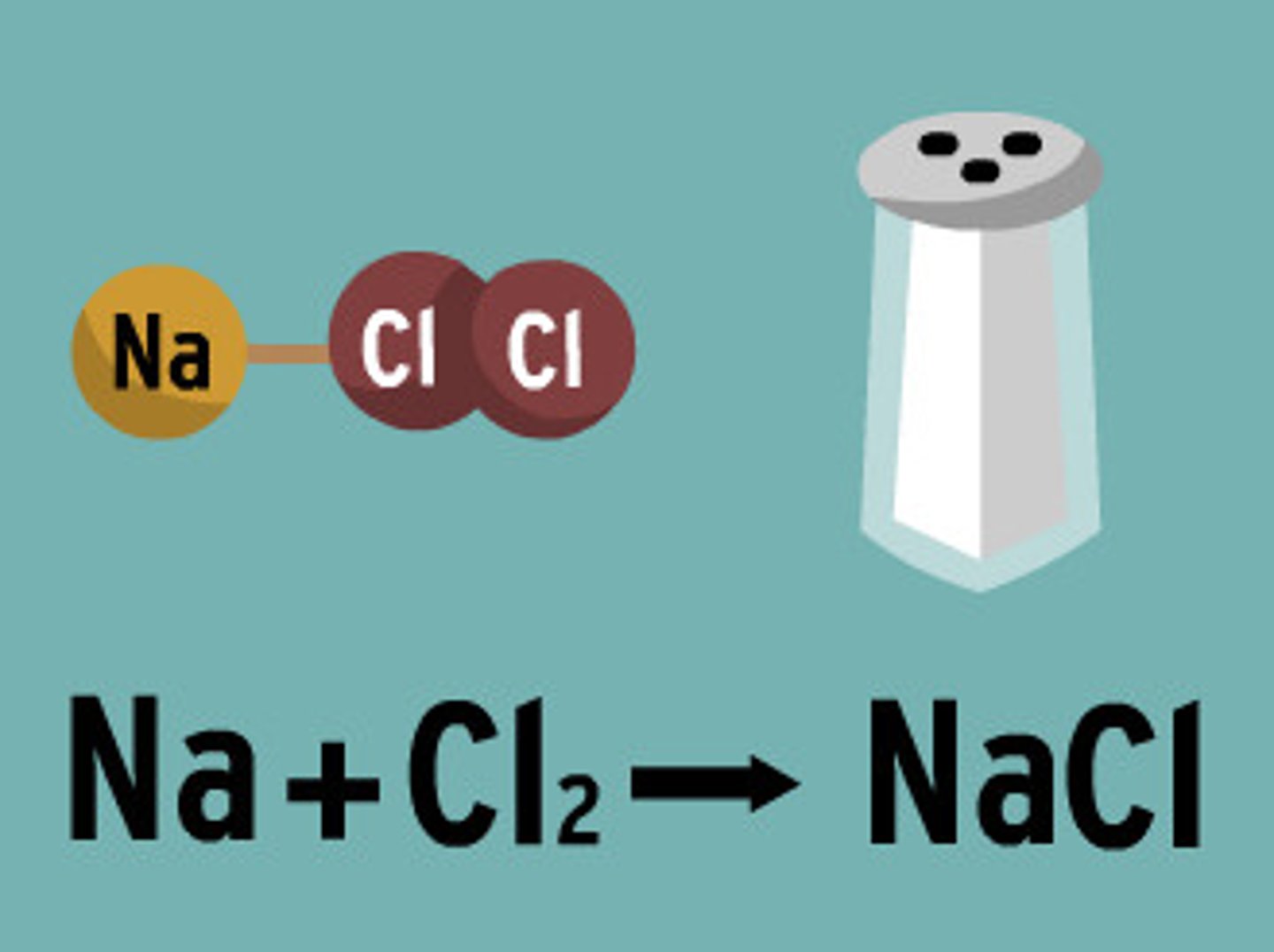
Products
The ending materials in a chemical reaction.
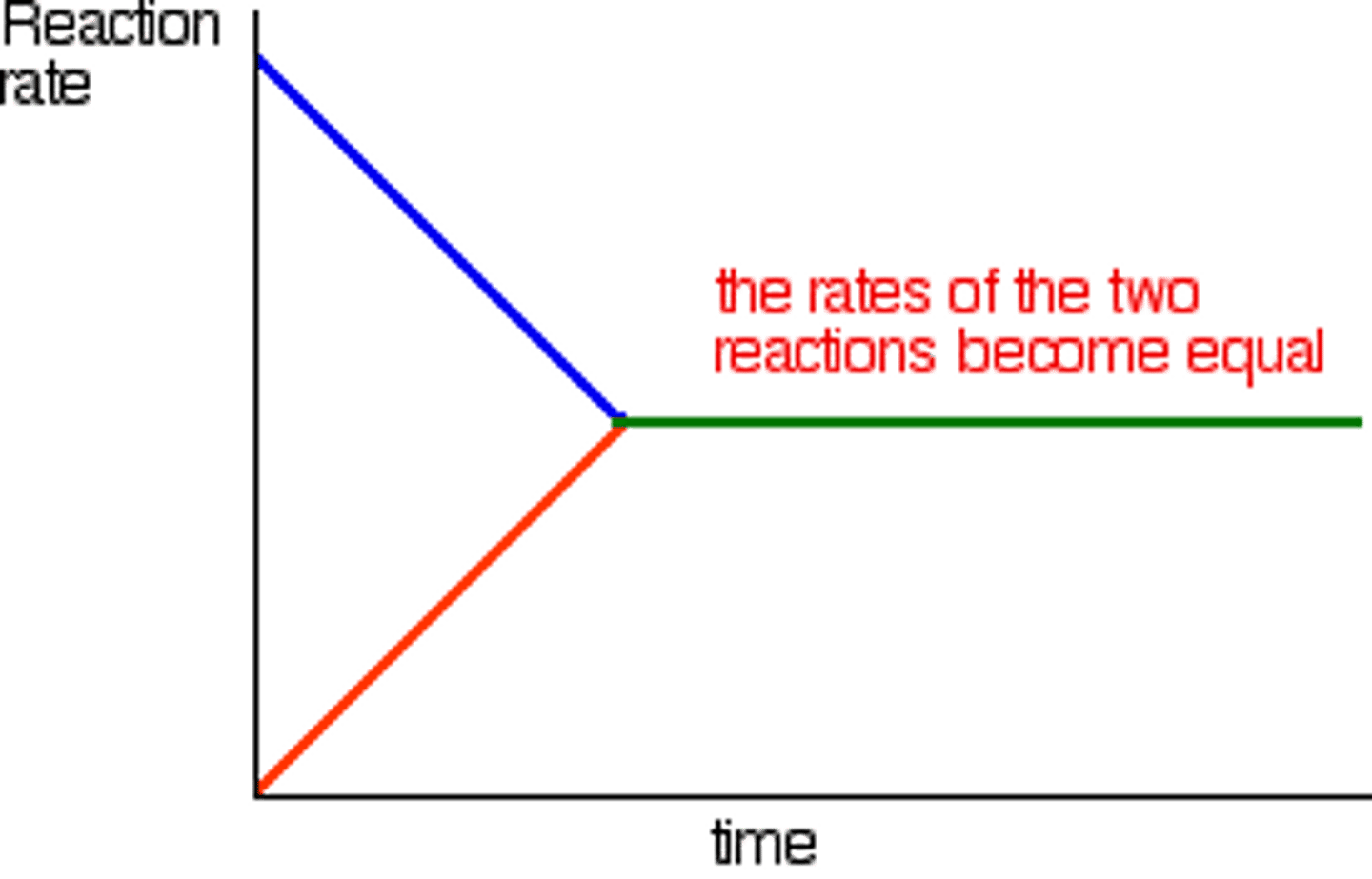
Chemical Equilibrium
The point at which chemical reactions offset one another and the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal.