AP Calc AB Flashcards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:30 PM on 3/11/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
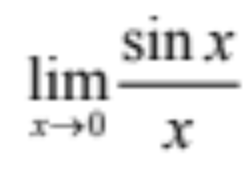
1
2
New cards
Intermediate Value Theorem
If f is continuous on [a, b], then f takes on every y value between f(a) and f(b).
3
New cards
Definition of Derivative
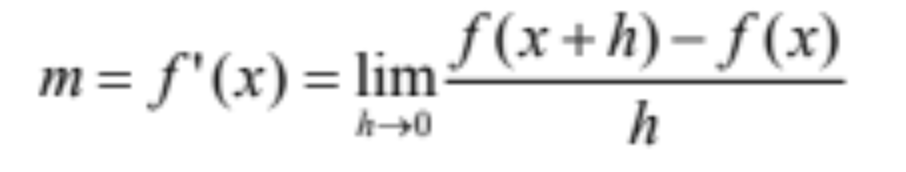
4
New cards
Alternate Definition of Derivative/Derivative at a Point
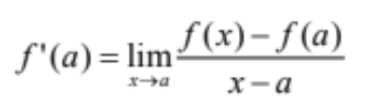
5
New cards
Power Rule
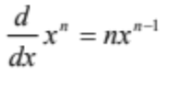
6
New cards
Product Rule
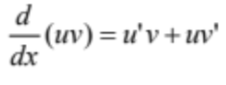
7
New cards
Quotient Rule
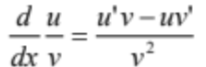
8
New cards
d/dx sinx
cosx
9
New cards
d/dx cosx
-sinx
10
New cards
d/dx tanx
sec2x
11
New cards
d/dx cotx
-csc2x
12
New cards
d/dx secx
secxtanx
13
New cards
d/dx cscx
-cscxcotx
14
New cards
Chain Rule
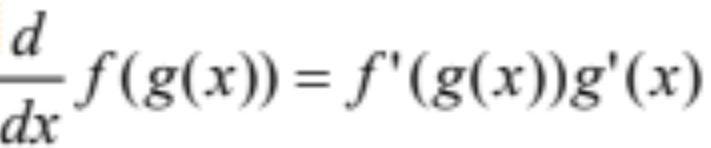
15
New cards
d/dx sin-1x
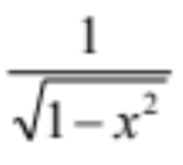
16
New cards
d/dx cos-1x
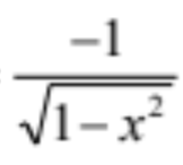
17
New cards
d/dx tan-1x
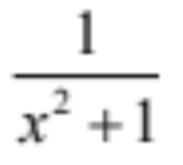
18
New cards
d/dx cot-1x
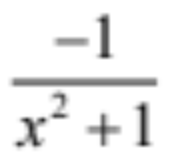
19
New cards
d/dx sec-1x
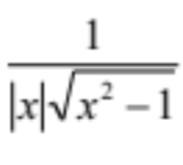
20
New cards
d/dx csc-1x
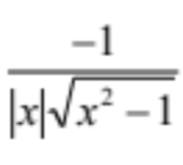
21
New cards
d/dx ex
ex
22
New cards
d/dx ax
axln(a)
23
New cards
d/dx lnx
1/x
24
New cards
d/dx logbx
1/xln(b)
25
New cards
Extreme Value Theorem
If f is continuous on [a, b], then f has both an absolute maximum and absolute minimum on that interval.
26
New cards
Mean Value Theorem
If f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b), then there exists a c in (a, b) such that f'(c) = (f(b) - f(a))/(b - a).
![If f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b), then there exists a c in (a, b) such that f'(c) = (f(b) - f(a))/(b - a).](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c7c7d2ae-fa1c-41e3-9c6d-0d4eabb05d06.png)
27
New cards
Average Value
If f is integrable on [a, b], its average value on [a, b] is 1/(b - a) ∫ from a to b of f(x)dx.
![If f is integrable on [a, b], its average value on [a, b] is 1/(b - a) ∫ from a to b of f(x)dx.](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/259eefa1-b3ec-45dc-9ecc-34b5e0b82028.png)
28
New cards
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part 1
If f is continuous on [a, b], then the function F defined by F(x) = ∫ from a to x of f(t)dt has a derivative F'(x) = f(x).
![If f is continuous on [a, b], then the function F defined by F(x) = ∫ from a to x of f(t)dt has a derivative F'(x) = f(x).](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a775a0dc-3d63-44ef-a813-7250e7926572.png)
29
New cards
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part 2
If F is any antiderivative of f on [a, b], then ∫ from a to b of f(x)dx = F(b) - F(a).
![If F is any antiderivative of f on [a, b], then ∫ from a to b of f(x)dx = F(b) - F(a).](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4da2c839-82cf-4392-b033-48f2613302e0.png)
30
New cards
Y changes at a rate proportional to the amount
present
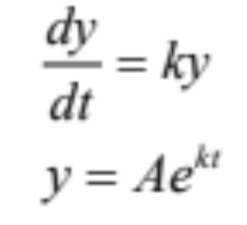
31
New cards
Fundamental Theorem in Morgan Language
Given a velocity v(t) and a position at a given time... ex: when t = 8, the position is 4. Find the position at 2 seconds.
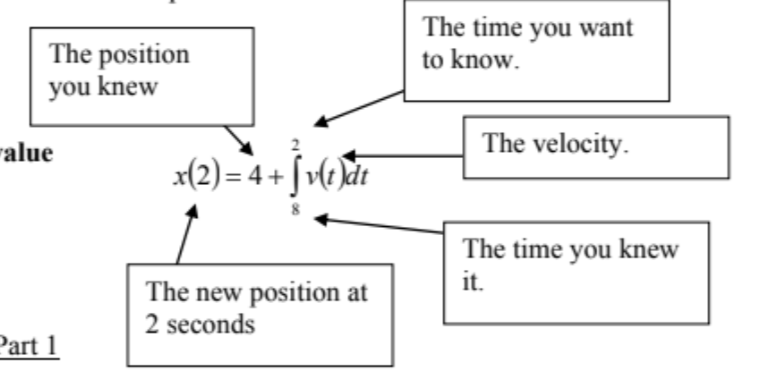
32
New cards
Displacement
The change in position of an object over time, calculated as the difference between initial and final positions.
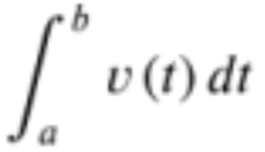
33
New cards
Total Distance Traveled
The integral of the absolute value of velocity over a given time interval.
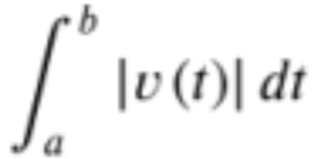
34
New cards
Derivative of Inverses
If f is the inverse of g, then d/dx[f(g(x))] = 1/g'(f(g(x))).
![If f is the inverse of g, then d/dx[f(g(x))] = 1/g'(f(g(x))).](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5fa04037-a202-41fd-8f8c-5ea302e4ee87.png)