Containment - lecture 4 - blood borne diseases
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
sanquin
non profit
monopoly of Nl blood bank
blood borne infections
classical BBIs
syphillis
bacterial contaminaton (platelets)
silent yersinia bacteremia (coli bacteria may linger in the blood and end up in the blood donation).
emerging BBIs (threats)
arboviruses → dengue, west nile virus
zooonotic → vCJD, Q fever, HEV
irrelevant BBIs
GBV-C
tenoviruses
usutuviruses
what do the impact of BBIs depend on
prevalence among donors
transmissibility
severity of disease in recipient
transmission routes of viruses
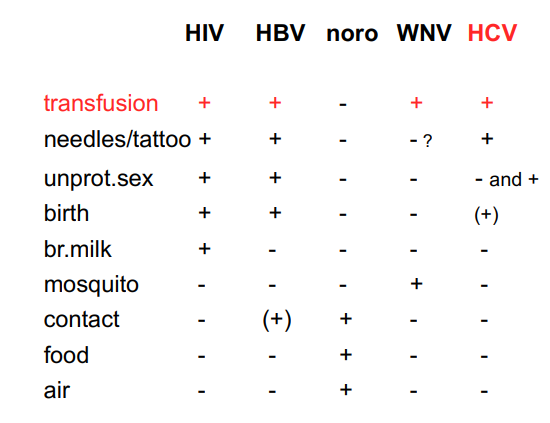
hepC
human pathogen with exclusive parenteral transmission via blood
hepC → can cure with taking pills for few weeks
pamela anderson had it → shared needle with husband Tommy Lee
hepB and HIV can only be supressed not cured
silent killer, can walk around for years and then get sick (liver) and die
BBIs, infectious materials
green can be sterilized → immunoglobulins etc.
needles → in hospital, drugs etc.
you&me → birth, unprotected sex, tattoos etc.
new versus old donors
new donor represents the prevalence of an infection (no idea when the infection was acquired)
repeat donor represents the incidence → new infections acquired.
window donation
donor already has the infection but the test does not pick it up yet
missed early infection
transfusion recipients
one very clear time where transfusion saves life → pregnancy, when women lose a lot of blood during child birth can be saved with transfusion
prevention of transmission via blood
donor selection
first visit donor; testing only, no donation
screening of each donation
inactivation / removal of agents
restrictive use of blood
monitoring of emerging infections
recipient tracing (treatment etc.)
serological versus DNA/RNA screening of each donation
Serological screening: detects antibodies or antigens made by the immune system in response to infection.
DNA/RNA screening (NAT – Nucleic Acid Testing): detects the virus’s genetic material directly, allowing much earlier detection.
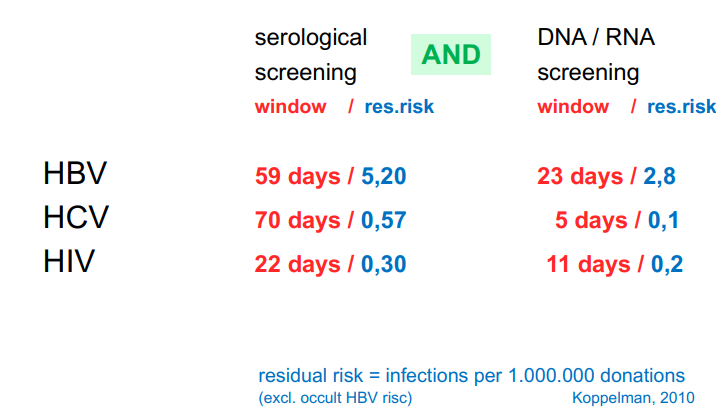
serology versus PCR for picking up infections
PCR only picks up a few cases (but is used because it detects certain diseases earlier (window detecting))
but only picked up 1 HIV case → still is done.
The benchmark to do a medical measure in the Netherlands in 80000 euros. However it costs 13 million to do the PCR measure of HIV. Still do it to assure the trust of all the patients (emotion management).
hep.E
all piglets get hep.E virus → 1:10 is viremic at time of slaughter
alot of hep.E virus in our food (leverworst)
hep.E is confusing → 2 different kinds of diseases
tropical acute one, genotype 1 and 2
20% fatality
western silent one, genotype 3
no disease
except in organ, stem cell patients, they can not clear the virus. → rapid liver cirrhosis and liver failure in a few years.
free vaccination for the dangerous Hep.E
why are there Mpox outbreaks
1980 small pox were eradicated. now no more pox vaccination.
today no more cross reactive immunity in 70% of the world !!
so pox has started to
chickenpox is a herpesvirus → noting to do with pox!!
symptoms of pox → rash, fever, sore throat headache
Mpox complications
secondary bacterial infections can occur
skin lesions
pneumonia
infection cornea → blindness
Mpox transmission
no idea if it is transfusion transmissible → probably is according to Hans Zaaij
close contact → including within a household
skin to skin, outh to moith, mouth to skin, kissing, sex, touching face to face
via contaminated objects (linnen, towel)
to fetur or newborn
animal to human
mosquito borne infections
on the rise
80% of mosquito infections go asymptomatic
tiger mosquito on the rise → dengue, zika, chikungunya
often found in old pig cellars (old manure, rotting cellars).
in the Netherlands RIVM will kill all tiger mosquitos when found in a village.
dengue now endemic in certain areas in europe (italy, france, spain).
ordinary house mosquito → west nile virus, USUV
sheep tick → TBE, lyme
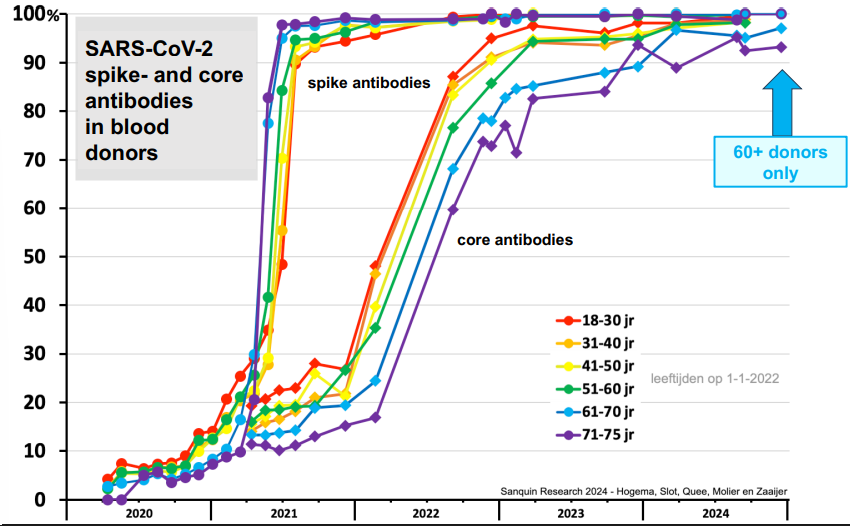
covid - why is the rainbow reversed
old people vaccinated earlier (but the very first, young nurses)
and the other piek shows the omicron variant. Young people were going out more, so they got infected first.
very first red line is the young female health care workers that got the first vaccine.
re-infection
the level of core antibodies (in blood donors) was used as an indicator of re-infection
also the water in riool wateringszuiverings installaties is checked each day for core antibodies.