Molecular Cell Biology in Veterinary Science
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is molecular biology?
The study of biological processes at a molecular level (DNA, RNA, proteins)
What is the importance of molecular biology?
Crucial for understanding cellular function, genetics and disease mechanism
Applications in diagnostics, disease treatment and animal care
What are the 3 key biomolecules?
DNA (blueprint of life)
RNA (mediates gene expression)
Proteins (workhorses that perform cellular functions)
What is the concept of central dogma?
(DNA replication) —> DNA —> (transcription) —> mRNA —> (translation) —> Protein
What is omics sciences?
Share the aim of identifying, describing and quantifying the biomolecules and molecular processes that contribute to the form and function of cells and tissues
What is genomics?
The identification of genetic variant in DNA sequence including coding or non-coding regions
What is epigenomics?
Evaluation of non-DNA sequence changes such as methylation
What are transcriptomics? #ff7700
Evaluation of quantity and quality of RNA
What are proteomics?
Evaluation of protein map network, production and modification
What are metabolomics?
Evaluation of endogenous/exogenous metabolites
Name the 9 molecular techniques used in veterinary diagnostics
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
DNA sequencing
FTIR
Next generation sequencing
ELISA
Flow cytometry
Southern/Northern/Western blotting
IFA
Mass spectrometry
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) #ea00ff
What
Importance
Uses
Focuses on which aspect of central dogma
Why is it difficult to find evidence of disease in earliest stages of infection?
4 Steps
What: Laboratory technique used to make multiple copies of a segment of DNA
Importance:
Detecting bacterial and viral infections
Quantification of pathogen load in infectious diseases
Uses: The genome that is stored inside DNA
Focuses on: DNA replication and connected to central dogma as it amplifies DNA
Why is it difficult to find evidence of disease in earliest stages of infection: Not enough pathogens and insufficient time to develop antibody response
4 steps:
Denaturation
Annealing
Extension
Amplification
PCR: Denaturation
Temperature
What occurs
Central dogma step does it relate to
Temperature: 95 degrees
What occurs: Separation of dsDNA template into 2 single strands by breaking hydrogen bonds between complementary bases
Central dogma step it relates to: DNA replication
PCR: Annealing
Temperature
What occurs
Central dogma step does it relate to
Temperature: 68 degrees
What occurs: Allows primers to bind to complementary sequences on single stranded DNA template
Central dogma step it relates to: Transcription
Why: Because in transcription, RNA primers bind to DNA template and in annealing, primers bind to single stranded DNA template
PCR: Extension
Temperature
What occurs
Central dogma step does it relate to
Temperature: 72 degrees
What occurs: Taq polymerase enzyme adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of primers to synthesise new strands of DNA complementary to template strand
Central dogma step it relates to: DNA replication
Why: DNA polymerase in PCR extends primers and synthesise new DNA strands, mirroring replication process of DNA replication
PCR: Amplification
What
The 3 steps (D A E) are repeated multiple times where each cycle, DNA target is doubled
So which steps in central dogma is not mirrored in PCR and why?
mRNA synthesis and translation because PCR doesn’t involve RNA
ELISA #b600ff
Stands for
What
Relies on
Used in
4 key components
4 types
Stands for: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
What: Technique used to detect and quantify substances such as peptides, proteins, antibodies and hormones
Relies on: Antigen-antibody interactions coupled with an enzyme that produces a detectable signal
Used in: Diagnostic applications, research and veterinary medicine
4 key components:
Antigen: Target substance to detect
Antibody: Specific to antigen
Enzyme: Linked to antibody and facilitates detection signal
Substrate: Reacts with enzyme to produce detectable signal
4 types:
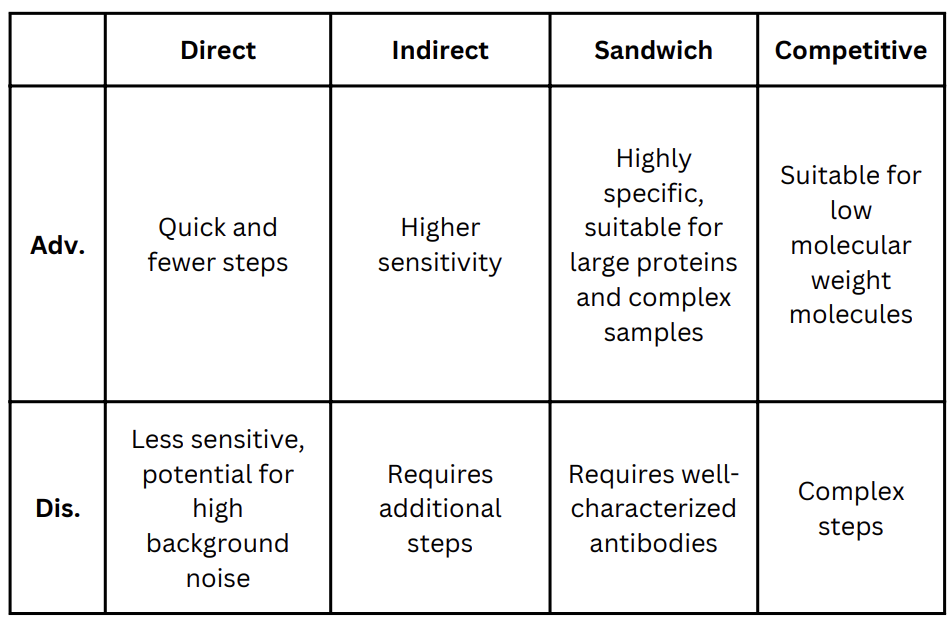
Direct
Indirect
Sandwich
Competitive
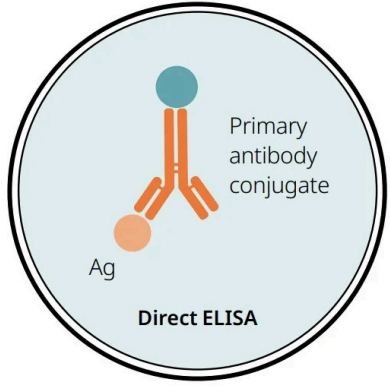
Direct ELISA
Antigen immobilised where
Antigen detected with
Detection of
#b600ff
Antigen immobilised: On surface
Antigen detected with: Specific primary antibody that is directly conjugated to an enzyme (detection molecule)
Detection of: Pathogens (parvovirus in feces)
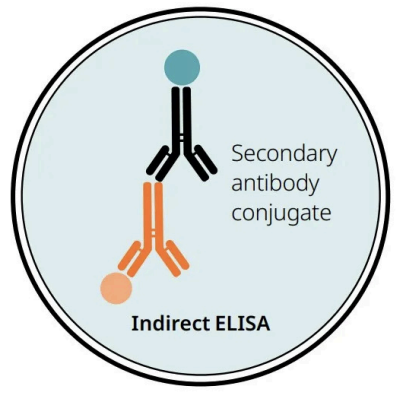
Indirect ELISA
Antigen immobilised where
2 step process
Detection of
#b600ff
Antigen immobilised: On the surface of multi-well plate
2 step process:
Primary antibody specific for antigen binds to target
Labeled secondary antibody binds to primary antibody binds for detection
Detection of: Immune responses or infections (FIV antibodies in cats)
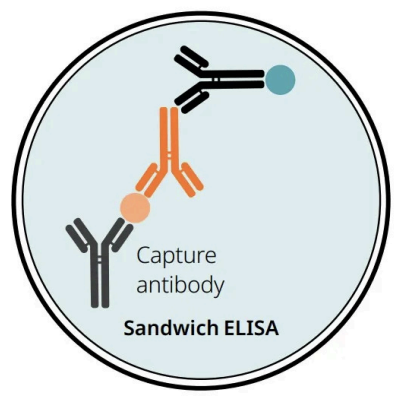
Sandwich ELISA
Requires
AKA
Process
Detection of
#b600ff
Requires: 2 antibodies specific to different epitopes of antigen
AKA: Matched antibody pairs
Process:
1 antibody coat the surface of the multi-well plate to facilitate the immobilisation of antigen
The other antibody conjugated and facilitates detection of antigen
Detection of: Antigens, highly specific (Dirofilaria immitis antigen in blood)
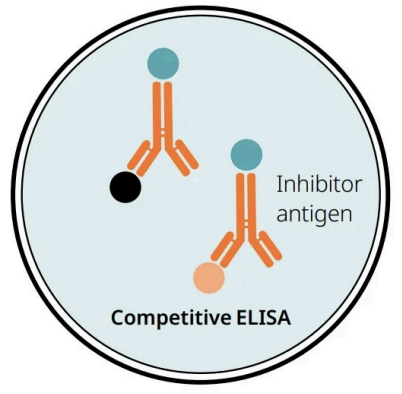
Competitive ELISA
Principle
Measure antigen concentration by
Process
Detection of
#b600ff
Principle: Inhibition ELISA
Measure antigen concentration by: Detecting signal interference
Process:
Sample antigen competes with a reference antigen for binding to a specific amount of labeled antibody
Multi-well plate is pre-coated with reference antigen
Sample is added with labeled antibody
Detection of: Antibodies to Leptospira species or other small antigens
ELISA: Pros and Cons for each Type
Table
Immunofluoresence Assay (IFA)
To detect
Relies on
Types
Importance
Key components
#02d319
To detect: Specific antigens in cells or tissue sections using antibodies tagged with fluorescent dyes
Relies on: Antigen-antibody binding and visualised using fluorescence microscope
Types:
Direct immunofluorescence
Indirect immunofluorescence
Importance:
Localisation of proteins within cells
Study of cell signaling pathways
Diagnosis of autoimmune diseases
Detection of pathogens
Key components:
Sample
Fixation reagent
Permeabilisation reagent
Blocking reagent
Antibodies (primary and secondary)
Mounting medium
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
Measures
Based on
Instrumentation
#009aff
Measures: The absorption of infrared radiation by a sample to identify chemical bonds and molecular structures
Based on: The principal that different functional groups absorb IR radiation at characteristic frequencies
Instrumentation:
Transmission FTIR
ATR-FTIR
FTIR imaging