2.8 Tonicity and Osmoregulation
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cells have membranes that allow them to establish and maintain internal environments that are different from their external environments. Explain how concentration gradients affect the movement of molecules across membranes. External environments can be hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic to internal environments of cells-- Water moves by osmosis from areas of high water potential/low osmolarity/low solute concentration to areas of low water potential/high osmolarity/high solute concentration. Explain how osmoregulatory mechanisms contribute to the health and survival of organisms. Growth and homeostasis are maintained by the constant movement of molecules across membranes. Osmoregulation maintains water balance and allows organisms to control their internal solute composition.water potential.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
osmosis
diffusion of water across membrane from high water potential/low osmolarity/low solute concentration to low water potential/high osmolarity/high solute concentration
water potential
measures eagerness of water to flow from high to low potential
adding solute lowers water potential because water is more likely to enter than exit
water potential equation
water potential = pressure potential + solute potential

solute potential/osmotic potential
tendency of water to move by osmosis in response to differences in solute concentrations, effect of solute on water flow
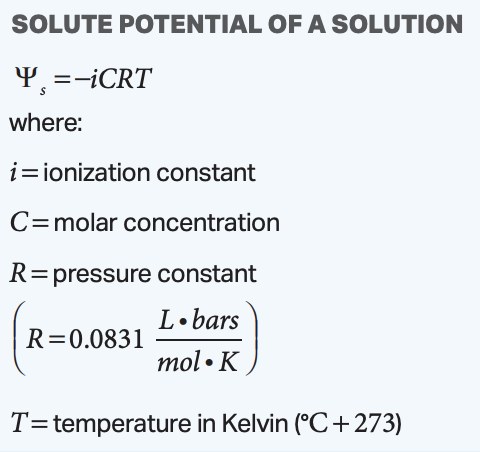
solute potential of a solution equation
solute potential = -ionization constant * molar concentration * pressure constant * temperature in Kelvin
tonicity
ability of solution/environment (based on solute concentration) to cause cell to lose/gain water, organisms must use osmoregulation to maintain homeostasis (ex. contractile vacuoles)
isotonic solutions
same concentration of solute
no net movement of water
in plants, water doesn’t enter, cell becomes flaccid, plants wilt
hypertonic solutions
higher concentration of solute
water moves out of submerged cell
cell shrivels
in plants, membrane pulls away (plasymolysis), plant wilts and dies
hypotonic solutions
lower solute concentration
water moves into submerged cell
cell swells and bursts
in plants, cell wall opposes water uptake, cell is turgid and healthy