Formation of Species
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the formation of a new species?
speciation
When does speciation begin?
gene flow ceases between two sections of a population
What is a group of individuals capable of interbreeding?
species
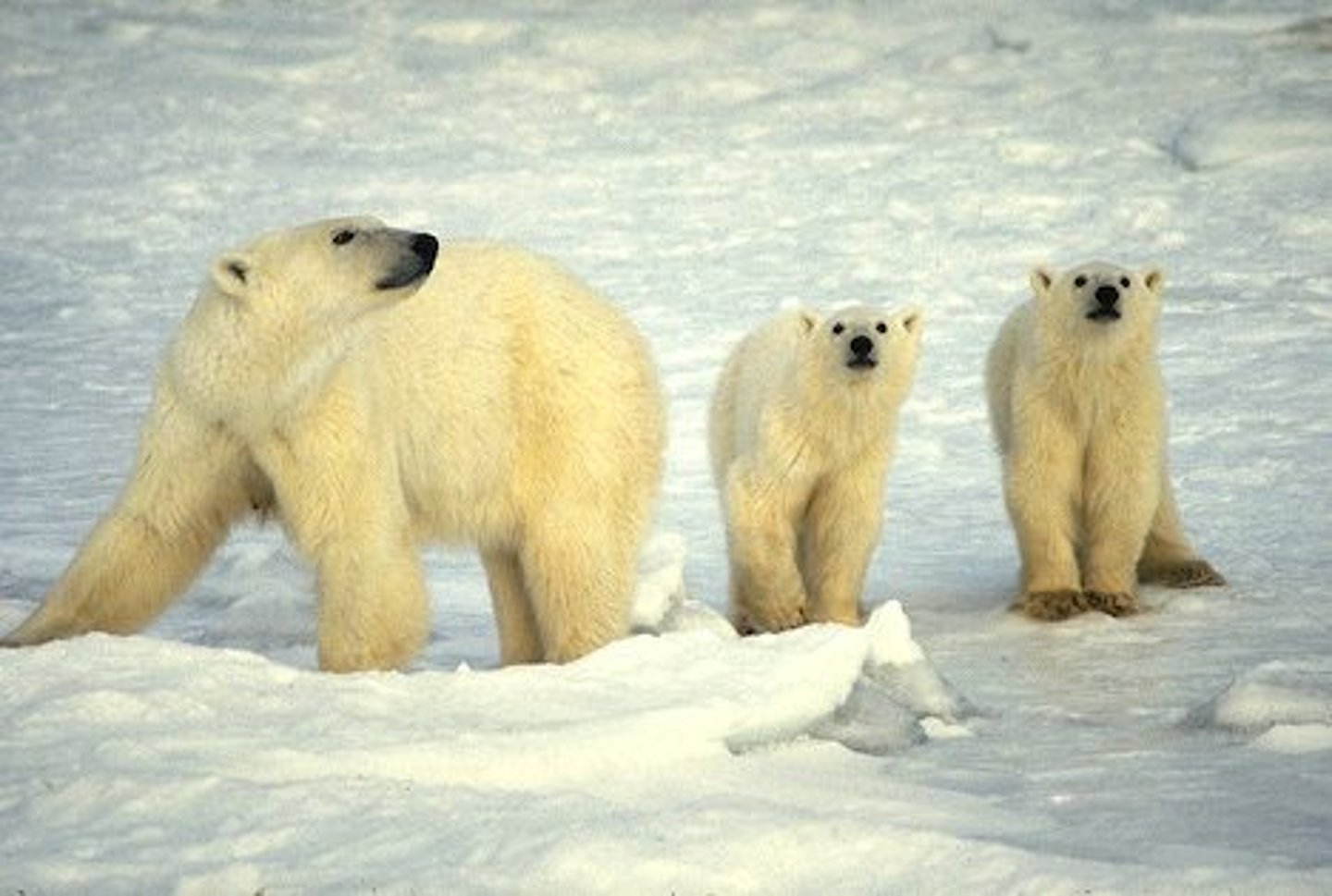

Which type of speciation occurs when the population is divided by a geographic barrier?
allopatric speciation
(Note: interbreeding prevented by barrier)
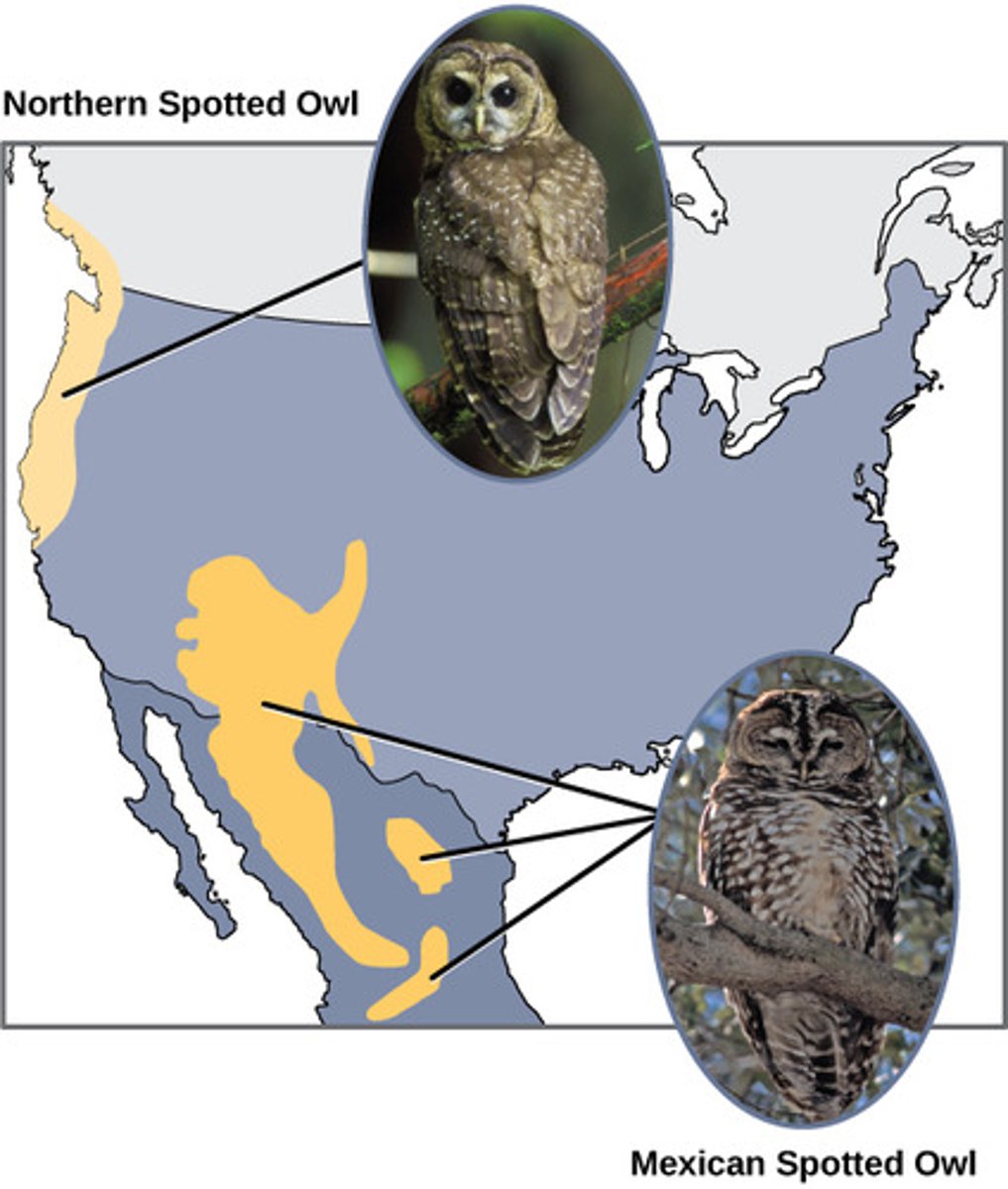
After the introduction of a barrier in allopatric speciation, by what processes can the populations now diverge?
1. natural selection
2. mutation
3. genetic drift
In allopatric speciation, why won't the separated populations not interbreed when the barrier is removed?
the gene pool sufficiently diverged
If two originally separated populations cannot interbreed, what has occurred?
speciation
What process occurs when a group is isolated by being physically removed from the original location of the larger group?
dispersal
(Note: can induce allopatric speciation
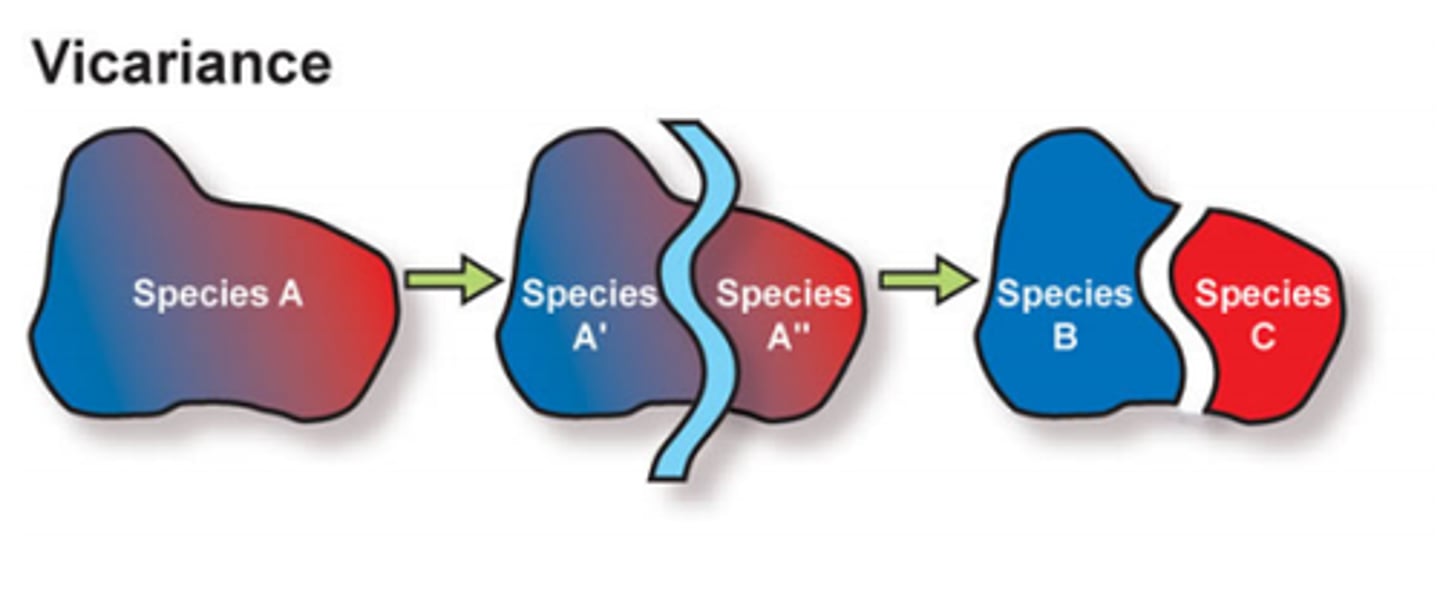
What process occurs when a group is isolated by a geographic barrier but is in the same overall location of the larger group?
vicariance
(Note: can induce allopatric speciation)
Which type of speciation involves the formation of new species without the presence of geographic barriers?
sympatric speciation
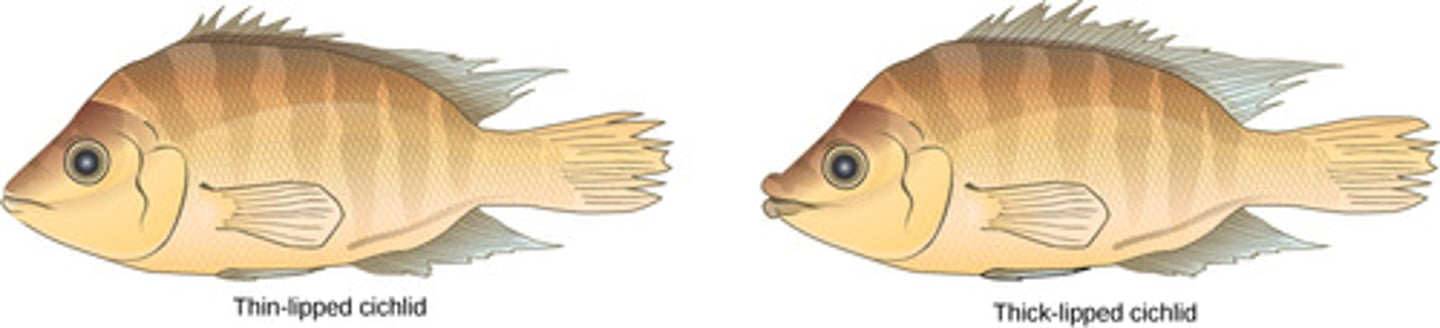
What process involves natural selection due to polymorphism?
balanced polymorphism
(Note: favorable traits differentiate individuals - can induce sympatric speciation)
What genetic occurrence involves organisms carrying more than the normal two sets of chromosomes, such as 3n or 4n?
polyploidy
(Note: can induce sympatric speciation)
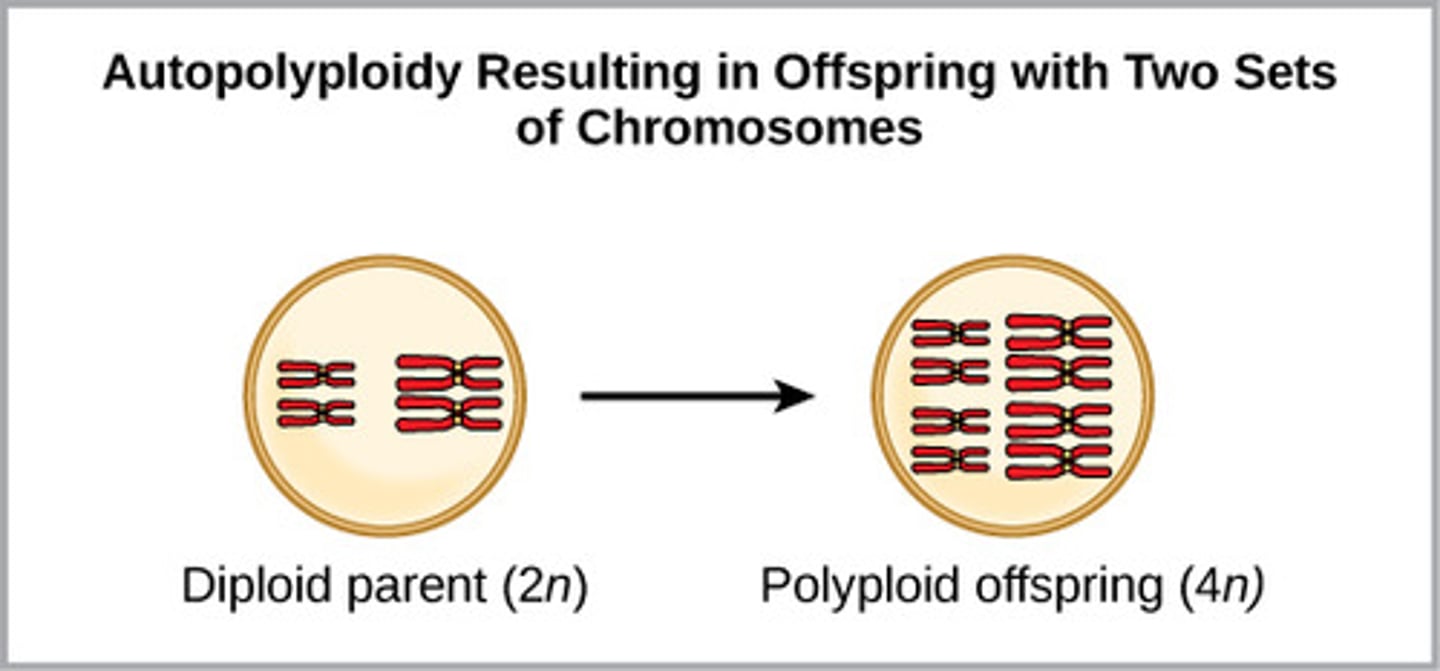
What isolation can polyploidy lead to?
reproductive isolation
(Note: nondisjunction of a 2n plant results in gametes that are still diploid)

In plants, which type of polyploidy occurs when an organism
has more than two sets of chromosomes, both of which are from the same parental species?
autopolyploidy
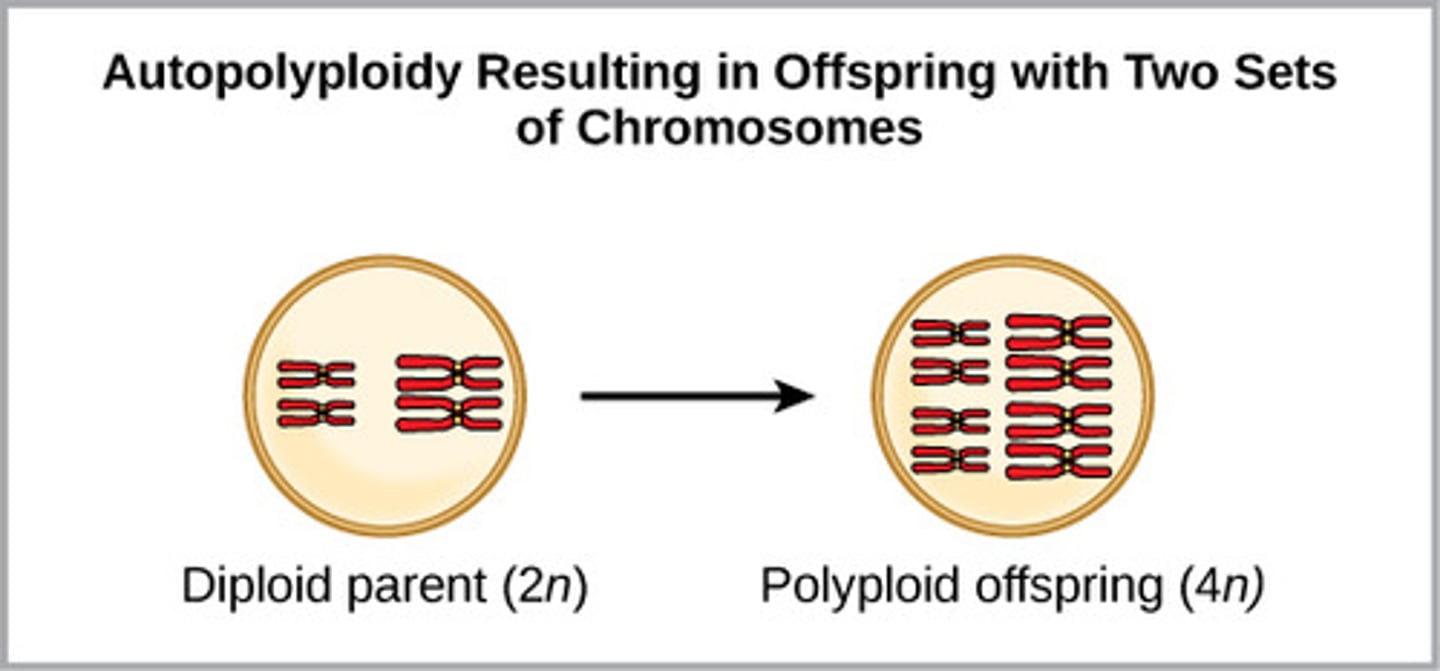
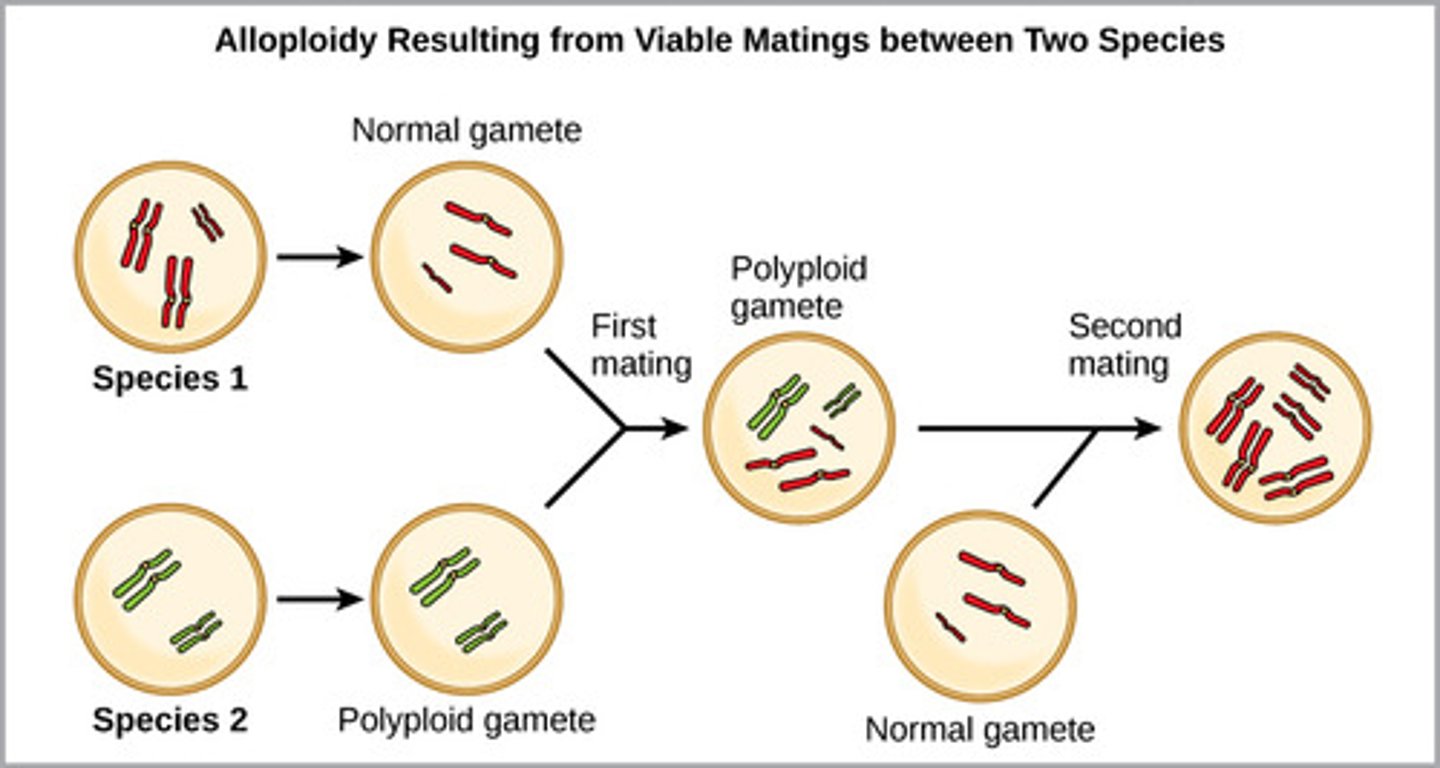
In plants, which type of polyploidy occurs when an organism has more than two sets of chromosomes, but they come from different species?
alloploidy
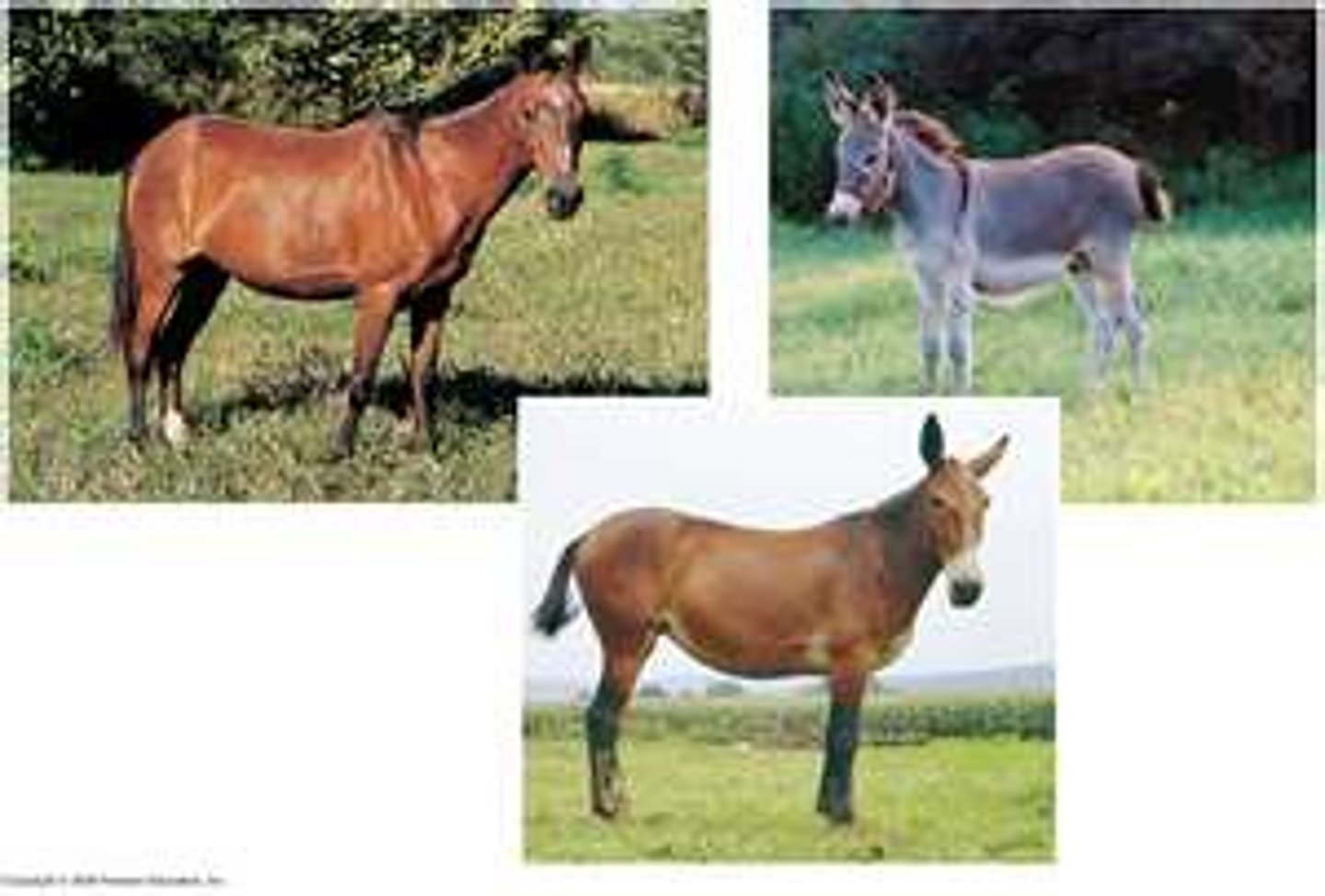
What process occurs when two different closely related species mate and produce a hybrid along a geographic boundary?
hybridization
(Note: the place where a hybrid is created is called a hybrid zone)

What is the rapid evolution of many species from a single ancestor?
adaptive radiation
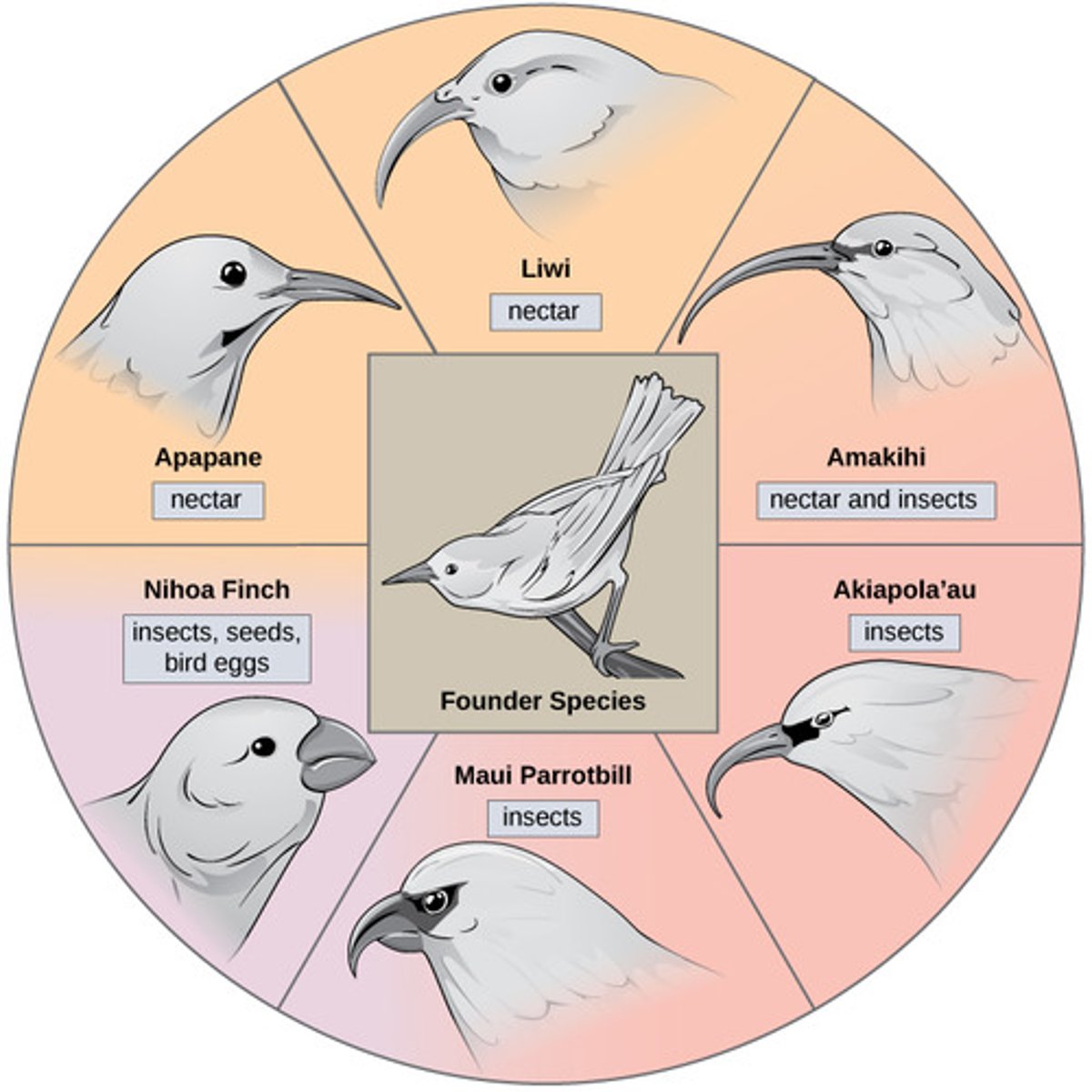
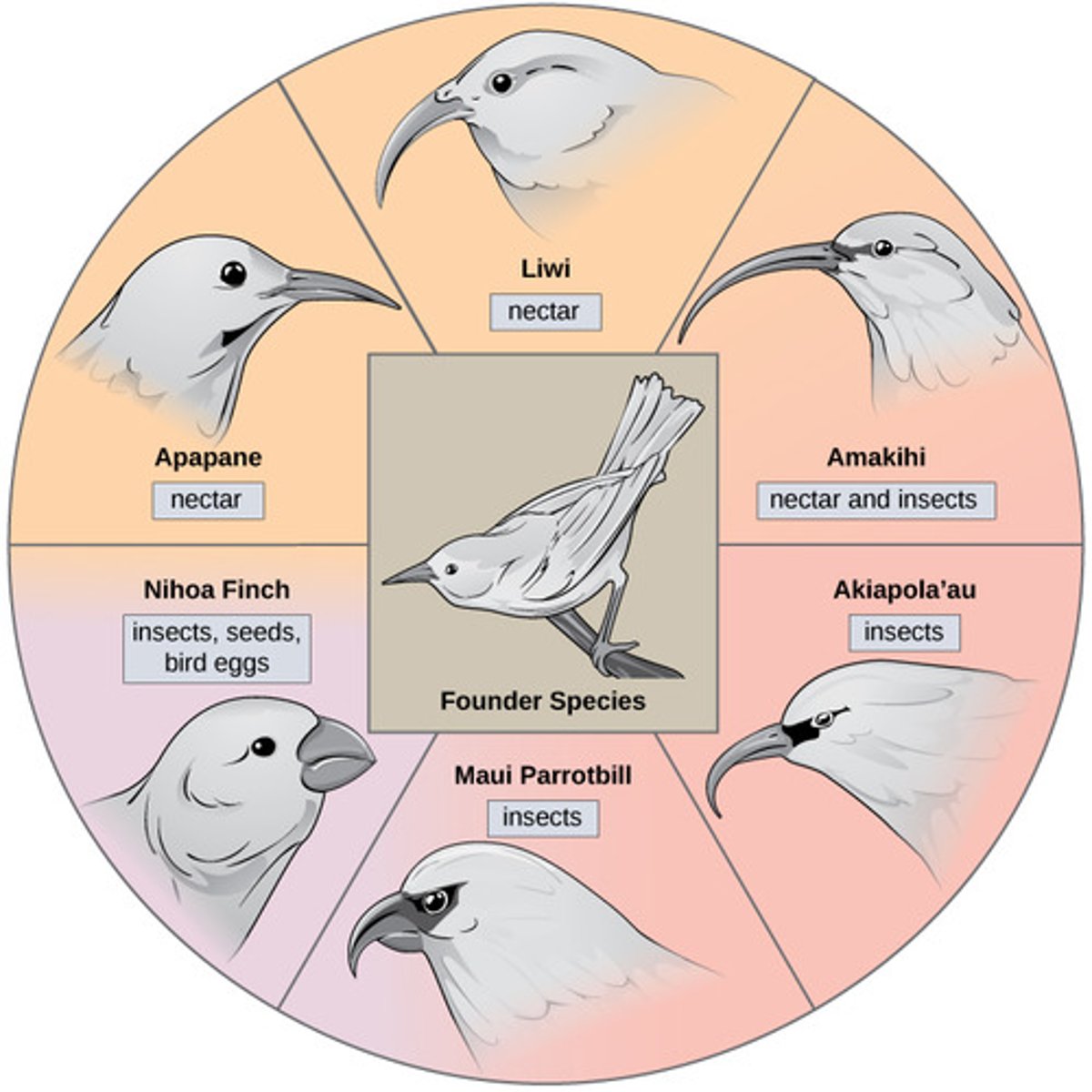
What process occurs when an old species is introduced to an area where diverse geographic and ecological conditions are available for colonization?
adaptive radiation
What is the state where gene flow is prevented between species?
isolation
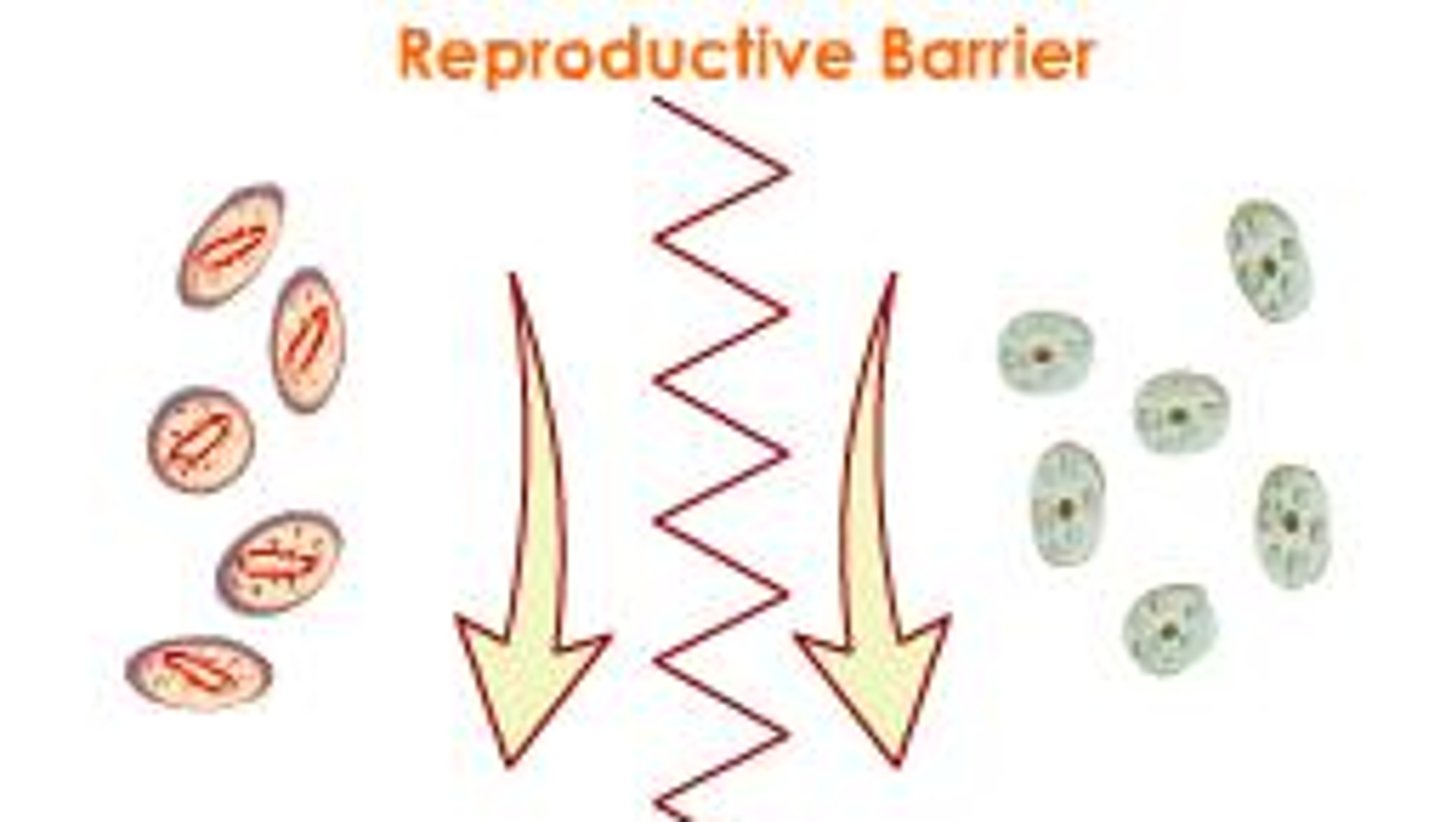
Which type of isolation prevents fertilization before mating is attempted, and so a zygote is not formed?
pre-zygotic isolation

Which pre-zygotic isolation occurs when species do not encounter each other because they live in different habitats?
habitat isolation
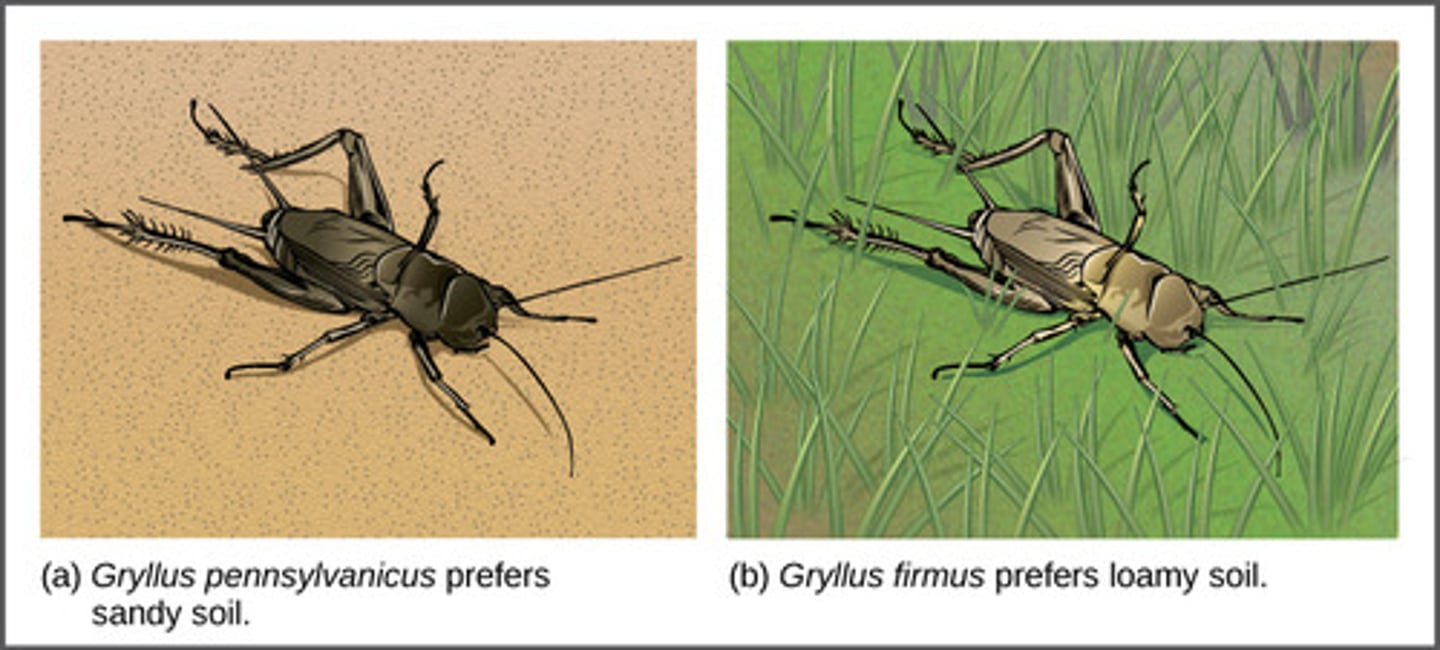
Which pre-zygotic isolation occurs when species reproduce at different seasons/times?
temporal isolation
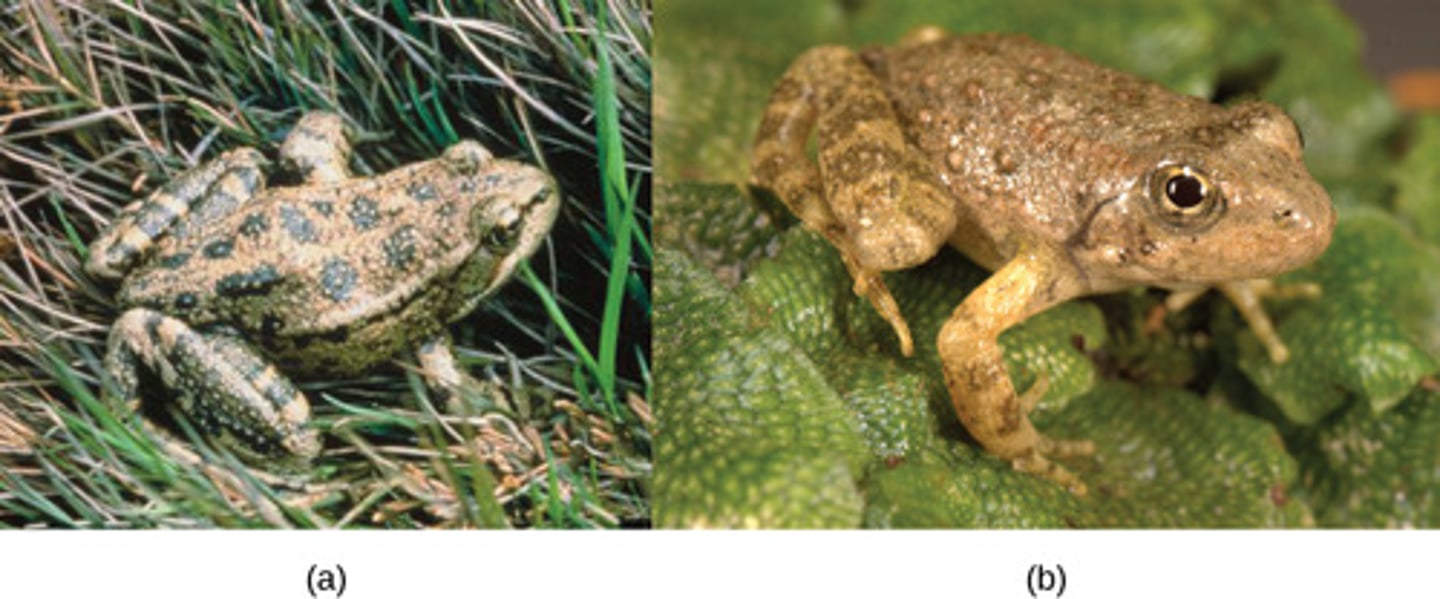

Which pre-zygotic isolation occurs when some species will not reproduce with each other if they do not perform the correct courtship rituals?
behavioral isolation
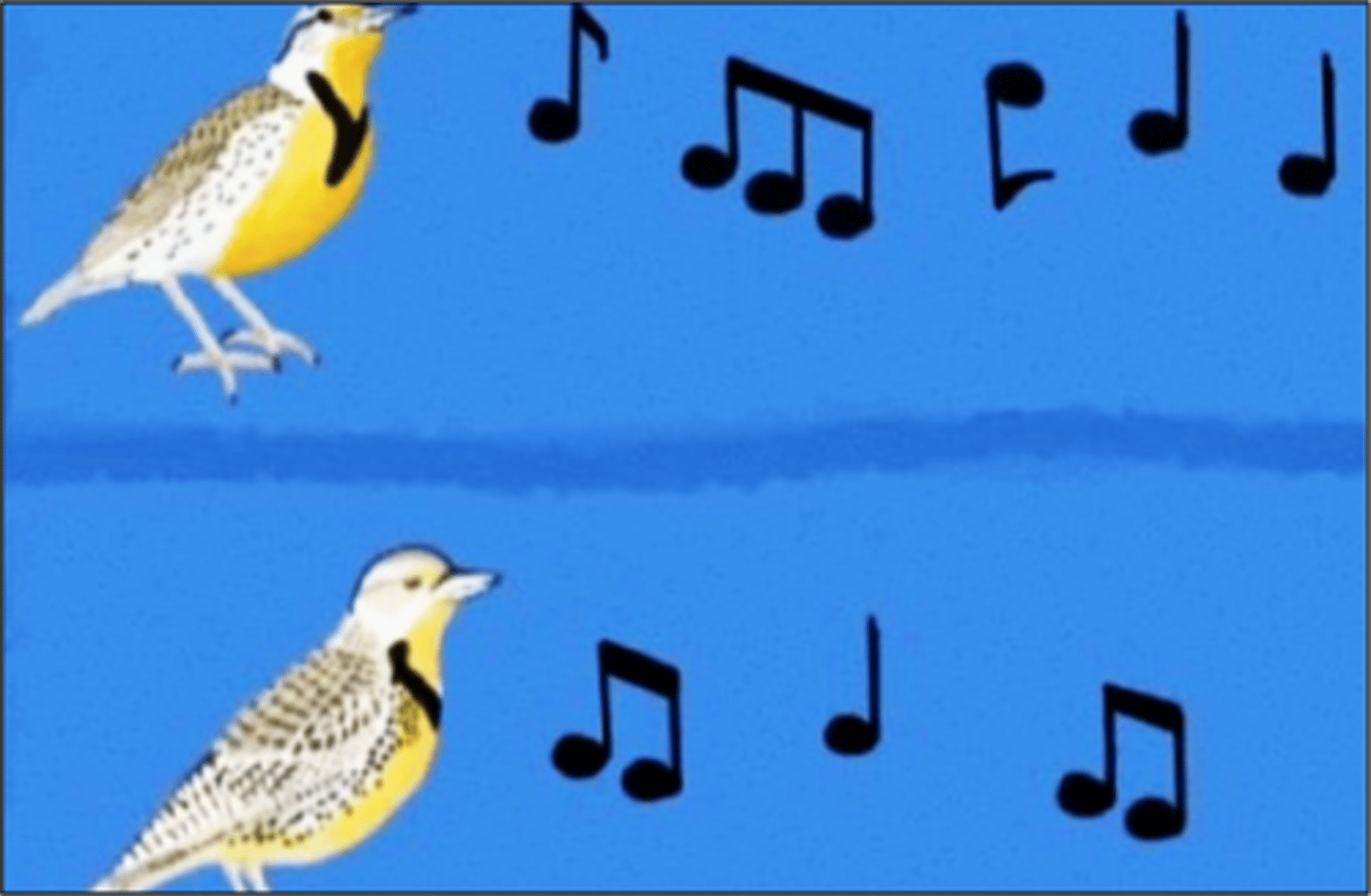

Which pre-zygotic isolation occurs when male and female genitalia are not compatible?
mechanical isolation

Which pre-zygotic isolation occurs when male and female gametes do not recognize each other?
gametic isolation
Which isolation occurs if a zygote forms?
post-zygotic isolation
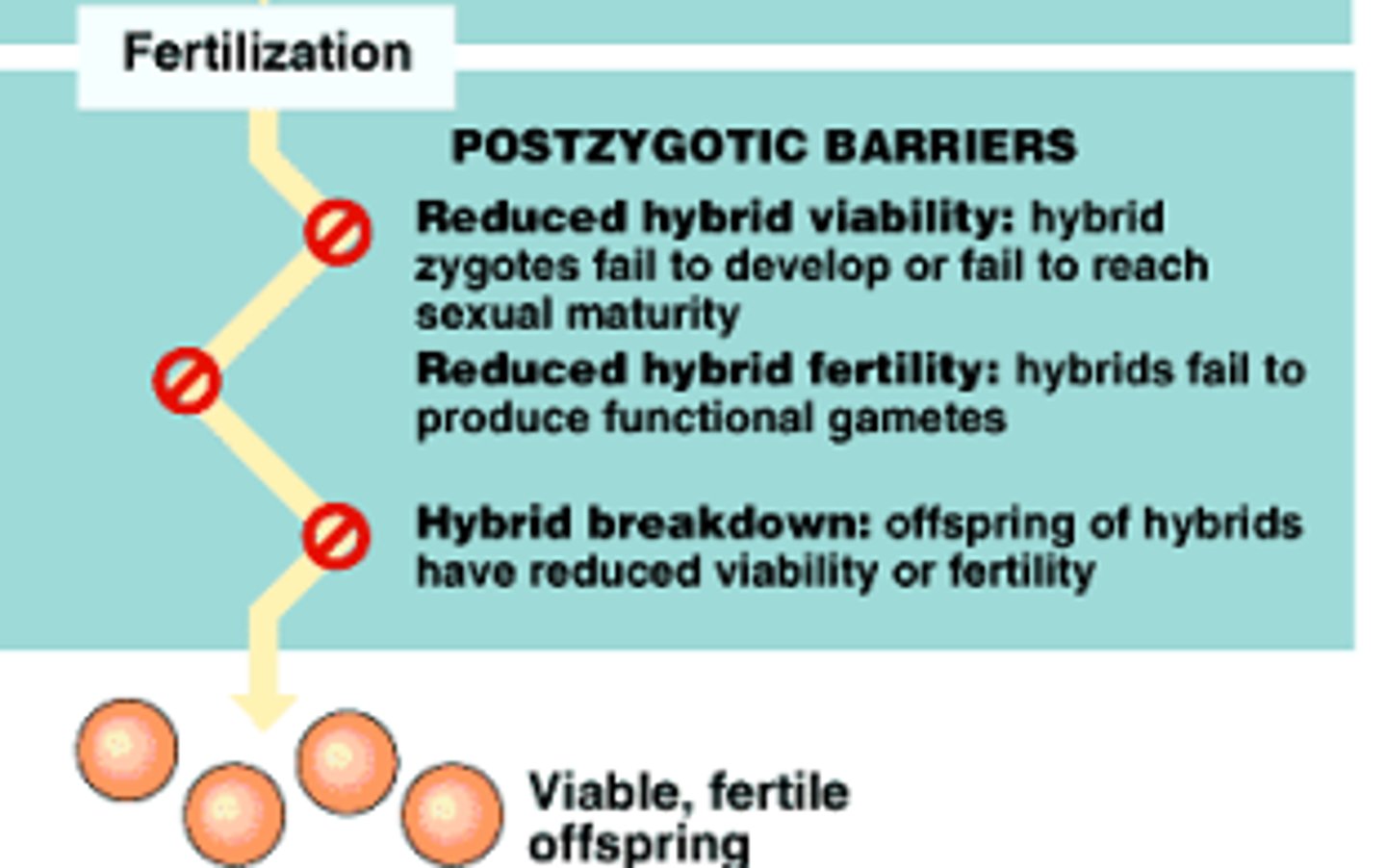
Which post-zygotic isolation occurs when the zygote fails to develop properly and dies before reaching reproductive maturity?
hybrid inviability
Which post-zygotic isolation occurs when hybrids become functional adults but cannot reproduce?
hybrid sterility
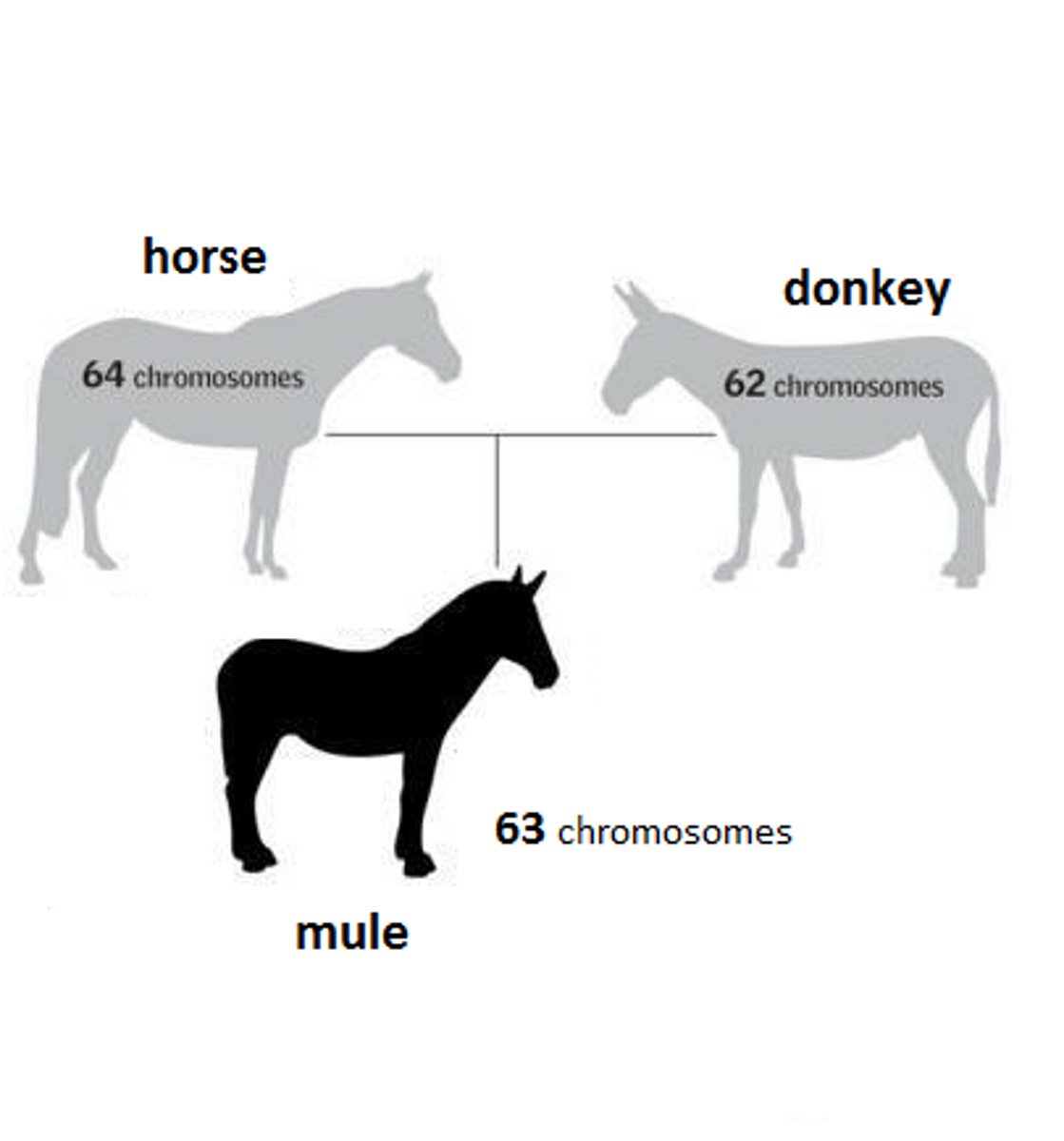
Which post-zygotic isolation occurs when hybrids produce offspring that cannot reproduce?
hybrid breakdown
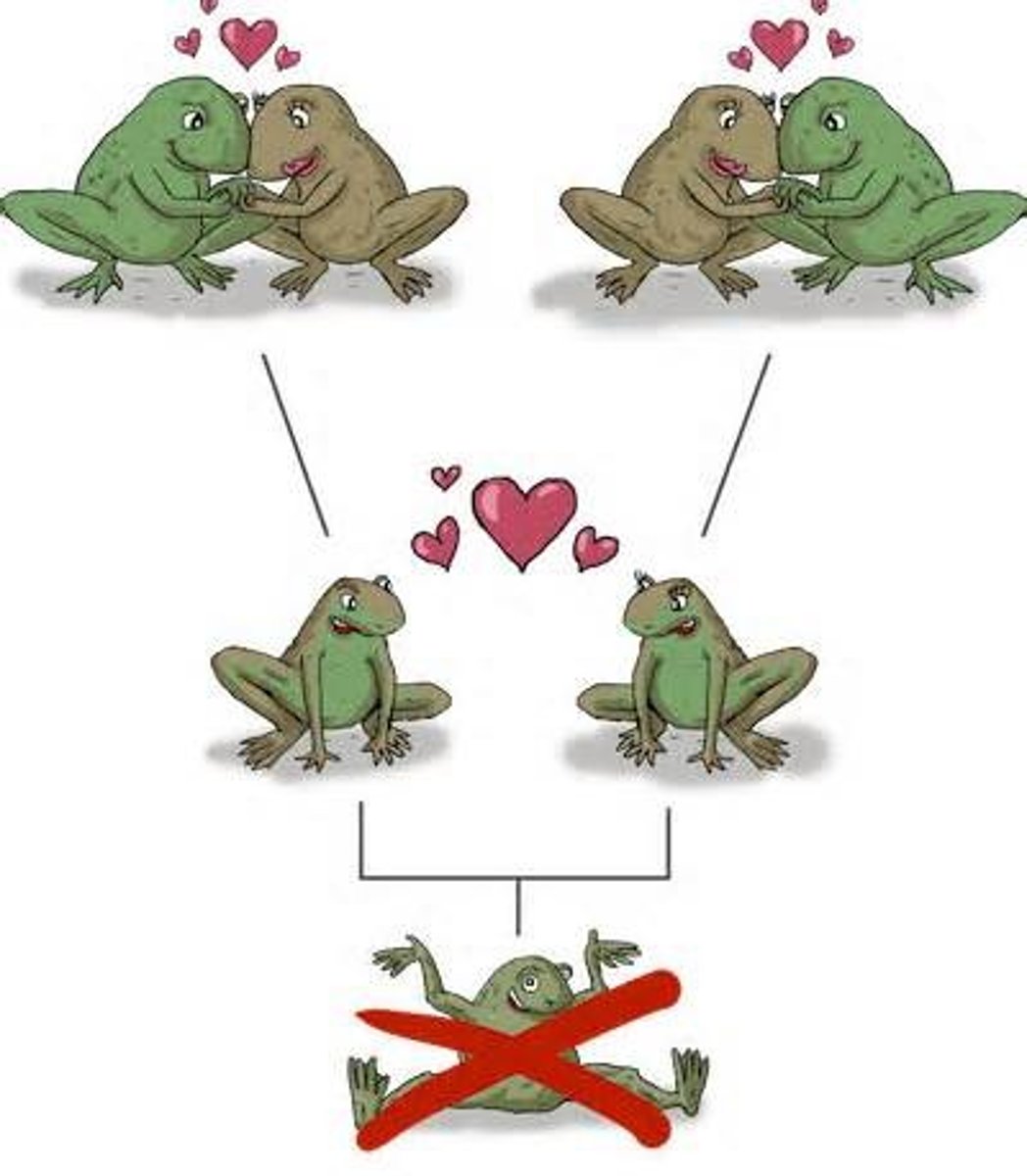
Which type of evolution occurs when two or more species that originated from a common ancestor become increasingly different over time as a result of speciation?
divergent evolution

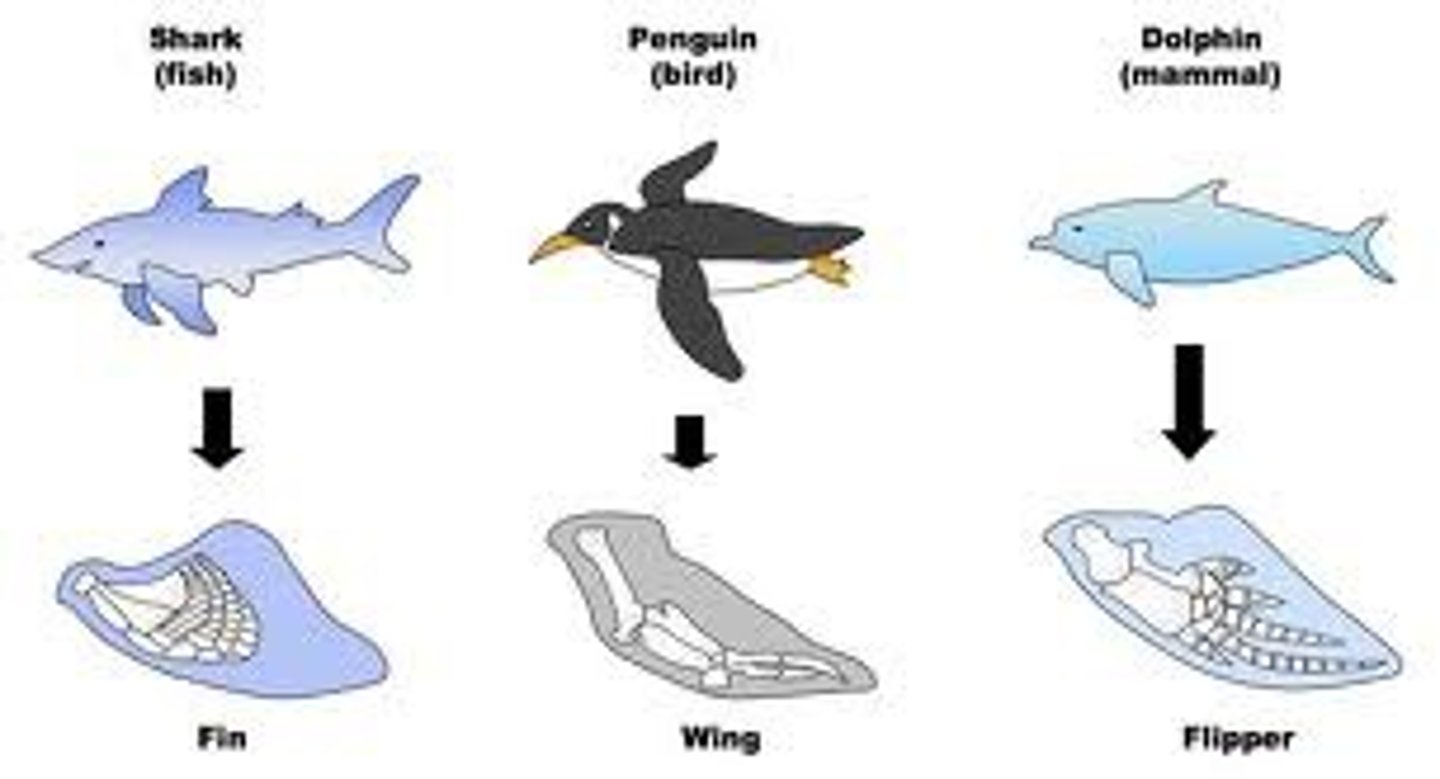
Which type of evolution occurs when two unrelated species evolve to share more similar traits due to adapting to a similar environment (analogous traits)?
convergent evolution
Which this type of evolution occurs when two related species make similar evolutionary changes after their divergence from a common ancestor?
parallel evolution
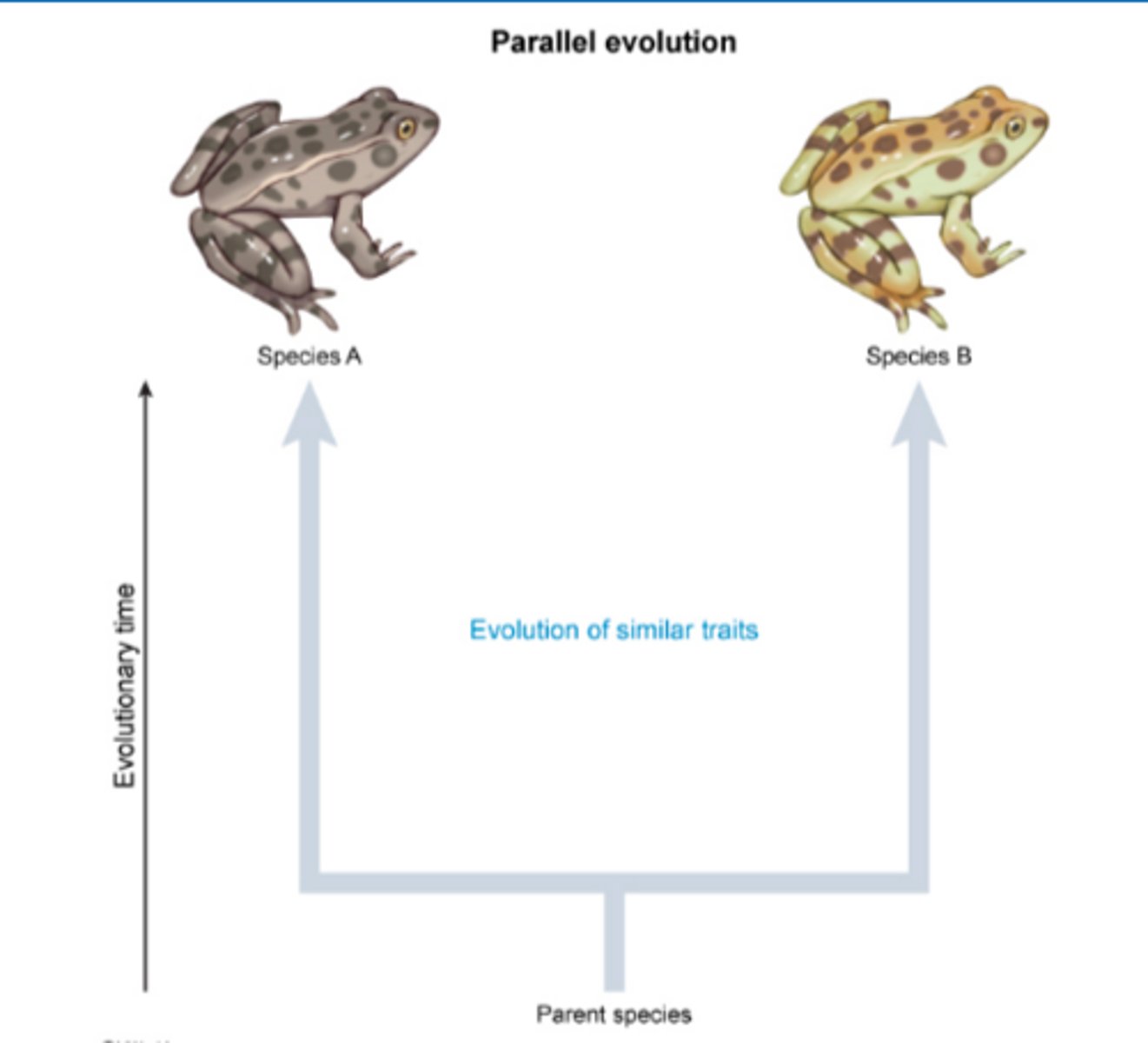
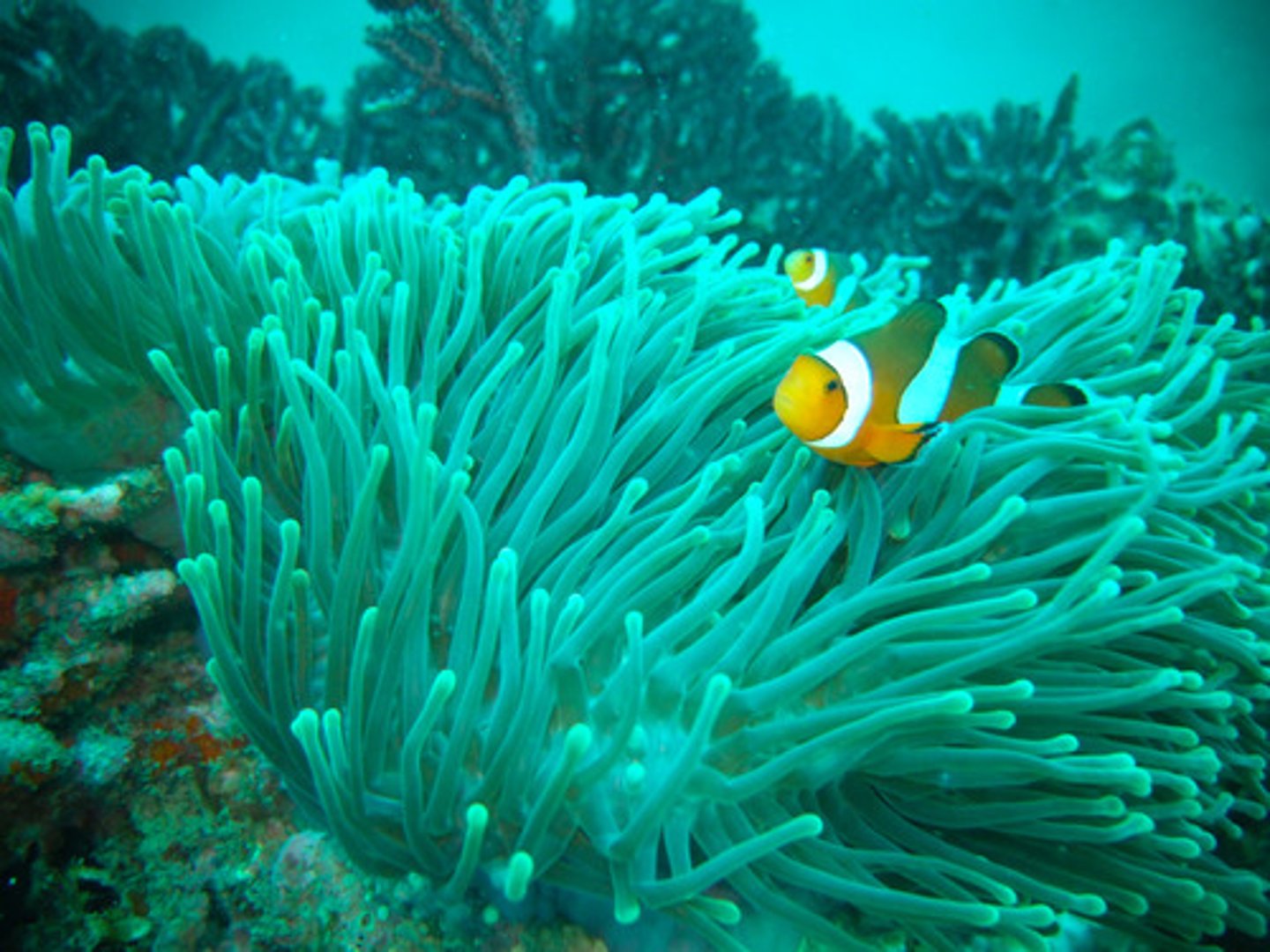
Which type of evolution occurs when two species each causes the other one to evolve, which results in the evolution of both species?
coevolution

Which theory says that evolution occurs by the gradual accumulation of small changes?
phyletic gradualism
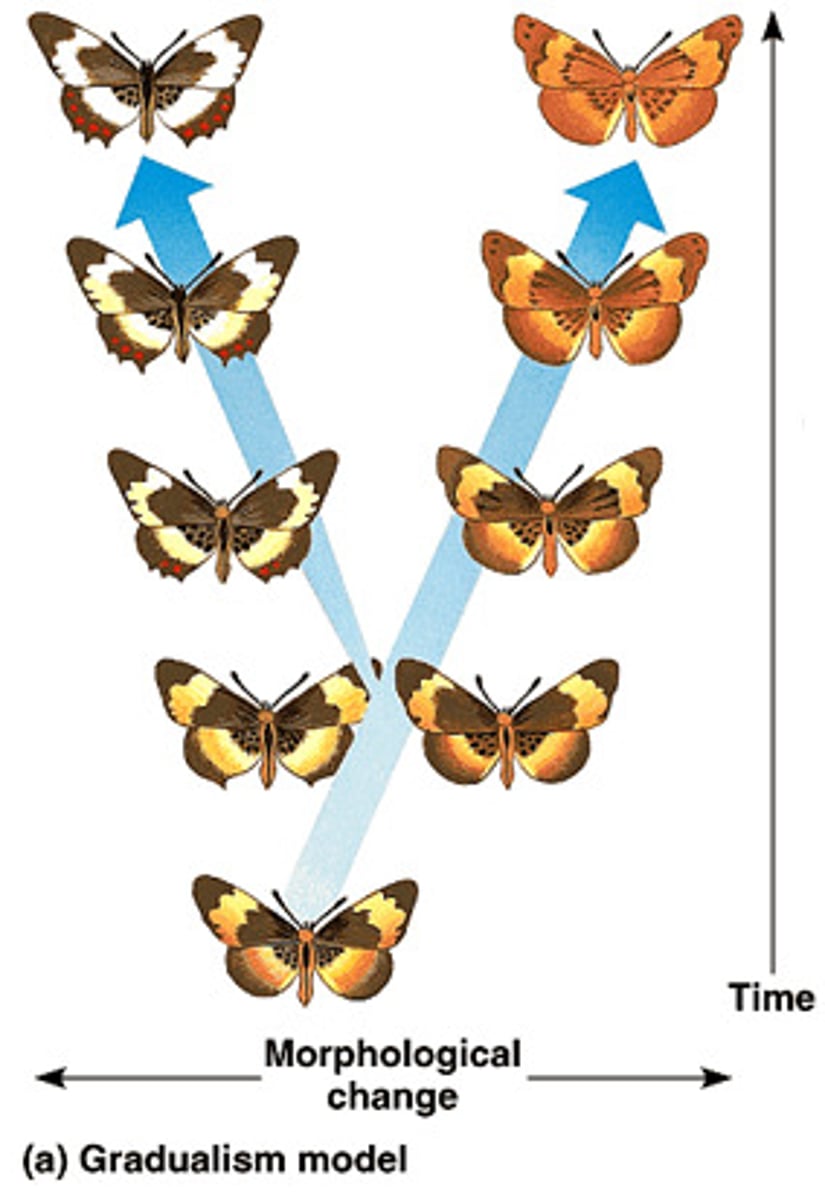
Why is phyletic gradualism unlikely?
intermediate stages of evolution are missing in the fossil record
What theory says that evolutionary history consists of geologically long periods of stasis (stability) with little or no evolution followed by geologically short periods of rapid evolution?
punctuated equilibrium
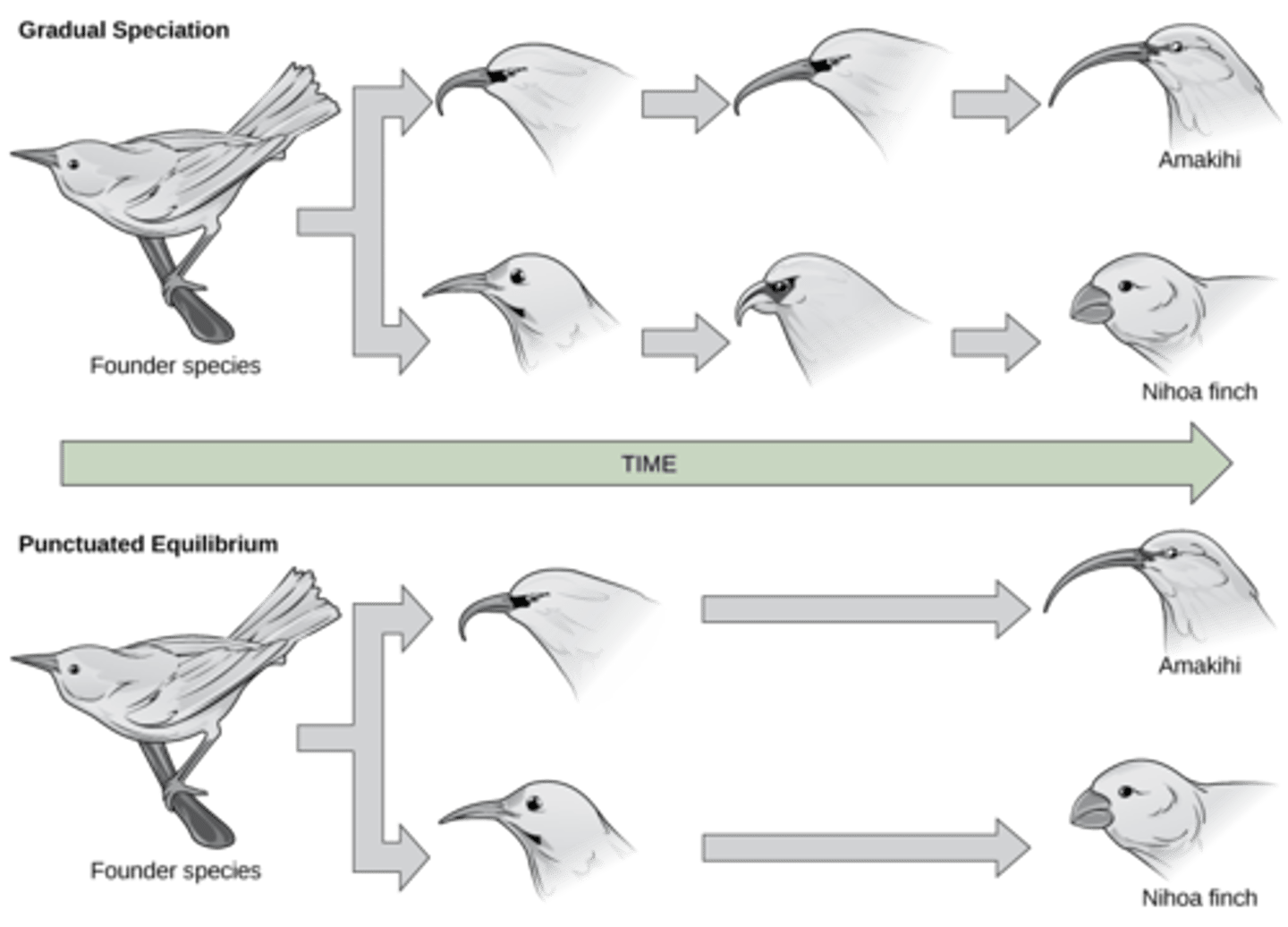
Why is there support for the punctuated equilibrium theory?
The absence of fossils revealing intermediate stages of evolution is considered data that confirms rapid evolutionary events