Nervous system
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
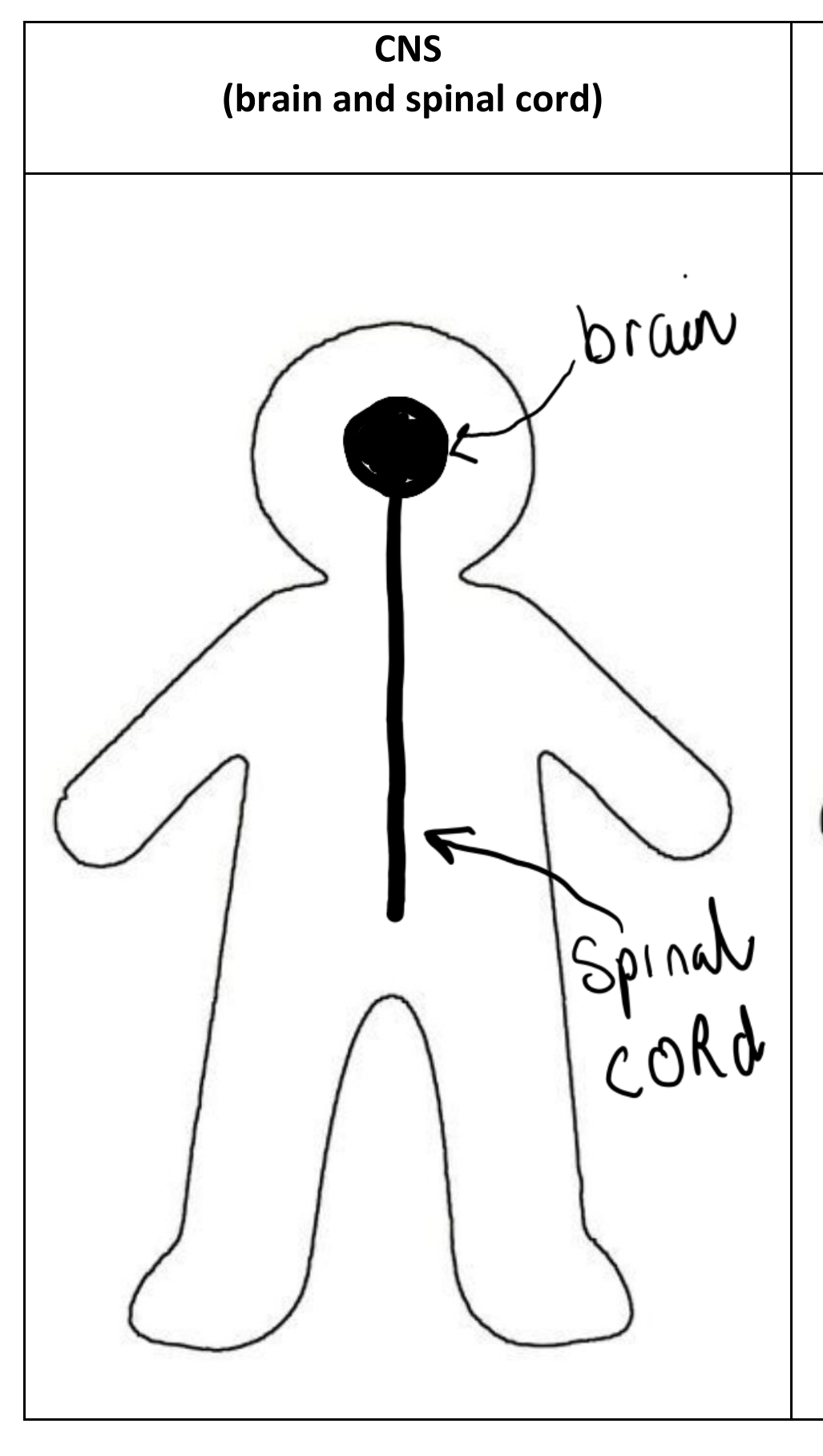
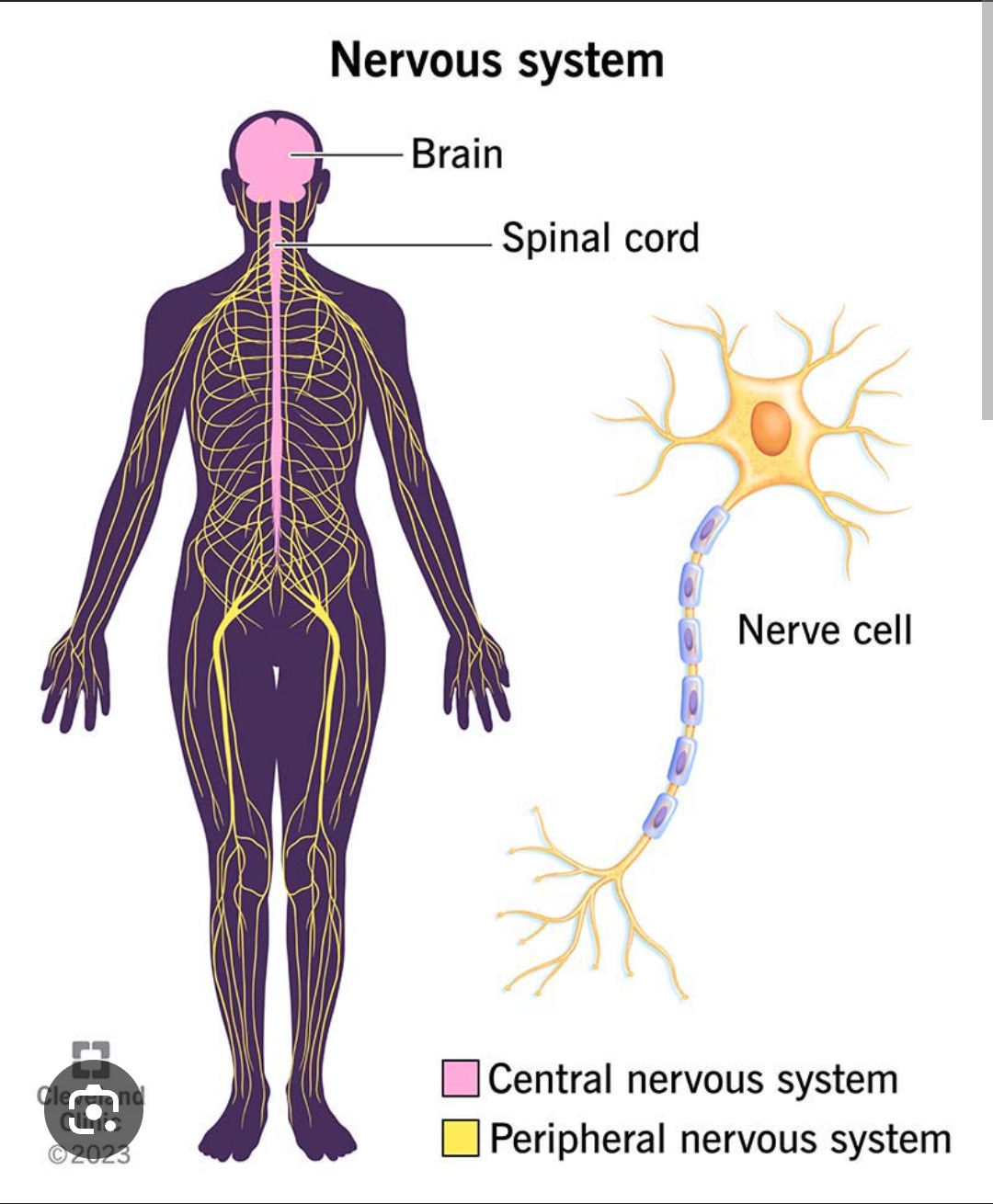
Central nervous system
Brain and spinal cord.
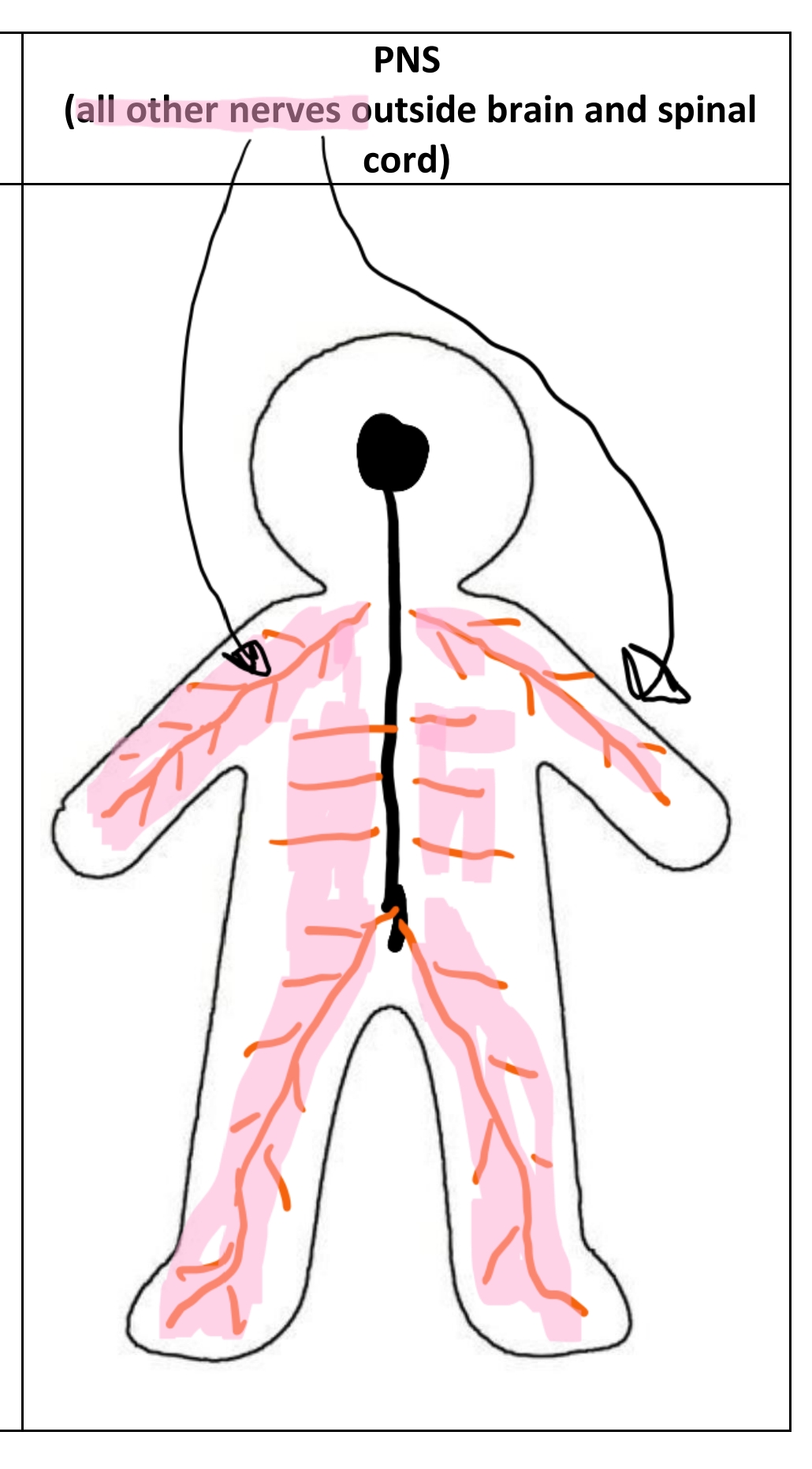
Peripheral nervous system
All other nerves in the body. They feed into the CNS.
CNS- The Brain
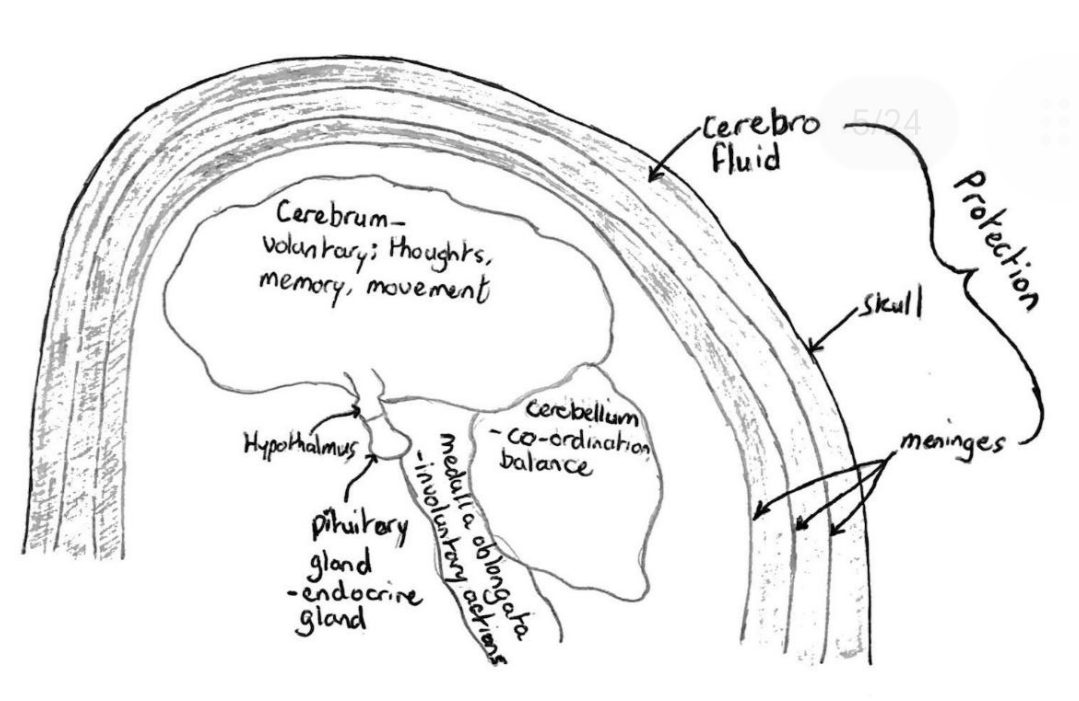
Cranium (skull)
Protection

Meninges membrane (3 layers)
Protection

What is the Infection of the meninges by bacteria or viruses called?
Meningitis
Cerebrofluid (between meninges)
Protection

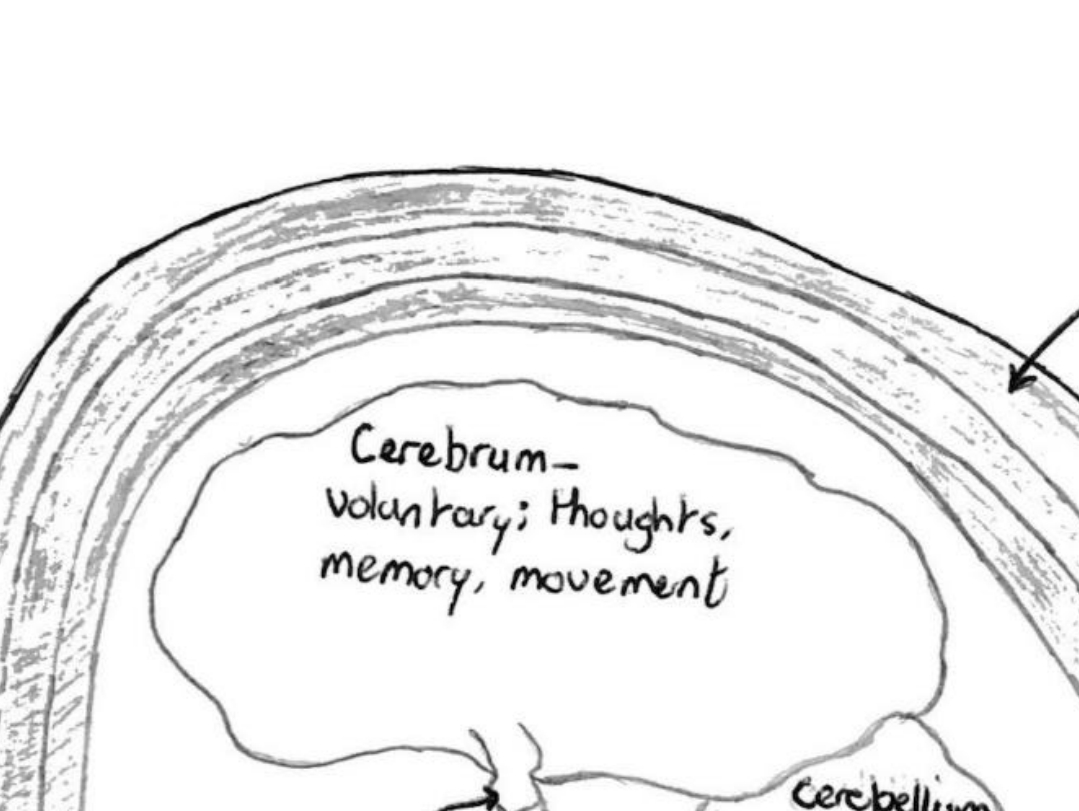
Cerebrum (largest part of brain)
Voluntary movement, memory, speech and language, learning and intelligence, hearing
Hypothalamus
Maintains a constant internal environment in the body including thirst, hunger, water balance, body temp.

Pituitary gland
Produces hormones including ADH, TSH, FSH and LH.

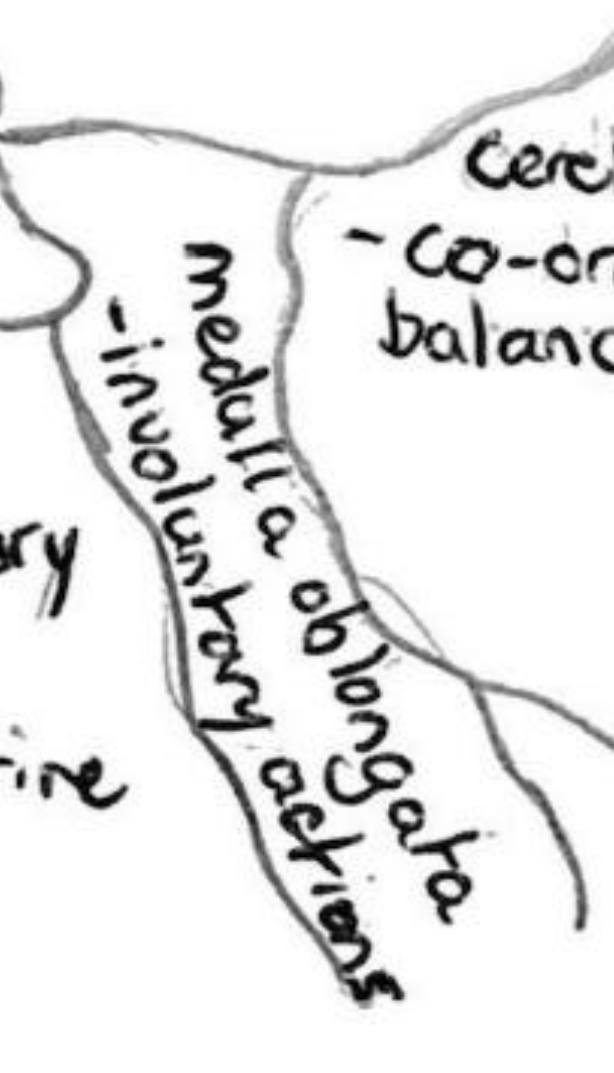
Cerebellum (connected to ear)
Co-ordinates movement and balance as well as hand-eye co-ordination.

Medulla oblongata
Controls involuntary movement including breathing, heart rate, swallowing.
Neuron
A single nerve cell.
CNS- Spinal Chord
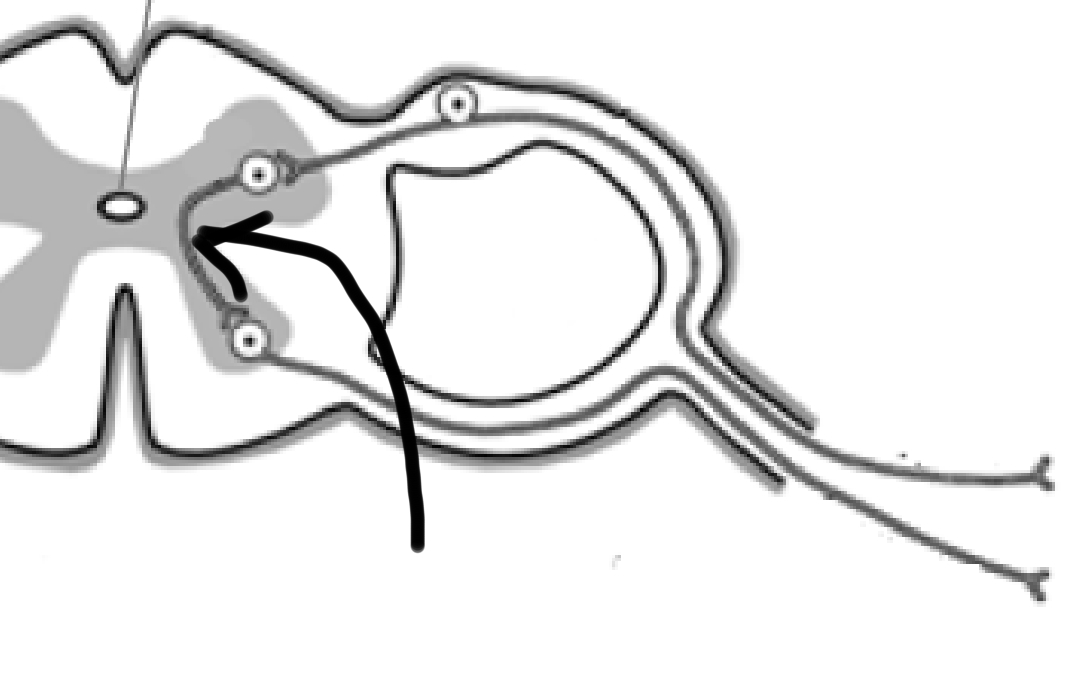
Mechanism of reflex action/arc
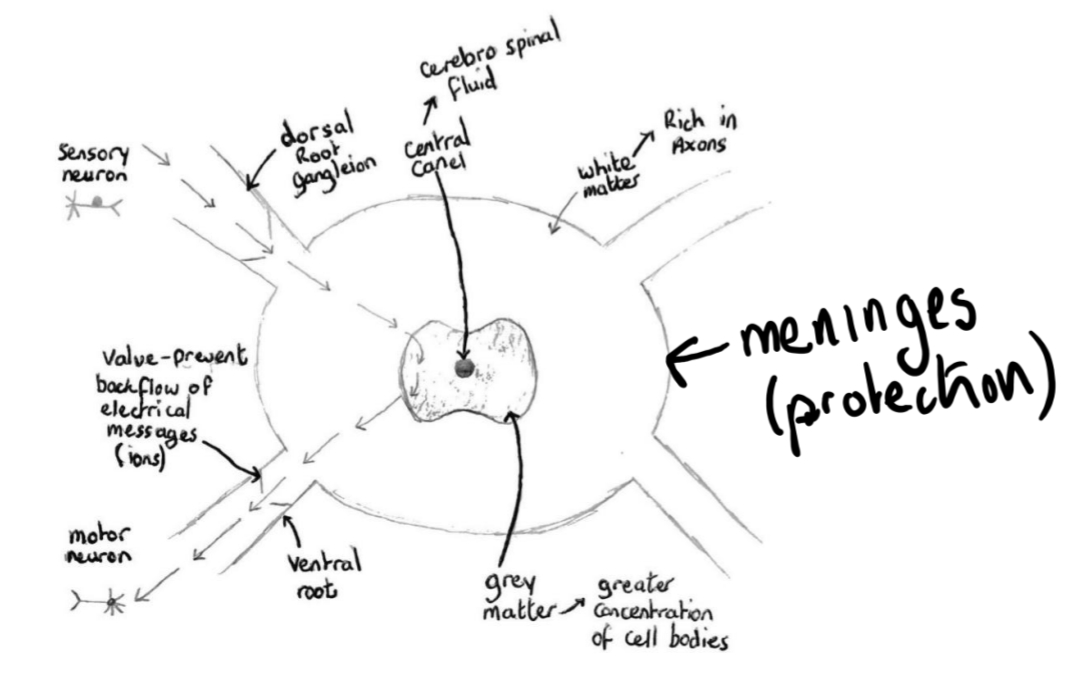
1. Electrical message carried to spinal cord via sensory neuron.
2. Enters spinal cord via dorsal root ganglion (one-way door in).
3. Converted into a motor neuron via the interneuron located inside spinal cord. Message passed out of spinal cord on the motor neuron via ventral root (one-way door out).
4. Message carried to muscle where reaction occurs.
1.
Electrical message carried to spinal cord via sensory neuron.

2.
Enters spinal cord via dorsal root ganglion (one-way door in).

3.
Converted into a motor neuron via the interneuron located inside spinal cord.

4.
Message passed out of spinal cord on the motor neuron via ventral root (one-way door out).
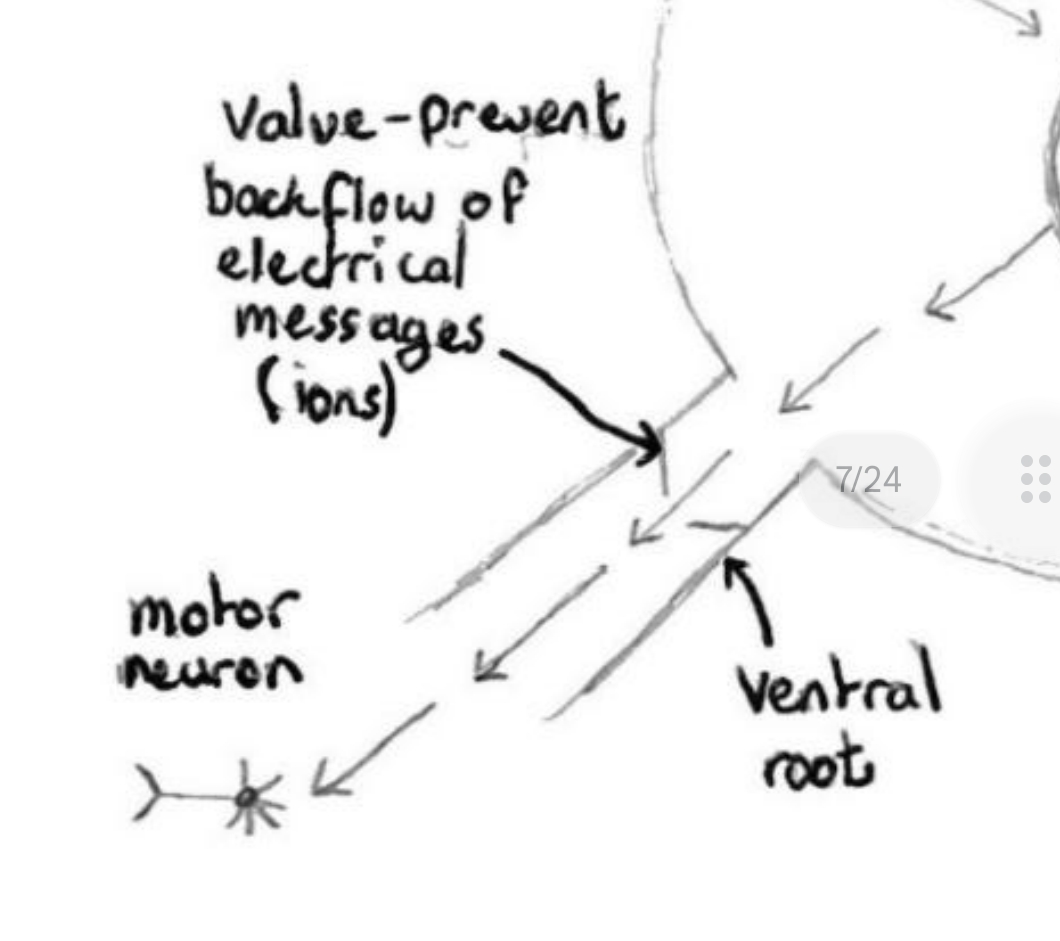
5.
Message carried to muscle where reaction occurs.
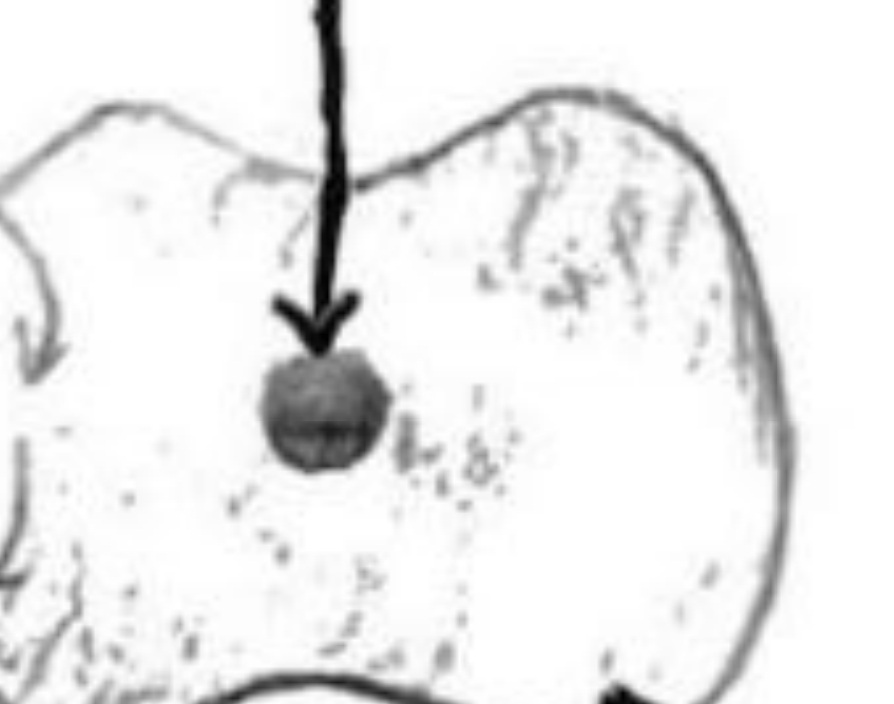
Central canal
Centre of the spinal chord is called the central canal and contains cerebrospinal fluid.
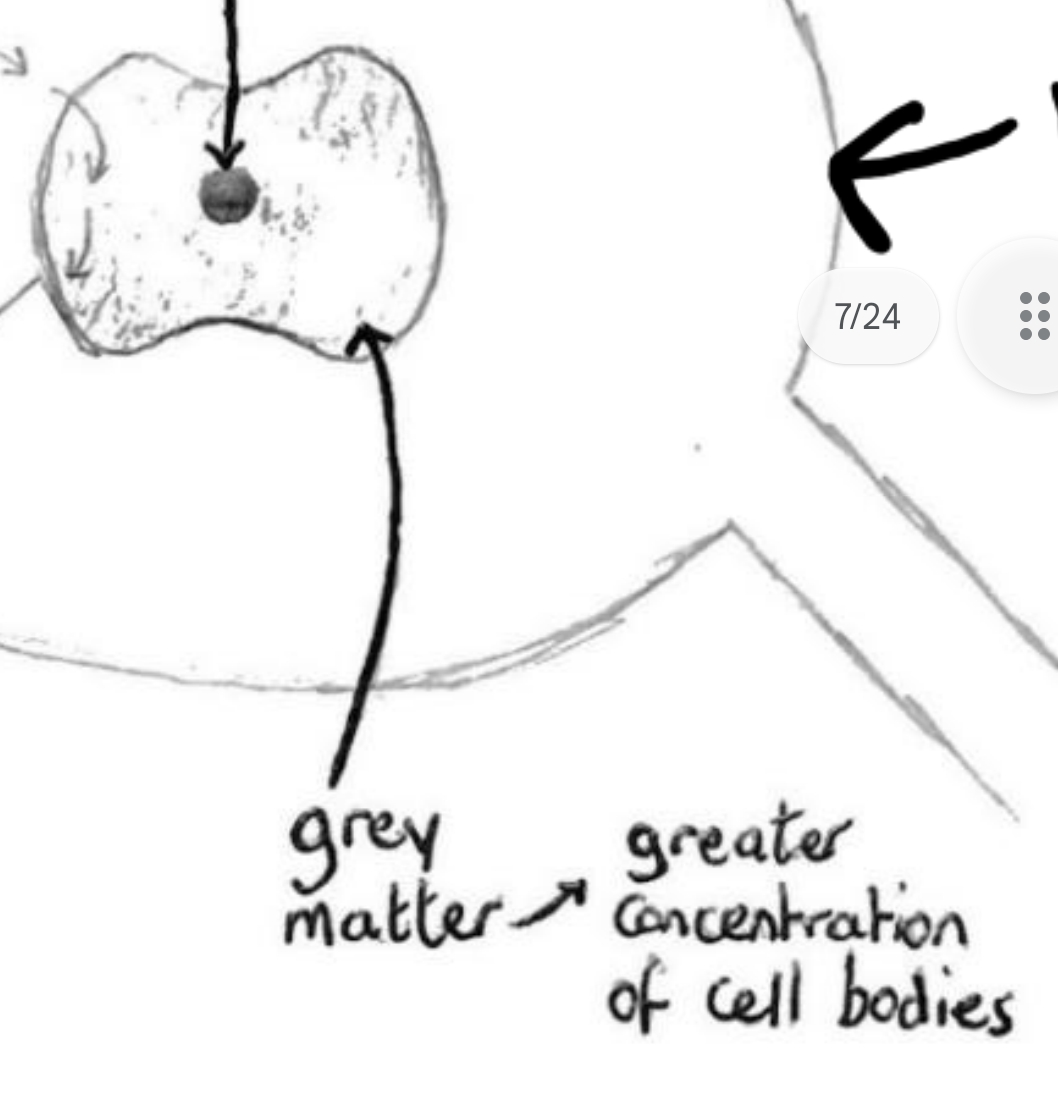
Grey matter
The dark grey area that surrounds the central canal is called grey matter and is composed of cell bodies.
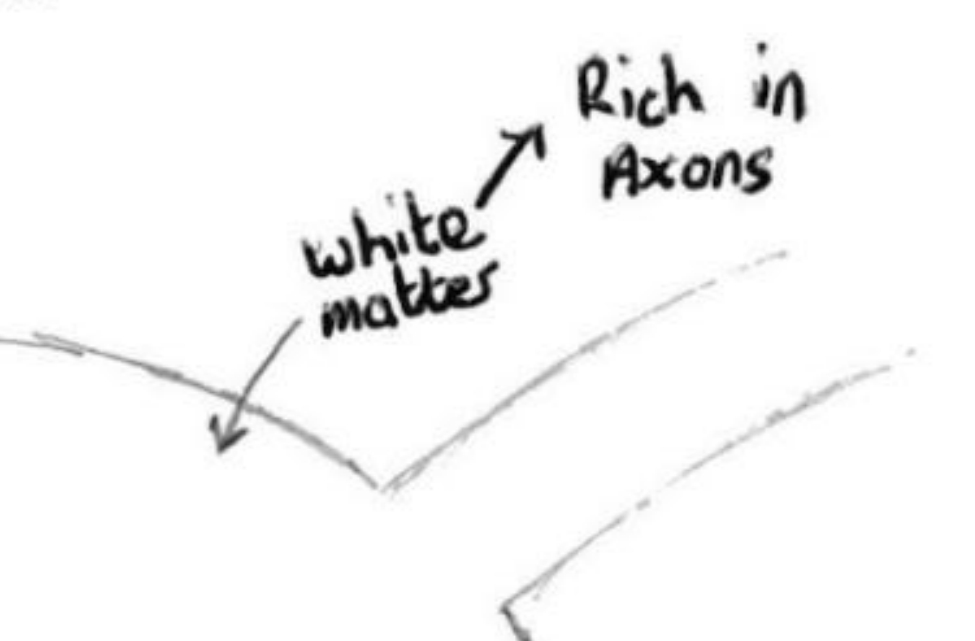
White matter
The white area outside of the grey matter is called white matter and is composed of axons.
Nerves
Carry messages around the human body in the form of electrical impulses known as ions.
Nerves are made up of many nerve cells called neurons (need to know structure of neuron) in close proximity but not touching.
3 types of nerve cells/neurons
Sensory neurons
Motor neurons
Inter neurons
Sensory neurons
Carry electrical messages (ions) to the Central Nervous System from Peripheral Nervous System.

Motor neurons
Carry electrical messages away from Central Nervous System to Peripheral Nervous System.
Inter neurons
Convert sensory messages to motor messages in the brain/spinal cord. Remember: sensory and motor neurons can be found in peripheral nervous system but interneurons can only be found in central nervous system.
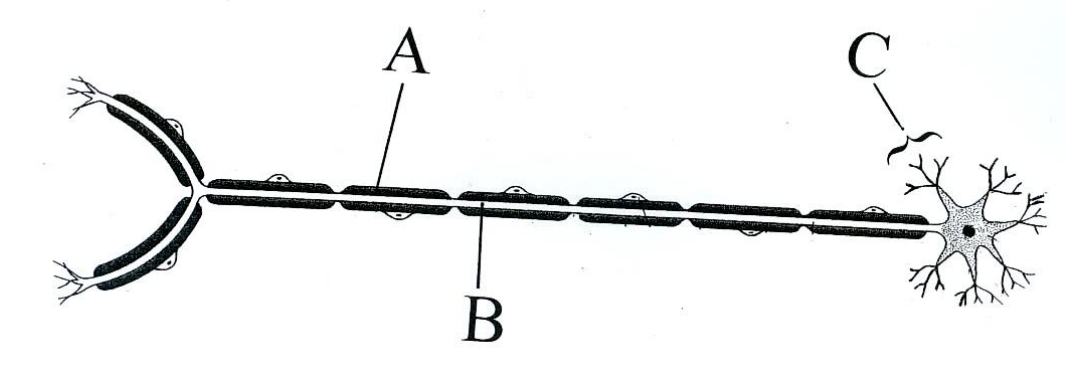
Structure of a neuron and the functions of each part

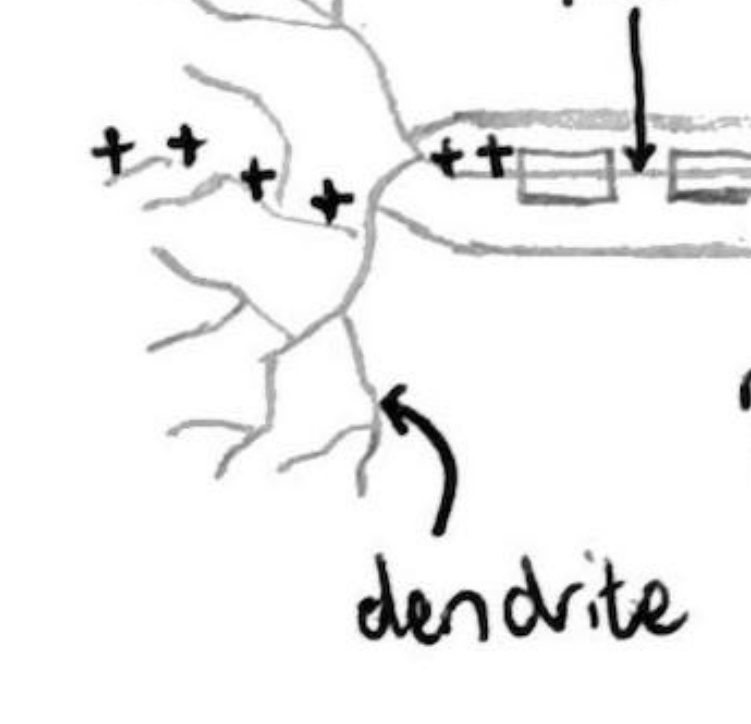
Dendrite
Located at one end of neuron. Picks up electrical impulse from axon of previous nerve cell.
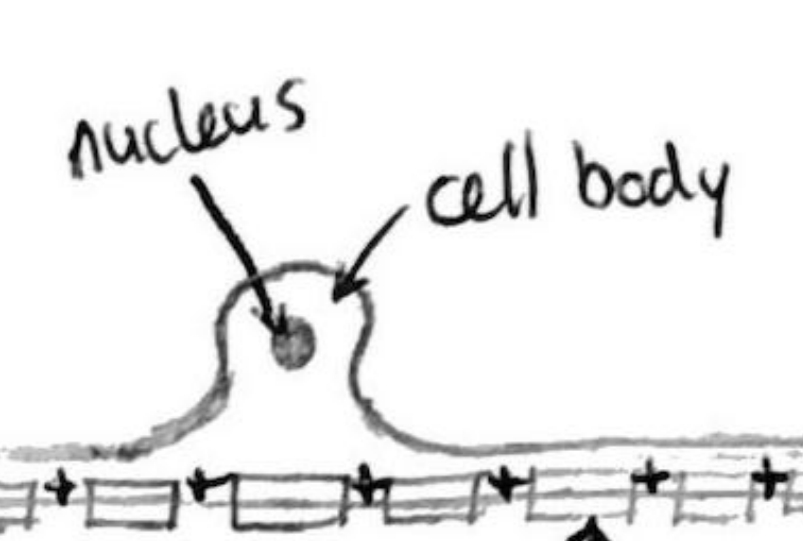
Cell body
Contains a nucleus and controls activities of the neuron. Produces neurotransmitters that then travel to neurotransmitter swellings where they are stored before being released into synaptic cleft.
Schwann cell
Produce the myelin sheath.

Myelin Sheath
Myelin sheath is produced by Schwann cells and is composed of lipids. This layer (or sheath) is wrapped around the axon. It acts as an insulator and speed up the rate of transmission of the electrical impulse.

Axon
Carries electrical impulse along nerve.

Neurotransmitter swellings
Found at end of axon (at axon terminal), stores and secretes neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft.

Synaptic cleft
Gap between axon of one neuron and dendrite of another neuron.

Synapse
Region including axon terminal of one neuron and dendrite of another neuron.

Neurotransmitter
Chemical produced to carry electrical impulse across synaptic cleft gap. Produced in the cell body but stored in neurotransmitter swellings. Examples include dopamine, acetylcholine and noradrenalin.
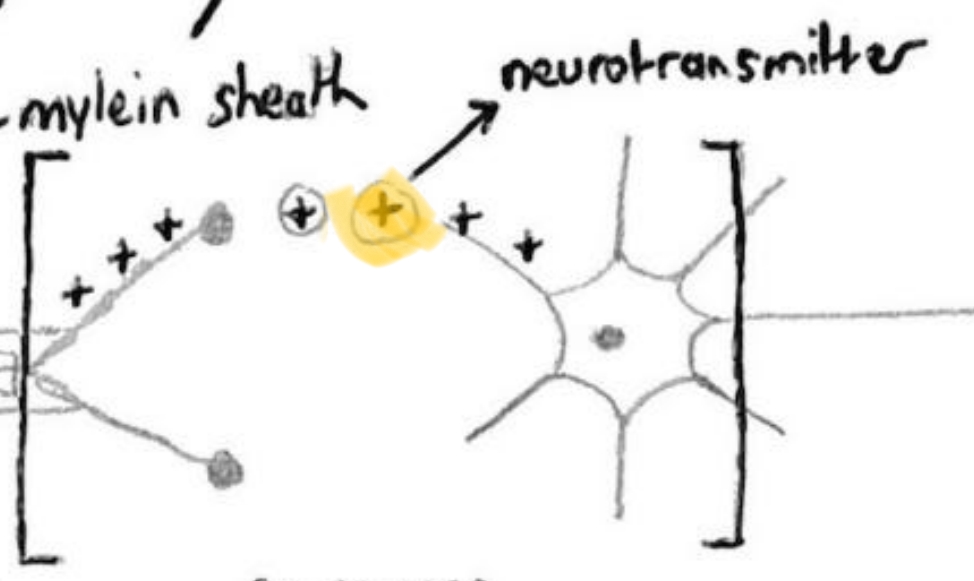
In which direction does the electrical impulse (in the form of ions) travel in the neuron (nerve cell)?
Electrical impulse always travels in the direction from dendrite to axon terminal.
Motor neuron
Similar to the structure of sensory neuron and various parts have the same function. However, the cell body is located in the centre of the neuron in a sensory neuron but next to the dendrite in a motor neuron.
What is the Deficiency disease of the nervous system?
Parkinson’s disease
Symptoms
Cause
Prevention
Treatment
Symptoms: Hand tremors, muscle contraction that cannot be controlled
Cause: Failure to produce neurotransmitter dopamine
Prevention: None
Treatment: Medication that mimics dopamine or produces dopamine (L-dopa), physiotherapy and gentle exercise
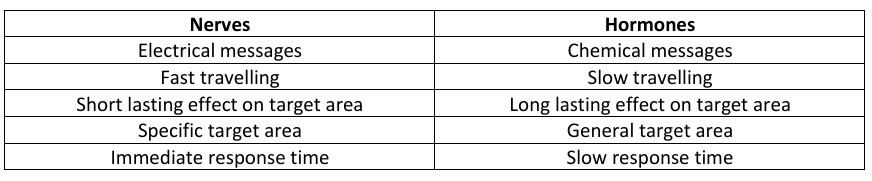
Differences between nerves(nervous system) and hormones(endocrine system)