Neuroanatomy: Cerebrum and Higher Cortical Functions
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
Cerebrum
Largest brain part, responsible for higher functions.
Forebrain
Region containing the cerebrum and diencephalon.
Diencephalon
Part of forebrain including thalamus and hypothalamus.
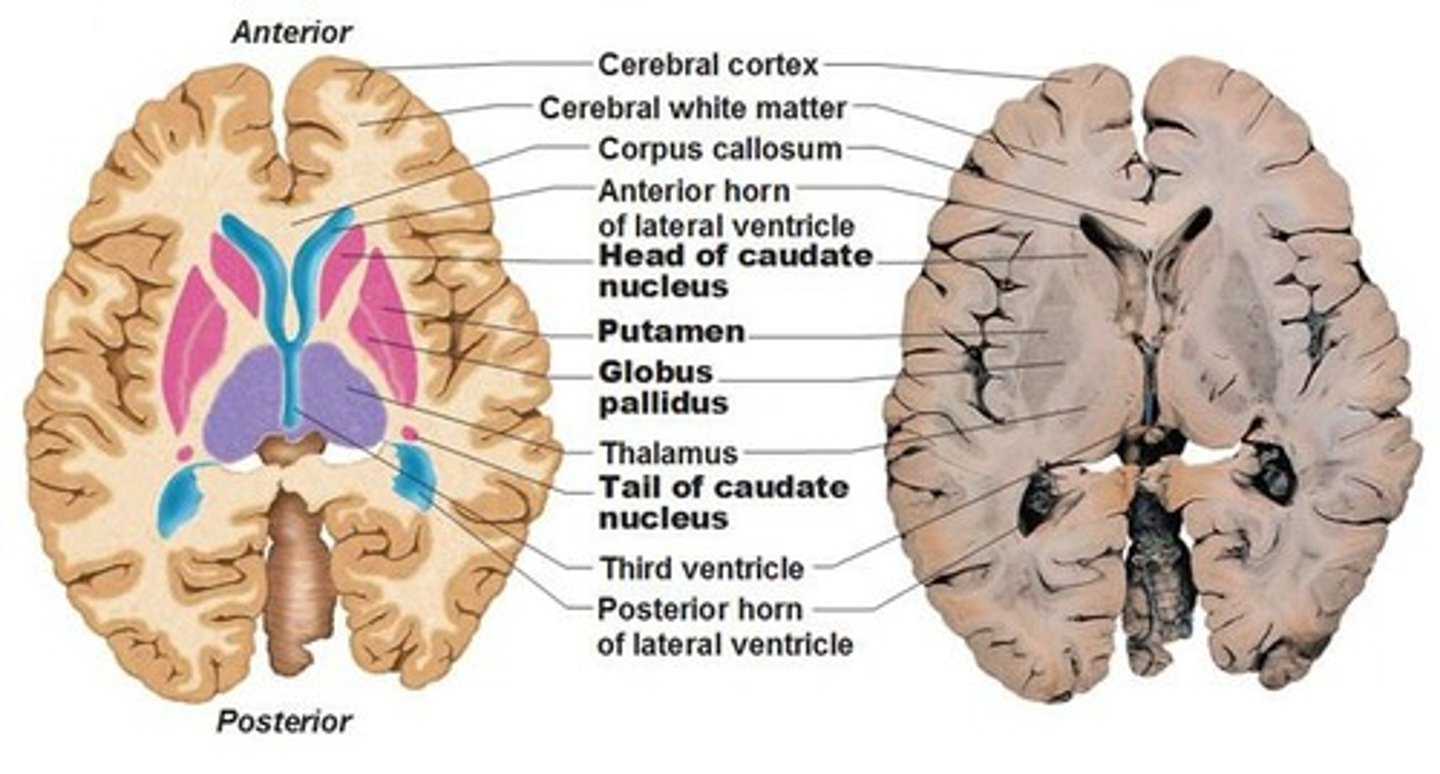
Thalamus
Relay station for sensory information in the brain.
Hypothalamus
Regulates autonomic functions and homeostasis.
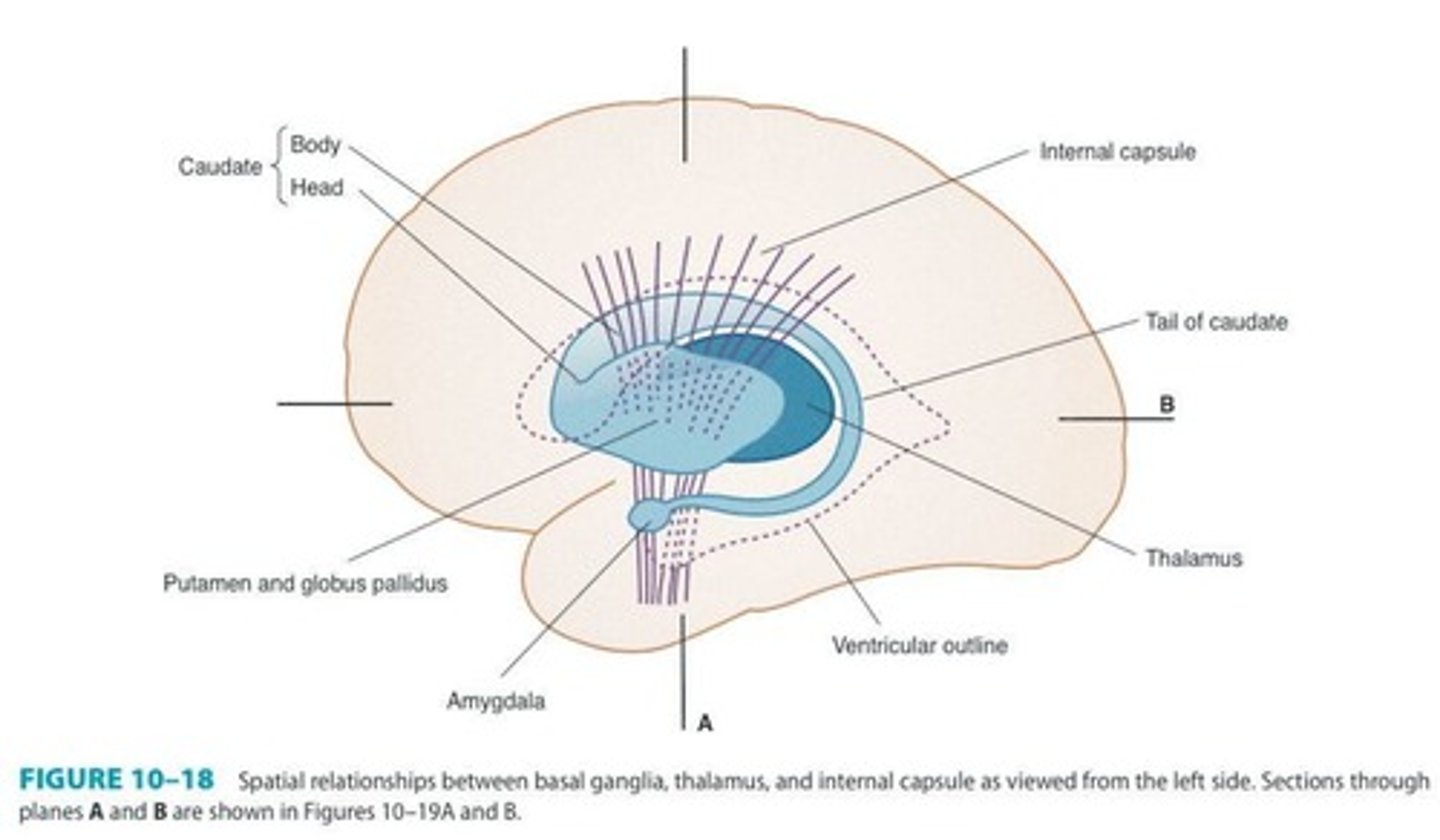
Internal Capsule
Main conduit for ascending and descending tracts.
Sulcus
Groove separating gyri in the cerebral cortex.
Gyrus
Raised fold of the cerebral cortex.
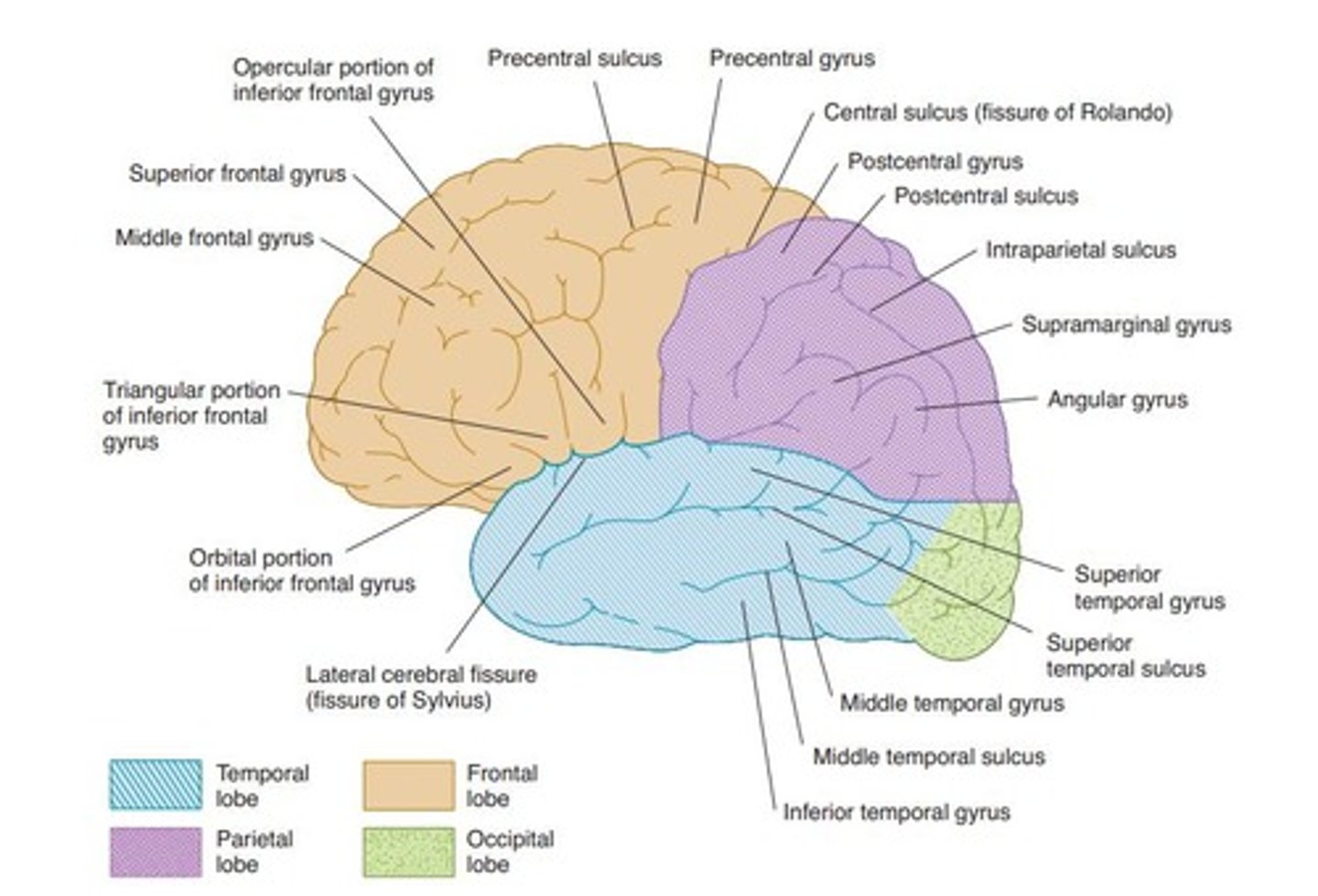
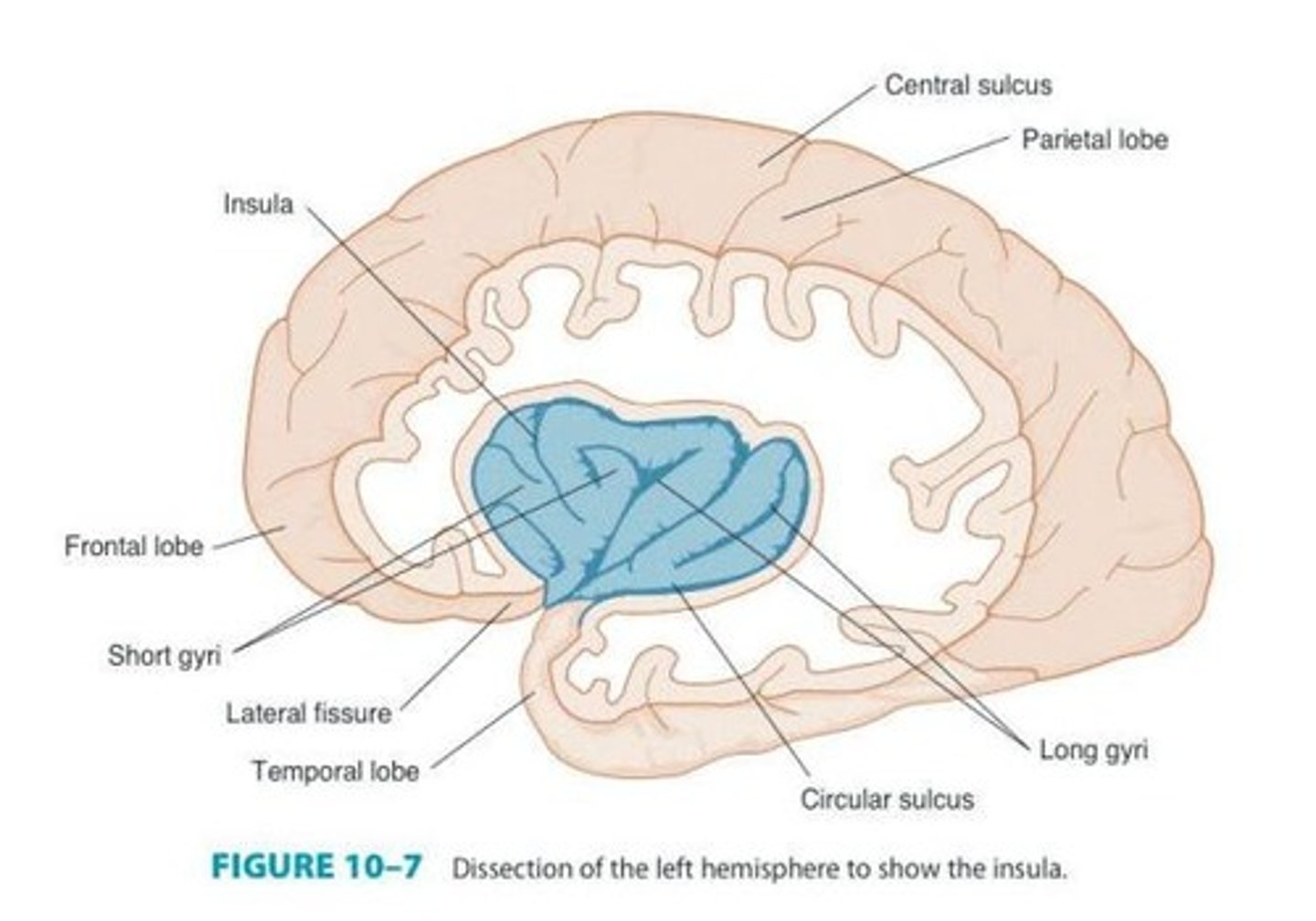
Lateral Cerebral Fissure
Separates temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes.
Insula
Cortex portion lying deep within the lateral fissure.
Circular Sulcus
Surrounds the insula, separating it from adjacent lobes.
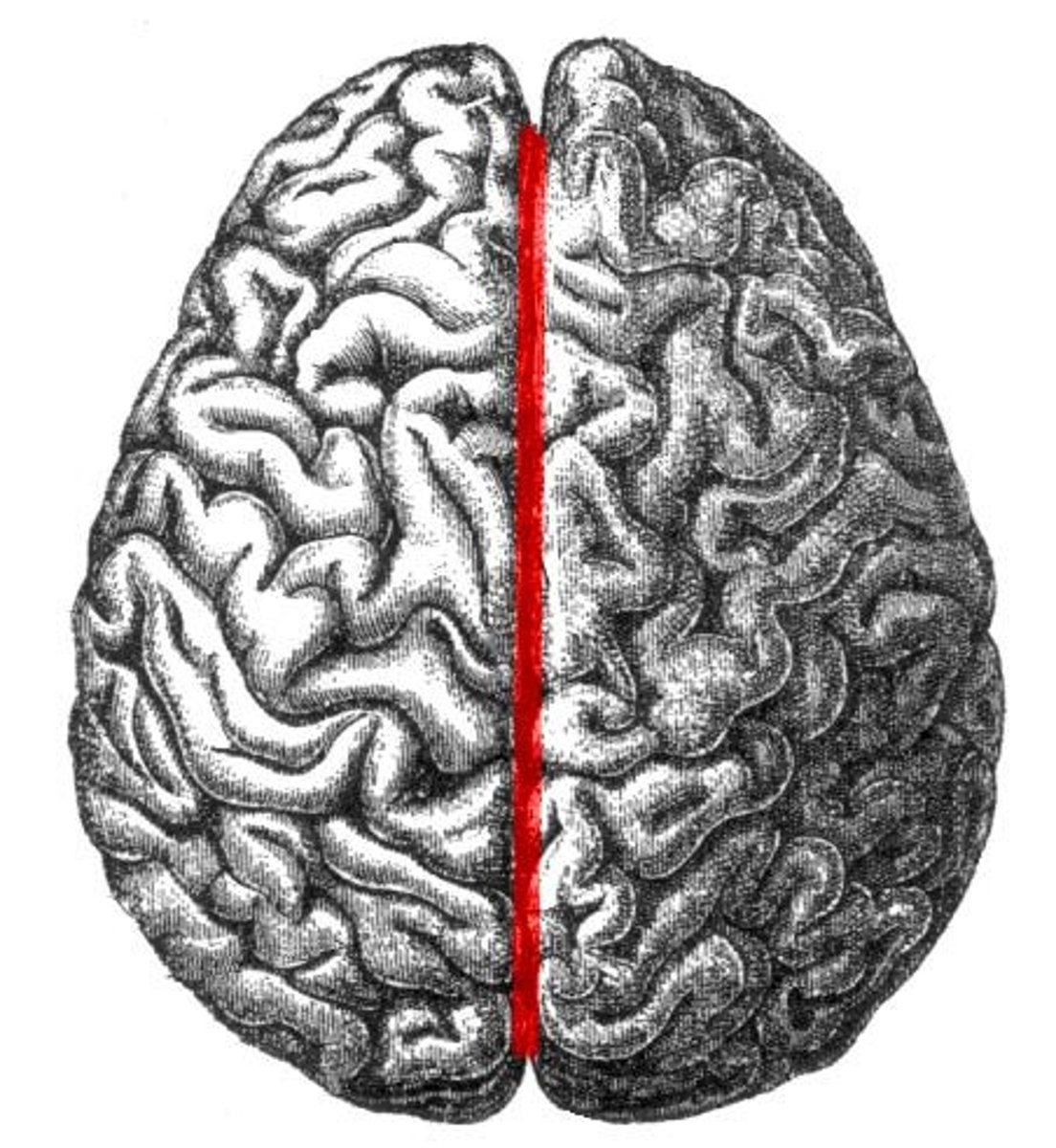
Longitudinal Cerebral Fissure
Divides the right and left cerebral hemispheres.
Central Sulcus
Separates frontal lobe from parietal lobe.
Parieto-occipital Fissure
Separates parietal lobe from occipital lobe.
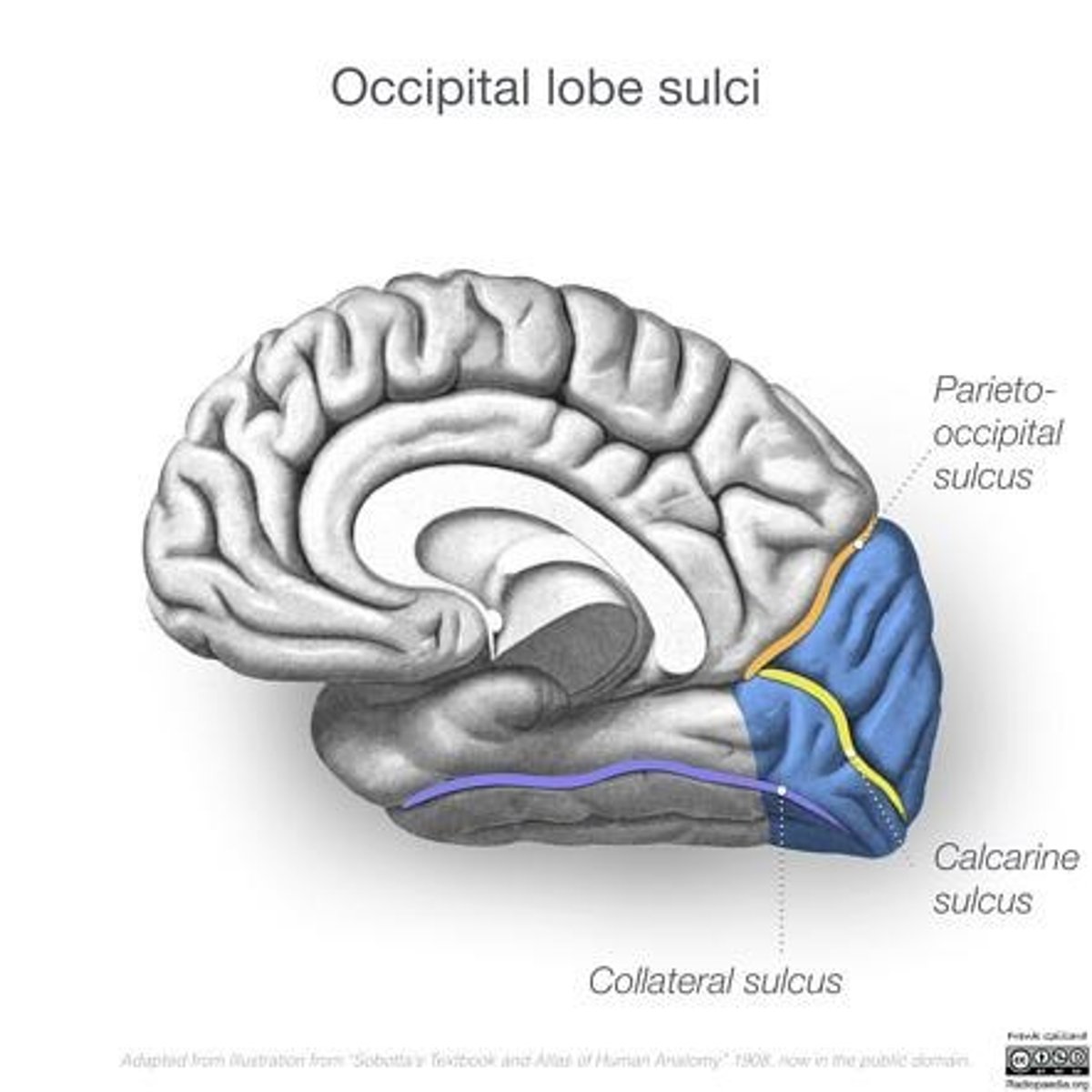
Calcarine Fissure
Located near the occipital pole, involved in vision.
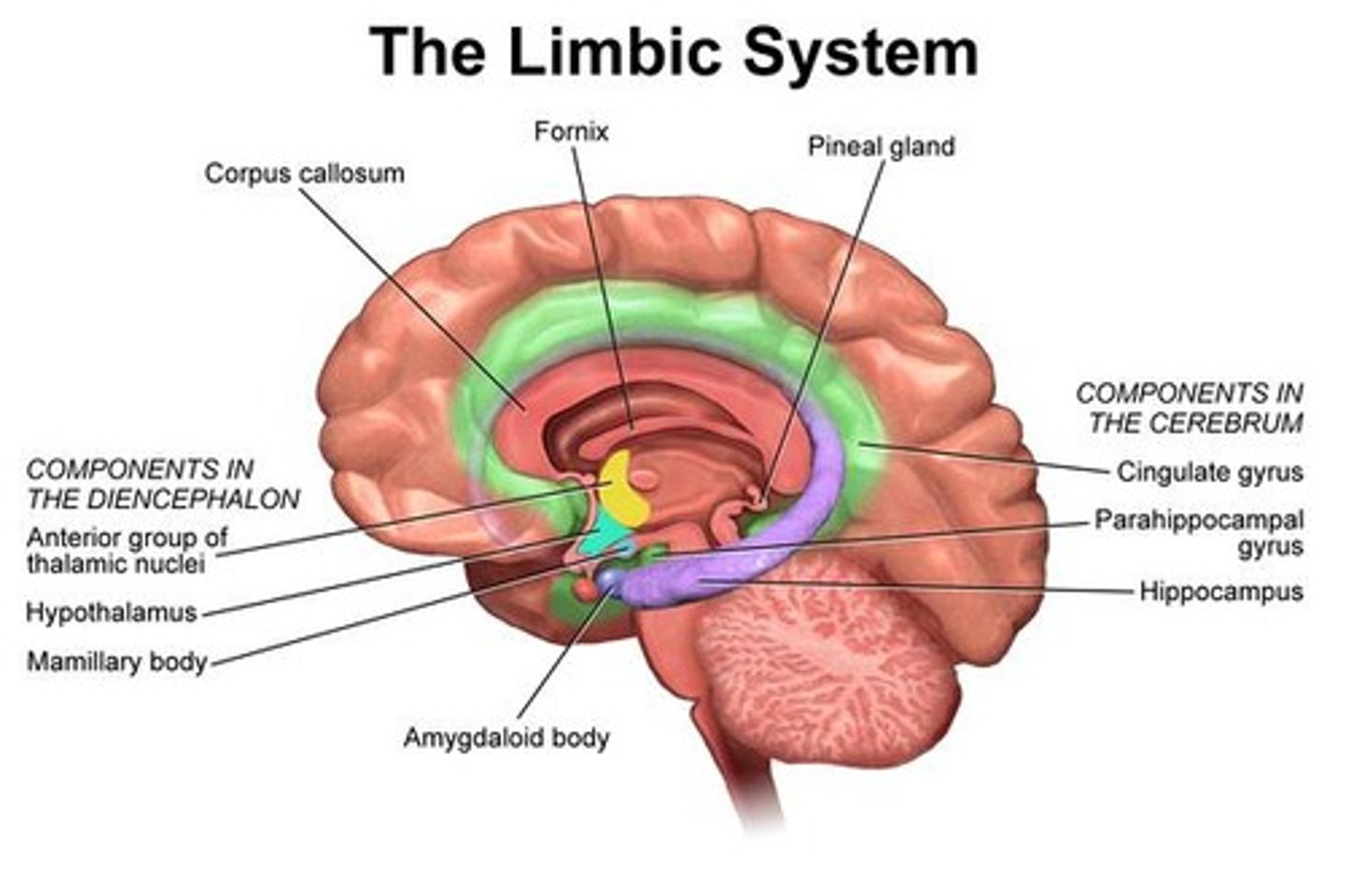
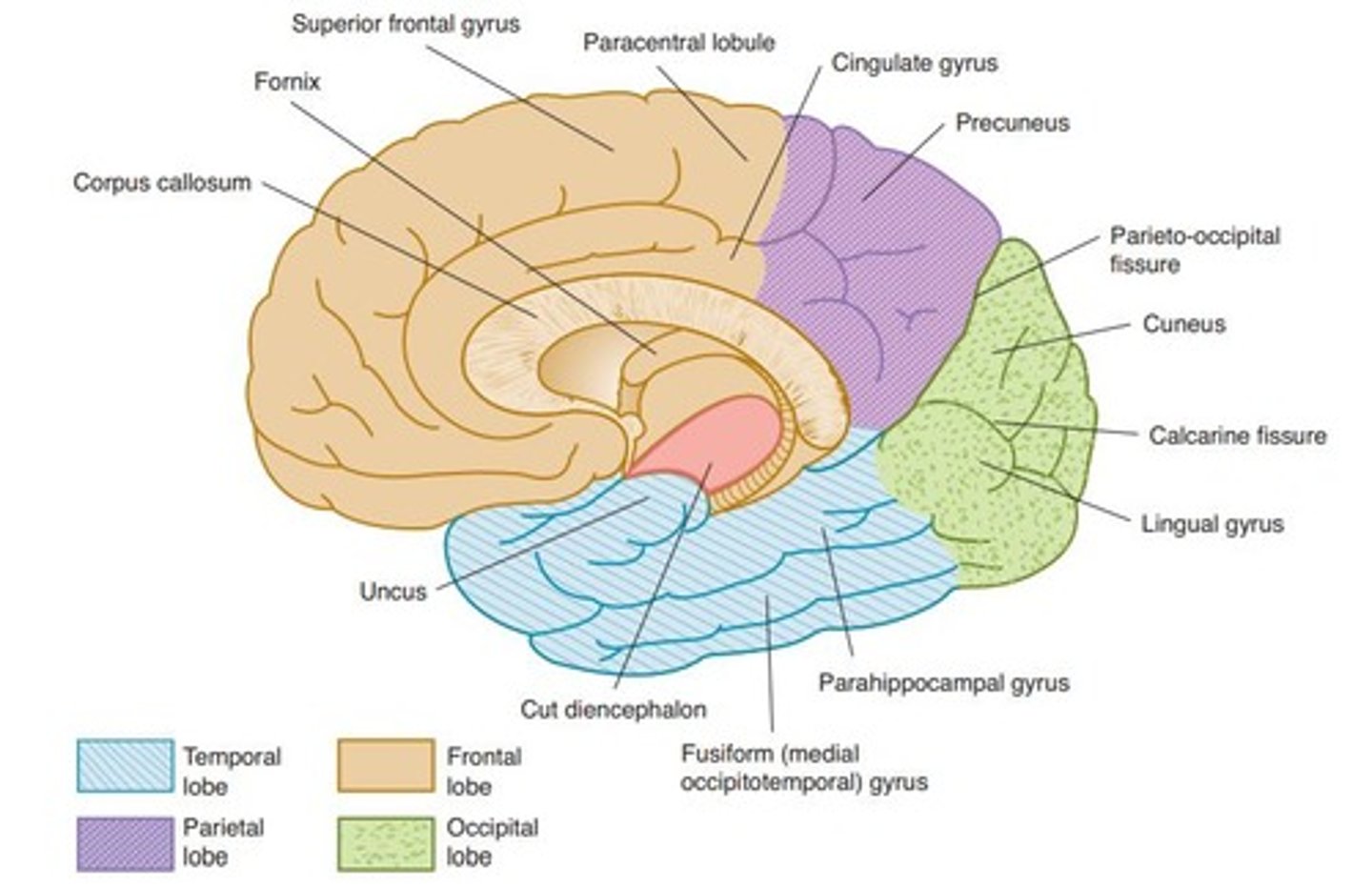
Corpus Callosum
Connects left and right cerebral hemispheres.
Genu
Anterior curved portion of the corpus callosum.
Splenium
Thick posterior portion of the corpus callosum.
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for initiative, judgment, and creativity.
Precentral Sulcus
Located anterior to the precentral gyrus.
Superior Frontal Sulcus
Divides superior frontal gyrus from middle frontal gyrus.
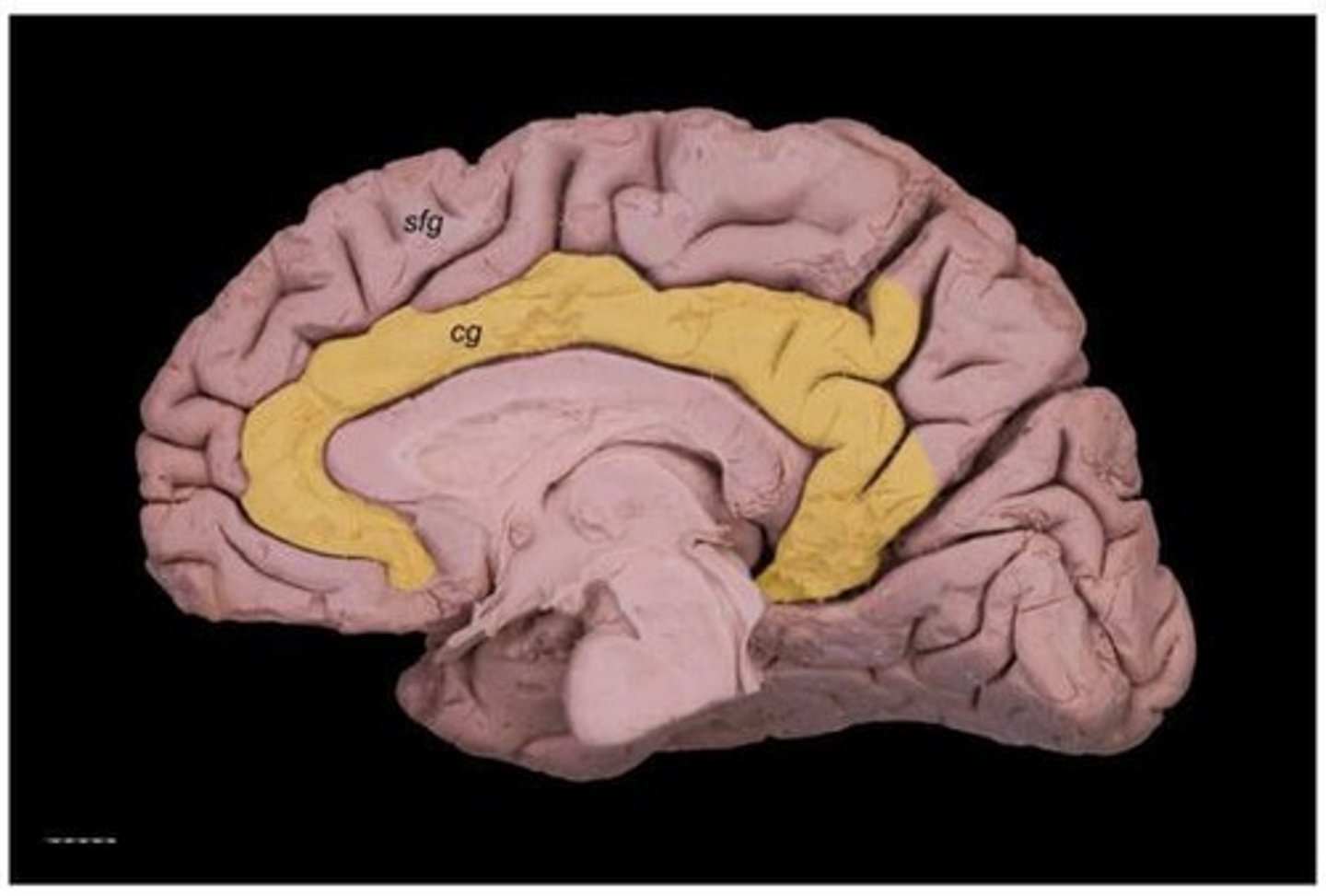
Cingulate Gyrus
Convolution between cingulate sulcus and corpus callosum.
Prefrontal Cortex
Involved in complex cognitive behavior and decision-making.
Higher Order Association Cortex
Involved in judgment, reasoning, and social behavior.
Parietal Lobe
Extends from central sulcus to parieto-occipital fissure.
Postcentral Sulcus
Located behind the postcentral gyrus.
Intraparietal Sulcus
Horizontal groove connecting with postcentral sulcus.
Superior Parietal Lobule
Located above the intraparietal sulcus.
Inferior Parietal Lobule
Located below the intraparietal sulcus.
Supramarginal Gyrus
Arches above the posterior ramus of lateral fissure.
Angular Gyrus
Arches above superior temporal sulcus, connects to middle temporal gyrus.
Occipital Lobe
Houses primary visual cortex behind parieto-occipital fissure.
Temporal Lobe
Lies below lateral cerebral fissure, extends to parieto-occipital fissure.
Transverse Temporal Gyrus
Occupies posterior part of superior temporal surface.
Hippocampal Gyrus
Extends along inferomedian aspect of temporal lobe.
Uncus
Most medial part of temporal lobe, hook-shaped.
Limbic System
Includes cingulate, parahippocampus, subcallosal gyri, hippocampal formation.
White Matter of Cerebrum
Contains myelinated nerve fibers and neuroglia.
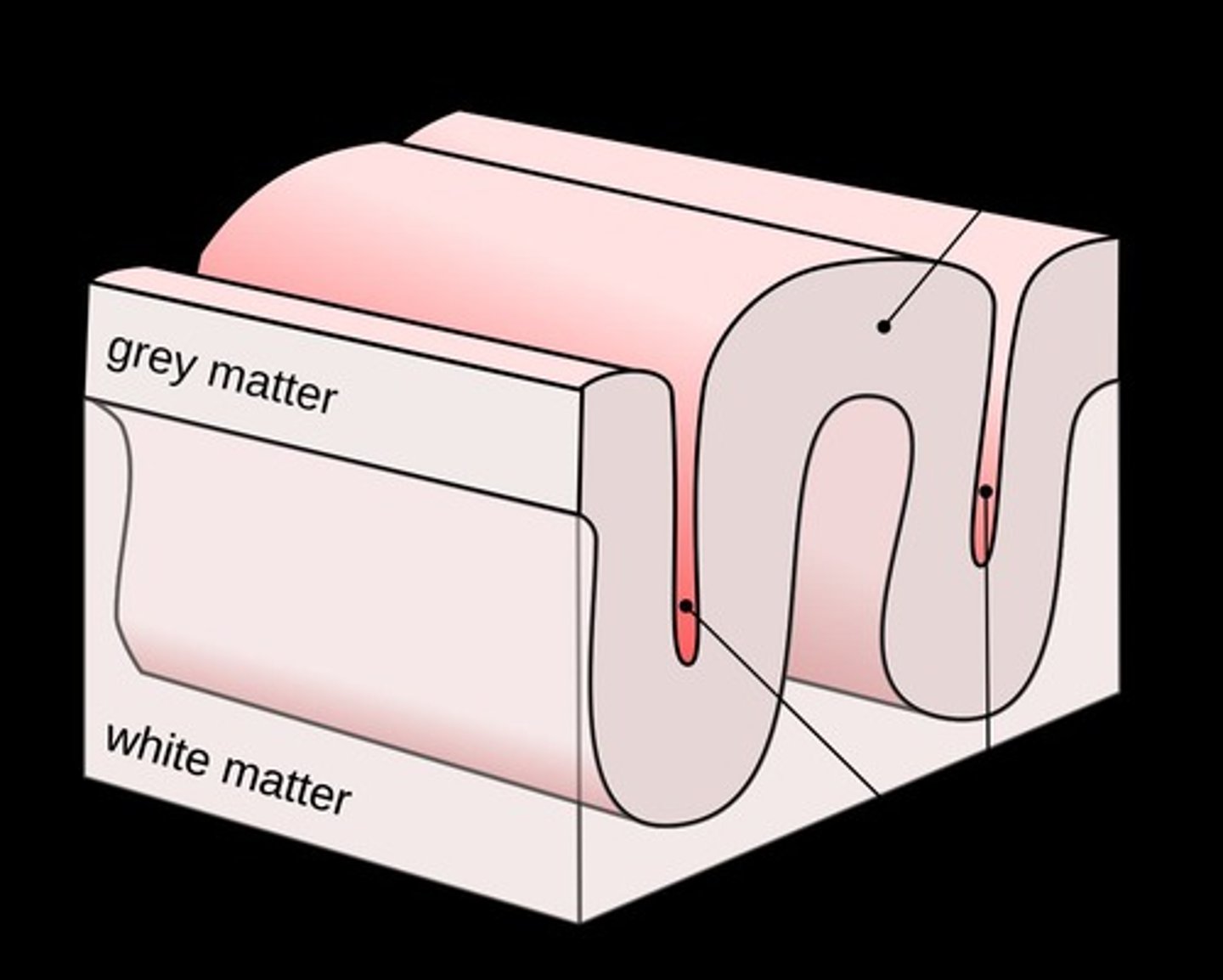
Centrum Semiovale
Myelinated fibers in the white matter of cerebrum.
Transverse (Commissural) Fibers
Interconnect both cerebral hemispheres.
Anterior Commissure
Connects olfactory bulbs and temporal lobe structures.
Projection Fibers
Connect cortex to lower brain or spinal cord.
Association Fibers
Connect various portions of a cerebral hemisphere.
Pyramidal Cells
Type of neuron in the cerebral cortex.
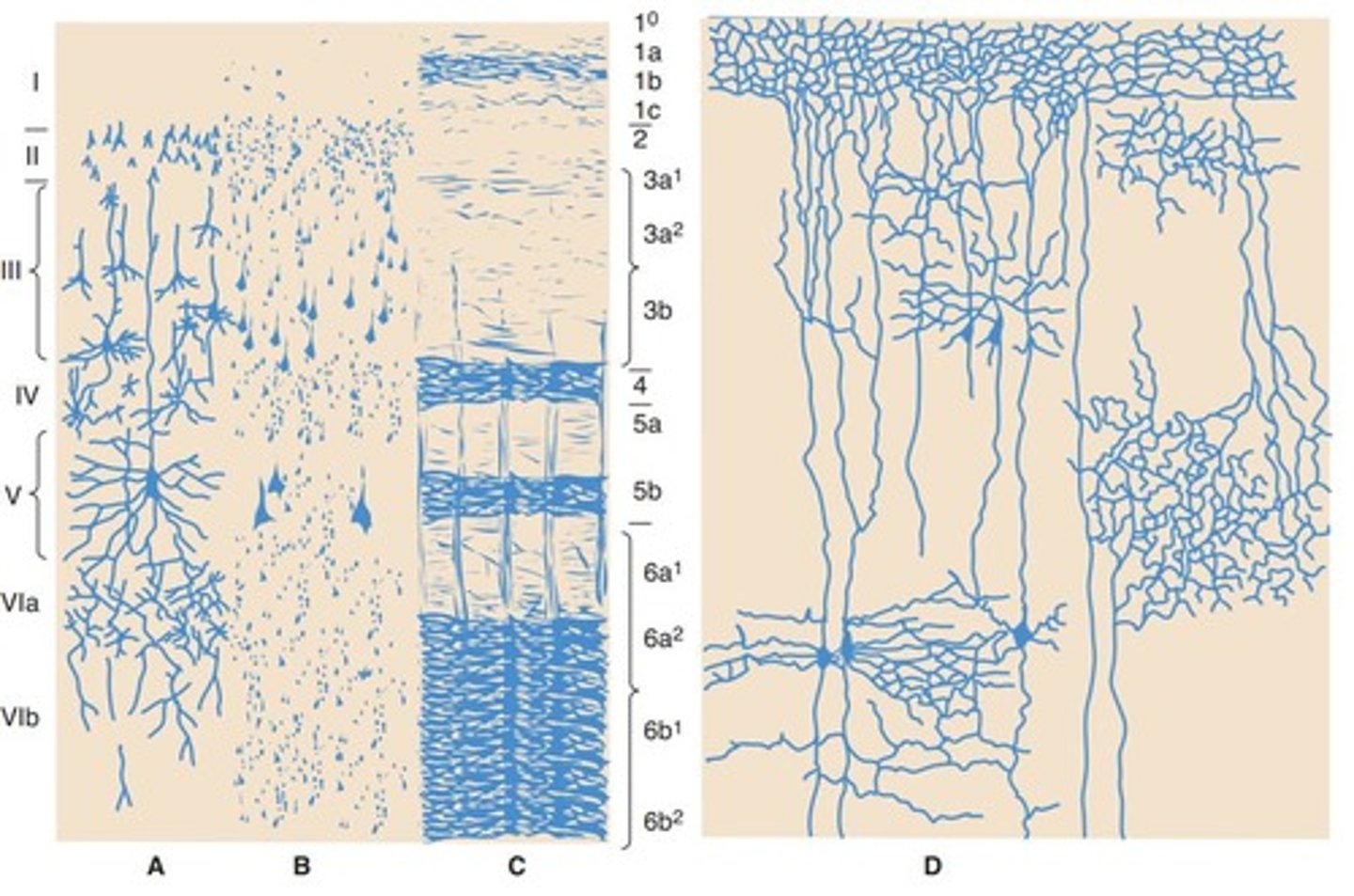
Stellate Neurons
Another type of neuron in the cortex.
Fusiform Neurons
Third type of neuron in the cortex.
Allocortex
Found in limbic system, fewer layers than isocortex.
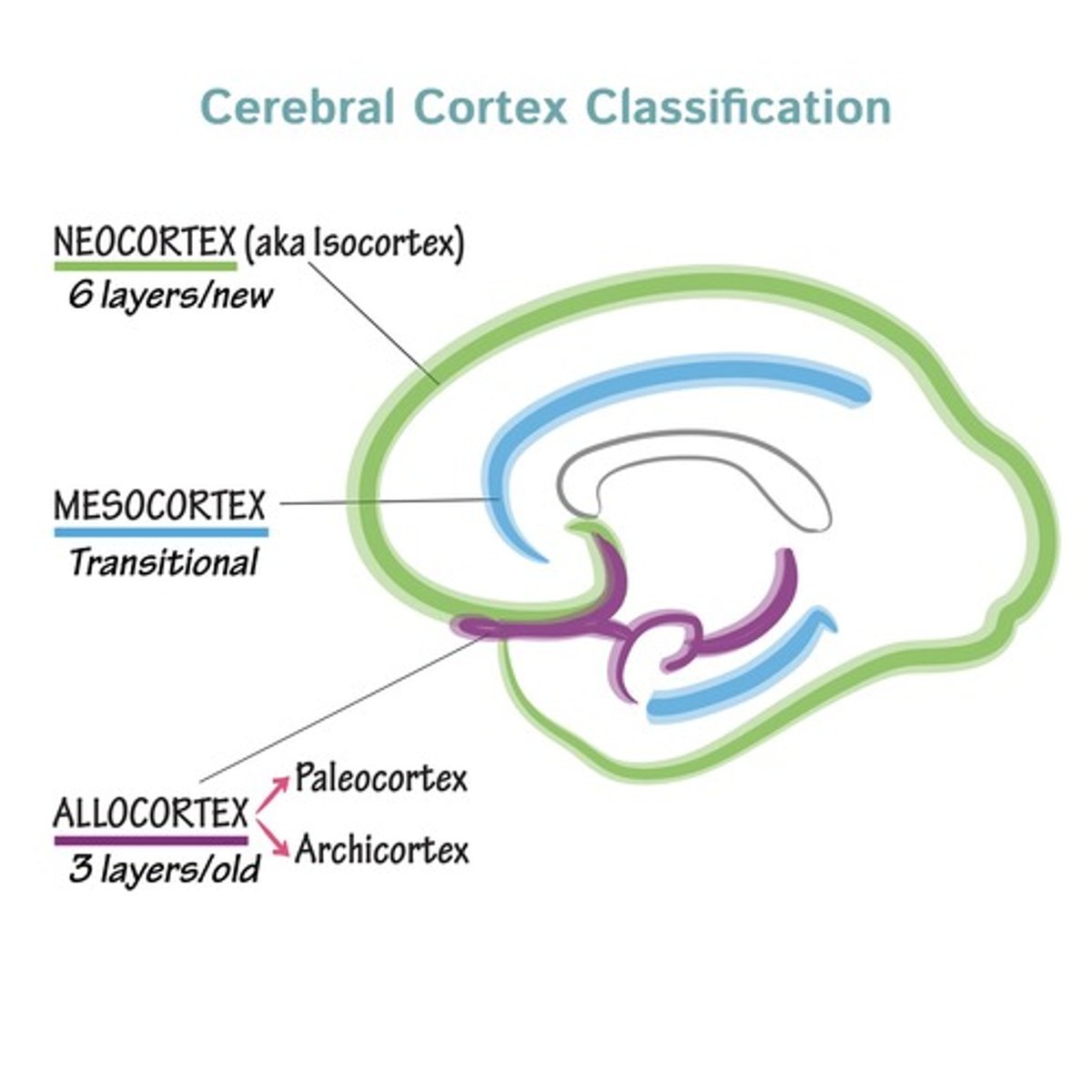
Isocortex (Neocortex)
Common in cerebral hemisphere, contains six layers.
Juxtallocortex (Mesocortex)
Transition area between allocortex and isocortex.
Molecular layer
Layer I of the isocortex, superficial layer.
External granular layer
Layer II of the isocortex, contains small neurons.
External pyramidal layer
Layer III of the isocortex, contains pyramidal neurons.
Internal granular layer
Layer IV of the isocortex, receives sensory input.
Internal pyramidal layer
Layer V of the isocortex, sends output to subcortical areas.
Fusiform layer
Layer VI of the isocortex, involved in integration.
Brodmann's Classification
System for naming functional areas of the cortex.
Area 4
Primary Motor Area for voluntary muscle activation.
Corticospinal Tract
Pathway for voluntary motor control from the brain.
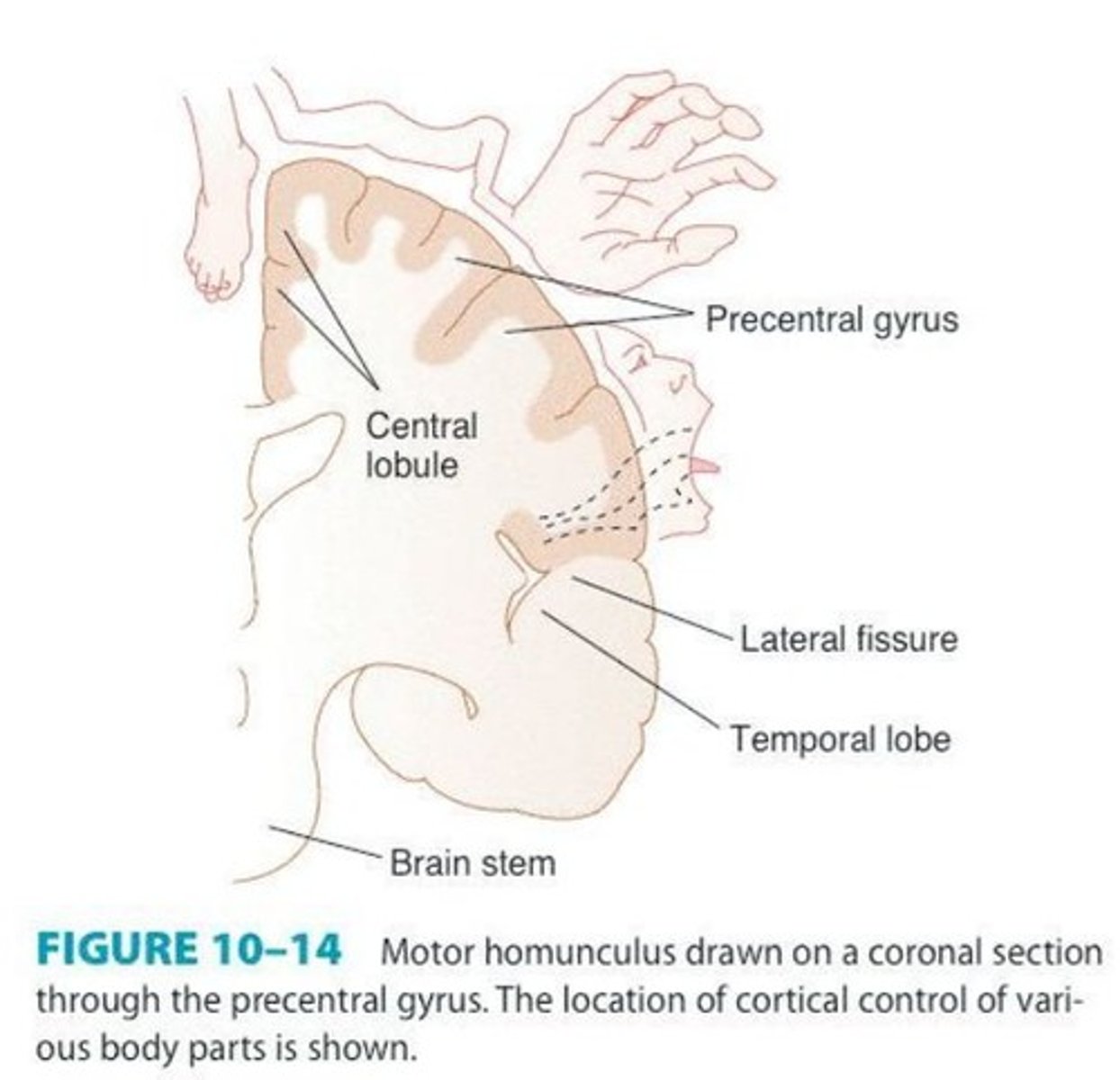
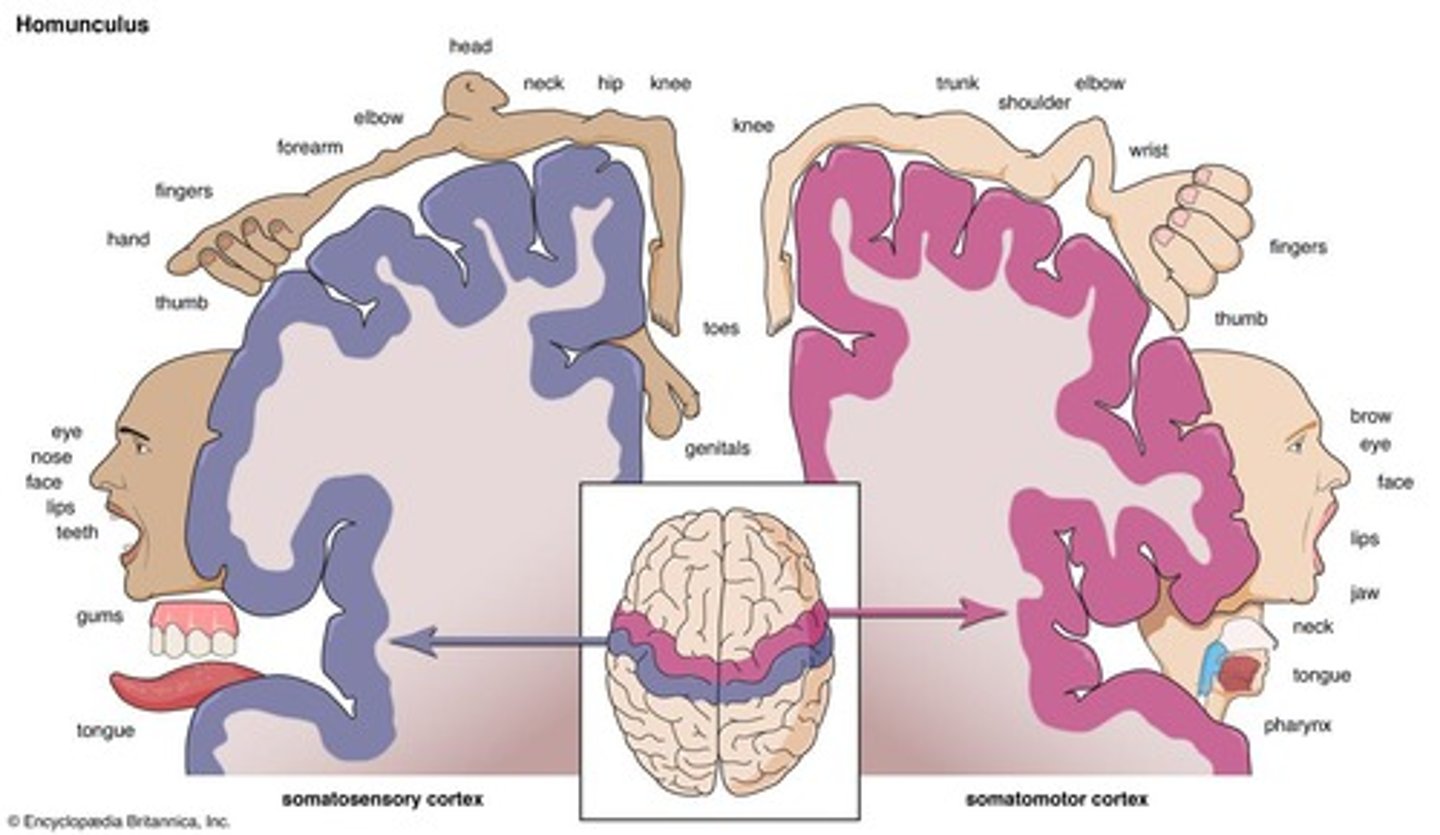
Motor homunculus
Representation of body parts in the motor cortex.
Area 6
Premotor Area for planning and organizing movements.
Area 8
Frontal Eye Field, controls eye movements.
Broca's area
Areas 44 and 45, involved in speech production.
Areas 3, 1, 2
Primary Sensory Area for processing sensory information.
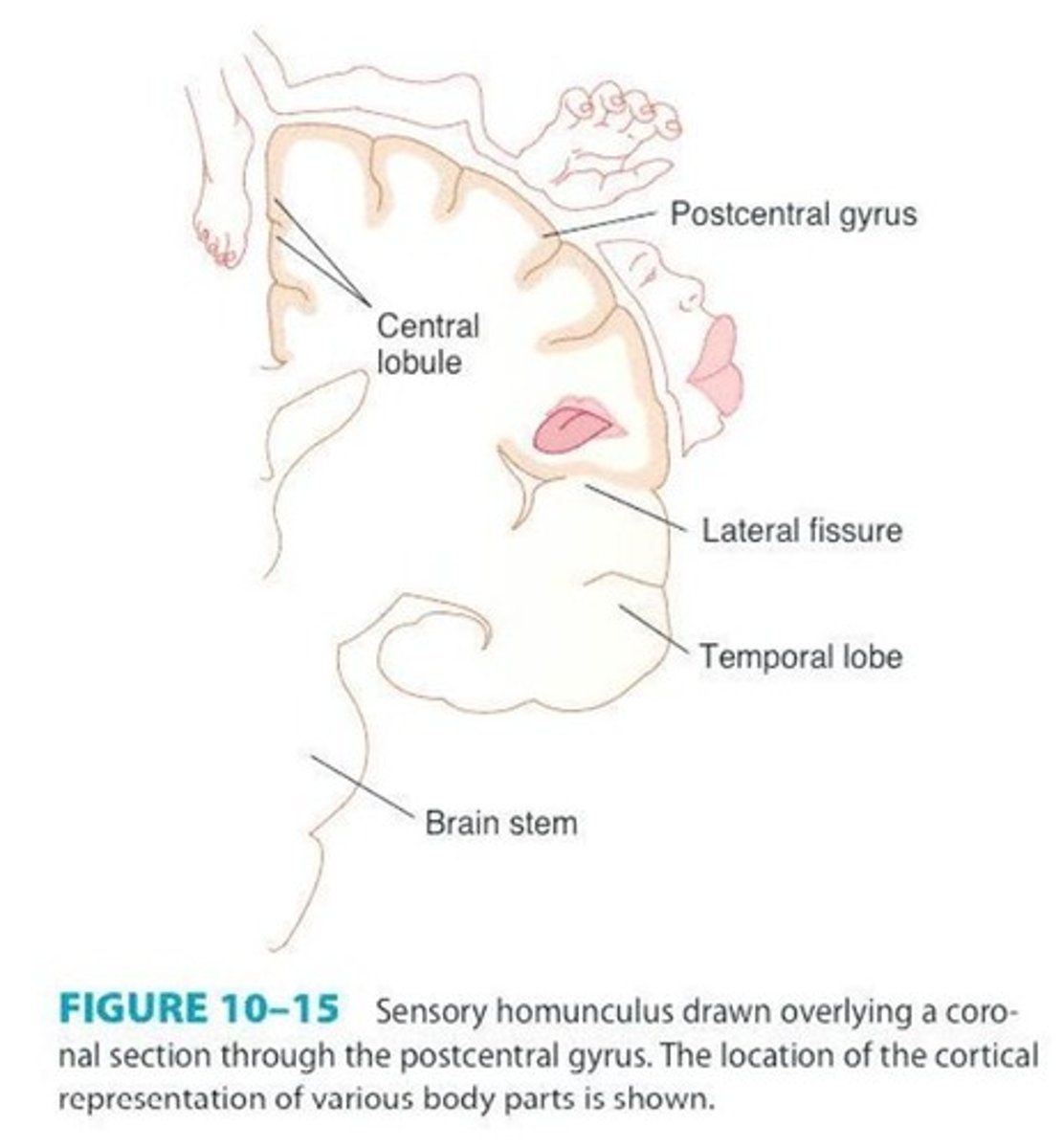
Sensory homunculus
Representation of body parts in the sensory cortex.
Area 17
Primary Visual Cortex, processes visual stimuli.
Area 41
Primary Auditory Cortex, processes auditory stimuli.
Area 42
Associative Auditory Cortex, enhances auditory processing.
Heschl's gyrus
Combined areas 41 and 42 for auditory processing.
Area 22
Auditory Association Cortex, involved in language comprehension.
Planum Temporale
Region for language and music processing.
Primary Motor Cortex
Located in precentral gyrus, controls voluntary movements.
Giant pyramidal cells
Betz cells controlling skeletal muscle movements.
Jacksonian epilepsy
Focal twitching progressing to larger muscle involvement.
Contralateral flaccid paresis
Weakness on opposite side due to lesions.
Primary Sensory Cortex
Processes sensory information from body and face.
Somatesthetic area
Located in postcentral gyrus, processes touch sensations.
Cortical Taste Area
Processes gustatory information from the body.
Irritative lesions
Cause abnormal sensations like tingling or numbness.
Destructive lesions
Lead to impaired sensory perception and localization.
Primary Visual Cortex
Located in occipital lobe, processes visual information.
High-resolution macular vision
Posterior portion of Primary Visual Cortex function.
Peripheral vision
Anterior portion of Primary Visual Cortex function.
Visual Association Area
Includes Areas 18 and 19 for visual processing.
Visual hallucinations
Irritative lesions cause flashes or bright lights.
Contralateral homonymous defects
Destructive lesions affect visual fields opposite side.
Visual disorganization
Injury to Areas 18-19 affects spatial orientation.
Primary Auditory Receptive Cortex
Located in transverse temporal gyrus, processes sound.
Low tones representation
Frontolateral portion of Area 41 for low frequencies.
High tones representation
Occipitomedial portion of Area 41 for high frequencies.
Wernicke Area
Area 22, crucial for speech comprehension.
Buzzing sensations
Irritation of auditory cortex causes abnormal sounds.
Unilateral lesion effects
Results in mild hearing loss on one side.
Bilateral lesion effects
Causes complete deafness in both ears.
Wernicke's Aphasia
Damage to Area 22 leads to pure word deafness.
Basal Ganglia
Gray matter masses essential for motor control.
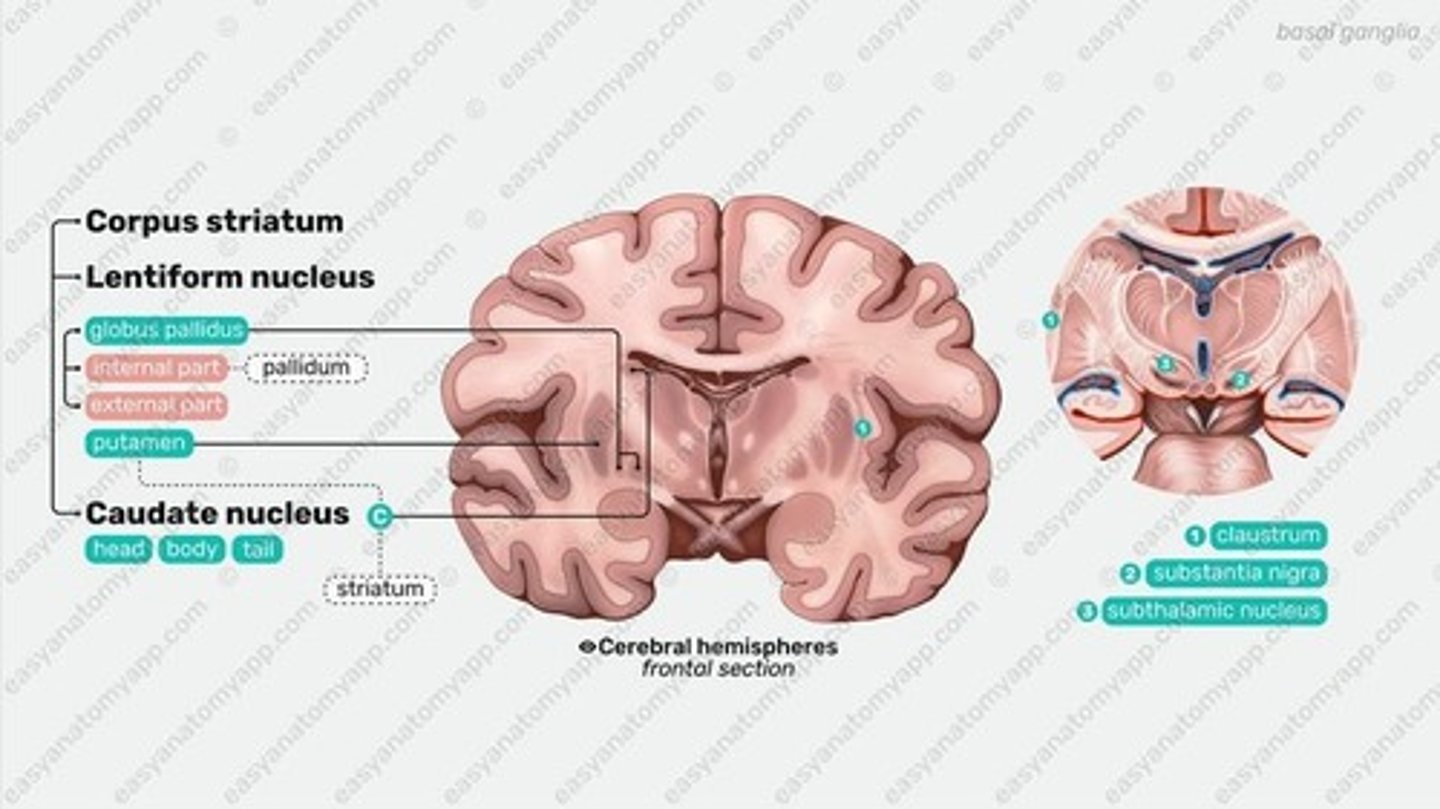
Corpus Striatum
Combined term for caudate nucleus and putamen.
Striatum
Caudate nucleus and putamen develop together.
Lenticular Nuclei
Putamen and globus pallidus form lensed shape.
Caudate Nucleus
Elongated mass, major input site for basal ganglia.
Lenticular Nucleus
Divided by External Medullary Lamina into two parts.