Chapter 25 - Internal Balance
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
homeostasis
The maintenance of the internal conditions in your body.
arteries
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart and finally branch into capillaries.
circulatory system
heart, blood vessels, and blood
What’s the main system for maintaining homeostasis?
The circulatory system
The body’s defense system
Also helps maintain homeostasis. This includes the skin.
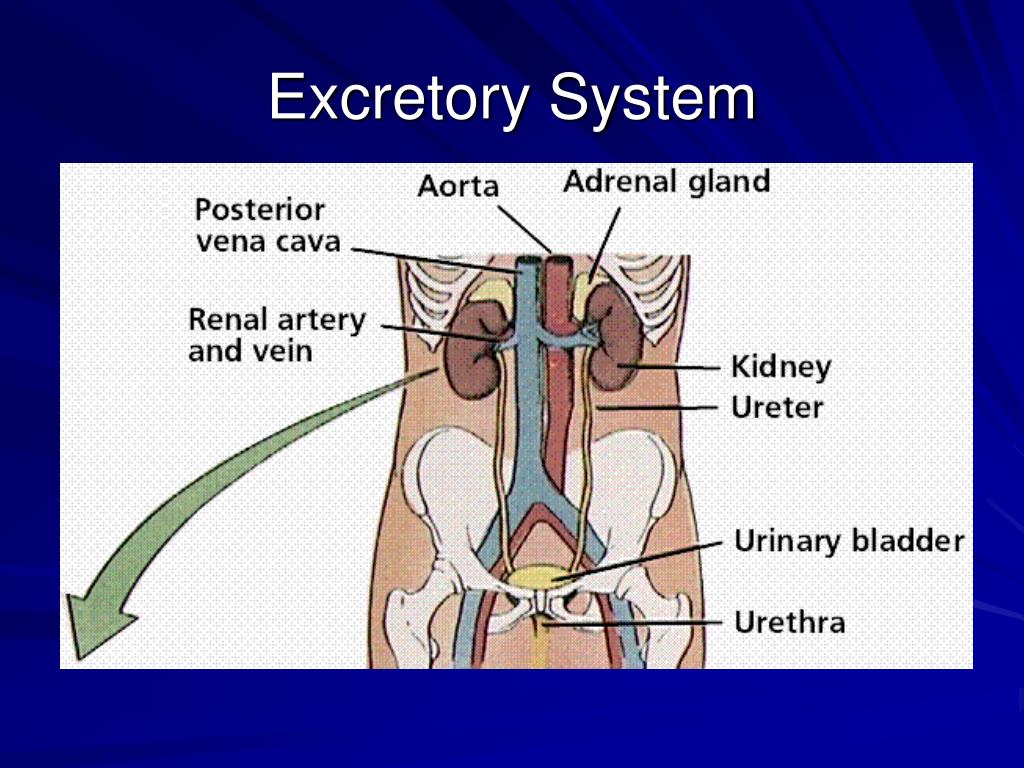
extretory system
Also helps maintain homeostasis. This includes the kidneys which filters wastes from your blood.
cardiovascular
“heart vessel”

capillaries
The smallest blood vessels where materials are exchanged between the blood and the body cells.
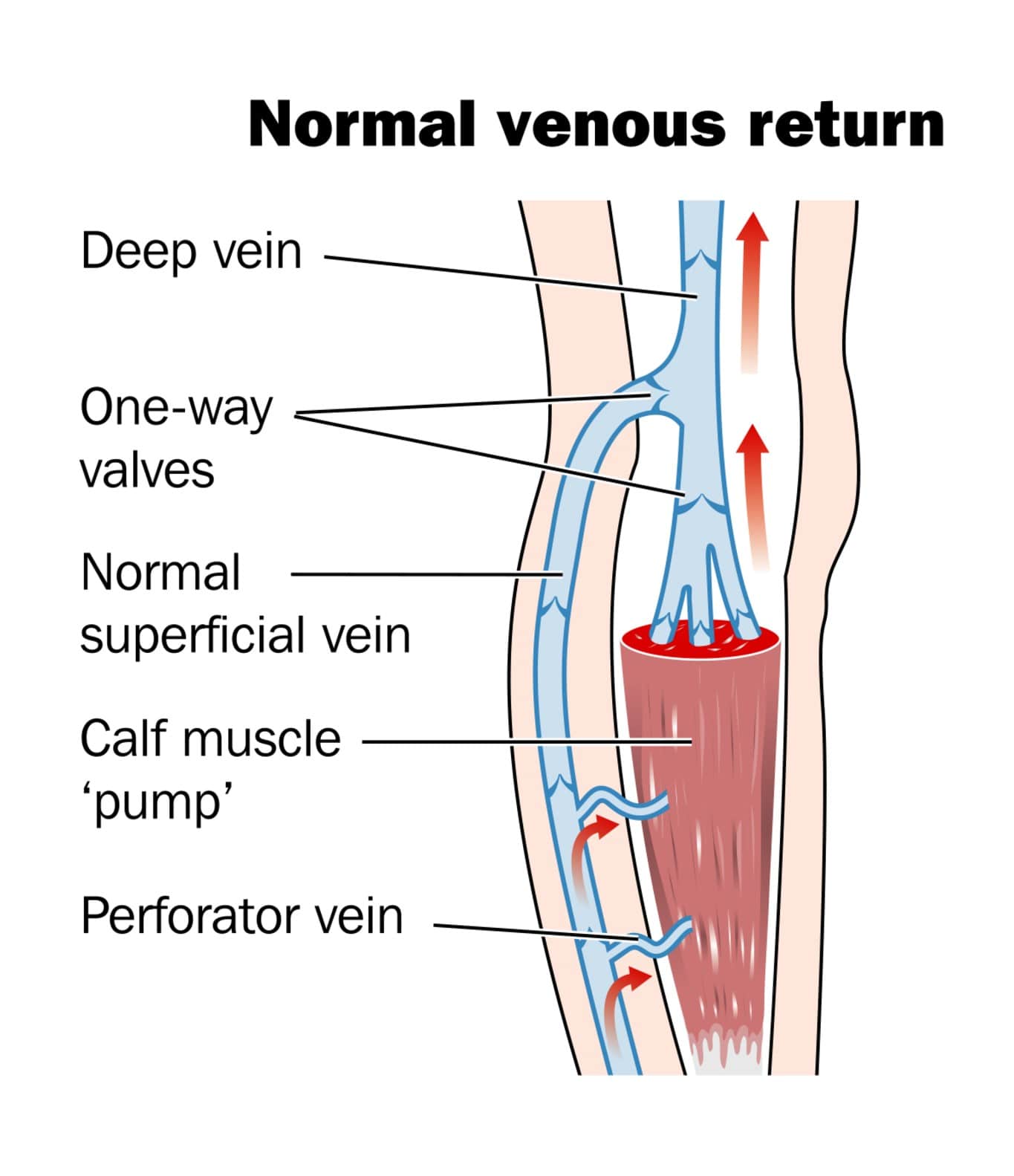
Which vessels have valves?
Veins, which take blood to the heart have one-way valves. This way your blood flows in only one direction.
How many beats per minutes does the average person’s heart beat while resting?
70 bpm (beats per minute)

What do capillaries merge to form?
veins
pacemaker
The part of the heart that automatically causes it to beat at your normal heart rate.
pulse
The rhythmic expansion of the arteries caused by pressure from blood being forces through an artery.
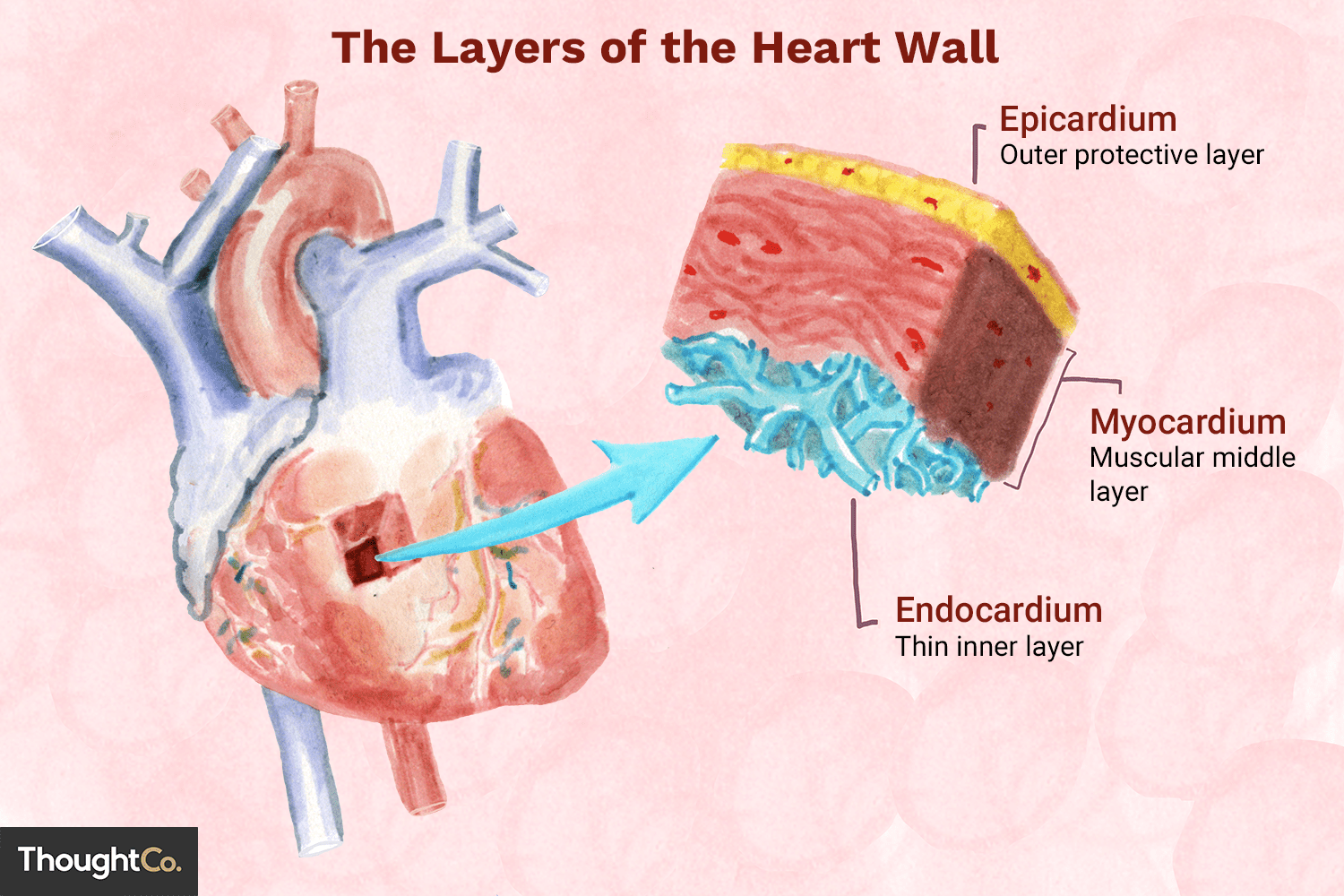
Which section of the heart has the thickest walls?
mayocardium
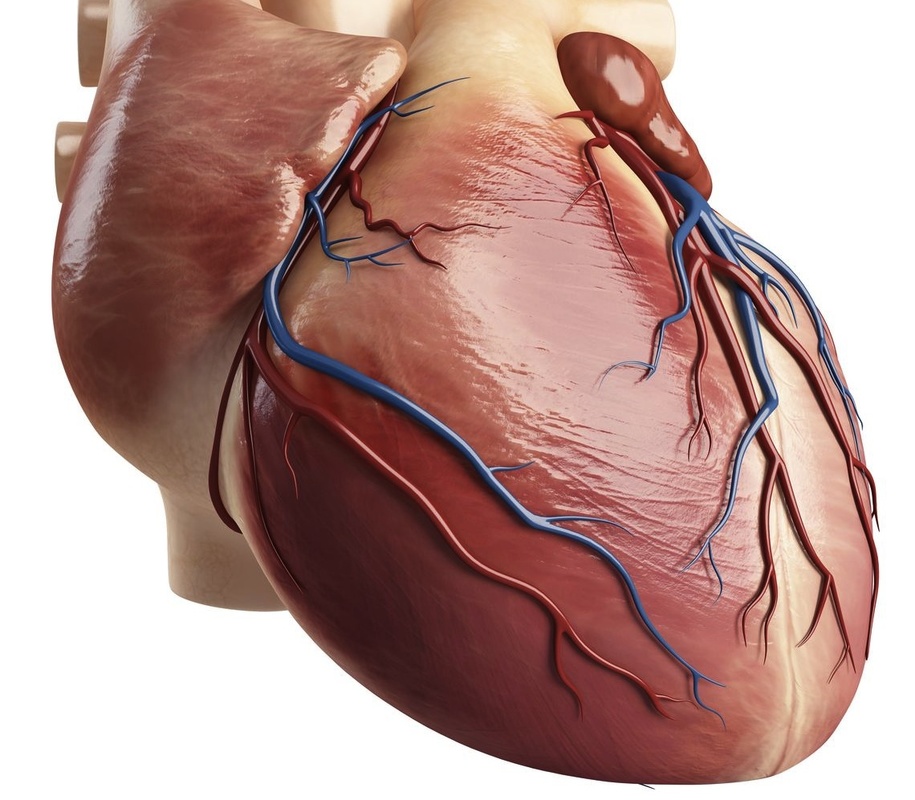
What’s the hearts only function?
to pump blood
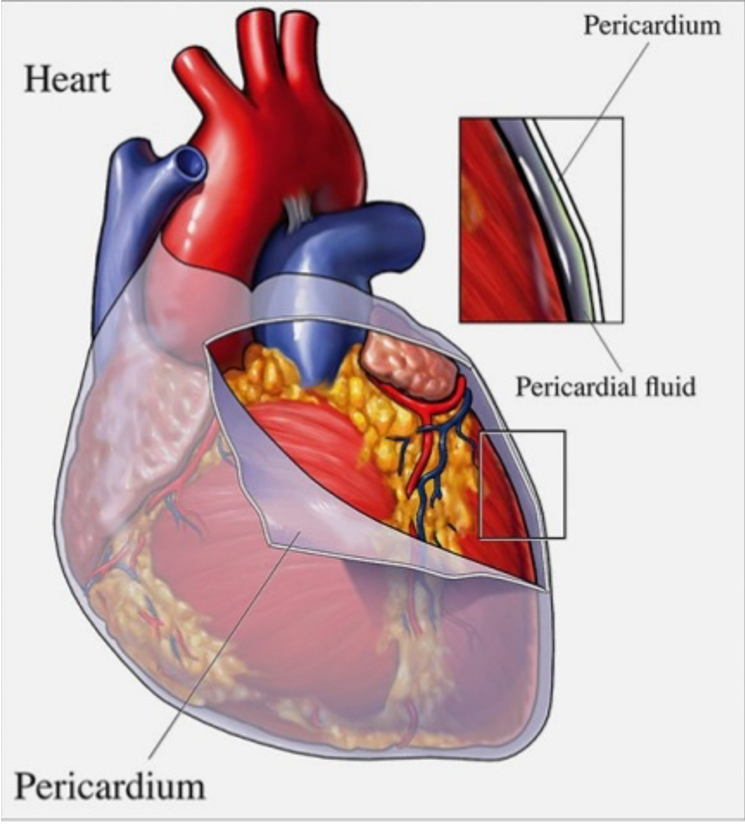
pericardium
The fluid-filled sac that your heart is in. It helps prevent friction.
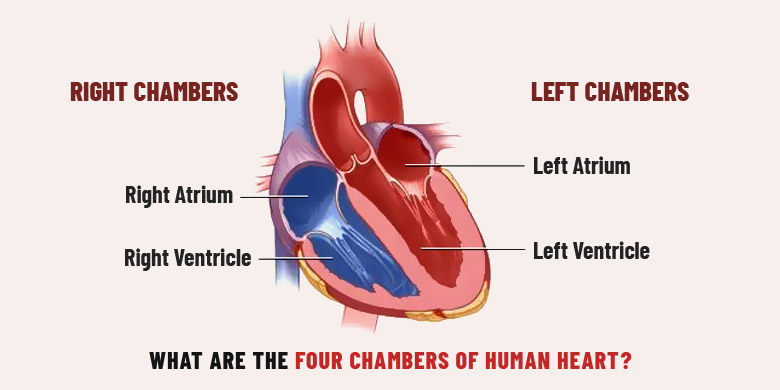
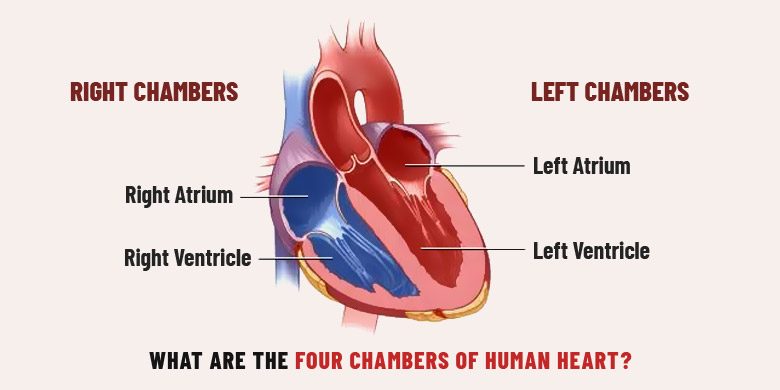
artria
The upper two chambers of the heart. H
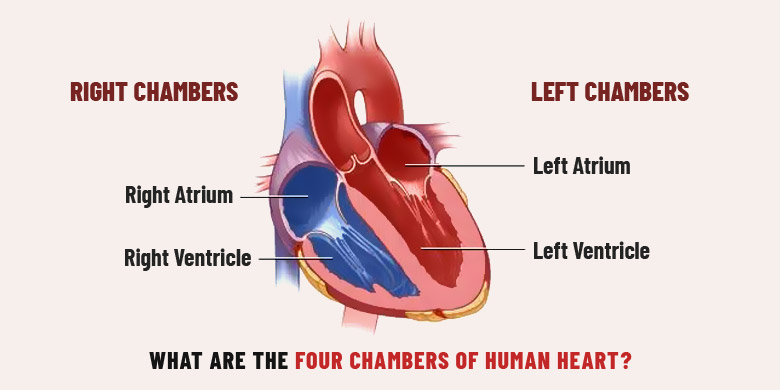
How many chambers does the heart have?
Four
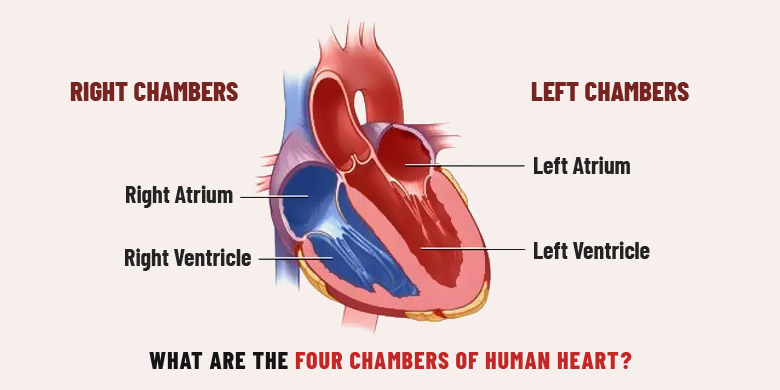
ventricles
The lower two chambers of the heart. They are thick-walled and larger than the upper chambers (the atria).
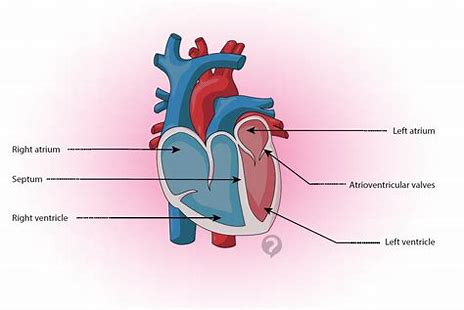
septum
The muscular wall of the heart that separates the left and right sides on the heart.
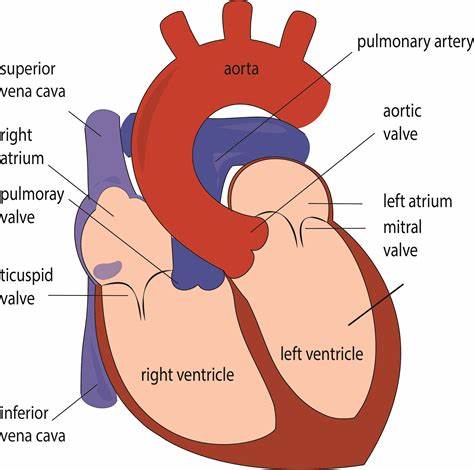
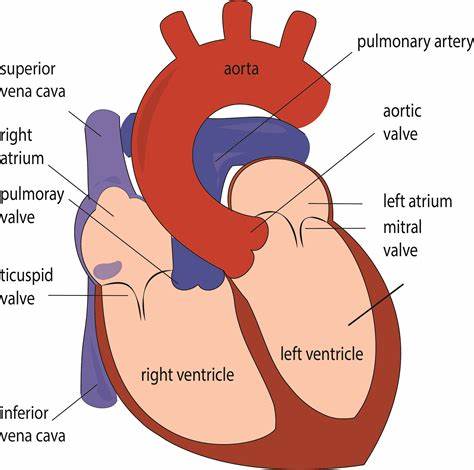
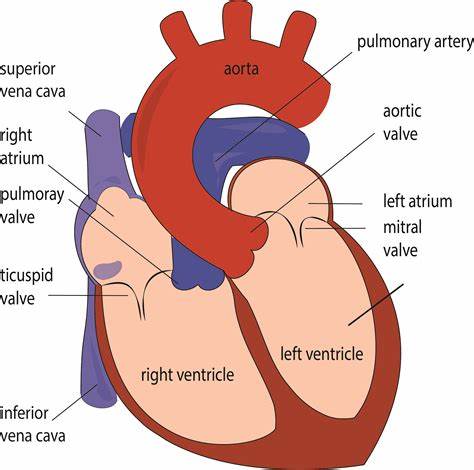
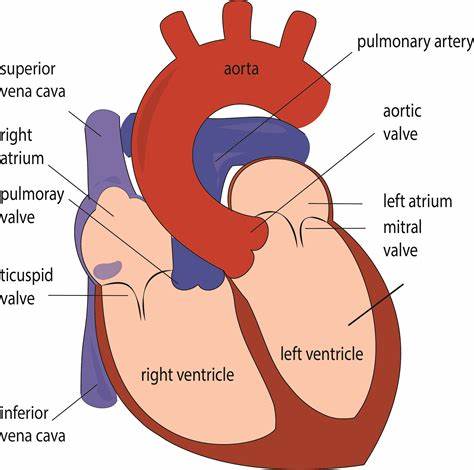
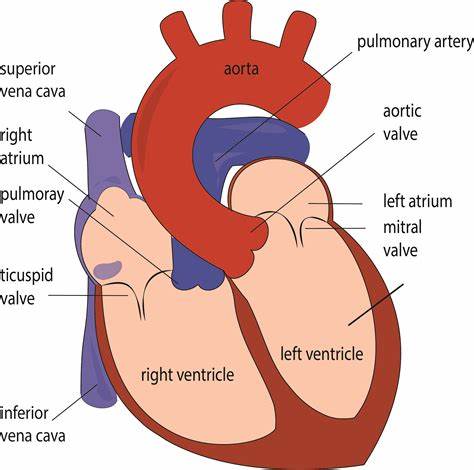
Memorize the location of the aorta
aorta (The largest artery. It branches out to supply blood to all of the body.)
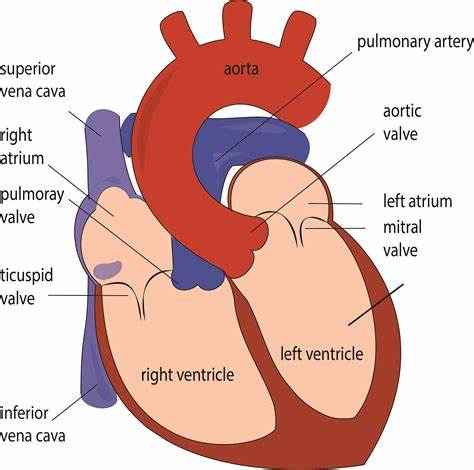
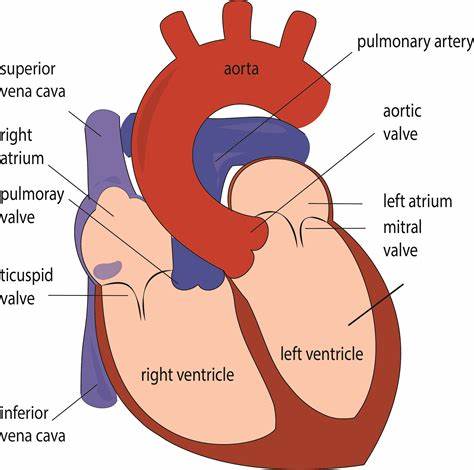
Memorize the location of the pulmonary arteries
pulmonary arteries (Notice them on both sides of the heart. They carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs.)
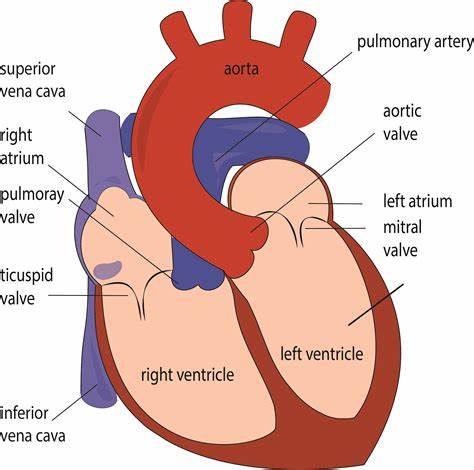
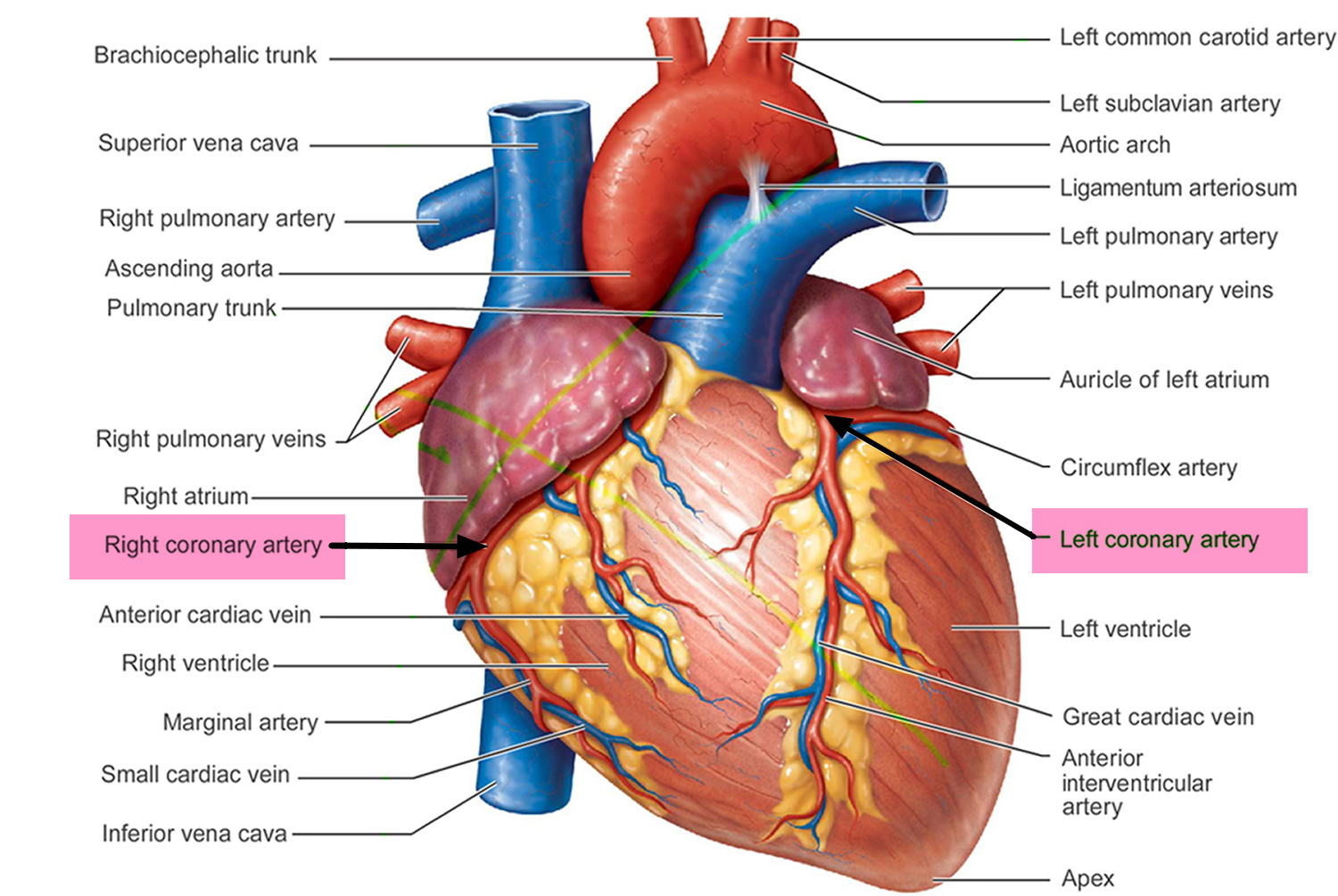
Memorize the location of the pulmonary veins
pulmonary veins (notice them on both sides of the heart)
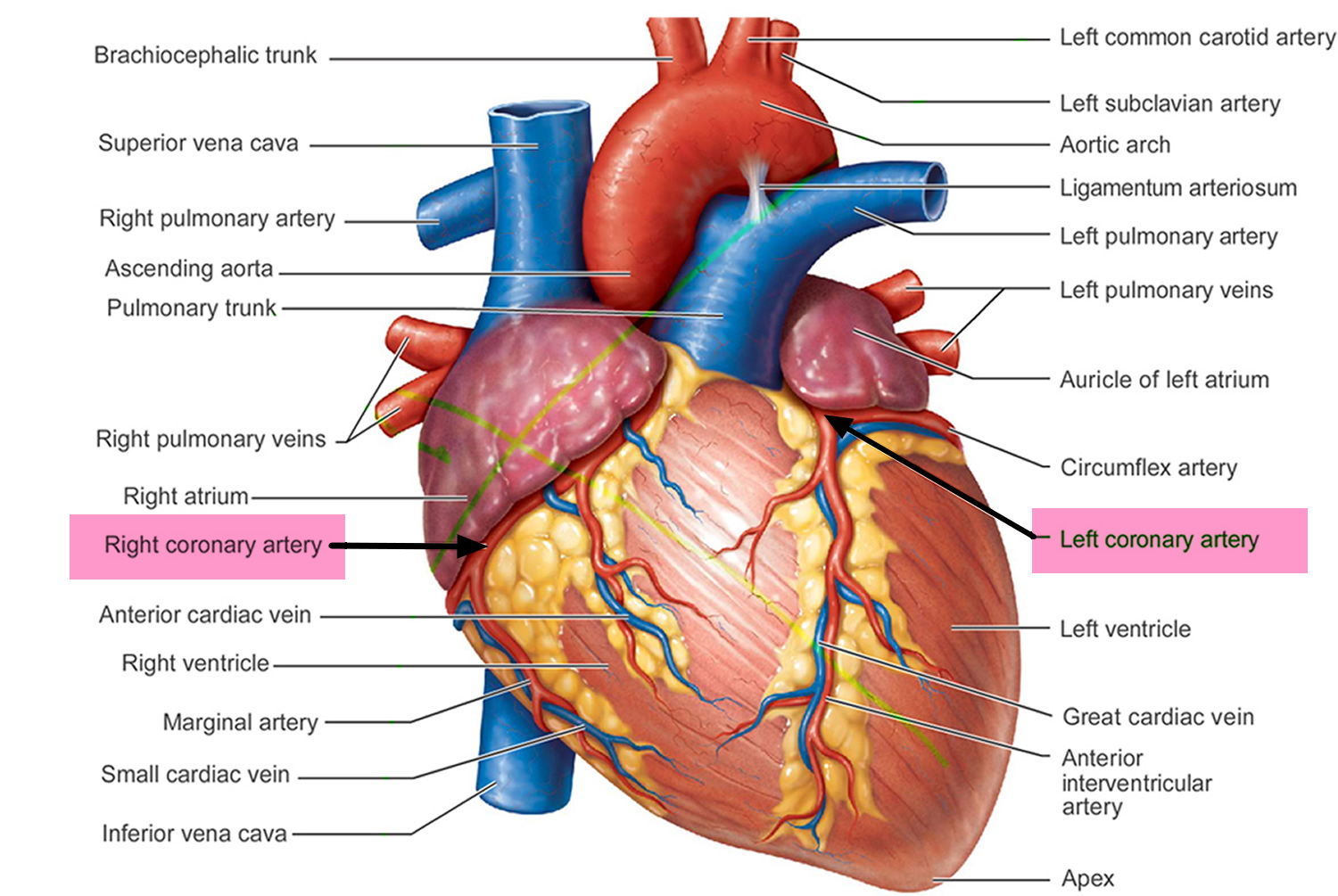
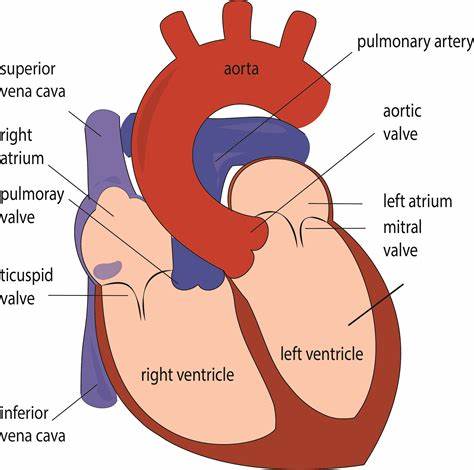
Memorize the location of the left atrium
left atrium
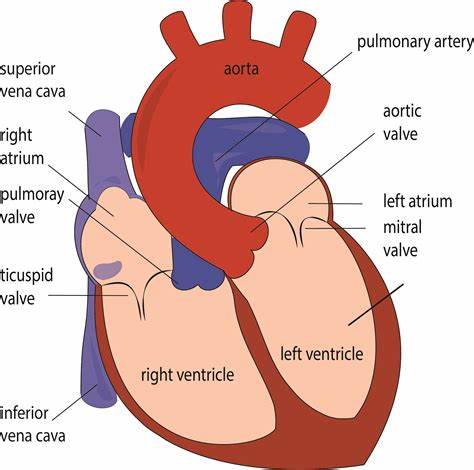
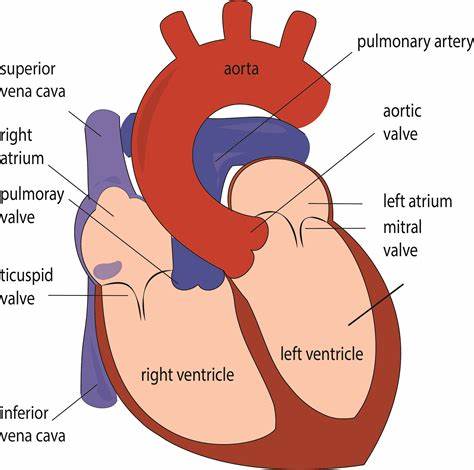
Memorize the location of the mitral valve
mitral valve (This is also known in your book as one the Atrioventricular, AV valves. It prevents the valves from swinging back into the atria.)
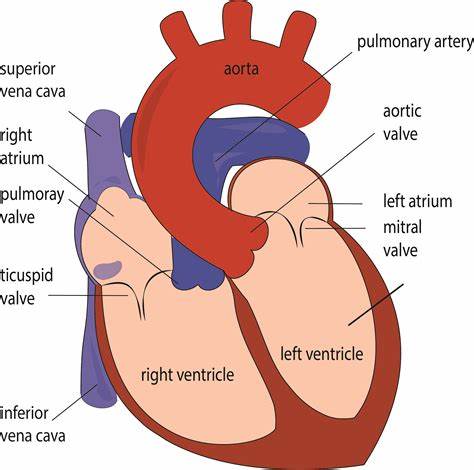
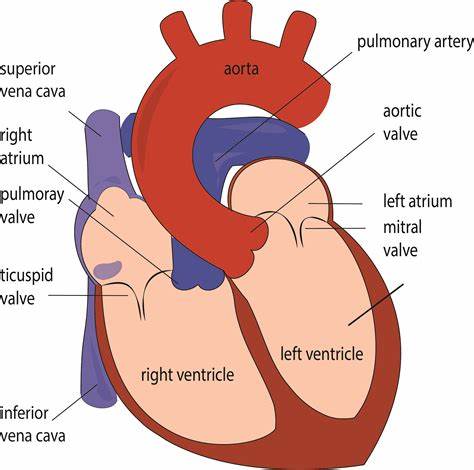
Memorize the location of the left ventricle
left ventricle
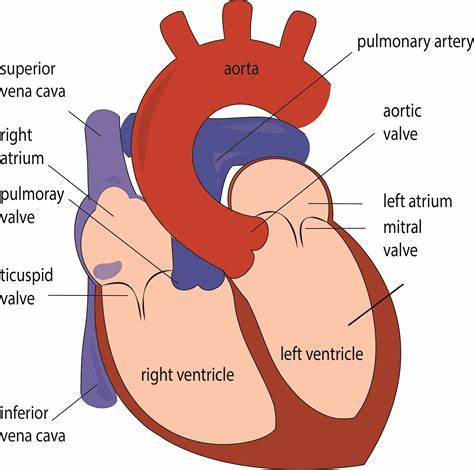
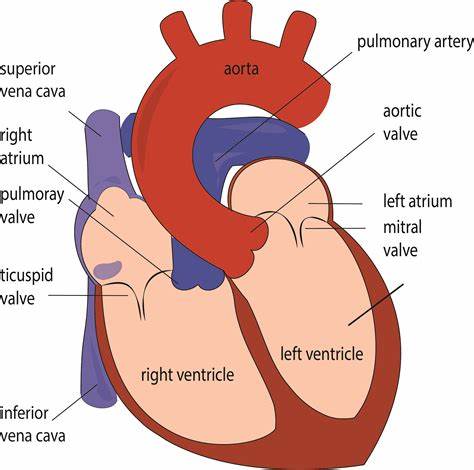
Memorize the location of the septum
septum
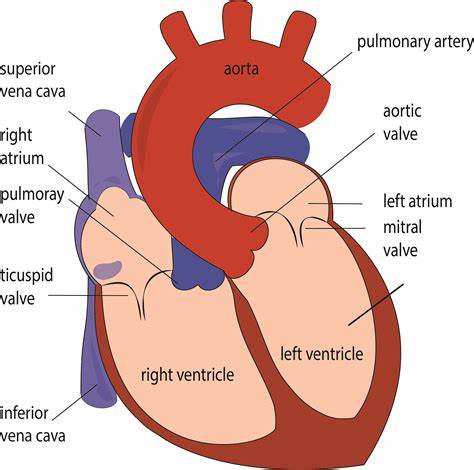
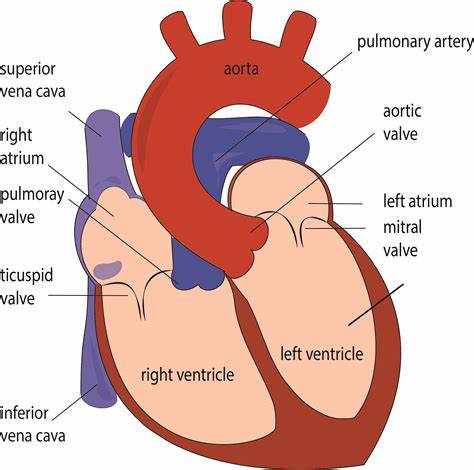
Memorize the location of the right ventricle
right ventricle
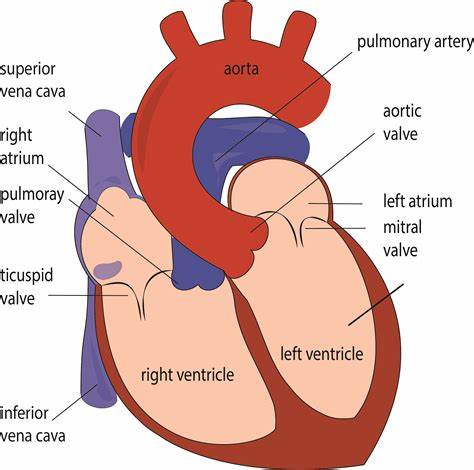
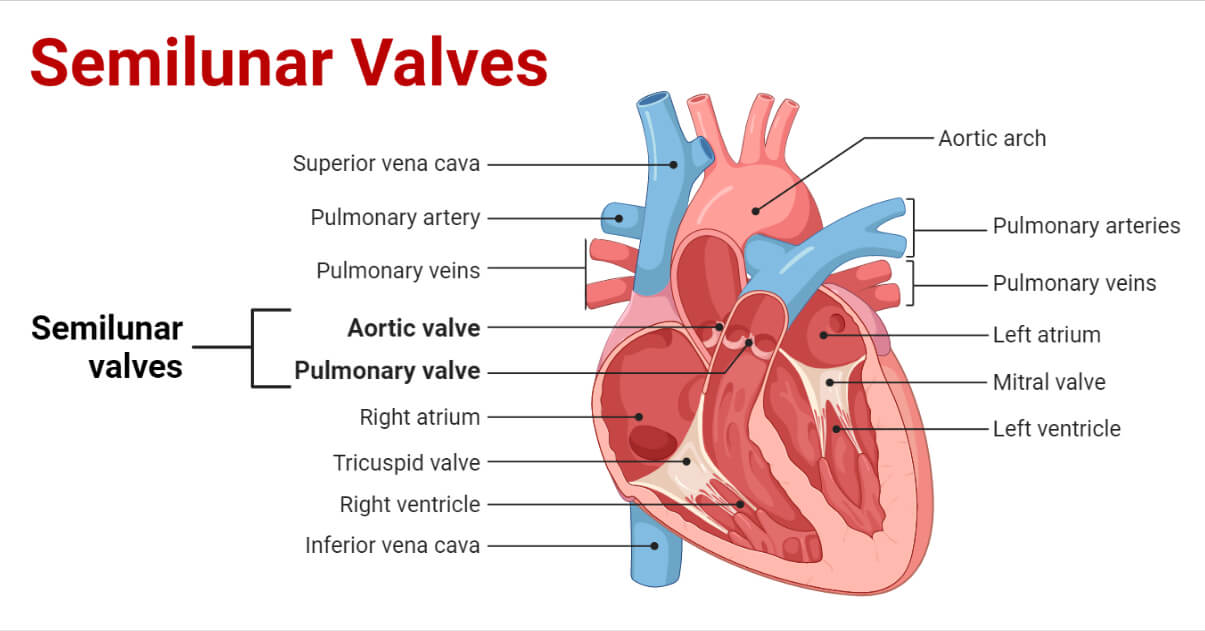
Memorize the location of the semilunar valves
semilunar valves (It returns blood from the upper body regions.)
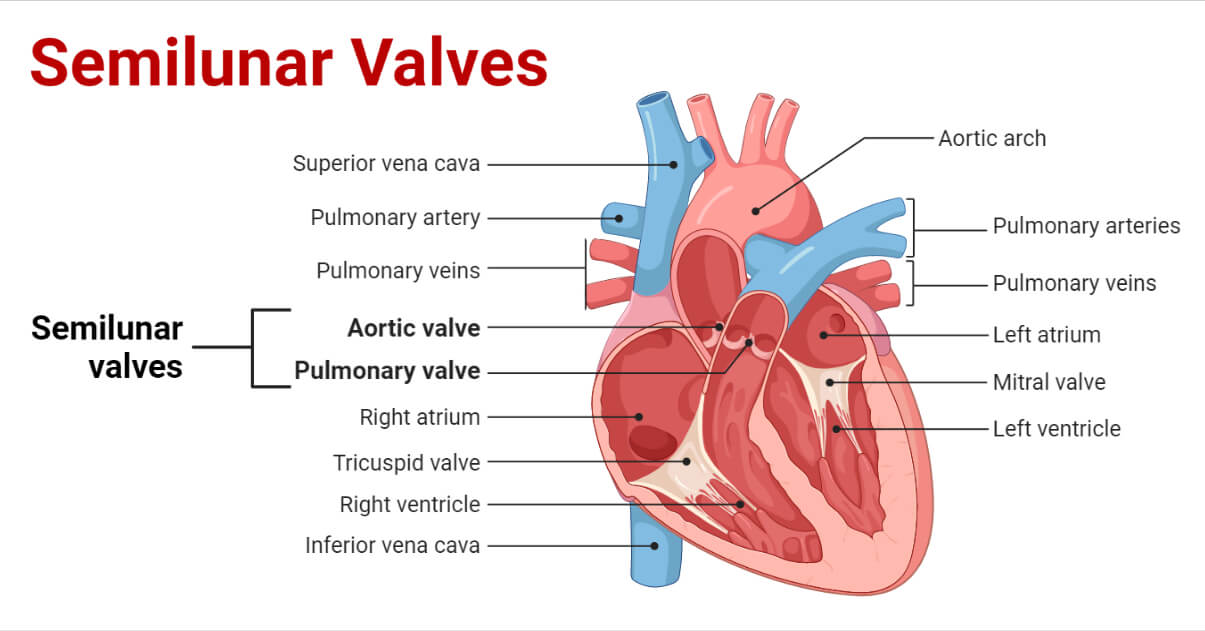
Memorize the location of the right atrium
right atrium
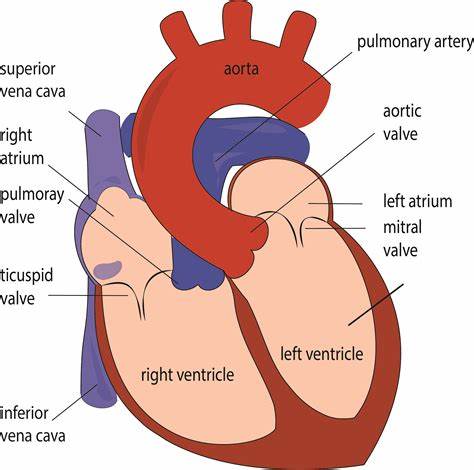
Memorize the location of the superior vena cava
superior vena cava
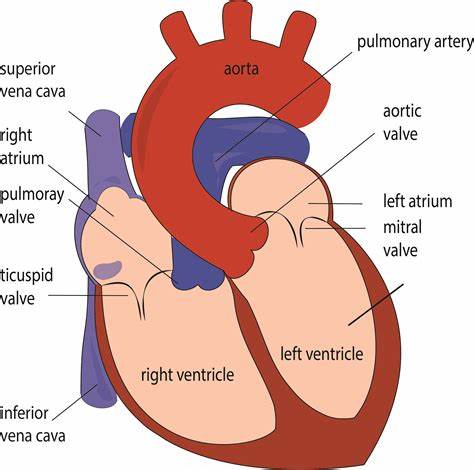
Where does blood enter the heart?
At the right atrium through the superior and inferior venae cavae.
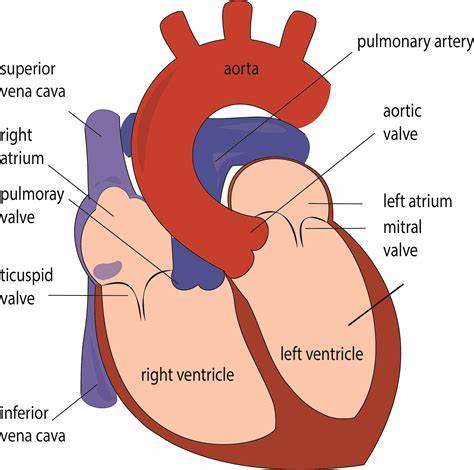
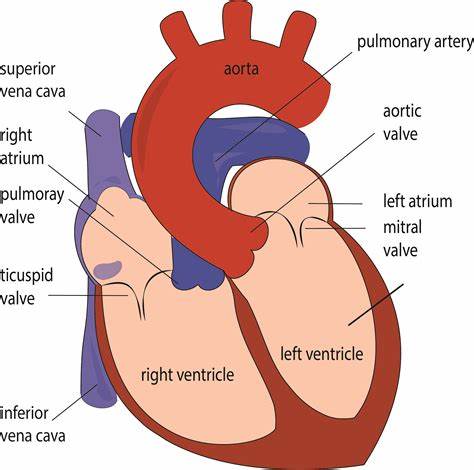
Memorize the location of the inferior vena cava
inferior vena cava (returns blood from the lower body regions)
deoxygentated blood
Blood that comes from the body that is low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide.
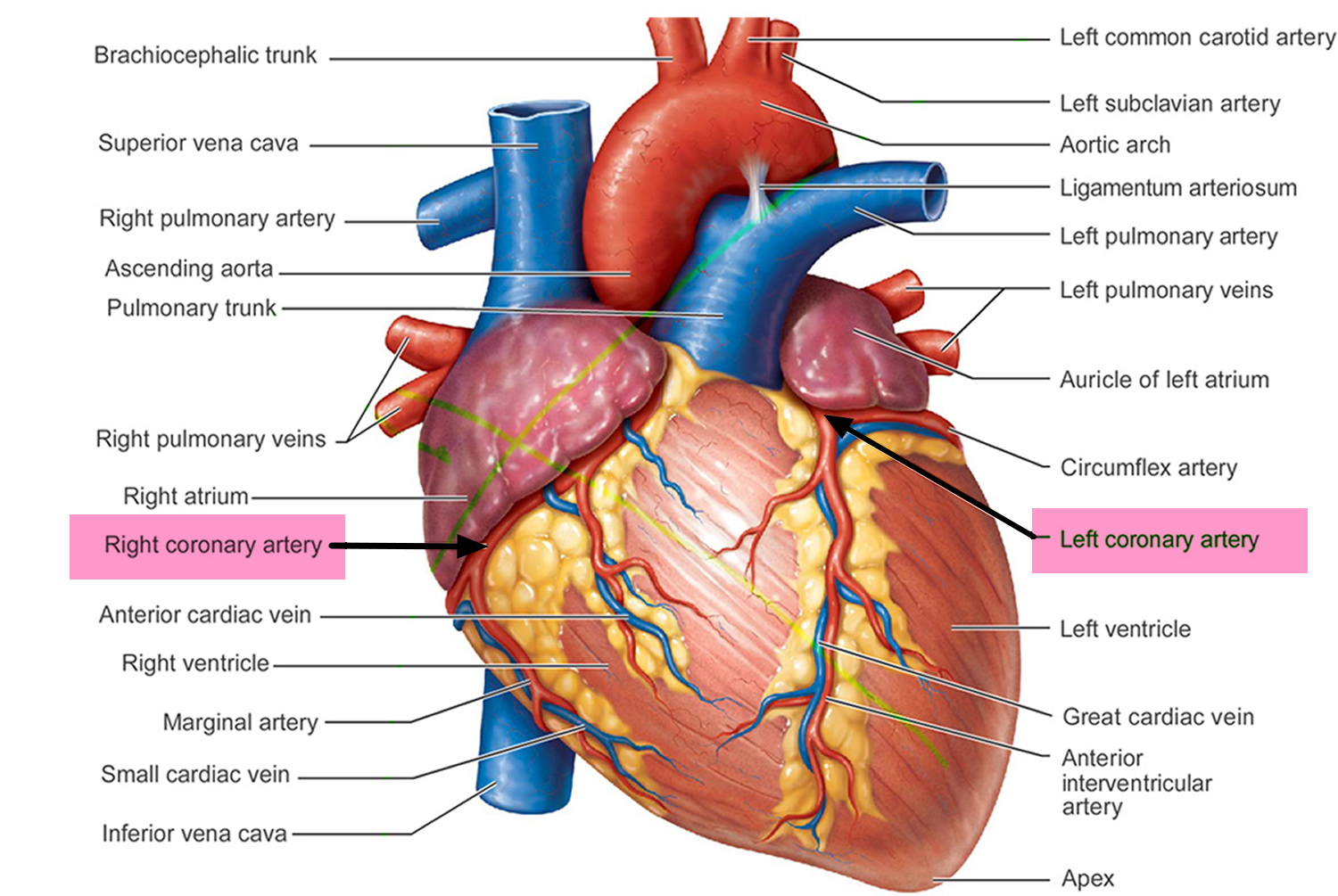
coronary artieries
The vessels that carry oxygen to the heart muscles.
What side of the heart contains all of the deoxyegntated blood?
The right side
When studying the body in science, what side is left and right?
You have to pretend that you are the patient. It would be the patient’s actual left or right. Not what looks to be your left or right.
oxygenated blood
Blood that became oxygen-rich from air going into the lungs and then into the blood.
How does science prove that Jesus really sweat blood?
If there is a violent disturbance of the nervous system, you can sweat blood. This may force the blood pressure in the blood vessels and sweat ducts break from pressure for blood to escape through the sweat pores.
stethoscope
Tool to listen to heart and lungs
What is the scientific term used for the sound the heart makes?
lubb-dubb
When you listen to the heart and it makes the lubb-dubb sound, what is going on during the “lubb”?
The ventricles are contracting and the AV valves close. You are hearing the sound of the vales shutting.
When you listen to the heart and it makes the lubb-dubb sound, what is going on during the “dubb”?
The semilunar valves close, producing the dubb sound. You’ll hear the lubb sound longer and louder than the dubb.
heart murmur
An abnormal sound usually cause by defective heart valves. If the valves do not close properly, blood may leak backward, causing a gurgling sound.
arrhythmia
A heart problem where the heart beats out of rhythm.
What is the greatest cause of death in the United States?
cardiovascular disease (heart disease)
What is the average life expectancy of Americans?
76.4 years old
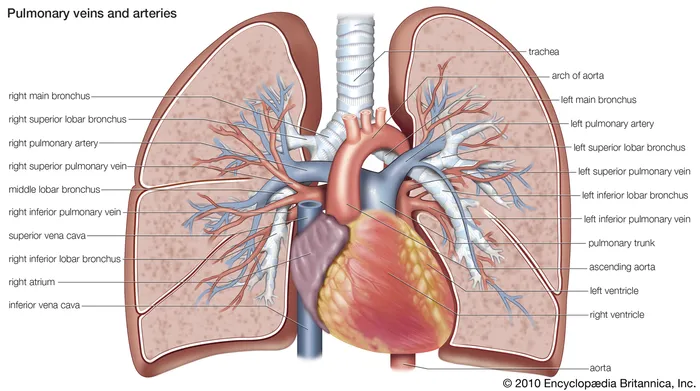
What 2 organs do the pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins connect?
the heart and lungs
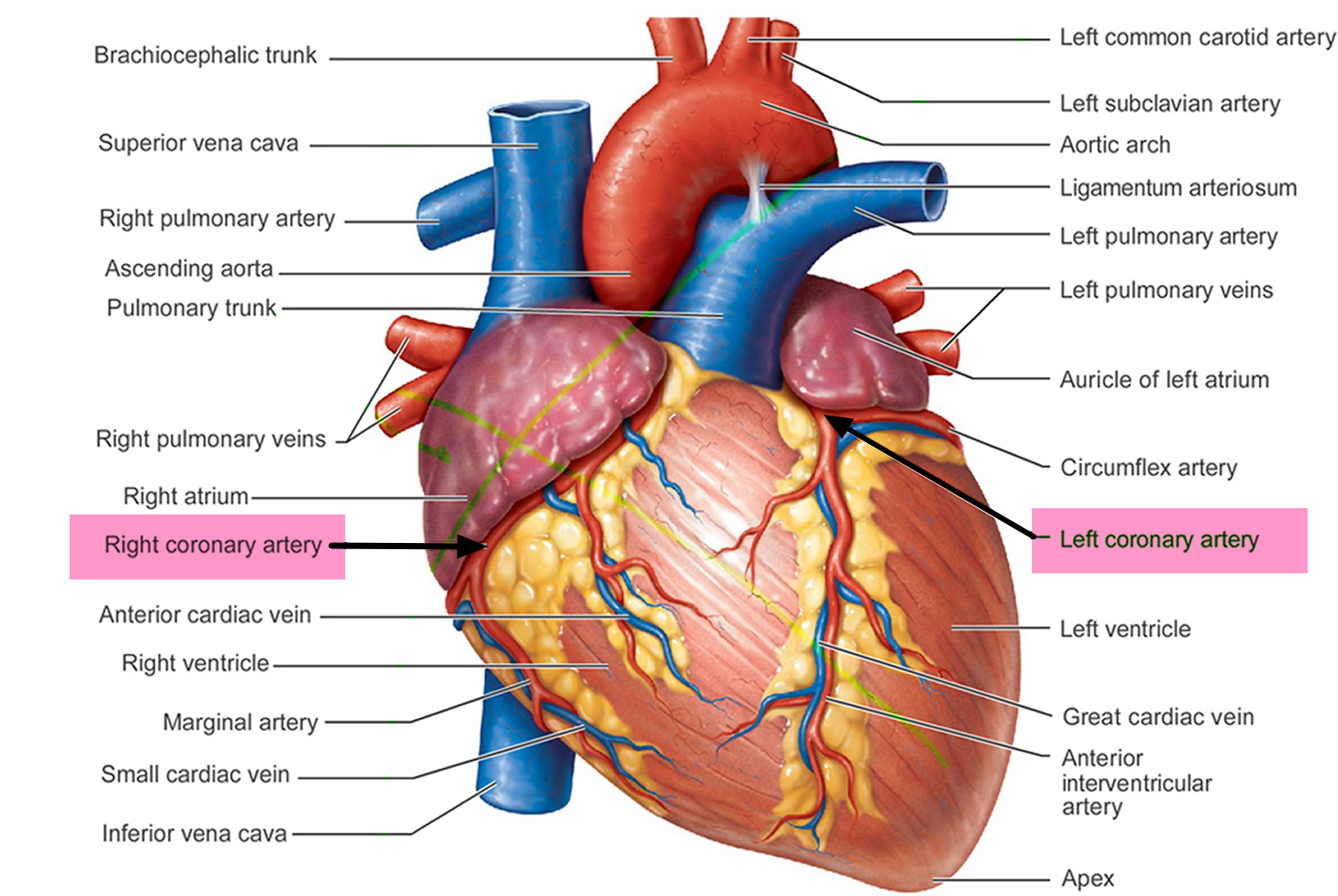
What arteries nourish the heart?
The coronary arteries
How are heart attacks caused?
A decrease supply of blood to the hard-working heart muscle.
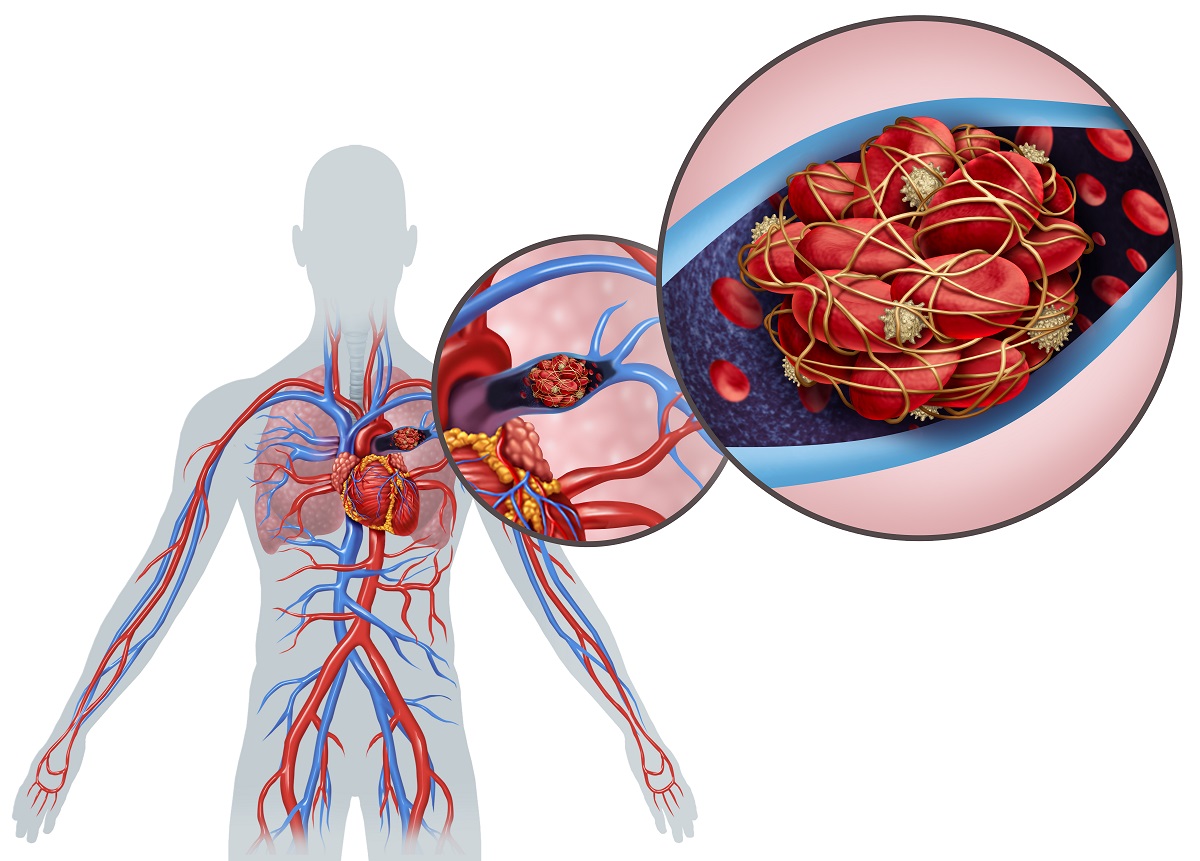
emboli
clots that clog the arteries
What is the name for a heart attacked caused by emboli floating in the blood?
coronary embolism
What is the medical term for a heart attack?
myocardial infarction
ventricular fibrillation
An arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat) is caused by the ventricles quivering vigorously, but are not pumping blood.
defibrillator
Shocks the heart with a direct electrical current to restore the heart to a normal rhythm.
anemia
The inability of the blood to carry enough oxygen.
hemoglobin
The molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. It contains iron. It makes red blood cells, erythrocytes, appear red.
erythrocytes
The proper name for red blood cells.
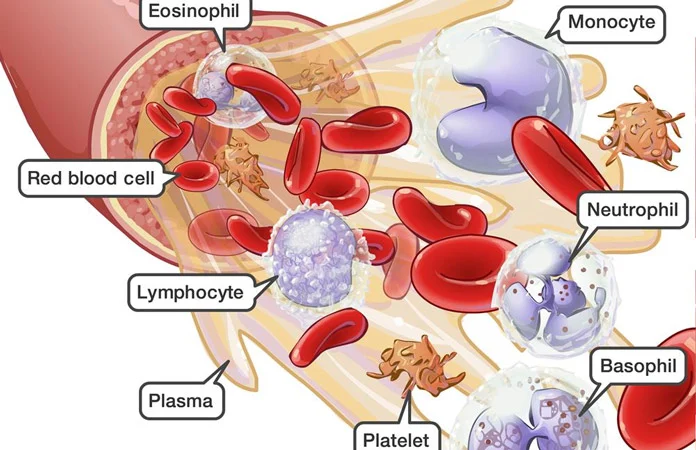
leukocytes
The proper name for white blood cells.
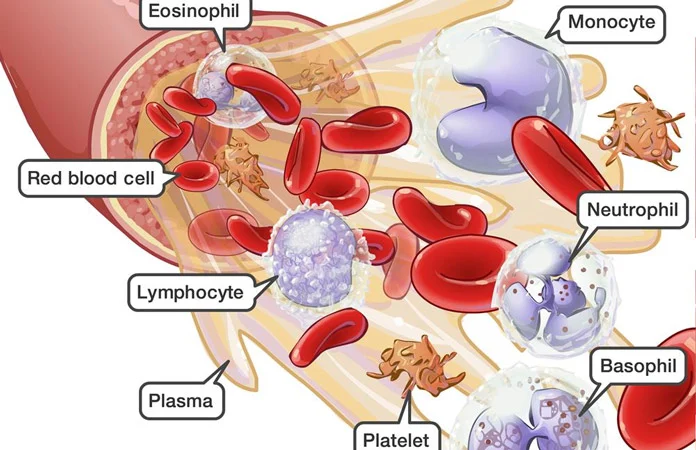
platelets
help in blood clotting
smaller than red blood cells
formed in the bone marrow
plasma
The fluid portion of the blood.
What are substances that are transported by the blood?
dissolved foods, wastes, minerals, hormones, and various other substances that cells need to produce.
What are substances that regulate the blood?
proteins and other substances
blood pressure
The amount of pressure the blood puts on artery walls.
How can the body increase blood pressure?
Having the heart pump more blood.
What molecule in erythrocytes carry oxygen?
hemoglobin
Who donates blood to the recipient in an autotransfusion?
Himself
Why is it important to have platelets?
Without them, you would be unable to form blood clots.
What can cause you to have high blood pressure?
tension or stress
Body’s non-specific defences?
inflammation, mucus protection, skin, stomach acid (kills organisms), fever, and cilia movement
pathogens
bacteria and viruses (T cells work to destroy these when you get them)
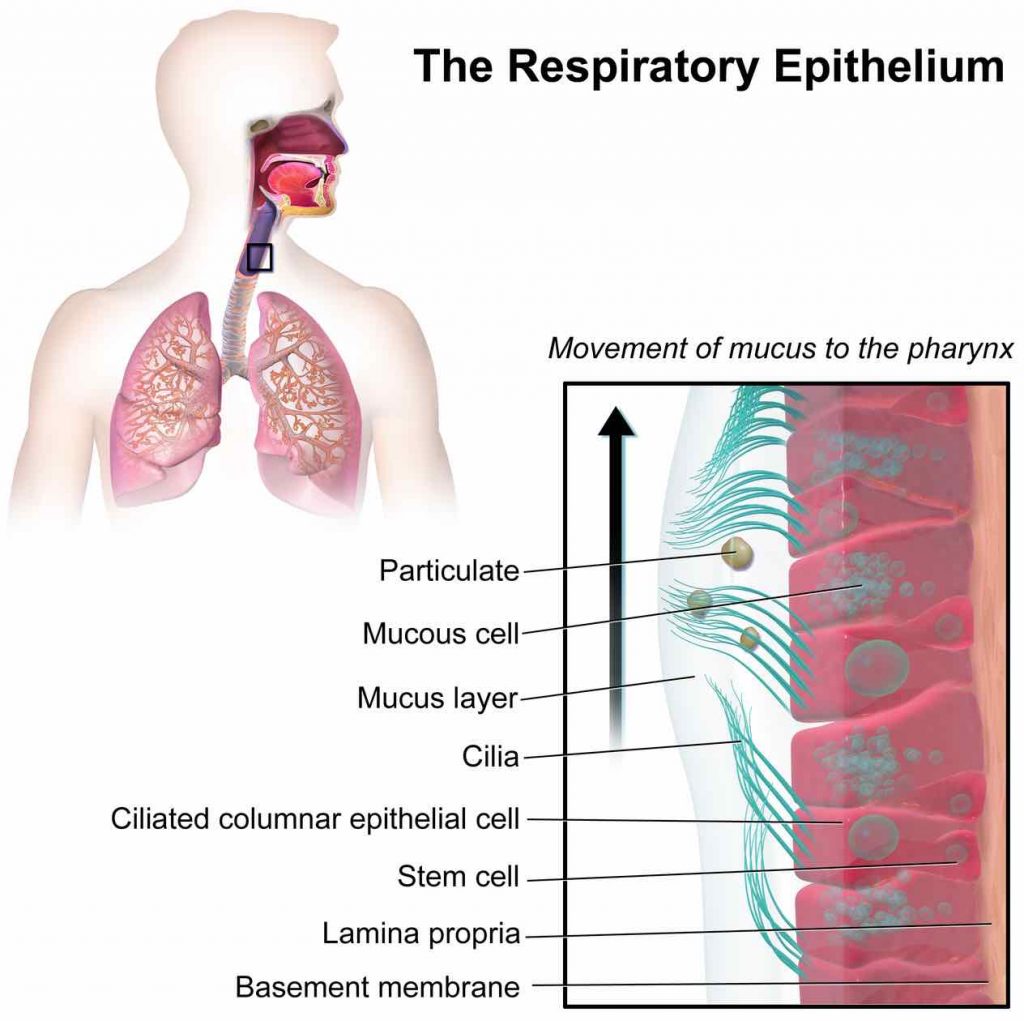
cilia
finger-like projections that move the mucus and trap organisms in the throat.
What produces antibodies?
plasma cells
antigens
molecules that are foreign to the body
What is the body’s final line of defense?
the immune system
T cells
recognize antigens (molecules that don’t belong in the body)
helper T cell
A type of T cell that activates killer T cells
killer T cells
attack the antigen (molecule that doesn’t belong in the body)
antibodies
destroy the pathogen or inactivate it so that other cells can destroy it
What happens to the body when normal cells are attacked by an autoimmune disease?
It becomes unable to tell the difference between pathogens and normal cells.
immunity
The body’s ability to recognize and respond to a foreign substance.
allergy
An overreaction of the immune system to a nonpathogen.
active immunity
When you have an infection and your immune system has responded.
memory cells
B and T cells left over from attacking antigens that now help your body remember the specific antigen it attacked if it returns for war!
vaccine
a weakened form of the virus or bacterium that still contains antigens
passive immunity
When you receive ready-made antibodies.
What 2 major events changed God’s creation?
Adam and Eve’s disobedience and the Curse God placed on the earth. Both changed the relationship between man and the physical environment.
T and B cells similarities
Both are part of the immune system
type of lymphocyte
play a role in immunity
respond to a specific antigen
T and B cell differences
Helper T cells activate other cells
Killer T cells, once activated, attack the foreign organism or substance.
Activated B cells produce antibodies
Which kind of immunity is caused by an injection or preformed antobodies?
passive immunity
Types of immune system malfunctions
allergies, autoimmune diseases, and AIDS
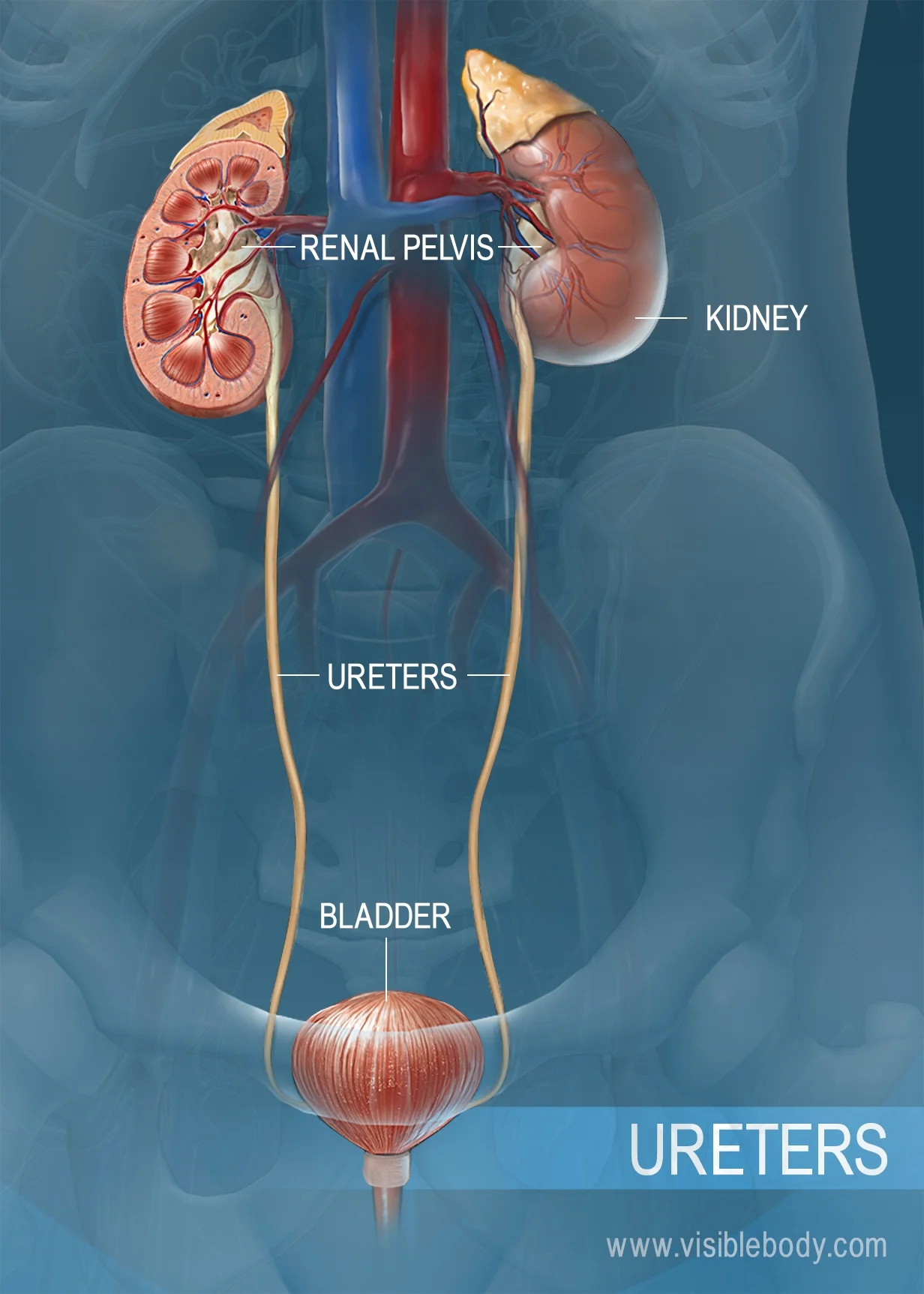
kidneys
The filtering organs of the excretory system
nephron
The microscopic unit that filters the blood.
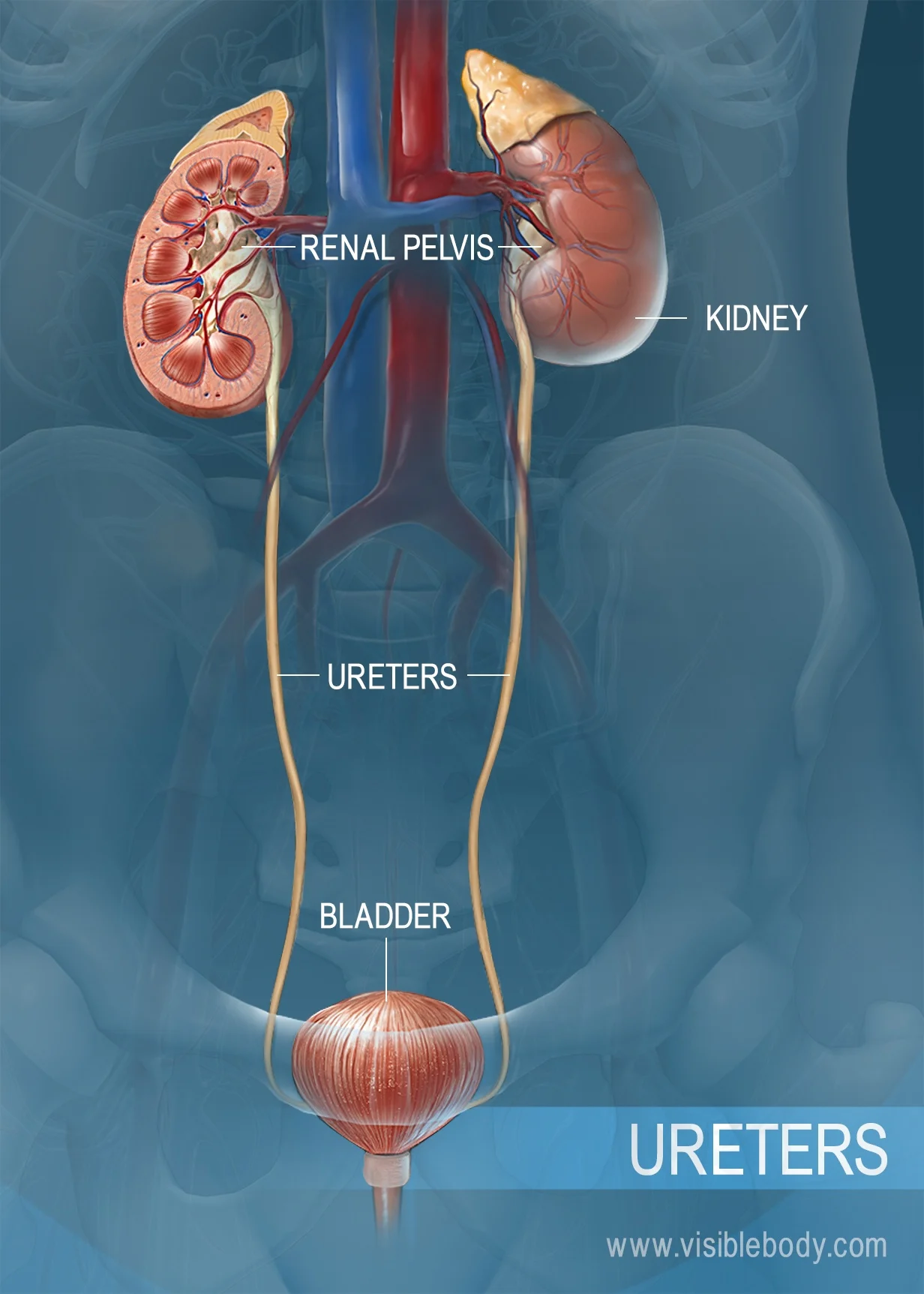
ureter
The tube that leads from a kidney to the bladder.
urinary bladder
A muscular bag that temporarily stores waste liquids before they are passed from the body.
What is the primary function of the excretory system?
To remove wastes from the blood and to release them from the body.
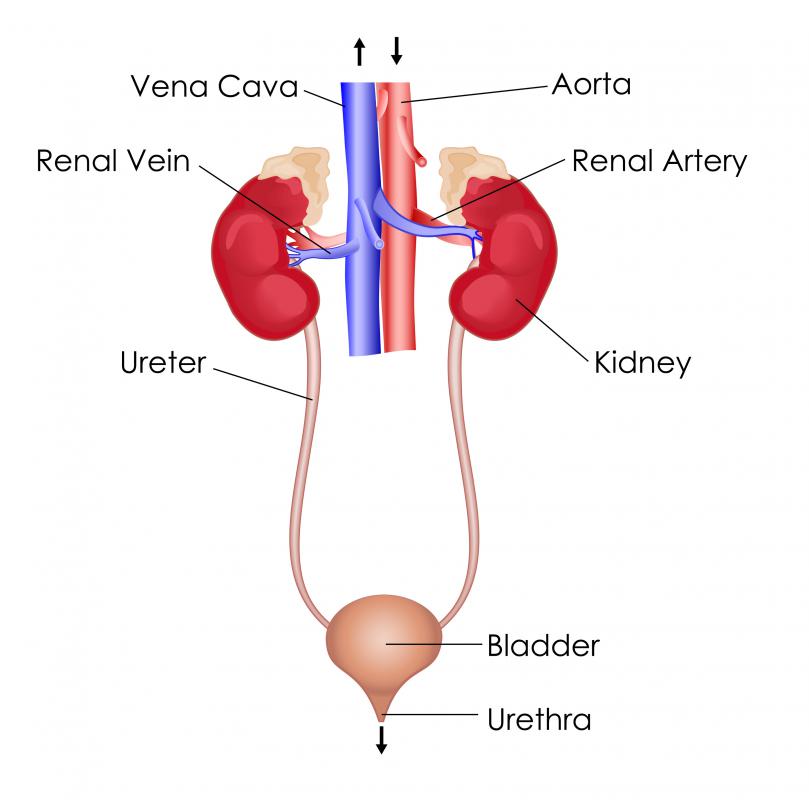
urethra
A muscular tube that leads to the outside of the body.
dialysis
A machine that is used as a substitute kidney
urea
a waste product produced by the action of the liver on ammonia
diabetes mellitus
Occurs when the pancreas, which regulates blood sugar, fails and there is too much sugar in the blood.