U5 Ch1 - Bio, Food Production
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
How does artificial heating help increase the rate of photosynthesis?
Enzymes controlling photosynthesis can work faster at higher temperatures
How does artificial lighting help increase the rate of photosynthesis?
Increasing light intensity enhances the energy available for photosynthesis, promoting more glucose production, the plants can photosynthesise for longer and are not restricted to daytime.
How does increasing carbon dioxide content help increase the rate of photosynthesis?
Higher carbon dioxide levels provide more substrate for the photosynthesis, leading to increased glucose production and overall plant growth.
How does regular watering help increase the rate of photosynthesis?
helps maintain turgor pressure ( pressure exerted by a fluid within a cell against its cell wall) in plant cells
facilitates the transport of nutrients and carbon dioxide.
What are the drawbacks of using a greenhouse?
They’re expensive and they may trap too much heat inside, causing enzyme denaturation so they need to be properly ventilated
What are Polythene tunnels?
Polythene tunnels are structures covered from the top with a plastic pipes that create a controlled weather environment for plant growth
What are limiting factors that effect the rate of photosynthesis?
Temperature
Light intensity
Carbon dioxide levels
How do glasshouses help increase the rate of photosynthesis?
They can provide:
Artificial lighting with intensity control
Temperature control
The levels of CO2 control
What happens to plants if the temperature is too high?
They start to denature, the substrate no longer fits the shape of the active site and the rate of photosynthesis decreases.
What is a limiting factor?
An environmental factor that restricts the rate of biological process
What is the purpose of using fertilisers?
They increase the amount of nutrients in the soil so that the crops can grow larger and healthier
What are pesticides and what are they used for
Chemicals to kill of unwanted insects, fungi and weed species
What are the 2 types of fertilisers?
Organic and Chemical
Describe the compositions of organic fertilisers
Consist of manure and compost
Describe how chemical fertilisers are applied to crops
Applied to soil as dry granules or sprayed by liquid form
What are the nutrients present in fertilisers?
Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium
How is Nitrogen absorbed?
As nitrates
How is Phosphorous absorbed
As Phosphates
How is Potassium absorbed?
In the form of various compounds of potassium
What is Nitrogen needed for in plants?
To make amino acids, the building blocks of proteins
What is Phosphorous used for in plants?
To make DNA and cell memberanes
What is Potassium used for in plants?
Helps regulate water balance
Promotes root growth
Develops flowers and fruits
What is an indication for a lack of Nitrogen in plants?
Weak growth and yellowing of leaves
What is an indication of a lack of Phosphorous in plants?
Poor root growth and discoloured leaves
What is an indication for a lack of Potassium in plants?
Poor growth of flowers and fruits as well as brown spots on leaves
What is the effect on pests and insects on crops?
They damage crops by eating them
What is the effect of weed on a crop?
They outcompete the crop for space, water and nutrients
What is the effect of fungi on crops?
They can infect and spread diseases
What are the 3 types of pesticides?
Insecticides, Herbicides and Fungicides
Name 3 advantages of using pesticides to kill pests rather than using biological control
Easily available
Cheap
Has immediate effect
Kills the entire population of pests
Name 3 disadvantages of pesticides
Pests or organisms may develop resistance
May kill beneficial organisms
Do not break down, so they have the tendency to accumulate in great concentrations at the top of the food chain (bioaccumulation)
Needs to be reapplied repeatedly
What is biological control in crops?
Involving a natural predator to eat the pest species and reduce the impact of pests on crops
Name 5 advantages of biological control
No pollution
No resistance is developed
Can target specific species
Long lasting
Does not need to be reapplied repeatedly
Name 5 disadvantages of biological control
May eat other organisms other than the pest
Takes longer period of time to be effective
Cannot kill entire population
May not adapt to a new environment and evacuate the area
May become a pest itself
How to yeast obtain glucose to conduct anaerobic respiration?
Yeast produces enzymes that break down starch the the flour to release sugars to be used for respirration
What is the chemical equation for anaerobic respiration?
C6H5O6 ( glucose ) → 2C2H5OH ( ethanol ) + 2CO2 ( carbon dioxide )
How does bread dough rise?
During bread making, yeast is added to the dough. Yeast produces enzymes that break down starch in the flour to form glucose. In the absense of oxygen, anaerobic respiration takes place, where glucose turns into ethanol and carbon dioxide ( C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 ) The gas is trapped in air packs in the dough, causing it to rise and increase in volume. When the dough is baked, the ethanol, which has a low boiling point, evaporates. The yeast is also killed when baking, no more respiration takes place.
What is fermentation?
Anaerobic respiration in yeast cells
How would you investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of fermentation?
Apparatus :
Boiling tube
Capillary tubes
Bungs
Yeast
Sugar solution
Oil
Stopwatch
Water bath
Limewater
Mix the sugar solution with the yeast ( this provides the yeast with glucose so it can conduct anaerobic respiration ) in a test tube. Add a layer of oil to the solution ( this prevents the solution from reacting with oxygen ). Secure the test tube with a bung ( this prevents any CO2 gas made from escaping ). Place the tube in a water bath of a measured temperature. Connect a tube to another test tube filled with limewater. Using a stopwatch, allow the test tube to stay in the water bath for a fixed amount of time. During this time, count the number of bubbles of CO2 gas in the limewater. Repeat the experiment with different temperatures at uniform, regular intervals. Use a new glucose-yeast solution and limewater each time. Ensure that each time, the duration is kept constant and the amount of sugar and yeast in the solution is the same. Repeat the experiment multiple times to get accurate results. Make a table listing your results and plot a graph to compare.
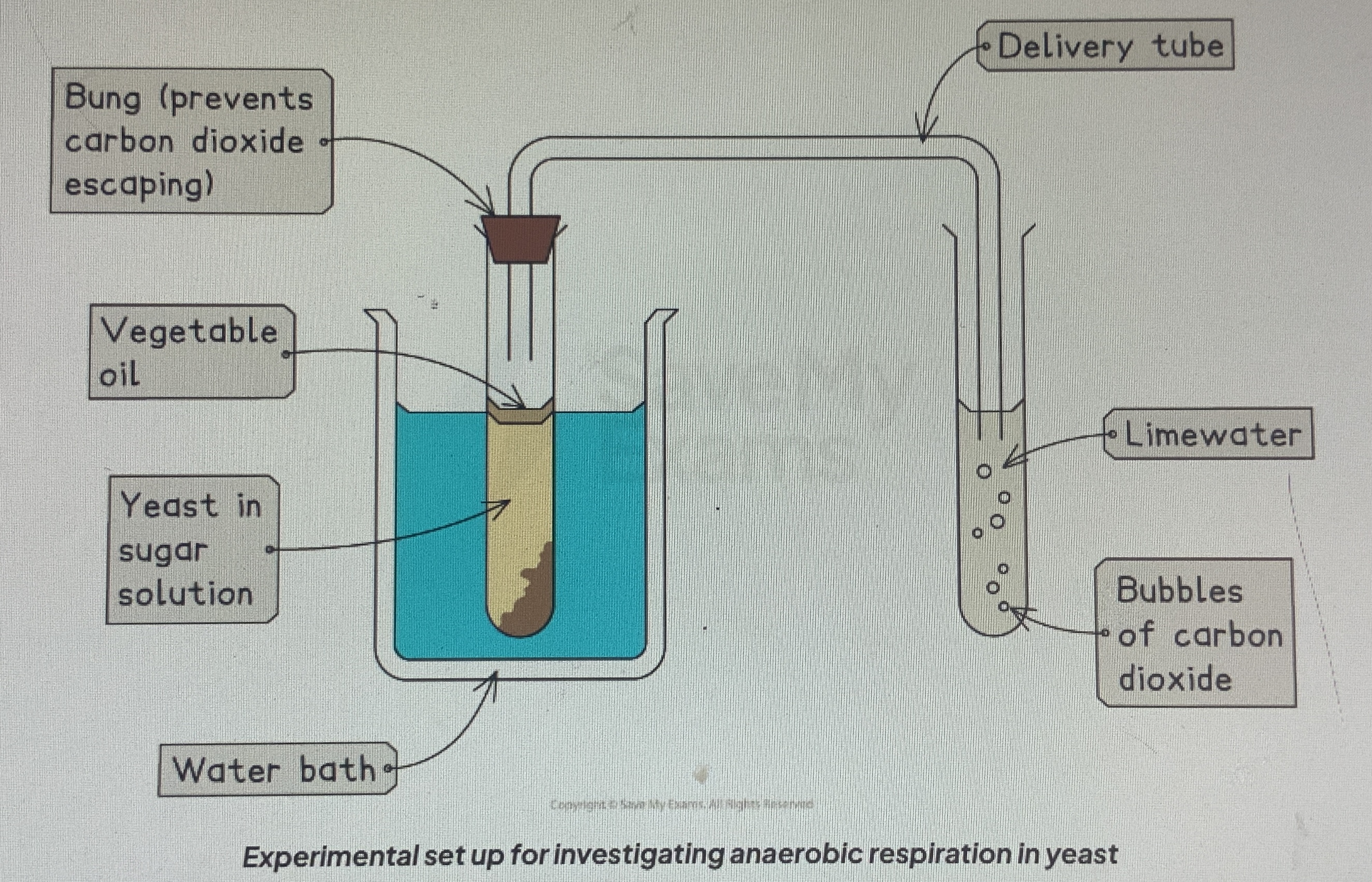
What is the effect of increasing the temperature in fermentation?
More CO2 is produces because the yeast respires faster and the enzyme activity increases until the optimum temperature is reached, after which the temperature becomes too high and the enzymes start to denature, decreasing the overall activity and the rate of respiration decreases until it eventually stops.
Why is bacteria useful?
They produce complex molecules called bacterium and reproduce rapidly, so the amount of chemicals they produce can also increase rapidly.
Describe how yoghurt is made using bacteria
Firstly, all equipment is sterilised to prevent unwanted bacteria from interfering. Milk is then pasteurised (heated) at 85 - 95 degrees Celsius to kill the unwanted bacteria in the milk. Contamination could slow the production because the bacteria could compete with the Lactobacillus for the lactose in the milk and as a result, spoil the taste of the yoghurt. The milk is then cooled to 40 - 45 degrees and Lactobacillus is added. The mixture is incubated at this temperature for several hours. During this time, the Lactobacillus bacteria digests the milk proteins and ferments the sugar to convert lactose into lactic acid. This increases the acidity, souring and thickening the milk. Lowering the pH acts as a preservative, helping prevent the growth of other microorganisms that may act as preservatives. The yoghurt is then stirred and cooled to 5 degrees to stop the bacterium.
What are fermenters and what are they used for?
To allow large-scale production of microorganisms
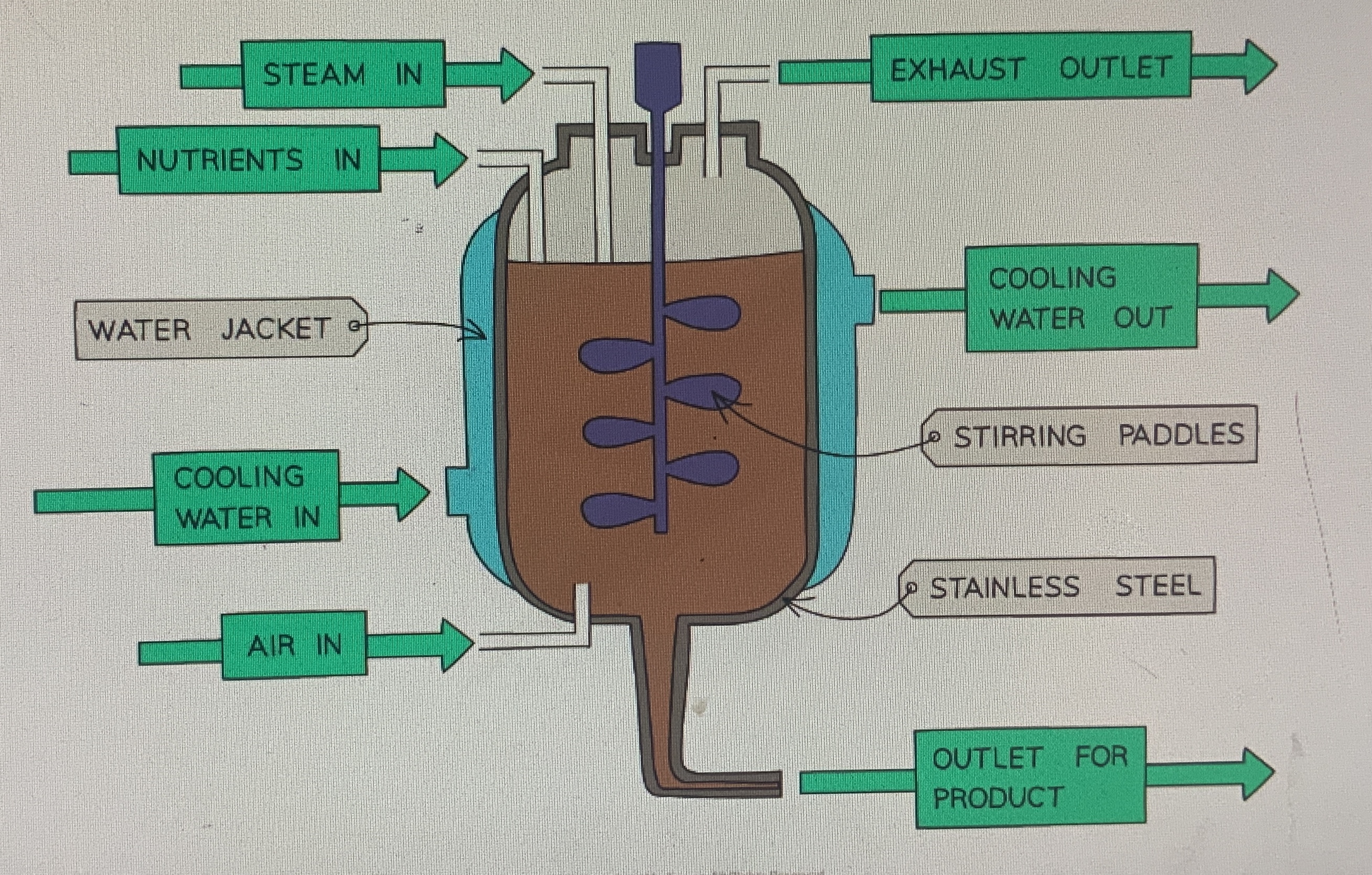
How does a fermentor work?
Firstly, it is sterilised (.e.g. steamed) to prevent contamination so that so that only the desired species grow. Then a culture medium is added and the necessary nutrients to support growth. The water jacket maintains optimal temperature for enzyme activity, preventing desaturation. PH monitors maintain optimal pH using acids or alkalis. Air is pumped into the fermenter to supply oxygen necessary for aerobic respiration. Stirring paddles mix the culture, ensuring even distribution of nutrients, oxygen and temperature.
What are fish farms
Ways of raising large numbers of wild fish in a small space to provide food for humans
Name 4 advantages of fish farming over wild caught fish
Selectively bred fish are high quality and fast growing
Protects against predators
Protection from pollutants such as pollutants in water
Controlled feeding ensures rapid growth
What are the disadvantages of fish farming?
Can be labour intensive and costly
What are the 7 ways to ensure high yields in fish farms?
Control and maintenance of water quality - Removes waste and harmful bacteria, saves from pollutants present in natural environments, maintains high levels of oxygen
Control of intraspecific predation - Predation within the same species, fish are separated by size and age so they don’t fight eachother
Control of inter specific predation - Predation between different species
Control of disease - Antibiotics are given to fish to prevent spread of disease and they’re also kept in small number to prevent this
Control and removal of waste products - Water can be filtered to remove waste products and tanks can be cleaned
Control of quality and frequency of feeding - Fed food that is balanced and high in nutrition in low amounts, but fed frequently so they do not over eat or eat each other
Use of selective breeding - Fish are sperated by gender and farmers select fish with desired characteristics to mate and ensure fast growing stock of fish