Analytic Geometry, Part 2: Conic Sections (Circle)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
When a plane cuts a three-dimensional figure like a cylinder, cone, cube, or the likes, the intersection of the points on the plane and the points on the three-dimensional figure forms a set of points on the plane. This set of points on the plane is called?
Cross Section
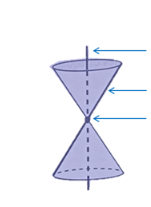
Vertical Axis
Generator
Vertex
Use the plane to cut the two-napped cone in different angles as shown in the next figures. The resulting cross sections are now called?
Conic Sections
They are special curves and are classified into four types, namely circle, parabola, ellipse, and hyperbola.
Conics
When the plane cuts one of the circular cones perpendicular to its vertical axis and parallel to its base, the conic section is a?
Circle
When the cutting plane is parallel to one side of the cone and intersects one of the two cones, the conic section is a?
Parabola
If the plane cuts the cone in the similar fashion but at a certain angle, then the conic section is an?
Ellipse
Lastly, when the cutting plane intersects the two cones parallel to their vertical axes and perpendicular to their bases, then the conic section is a?
Hyperbola
The equation of the conic section is a second-degree polynomial in two variables; that is?
Ax2 + Bxy + Cy2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0
It s the set of points on the coordinate plane that satisfies the equation.
Graph or Curve of an Equation
The equation of the circle is a second-degree polynomial in two variables, that is,
Ax2+ Ay2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0
It is the center of the circle and the line connecting it to a point on the circle is the radius.
Origin
Standard Forms of the Equation of the Circle:
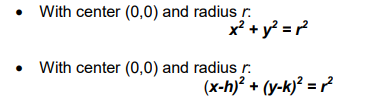
The coefficients of the squared terms are equal and have the same sign
Circle
There is only one squared term
Parabola
The coefficients of the squared terms are not equal but have the same sign
Ellipse
The coefficients of the squared terms have different signs
Hyperbola
A=C
Circle
Either A=0 or C=0
Parabola
AC>0
Ellipse
AC<0
Hyperbola
It is a set of points on the coordinate plane that are of equal distance from a fixed point
Circle
The fixed point of the cirlce is the?
Center
The equal distance of the circle is the?
Radius
The equation of the circle is a second-degree polynomial in two variables, that is:
Ax2 + Ay2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0
This equation is the standard form of the circle whose center is the origin, also referred to as the center-radius form
x2 + y2 = r
This equation is the standard form or the center-radius form of the equation of the circle with a center C(h,k) and radius r.
(x-h)2 + (y-k)2 = r2
It is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant to a specific point and to a specific line called focus and directrix
Parabola
Vertical Parabola equation:
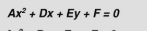
Horizontal Parabola equation:

Standard form of a vertical parabola:
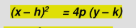
Standard form of horizontal parabola:

The standard equation of a parabola is commonly referred to as the?
Vertex Form
Abscissa
h
Ordinate
k
It is the highest or the lowest point of the parabola, usually denoted as “v”.
Vertex
It is the fixed point of the parabola that is denoted by “f”.
Focus
It is a fixed line that is perpendicular to the axis of symmetry of the parabola and does not intersect to any point in parabola
Directrix
It is a line segment that passes through the focus and parallel to the directrix. Its endpoint and start point lie on the parabola. It also determines the width of the opening of a parabola. Denoted as “4p”.
Latus Rectum
It is the set of all points in a plane whose sum of the distance from two fixed point, foci, are constant
Ellipse
General equation of Ellipse":
Ax2 + By2 + Cx + Dy + E = 0
Standard equation of Ellipse:
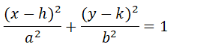
It serves as the reference point for your ellipse
Center
Theye are the points positioned inside the ellipse. It is the one that determines the curvature and shape of the ellipse
Foci
It is the longest line segment that passes through the center. It contains three of the major points in your ellipse, the center and foci. It also determines the axis of the ellipse.
Major Axis
Is it the endpoints of the longest line segment in ellipse or the major axis
Vertex
It is the endpoints of the shortest line segment of an ellipse or the minor axis
Co-vertex
It is the shortest line segment in ellipse that passes through the center and perpendicular to the major axis
Minor Axis
Is unlike to other properties of ellipse, it is not something that can be visually seen. But, it is a property that describes any conic section how it deviates from being a circle. It has a value between 0 and 1
Eccentricity
Is a set of points on the coordinate plan such that the absolute value of the difference of the distances of any point from the two fixed points is constant.
Hyperbola
Equation of the Hyperbola”
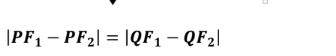
Are the line segments of the hyperbola that contain two points and passes through the foci.
Focal chords or Latera Recta
Are the fixed points in a hyperbola with the distance c which can be contained using c² = a² + b²
Foci
It is the midpoint of the hyperbola F1F2, V1V2, B1B2, and intersection of the asymptote
Center
V1V2
Transverse axis
B1B2
Conjugate axis
They are thend points of the transverse axis, and the principal axis intersects the hyperbola at these points
Vertices
It is a segment of the principal axis that connects the vertices and has a length of 2a
Transverse axis
Are the endpoints of the conjugate axis with the coordinates of B1 and B2
Covertices
It is a segment of the principal axis that connects the covertices and ahs a length of 2b
Conjugate axis
Are the two disconnected curves which extend indefinitely and are asymptotic to the two intersecting lines or the asymptote
Branches
It is the straight line of the curve which the curve approaches indefinitely but never touches
Asymptote