CH 3: Anatomy
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Anatomy
anatomy is naming structures
Anatomical positions
- Standing up
- head forward
- toes forward
- palms foward
Directional Terms
Based on the assumption that the body is in anatomical position
Supine
Laying on the back
Prone
face down
Lateral
farther from the median plane
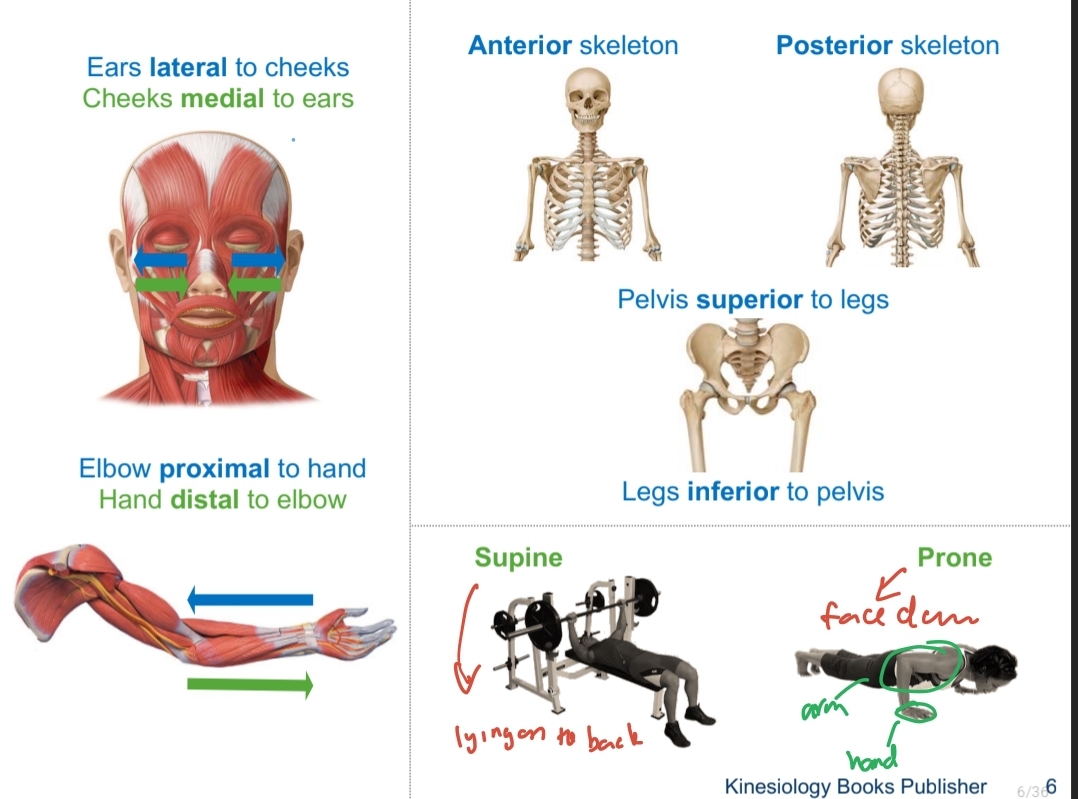
Distal
farther from the trunk
posterior
Nearer to the back
anterior
Nearer to the front
inferior
Nearer to the feet
superior
Nearer to the head
proximal
nearer to the trunk
Medial
Nearer to the median plane
starting reference point
specifies location of specific body parts relative to other body parts
body planes
divides the body in anatomical position
at right angles to each other
describes movements parallel to the planes
Midsaggital /Saggital /Median Plane
divided the body into right and left halves
parallel to the median plane
movements in the saggital plane AND examples
flection and extension of body parts
examples are squatting and bicep curls
Frontal/Coronal Plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior sections
movements in frontal/coronal plane AND examples
abduction and adduction of limbs
examples include jumping jacks and lateral raises
transverse plane
divides the body into superior and inferior sections.
movements of transverse plane
rotation
centre of gravity
the point where the body's mass is located when in anatomical position
male centre of gravity
below the umbilical cord
female centre of gravity
around the pelvis
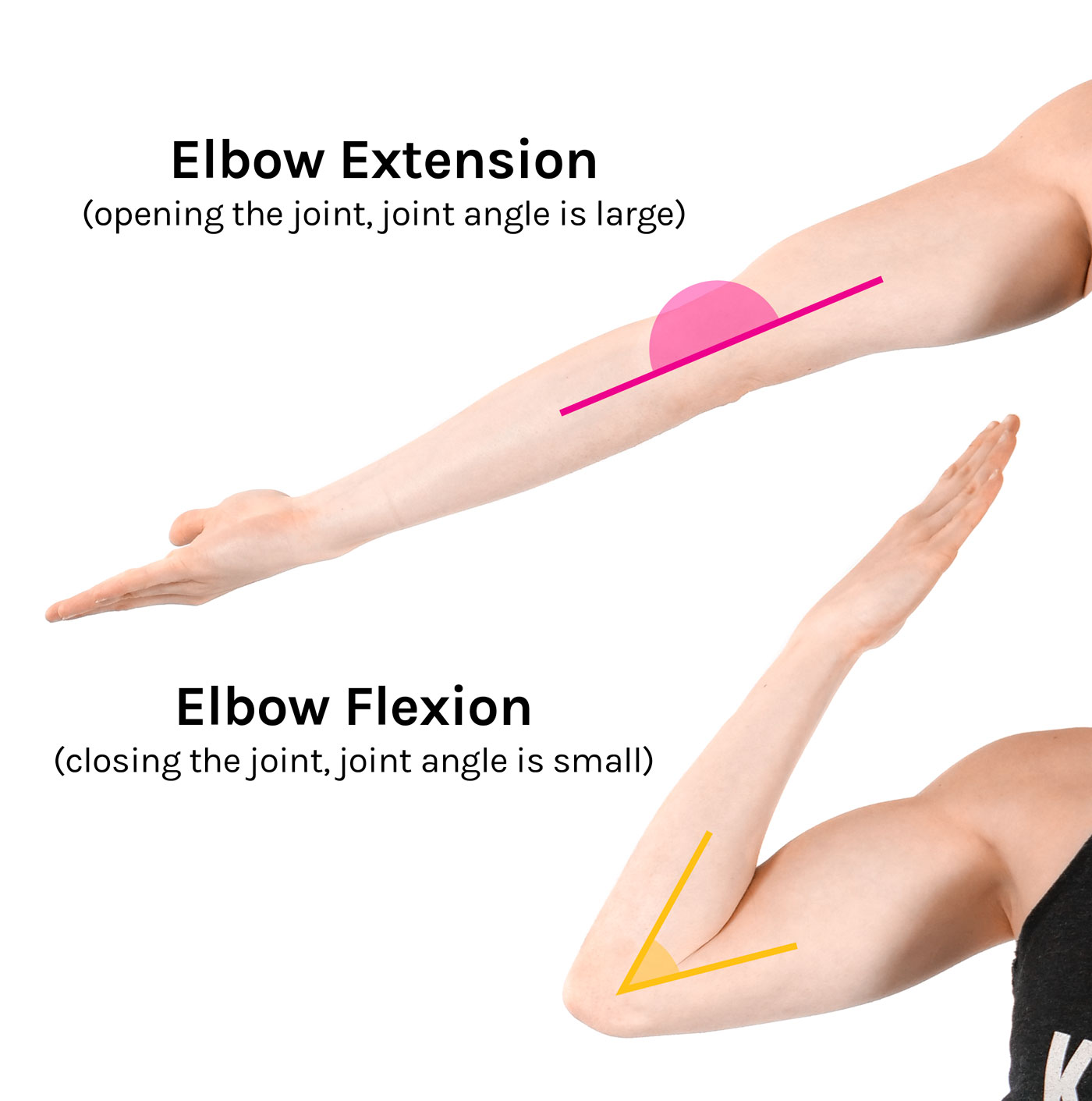
flexion and extension (action, reference and example)
Action: reduces/increases angles between joints
Reference: Saggittal plane
example: bicep curls.
abduction and adduction (action, reference and example)
Action: moves limbs away/toward midline
Reference: Frontal plane
Example: lateral arm raises & jumping jacks
pronation and supination (action, reference and example)
Action: palm faces posterior/anterior
Reference: transverse plane
example: holding bowl of soup
dorsi-flexion and plantar flexion (action, reference and example)
Action: foot up/foot plants
Reference: saggittal plane
example: toe raise
inversion and eversion (action, reference and example)
Action: soles move in/out
Reference: frontal plane
example: rolling over ankle
into and away from midline
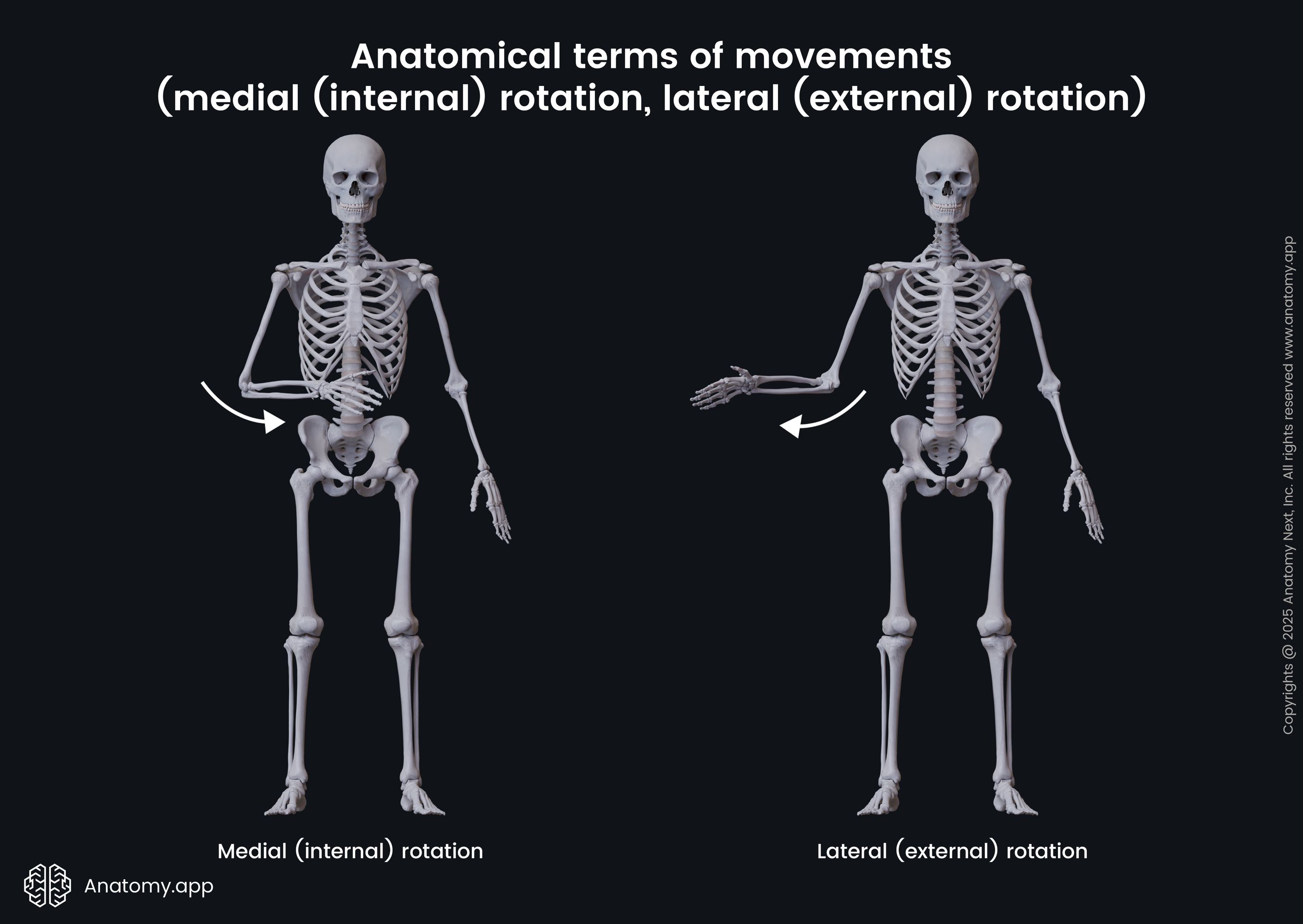
medial/internal rotation & lateral/external rotation (action, reference and example)
Action: flexed forearms moves in/out
Reference: transverse plane
example: opening and closing doors
moves towards and away from midline
circumduction
Action: flexion/extension + abduction/adduction
reference: transverse plane and sagittal
not rotation
cone of movement
division of the human skeleton
axial and appendicular
axial skeleton bones
Cranium (skull)
sternum
ribs
vertebrae (vertebral column)
sacrum
axial skeleton characteristics
80 bones in total
supports, stabilizes and protects vital organs
part of the midline
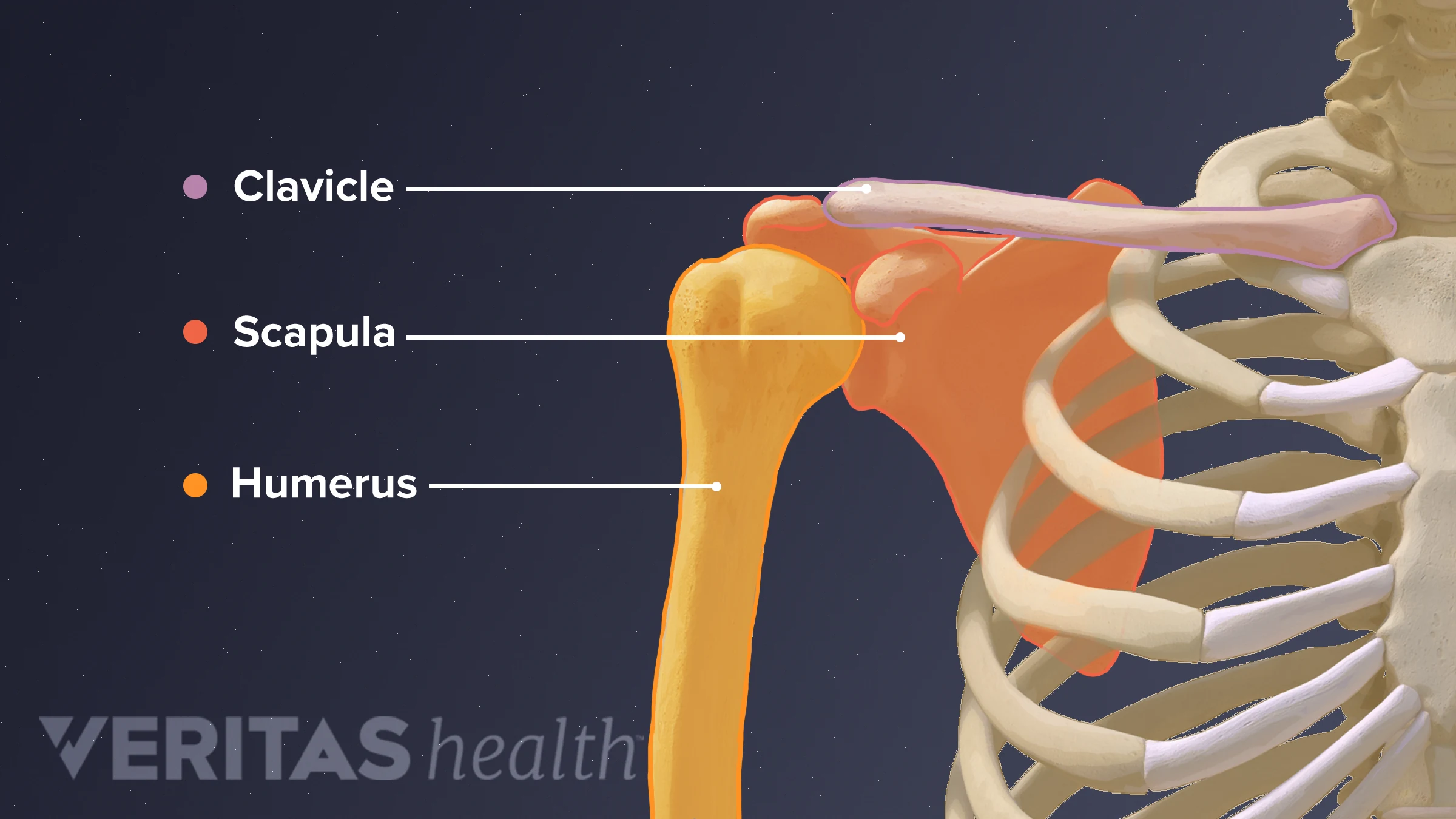
appendicular skeleton bones
clavicle
shoulder blade/scapula
upper limb
pelvic bone
lower bone
appendicular skeleton characteristics
126 bones
responsible for a large portion of movement
short bones (examples and functions)
examples: carpals and tarsals
function: shock absorbers
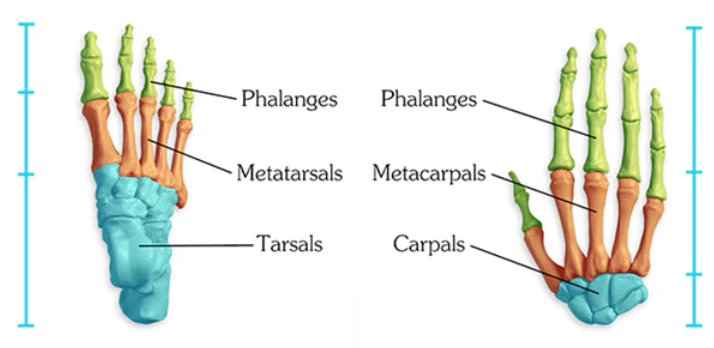
long bones (examples and function)
examples: femur and humerus
function: levers
flat bones (examples and function)
example: skull, scapula, ribs
functions: protect organs
irregular bones (examples and function)
example: facial bones and vertebrae
functions: special functions
sesamoid
exists within tendons
example: patella
function: leverage
classes of bone tissue
compact/cortical: strong, resists force, heavy
spongy/cancellous: makes bone lightweight
bone composition
calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate (60%-70% of bone)
collagen protein: gives bone flexibility
water (20% of bone)
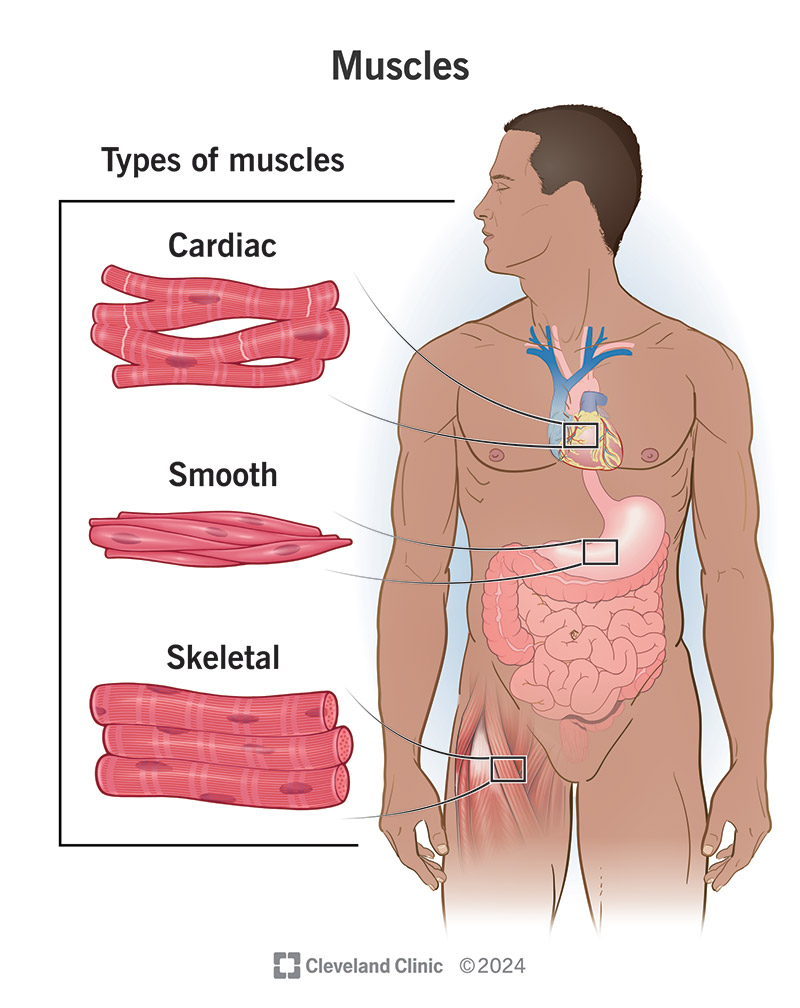
muscle types
skeletal muscle (voluntary muscle)
cardiac (involuntary)
smooth (involuntary): found in digestive system
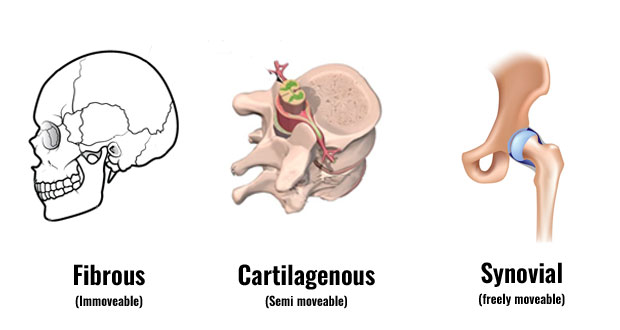
A Joint
connection between two or more bones
classes of joints and function
fibrous joints: made of fibrous tissue
cartilaginous joints: made of cartilage
synovial joint: allow the most movements
components of synovial joints
joint capsule
joint cavity
hyaline cartilage
ligaments
synovial fluid
uniaxial
movement about one axis
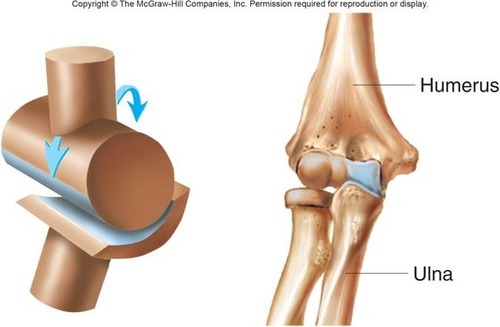
biaxial joints
movement about two perpendicular axes
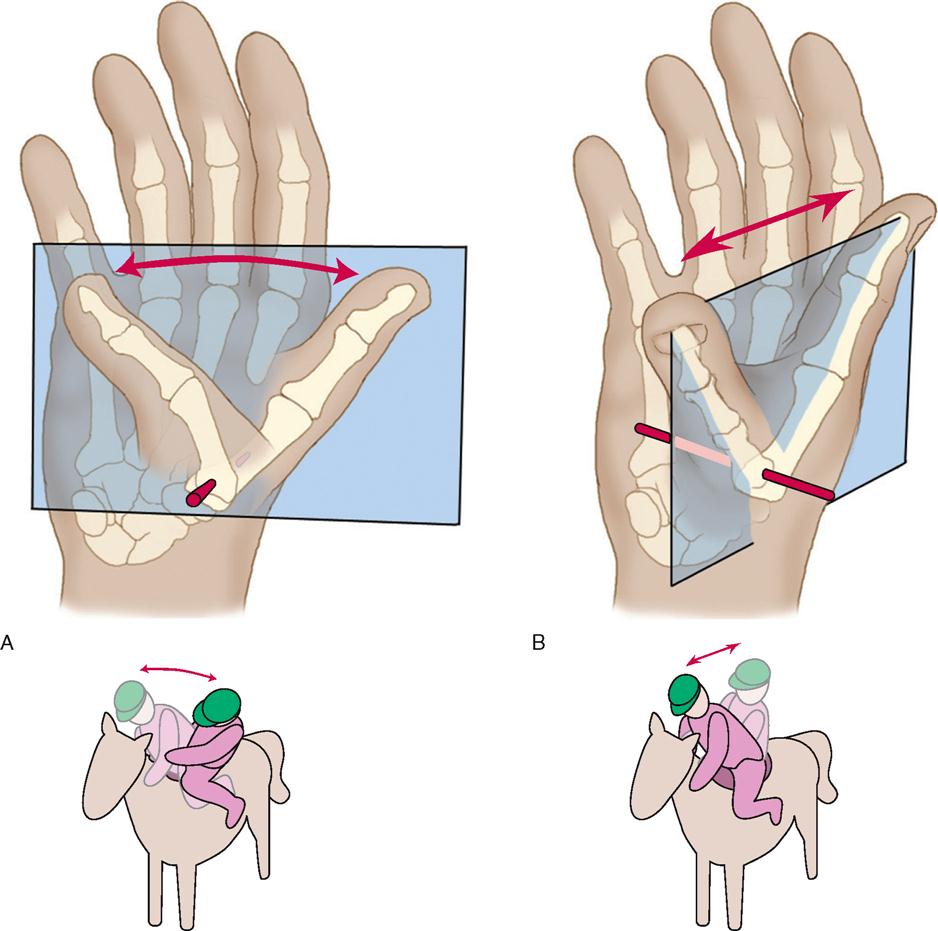
multiaxial joints
movement across all three axis
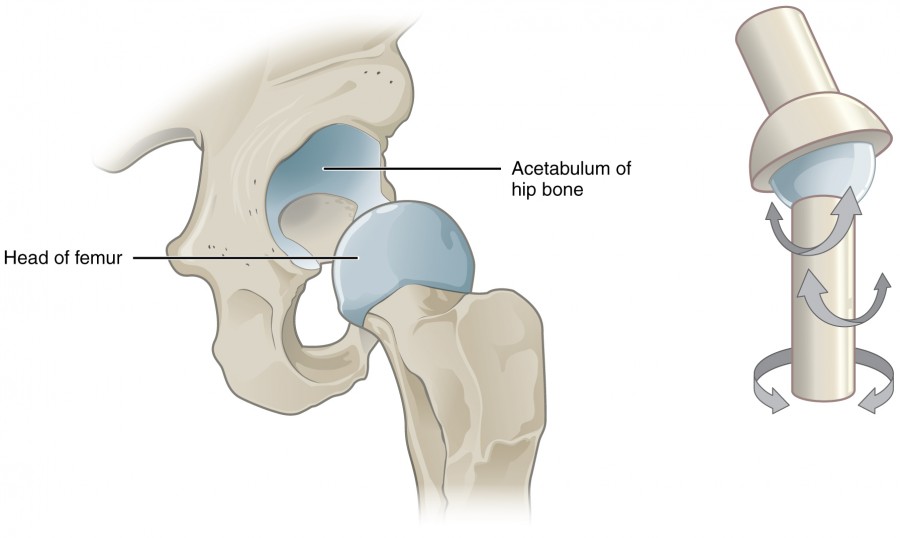
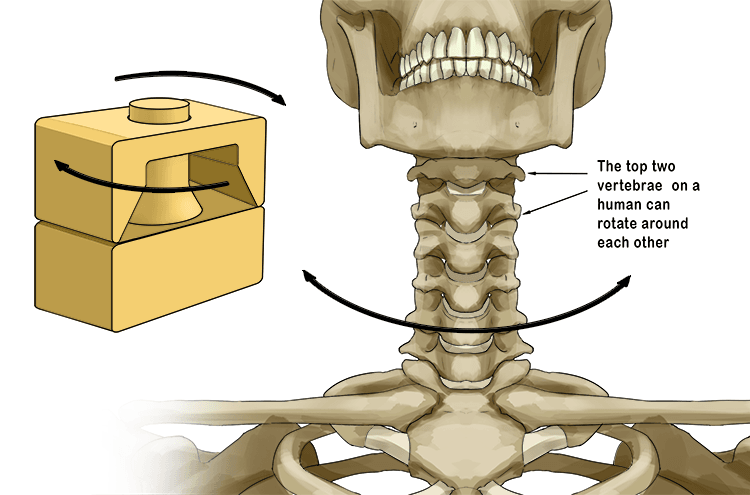
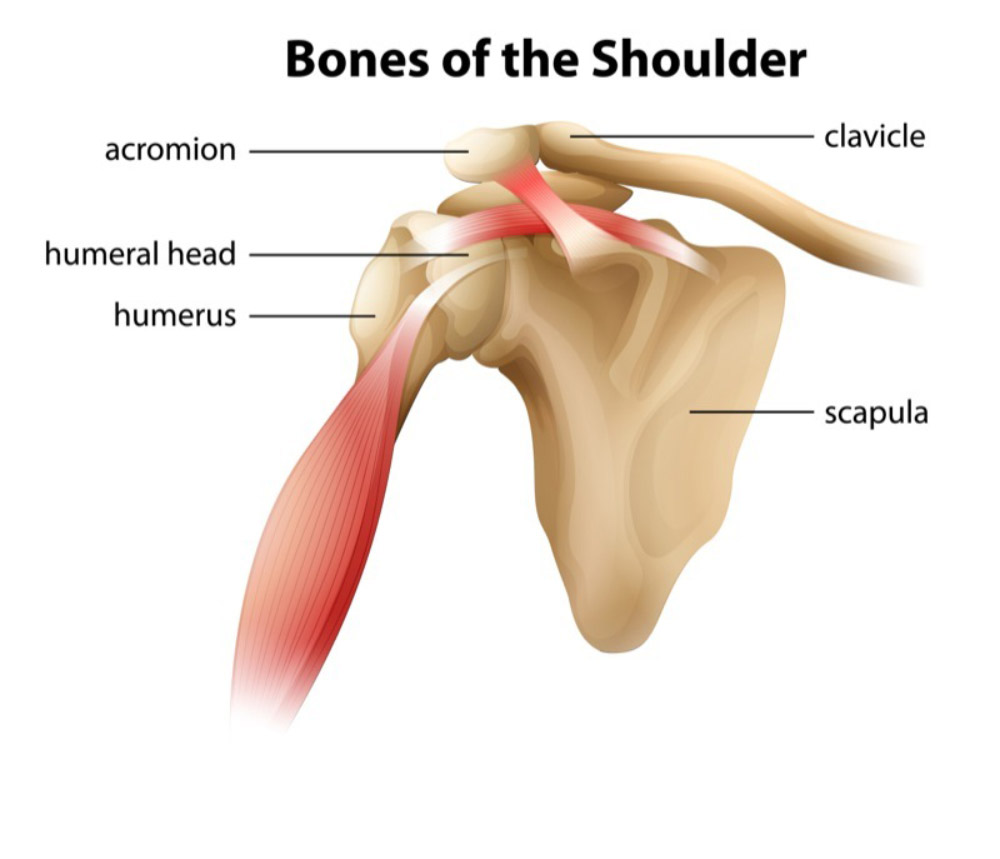
types of synovial joints
pivot
gliding
hinge
saddle
condyloid
ball and socket
pivot joints
one bone rotates around one axis (uniaxial)
eg; neck
gliding joints
bone surface involved are nearly flat
uniaxial gliding
eg: acromioclavicular joints
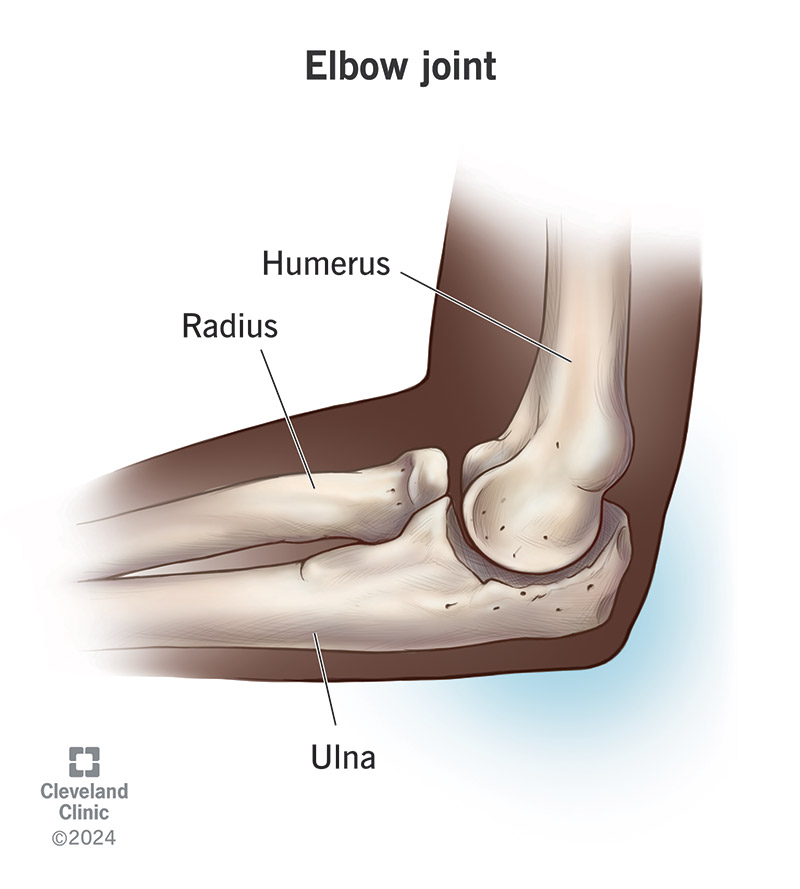
hinge joints
convex and concave articulating surfaces
uniaxial flexion extension
eg: elbow
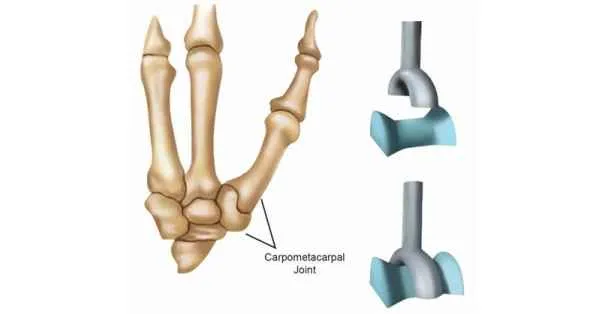
saddle
bones set together like setting on a horse
biaxial: flexion-extension, abduction-adduction
eg: thumb
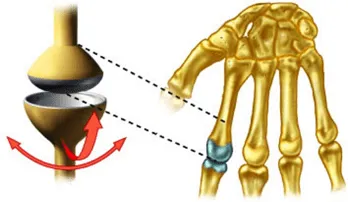
condyloid
ovular convex shape and reciprocal concave surfaces
biaxial: flexion-extension, abduction-adduction
eg: knuckles
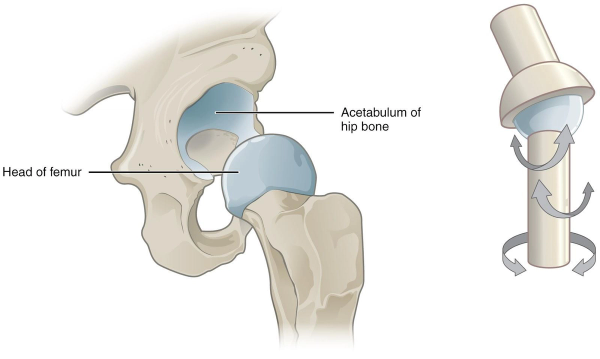
ball and socket joint
rounded bone fitted into a cup-like receptacle
multiaxial
eg: hip
epiphyseal line/growth plate
where the bone grows in length
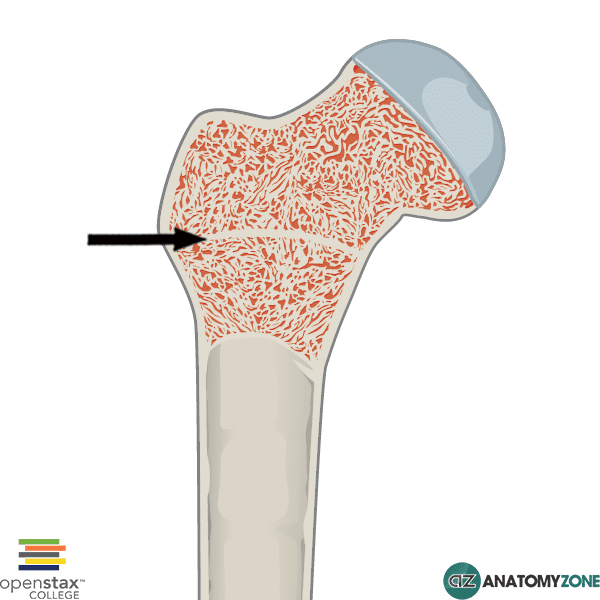
proximal epiphysis
end of the bone closer to the centre of the body
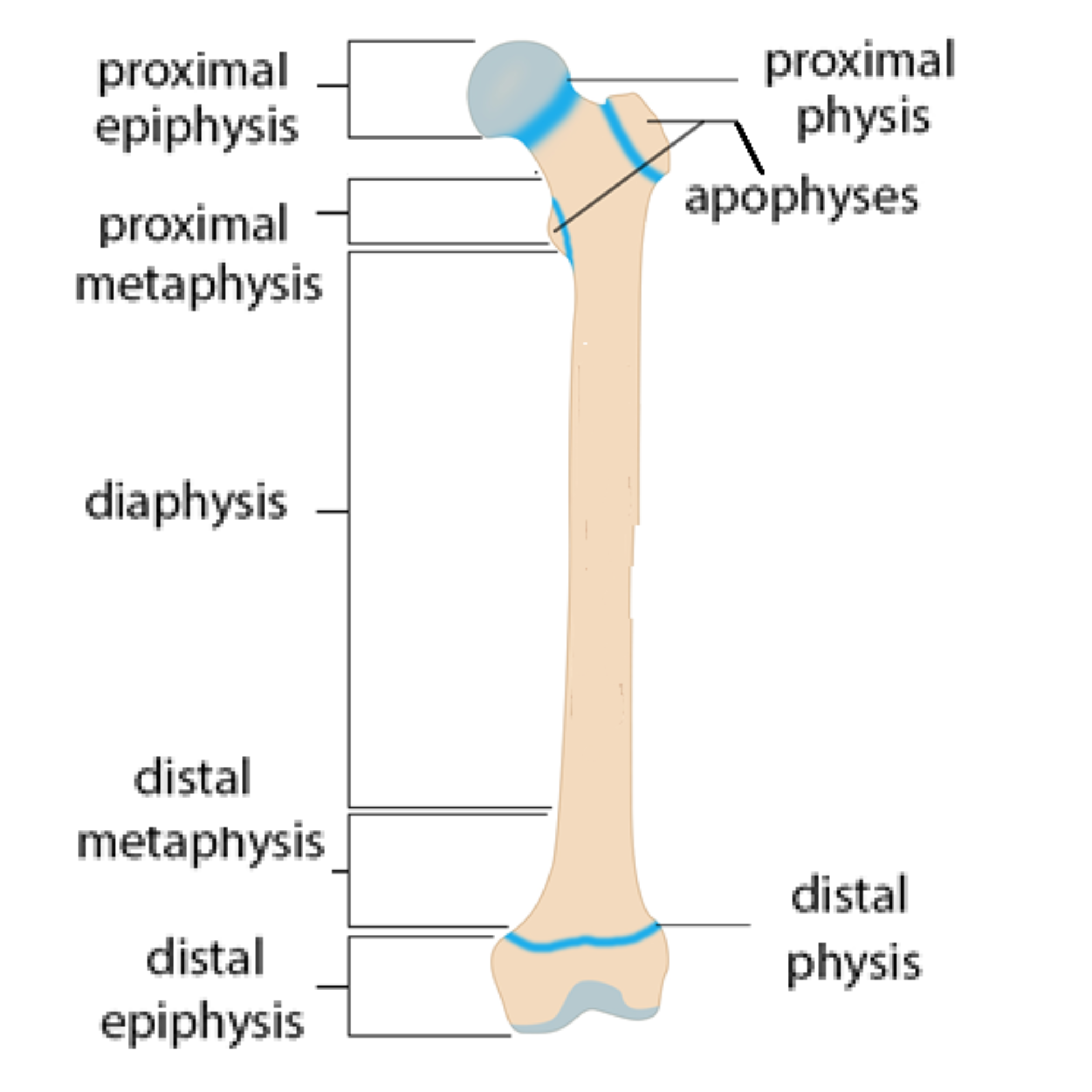
diaphysis
shaft of the bone
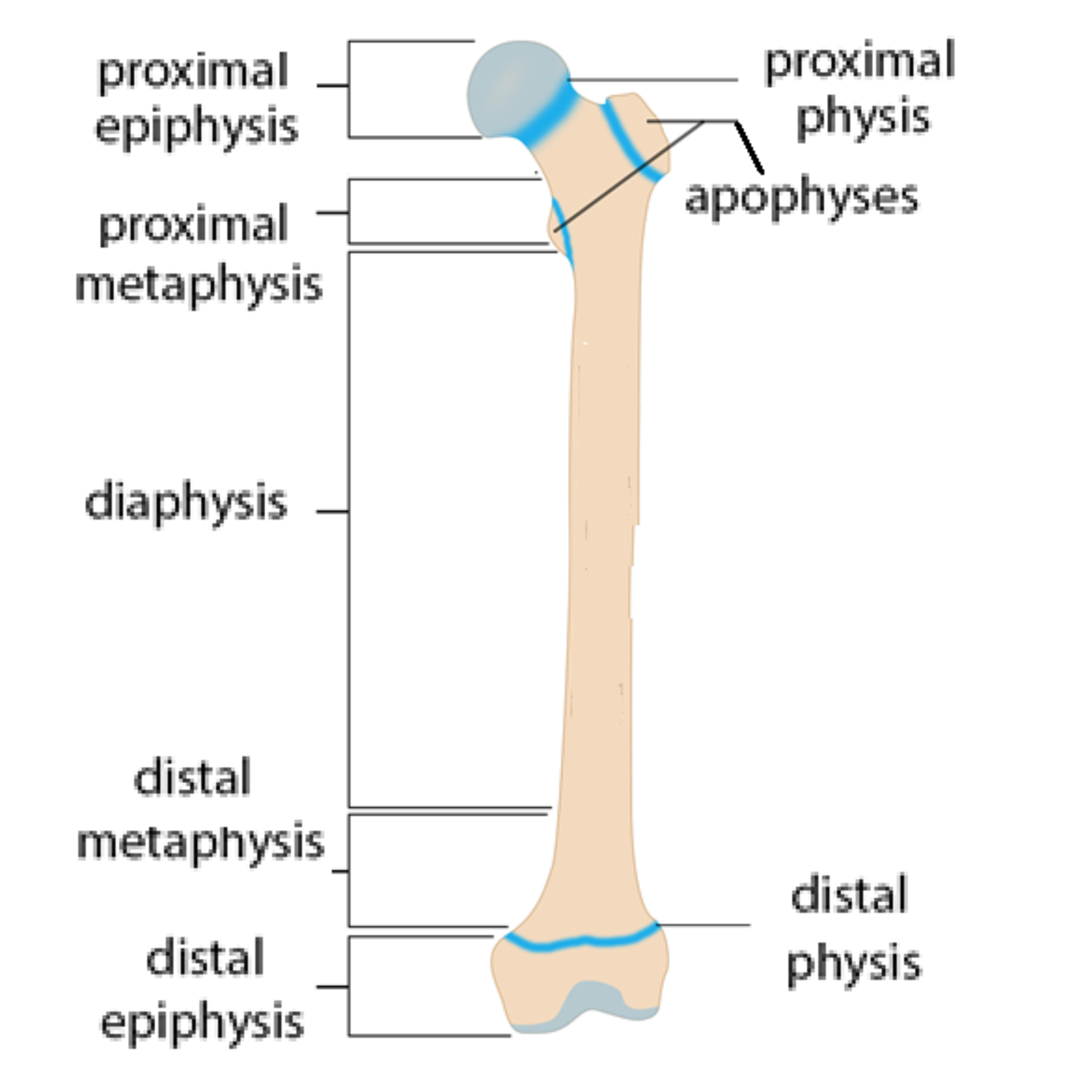
periosteum
outer covering of the bone
distal epiphysis
end of the bone farther from the centre of the body
cancellous bone + red marrow
red blood cells
medullary cavity + yellow marrow
white blood cells
articular cartilage
the smooth, white connective tissue that covers the ends of bones where they form joints
