Micro chem 1&2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is microbiology?
The study of microscopic living organisms (microorganisms), including unicellular, multicellular, and acellular organisms.
What organisms are included in microbiology?
Includes bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, algae, and sometimes viruses.
What is the definition of a microbiome?
Microbes associated with normal human tissues.
What is a commensal relationship between a host and microbe?
A relationship that causes no harm to the host by the microbe.
What is the composition of viruses?
Consist of proteins and genetic material (either DNA or RNA) and require a host to survive.
What are prokaryotes?
Unicellular organisms without a membrane-bound nucleus, including bacteria and archaea.
What is the cell wall composition of bacteria?
Made from peptidoglycan.
What defines eukaryotic cells?
Contain a nucleus surrounded by a membrane and can be unicellular or multicellular.
What are the main components of fungi?
Can be unicellular or multicellular with cell walls made from chitin, and can be human pathogens.
What is the primary role of carbohydrates?
Store energy and are important components of bacterial structure.
What are the three domains of microorganisms?
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotic cells.
What constitutes the genetic material of cells and viruses?
Nucleic acids, specifically DNA and RNA.
What are the monomers that make up nucleic acids?
Nucleotides, which consist of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
What is ATP and its role in metabolism?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is used as an energy carrier in cells and is produced from catabolic reactions.
How are proteins structurally defined?
Proteins have four structural levels: primary (sequence of amino acids), secondary (local folding), tertiary (3D structure), and quaternary (multiple polypeptides interacting).
What is the significance of R groups in amino acids?
R groups determine the chemical nature and properties of each amino acid.
What is a polar covalent bond?
A type of bond where electrons are shared unequally between atoms with different electronegativities.
What is the function of enzymes?
Proteins that enhance the speed or likelihood of a reaction.
What type of reaction is hydrolysis?
A decomposition reaction that breaks larger molecules by adding water.
Define synthesis reactions.
Chemical reactions that form larger, more complex compounds from smaller molecules.
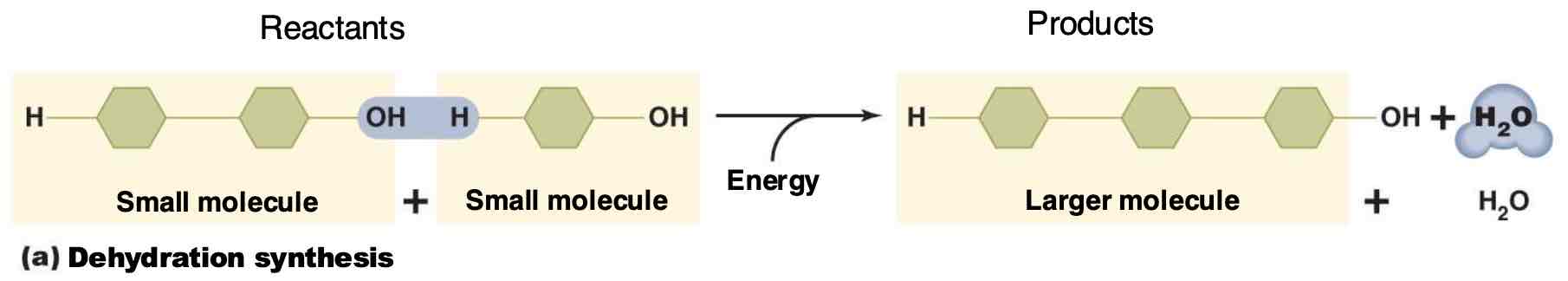
What are ionic bonds?
Bonds formed through the attraction between oppositely charged ions, resulting from the transfer of electrons.
Covalent bond
Sharing electrons, a strong bond
Single bond
Formed between two atoms that share ONE pair of electrons
Double bond
Forms between two atoms that share TWO pairs of electrons
Triple bond
Forms between two atoms that share THREE pairs of electrons
Two molecules with VASTLY different electronegativies will form which type of bond:
Ionic Bond
Reactants
Ingredients in a chemical reaction
Products
Chemicals formed after reactants combine
What is a decomposition reactions
Break bonds in large compounds to create smaller atoms/ molecules
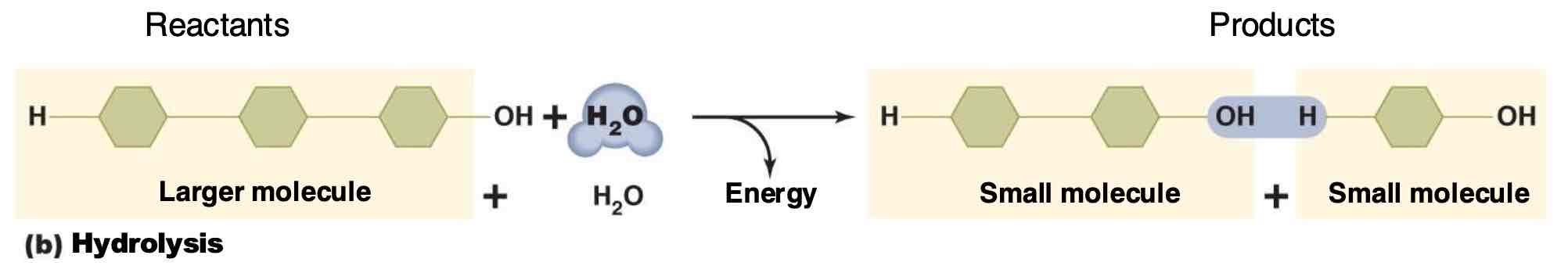
What does metabolism mean
The sum of all chemical reactions within an organism canabolism+ catabolism+ exchange reactions)
Organic molecules
Have the element of carbon
Inorganic molecules
Tend to not have carbon (water is the most important)
Functional groups
Groups of atoms within a molecule that confer specific properties to these molecules
Central dogma correct order:
DNA → RNA → protein
What are nucleotides composed of?
Nitrogenous base,a Penrose sugar, and a phosphate group
What monomers that make up nucleis acids and proteins are_____ and _____, respectively
Nucleotides, amino acids
The four macromolecules cells require to survive
Nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates