vascular and cellular events of inflammation
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
first cell responders during inflammation
macrophages
dendritic cells
mast cells
macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells release what mediators
amines and cytokines
amines and cytokines will recruit
leukocytes: monocytes and granulocytes and plasma proteins (complement, kinins and others)
leukocytes: monocytes anad granulocytes will
phagocytose and eliminate microbes and dead tissue
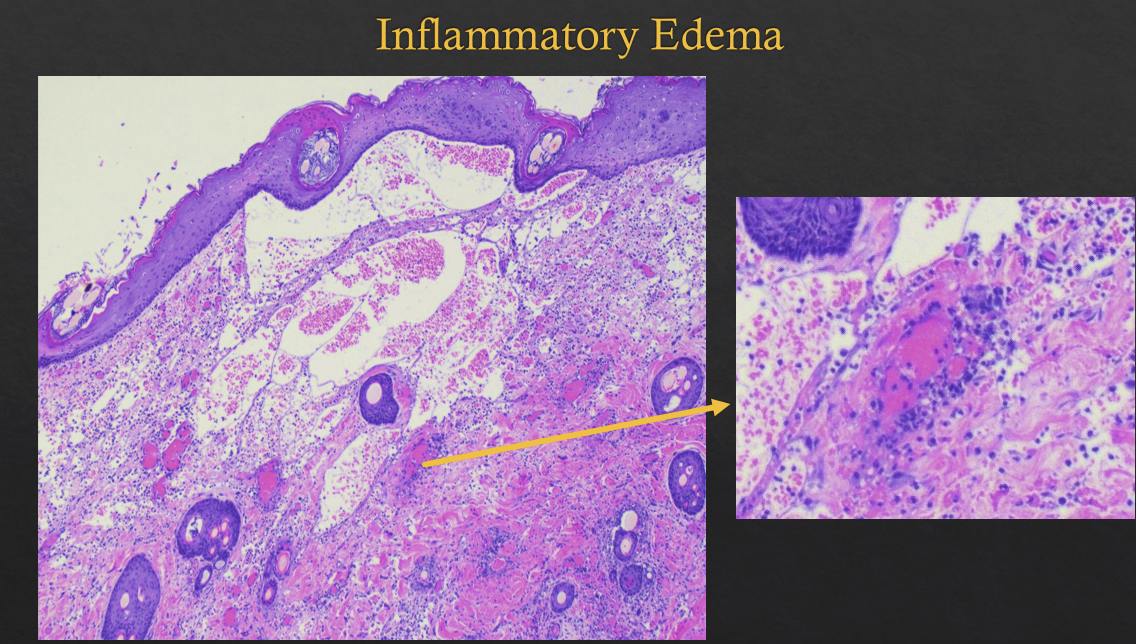
edema will also occur
once elimated the microbes
cytokines will still be released and fibroblasts for tissue repair
acute inflammation: vascuar fluidic phase is divided in 4 stages
transient vasoconstriction
vasodilation
increased vascular permeability
slowing and stasis of blood flow
transient vasoconstriction
not always seen, immediate and lasting a few seconds
primarily a neurogenic/direct endothelin response
transient vasoconstriction occurs in
precapillary sphincters
vasodilation and increased blood flow
consistently observed with inflammation
responsible for rubor and calor
opens capillary beds
blood vessels get distended by blood
ACTIVE HYPEREMIA
vasodilation will cause the opening of
pre-capillary sphincters
there are 2 types of mediators in vasodilation
early
late
early mediators for vasodilation
vasoactive amines: hitsamine and serotonin
late mediators for vasodilation
prostaglandins: PgD, PgE,prostacyclin
nitric oxide
increased vascular permeability:vascular leak
progresses from transudate-exudate
dilutes,confines, isolate stimulus
causes swollen lymph nodes
increased vascular permembility occurs in 2 stages
early
late
acute inflammation: vascular fluidic phase is divided in
transient vasoconstriction
vasodilation
increased vascular permeability
slowing and stasis of blood flow
transient vasoconstriction
not always seen, immediate and lasting only a few seconds
caused by constriction of the precapillary sphincters
primarily a neurogenic/direct enothelin response
example of transient vasoconstriction
delay of bleeding from a sharp cut
vasodilation and increased blood flow = active hyperemia
consistently observed with inflammation
responsible for rubor/redness and calor/ heat
relaxation of the precapillary sphincters
opens capillary beds
blood vessels will get distended by blood
2 stages of vasodilation mediators
early
later
later vasodilation mediators
prostaglandins = PgD, PgF, prostacyclin
nitric oxide
in increased vascular permeability it will progress from
transudate - exudate - inflammatory edema
serves to dilute, isolate, confine stimulus
causes swollen lymph nodes
early vascular permeability
protein-poor fluid transudate
INCREASED hydrostatic pressure
slower blood flow
congestion
later vascular permeability
chemical mediators affect the endothelial cells causing contraction and increased gaps between cells
primary site of action of the later vascular permeability
post-capillary venules
mechanisms of vascular leak
retraction of endothelial cells
endothelial injury
leukocyte-mediated vascular injury
increased transcytosis
vascular leak: retraction of endothelial cells
occurs mainly in venules
induced by HISTAMINE
rapid and short lived
vascular leak: endothelial injury
in arterioles, capillaries, venules
caused by burns, microbial toxins
rapid: hours to days
vascular leak: leukocyte mediated vascular injury
occurs in venules, pulmonary capillaries
assoc. with late stage of inflammation
long lived hours
vascular leak: increased transcytosis
occurs in venules
mediated by VEGF
edema: transudate
low protein levels
fluid accucmulation due to hydrostatic imbalances between intravascular and extravascular compartments depsite normal vascular permeability
clear,colorless, slightly yellow
edema: exudate
high protein levels
related to increased vascular/endothelial permeability
caused by leakage of plasma proteins = albumin and leukocytes
cloudy to opaque
permeability mediators
vasoactive amines
complement fragments = C3a C5a
bradykinin = pain inducer
leukotrienes = LTC 4, LTD 4, LTE 4
platelet activating factor
cytokines
substance P
blood flow slowing/stasis
secondary effect of the combination of vasodilation and increased permeability, decreasing fluid content
causes loss of laminar flow in the capillaries and allowa the margination of leukocytes
slowing of blood flow breaks leukocyte arrangement and allows leukocyte sto go toward periphery of blood vessels
macrophages with microbes induce the activation of
cytokines and chemokynes
cytokines and chemokynes will induce the activation of
integrins= protein cell receptors allowing the adherence of leukocytes
acute inflammation: cellular phase
delivers phagocytic cells to engulf, neutralize and remove stimulus
cellular phase can be divide in
margination
rolling
adhesion
chemotaxis
rollling of polymorphonuclear cells is
loose transient adehsion between leukocytes and endothelium, mediated by surface expression of pre-formed selectins
rolls along endothelial lining
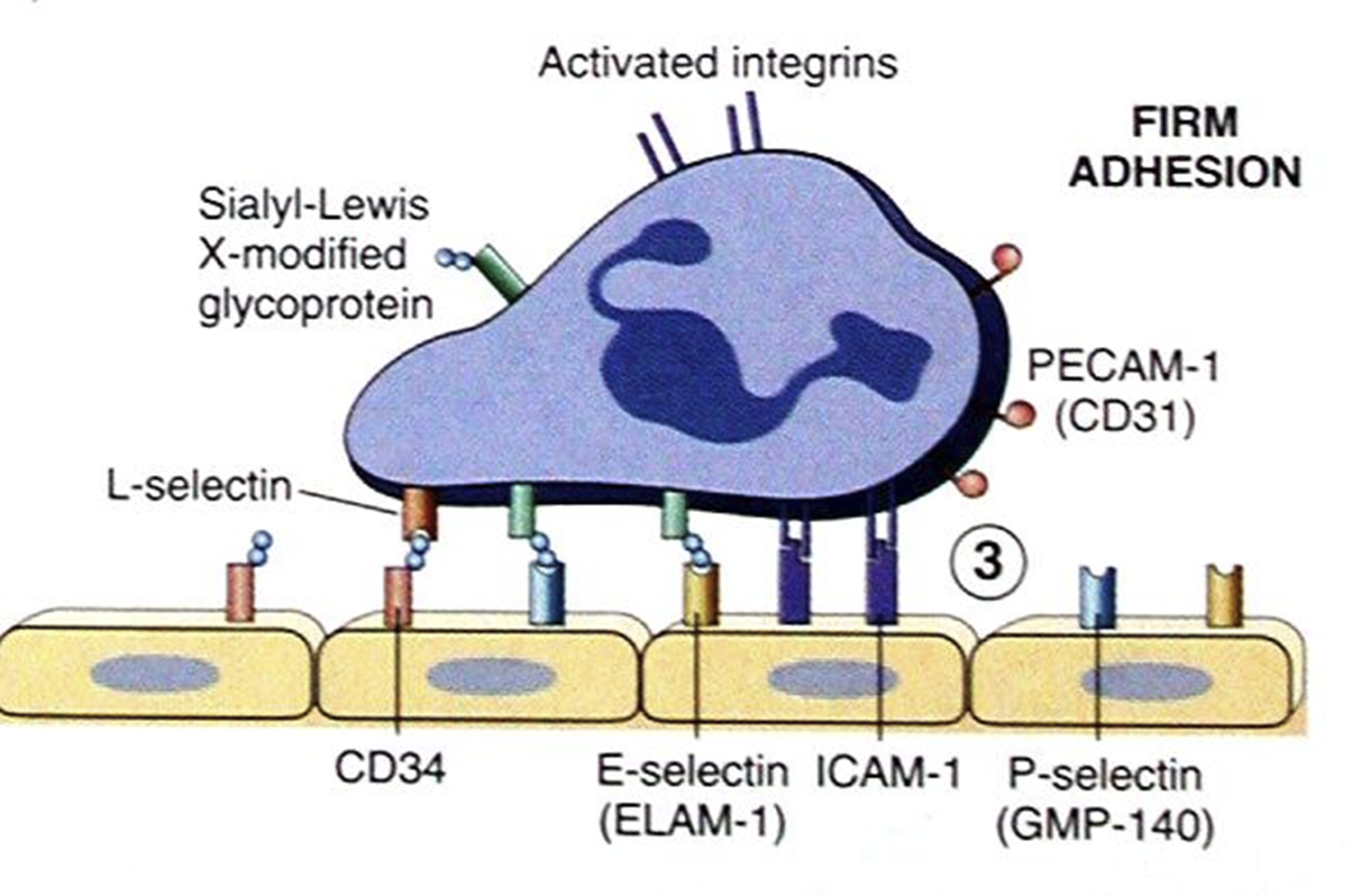
firm adhesion of leukocytes
induced de-novo production of adhesion molecules on EC of immunoglobulin superfamily: VCAM-1, ICAM-1-2-3
MEDIATORS OF firm adhesion of leukocytes
IL-1
TNF
IL-6
bacterial LPS
integrins are where?
on leukocyte surface
in form adhesion, integrins will adhere to
immunoglobulins on EC
mediators for the expression of integrins on leukocytes
PAF
chemokines = IL8
chemotaxins
cause cytoskeletal reorganization and extension of pseudopodia in direction of concetration gradient = ameboid crawl
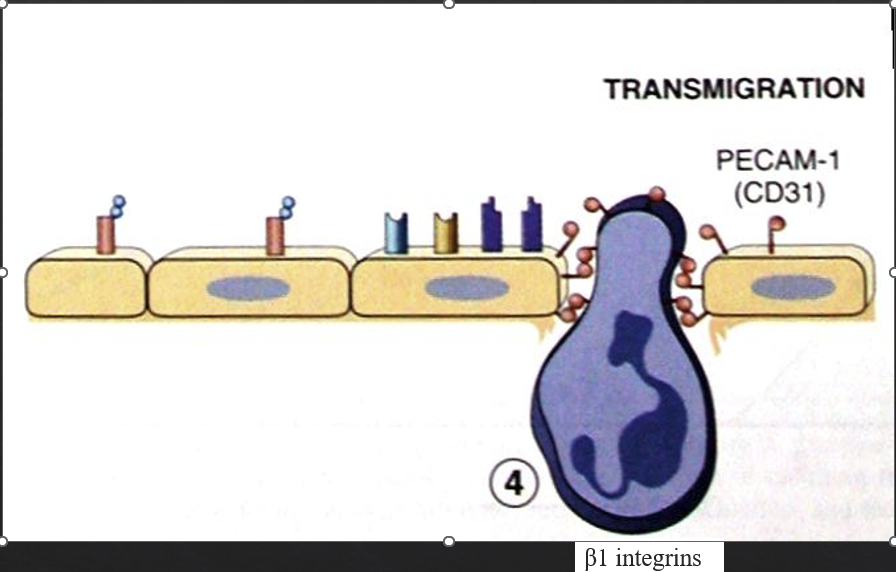
during emigration and chemotaxis
adhesion molecules along EC intracellular gaps adhere to extracellular matrix proteins in tissues
chemotaxins can be
endogenous
exogenous
endogenous chemotaxins
chemokines
CX-C ALPHA: IL-8/CXCL8 = attract neutrophils
C-C chemokynes beta = attract WBC
LTB 4, HETE, PAF
NECROTIC CELL DAMP’s
plasma: C5a, fibrin degeneration products
exogenous chemotaxins
bacterial peptides with terminal N-formylmethionine
basically, the cellular phase is the triggering of
leukocytes adhesion cascade
leukocytes adhesion deficiency affects
Holstein cows
irish setters
humans
LAD is caused by
point mutations on B-integrins on leukocytes
neutrophilia occurs without transmiggration
LAD will cause
recurrent mucosal infections such as
gingivitis
gastrointestinbal ulcers
pneumonia
cutaneous ulcers
phagocytosis
engulf, kill, remove offender
main phagocytes
macrophages
neutrophils
stages of phagocytosis
recognition and attack
engulfing = phagosome
phagolysosome
respiratory burst
extrusion of debris
in the first stage of phagocytosis, recognition and attack is aided by
OPSONIZATION via:
Ab
C3b
fibronectin
in the second satge of phagocytosis, engulfing is done by
extension of pseudopodia around object
fusion of cellular membrane which creates a phagosome
in the third stage of phagocytosis what occurs?
phagosome + lysosome fusion = phagolysosome
expulsion of lysosome contents into phagolysosome
in the 4th stage of phagocytosis what occurs?
respiratory burst = production of reactive oxygen species and activation of enzymes
BACTERICIDAL
t/f neutrophils are sloppy eaters and short lived in tissue
ture
systemic effects of acute inflammation
fever
decreased apetite
increased slow wave sleep
accelerated release of WBC from marrow
stimulation of colony stimulator factors
protein catabolism
release of acute phase proteins from liver
IL-6 AND 1 + TNF will cause
fever
decreased apetite
increased slow wave sleep
accelerated release of WBC from marrow
stimulation of colony stimulator factors
protein catabolism
release of acute phase proteins from liver
are caused by:
IL-1 + TNF