Biological molecules
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Structure of water
In water each hydrogen atom shares a pair of electrons with the oxygen atom forming a covalent bond.
There are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom
Why is water described as being polar?
Contains 2 slightly positive hydrogen atoms and 1 slightly negative oxygen atom (overall slightly positive charge)
Results in an uneven distribution of charge = Polar
Results in the formation of hydrogen bonds between adjacent water molecules
What is waters value as a solvent?
Most of a cells reactions take place in aqueous solution
Ability to act as a trasnport medium
Effects on hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecules
What are buffers
Chemicals or substances that resist changes to pH and ensure that a particular environment maintains a certain pH
Give two examples of buffers
Hydrogen carbonate ions
Albumin (blood protein)
Calcium role
Calcium pectate in the middle lamella
Iron role
Haem group in haemoglobin -oxygen binds to this haem group
Magneisum role
Gives chlorophyll its light absorbing property
Potassium role
Maintains electrical gradients during nervous communication
Nitrate role
Are found in amino acids, nucleic acids (Nitrogenous base)
Phosphate role
Found in nucleic acids, phopholipds
Hydrogencarbonate role
Natural buffer
What are organic molecules
Complex carbon containing molecules
Examples of organic molecules
Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins
When monomers join to form polymers, this is known as
Polymerisation
Glucose is a hexose monosaccharide with the formula
C6H12O6
in what glucose is hydorixde group below C1
alpha glucose
in what glucose is hydorixde group above C1
beta glucose (ABBA alpha below beta above)
Name another monosacchardie
Fructose
Why are these monosaccharides desribed as being isomers
Same chemical formula but different structural formula
How are disaccharadies? Name the reaction and the bond formed?
2 monosaccharides joined in a condesantion reaction with a 1-4 glycosidic bond.
What happnes during a codnesation reaction
joining of molecules (removing water)
what is the general formula for all disacchardies
C12H22O11
Give two examples of disaccharides and how they are formed
Maltose- 2 alpha glucoses joined in a condesation reaction with a 1-4 glycosidic bond
Sucorse- 1 alpha glucose and 1 fructose joined in a condensation reaction with a 1-4 glycosidic bond
What is a polysaccharides
More than 2 monosaccharides joined in a condensation reaction with a 1-4 glycosidic bond
They aren’t sugars and are insoluble in water
what is starch
a polymer of a alpha glucose and storage molecule in plants
amylose vs amylopectin diagrams
Amylose | Amylopectin | |
|---|---|---|
Elements, | ||
Monomer | ||
Bonds | ||
Branched? | ||
many terminal ends |
Amylose | Amylopectin | |
|---|---|---|
Elements, | C, H , O | C, H, O |
Monomer | alpha glucose | alpha glucose |
Bonds | 1-4 glycosidic bonds | 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds |
Branched? | No | yes |
many terminal ends | no, 2 | many |
One of the two chains of starch discussed has many terminal ends. Why is this an advanatge?
Allows for faster hydrolysis of glucose e.g to be used in respiration
Why is starch a good storage molecule
Very compact (amylopectin)
Insoluble - doesnt affect osmotic gradient
Large- is retained within the cell as it is too large to pass through the membrane
Amylopectin branching = many terminal ends for fasted hydrolysis of glucose
What is glycogen
storgae in animals, - liver, fungi cells (fungi)
Desribe the strucutre of glycogen
Formed of alpha glucose
contains 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds,
highly branched therefore many terminal ends for fast hydrolysis of glucose
Glycogen is similar to which starch?
Amylopectin
How are glycogen and amylopectin different?
Glycogen is more highly branched, many more terminal ends and therefore faster hydrolysis of glucose. This is is bcus animals are more metabollicaly active than plants.
Cellulose role
structural role, in plant cell walls
Structure of cellulose
Long chains of beta glucose monomers held withing 1-4 glycosidic bonds. Adjacent chains are held together with hydorgen bonds to form microfibrils. Every second beta glucose in inverted (flipped 180°) to allow for 1-4 glycosidic bond to be formed.
How does the structure of cellulose relate to its function
Microfibrils provide tensile strenth in cell walls
Amylose | Amylopectin | Glycogen | Cellulose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Monomer | ||||
Bonds | ||||
Branching | ||||
Terminal ends | ||||
Location | ||||
Function |
Amylose | Amylopectin | Glycogen | Cellulose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Monomer | α glucose | α glucose | α glucose | β glucose |
Bonds | 1-4 glyco | 1-4 + 1-6 | 1+4 + 1-6 | 1-4 |
Branching | no | yes | yes- more highly | no |
Terminal ends | 2 | many | many more | nope |
Location | chloroplasts of cells | chloroplasts of cells | animals - liver muscle fungi | plant cell walls |
Function | storage of glucose | storage of glucose | storage of glucose | proivde tensile strength |
what are the properties of lipids
They contain carbon hydrogen oxygen
They are not polymers
They are not soluble in water (hydrophobic) , but they are soluble in organic solvents such as ether or ethanol
The main types of lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, waxes and steroids
What are triglycerides made up of
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids tails
What are triglycerides function
Energy store, insulation , protection
How is the triglyceride formed
Condensation reaction between each fatty acid tails and the glycerol
What bond is formed in a triglyceride
Ester bond formed between fatty acid tails and an OH group on the glycerol
What reaction takes place to create a triglyceride
Condensation
Describe the structure of a phospholipid
1 glycerol, 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group
How does a phospholipid differ to a triglyceride
Instead of a 3rd fatty acid chain it has a phosphate group
What part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic
Fatty acid tails
What part of the phospholipid is hydrophilic
the phosphate head
What is the orientation of phospholipids and what is created (what is a the function)
Phosphate headed oriented towards water and fatty acid tails away from water.
Phospholipid bilayer that forms the cell surface membrane is created as a result with fatty acid tails away from water (cytoplasm and fluid) and phosphate head towards.
What’s the different between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid
Unsaturated has a C=C
A fatty acid with one C=C bond is a
Monounsaturated fatty acid
A fatty acid with more than one C=C is a
polyunsaturated fatty acid
Unsaturated fatty acids are _____ at room temperature and why
Liquid because the C=C makes the unsaturated fatty acid more fluid
Saturated fatty acids are ________ at room temperature
Solid
What elements do proteins contain
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes Sulfur
What are proteins
proteins are large polymers of amino acids joined in a condensation reaction and held with a peptide bond
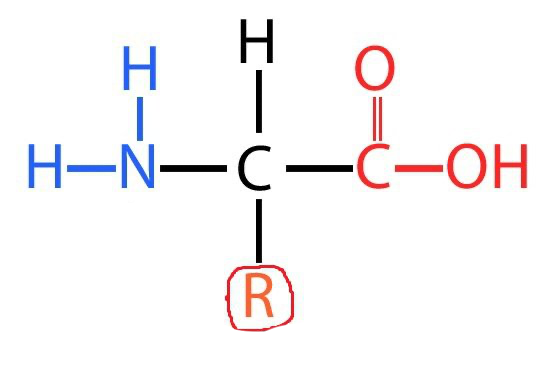
Amino acid diagram
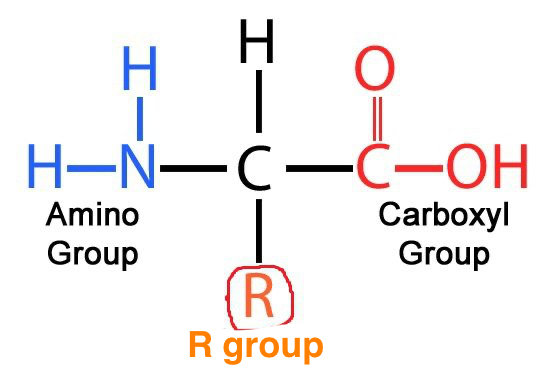
What is the role of the R group
Allow bonding in the tertiary structure
If the R group is Sulfur, what bond can be formed between similar R groups
Disulfide bond
What is a dipeptide bond
2 amino acids joined together in a condensation reaction and held with a peptide bond. The peptide bond forms between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group on the other.
What is a polypeptide
Many amino acids joined together in a condensation reaction and held with peptide bonds
Describe the structure of a primary structure protein
A sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
Desribe the structure of a secondary structure protein
Alpha helix vers
Hydrogen bonds formed between amino acids at regular intervals. These bonds twist the polypeptide chain into a helical shape. Making an alpha helix
How are betapleated sheets formed
Folding of the polypeptide chain caused by the sections of the chain lying in opposite directions
More rigid and less flexible
Hydrogen bond between C=C and NH group
How is the tertiary structure formed
Further folding of secondary structure
What bonds are involved in the tertiary structure
Hydrogen (weakest)
Ionic ( break when pH moves from optimum)
Disulphide (if sulphur group is present)
Peptide (in all structures)
Hydrophobic interactions are involved
Describe the quaternary structure
2 or more polypeptide chains bonded together
Some protein structures contain prosthetic groups, what does this mean
Non protein
What are these proteins known as
Conjugated protein
Give an example of a conjugated protein and describe its structure
Haemoglobin consists of 4 polypeptide chains (2 alpha helixes, 2 beta pleated sheets) with a haem group (prosthetic group) attached to each
Oxygen bonds to the haem group for transport
What is another example of a conjugated protein
Glycoprotein
Give details and examples of fibrous
Collagen - 3 polypeptide chains held with H bonds (alpha helices) wound around each other and is therefore a quaternary structure protein. The structure of collagen gives it tensile strength for its function in tendons that link muscle to bone.
give details and example of globular
Globular have a specific function and are 3D e.g enzymes, hormones, antibodies, haemoglobin
What are prions
A particular type of protein found in mammals and some other animal groups. They are found in the nervous system and are thought to be involved in synapic transmisson.
What is the normal form of prion protein?
PrPC
What is the formula for the disease causing Prion
PrPsc
How can the disease casuing form PrPsc be identified
Has a higher proportion of beta pleated sheets than the normal
How can diseases associated with the diseas causing form PrPsc form arise.
Eating contaminated meat
Mutation
Arise spontaneously
Prions diseases includes
Scrapie in sheep
BSE - (bovine spongiform encephalopathy) in cattle
vCJD - human form of BSE
What are the two key features of disease causing proteins
infectious
can replicate
What is the subunit of nucleic acids?
nucleotide
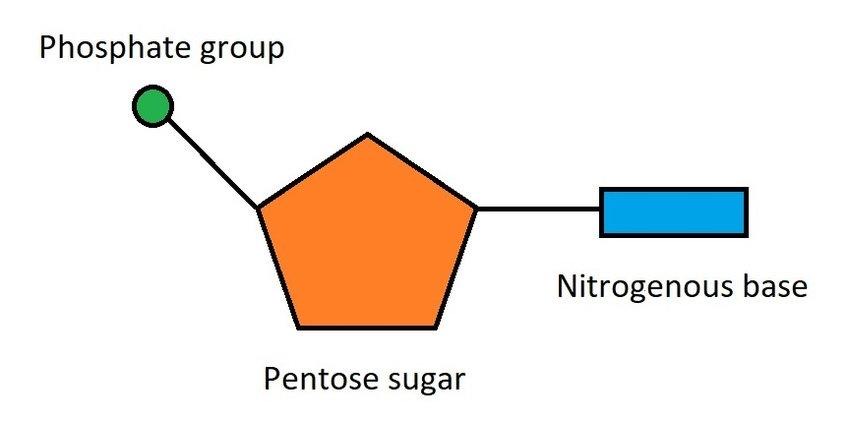
name the three components a nucleotide consits of
phosphate group
nitrogenous base
pentose sugar
nucleotide diagram
What does DNA stand for
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
What does RNA stand for
Ribonucleic acid
Describe the structure of RNA
Ribose pentose sugar
phosphate group
nitrogenous base single stranded
contains vracil instead of Thymine
its shorter than DNA
There are 3 types of RNA, name them at give their role
mRNA - carries code from the DNA in nucleus to a ribosome in the cytoplasm where protein synthesis takes place
tRNA - transfers amino acids to the mRNA (clover shaped)
rRNA - made in nucleoulus and forms overhalf the mass of each ribosome.
Desribe the structure of DNA
Double helix, 2 antiparralel strands of DNA are held to hydrogen bonds following base pairing rules.
What are base pairing rules
Adenine bonds to thymine
Cytosine bonds to guanine
Mammals have very similar/ the same percentages of base pairs in their DNA. So, what makes them different to each other?
Order of bases/ base sequence
Describe the steps in DNA replication
The enzyme DNA helicase ‘unzips’ the two strands of DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs.
2. Each original strand becomes a template.
3. Free DNA nucleotides are linked to the template strands following base pairing rules and hydrogen bonds form.
4. The nucleotides of the new strand are joined together by the enzyme DNA polymerase which forms phosphodiester bonds between them.
What is semi- conservative replication?
New DNA contains one original strand and one newly synthesised strand of DNA.
What were the two alternate methods of replication?
1. Conservative model
2. Semi Conservative model
Density - gradient centrifugation was used. Describe how
To separate the bacterial DNA following sampling based on density.
Samples are spun at a high speed.
Lighter 14 N accumulates at the top of the centrifuge tube Heavier 15 N accumulates near the
One geneartion
– The DNA positions in the middle as all of the DNA contains one strand of 14N bases and one strand of 15N bases.
Two generations
Half of the DNA consists of mixed DNA (14N and 15N) and the other half only contains 14N.
How can these results by explained by the semi - conservative model?
After one generation the DNA contained one original template strand and one new strand (one 14N strand and one 15N strand)
Describe the composition of a third generation.
The light 14N band would get thicker and the mixed 14N and 15N band would remain the same.