Late Medieval/Pre-Renaissance/Early Renaissance Art
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
atmospheric perspective
use of shades of color and clarity to create the illusion of depth. Closer objects have warmer tones and clear outlines, while objects set further away are cooler and become hazy

buon fresco
true or wet fresco; pigments are mixed with water and become chemically bound to the freshly laid lime plaster

cartoon
In painting, a full-size preliminary drawing from which a painting is made.
chapter house
Where the monks held daily meetings

chiaroscurro
It means "light & dark"; use of light and shadow to make something look realistic and 3-D.

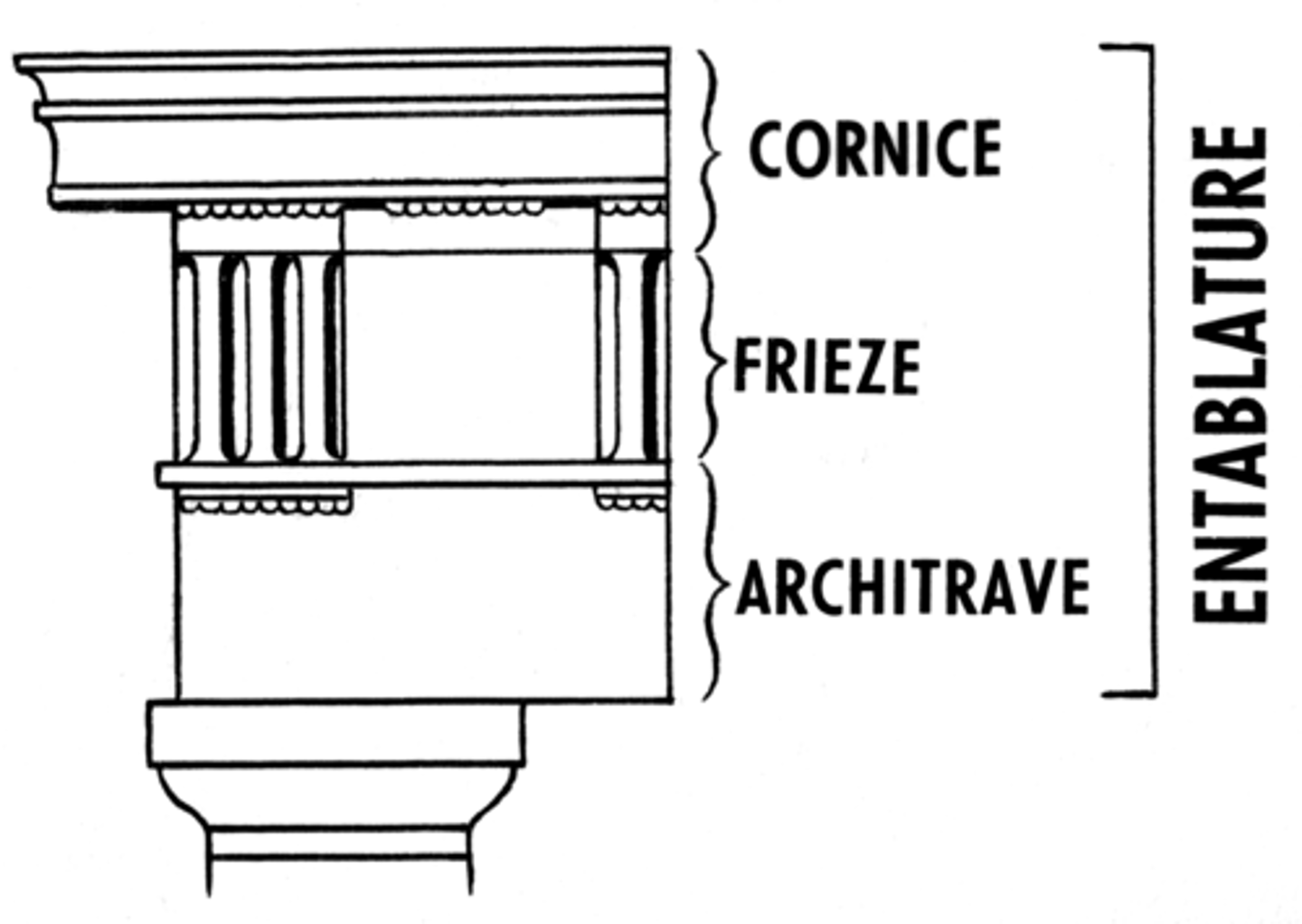
Entablature
a horizontal, continuous lintel on a classical building supported by columns or a wall, comprising the architrave, frieze, and cornice.
foreshortening
portray or show (an object or view) as closer than it is or as having less depth or distance, as an effect of perspective or the angle of vision.
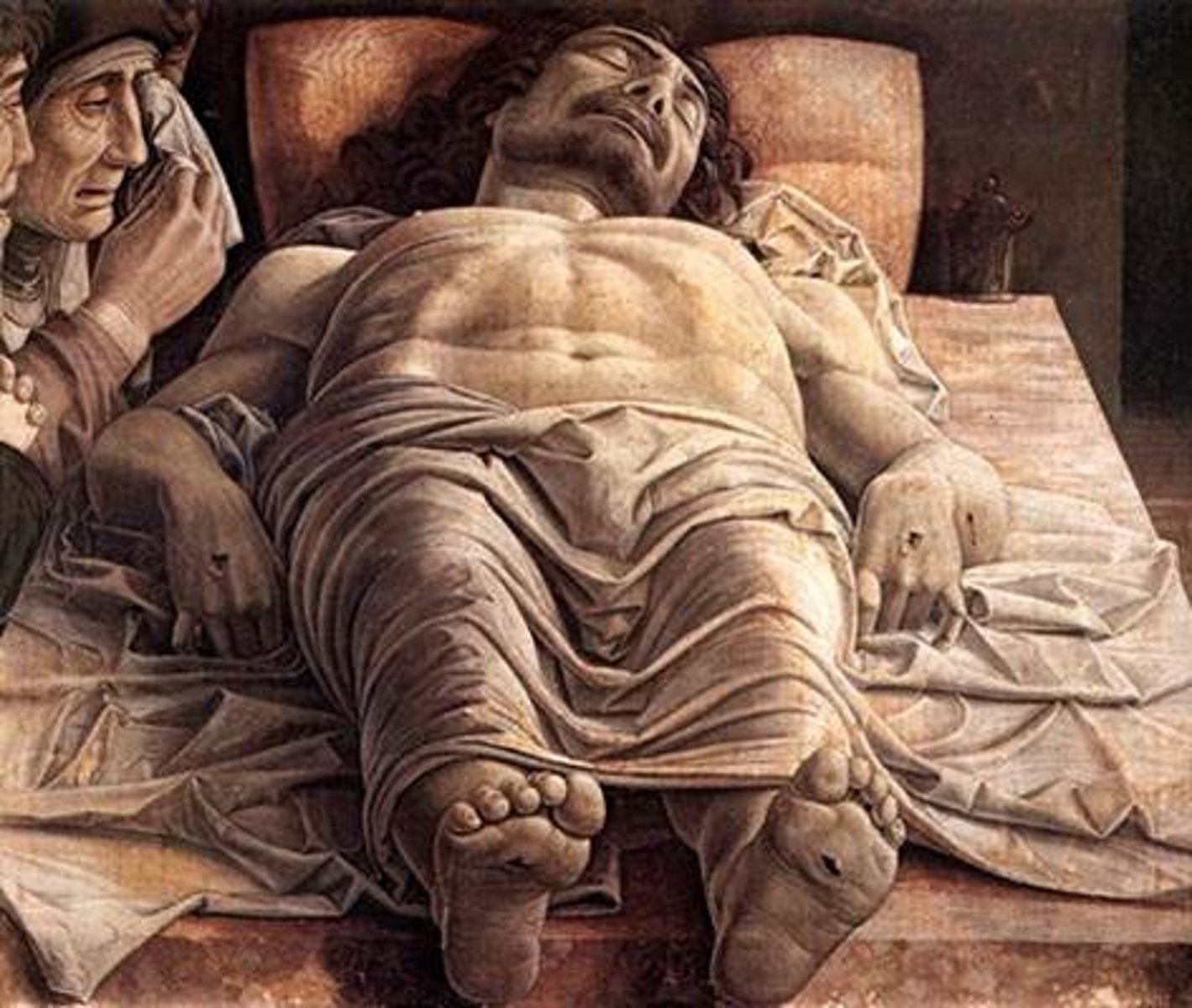

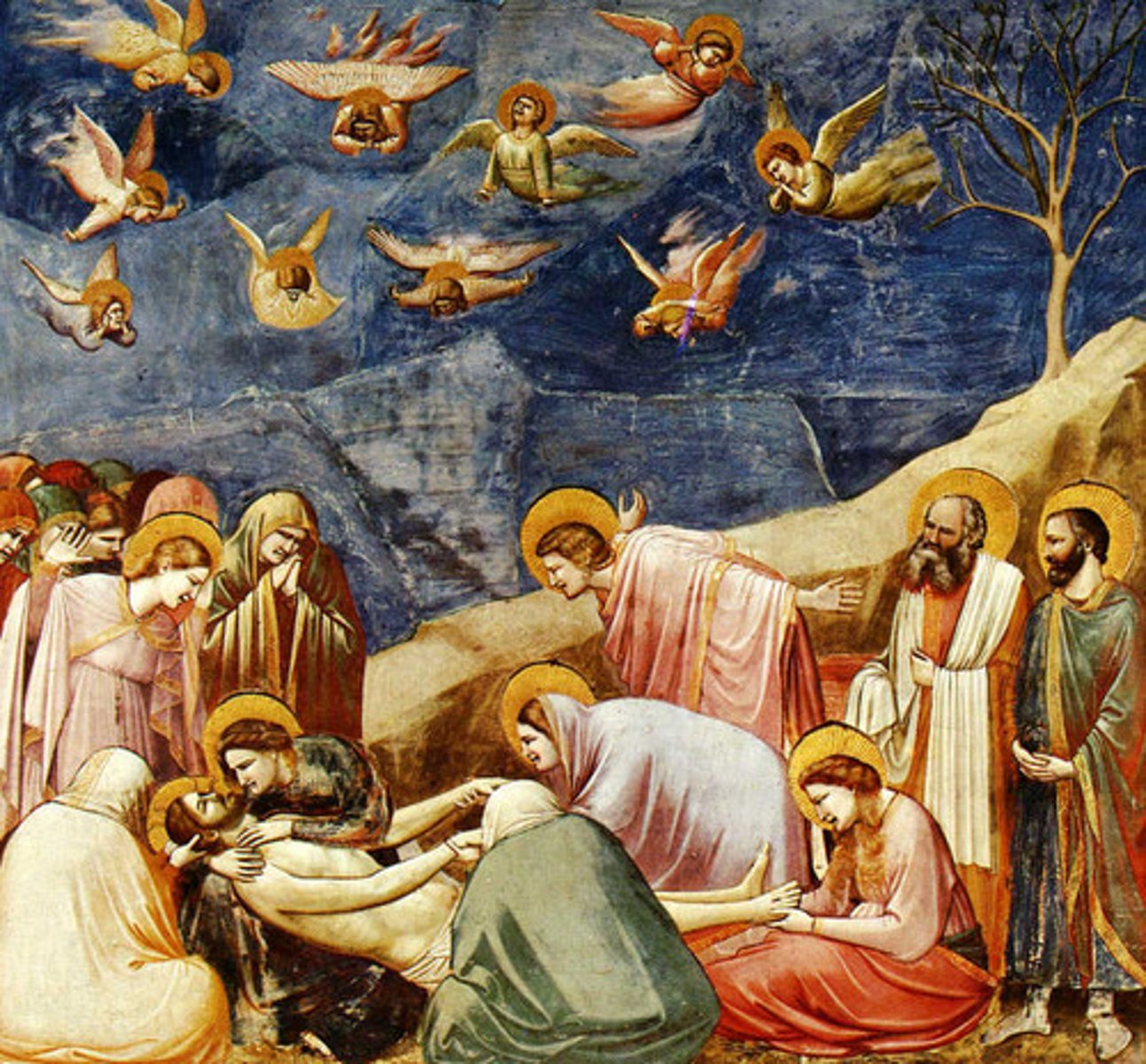
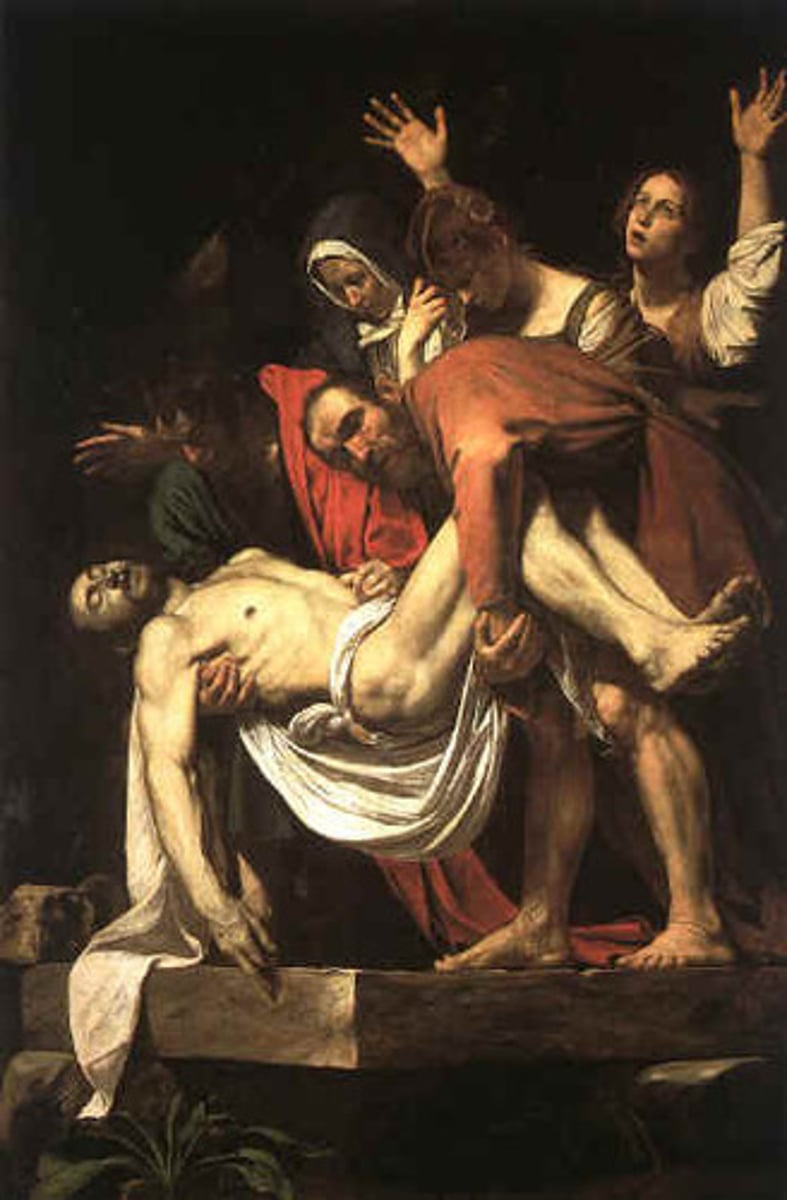
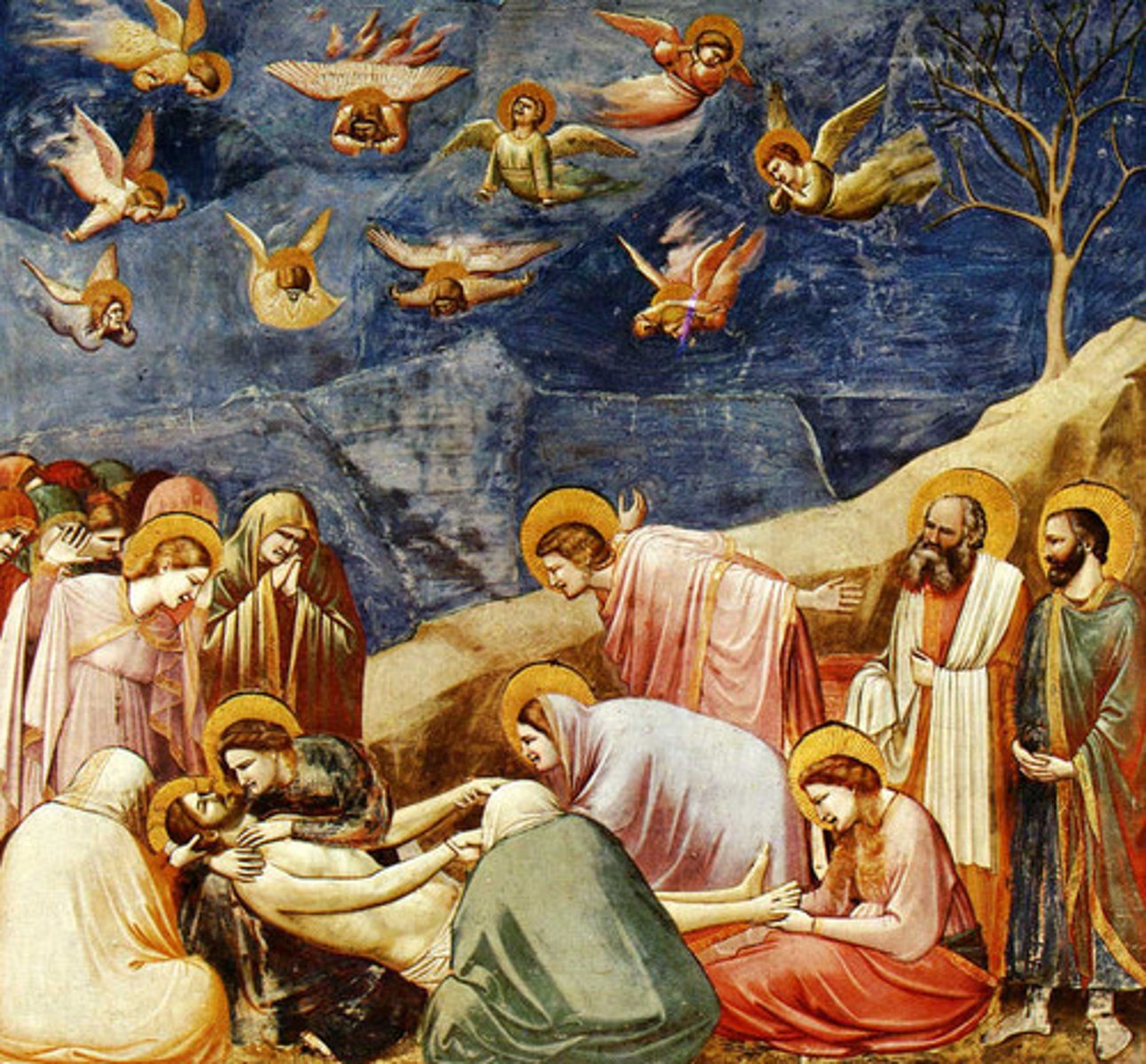
Lamentation
the passionate expression of grief or sorrow

linear perspective

pietra serena
A greenish-gray Tuscan sandstone used in Florentine architecture
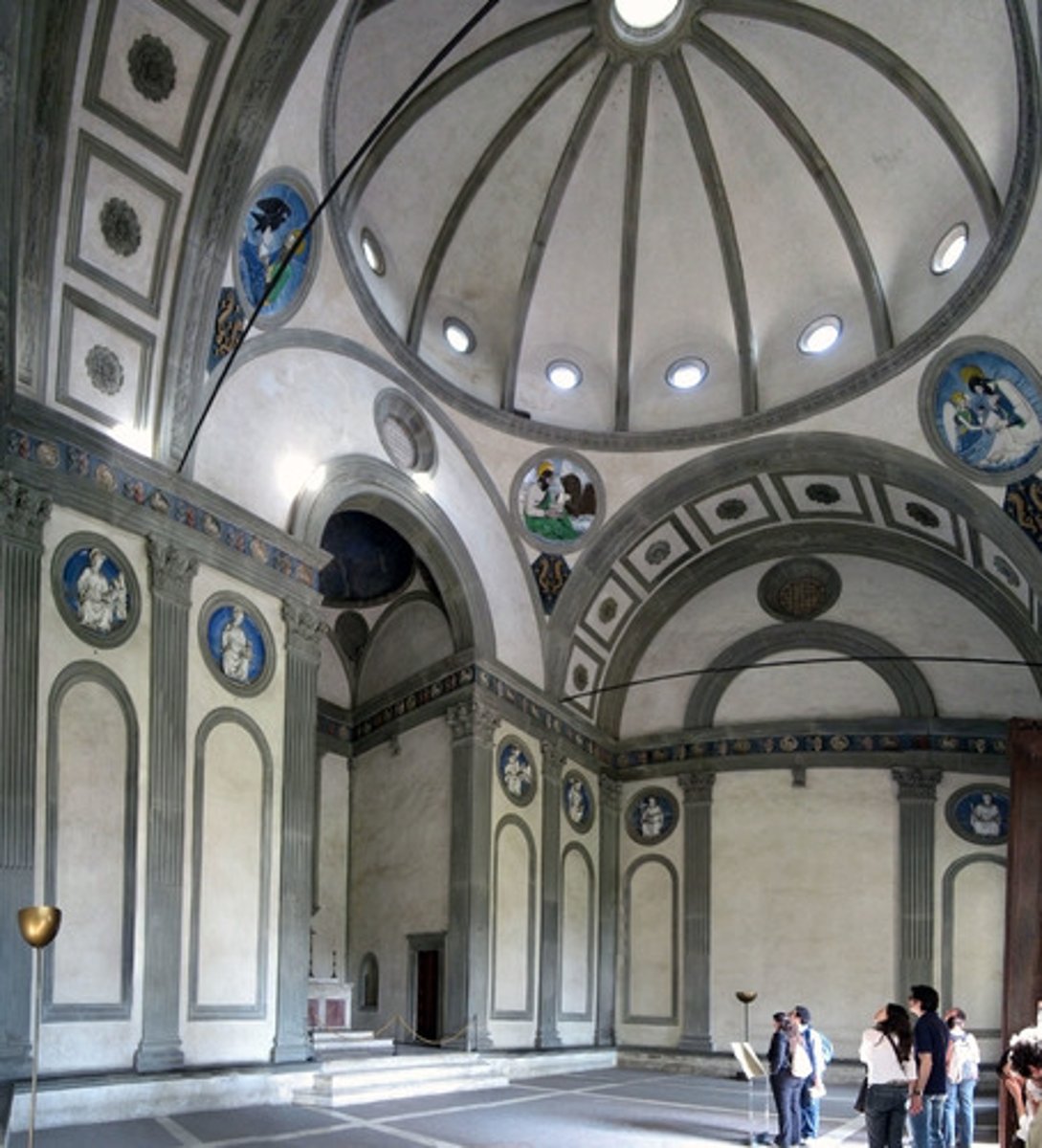

Pilasters
a rectangular column, especially one projecting from a wall.

pyramidal composition
subjects organized in a triangle; Italian Renaissance

roundels
any ornamental element with a circular format, often placed as a decoration

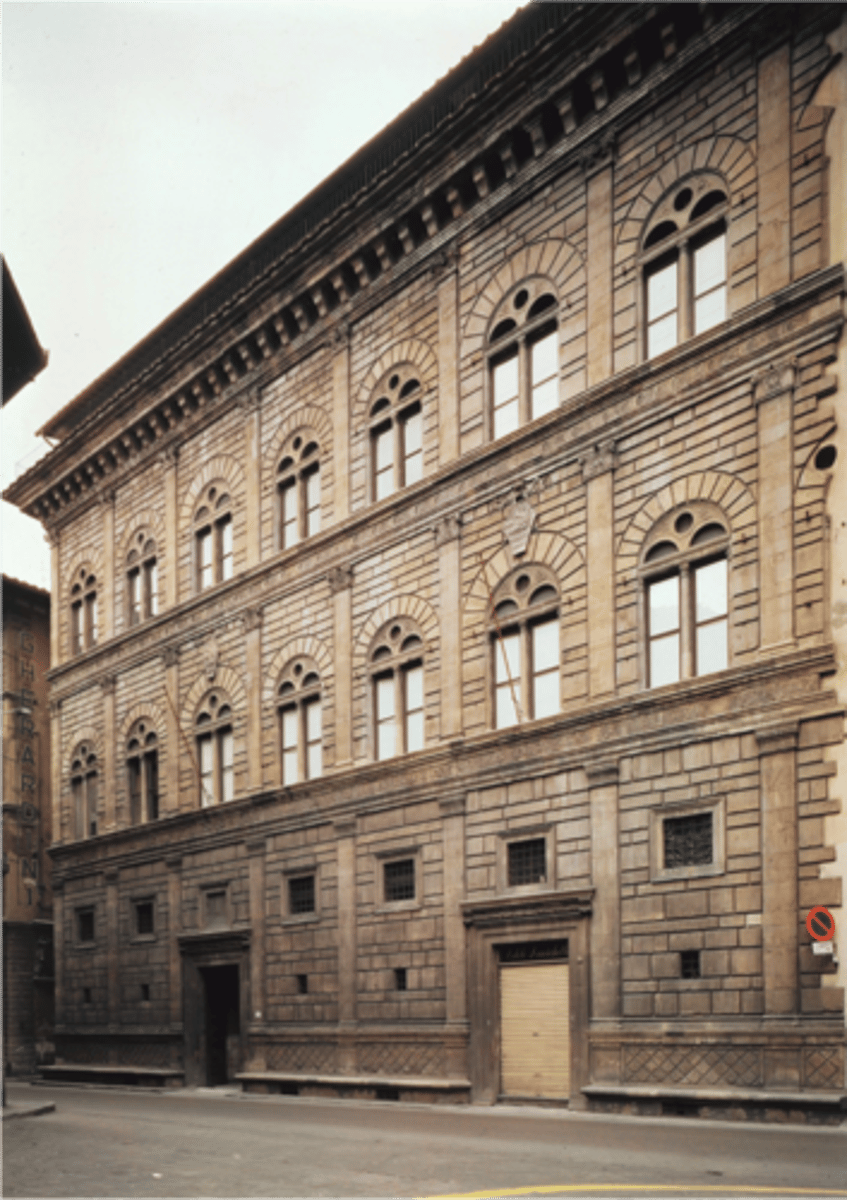
rustication
Heavy stonework with a surface left rough, or with deeply channeled joints, used principally on Renaissance buildings

Renaissance Humanism
an intellectual movement centered in Italy that valued scholarship, language study, the arts, and particularly the ancient Greek and Latin classics in order to begin developing a worldview that could celebrate the human being as the unique pinnacle of God's creation

Neoplatonism
Neo-Platonism was a philosophical movement that reinterpreted the ideas of the ancient Greek philosopher Plato. It argued that the world which we experience is only a copy of an ideal reality which lies beyond the material world. The artist in creating his work directly imitates the forms of this ideal reality, which are experienced as Beauty; Prevalent in Florentine art of the second half of the 15th century and especially with Botticelli.

trompe l'oeil
visual illusion in art, especially as used to trick the eye into perceiving a painted detail as a three-dimensional object.

usurer
a person who lends money at unreasonably high rates of interest

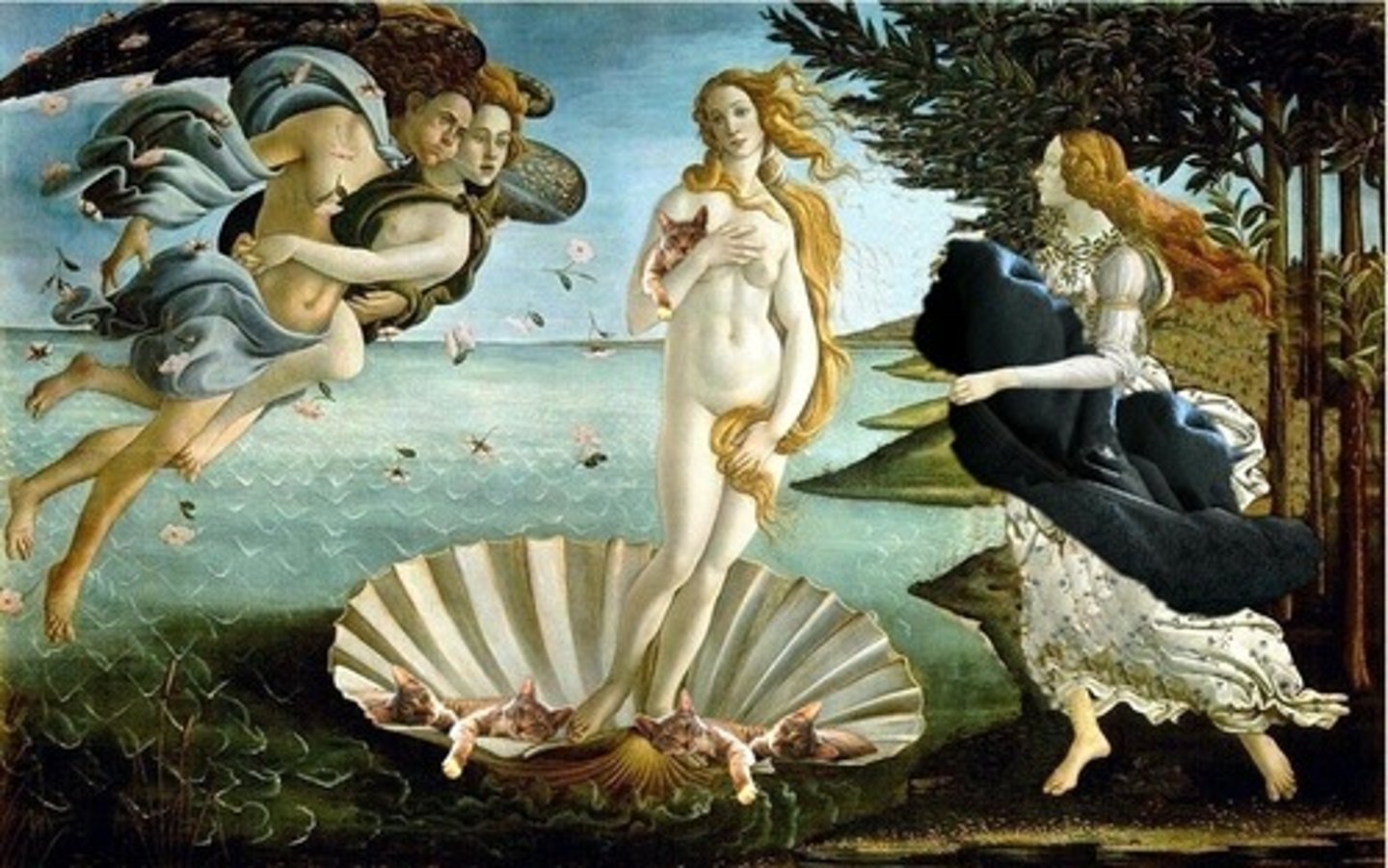
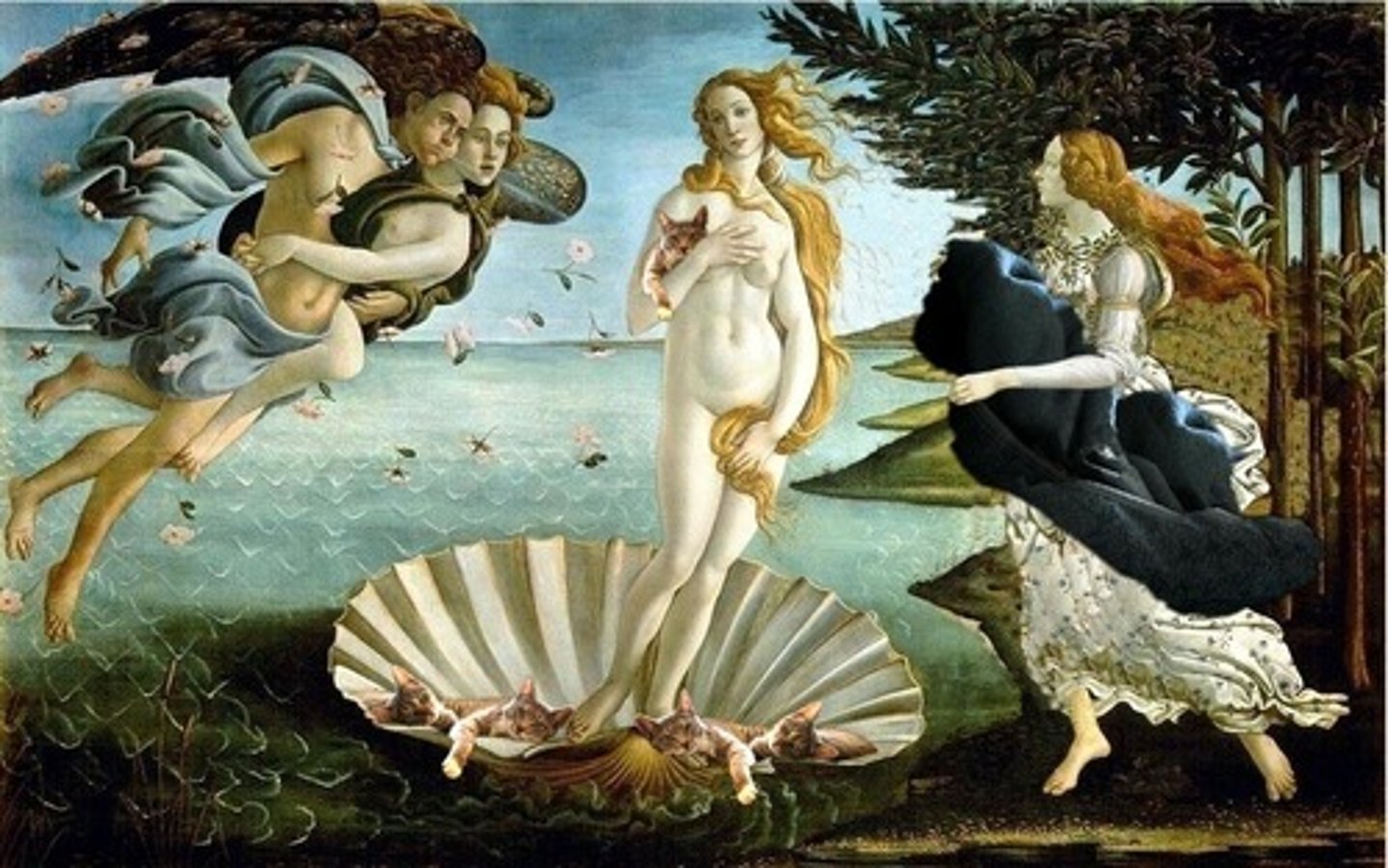
Botticelli
One of the leading painters of the Florentine renaissance, developed a highly personal style. The Birth of Venus

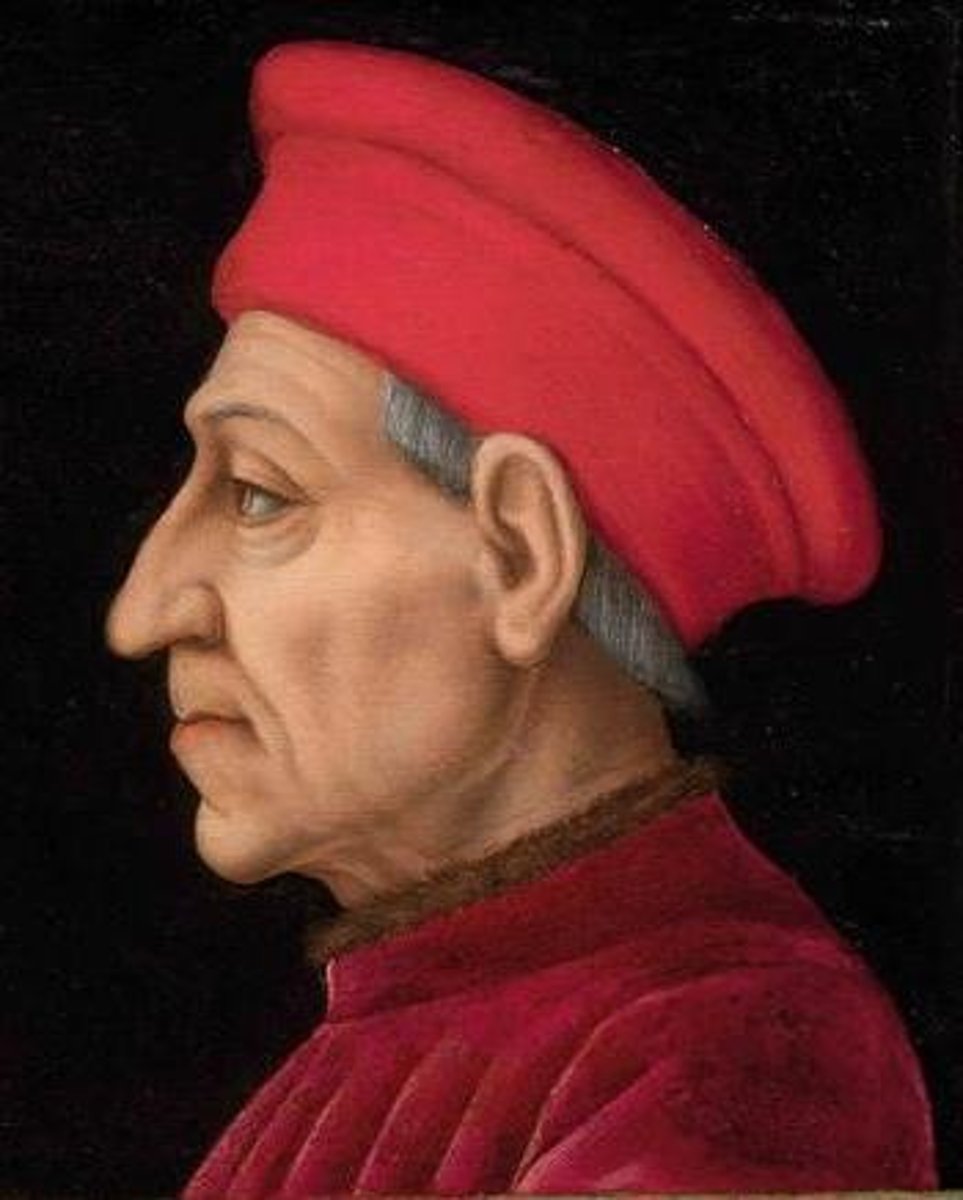
Cosimo de Medici (1389-1464)
Italian banker and leader of Florence, he wanted to make Florence the greatest city in the world. His actions helped bring about the Renaissance.

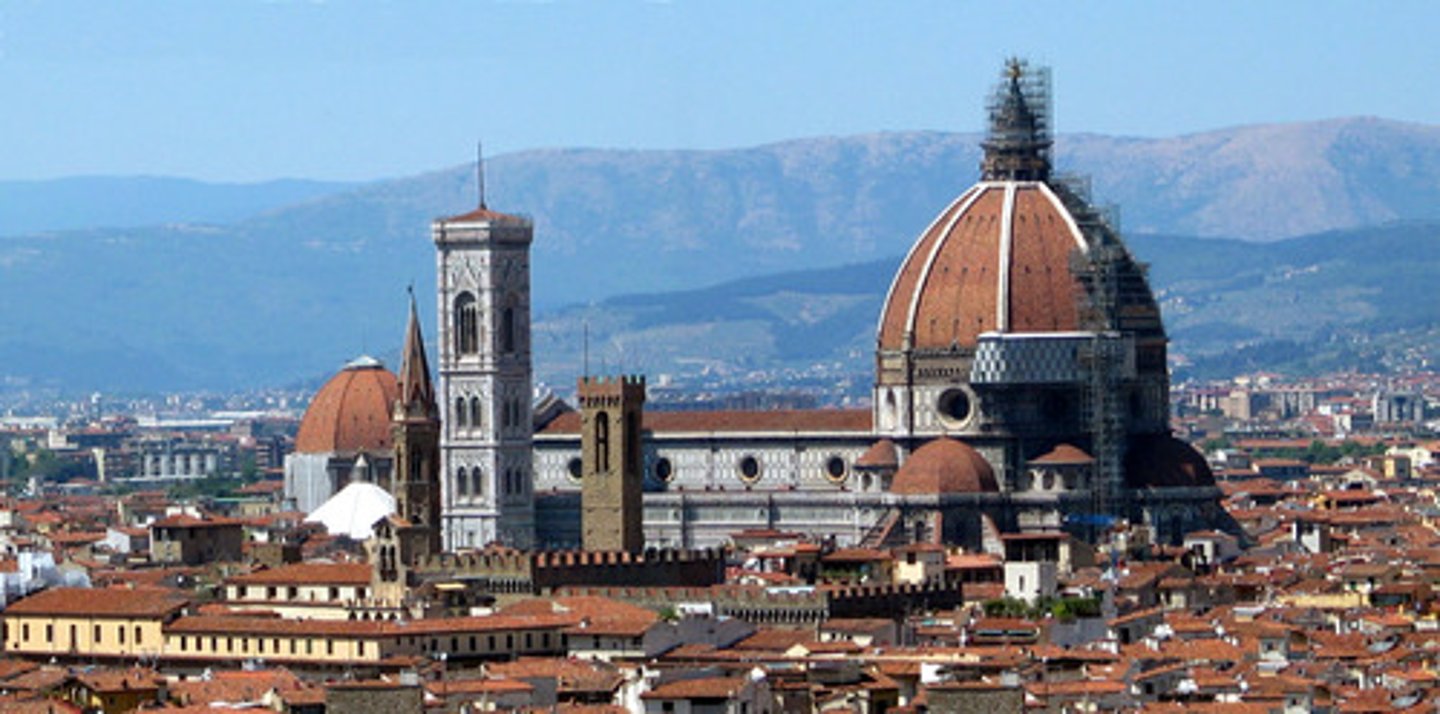
Florence
a city in the Tuscany region of northern Italy that was the center of the Italian Renaissance

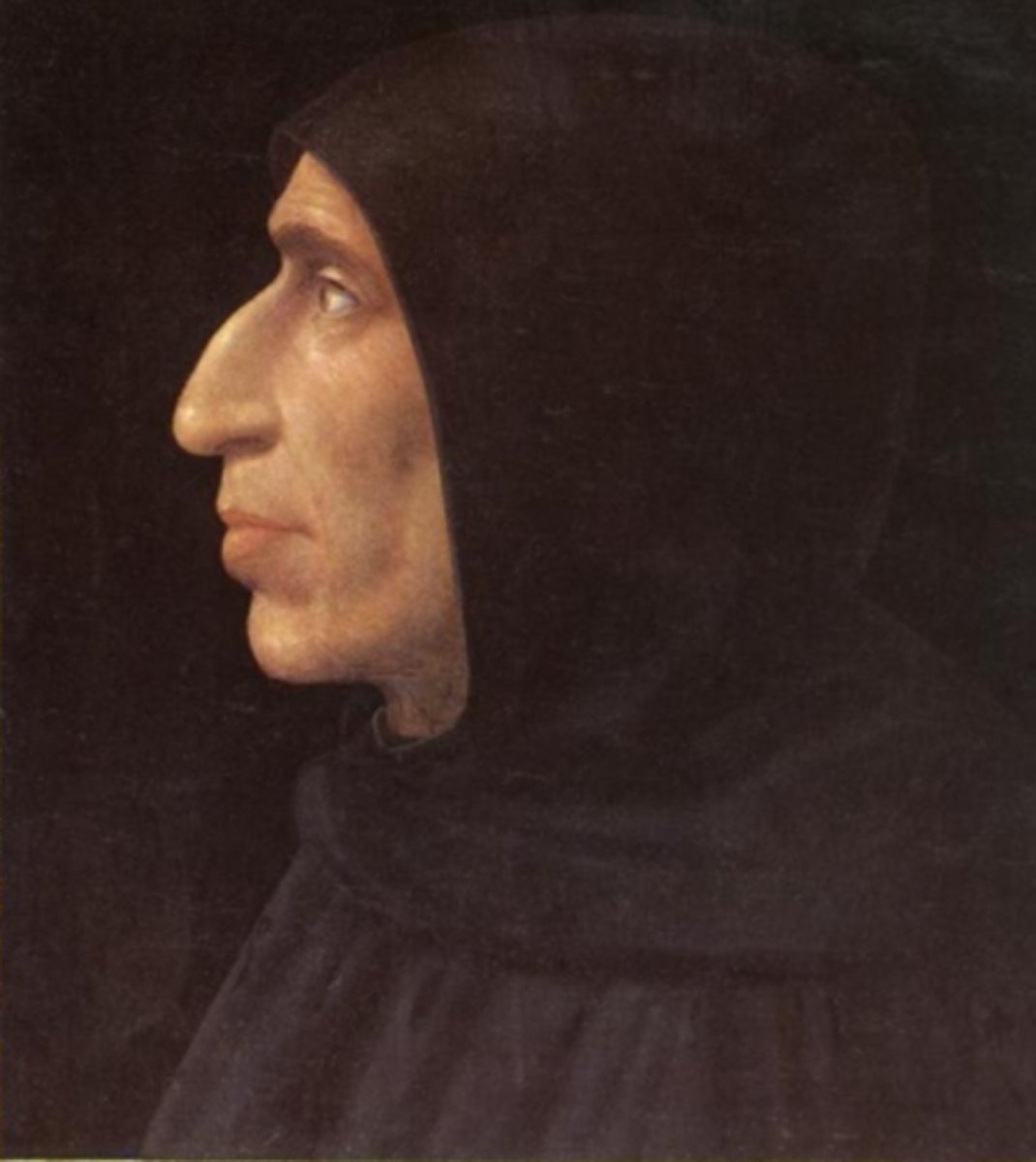
Fra Girolamo Savonarola
He denounced Florentine Renaissance art as too profane and believed only proper art was Biblical art.

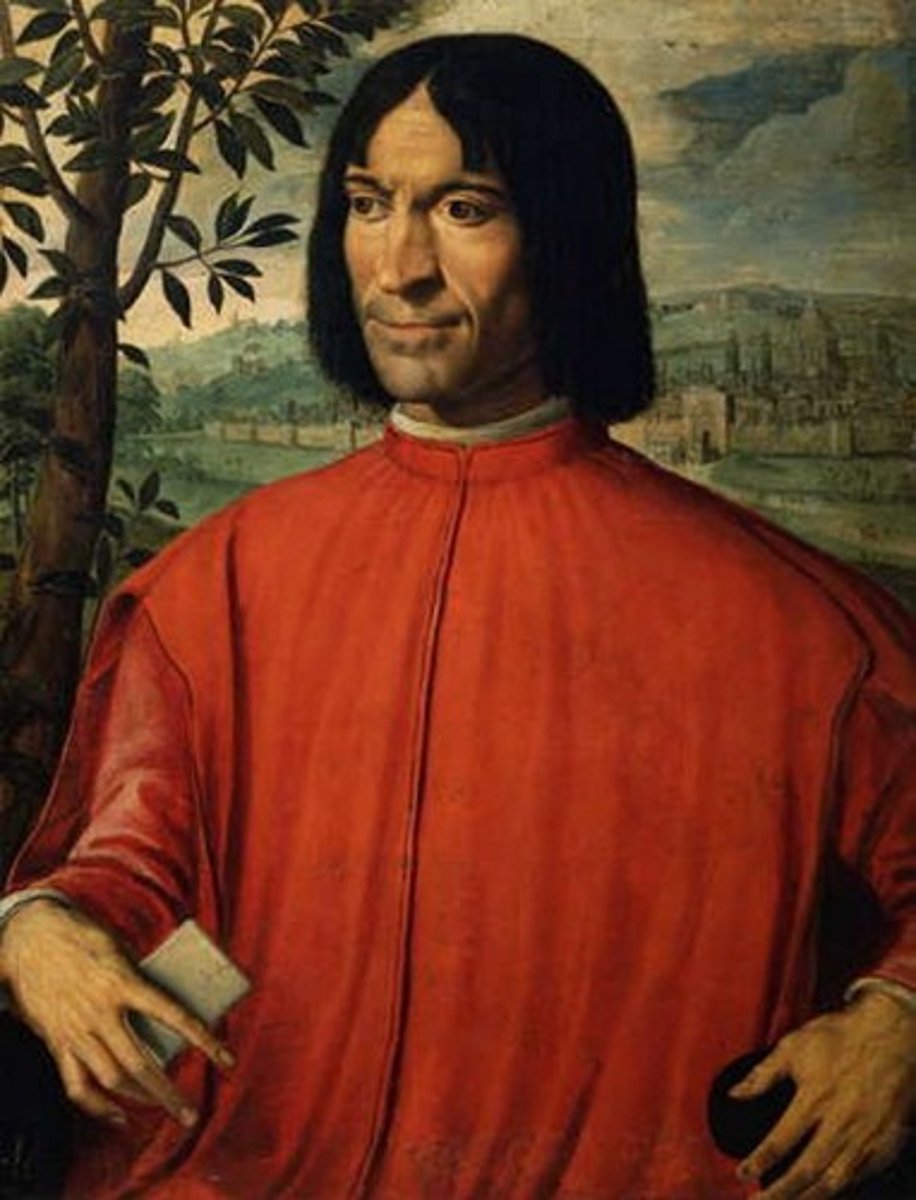
Lorenzo de Medici
Italian statesman and scholar who supported many artists and humanists including Michelangelo and Leonardo and Botticelli (1449-1492)

Pazzi Family
Wealthy family that was a rival of the Medici in Florence

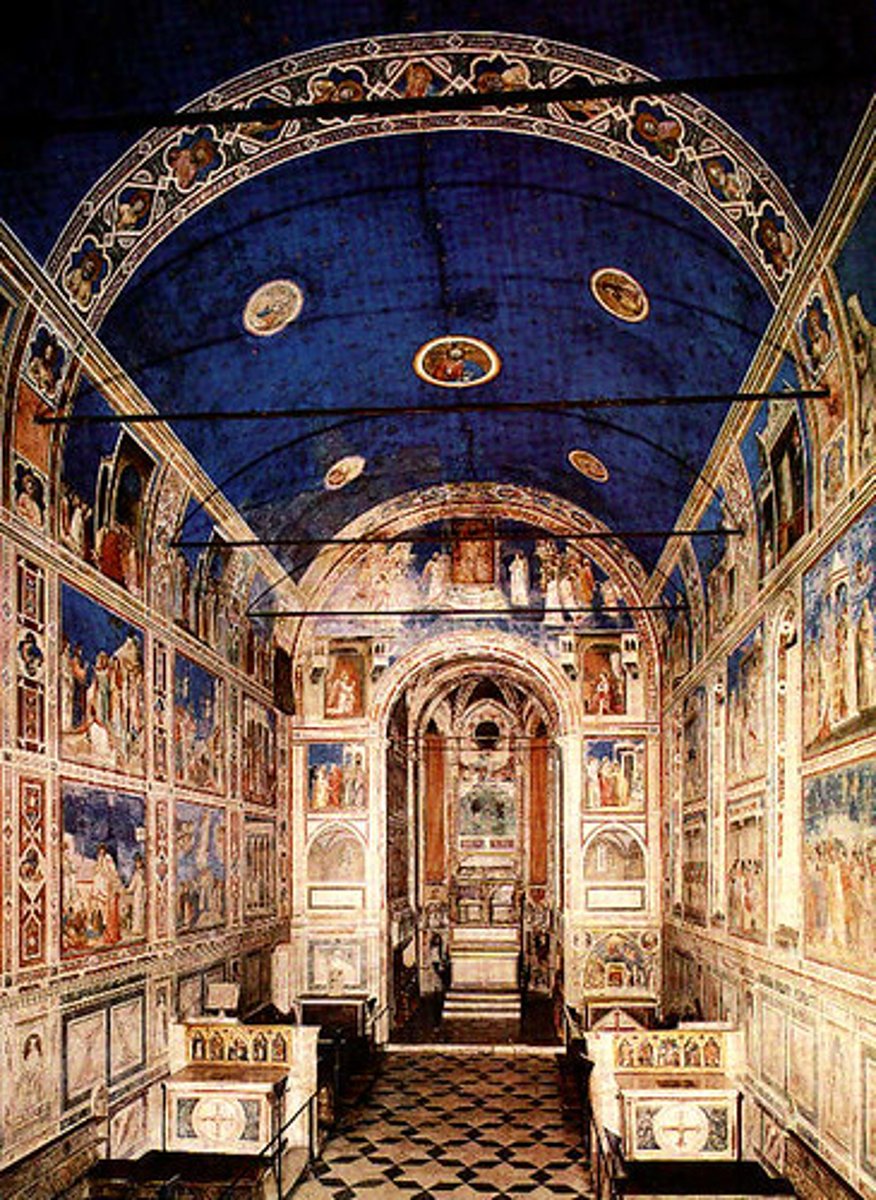
Arena (Scrovegni) Chapel, including Lamentation
Artist: Giotto di Bondone; Architect: Unknown
Period: Late Medieval/Pre-Renaissance
Dates: Chapel 1303 C.E., Fresco 1305
Culture: Padua, Italy
Material: Brick (architecture)

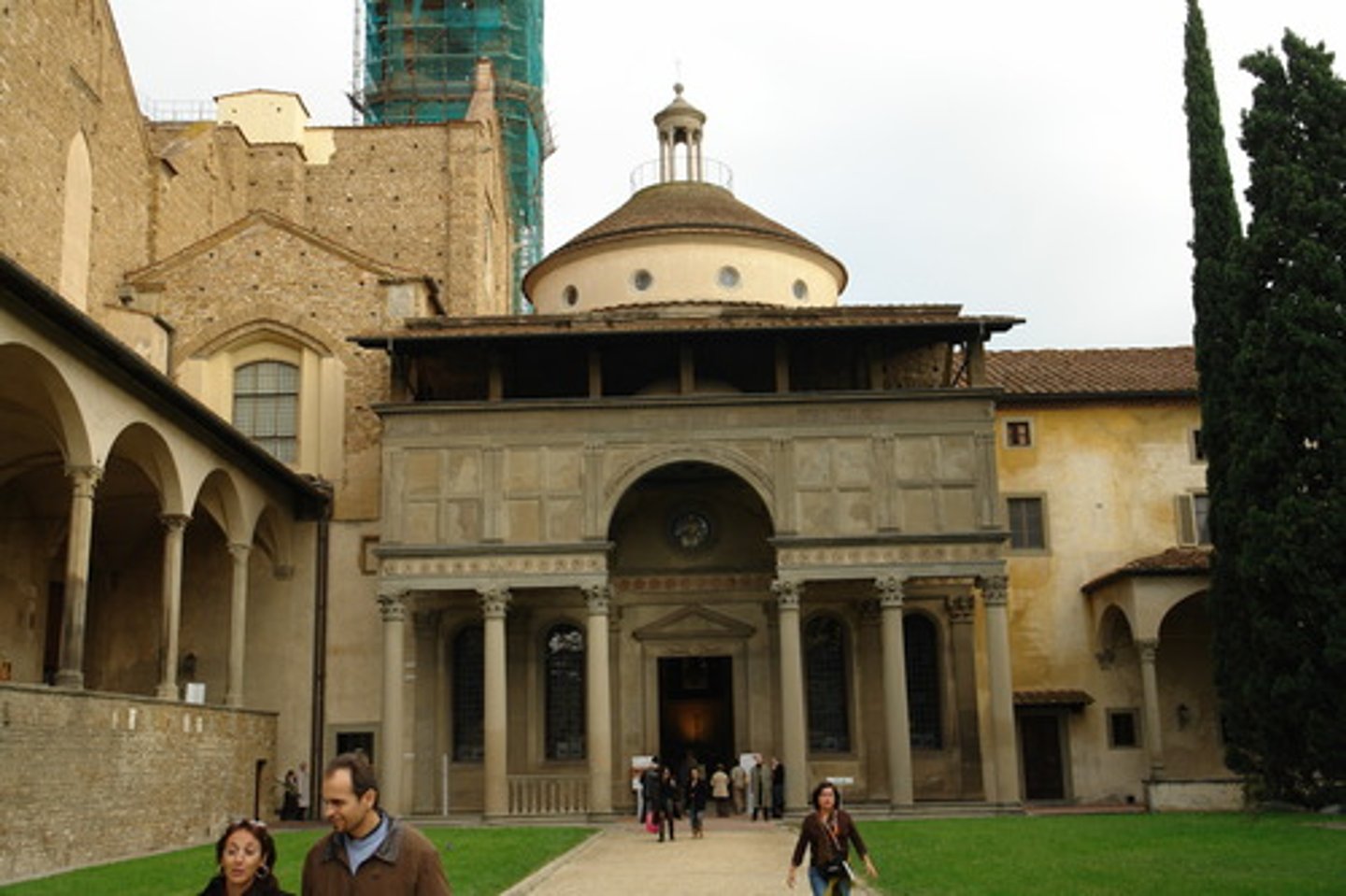
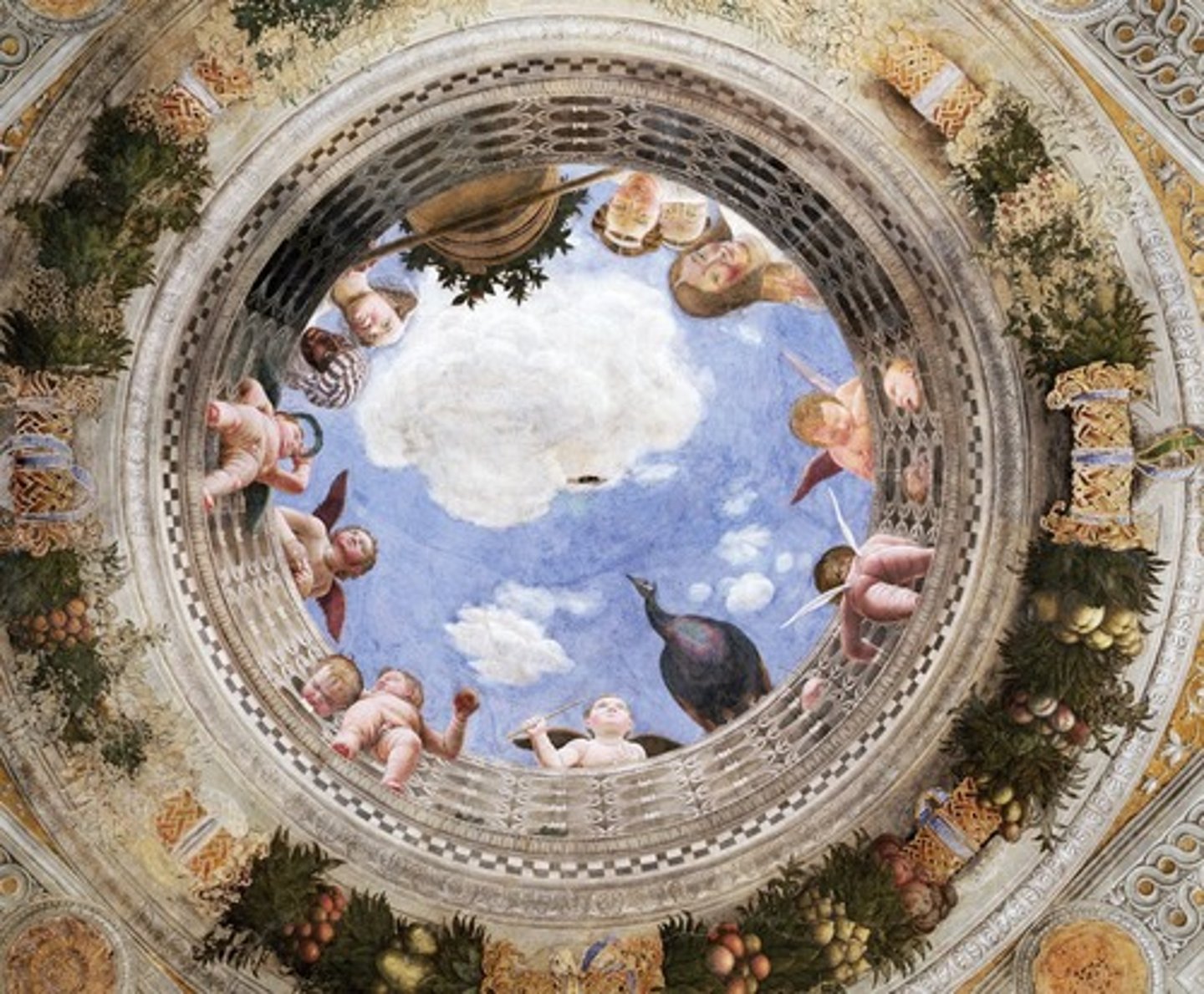
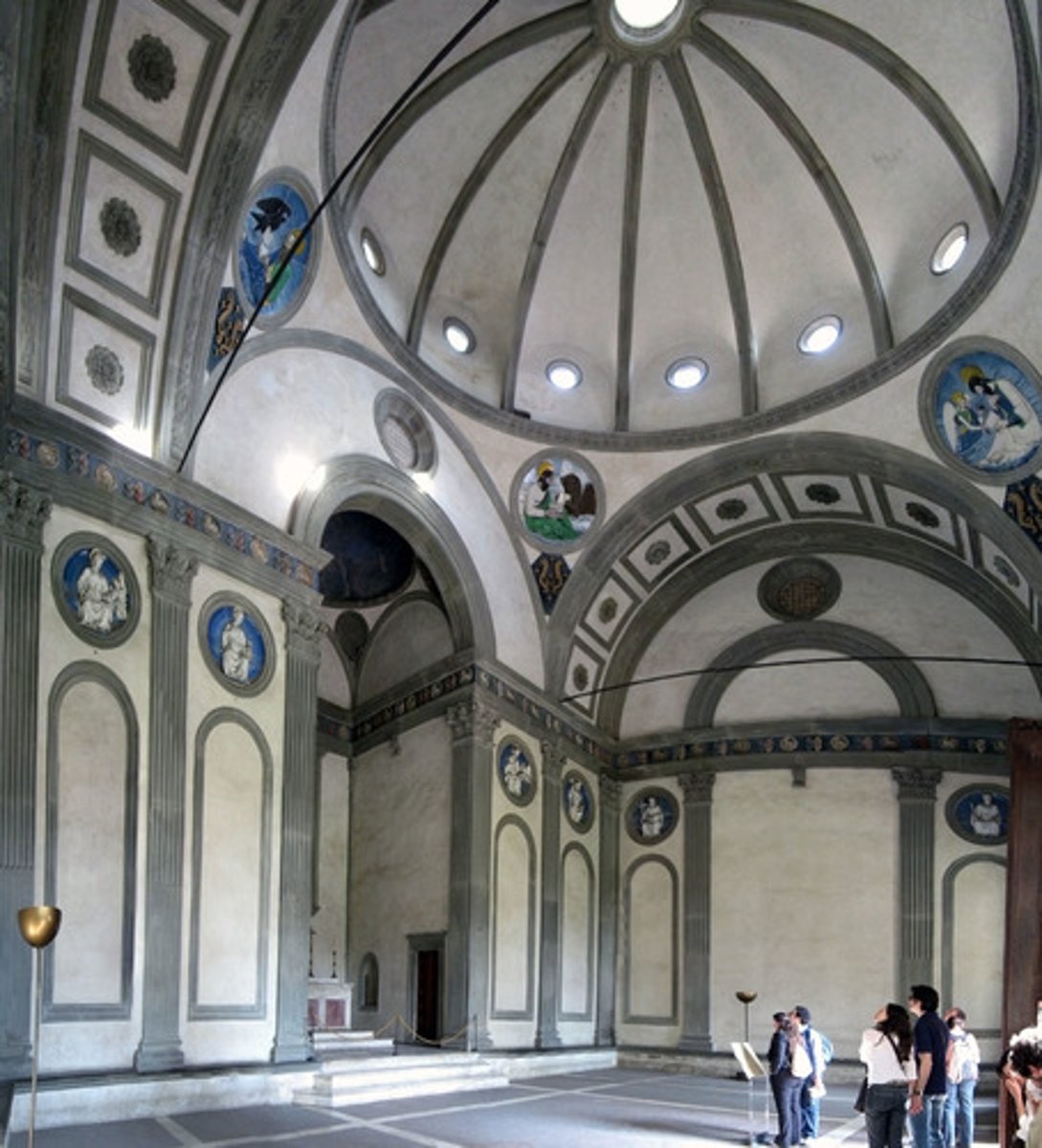
Pazzi Chapel (Basilica di Santa Croce)
Architect: Filippo Brunelleschi
Period: Early Italian Renaissance
Dates: 1429-1461 C.E.
Culture: Florence, Italy
Material: Masonry
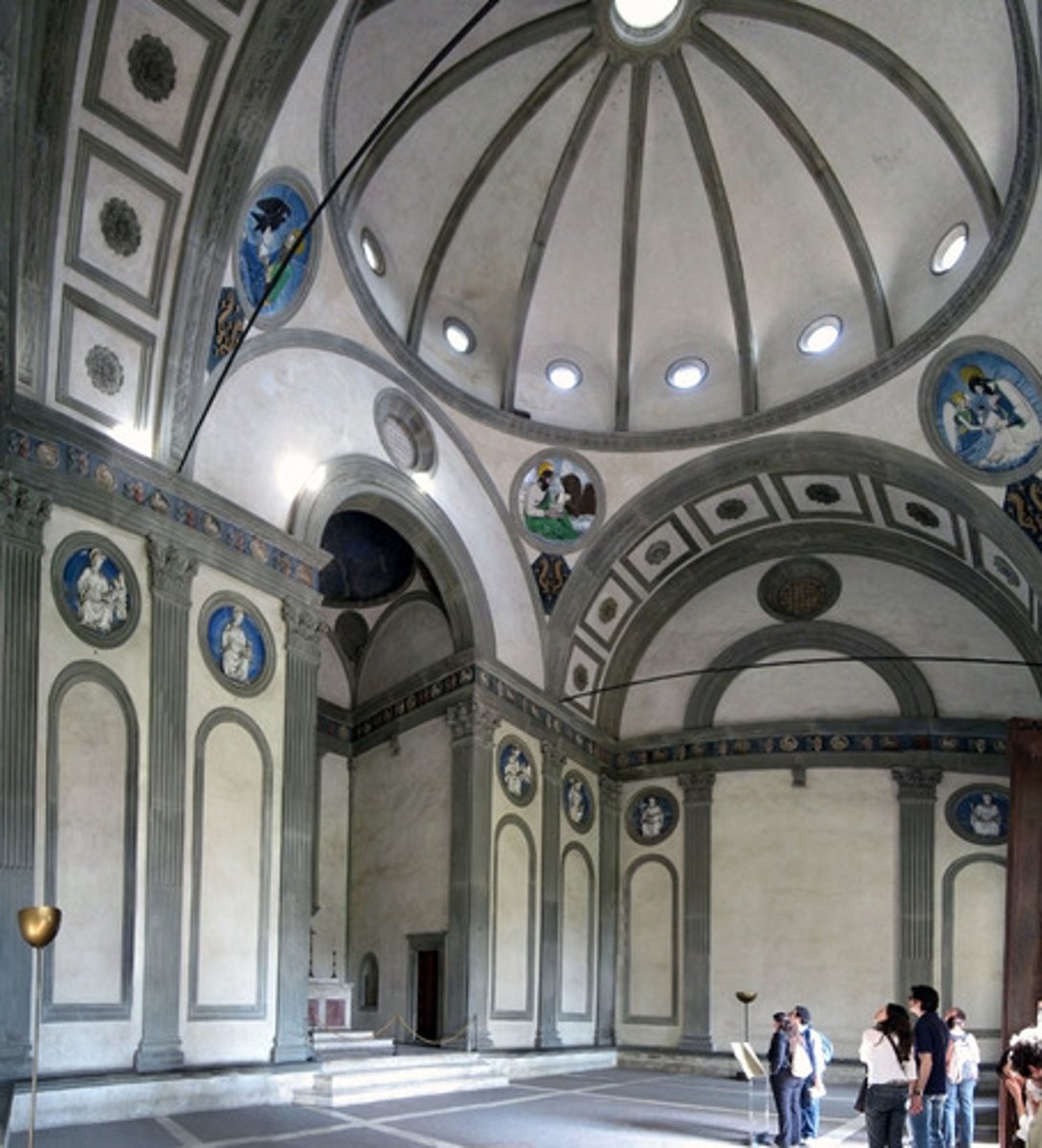

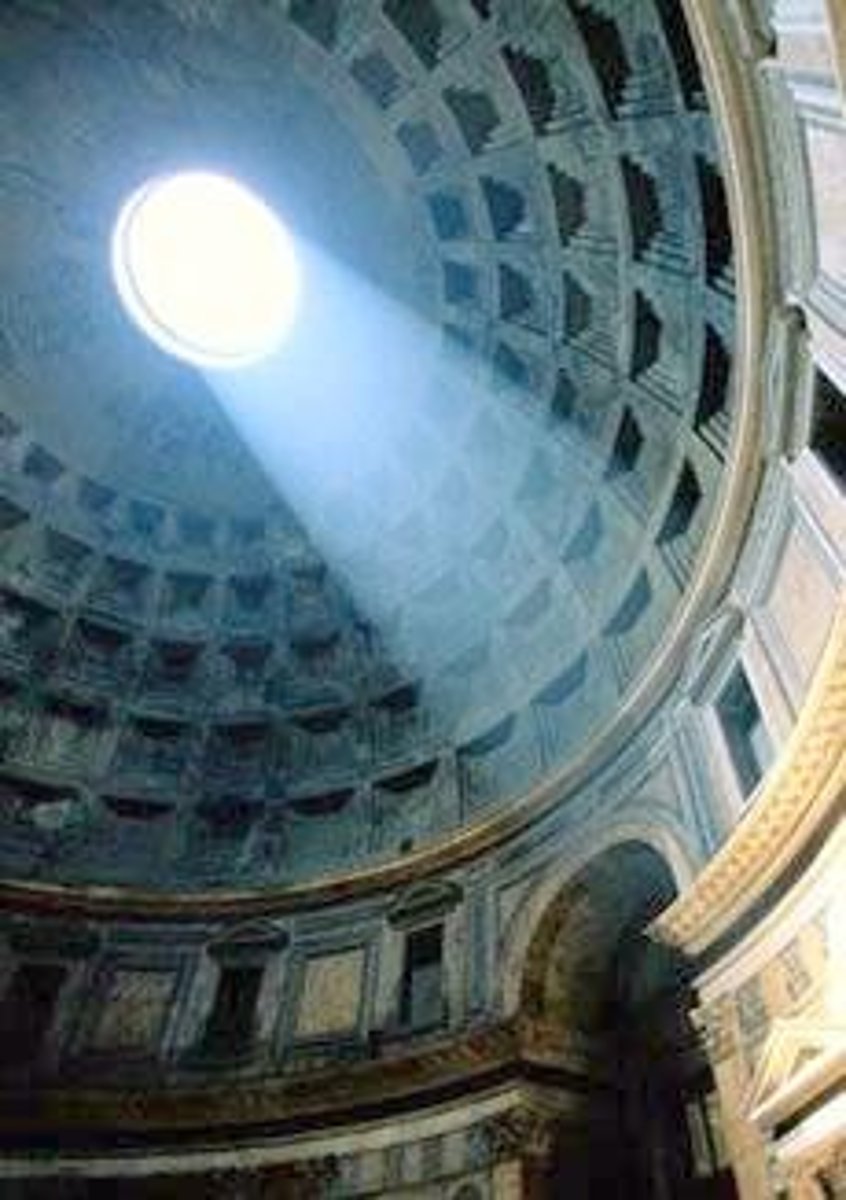
oculus
the round central opening of a dome

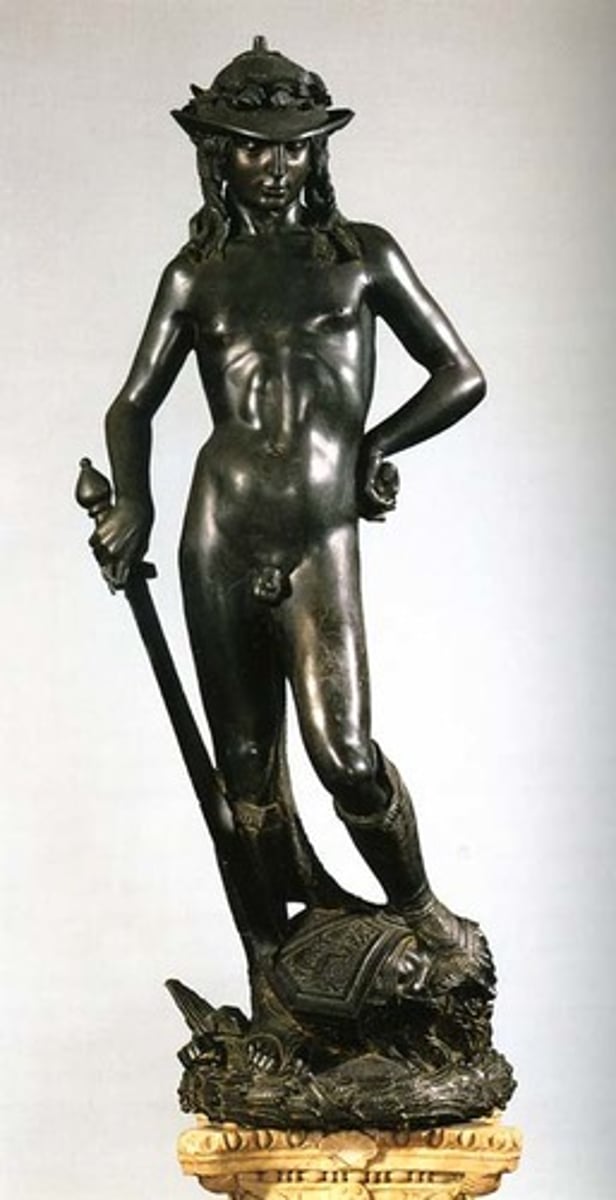
David
Artist: Donatello
Period: Early Italian Renaissance
Dates: 1440-1460 C.E.
Culture: Florence, Italy
Material: Bronze

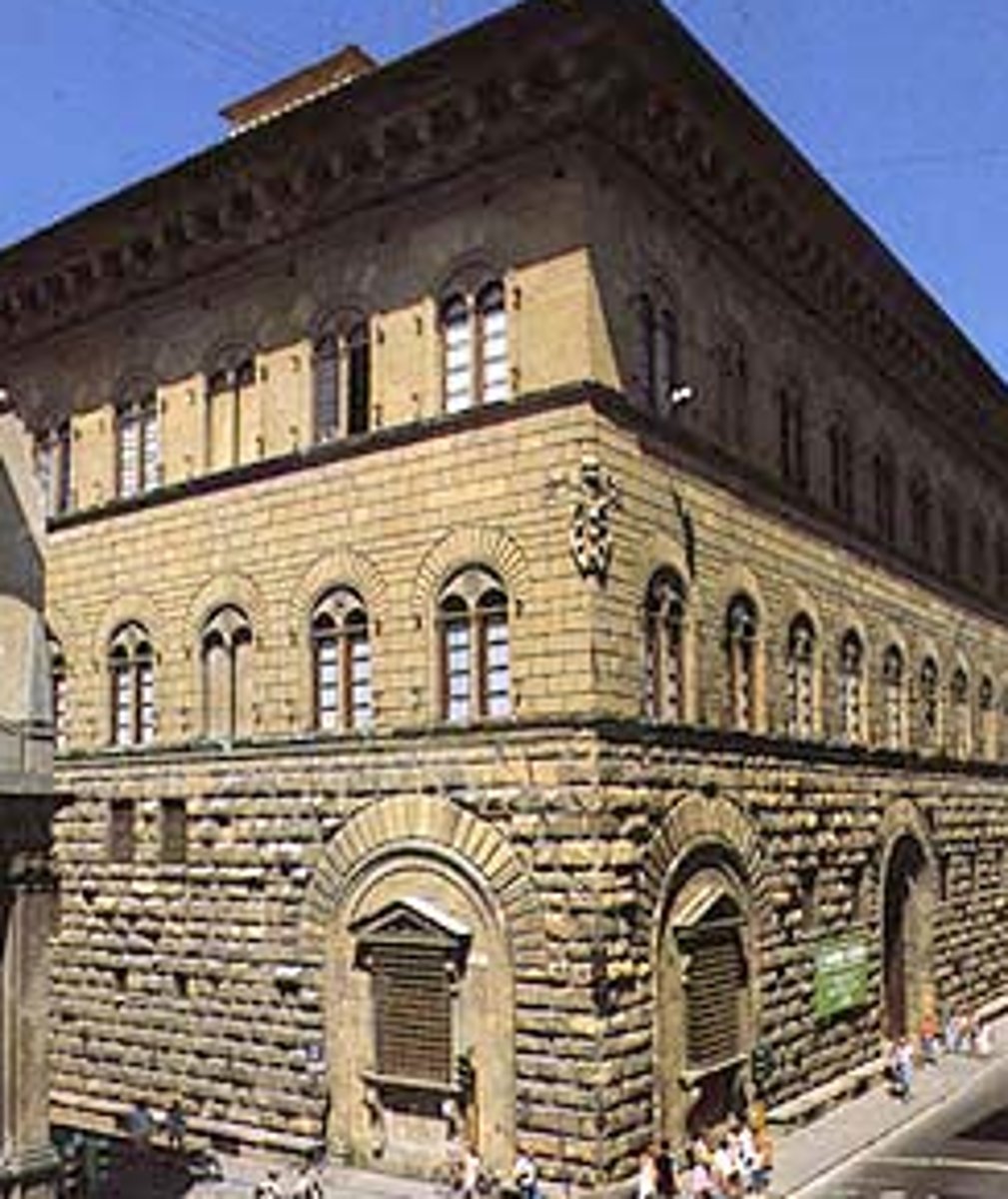
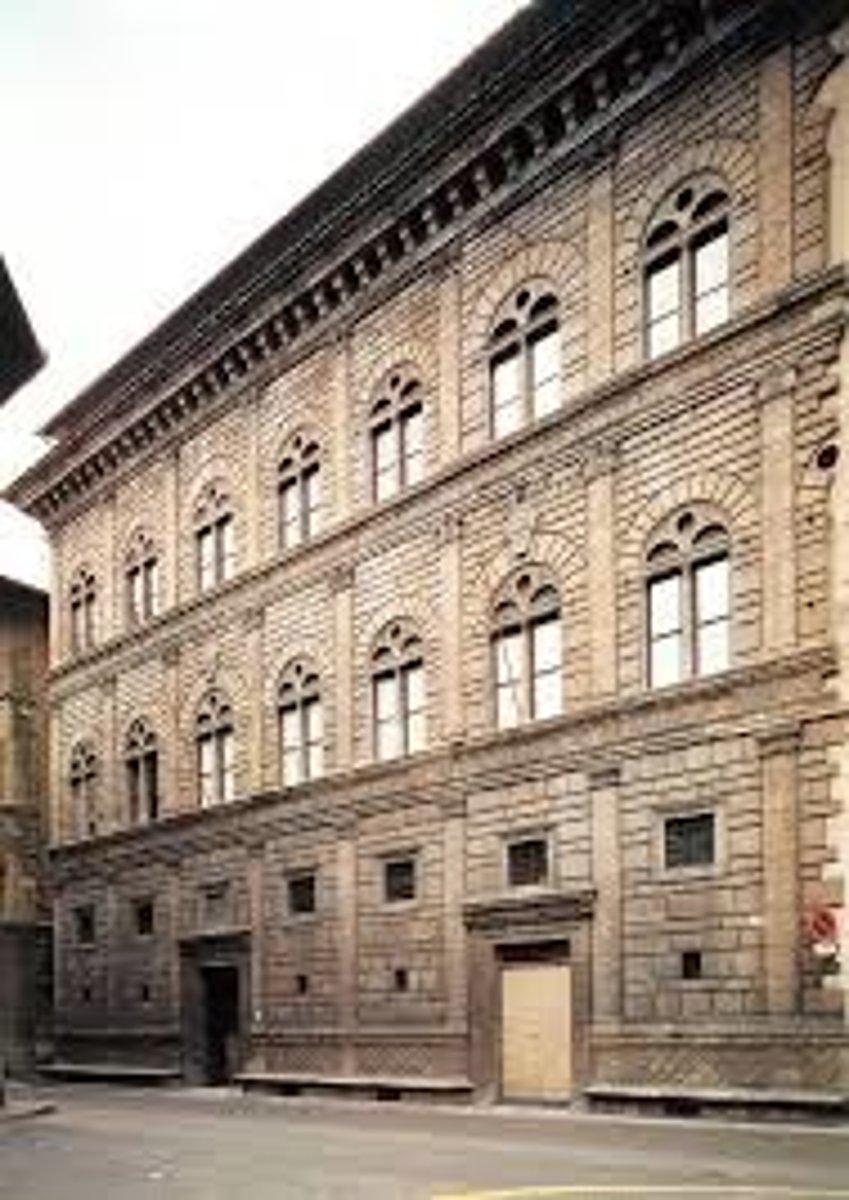
Palazzo Rucellai
Architect: Leon Battista Alberti
Period: Early Italian Renaissance
Dates: 1450 C.E.
Culture: Florence, Italy
Material: Stone, Masonry

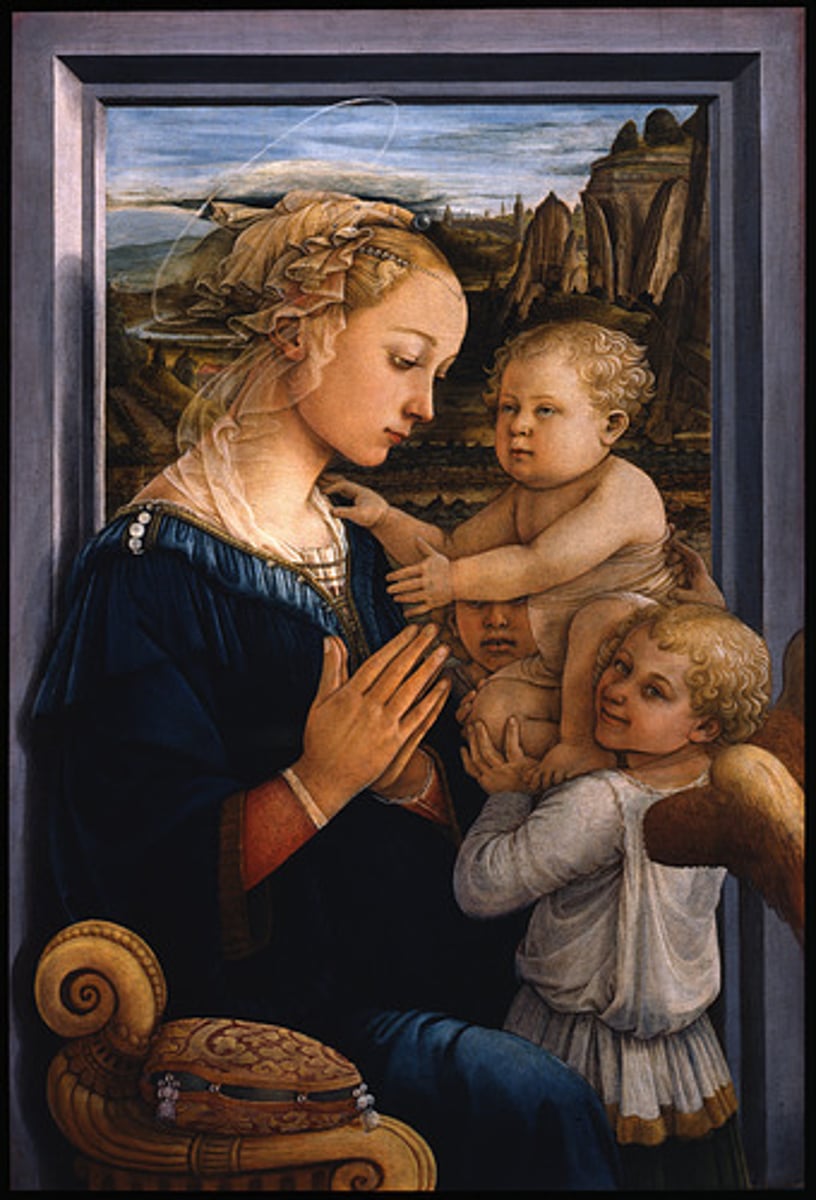
Madonna and Child with Two Angels
Artist: Fra Filippo Lippi
Period: Early Italian Renaissance
Dates: 1465 C.E.
Culture: Florence, Italy
Material: Tempera on wood

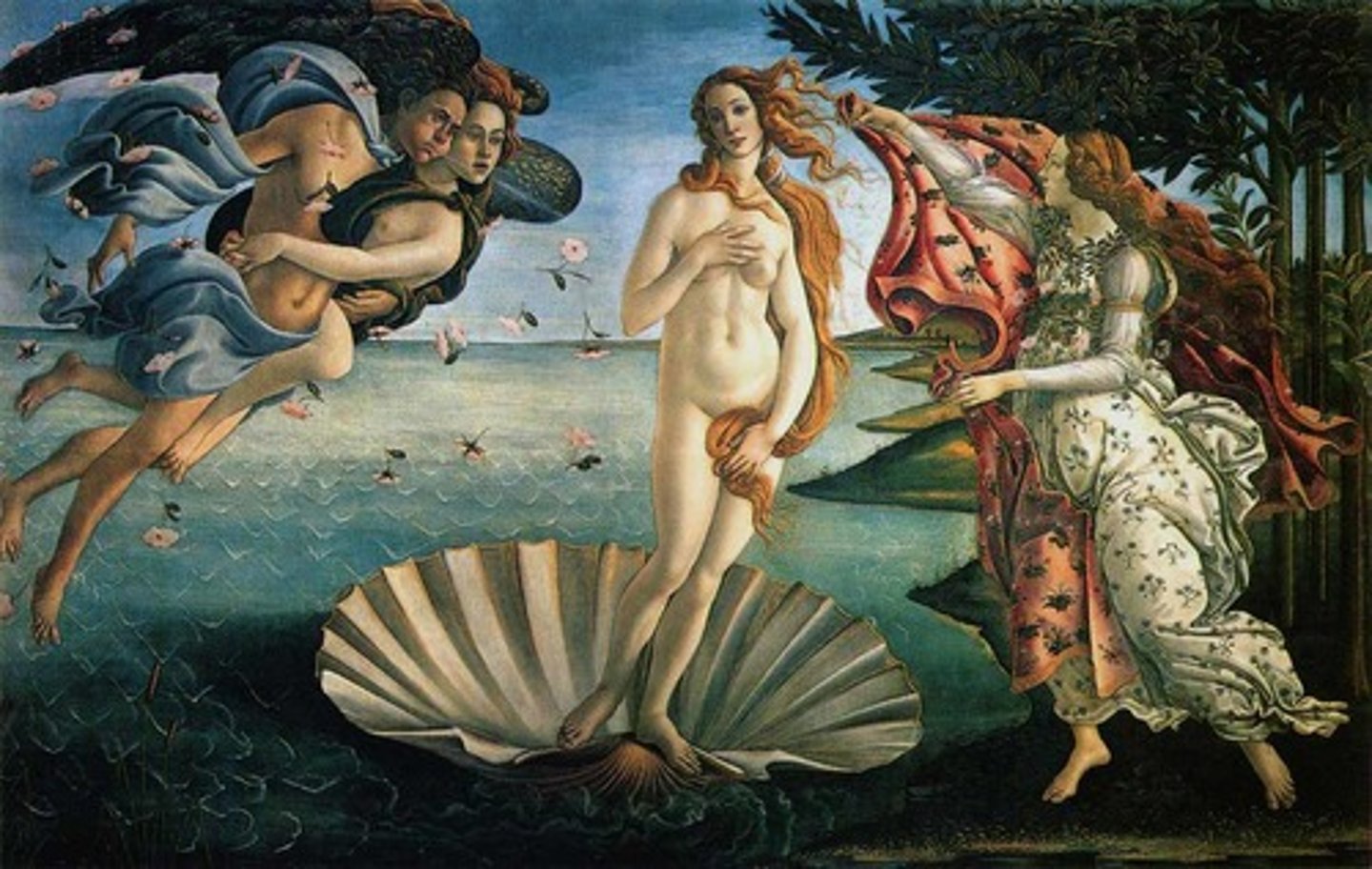
Birth of Venus
Artist: Sandro Botticelli
Period: Early Italian Renaissance
Dates: 1484-1486 C.E.
Culture: Florence, Italy
Material: Tempera on canvas
