MMW13 Midterm
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Silk Road
center for commerce and trade
concept in afro eurasia that connected many through exchanging goods and culture
Pax Mongolica
meant and represented security, stability, and access
easier to move throughout afro eurasia
facilitated cultural exchange and ideas on global scsale
led to “age of exploration”
more deciding to travel out of home
facilitate trade and foreign trade
fostered cultural integration
paiza= medallion allowing for safe passage through Mongol lands
Mongol population movements- Deployment
Mongols conquered people and forced them into military service
conscripted locals posted far from home
Soldiers traveled with family and dependents
ethnogenesis
Mongol population movements- Displacement
Mongol expansion led to massive refugee movements
Hundreds of thousands impacted
flight in eastern europe and middle east
Locals reactions:
Offers of shelter
Resistance
Panic in hungary
King, court, all moved west
Siege of Baghdad
Large groups from Iraq migrate to northern india
Mongol population movements- Replacement
Forced repopulation policy
Relocated people from other parts of empire
Replace dispersed people
Middle East->China
China->Iran
Germanic->Central Asia
Brought different cultures, outlooks, and ideas to different places
Yams
Travel stations
Every 20 miles
Like hotels
Get food, sleep, change camel
Along silk road trail
Ethnogenesis
The creation of new cultural groups and practices
As a result of population movement due to mongol deployment
Saharan commodities- Gold
West->North Africa
Traded to Europe and West Asia
Don't have materials for currency
Use kola beans as money
Peak trade in mid 14th century
Source for medieval world
Europeans rely on gold until encountering the americas
Mined by african slave
Saharan commodities- Salt
north->west africa
Key to diet
Preserved food
Protein goes bad if not salted
Mined also by the slaves
Saharan commodities- Slaves
west-> north africa
Captured in war or raids in sub-saharan africa
Sold to north african traders
Forced to work in trade, salt mines, or domestic
Still treated as people
Not property
Marrakesh
Urban center
Attracted merchants and craftsmen from across the region
Strategic trade junction
Move goods across africa->europe and asia
Became patrons
Recruited artisans, builders, and techniques
Mansa Musa
To this day, still the wealthiest person
Controlled gold trade
During pilgrimage to Mecca, he returned with books and scholars
Some say that he could have been carrying the plague during the pilgrimage
Brough people and culture diffused
Pilgrimage represents Mali’s trade routes and connections
Also shows their wealth
Interconnectivity and global reach
Medieval Warming Period
Mild and stable weather in north atlantic from 980-1250/1300
Warm summer weather
Greater production
High yield and dependable harvests
Grow crops on marginal soils and higher altitudes
Farm deep into alps
Wheat was a big part of their diet
Loved the warmth
Previously weather wasn’t well suited for wheat (wet springs, cool summers, severe winter)
Low yield, plant limitations
Medieval Warming Period- Outcomes
Modest technical innovations
Plow, mills, manuals
Larger population
Can withstand conditions since they have more food
Made more settlements
Deforestation
New villages
Urban revival
Revival of old cities
Influx of immigrants
Rise of civic values and autonomous city states
Building sprees
Cathedrals and public buildings
Urban economy
Rise in demand for trading sites
Merchants and great fairs
Money economy
Silver Coins
Rent in $$
Manufacturing- textiles
Demographic Turn
Demographic collapse by 1352
30-40% of entire population in some area
70-80% in some others
Caused by black plague
Also after plague, theres an economic change in europe
Rent and prices fall
Wages rise
Vacant land
Survivors have more of a say
Reconquest
Reconquista= policy that set the precedent for how the spanish would interact with people in the Americas
The crusades- christian reconquest
Led to centuries-long of armed struggles between christian and muslims
Integrated christendom with afro-eurasia
Recover “holy land” and iberia
Also wanted to expand christendom into pagan areas
Created opportunities for coexistence of diverse ethnic and religious groups
Reconquest iberian culture profound had influence on american encounters
Campo Santo Images
Old cemeteries
Triumph of death
Death in afro eurasia from black death
Go to see frescos of death
Depicted the black death which reflected the skeletons they had to live with forever
Previously, medieval warming art was cheerful
People would go to pisa for this not leaning tower
Mamluk Sultanate
Defender of Islam
cairo= trading capital of islamic world
Controlled the red sea route
Black Death
No cure, no one safe
Afro-eurasian pandemic
1347-1750
1348-1353= peak
Transmitted by wild rodents and fleas, lice, and tics
Symptoms included buboes= swelling of glands, pits, and groin
Ottoman Empire
Developed into a powerful fighting force
Like mongols
Created cultural bridges
greece= example
Increase contact with europe
Maritime trade increase
Merchant families sent sons to italy for education
Slowly limited italian intermediaries
Indian Ocean Trade
With mongol collapse
Greater volume of trade
Parts of silk road limited
More strategically important in unifying afro-eurasia
Islam spread
Facilitated trading relations
Muslim mercantile communities appear– in india, east africa, SE asia
Islamic influence spread to swahili coast through this trade route
Red Sea Route
Mamluk sultanate
cairo= trading capital of islamic world
Link indian ocean with middle east and europe
venetians= intermediaries
People wanted linens, sugar, and spices
Islamic influence spread to swahili coast through this trade route
Southeast Asian Spices
during/after medieval warm period= increase in population
Stimulate rise of trade and artisanal production
Drove demand for afro=eurasian goods
SPICES
Islamic Afro-Eurasian Expansion
Vast political and religious empire
Dominant political and cultural force in middle regions of afro-eurasia
Fragmentation within Muslim world
Divided into larger regional dynasties
Caliphate
Sultanates
Doesn’t make inroads in western europe and china
Peaceful and organic conversion
Trading networks and cultural exchange
Conquest and invasion- ottomans
Iberian Reconquest
Warfare a way of life; strong military culture
Created a large noble class– but middling economically
Settlers as immigrants taking over land
Tribute from subject peoples
Christian belief
Favored by God
Significance:
Spanish used torture device to convert Muslims and get info out of them
coexistence between Christians and muslim
Micropatriotism
Allegiance to local society and community
In afroeurasia, this was the global perspective
Late medieval attitude/outlook as well
Many provincial (sedentary, local, familial)
Family unit very important
Also meant fear of others
Look different
“Non-believers”
Strangers and “wandering peoples”
Significance:
outlook for many living in afro-eurasia, often led to ethnocentrism
repopulation attempts and relocation initiated by Mongols
Tolerance under the Mongols
Recruit people to run their empire
Recruited those who looked and thought differently
Confucian scholars and tibetan buddhist monks
May not like them or be like them
Created multicultural and ethnogenetic cultures
Tolerance under Medieval Iberia
Muslim domination
Eventually under christian control by portugal
Struggle for iberia
Violence and destructive
Control not complete for either group
In spain can see religious tolerance
Jewish synagogue in spain
built during rule of christian king by made by islamic architects
Mosque became christian church
Medieval attitudes towards tolerance
Fear of “others” in community
Looked different
“Non-believers”
heretics= spoke out
Witches
Infidels
Pagans
Strangers and “wandering peoples”
Actors
Missionary
Envoys
pilgrims
hermits(nomads)
mercenaries = people paid for service in military from different place
Tolerance under Ottoman rule
Practice of ahl-al-dhimma
Protected people living in conquered lands
Toleration and supervision of non-muslims
Christians and Jews
Reduced legal status (institutionalized discrimination)
Tolerance under Muslim rule
Christian jews
Muslims can’t marry non muslims
Paid a special text
Military service
Limited religious tolerance
Encourage to convert to Islam
Can’t convince conversion
Jews and christians allowed to live in their own neighborhoods
Segregation
aljamas : jewish neighborhoods
Expulsion and resettlement
Jewish people expelled from europe
Many flee to ottoman or muslim held lands
Tolerance under Christian rule
Political states start to coalesce
Define in opposition to “other”
Uniformity in social religion and religious views
Institutional violence
Unify
Neutralize opposition
Monitor
Ordinance
decrees
Ahl-al-dhimma
Ottoman rule
Practice of ahl-al-dhimma
Protected people living in conquered lands
Toleration and supervision of non-muslims
Christians and Jews
Reduced legal status (institutionalized discrimination)
Significance:
shows Ottomans tolerance of others
restrictions and obligations they enforced upon them- ottomans open to other peoples without heavy discrimnation
Printing press diaspora
Extent depended on tech and social conditions
Not an indicator of “progress”
Alternate forms of communication
Standardized, preserved, and destabilized knowledge
Knowledge can be lost-destabilized
Facilitated critique of authority/social order
Can be anonymous; many were
Spreads print culture in everyday life
Signifcance:
literacy more readily available and owning of books became less of a sign of status
maps became polarized
commoners given access to religious texts
political records spread allowing for centralized authority
Fall of Constantinople
Fall of Byzantine empire to ottomans
May 29, 1453
1453: Ottomans takeover Constantinople
Shifts in control of trade networks
Venice becomes a stronger monopoly and has more alliances
Genoa has a decline in trade science venice has more alliances
“End” of medieval period
Start of early modern period
Height of renaissance (1490-1520)
Arabic manuscripts
Leader of manuscript production
Arabic supersedes Greek preferred language of the arts
Preserves and transmits ancient greek and latin texts
Al warawiyyin library
Church Time/Clock Time
Shows shift church-> merchant time
Shows stuff becoming more secular and religion isn’t focus of peoples life now
Still important but whole life isn’t just focused around religion
separation of church and state
Humanism
Secular civic organization
Organization of secular and religious lives
Individual consumption
Seeing themselves as important now
Authority
Multiple
Textual
Corporate
Community
Humility
Piety
Austerity
Bells and clocks
Renaissance reflects humanist culture
Reworking of heritage into christian world
Shift in values from corporate to individual
Gunpowder
Invented in china
Travels to afro eurasia via silk road
Trade influences access to gunpowder and weapons
Longer, more expensive ,and deadlier wards
Rise of centralized states
Mongols- new tech
Mounted war
Siege warfare
Gunpowder for military purposes
For canon/”guns”
Gunpowder Empire= ottoman, safavid, and mughal empires
Military Revolution
Change nature of warfare
Trade influences access to gunpowder and weapons
Longer, more expensive ,and deadlier wards
Rise of centralized states
Mongols- new tech
Mounted war
Siege warfare
Gunpowder for military purposes
For canon/”guns”
Weapons
Gunpowder Invented in china
Travel to afro eurasia via silk road
Gunpowder cannons
Leveled traditional walled fortification
Gunners replace lance and pike
Can attack from distance
Armies
Larger
Discipline/training
triage/field support
Get money and funding from banks
Long distance oceanic exploration
Austronesian seafarers= long distance travel within known world
Cover vast distance
Navigation
Wave patterns
Trade winds
Moved them
Stars
Guided them
Bird observations
Lead them
More island to island
At sea for weeks
Did this for trade and migration
Navigation treatises
Ibn Majid
treatises come out from islamic world
Summarizes accumulated knowledge on indian ocean
Inspired direct contact with asia
Significance:
allowed for easier travel
more trade
Sea compass
Chinese invention
Dispersed by muslim merchants and traders
Adapted for sea travel
Venture into unknown waters
Stable reference point
Distance, location direction
Amerindian origins
derive from single ancestral populations
“first americans”
northeast asia
20,000-14,000 years ago
amerindian micropatriotism
no inherent unity among indigenous groups
no pan-indigenous identity
loyal to their own states
prone to autonomy
fragmentation
engaged in civil war, ritual sacrifices, slave trade
amerindian imperial systems
consolidated distinct linguistic and ethnic groups over a large stretch of territory
exerted control over subject peoples through an oppressive tribute and labor system
conquest allowed subject peoples to continue lifeways and practices
let you keep your ruler, temples, and gods
just living under their empire now
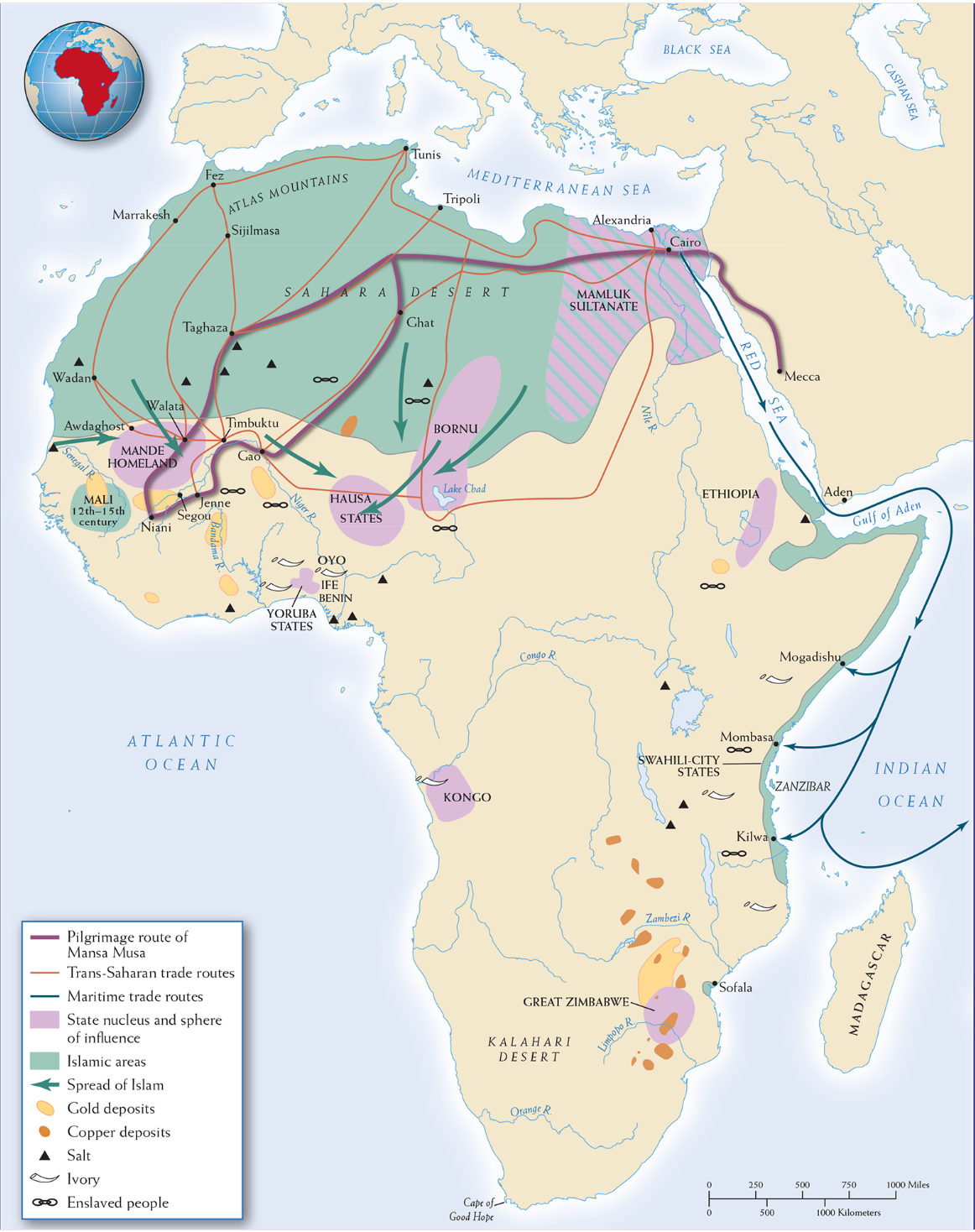
Trade Routes Sub-Saharan Africa, 1300
increased commercial contacts influenced religous and political dimensions of sub-saharan africa
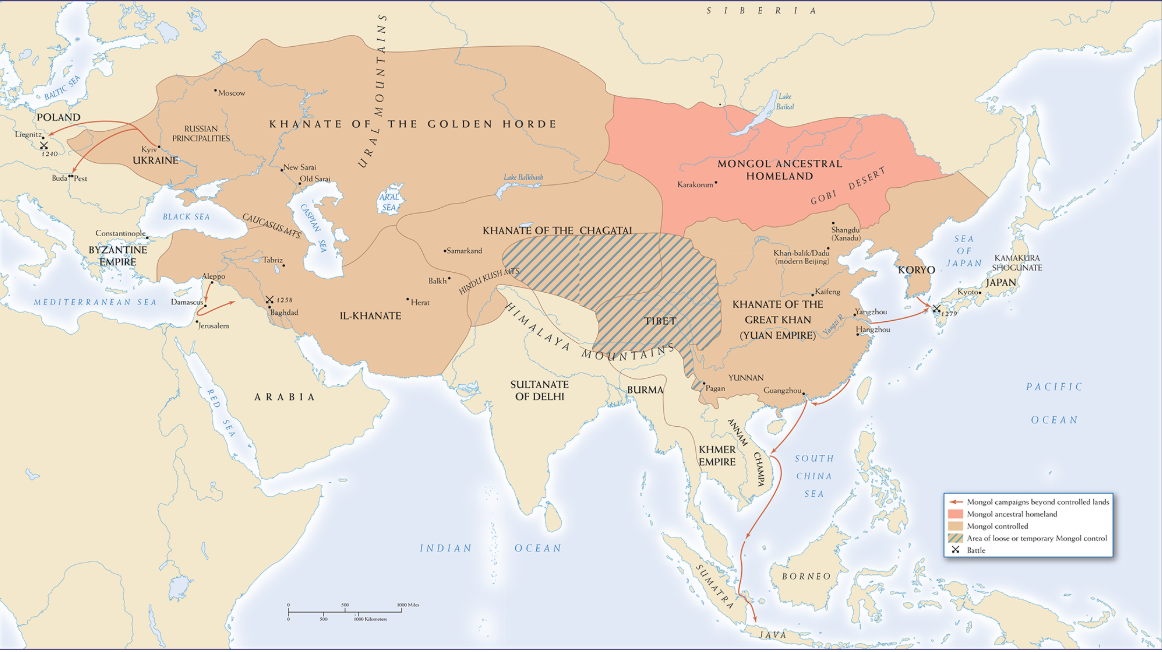
Mongol Conquests and Campaigns 1200-1300
Mongol campaigns and conquests brought Afro-Eurasian worlds together as never before
Mongols created empire connecting from east to west
connections that emerged across monol-controlled areas, sometimes called pax mongolica
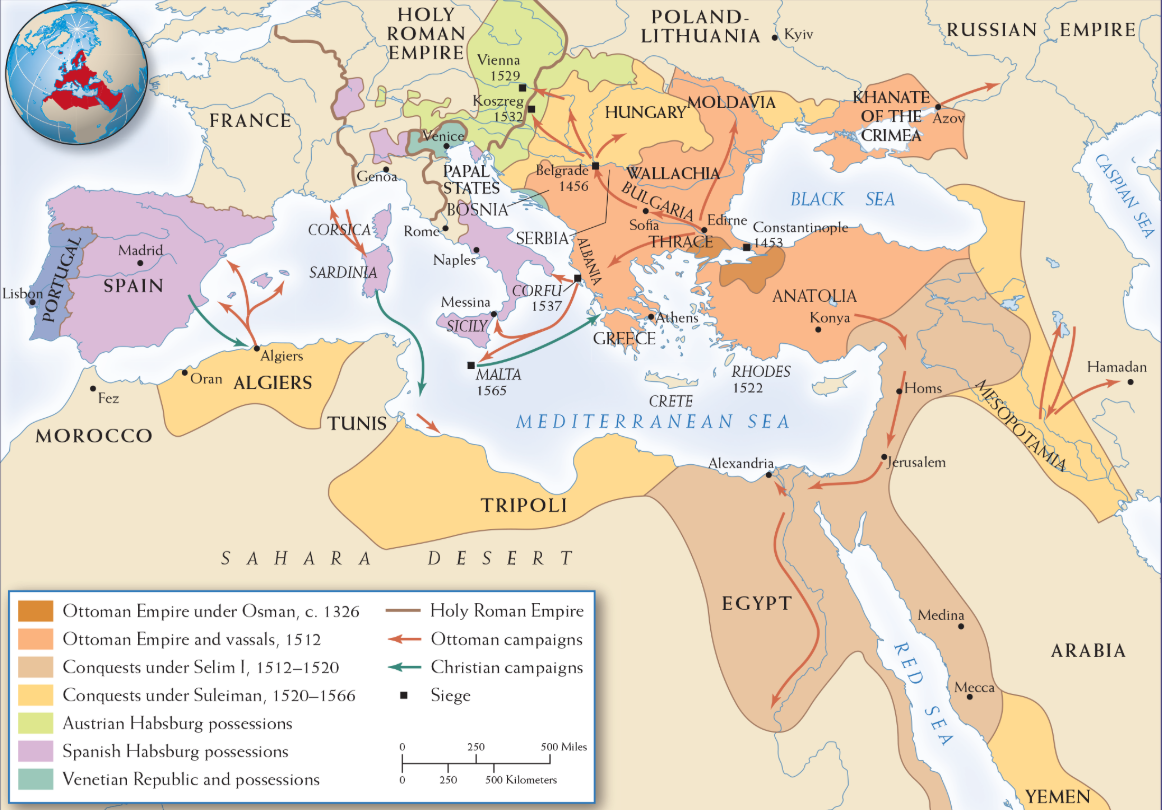
The ottoman empire 1300-1566
Expansion of the ottoman state from the time of its founder, osman, through the reign of suleiman, the empires most illustrious ruler
Chronology Late Medieval/Early Modern Periods
transition from late medieval to early modern on May 29th, 1453
caused by fall of Constantinople and leading to end of Byzantine Empire
Venetian trade
follows sack of Constantinople
venice became an incredibly powerful maritime trading monopoly often trading with Ottomans
Rise of centralized states
gunpowder allowed for larger armies and centralized states
Significance:
nomads lost power and centralized states saw tactical advantage
ottomans, originally nomads, centralized their power
Tribute and Labor Drafts
Dominant sedentary Amerindian societies would conquer smaller societies and force them into labor
allowed conquered societies to practice cultural practices
Significance:
conquered peoples built up disdain for rulers
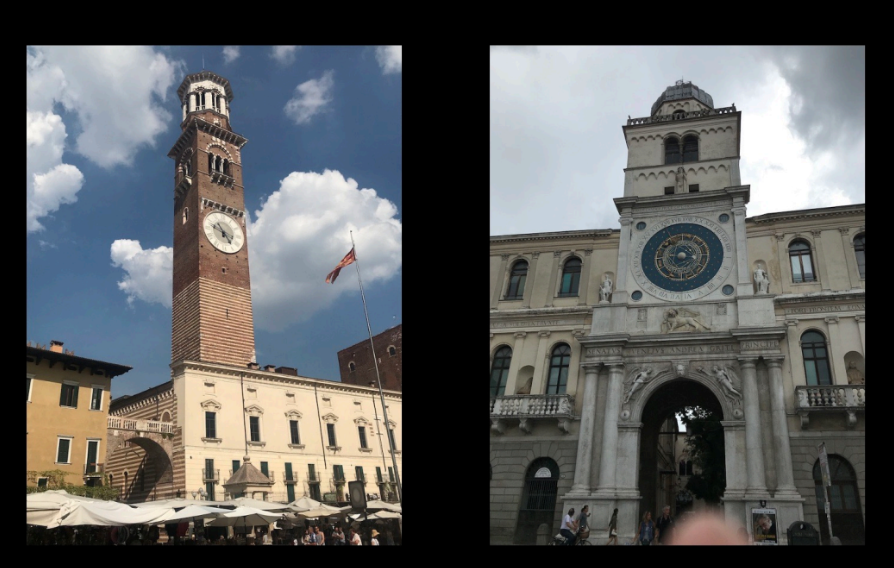

Bells vs. Clocks
Shows shift church-> merchant time
Shows stuff becoming more secular and religion isn’t focus of peoples life now
Still important but whole life isn’t just focused around religion
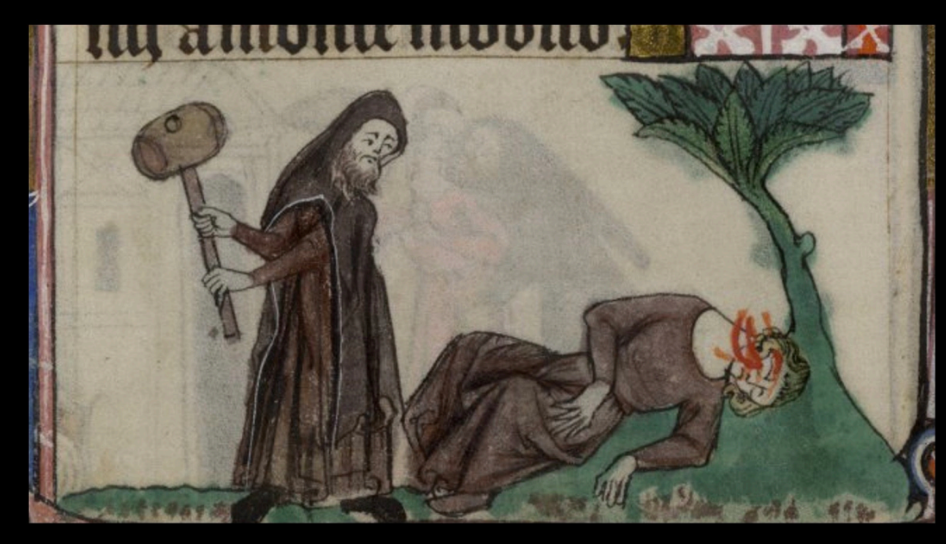

Miller and Hermit
How outsiders were viewed
Blamed the outsiders and trusting locals only
Everyone knows each other
Miller= make flour for bread
breadwinners/breadmakers
Hermit= nomad living near
Hermit slept with millers wife
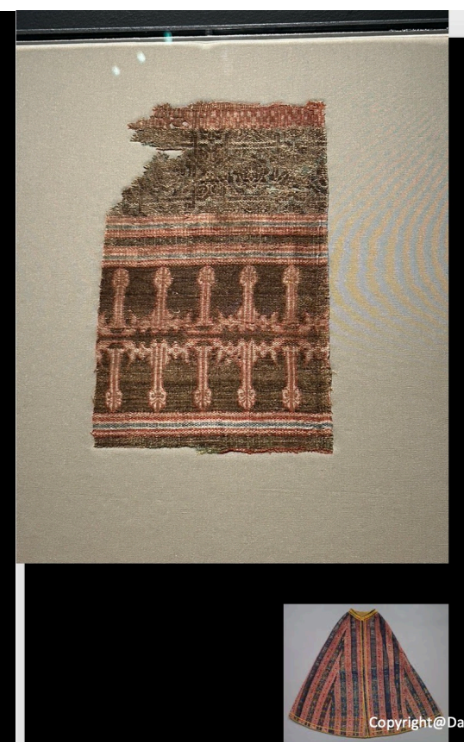

Mantle, Tiraz, and Kufic
Silk road
Mantle: Spain, Nasrid Workship
Tirz: from persian tarazida- to embroider
Textile has ottoman and persian elements
Lux item
Europe's interest in getting luxury items from China and Middle East
Spanish Monarch wanted to be buried in it
Shows status
Shows interconnectedness
Cultural tolerance
Kufic inscription: “al-Yumn” (happiness)
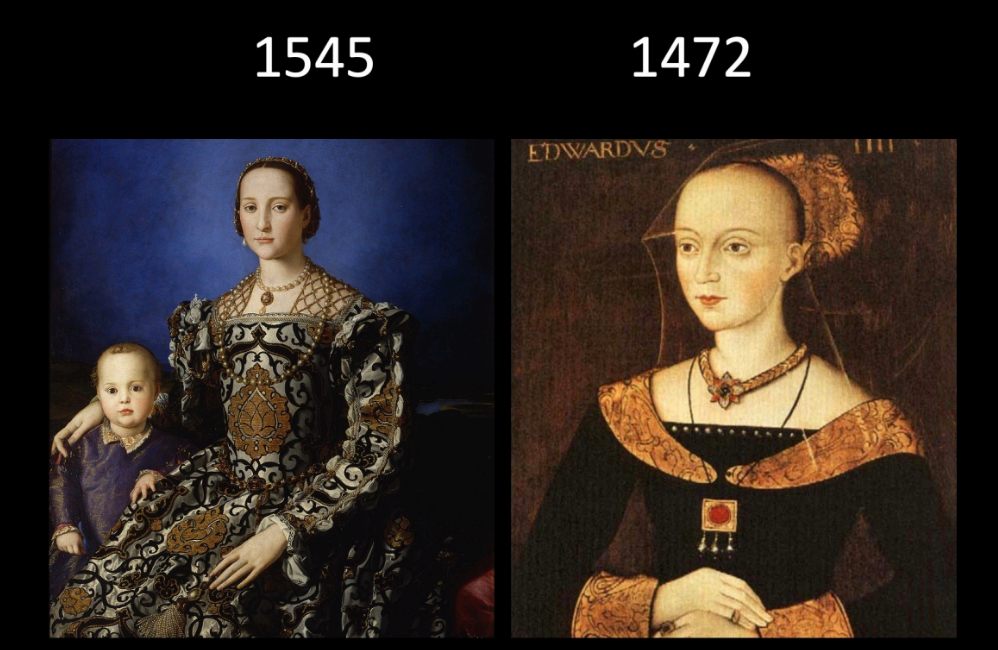
Two images of the women
Shift to secularism
1472: looking away towards God
Outfit more modest
Dark colors
1545: looking to audience showing importance
Fancier clothes
Renaissance trend
Strangers’ Hall, Norfolk England
Where “others” were put
Invited to England for textiles and that is where they love
Tolerance- allowed to live there and work alongside English but can’t live together