CHINESE ARCHITECTURE
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Takla Makan Deser
one of the four largest deserts in China. А greenbelt along the Huang He borders its southern edge. More than onefifth of China's territory is desert
Agriculture
a vital industry in China, employing over 300 million farmers. China ranks first in worldwide farm output, primarily producing rice, wheat, potatoes, tomato, sorghum, peanuts, tea, millet, barley, cotton, oilseed and soybeans.
holism
Chinese culture embodies the philosophy of ______. Ancient Chinese philosophers believed that all things are interrelated, and that Heaven, Earth, and Humanity form a unified whole
Pottery Culture
China‘s Stone Age lasted for at least one million years. The Chinese ancestors started to make pottery during the late Neolithic Period, around 5000 BC. This period is represented by Yangshao Culture, on the middle reaches of the Yellow River.
Jade Culture
The late Neolithic Age saw the advent of China's unique_______
Calligraphy
In China, a person who can produce beautiful ________ is considered to be highly cultured.
Traditional Chinese painting
uses brushes to apply ink and pigment to thin silk or paper, which is then mounted on scrolls. Great importance is placed on fluidity and expressiveness of line. Chinese painting holds that revealing essence is more important than representing form
Sculpture
This is the forerunner of all art.
SHIHUANGDI / HUANG DI
The Yellow Emperor
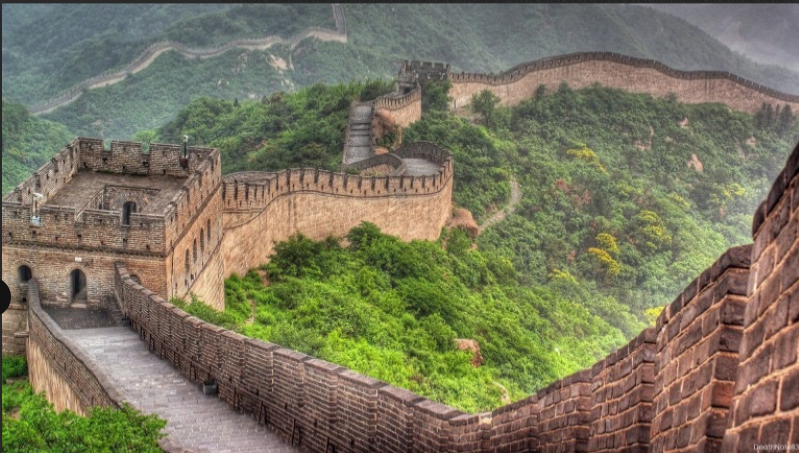
THE GREAT WALL OF CHINA
Known as chang cheng (long wall) of Shihuangdi
LEGALISM
Founded by Han FeiTzu
Traditional Chinese architecture
emphasizes harmony between structure and surroundings.
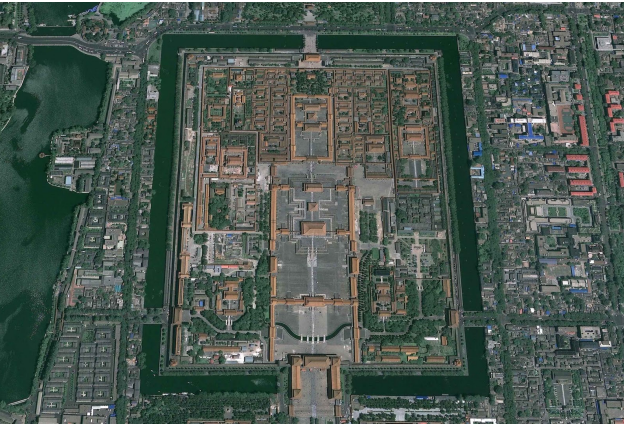
FORBIDDEN CITY, Beijing

CONFUCIANISM
emerged between the 6th through 5th century BC. Its founder, Confucius, expanded upon ancient Chinese concepts of humanism.
rén
Benevolence, showing humanity, mercy and kindness;
yì
Justness, to be righteous ;
lǐ
Rituals, custom and law, to be polite;
zhì
Wisdom, to be knowledgeable and well educated;
xìn
Royalty, faithful,reliable, accountable, responsible, creditable.
Lunyu
the most revered sacred scripture in the Confucian tradition, was probably compiled by the succeeding generations of Confucius' disciples.
DAOISM / TAOISM
teaches that although all things exist in a state of transformation, they also possess an underlying order. This constantly changing, self-balancing order is known as the Dao, or the Way
Integration of Heaven and Human
Heaven and Human are in a unity
Collectivism
The interests of a family, a group or a country are more important than those of an individual
Rule of virtue; rule of morals
“kingly way” vs. “hegemonical way”
Harmony
Chinese culture emphasizes
Foot binding
the custom of applying tight binding to the feet of young girls to modify the shape and size of their feet. Bound feet were at one time considered a status symbol as well as a mark of beauty. Yet, foot binding was a painful practice and significantly limited the mobility of women, resulting in lifelong disabilities for most of its subjects. Feet altered by binding were called lotus feet.
Chinese architecture
refers to a style of architecture that has taken shape in East Asia over many centuries.
Horizontal axis
The most important is the emphasis on the__________, in particular the construction of a heavy platform and a large roof that floats over this base, with the vertical walls not as well emphasized.
width of the buildings
Chinese architecture stresses the visual impact of the ________.
Forbidden City
have rather low ceilings when compared to equivalent stately buildings in the West, but their external appearances suggest the all-embracing nature of imperial China.
garden'scomposition
create enduring flow and also to emulate nature.
ZHUOZHENG GARDEN

wooden
may be built with either red or gray bricks, but ______ structures are the most common; these are more capable of withstanding earthquakes, but are vulnerable to fire.
Curve
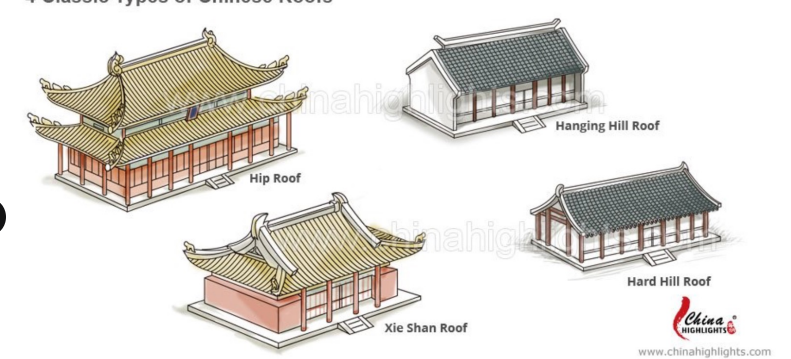
Roof of a typical Chinese building
4 Classic Type of Chinese Roofs
Hip Roof
Hanging Hill Roof
Xie Shan Roof
Hard Hill Roof
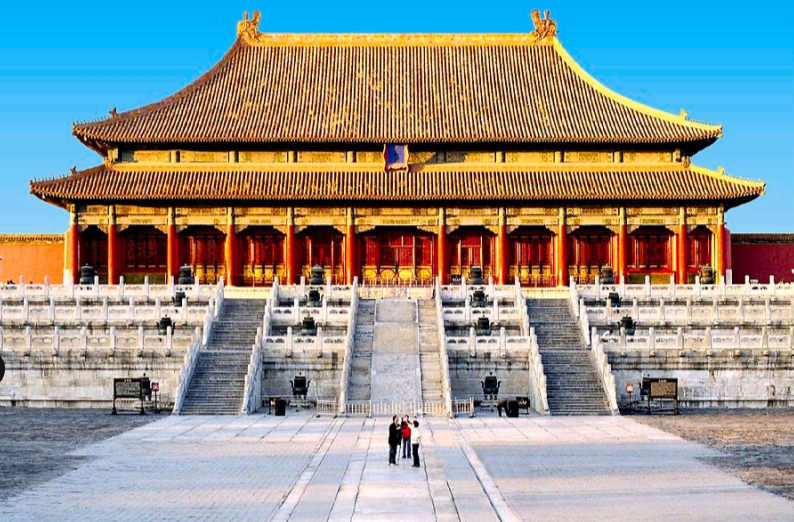
The Hall of Supreme Harmony

Red
Joy, good, wealth, bright, summer, south
Yellow
Emperor, earth, middle and China
Blue
Algid, ill, immortality
Black
"Color of death", darkness, glory, winter, north
White
Mourning, bad luck, age, autumn, west
Brown
Misfortune
Grey
Cheap, dull
Gold
Glory, royal, wisdom, perfection
Green
Life, vitality, spring, east
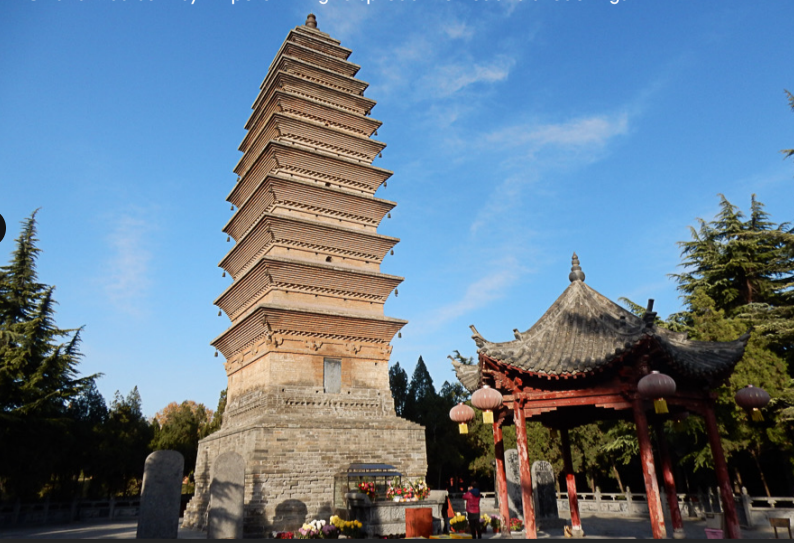
Chinese Pagoda
begins in ancient India with the death of the Buddha in the 5th century BCE.
Pagoda at White Horse Temple,

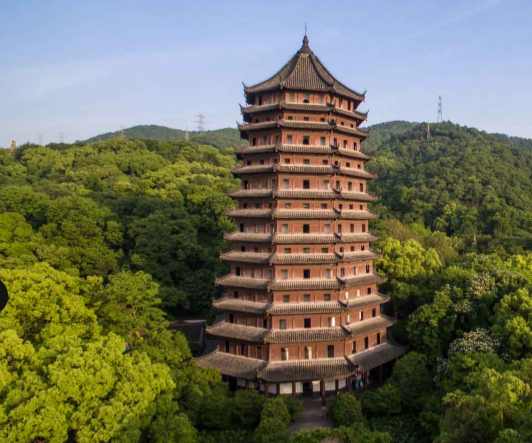
LIUHE PAGODASS
literally Six Harmonies
Pagoda of Hangzhou, China, built in 1165 AD
during the Song Dynasty.

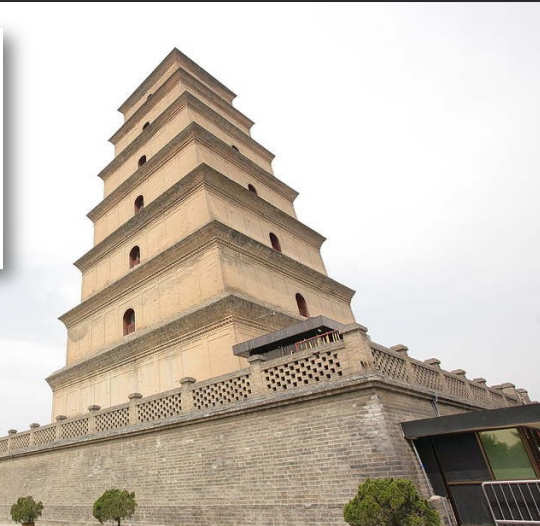
Giant Wild Goose Pagoda
built in 652 during the Tang Dynasty.

A typical pagoda has four (4) major architectural components:
underground palace
base
Sbody
steeple
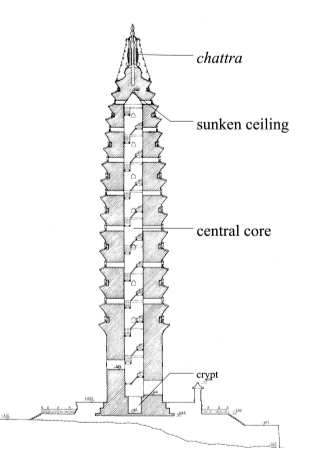
underground palace
was built first to enshrine the holy relics and any other precious items.
base
originally a simple, relatively low element that served to support the structure of the pagoda.
dougong
(interlocking wooden brackets,
used in clusters to support roofs)
lou (Multistory buildings)
means any building of two or more floors with a horizontal main ridge
tai
(terraces). is an elevated terrace with a flat top. Generally built of cement, stone and surfaced with brick, Tai were used as an open side gallery from where one can have a scenic view.
ting
(Chinese pavilions) were made either of wood, stone or bamboo. These were built in any shape such as hexagon, square, triangle, octagon etc.
ge
(Two-story pavilions) same as Lou means building of two or more storeys. The Ge had door and windows on the front side with the other three sides being walls.
ta
zaojing (Domed or coffered ceiling)
xuan
(Verandas with windows)
xie
(Pavilions or houses on terraces)
wu
(Rooms along roofed corridors)
Chinese gardens
In contrast to the buildings, ________ are a notable exception which tends to be asymmetrical.
Siheyuan
(Chinese house compound), which consists of an empty space surrounded by buildings connected with one another either directly or through verandas.
General Layout of Sihenyuan
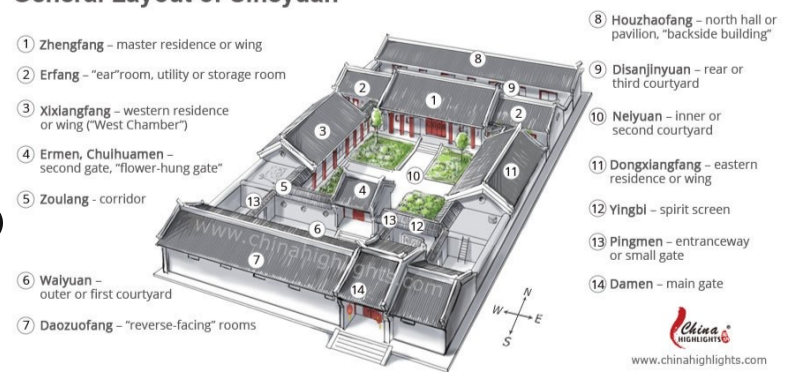
Northern courtyards
are typically open and facing the south to allow the maximum exposure of the building windows and walls to the sun while keeping the cold northern winds out.
Southern sky wells
are relatively small and serves to collect rain water from the roof tops while restricting the amount of sunlight that enters the building. It also serve as vents for rising hot air, which draws cool air from the lowers stories of the house and allows for exchange of cool air with the outside.
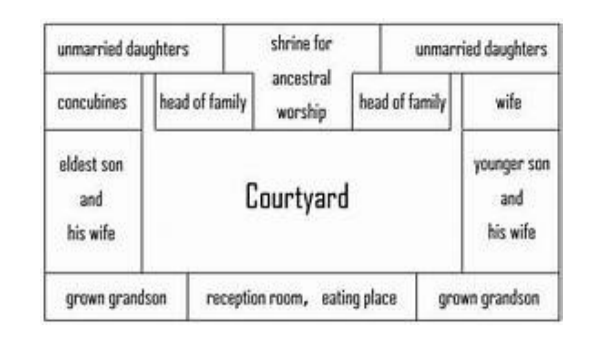
TRADITIONAL SIHEYUAN LAYOUTS
HALL OF THE SUPREME HARMONYS

Yingbi
Split screen

FU LU SHOU STATUE

Mortise and tenon
work of tie beams and cross beams, from Li Jie's building manual Yingzao Fashi, printed in 1103.
even, odd
Using ____ numbers of columns in a building structure to produce ____ numbers of bays (間). With the inclusion of a main door to a building in the centre bay, symmetry is maintained.
gabled roofs
are almost omnipresent in traditional Chinese architecture.
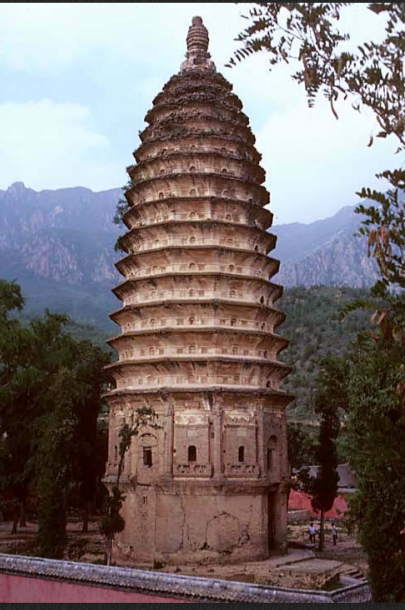
SONGYUE PAGODA
built in 523 is the oldest extant pagoda in China; its use of brick instead of wood had much to do with its endurance throughout the centuries.
SONGYUE PAGODA

GREAT WALL OF CHINA

The Ming dynasty
uses bright colors, painting detailed scenes, roof tiles, roof guardians, and many marble fence posts.
The Ming dynasty
Power is shown by space not height.
Forbidden City
was considered to be
the center of the world.
Emperor
was to be at the center of the cosmos, so the main axis of the city is North-South.
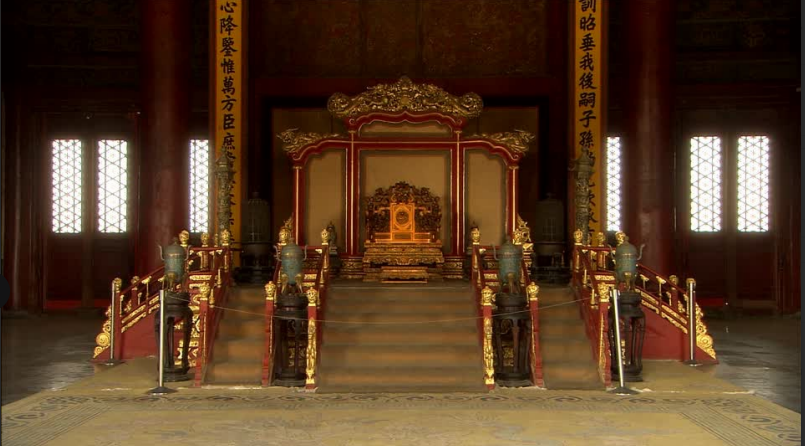
Hall of Supreme Harmony
the center of the city is where the Emperor held audiences.
Dragon Throne
(龙椅; Lóngyǐ), from which the emperor would preside over trembling officials.

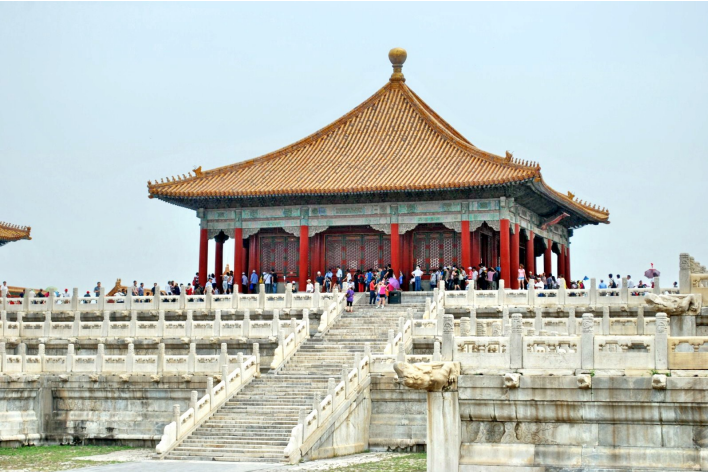
Hall of Central Harmony,
which was used as the emperor’s transit lounge. Here he would make last-minute preparations, rehearse speeches and receive ministers.

Hall of Preserving Harmony
used for banquets and later for imperial examinations.
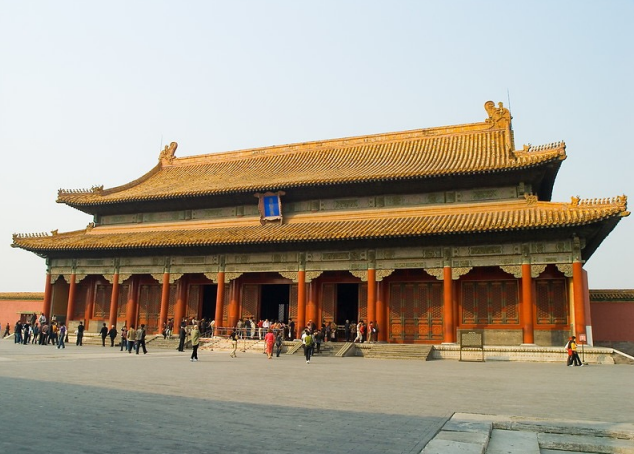

THREE GREAT HALLS
Hall of the Supreme Harmony
Hall of Central Harmony
Hall of the Preserving Harmony
Coal Hill
It must have a mountain at the back so they built an artificial one
MERIDIAN GATE
This is the grandest of all the palace gates. It is nearly 38m high. This marks the beginning of the palace complex.

Gate of Heavenly Peace
It was from here that Mao proclaimed the founding of the People’s Republic of China in 1949.

dragon
represents the Emperor
phoenix
represents the Empress.
Yellow roof tiles
reserved only for the Imperial family.
green roof tiles
Prince(ss) can only use
grey roof tiles.
Ordinary people use
Nine
lucky number in China so the Emperor will have 9 roof guardians the color of a roof reflects the social status of the people living inside.
Roof Guardians
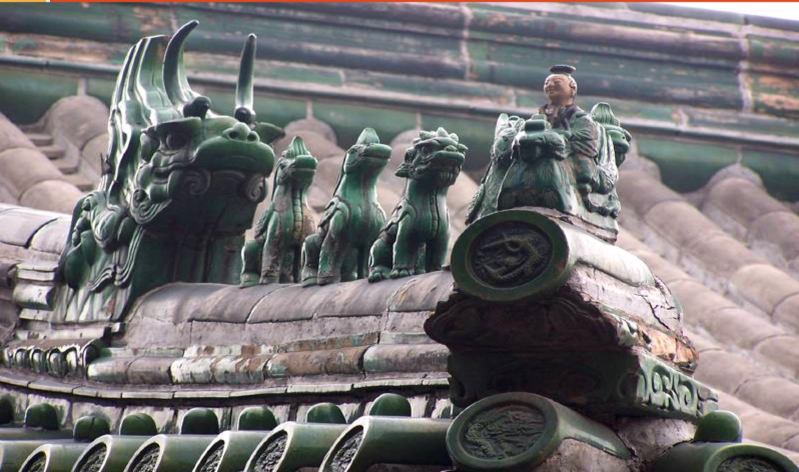

dragon
associated with the Emperor and is used extensively in the Forbidden City as a decorative element.
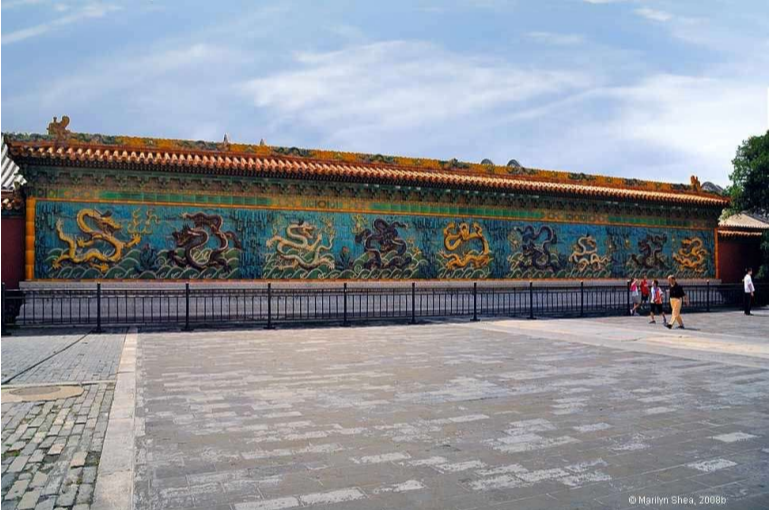
The Nine Dragon Wall

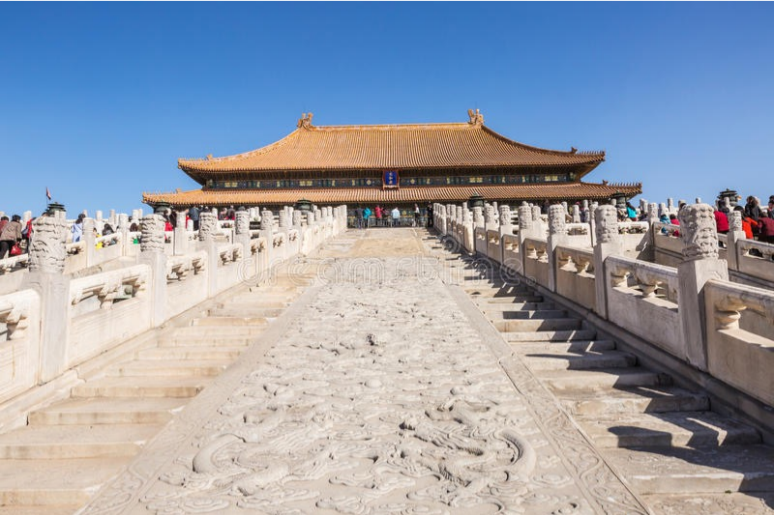
Emperor’s Dragon Way

Large pots
(menhai) are for fire prevention