Orgo II Proteins (Ch 24)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Amino acids in a peptide
<50
Amino acids in a protein
>50
How are amino acids joined
peptide bonds
What orientation do most amino acids take?
L, related to L-(-)-glyceraldehyde
Acidicty of amino acids
Less acidic than carboxylic acids, less basic than amines
Acidic amino acids
isoelectric pH ~3, deprotonated (anionic) at neutral pH
Basic amino acid
ioselectric pH ~9, protonated (cationic) @ neutral pH
Neutral amino acids
isoelectric pH ~5/6,
pKb of acidic, deprotonated OH in amino acid
12
pKa of basic, protonated amine in amino acid
10
Alpha-helix
carbonyl O hydrogen bonds with an N-H hydrogen on next coil turn
Pleated Beta-sheet
Carbonyl O hydrogen bonds with an N-H hydrogen on adjacent peptide chain
Tertiary structures
segments of alpha-helix with segments of random coil where helix is folded, imparts function
Quaternary structures
aggregated structures of protein with other proteins
Glycine
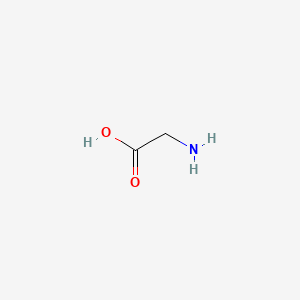
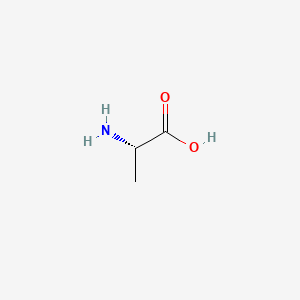
Alanine
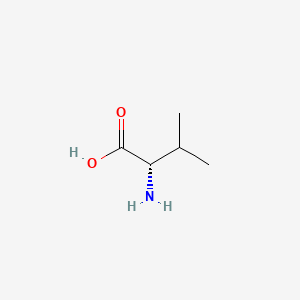
Valine
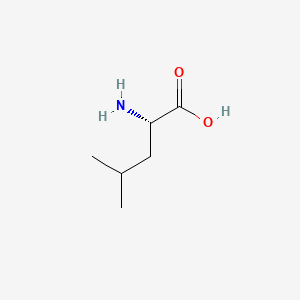
Leucine
Isoleucine
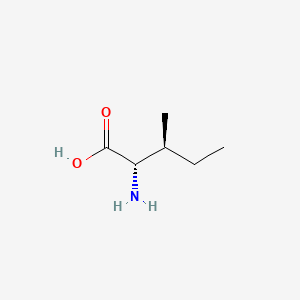
phenylalanine
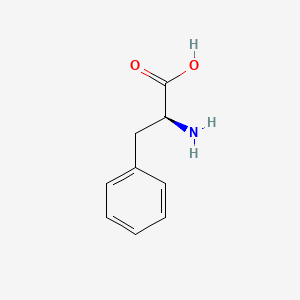
proline
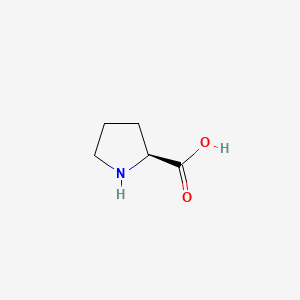
serine
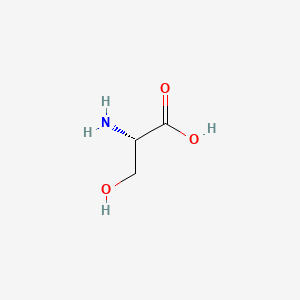
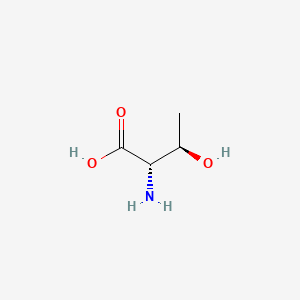
Threonine
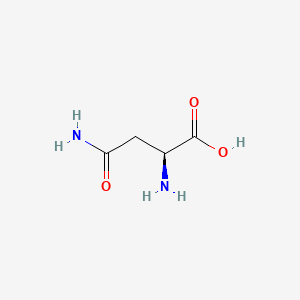
Asparagine
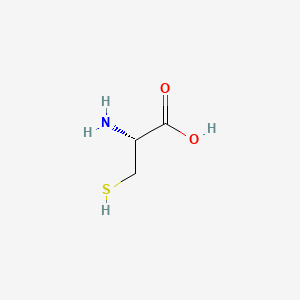
Cysteine
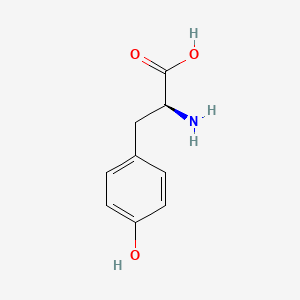
Tyrosine
Carbamate
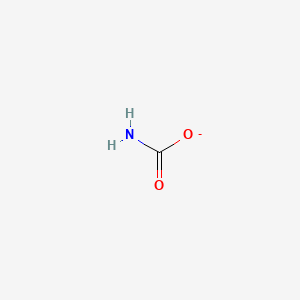
t-BOC
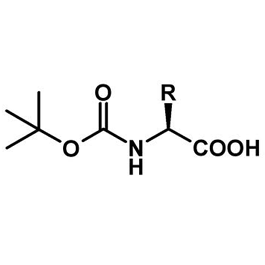
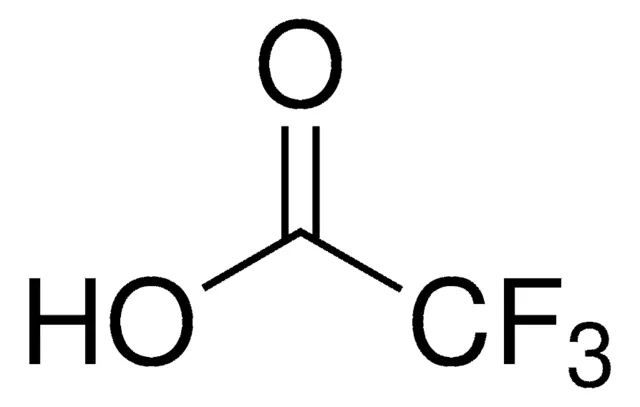
How is t-BOC removed?
TFA acid
TFA acid
cBz
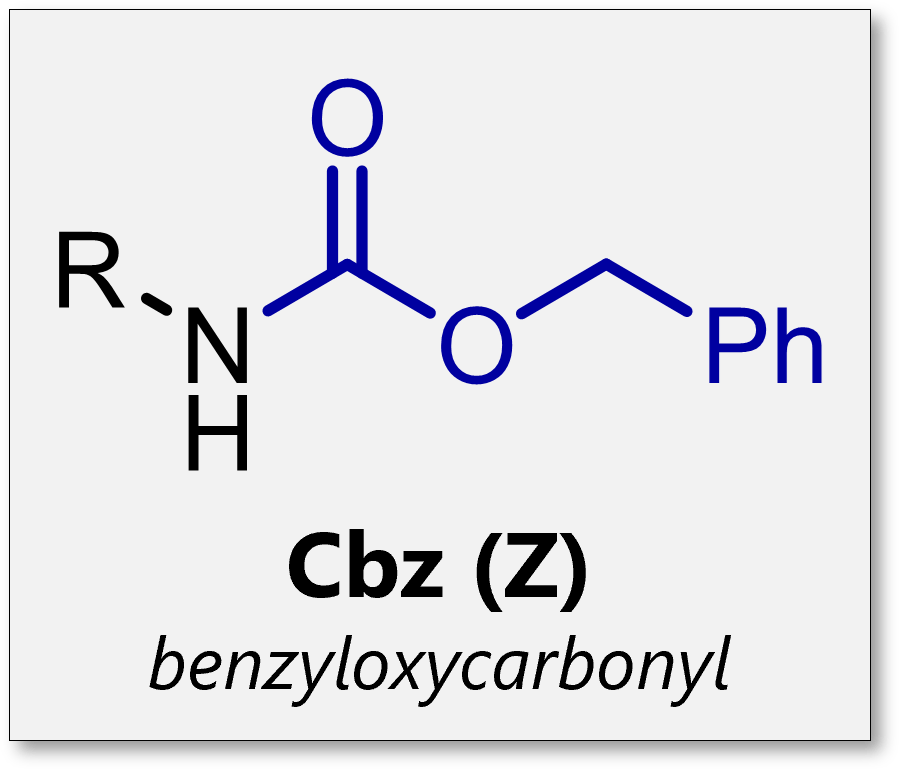
How is cBz removed
mild acid or hydrogenolysis
Hydrogenolysis
H2 / Pd-C
FMOC
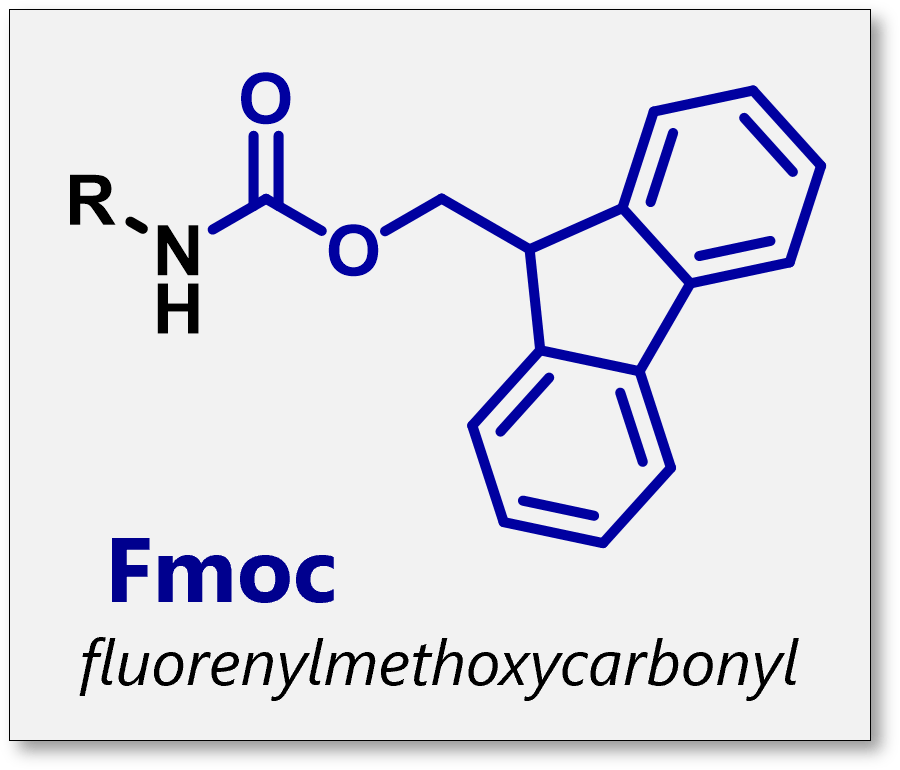
How is FMOC removed
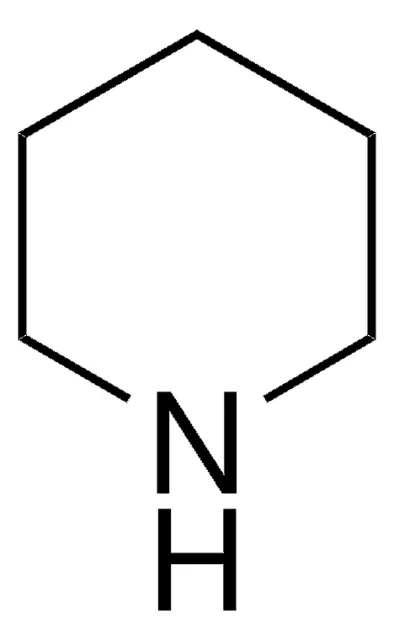
Piperidine
Piperidine
Protecting groups
t-BOC, cBz, FMOC
carbodiimide
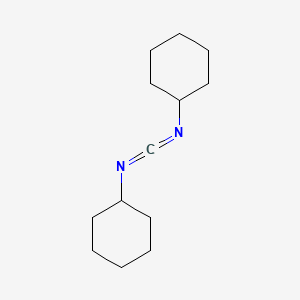
DCC (dicyclohexylarbodiimide)
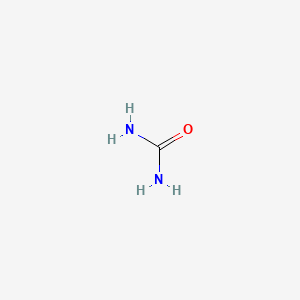
urea
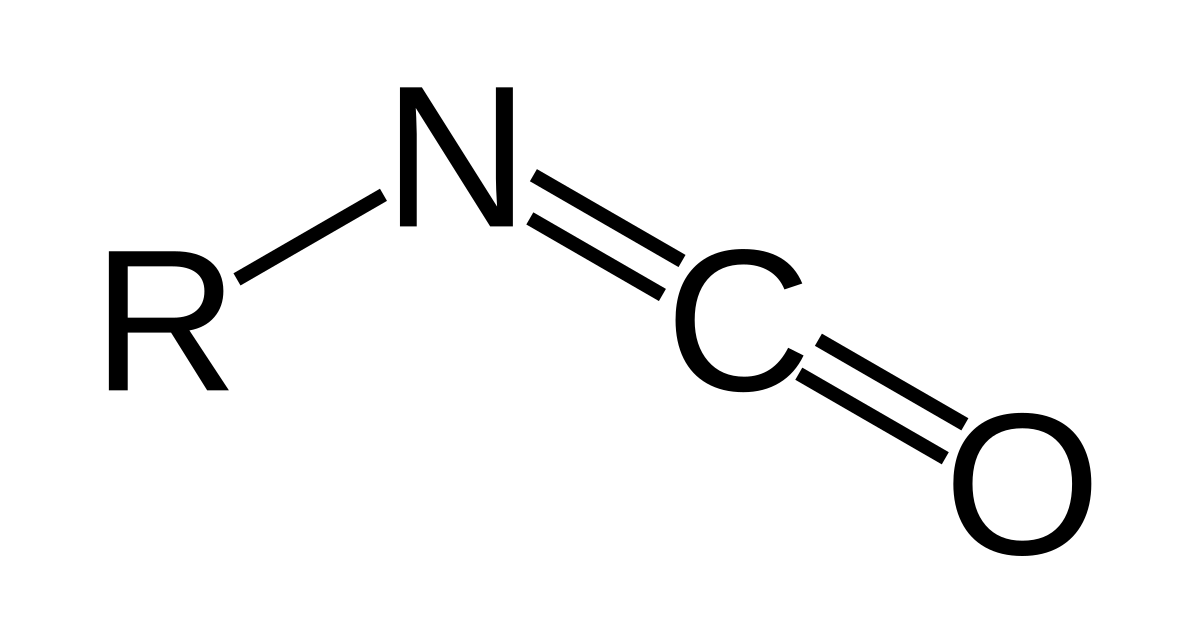
isocyanate
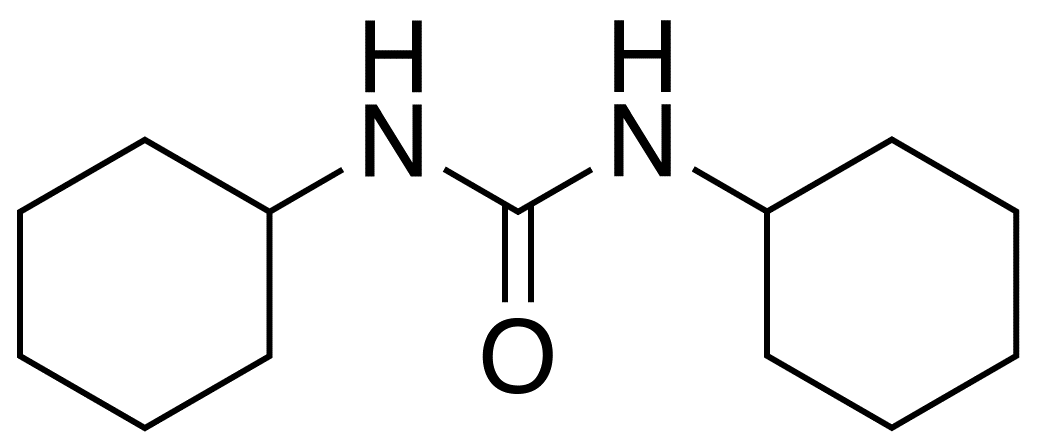
DCU
How to cleave polypeptide from solid support
HF