Heart Anatomy Quiz
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/39
Last updated 5:51 AM on 1/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
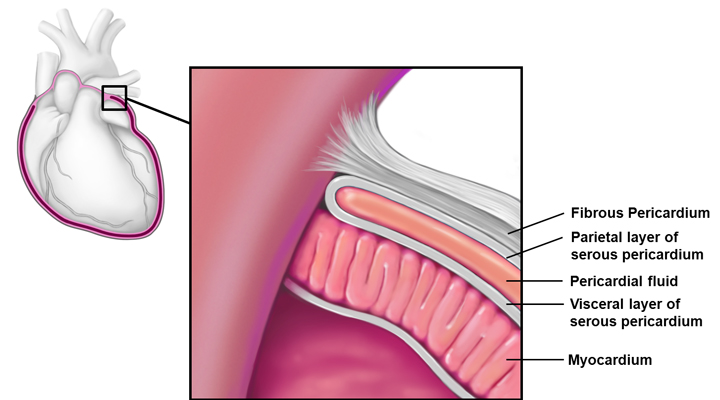
Pericardium
double-walled sac that covers the heart
2
New cards
Fibrous
protects the heart, anchors to surrounding tissues (e.g. diaphragm)
3
New cards
Serous
touches the heart itself and lines the mediastinum
4
New cards
Parietal
lines internal surface of the fibrous pericardium
5
New cards
Visceral
part of heart wall (covers myocardium); same as the epicardium
6
New cards
Endocardium
layer of squamous endothelium that lines the inside surface of the heart; very slick and continuous with tunica media in blood vessels; slick so that blood just slides through the heart
7
New cards
Myocardium
the muscle tissue of the heart, interlace in a spiral pattern around the heart; heart fibers go in a spiral so that it can narrow; interspersed with connective tissue (collagen) that acts as an insulator to e-charge, limiting action potential to specific pathways
8
New cards
Right Atrium
receives blood from the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus (collects blood from cardiac circulation); contains deoxygenated blood and has the tricuspid valve attached to it
9
New cards
Left Atrium
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins, send to left ventricle
10
New cards
Right Ventricle
receives blood from right atrium and pumps it to lungs via the pulmonary artery (left and right branches)
11
New cards
Left Ventricle
receives blood from left atrium, pumps blood out to body cells via the aorta; most heavily muscles of heart chambers because it has to pump blood to the whole body
12
New cards
Semilunar valves
located between ventricles and arteries
13
New cards
Aortic
prevents blood flow back into left ventricle after contraction
14
New cards
Pulmonary
prevents blood flow back into right ventricle after contraction
15
New cards
Atrioventricular Valves
located between atria and ventricles
16
New cards
Tricuspid Valve
right AV valve; composed of three flaps of endocardium
17
New cards
Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve
composed of two flaps of endocardium
18
New cards
Interventricular Septum
the triangular wall of cardiac tissue that separates the left and right ventricles; a hole in the heart can result in mixing of high and low O2 blood
19
New cards
Vein
sends blood to the heart (pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood)
20
New cards
Artery
sends blood to the rest of the body (pulmonary artery is the only artery to carry deoxygenated blood)
21
New cards
Cardiac Output
the amount of blood moved by the heart in one minute in each ventricle
22
New cards
End systolic Volume
the leftovers of blood after the contraction in the heart
23
New cards
End diastolic volume
the maximum that the ventricle can fill; total max amt of blood
24
New cards
Stroke Volume
amount of blood pumped out by one ventricle during each contraction (~70 ml)
25
New cards
Describe the pathway of blood through the heart starting in the right atrium
Coronary sinus (collects blood from cardiac circulation), superior and inferior vena cava collect blood from the body; right ventricle (receives blood from right atrium and pumps it to lungs via pulmonary artery; left atrium (receives oxygenated blood from lungs via pulmonary veins), left ventricle (pumps blood out to body cells via aorta; most heavily muscled because it has to pump blood to all parts of the body)
26
New cards
What is the purpose of the interventricular septum? What happens if this is compromised (e.g. hole-in-the-heart)
The interventricular septum separates the right and left ventricles. If it’s compromised, high and low oxygenated blood is mixed.
27
New cards
Describe the events leading to a myocardial infarction (heart attack). What is the end result of an MI
Coronary circulation can get blocked by damage or fatty deposits (plaque). The part of the muscle not getting any blood will eventually die, reducing the heart’s ability to pump blood depending on where the blockage is located.
28
New cards
Describe the forces that allow each of the heart valves to open and close
For example – the aortic valve closes when the pressure in the aorta is greater than that of the left ventricle. When the pressure in the left ventricle increases (over the aortic pressure) during contraction (systole), the aortic valve opens to let blood out of the heart. The papillary muscles and chordae tendineae adjust the tension of the valves which allows for more or less blood to come through.
29
New cards
What prevents the heart valves from prolapsing in a normal heart? What is it called if the valves DO prolapse
The chordae tendineae and papillary muscles by making sure there’s tension on the valves to prevent blood from backflowing. Incompetent valves
30
New cards
Autorhythmic Cells
sets the electrical impulse the heart reacts to when it beats; creates the EKG record
31
New cards
Coronary circulation
critical in supplying myocardium with O2, food, and in removing wastes; coronary arteries (arise from base of aorta and encircle the heart in the coronary sulcus), arteries (deliver blood to myocardium), veins (move deoxygenated blood back into circulation)
32
New cards
3 layers of blood vessels
tunica intima, tunica media, tunica externa
33
New cards
Tunica intima
innermost layer, directly in contact with flowing blood (continuous with endocardium)
34
New cards
Tunica media
mid-layer, made of smooth muscle and elastin, controls vessel diameter and blood pressure
35
New cards
Tunica externa
outermost layer, made of connective tissue but innervated and connected to lymph vessels
36
New cards
Vasa vasorum
small network capillaries that nourish the tissues in the outermost parts of larger blood vessels
37
New cards
Systole
contraction period
38
New cards
Diastole
relaxation period
39
New cards
Cardiac tamponade
the fluid sac around your heart fills with blood or other fluid, putting pressure on your heart
40
New cards
Autorhythmic centers
initiate their own contraction of the heart