1/2- intro + salivary gland, esophagus, stomach histo
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
chief goal of GI
break down macromolecules (proteins, fats, starch) → smaller molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) to be absorbed
3 fundamental processes of GI
secretion: delivery of enzymes, mucus, ions into lumen + hormones into blood
absorption: transport of water, ions, nutrient from lumen → across epithelium → blood
motility: contractions of smooth muscle in the wall of the tube that crush, mix, propel contents
7 organs of the GI in order
mouth
esophagus
stomach
liver
pancreas
small intestine
large intestine
which GI organ does not provide any digestive function
esophagus
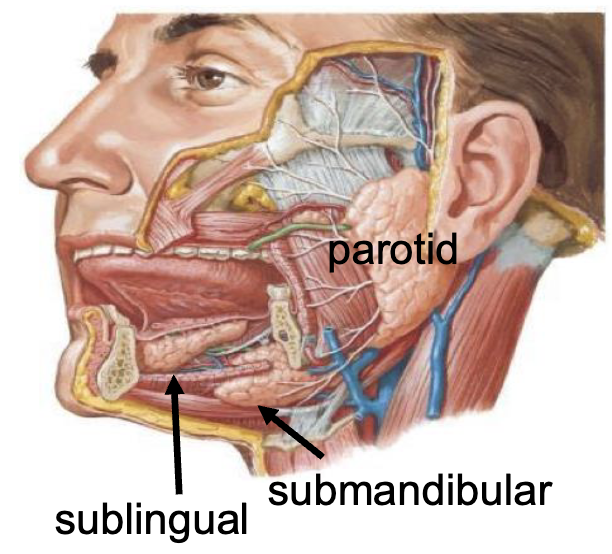
3 major salivary glands
parotid
submandibular
sublingual
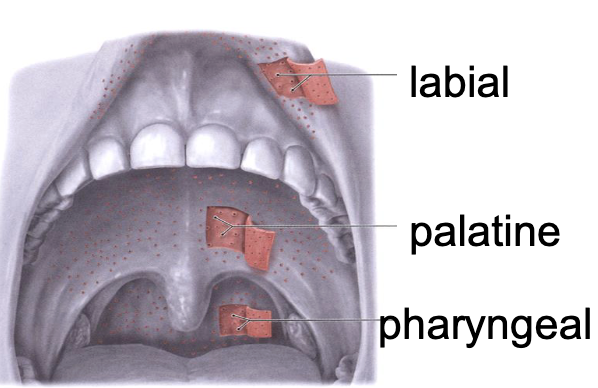
3 minor salivary glands
labial
palatine
pharyngeal
what % of saliva is secreted from the major salivary glands
90+%
what % of mucous is secreted from the minor salivary glands
~70%
4 ways saliva provides protection
moistens/lubricates oral mucosa
prevents drying
flush/cleanse/protects teeth
facilitates speech
2 ways saliva provides buffering
neutralizes acids
maintains pH through HCO3-
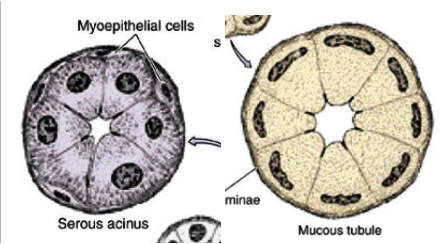
2 types of units found in salivary glands
serous
mucous
differentiate serous vs. mucous
serous: acinar (grape shape), watery fluid, darker stain
mucous: tubular, viscous fluid, lighter stain w/ squished nuclei
which gland has mostly serous units
parotid
which gland has more serous than mucous units
submandibular
which gland has more mucous than serous units
sublingual
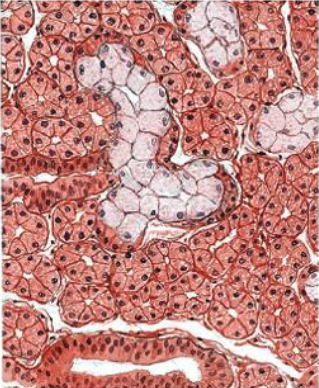
what is this
submandibular gland (note: more serous than mucous)
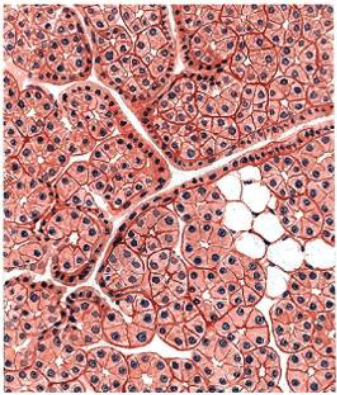
what is this
parotid (note: mostly serous units, no mucous pictured)
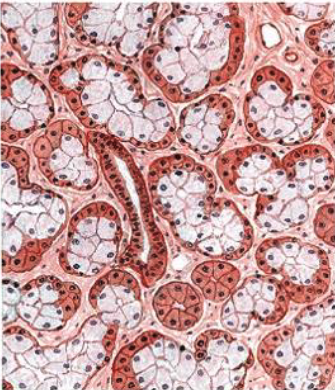
what is this
sublingual gland (note: more mucous than serous)
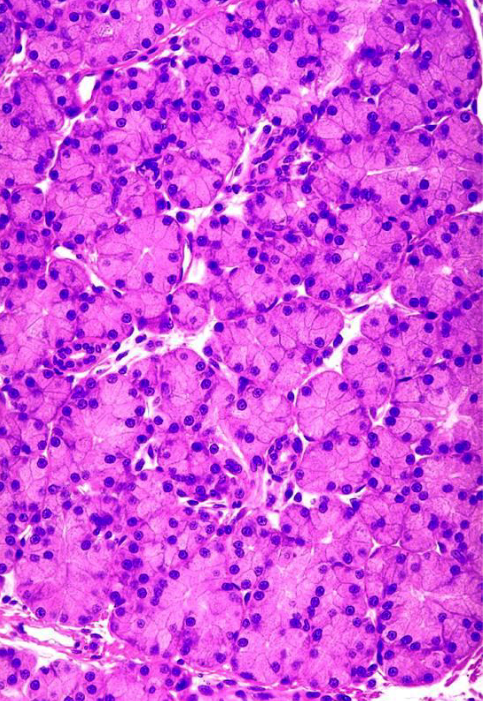
what is this
parotid gland
what is this
submandibular gland
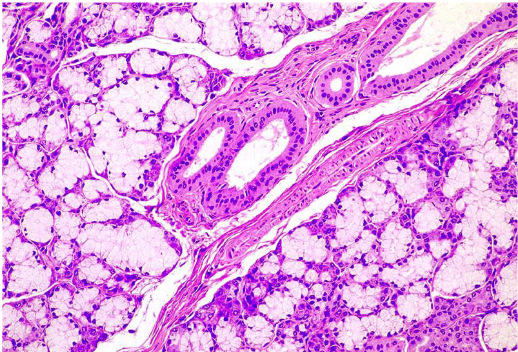
what is this
sublingual gland
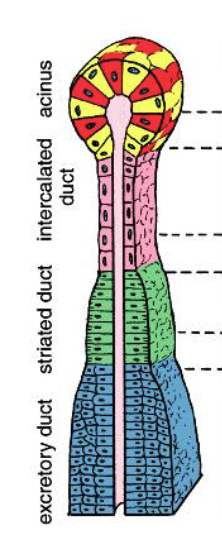
what are the 3 ducts found in all major salivary glands
intralobular ducts:
intercalated: simple cuboidal epithelium
striated: simple columnar epithelium
interlobular ducts:
excretory: psuedostratified epithelium
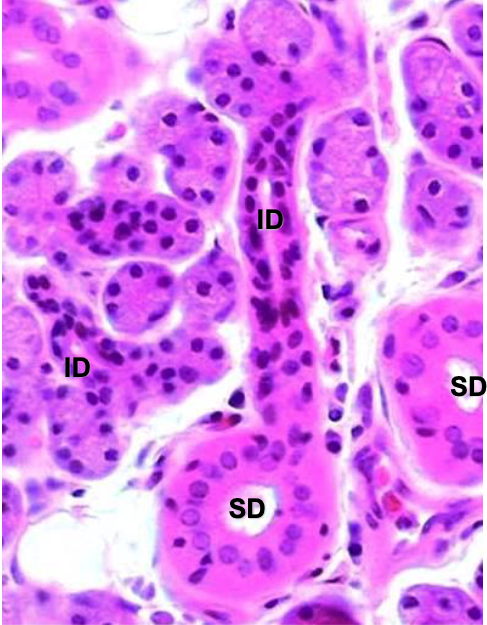
how do you differentiate between intercalated vs. striated ducts
intercalated: cannot distinguish a cell’s boundary
striated: can distinguish a cell’s boundary
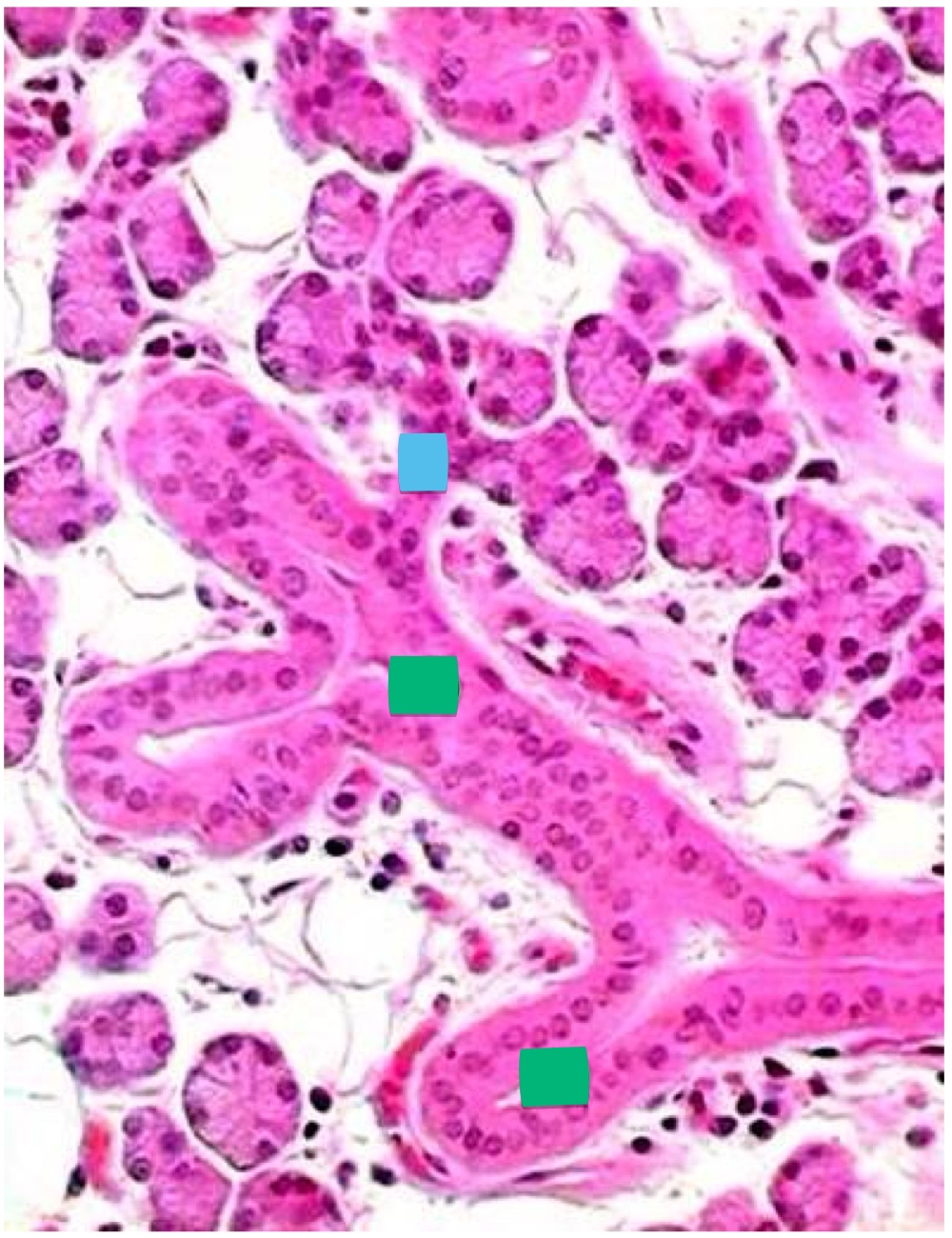
what’s the blue + green label
blue: intercalated duct
green: striated ducts
why are striated ducts “striated”
basal lamina (basement membrane) infoldings in between the mitochondria
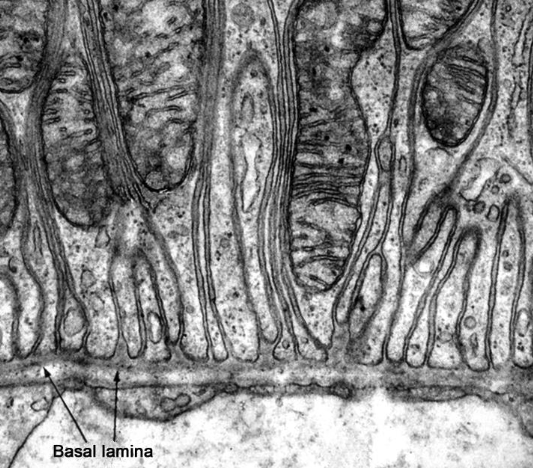
what are the big pink circles
striated ducts
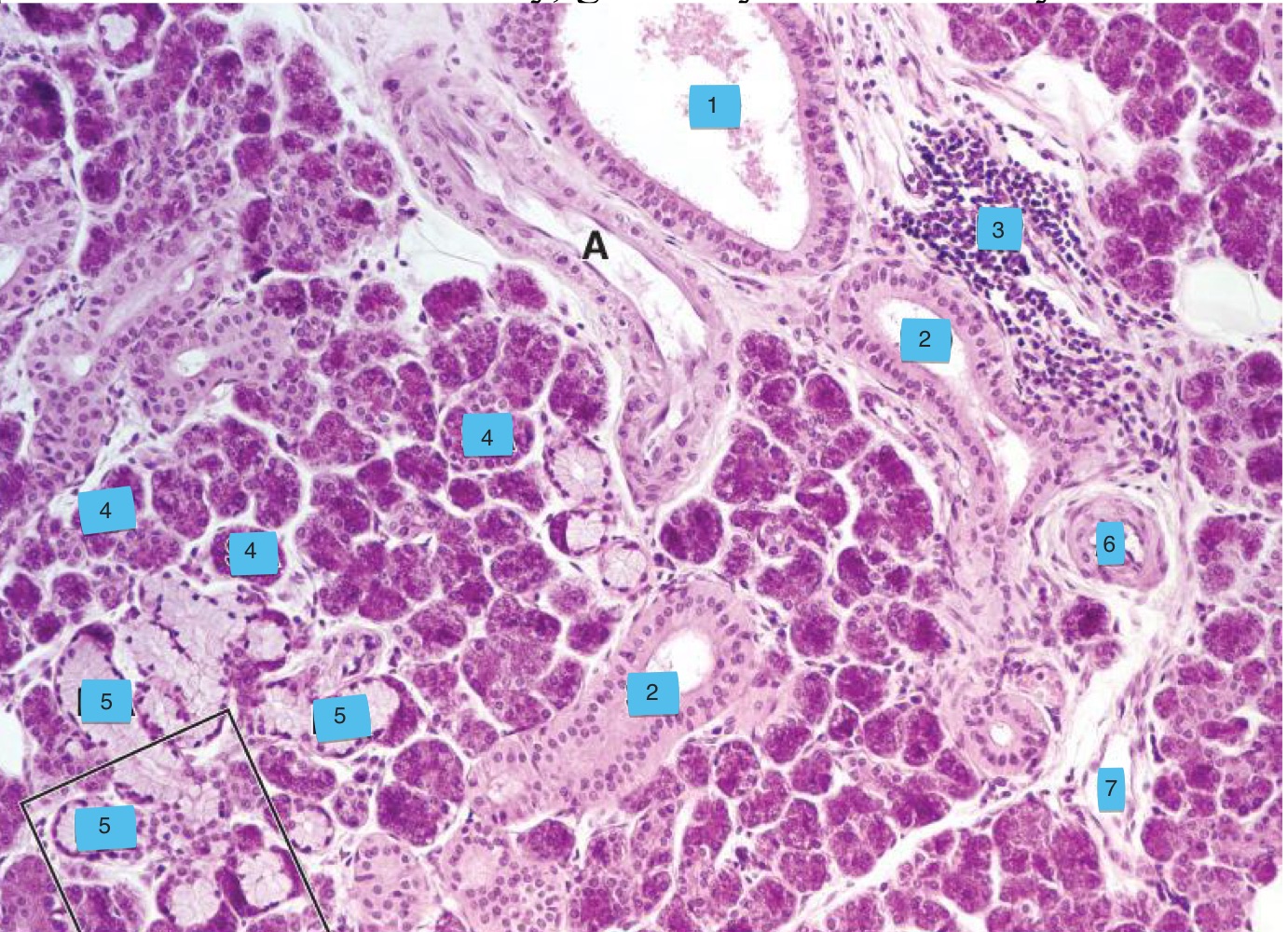
what are the numbers
excretory duct (interlobular) (note: pseudostratified epithelium)
striated duct (intralobular)
lymphoid tissue
serous acinar
mixed acinar
artery
vein
what are myoepithelial cells
branching cells w/ actin + myosin that wrap their processes around secretory cells to expel secretions
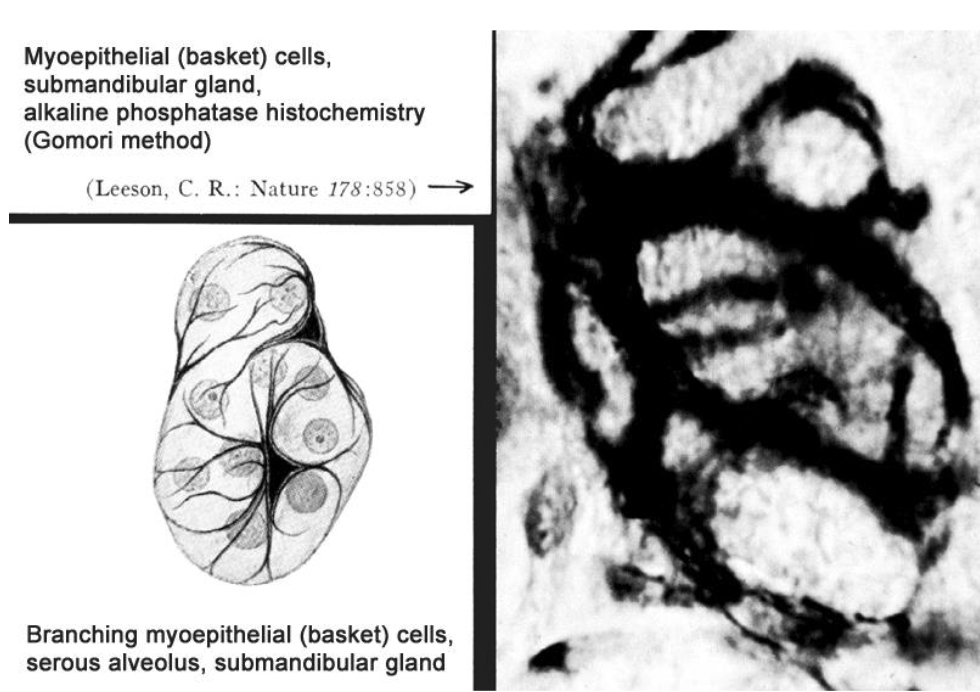
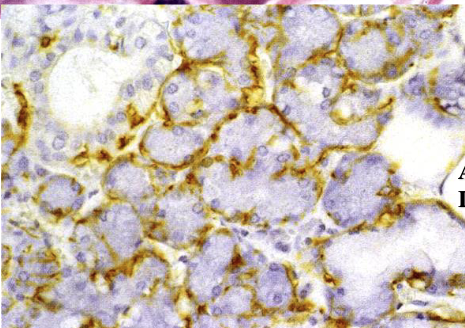
what’s the yellow
myoepithelial cell processes using actin stain
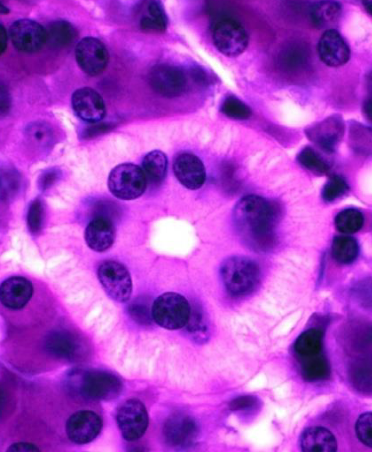
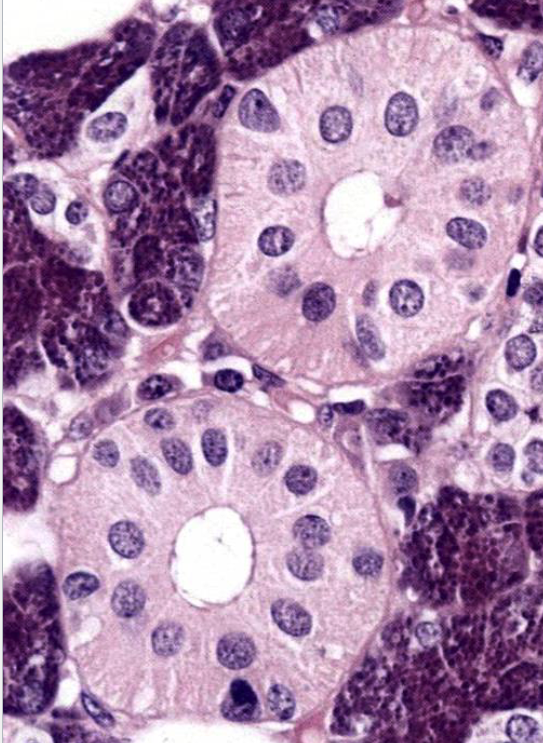
what’s the circular structure in the center
striated duct
which minor salivary gland has serous excretions
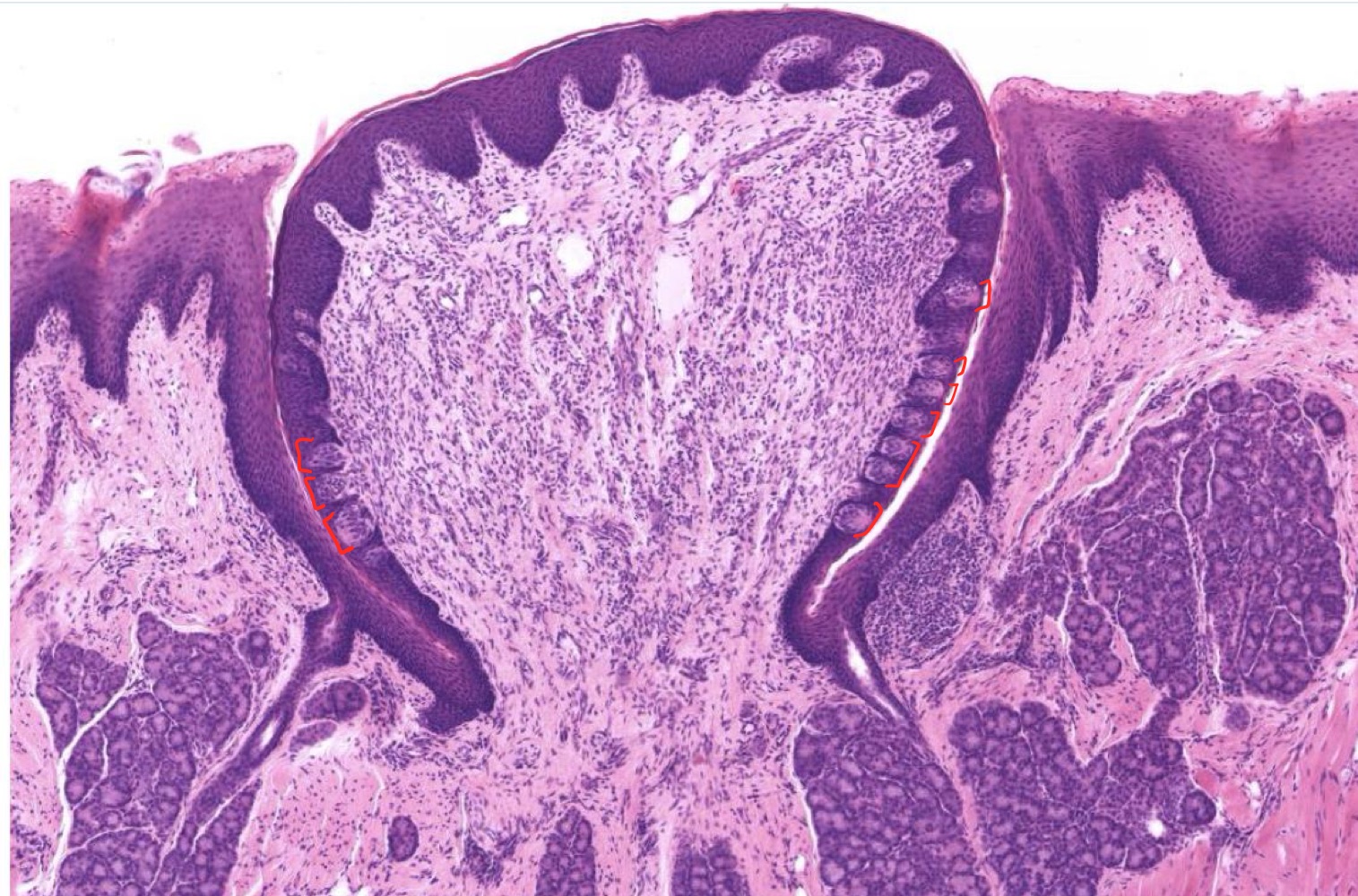
Ebner (gustatory) glands
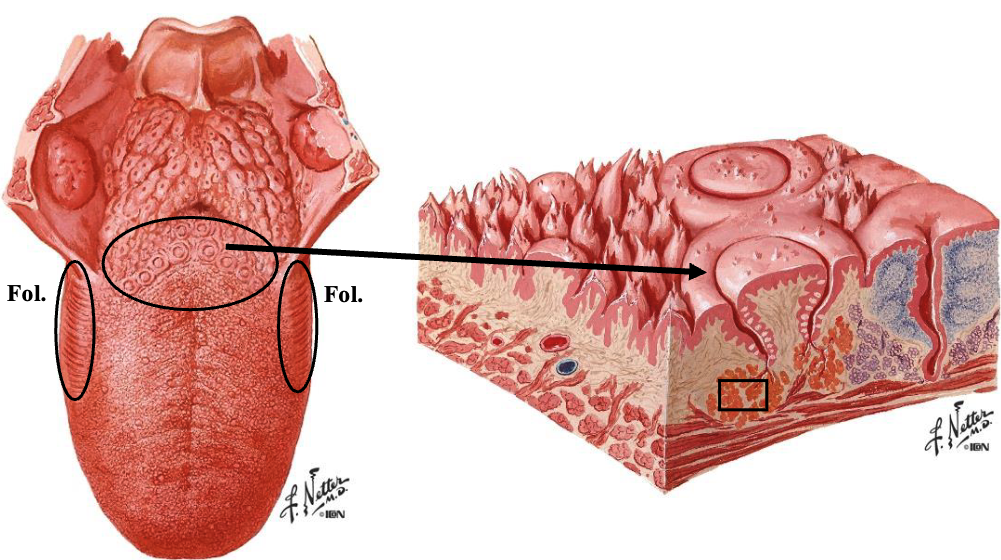
Ebner glands are located near which papillae
vallate + foliate papillae
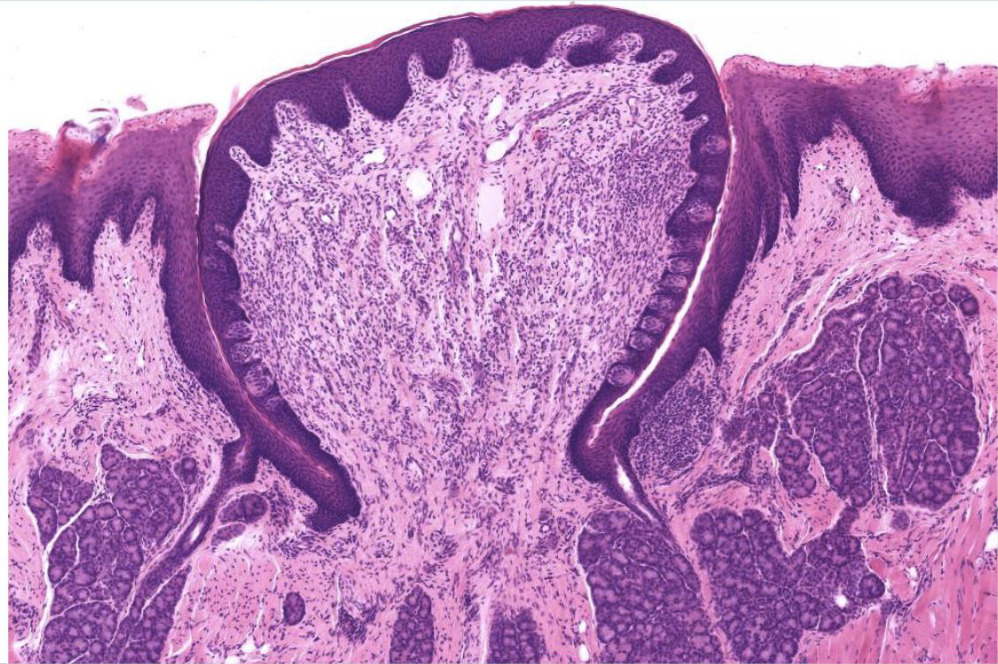
identify the Ebner glands in this image
what’s the 3rd most common autoimmune disease
Sjogren’s
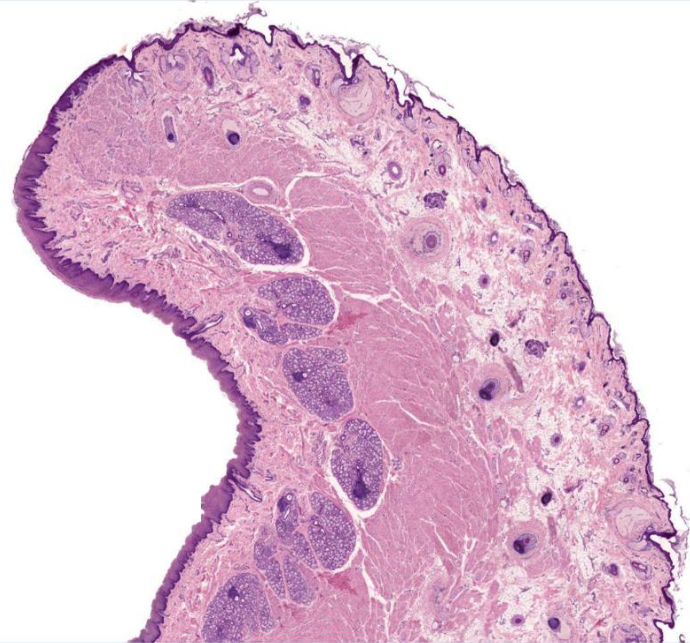
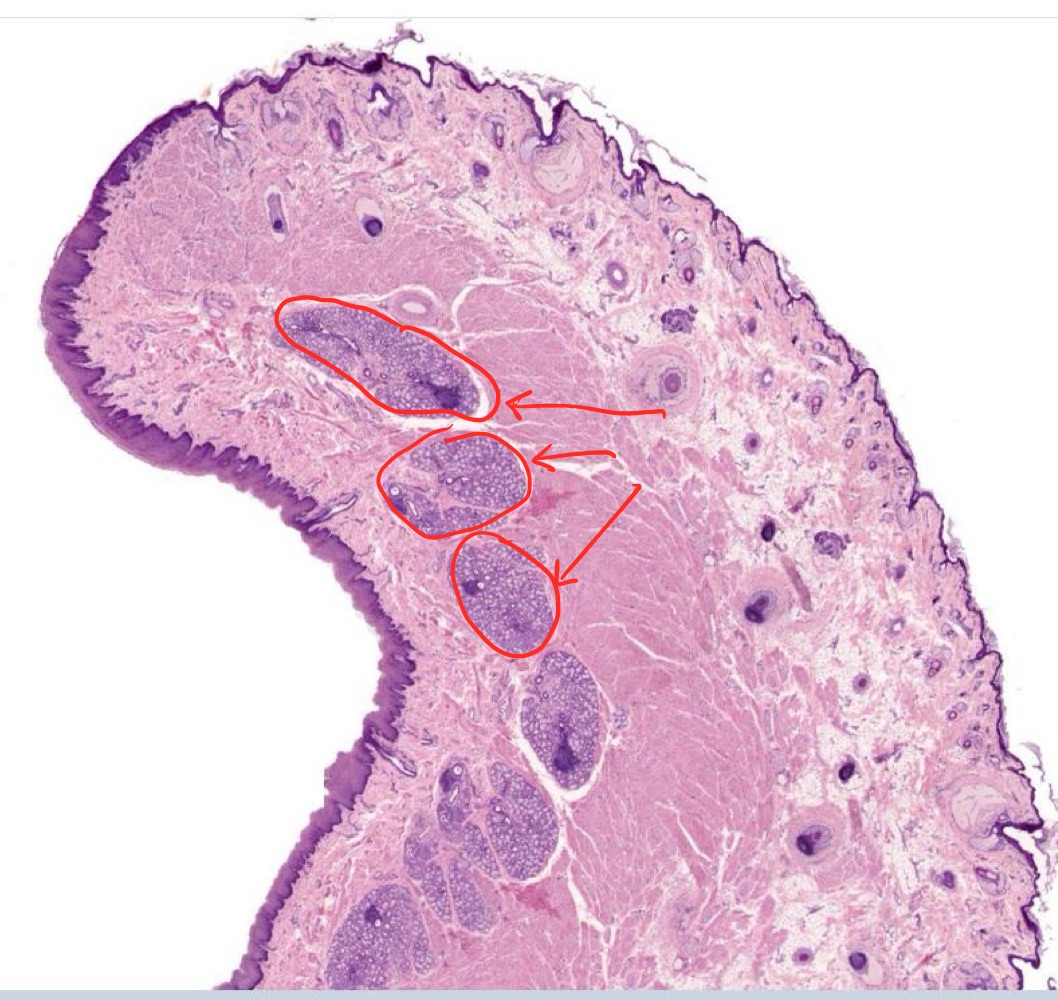
identify the labial glands in this image
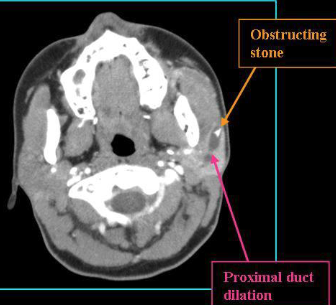
what’s Sialolithiasis
formation of calculi or mineralized concretion that blocks a salivary duct
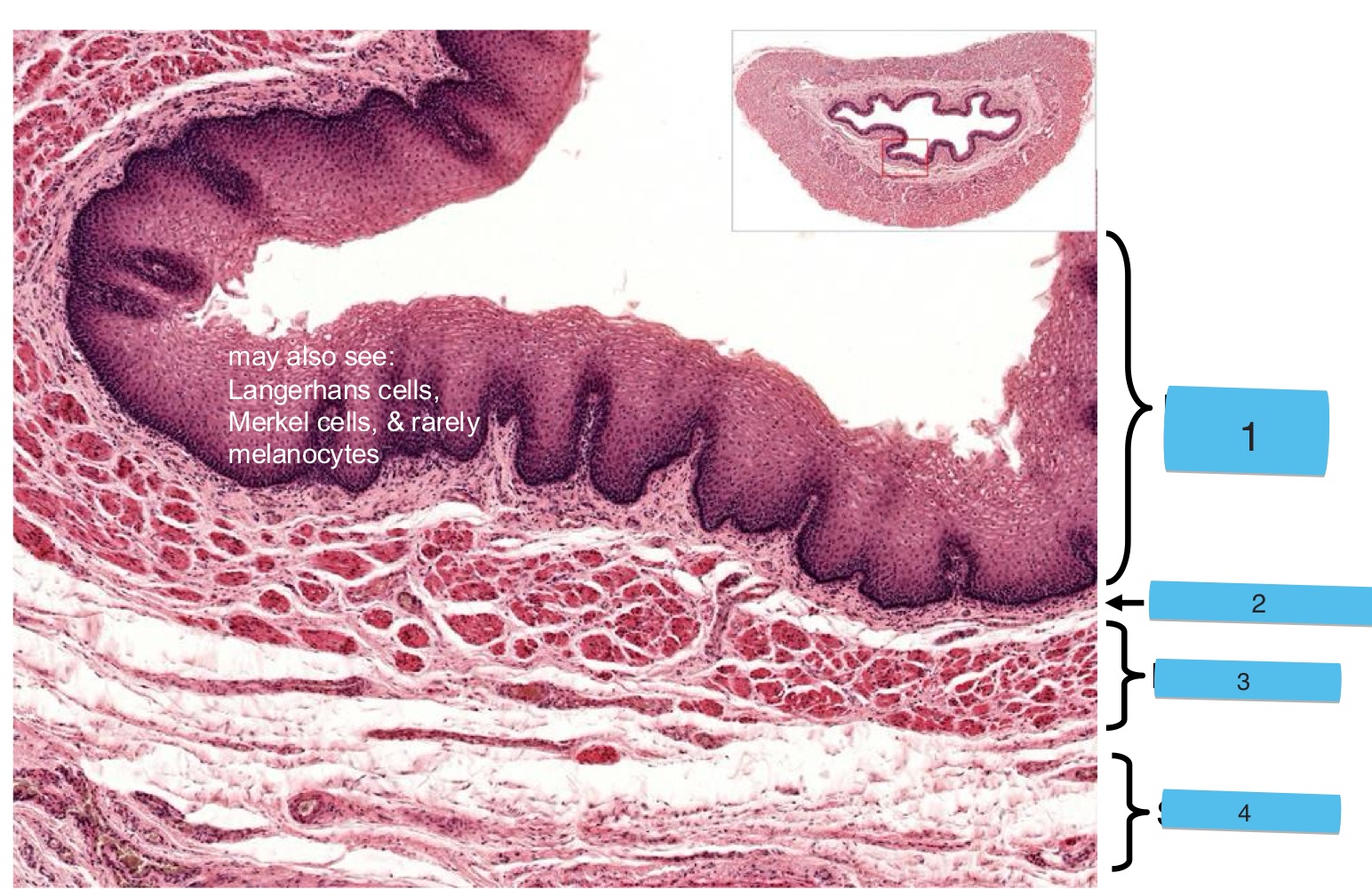
4 layers of the esophagus inside → out
mucosal lining
submucosa
muscularis externa
adventitia/serosa: thorax/abdominal cavity
3 things that make up the mucosal lining of the esophagus
simple stratified non-keratinized epithelium (SSNKE)
lamina propria
muscularis mucosae
2 things that make up the submucosa of the esophagus
loose CT
esophageal glands
2 things that make up the muscularis externa of the esophagus
inner circular muscle
outer longitudinal muscle
what type of muscle is in the muscularis externa of the esophagus
upper 1/3 of esophagus: only skeletal muscle
middle 1/3: skeletal/smooth mixed
lower 1/3: only smooth
what are the numbers
cross-section of esophagus:
SSNKE lining
mucosa
muscularis mucosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
adventitia/serosa
what are the numbers
cross-section of esophagus:
SSNKE
lamina propria
muscularis mucosa
submucosa
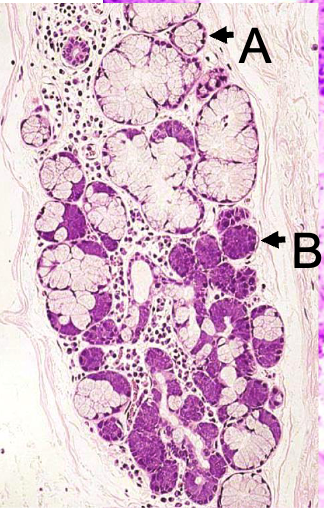
what are the letters
A: mucous unit of esophageal submucosal glands
B: serous unit
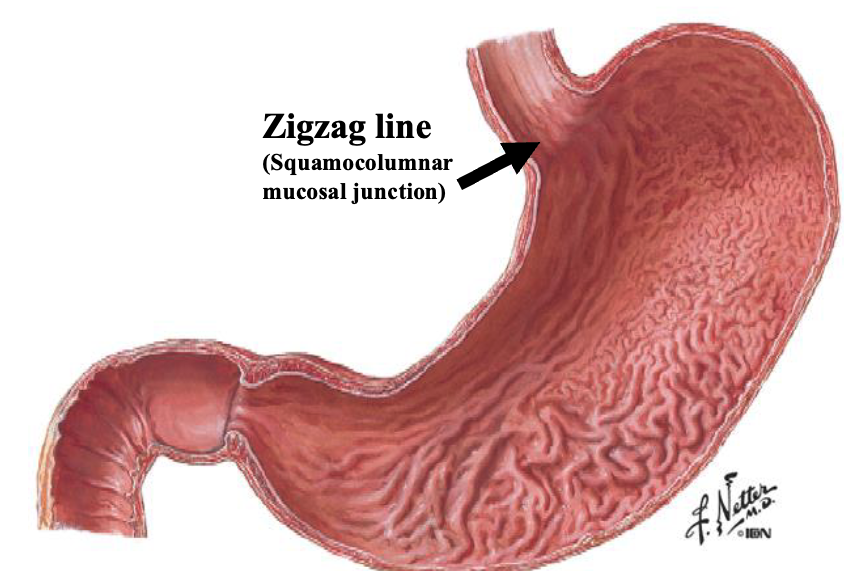
what the boundary between the esophagus + stomach
zigzag line: squamocolumnar mucosal junction
what’s Barrett’s esophagus
abnormal squamocolumnar mucosal junction where SSNKE of esophagus turns into gastric/intestinal epithelium
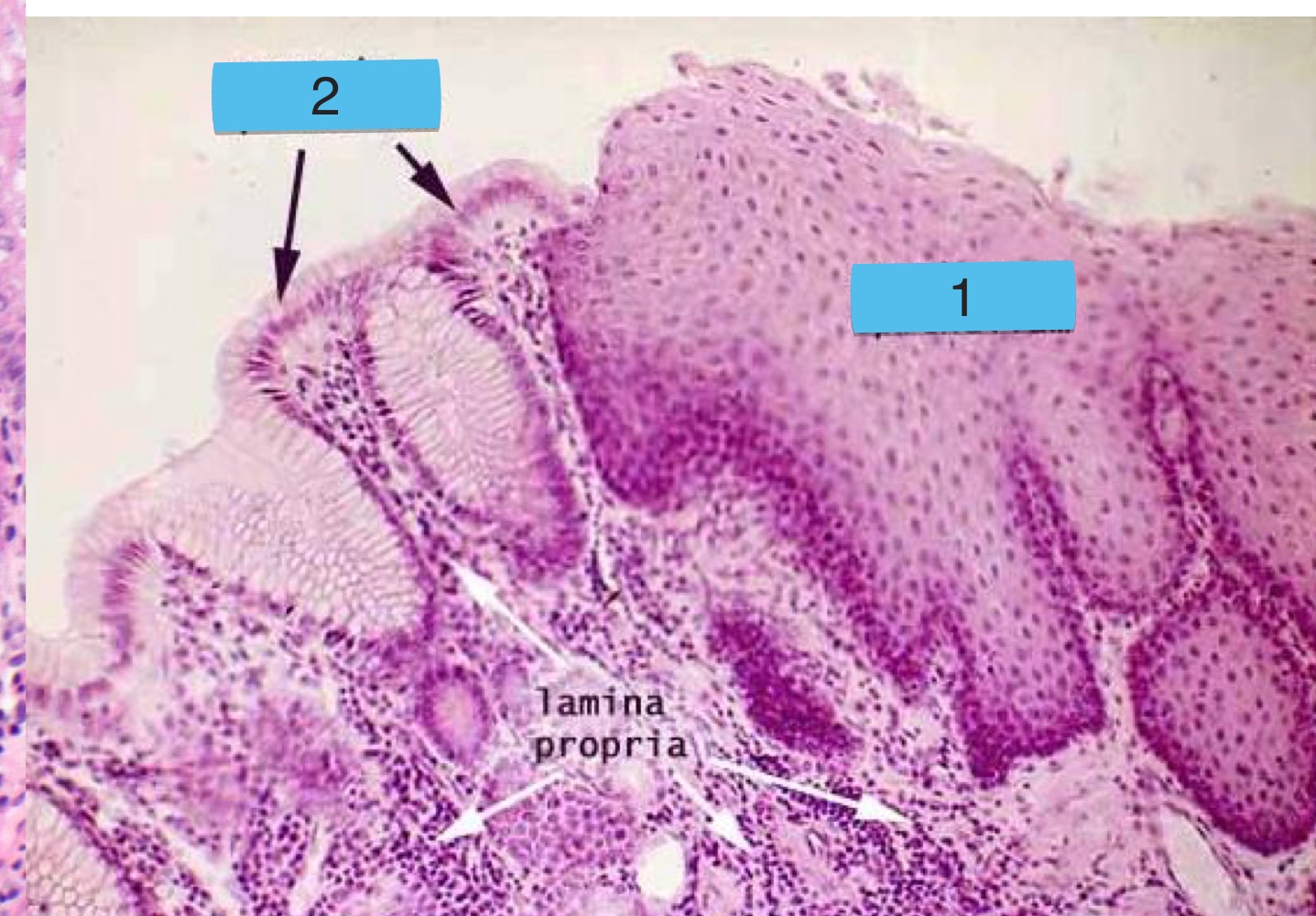
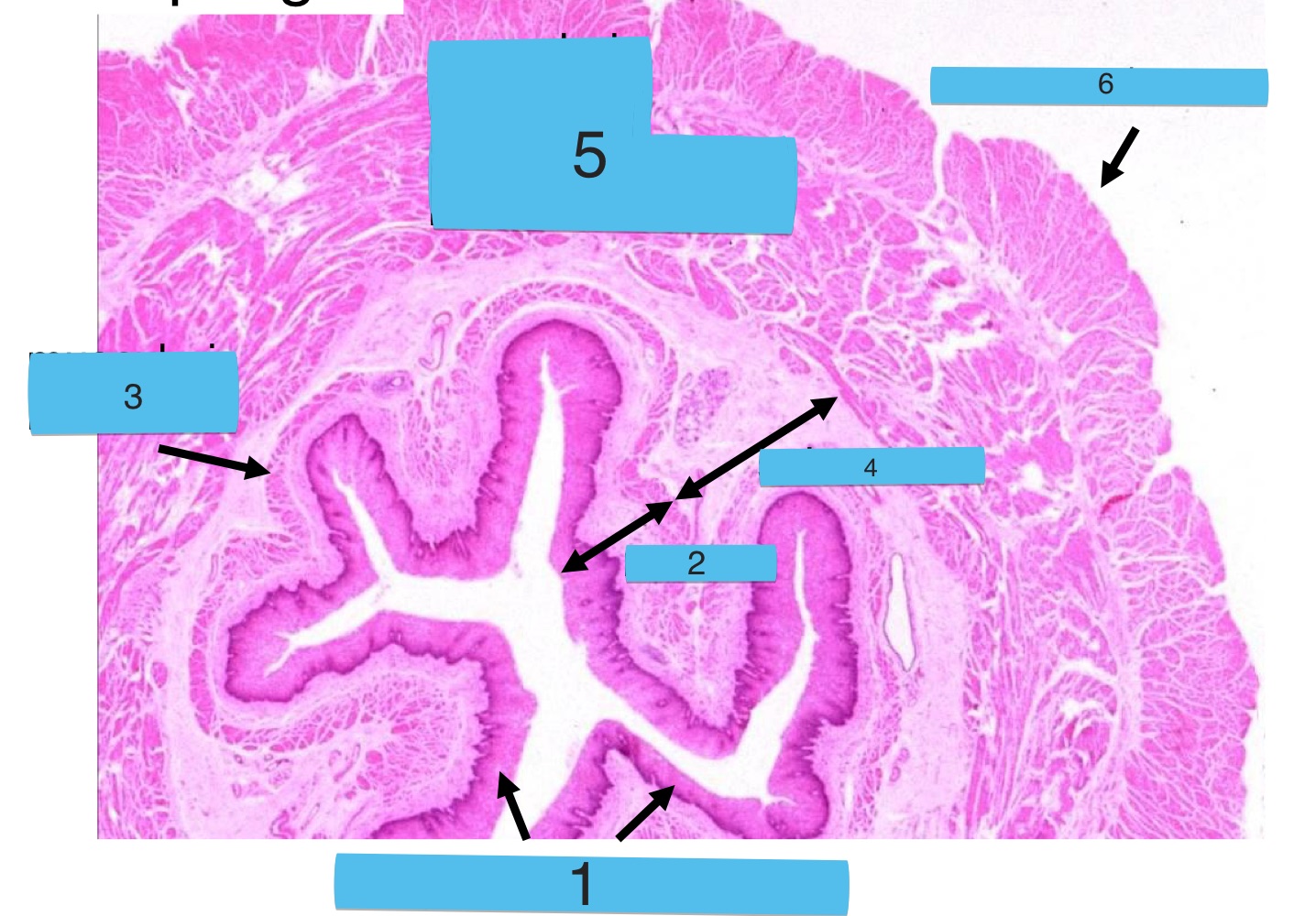
what is this + what are the numbers
normal squamocolumnar mucosal junction
esophageal epithelium
gastric (stomach) epithelium
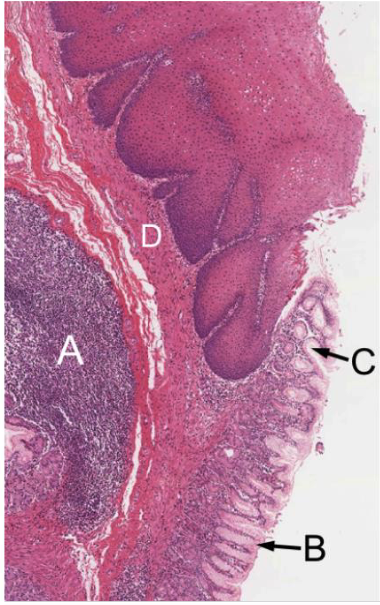
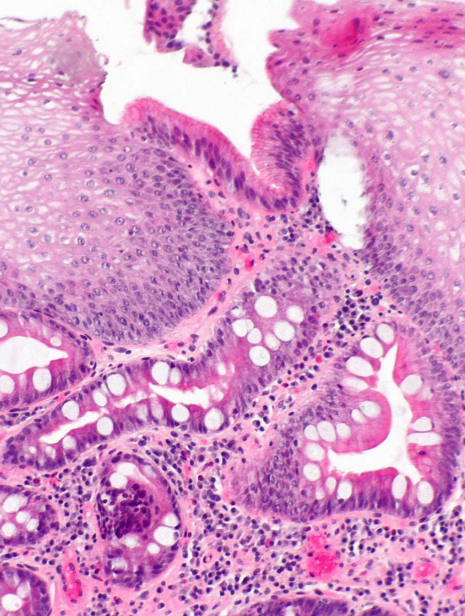
what is this + what are the letters
gastroesophageal junction
A: mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
B: surface mucous cells
C: gastric pit
D: muscularis mucosa
4 layers of the stomach (inside → out)
mucosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
serosa (mainly)/adventitia
which has no glands: mucosa or submucosa of stomach
submucosa
what 3 muscles are in the muscularis externa of the stomach
inner oblique (limited)
middle circular
outer longitudinal (limited)
3 types of stomach mucosal glands
cardial gastric
gastric glands proper (fundic)
pyloric
what type of cells are found in fundic glands of the stomach
mucous neck
stem
parietal
zymogenic chief
enteroendocrine
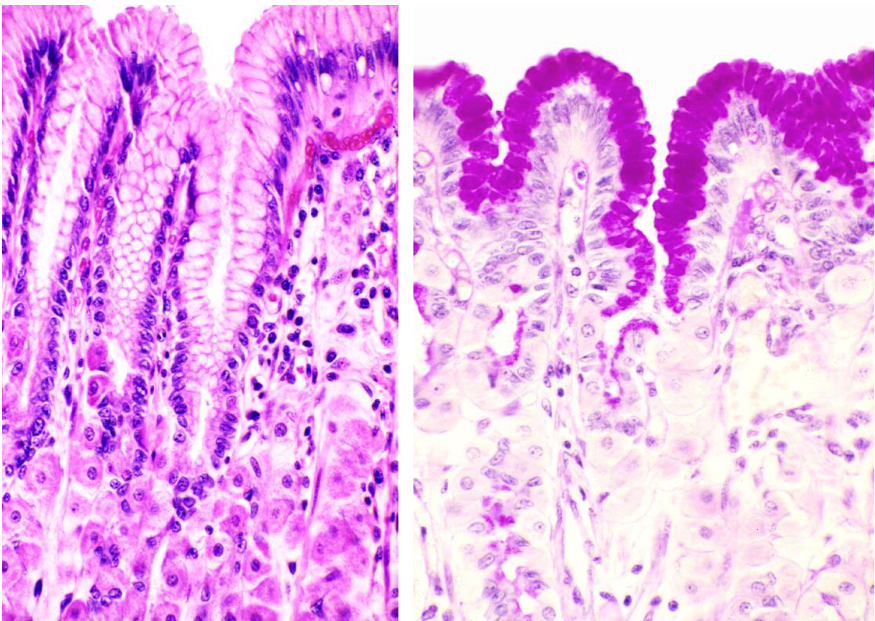
what’s important in this image
stomach surface mucous cells which cover inner surface + gastric pits
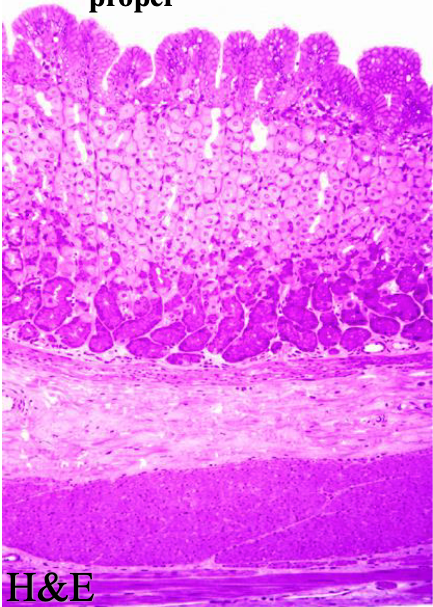
what type of stomach mucosal gland is pictured
gastric glands proper (fundic)
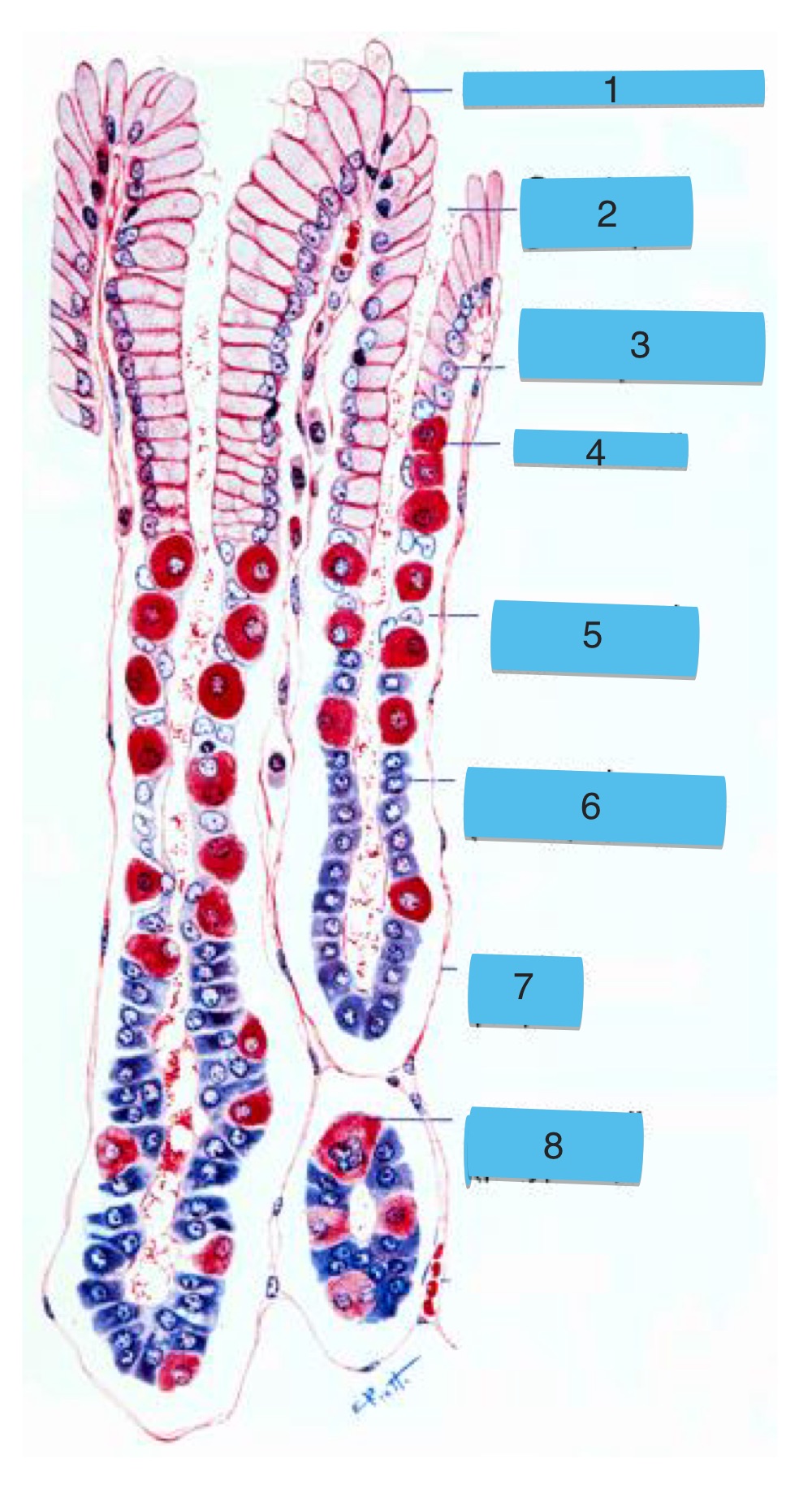
what are the numbers
fundic gland:
surface mucous cell
opening of gastric pit
surface mucous cell of pit
parietal cell
mucous neck cell
zymogenic (chief) cell
lamina propia
parietal cell (polyploid)
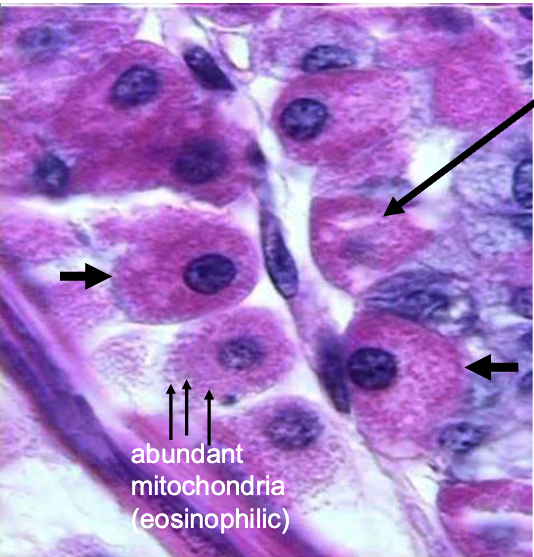
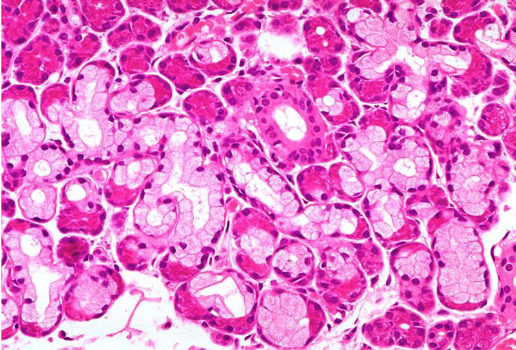
what are the arrows pointing to
parietal cells of fundic glands (note: egg appearance, abundant mitochondria, pink cytoplasm)
function of parietal cells in stomach
secretes:
HCl
intrinsic factor (for vitamin B12 absorption)
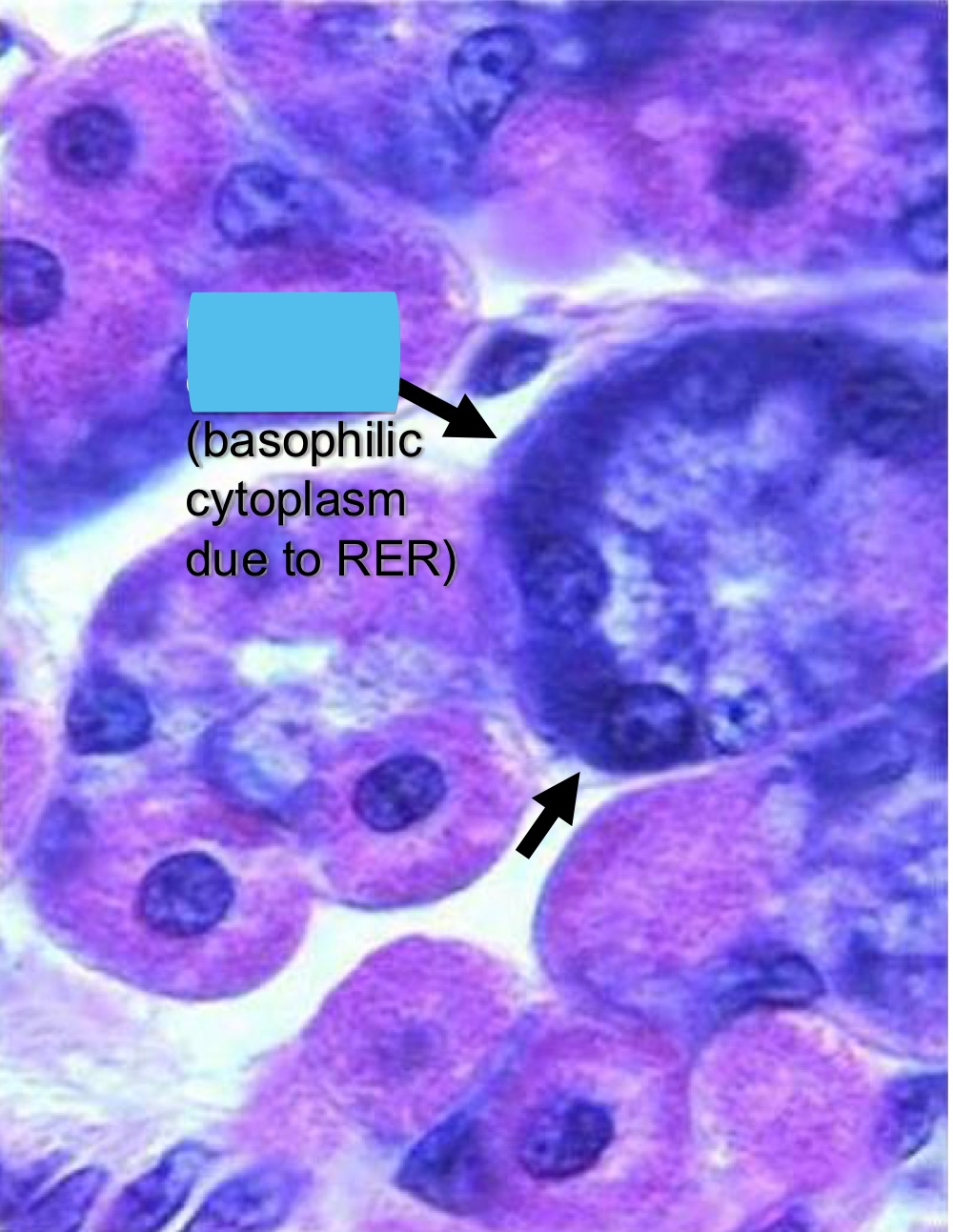
what are the arrows pointing to
zymogenic chief cells (note: basophilic cytoplasm)
function of zymogenic chief cells
secrete pepsinogen + lipase
which muscle of the stomach muscularis externa is used for churning
inner oblique
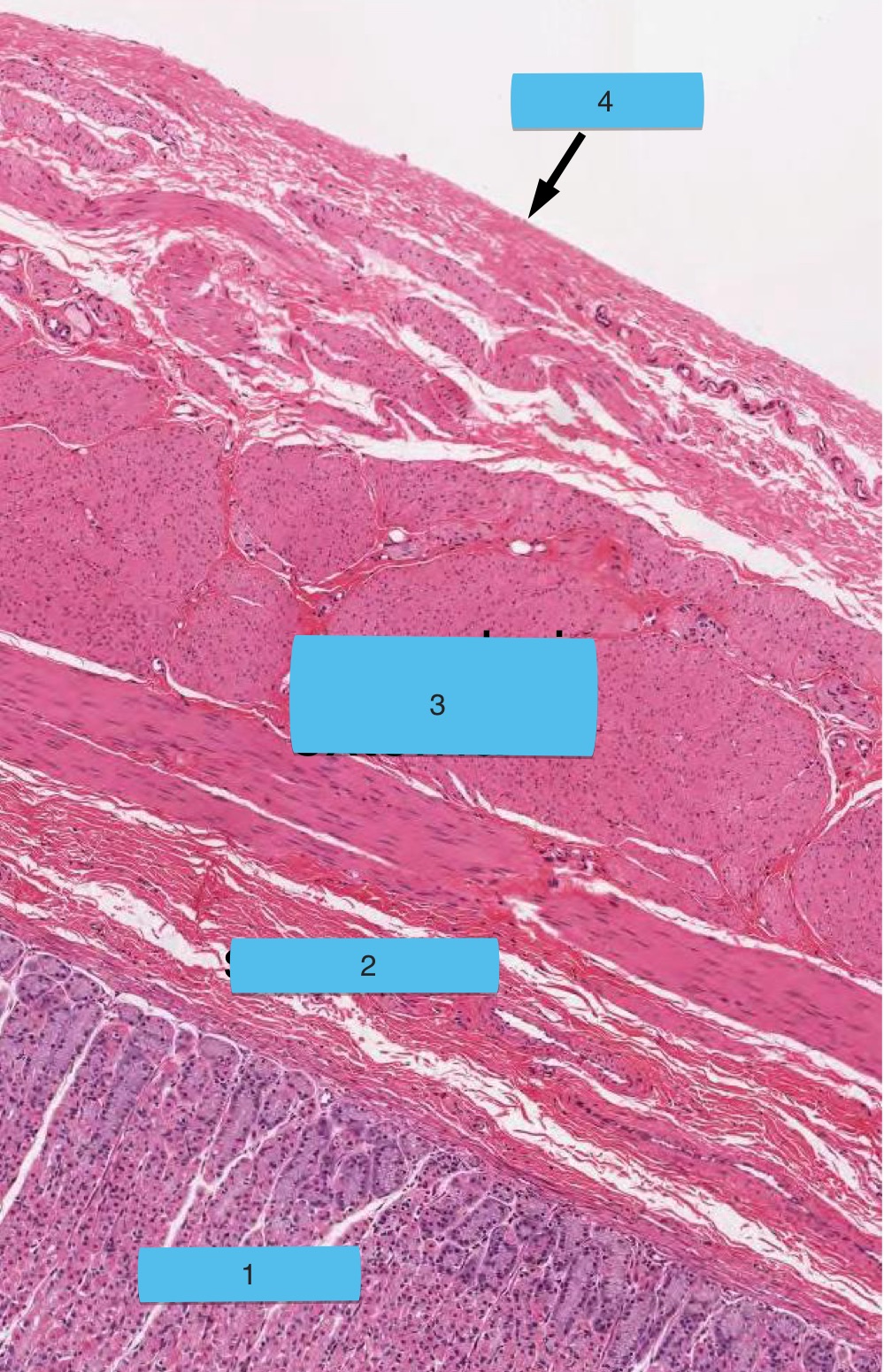
what are the numbers
stomach layers:
mucosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
serosa

which one is improperly matched
b. gastric glands are in mucosa
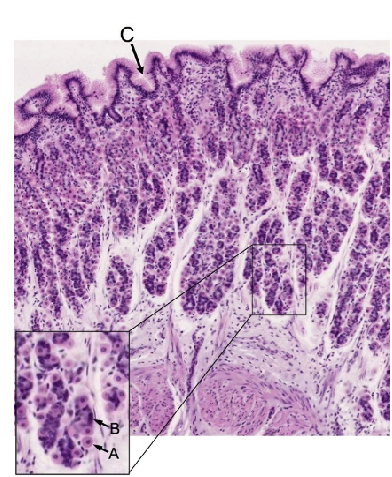
what are the letters
fundic gland of stomach:
A: parietal cell
B: chief cell
C: gastric pit