Module 1: Overview of History of Science and Technology in Culture
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Homo sapiens
Scientific name of modern humans
Family Hominidae, Tribe Hominini
Family and tribe of modern humans
Approximately 40,000 years ago
The time when Homo sapiens became the last species of the genus Homo
Africa
The continent of origin of hominids
Single wave dispersal model
The model which states that a primary dispersal out of Africa occurred, followed by a relatively rapid spread across Eurasia and eventually to Australia and the Americas
Multiple waves dispersal model
The model which states that humans left Africa in several waves of migration, with some populations moving back to Africa
Cognitive Revolution
According to Harari, this major part in human history is the start of behavioral modernity as we developed new ways of thinking and communicating.
Hunter-gatherer or forager
A human living in a community in which most food are obtained by either gathering food from naturally occuring sources or by hunting game
Average brain size
This has decreased in humans since the age of foraging 40,000 years ago.
Gorging gene theory
This theory states that our ancestors possessed genes that enabled them to efficiently store fat to survive times of food scarcity.
Nomadic living
This is the lifestyle of early humans described as “moving from place to place.” only carrying with them essential possessions.
Wildfires or bushfires
It is the source of fire of early humans before they were able to make it themselves.
Percussion and friction method
The two main methods used by early humans to make fire
Flint
It is the first mineral mined by humans to utilize in tool creation.
Gold and copper
These two prominent minerals were first mined by humans during the Neolithic Period.
Stone cores
Pieces of rocks from which flakes have been removed
Venus of Hohle Fels
An Upper Paleolithic Venus figurine made of mammoth ivory
Was found in Hohle Fels Cave in Germany
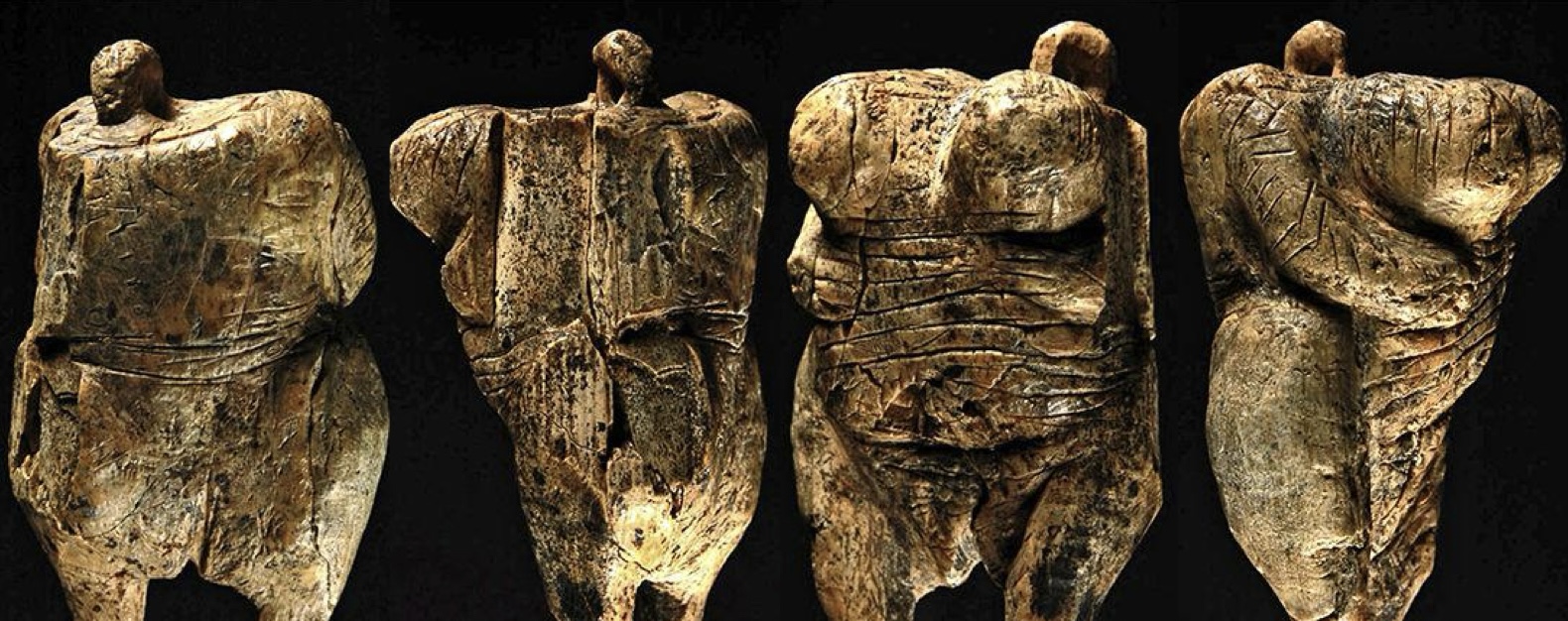
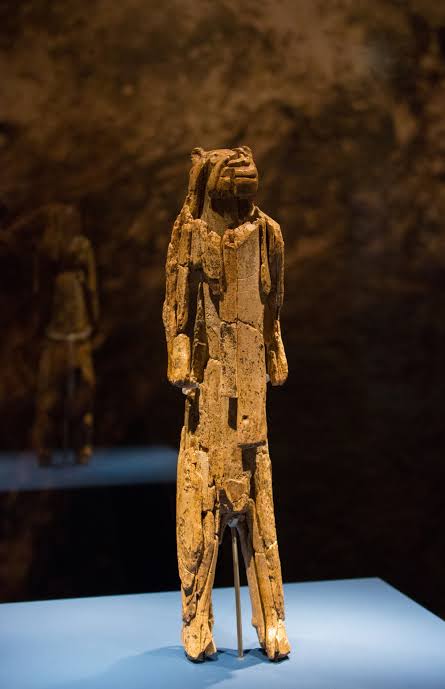
Löwenmensch
A prehistoric ivory sculpture depicting a human with a cave lion head
Was found in Hohlenstein-Stadel in Germany

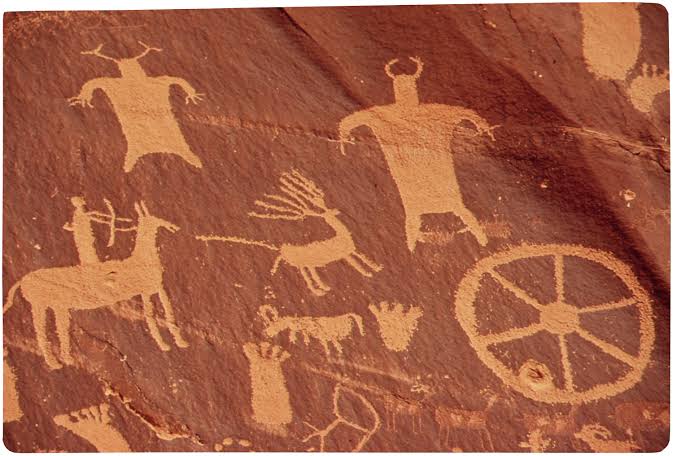
Petroglyphs
An image formed by removing a part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading

Lascaux Cave
A network of caves in France, known for its 600 parietal wall paintings depicting megafauna of the Upper Paleolithic

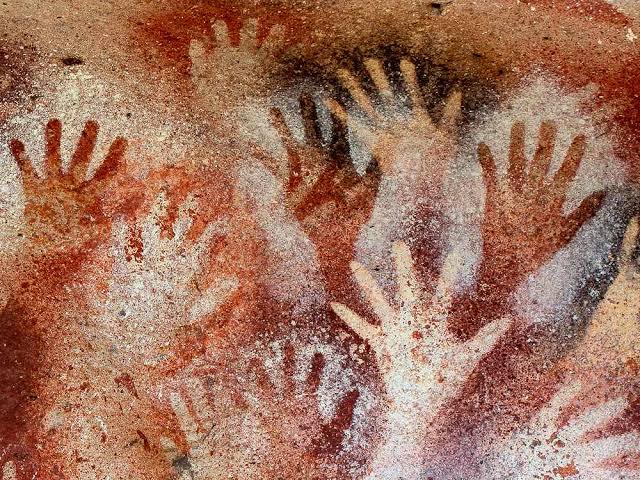
Cueva de las Manos
A cave complex in Argentina known for its paintings of hands stenciled on rock walls

Agricultural Revolution
According to Harari, this major part in human history involves the development of efficient food production.
Fertile Crescent
The region in Middle East regarded as the birthplace of agriculture
Persian Gulf through modern-day southern Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and northern Egypt
It is the modern day scope of the Fertile Crescent.
Occupational Stratification
Refers to the hierarchial arrangement of jobs within a society
Temple economy or temple-state economy
An economy where temples serve as central institutions wielding significant economic power and influence, often ruled by a religious personnel
Kingdoms
Unlike in temple economy, this refers to a state with secular rulers such as scholars or monarchs
Artisans or craftsmen
They are skilled craft workers who makes or creates material objects partly or entirely by hand.
Sumer
It is the earliest known civilization located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now Southern Iraq)
People of this civilization were known as Sumerians (called themselves Sag-giga)
Levees and canals
The infrastructures used by Sumerians to control irrigation for agriculture
Ziggurats
Rectangular stepped towers functioning as both temples and civic centers in Sumer
Epic of Gilgamesh
An epic from ancient Mesopotamia composed of five Sumerian poems about Gilgamesh, the king of Uruk
Babylonia
An anncient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area located in central-southern Mesopotamia (now Iraq)
Code of Hammurabi
An ancient Babylonian legal text inscribed on basalt stele
Tower of Babel
An origin myth in the Book of Genesis meant to explain the existence of different languages
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Ancient gardens considered one of the Seven Wonders of the World
Assyria
A major ancient Mesopotamian civilization known for its powerful military and cultural achievements
Located in what is now northern Iraq, Southeastern Turkey, and parts of Kuwait and Syria
Crete
An island in Greece populayed by the Minoan civilization
They exported timber, olive oil, and dye; and imported metals, ivory, and precious stones
Scientific Revolution
According to Harari, this major part in human history is marked by the emergence of objective science, including abstract reasoning and quantitative thought.
Early Mathematics
It was mostly about proving theorems and became the foundation of early philosophy.
A priori
Knowledge that is obtained by analyzing concepts independent of experience
A posteriori
Knowledge that is obtained through experience
Roman Empire
One of the largest and most powerful political, military, and cultural powers in Western civilization
Founded in ancient Italy
Etruria and Latium
The two main regions of ancient Italy
Regal, Republican, & Imperial
The three periods of the Roman Empire
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius)
First emperor of Rome
Pont du Gard
An ancient Roman aqueduct bridge built to carry water over 50km to the Roman colony of Nemausus

The Colosseum
An elliptical amphitheater in the center of Rome and is the largest ancient ampitheater ever built

Roman sarcophagi
An ancient Roman funerary art characterized by elaborate carvings in relief; often on marble and limestone

Christianity
Originated in the mid-1st century CE as a Jewish sect in Judea and spread throughout the Roman Empire and beyond
Classical Ages
During this age, technological and scientific advances were spearheaded through the Catholic church by the clergy in the monasteries
Developments in abstract thought and sciences were seen more in the Islamic and Chinese empires
Catholic Church
The most powerful institution of the medieval period (14th to 17th century)
Controlled the intellectual and administrative expression of the period
Roger Bacon
A Franciscan friar that first understood the process of making gunpowder, proposed flying machines, motorized ships and carriages, and invented magnifying glasses.
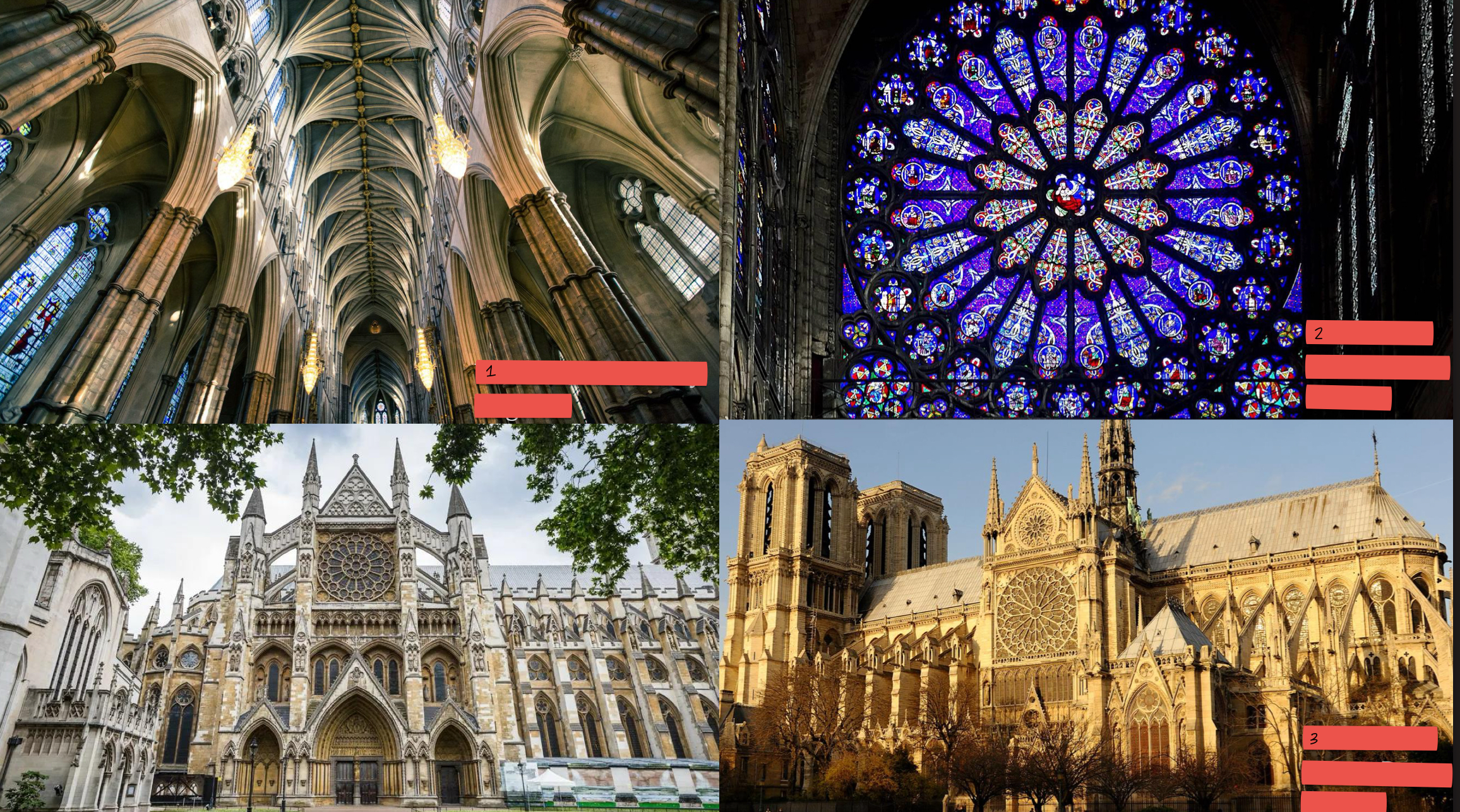
Cathedral schools and universities
Where the clergymen of the Catholic church trained
Monastery
Was the center of culture in the Western civilization during the Middle Ages
Islam
A monotheistic religion originated in the Middle East; flourished during the Middle Ages
