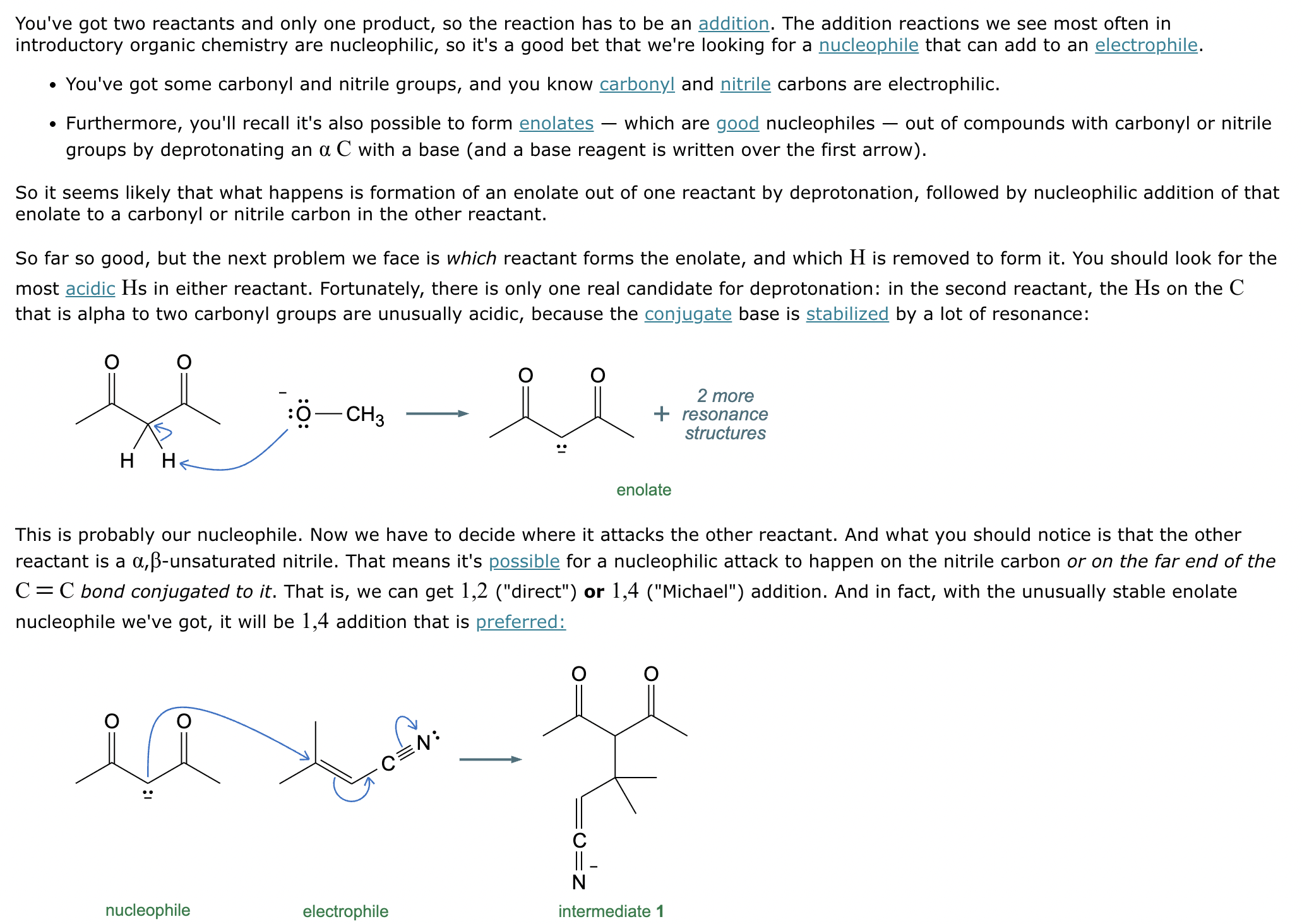
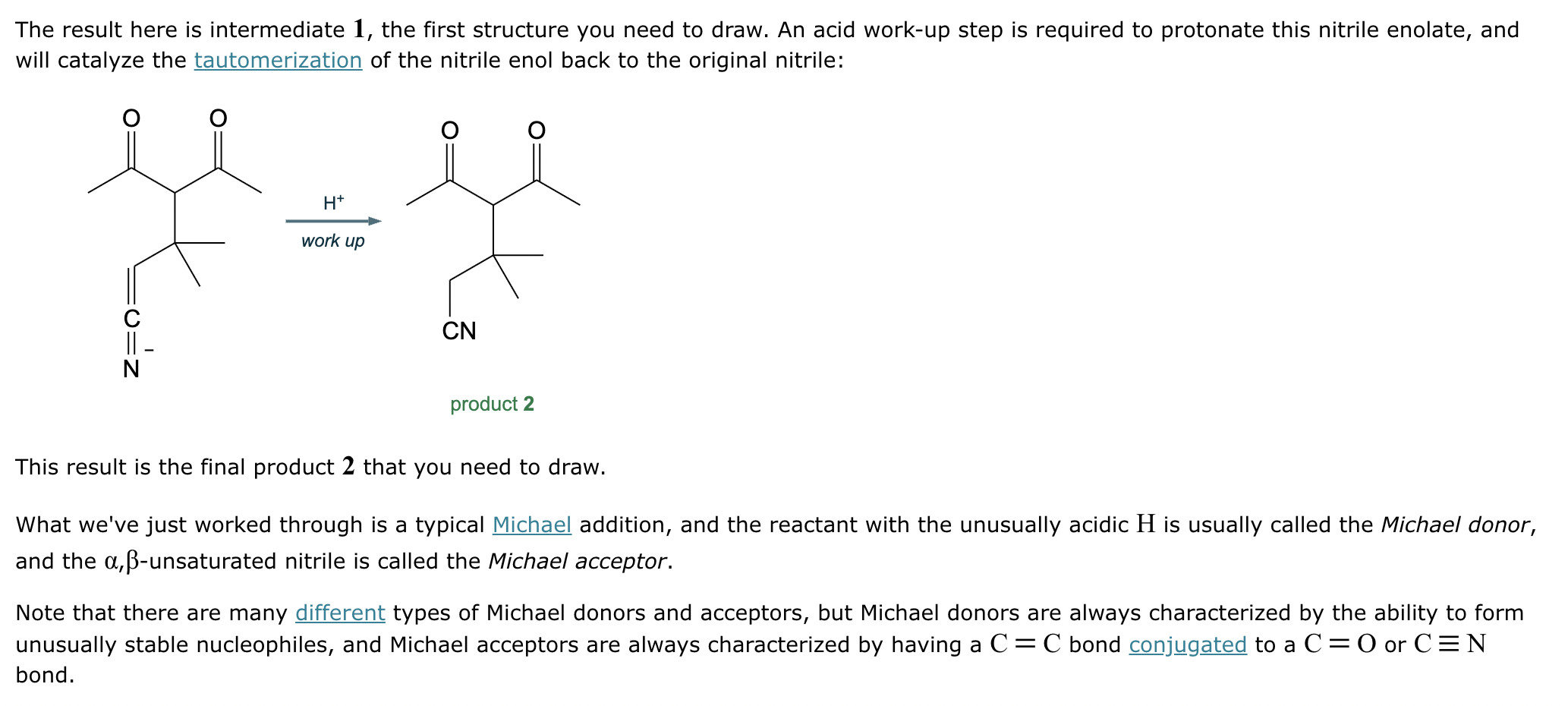
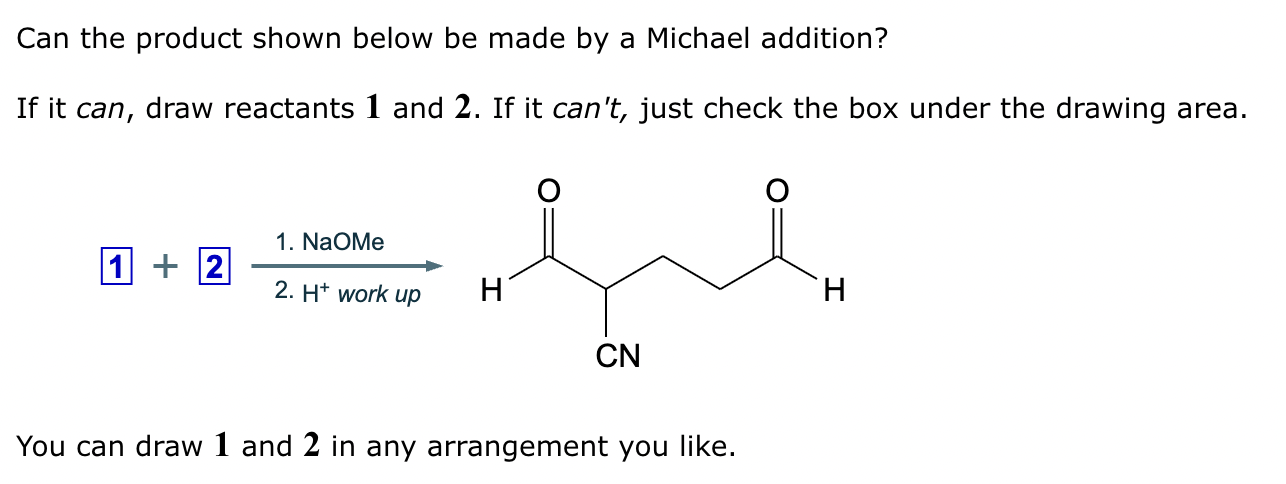
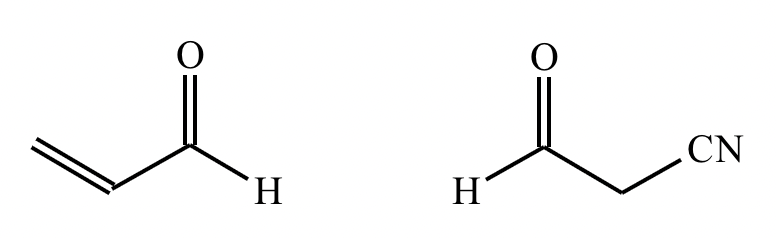
Unit 4 Aleks Assignments
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
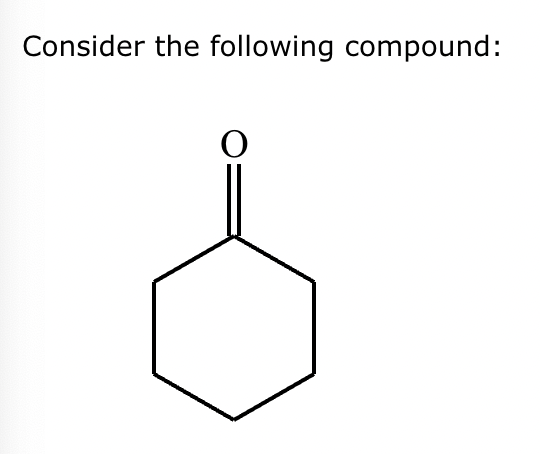
Consider the keto form of this compound:
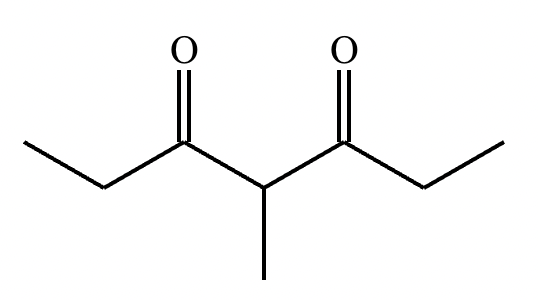
(a) How many mono enol tautomers could be formed for this compound?
(b) Draw a mono enol tautomer for this compound.
(a) 2
(b)
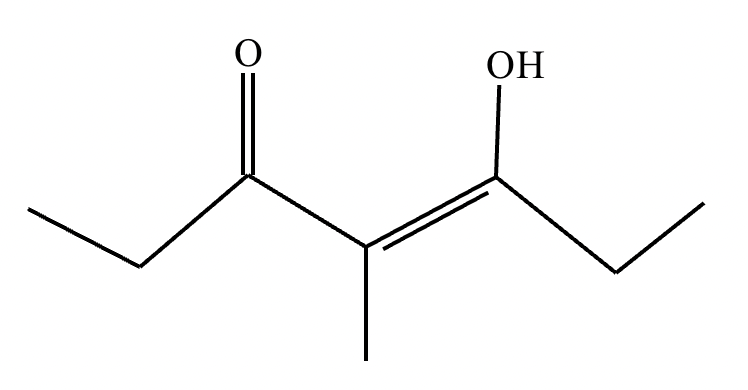
Explanation: Enol and keto forms are tautomers of the carbonyl group that differ in the position of a double bond and a proton. These constitutional isomers are in equilibrium with each other.
Draw the major enolate (or carbanion) formed when the following compound is treated with LDA in THF at -78 °C.
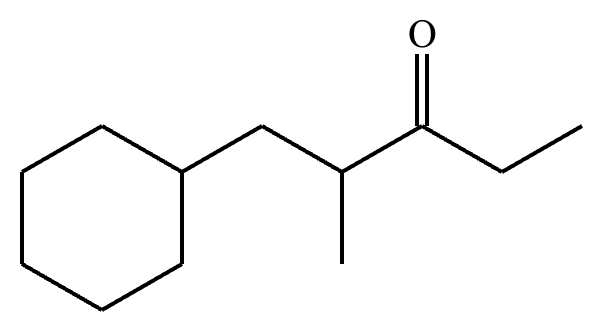
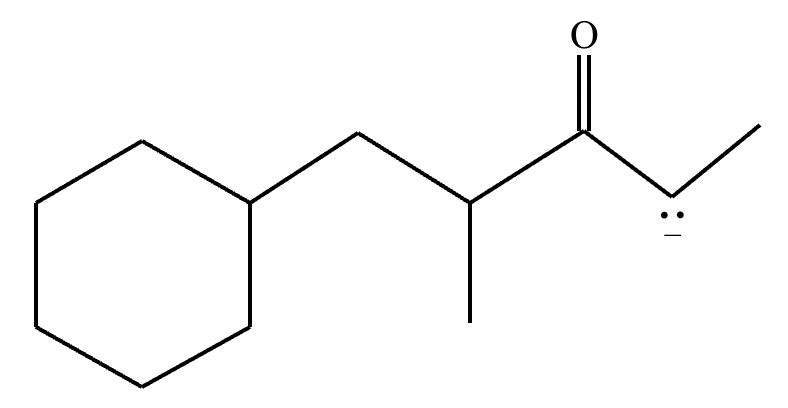
Explanation: LDA is a strong hindered base that can remove a proton from the α carbon of an aldehyde or ketone. Enolates are formed when strong bases remove a proton on the α-C bonded to a carbonyl group. At low temperatures, such as -78°C, the kinetic enolate is formed. In asymmetric ketones, the proton is abstracted from the less substituted carbon.
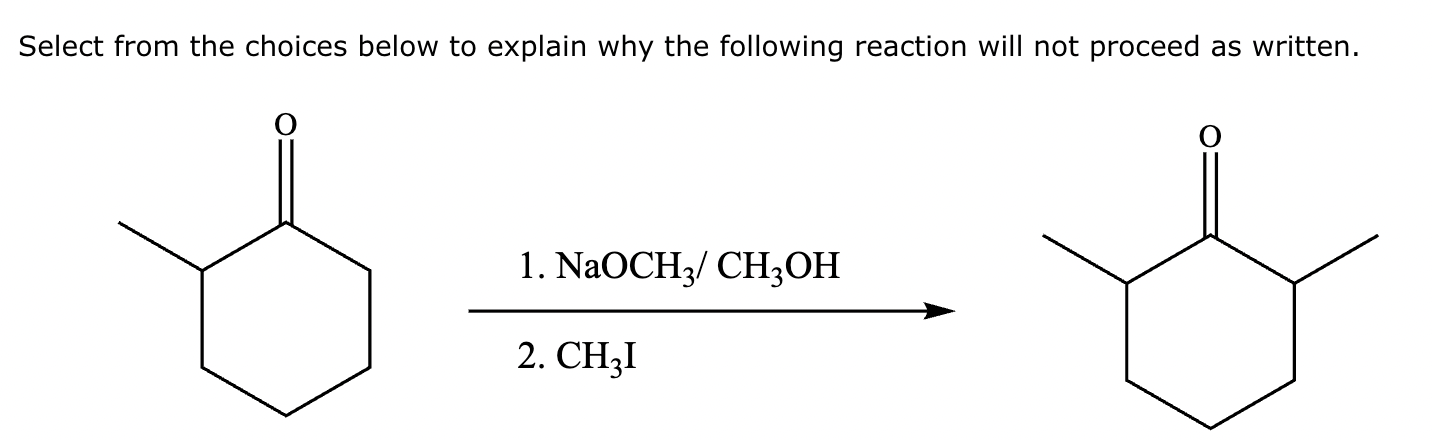

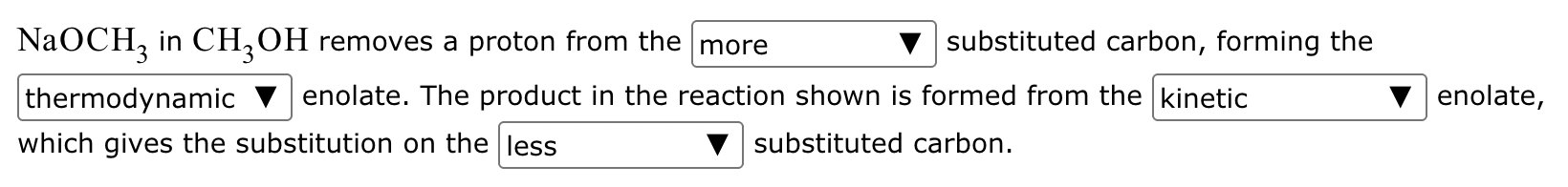
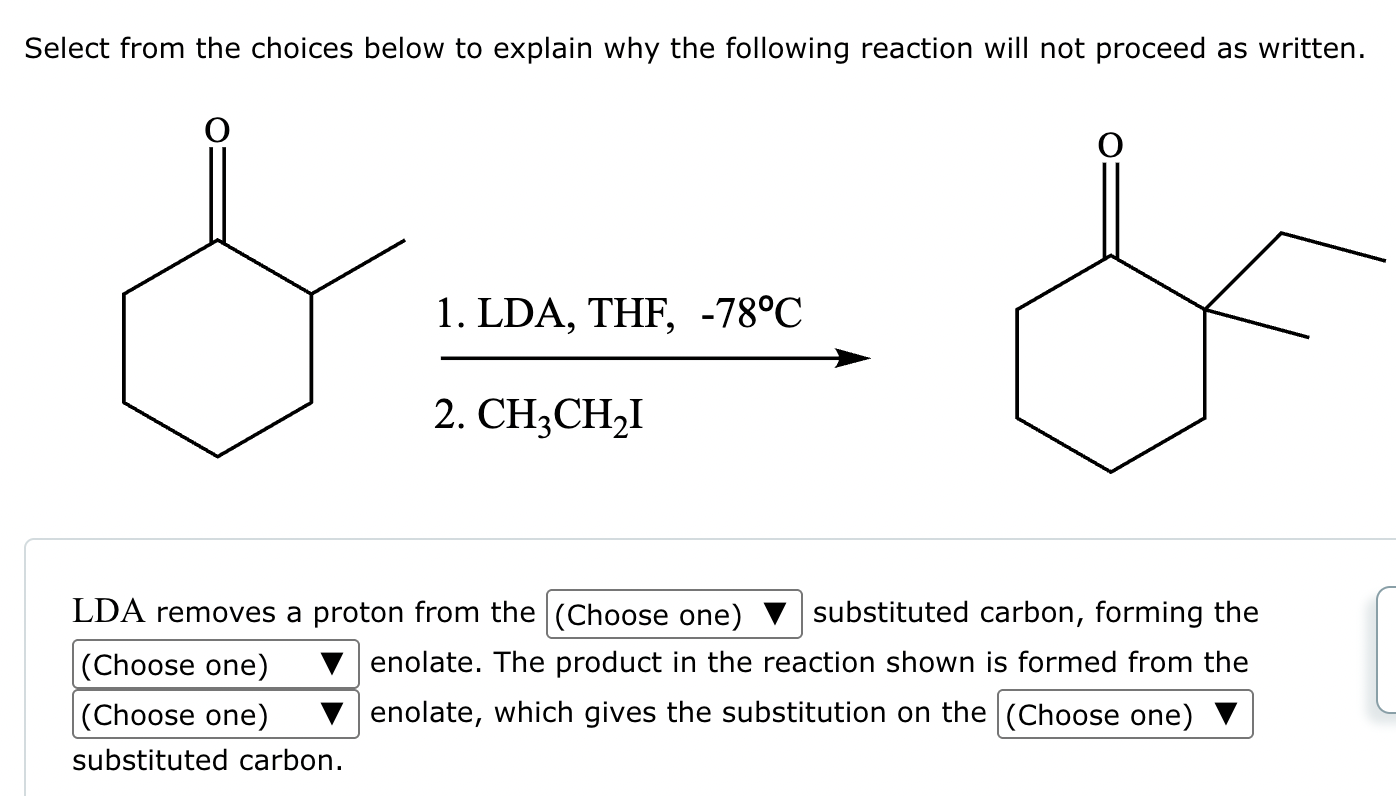
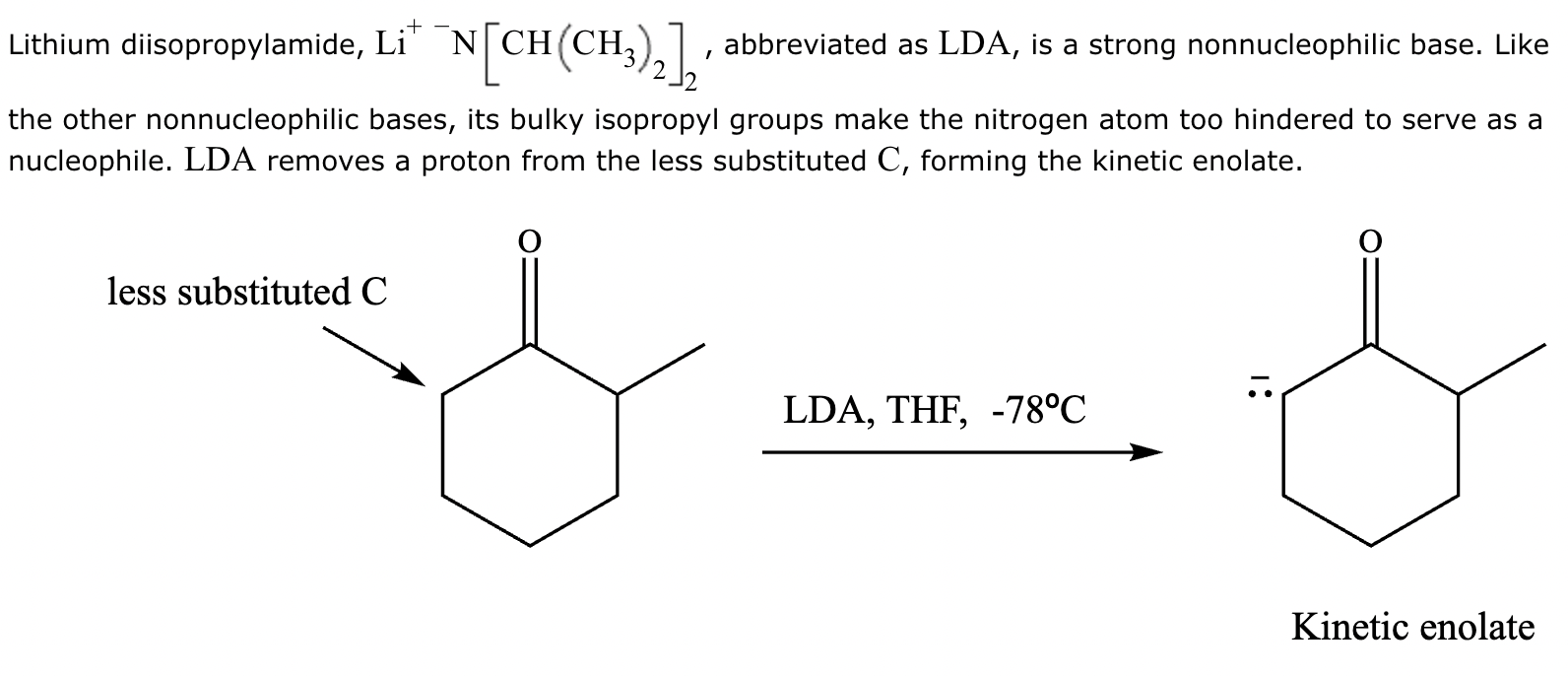

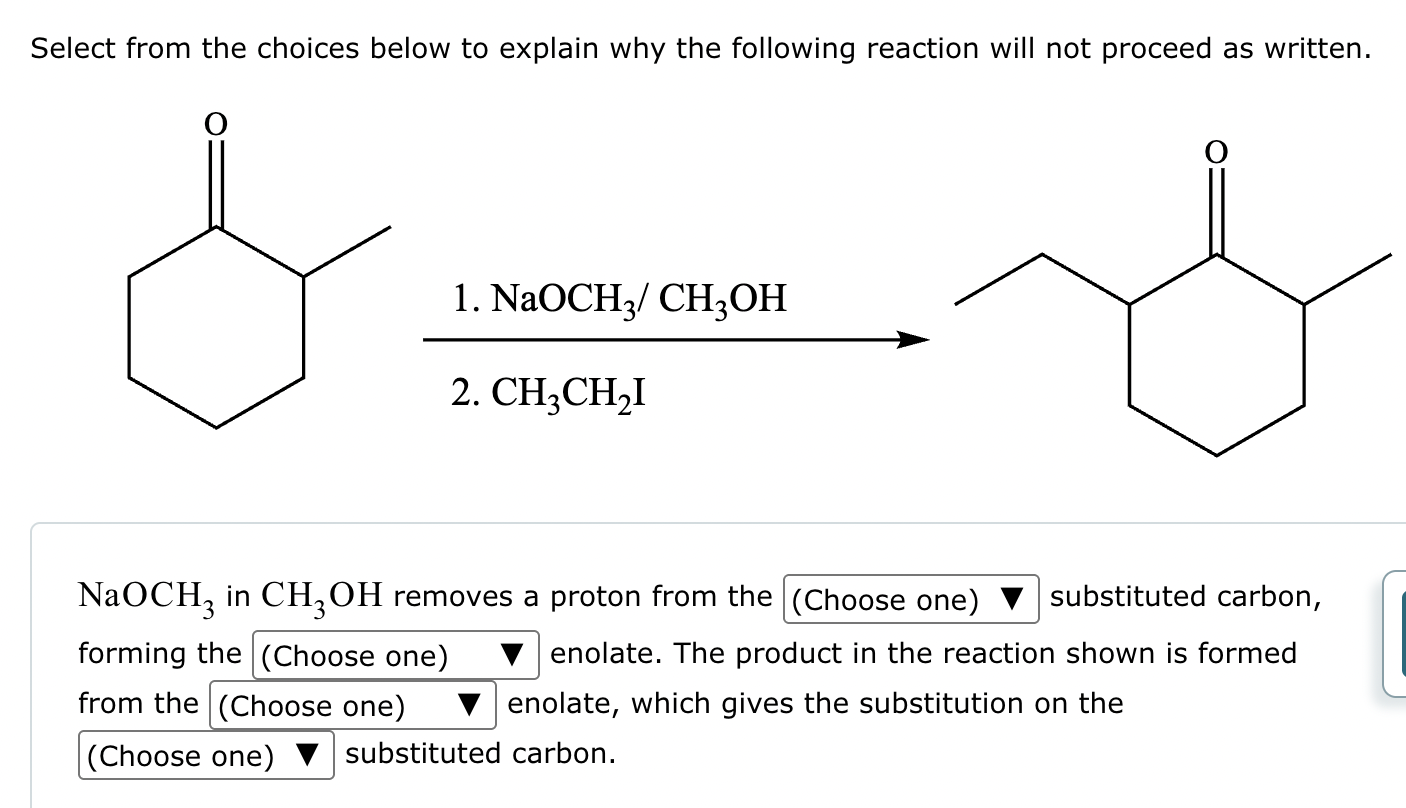
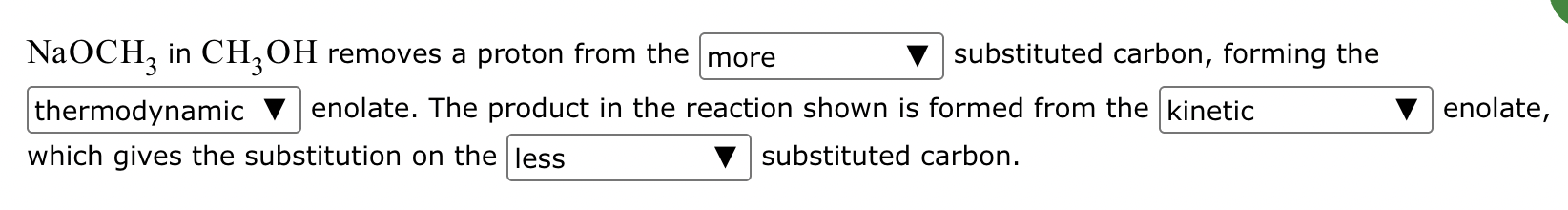
The ketone shown below can enolize, resulting in two different enolates depending on the conditions applied.
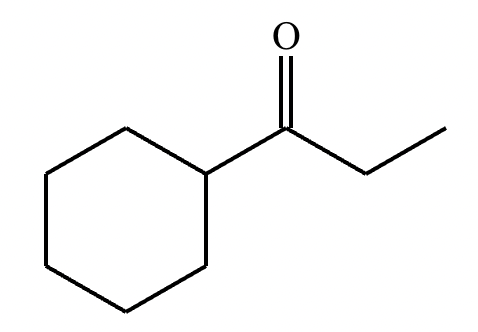
(a) Draw the structure of the kinetic enolate of the ketone. Be sure to include lone pairs and charges where relevant, as well as lone pairs on all heteroatoms.
(b) Draw the structure of the thermodynamic enolate of the ketone. Be sure to include lone pairs and charges where relevant, as well as lone pairs on all heteroatoms.
(a)
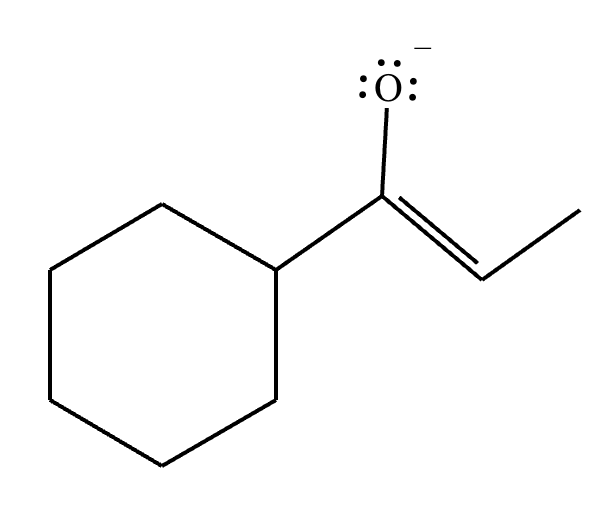
(b)
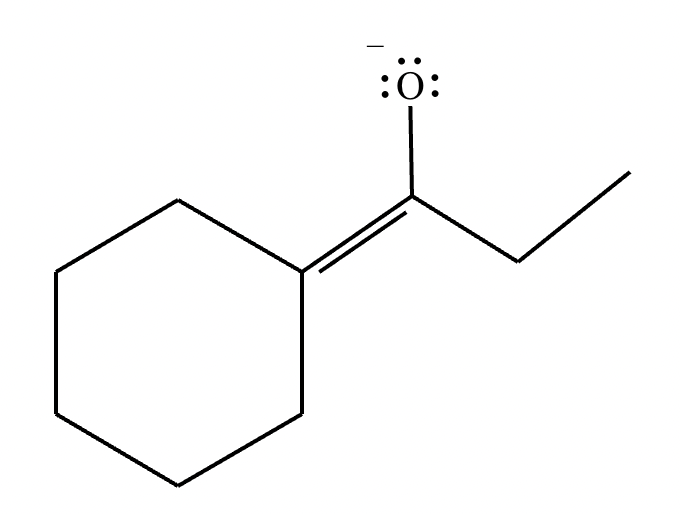
Which of the following bases will completely convert cyclohexane-1,4-dione into an enolate? Select the single best answer.
(a) Sodium hydride
(b) Sodium methoxide
(c) Sodium tert-butoxide
(d) Sodium hydroxide
(a) Sodium hydride
Highlight the atom, or atoms, in each molecule below from which an H could most easily be removed by a moderately strong base, like NaOH. That is, in each molecule, highlight the atom with the most acidic H’s attached.
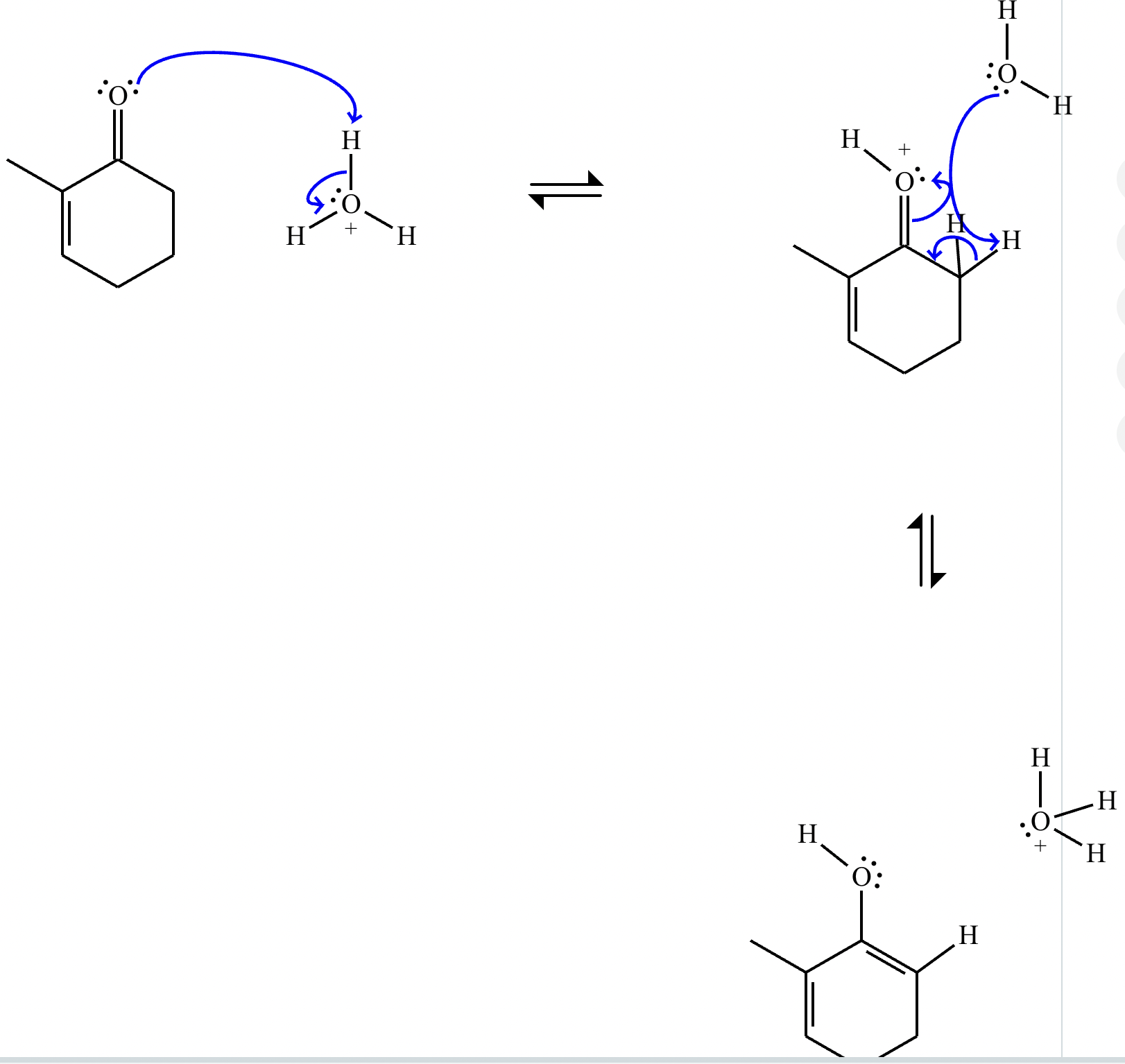
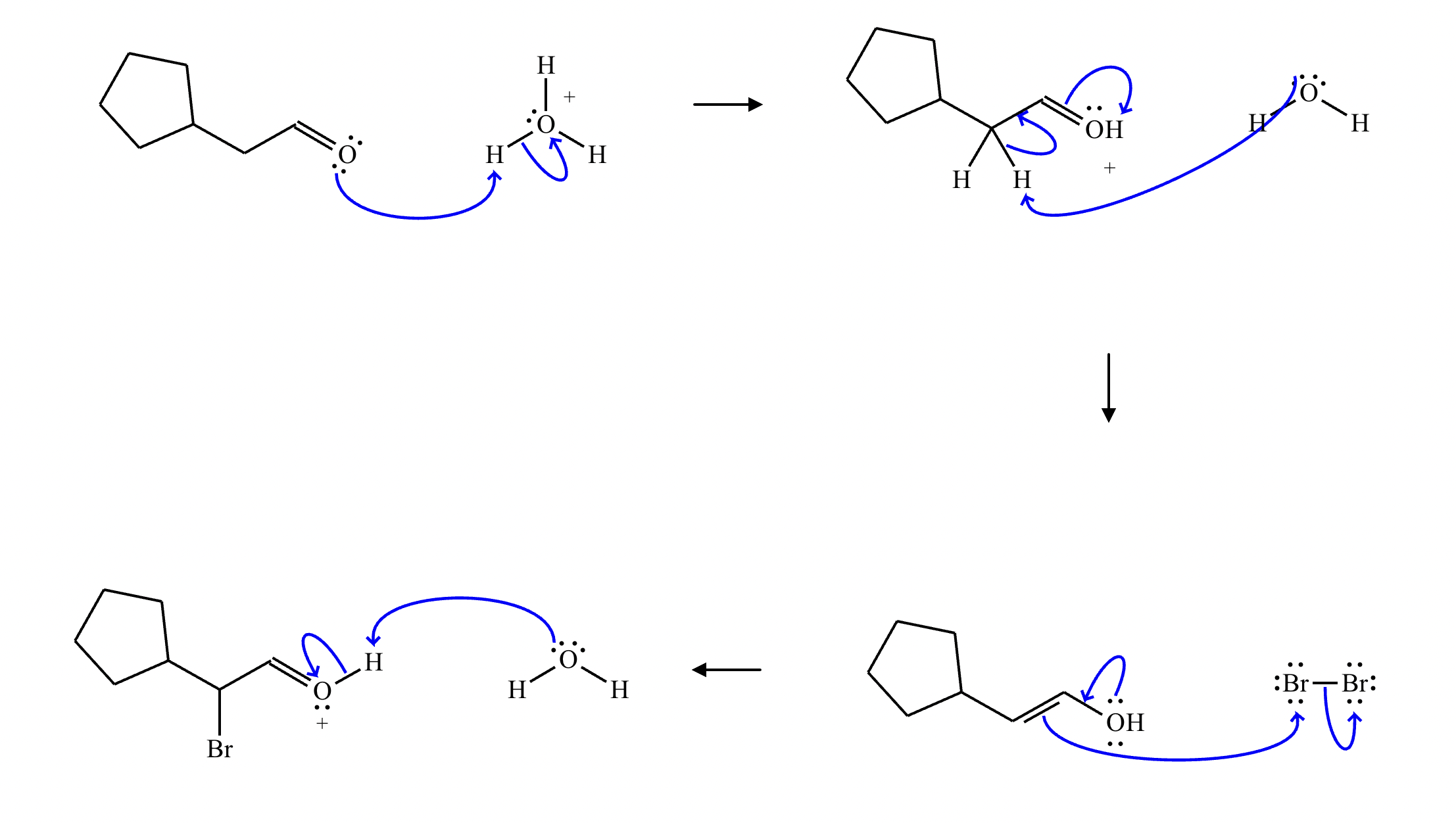
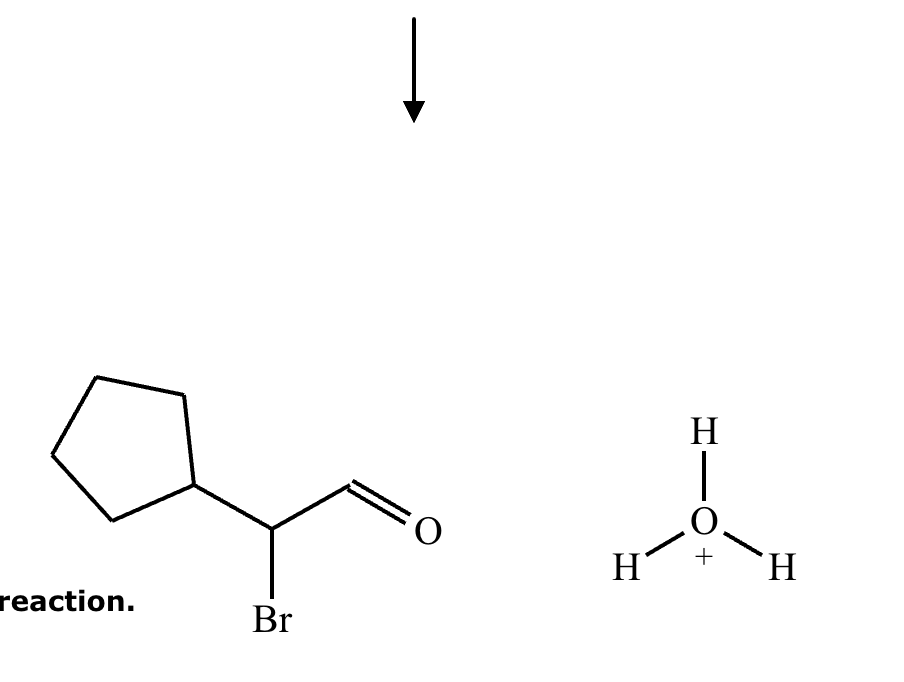
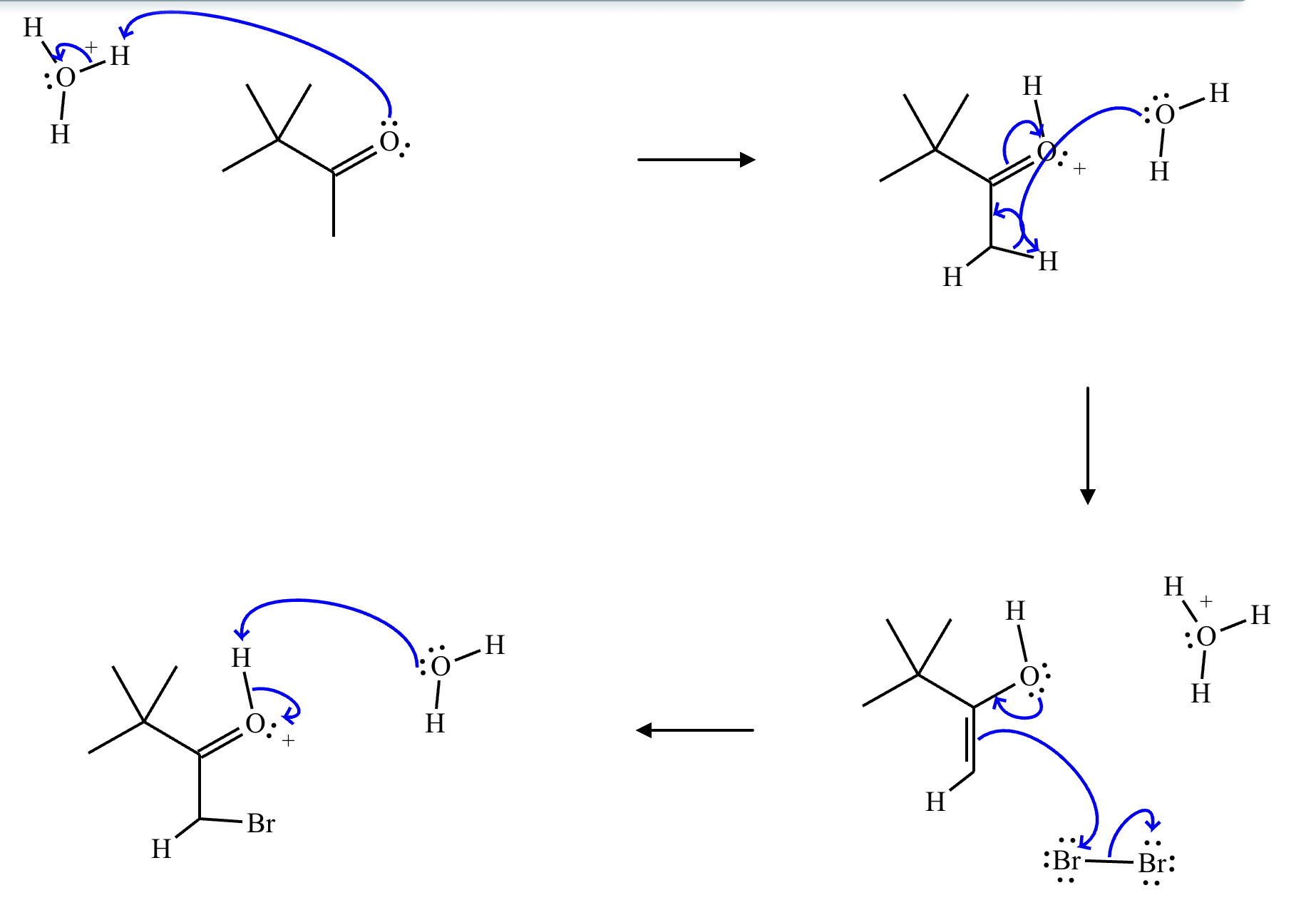
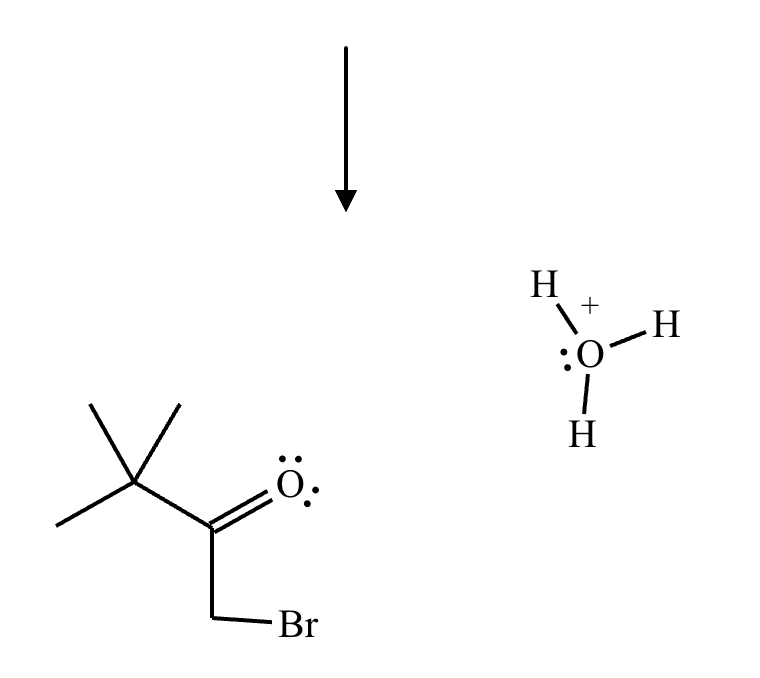
Draw a stepwise mechanism for the transformation of the ketone to the enol shown. Use curved arrows to show the flow of electrons. Be sure to include lone pairs on all heteroatoms, charges where relevant, and the correct arrow type between each step of the mechanism.

Which of the following compounds would undergo racemization in the presence of a base? Select the single best answer.
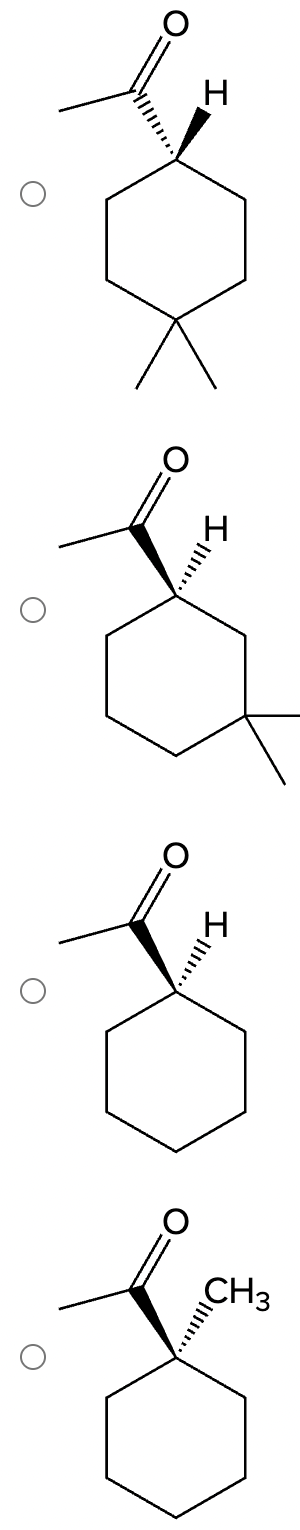
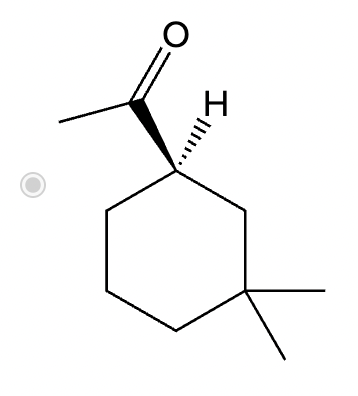
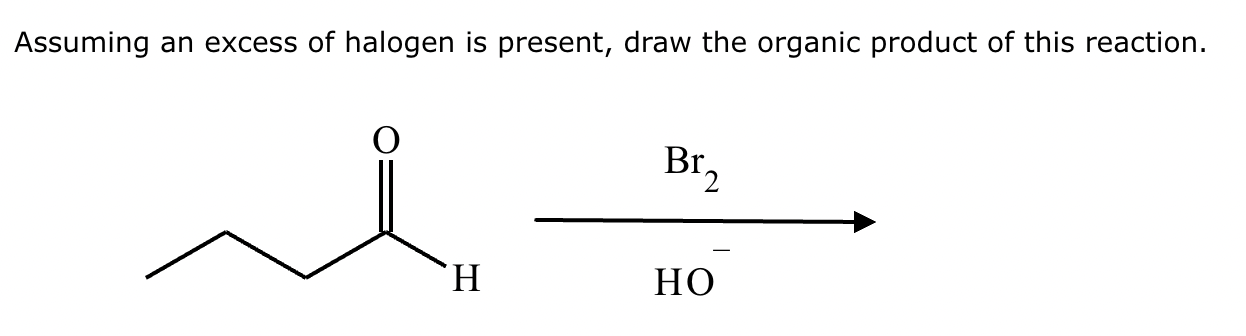

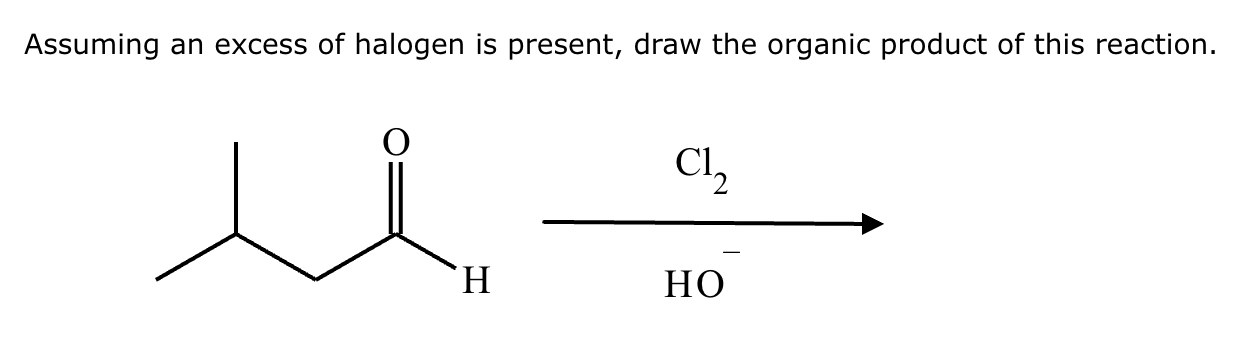
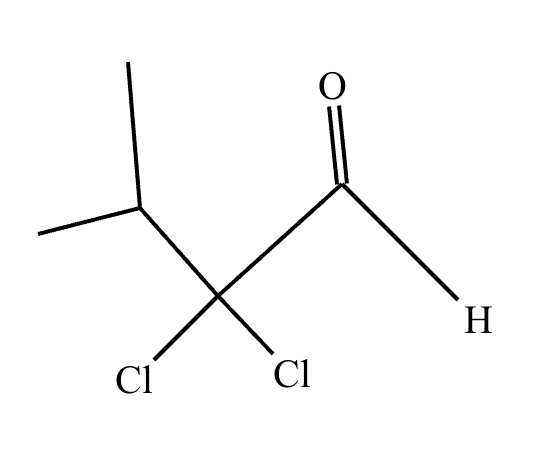
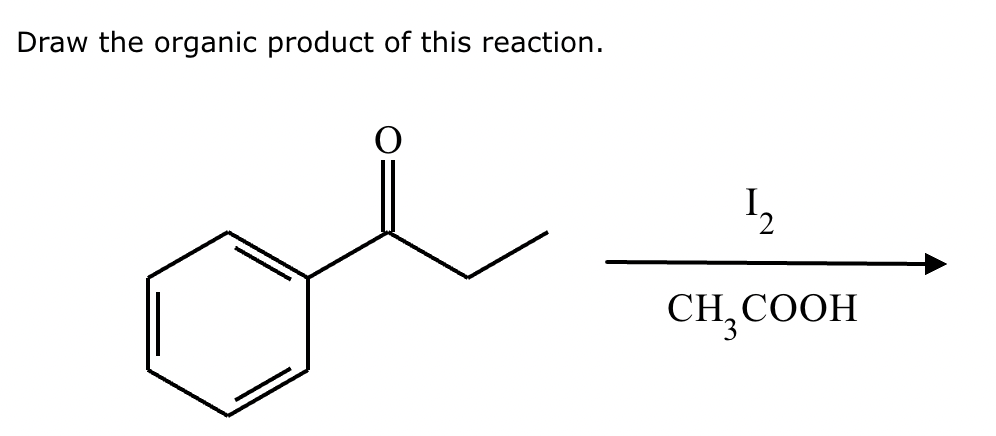
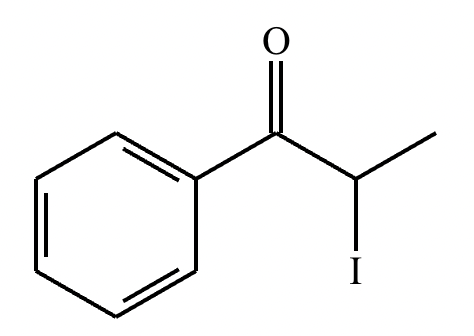
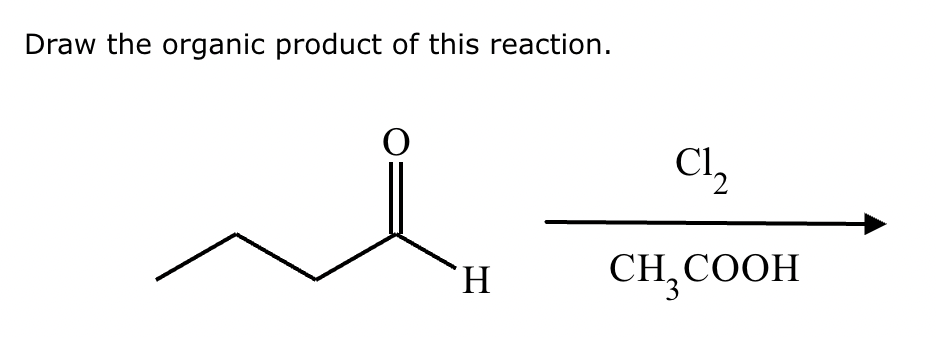
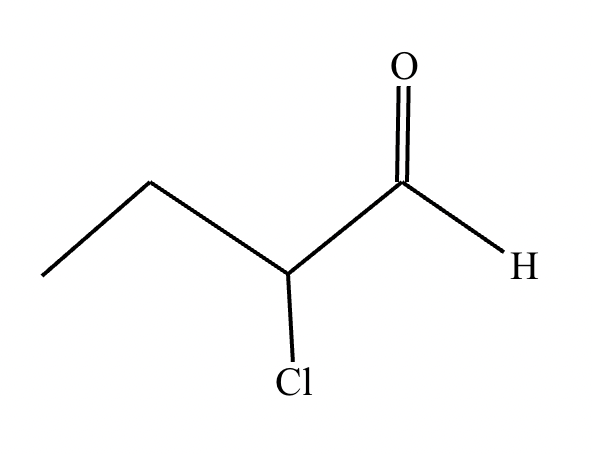
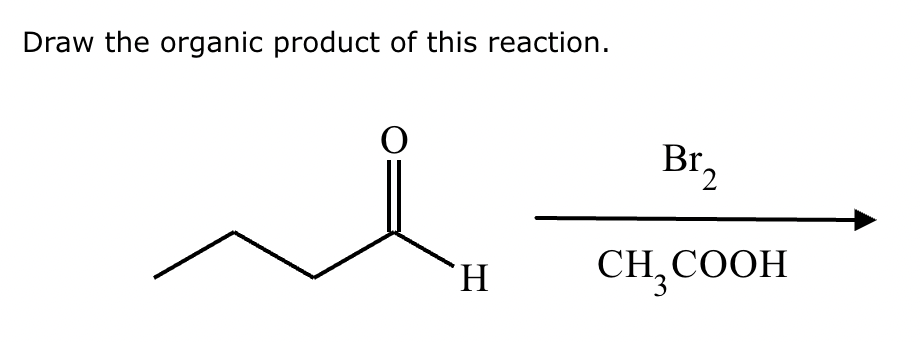
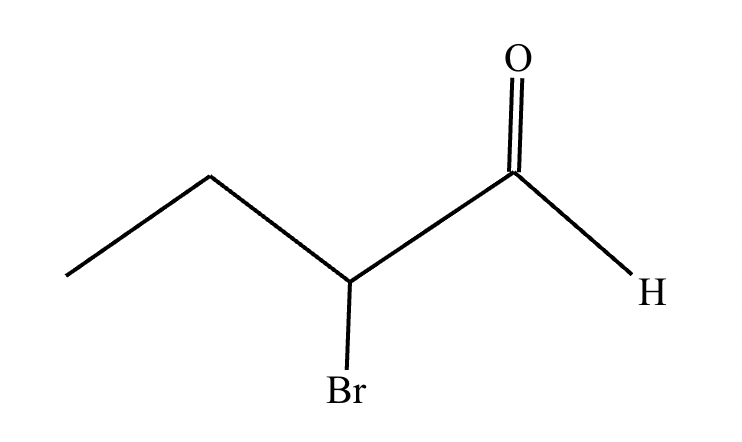
If it’s in acidic conditions, it replaces only one alpha hydrogen. If it’s in basic conditions, it replaces ALL alpha hydrogens at the alpha carbon.
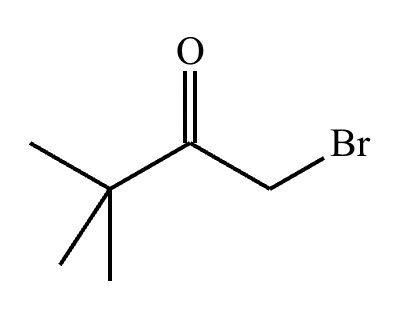
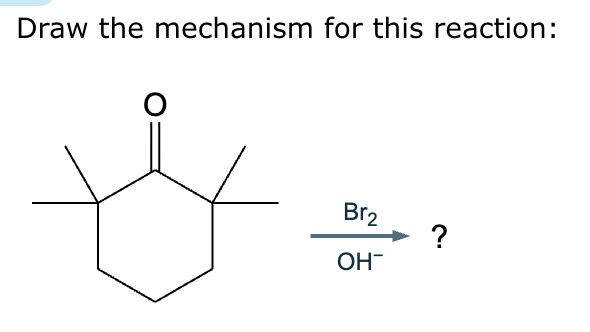
Why is it difficult to stop the halogenation of ketones under basic conditions at the mono-halogenated stage? Select the single best answer.
(a) The ketone is reduced.
(b) The bromine helps to stabilize the second enolate, making the product more acidic than the starting material.
(c) The ketone undergoes an aldol reaction.
(d) The ketone undergoes a Bayer-Villiger oxidation.
(b) The bromine helps to stabilize the second enolate, making the product more acidic than the starting material.
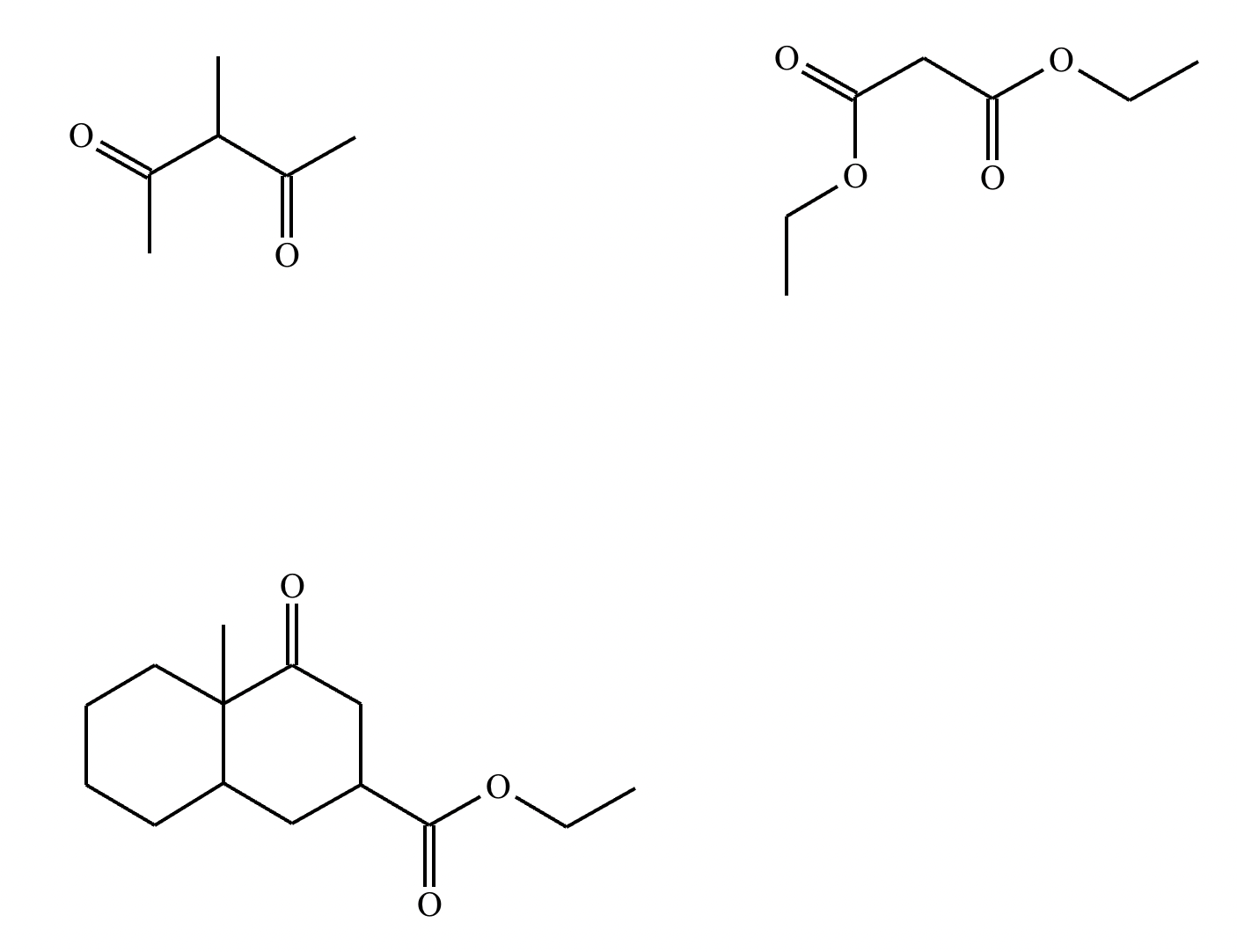
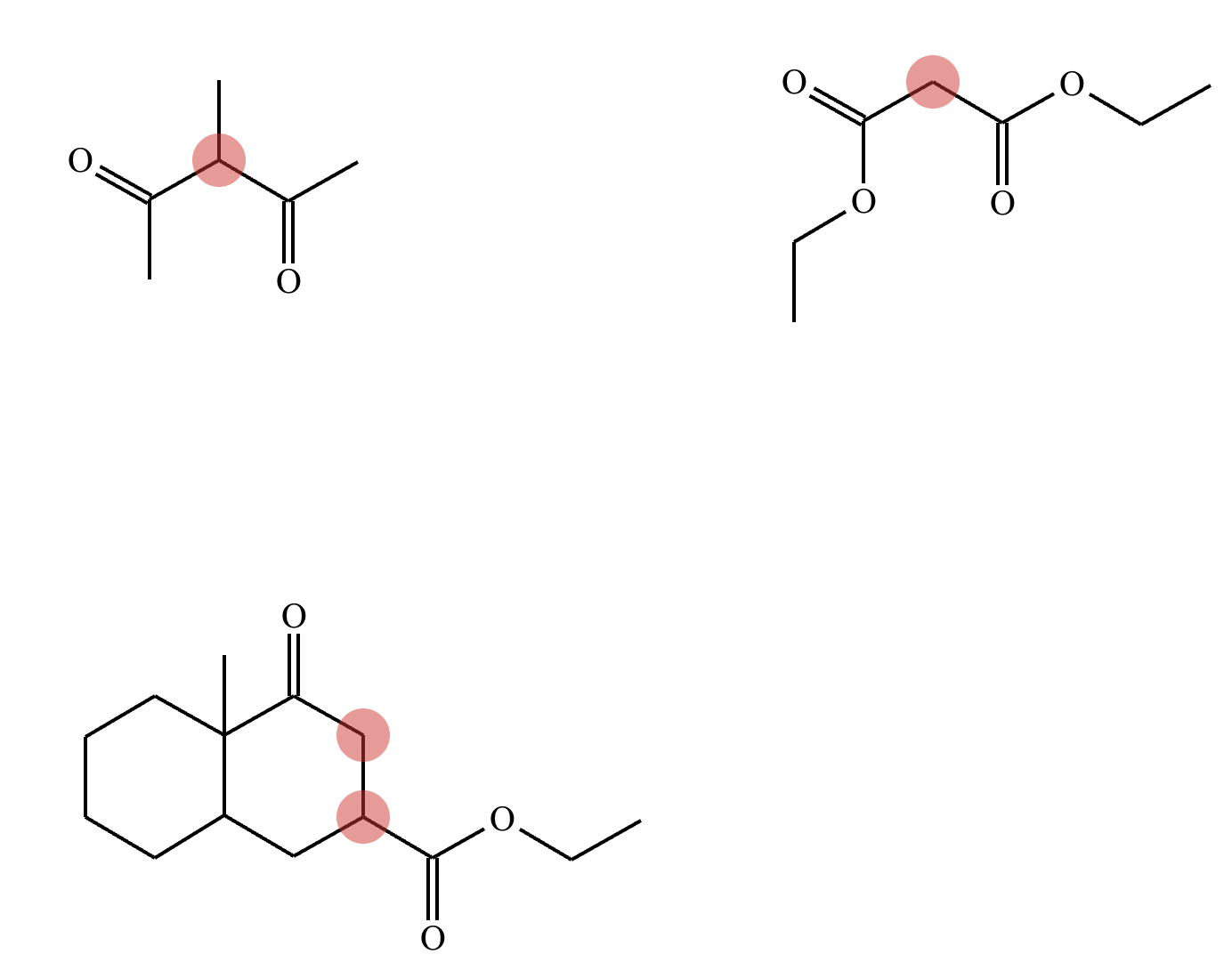
Highlight each atom in the molecules below from which an H could be removed by a reasonably strong base, like NaOH. Note: only highlight atoms with the most acidic H’s.
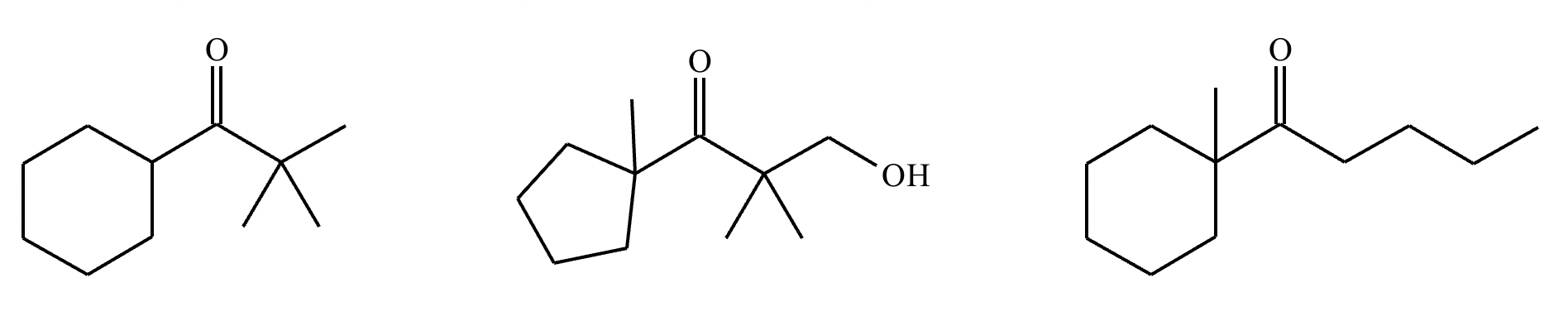
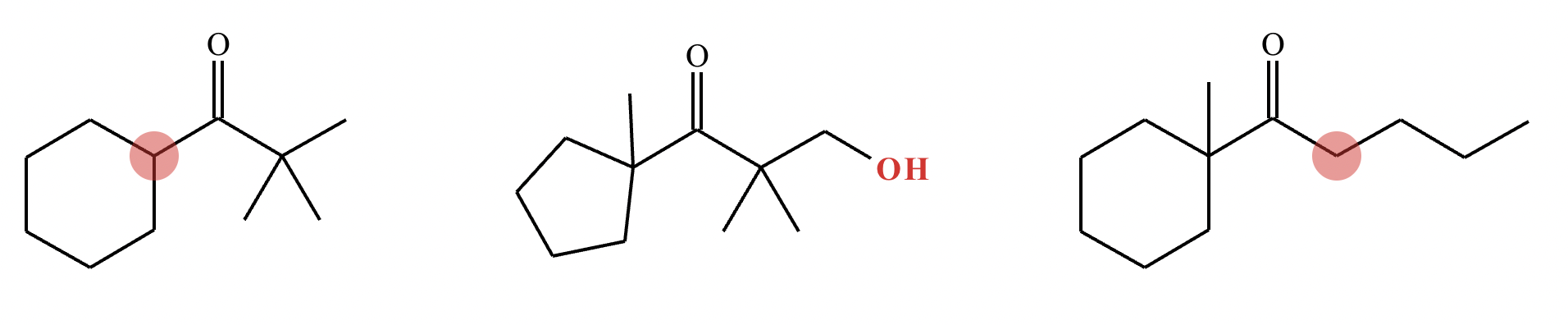
Highlight each atom in the molecules below from which an H could be removed by a reasonably strong base, like NaOH. Note: only highlight atoms with the most acidic H’s.
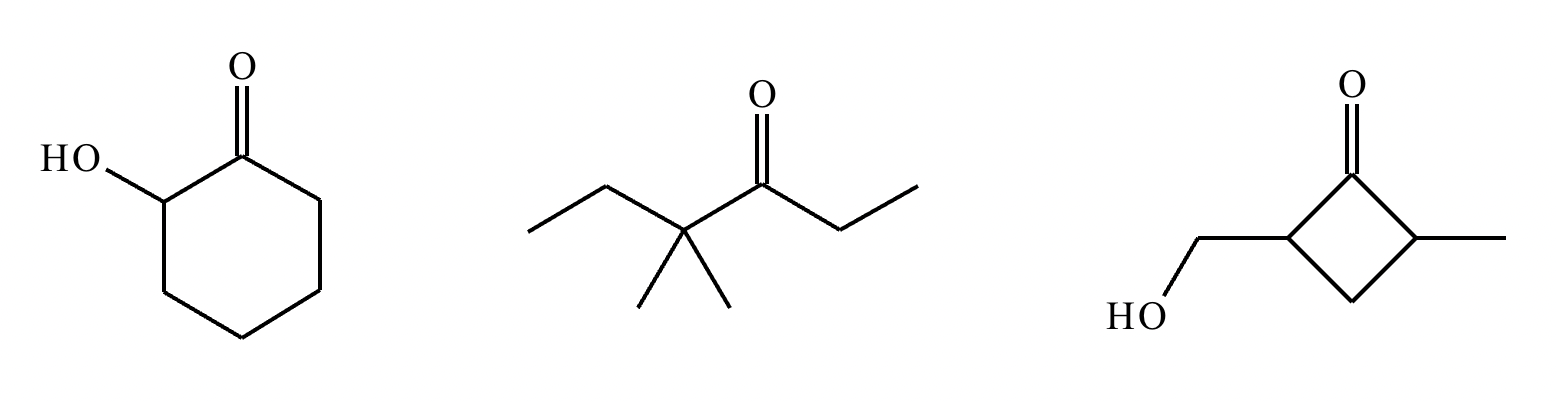
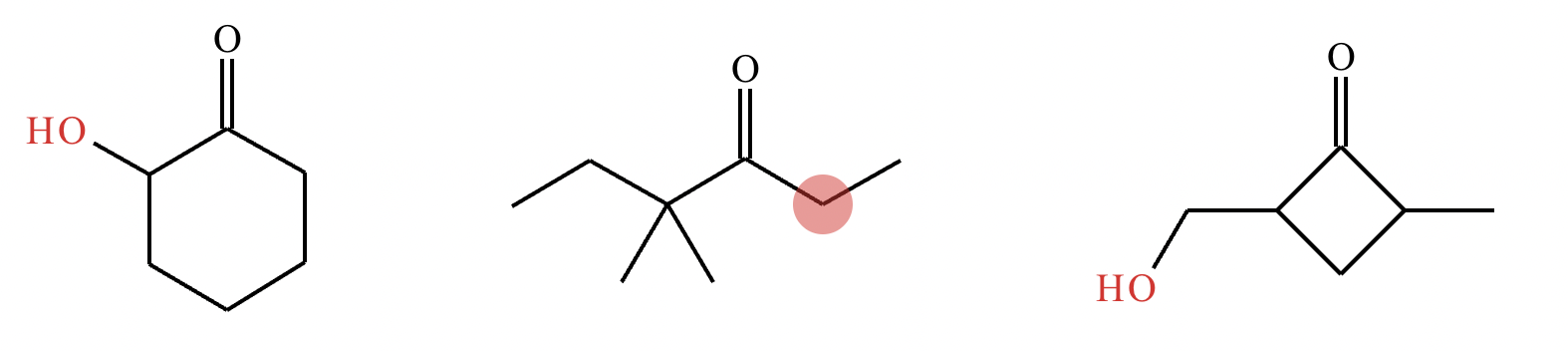
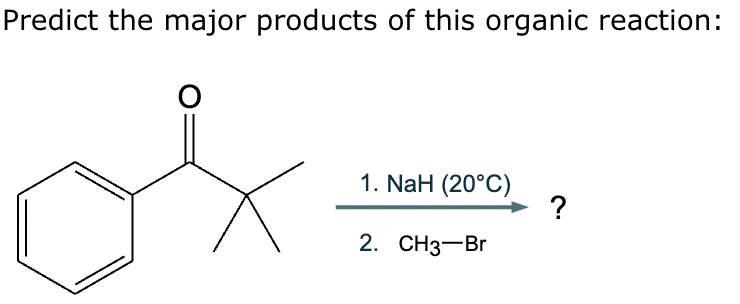
No reaction (no alpha hydrogens).
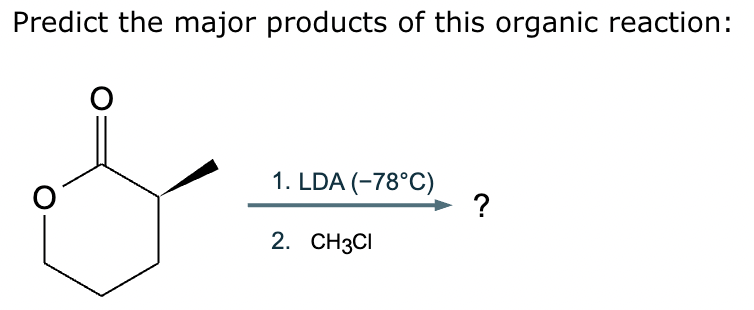
No reaction.
Highlight the atom, or atoms, in each molecule below from which an H could most easily be removed by a moderately strong base, like NaOH. That is, in each molecule, highlight the atom with the most acidic H’s attached. (Accidentally didn’t include image!)
Highlight the atom, or atoms, in each molecule below from which an H could most easily be removed by a moderately strong base, like NaOH. That is, in each molecule, highlight the atom with the most acidic H’s attached.
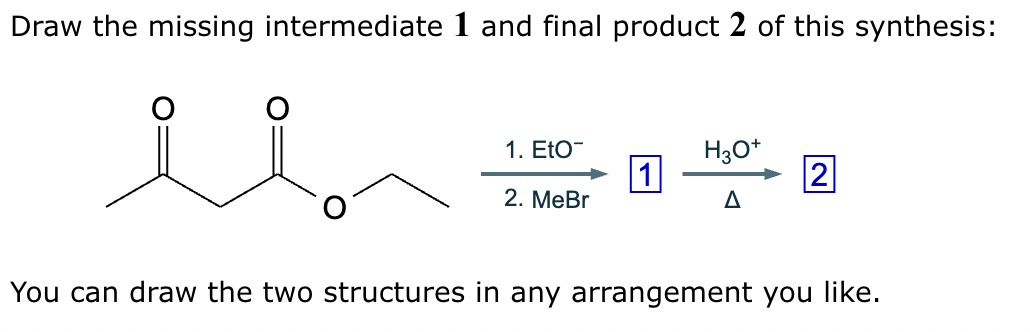
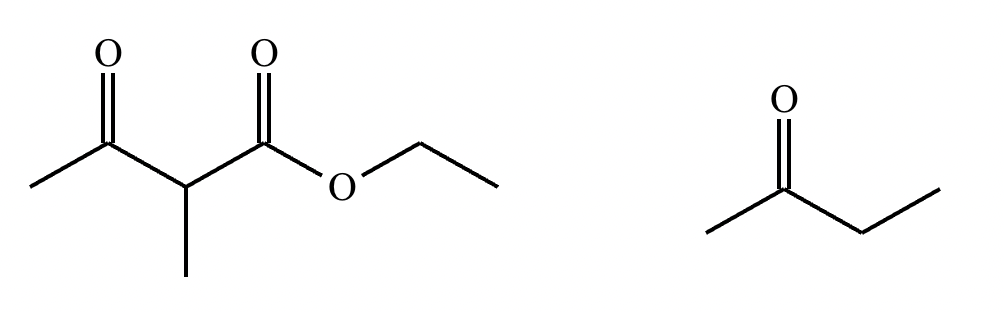

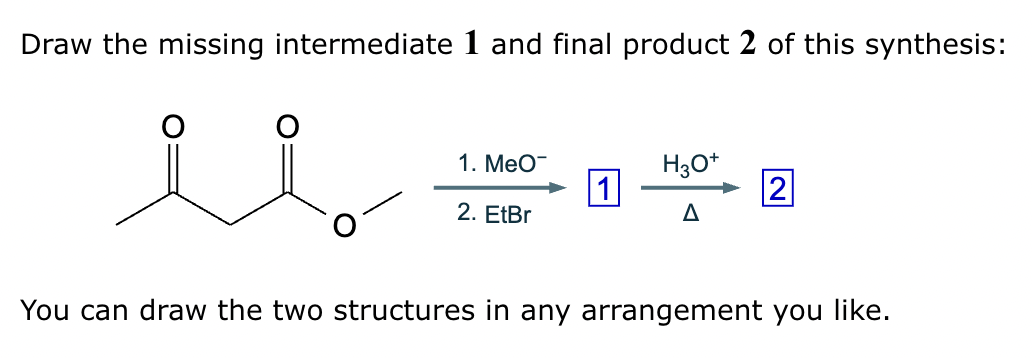
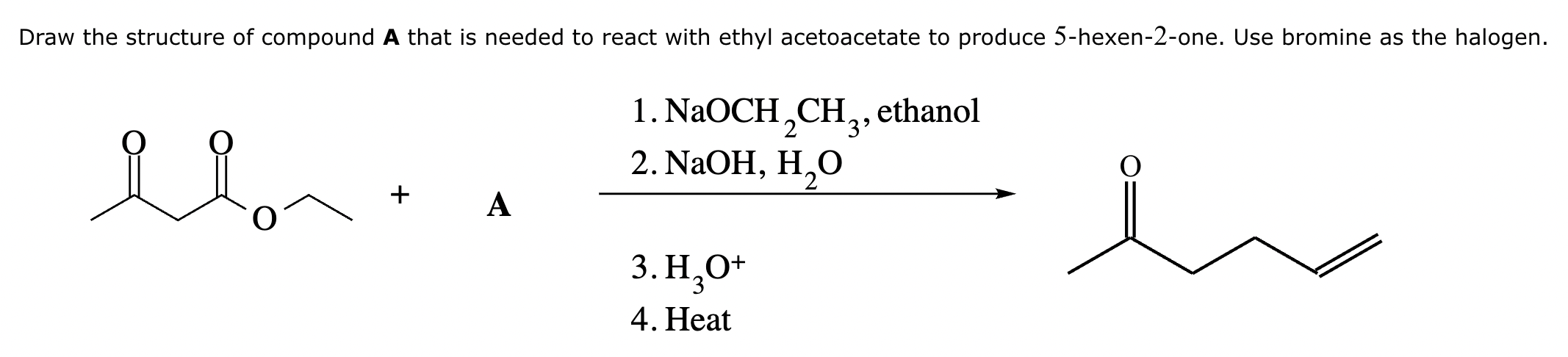
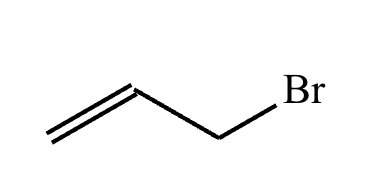
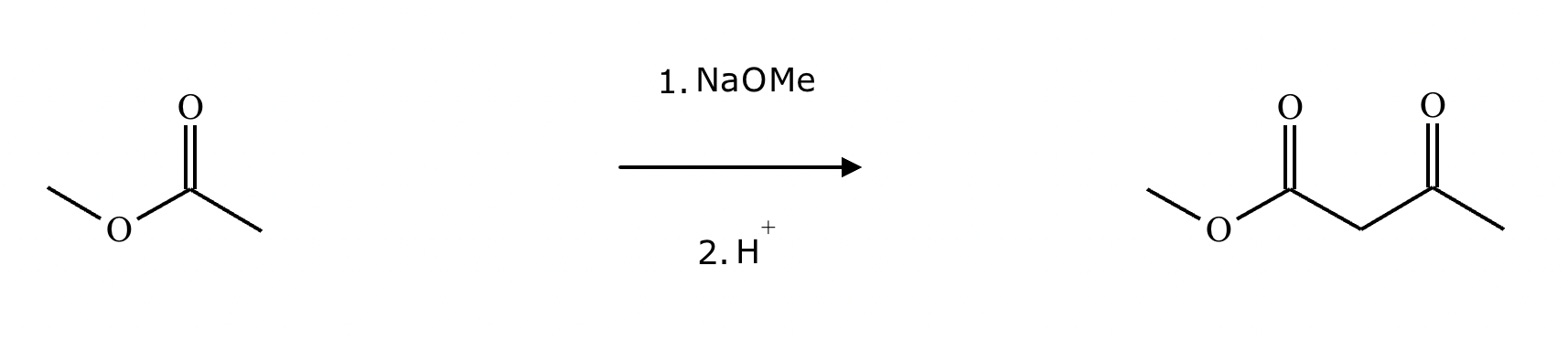
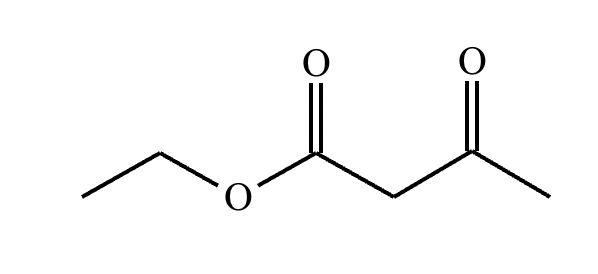
Add the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that complete this proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis. If that's not possible because an acetoacetic ester synthesis will not achieve this transformation efficiently, then check the box below the drawing area instead. Note: if you need to use alkyl halide reagents, please use only alkyl bromides.
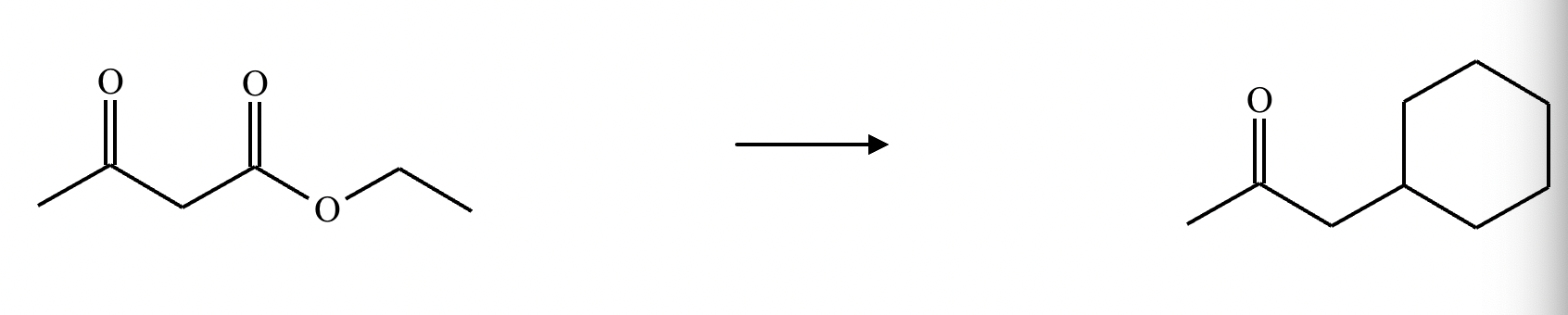
This reaction can’t be done efficiently with an acetoacetic ester synthesis.
Explanation:
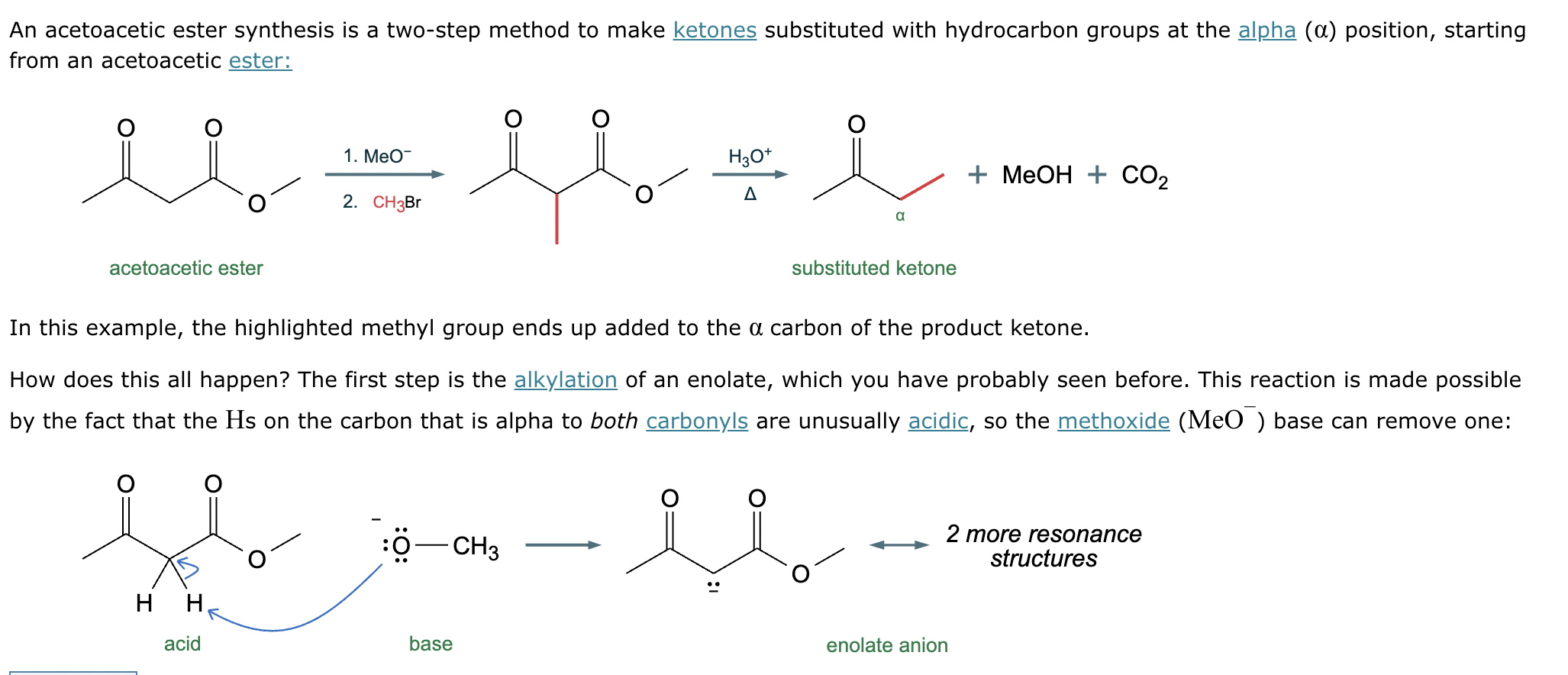
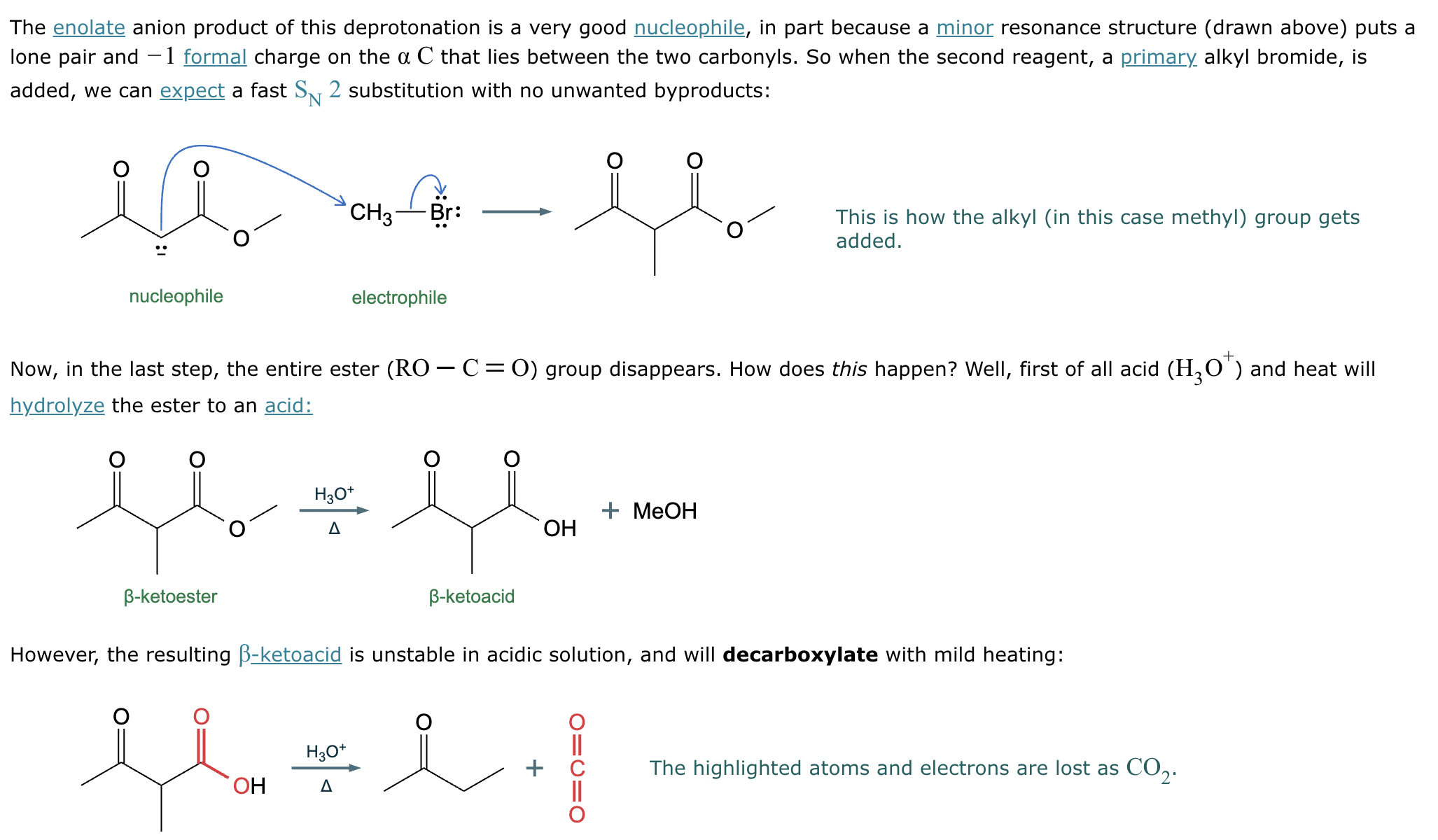

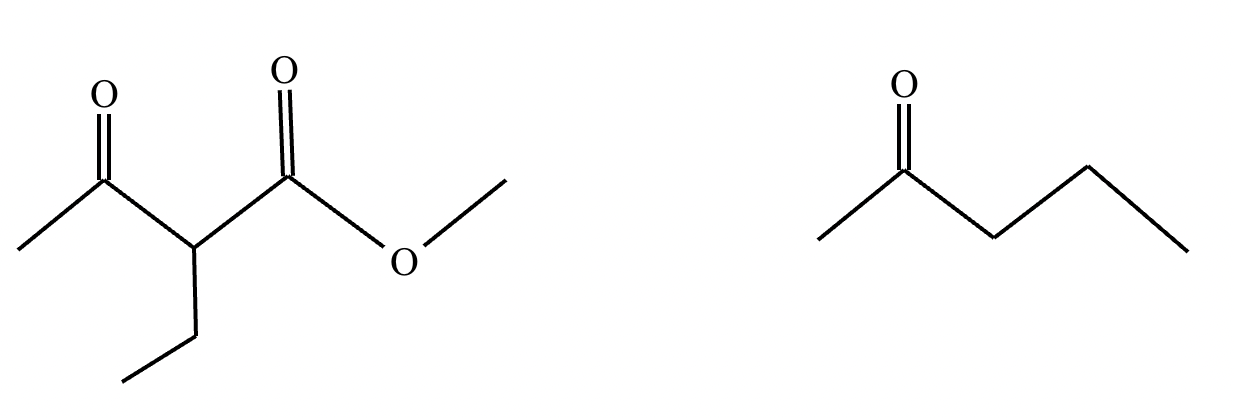
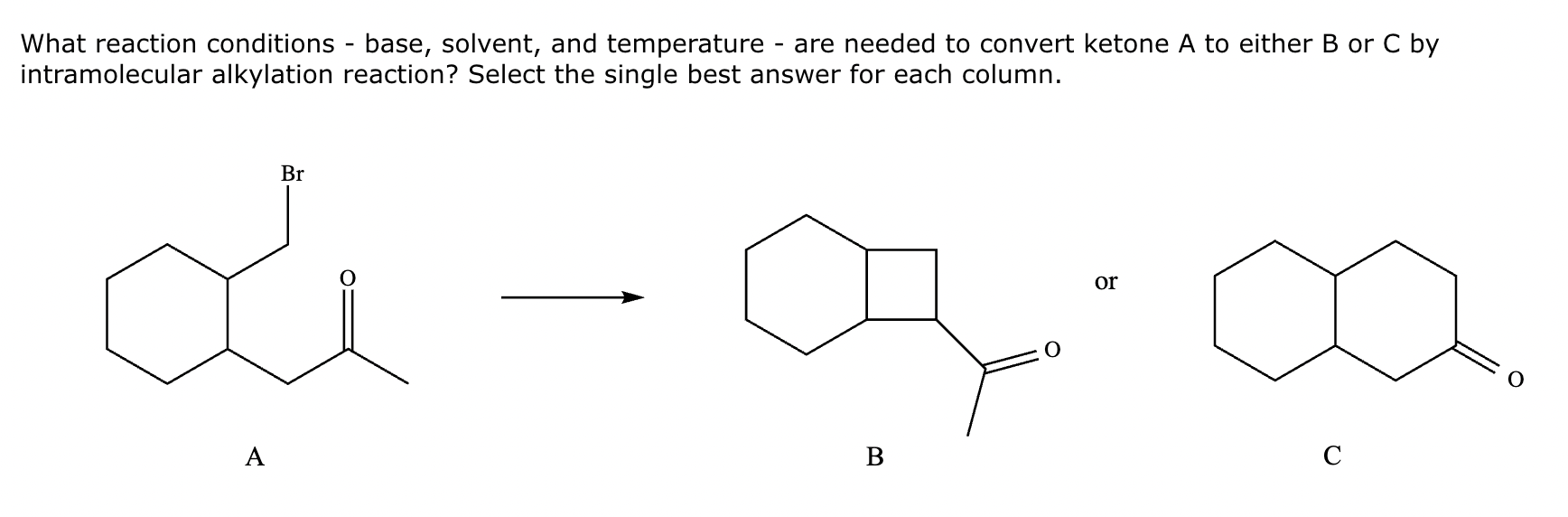
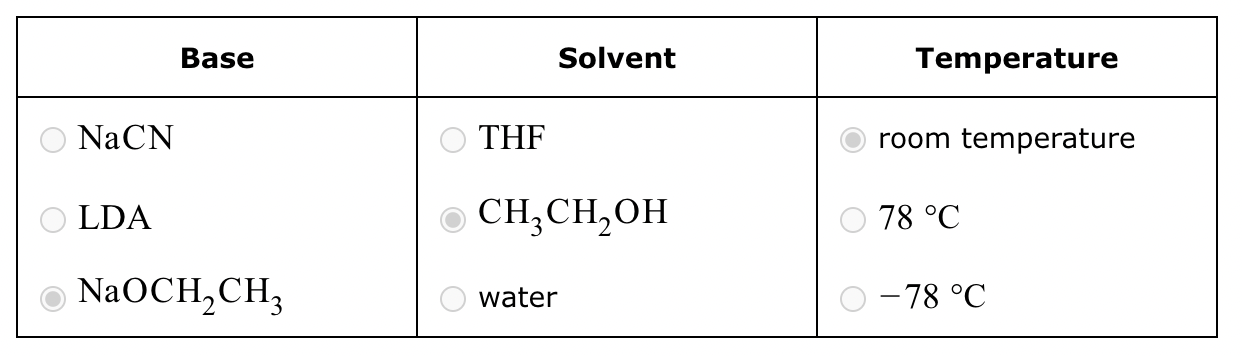
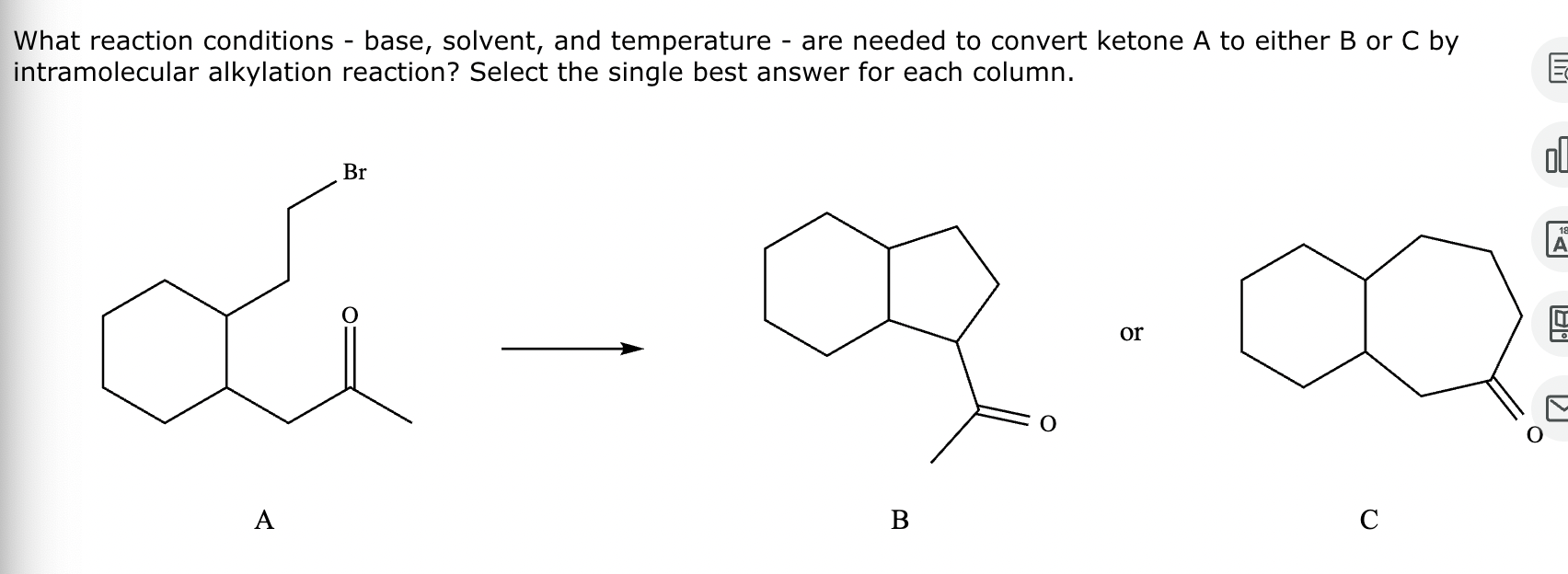
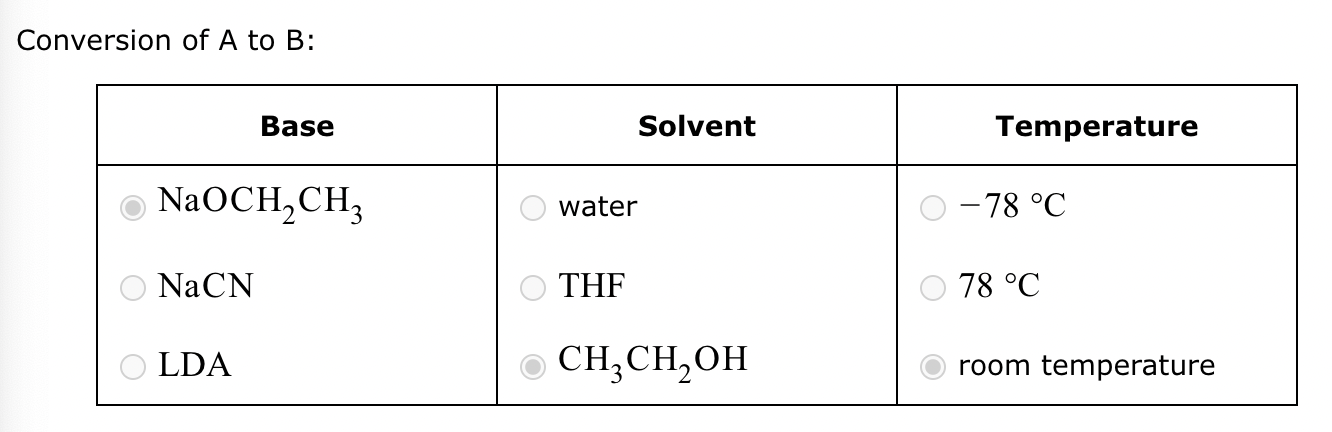
Conversion of A to B:
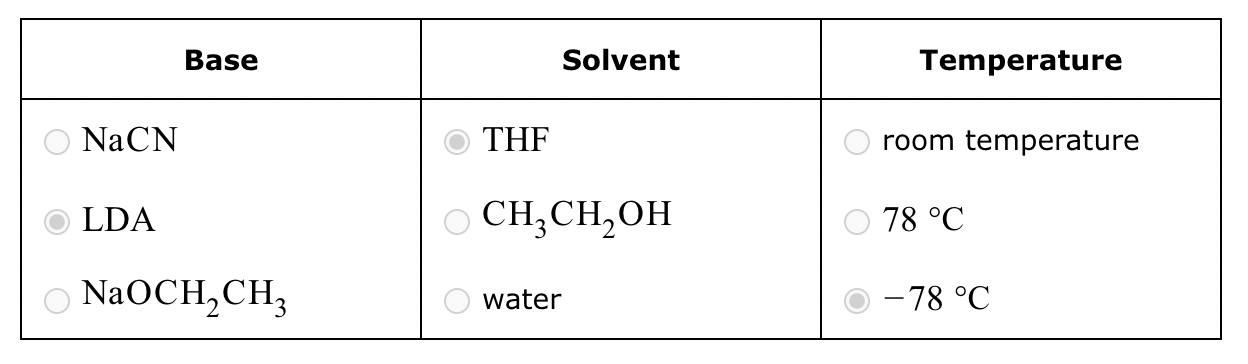
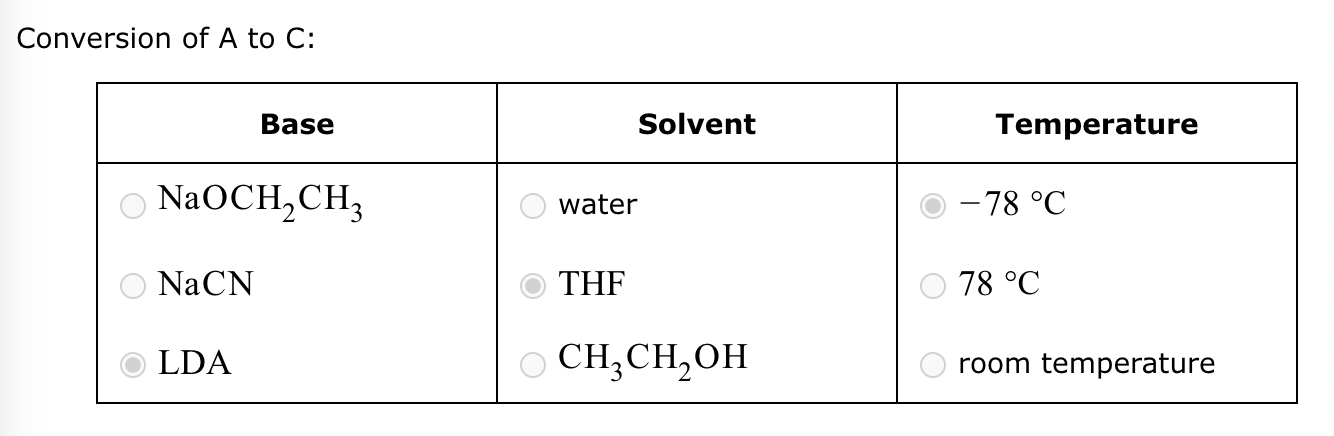
Conversion of A to C:
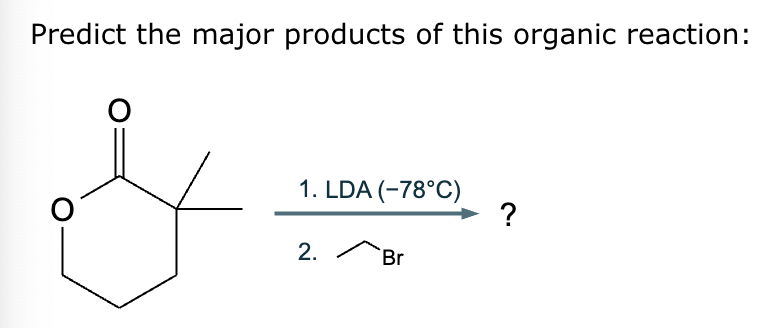
No reaction (no alpha H’s).
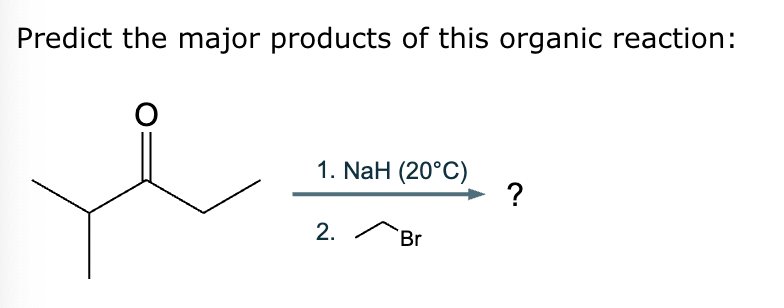
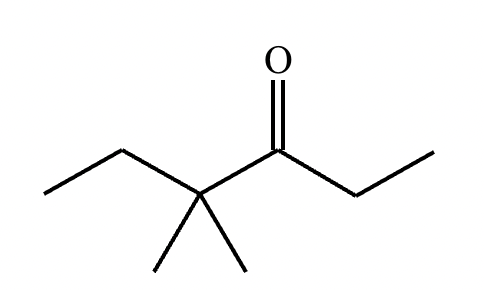
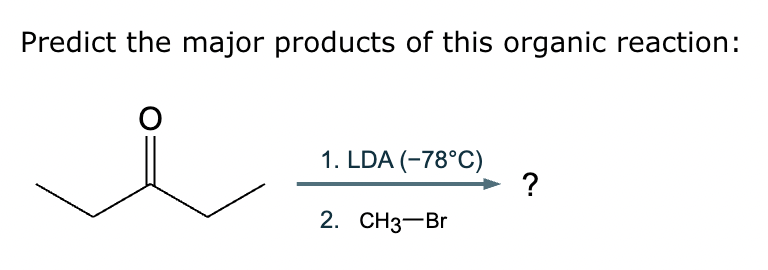
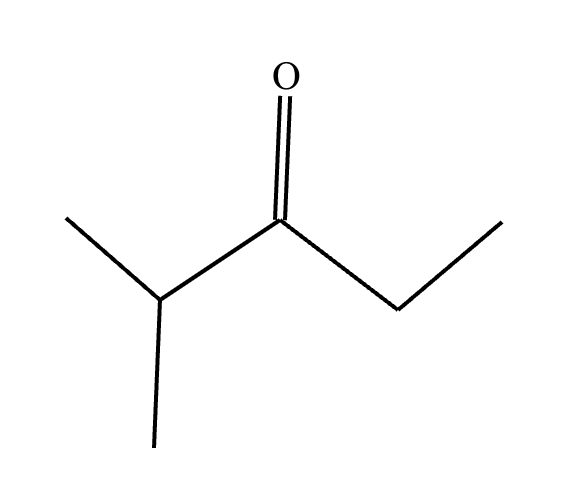
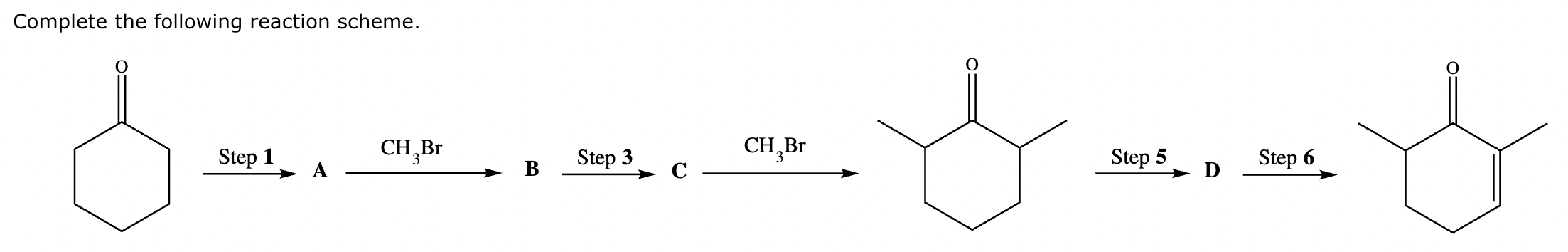
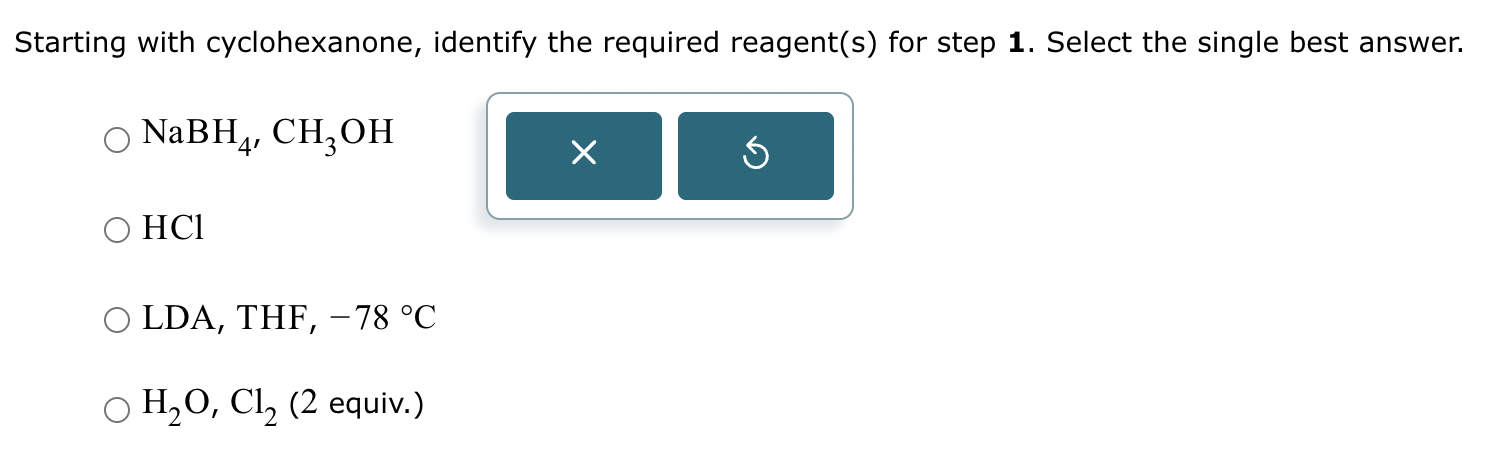
Part 2: Draw the structure for compound A. If there are more than one possible resonance structures, draw either one.
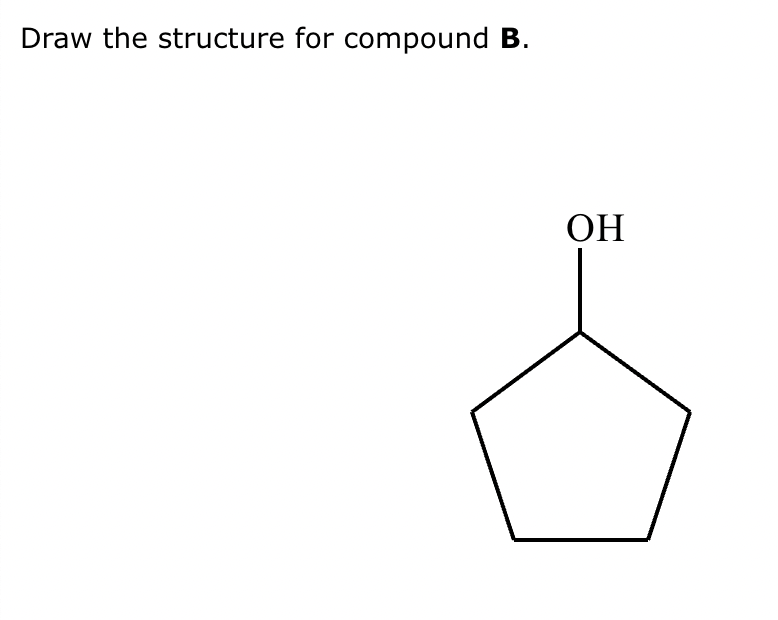
Part 3: Draw the structure for compound B.
Part 4:

Part 5: Draw the structure for compound C.
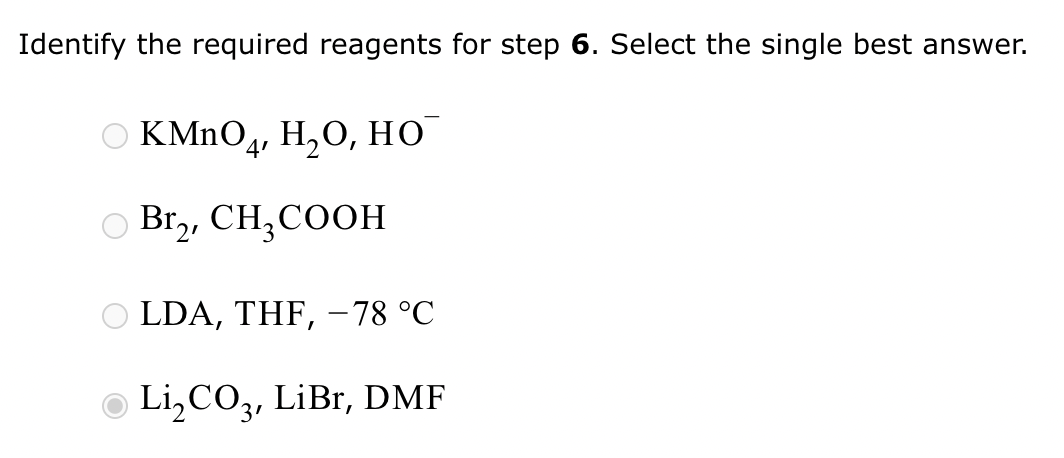
Part 6:
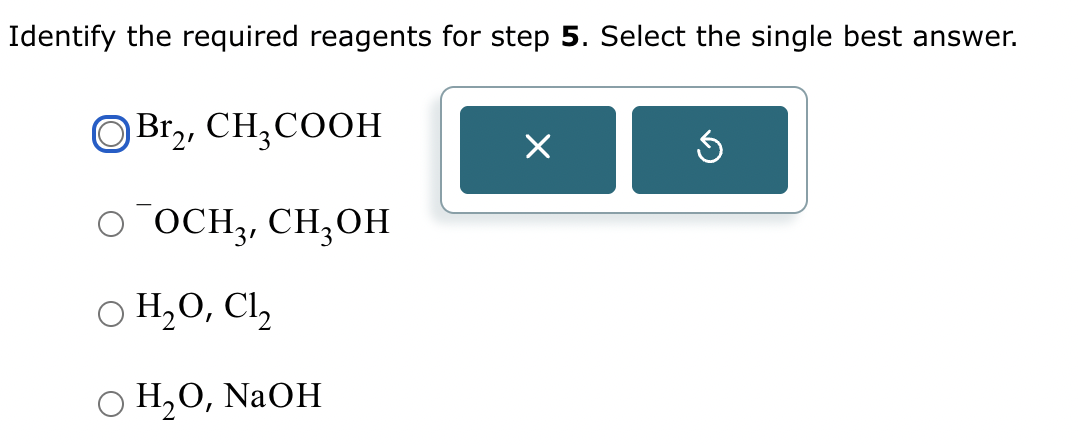
Part 7: Draw the structure for compound D.
Part 8:


Compound A:
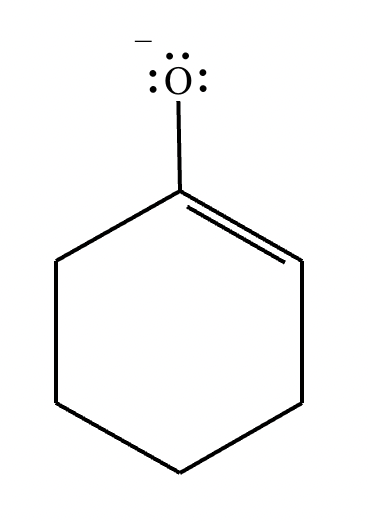
Compound B:
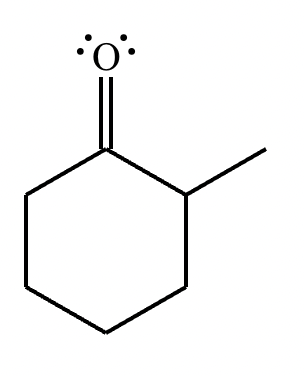



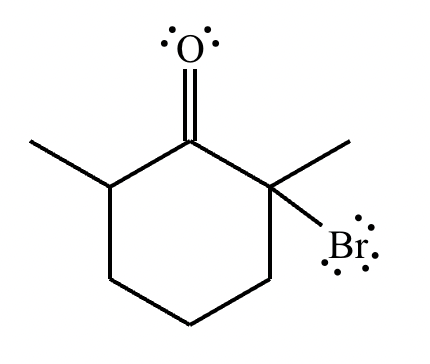
Part 1: Draw the structure of the aldol product formed from the given compound.
Part 2:
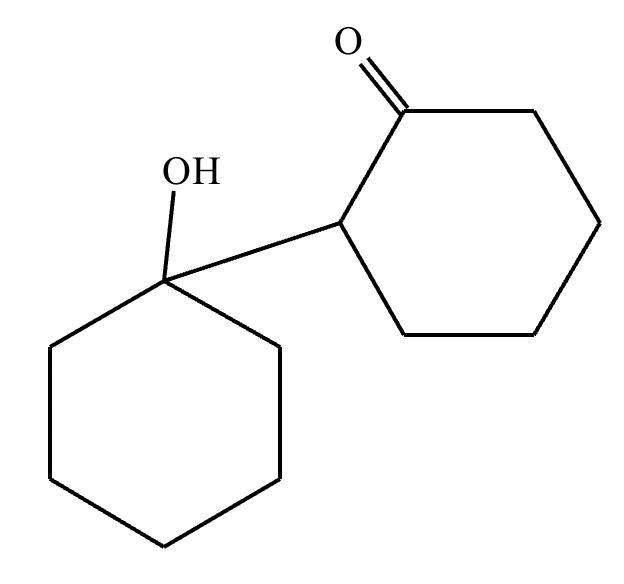
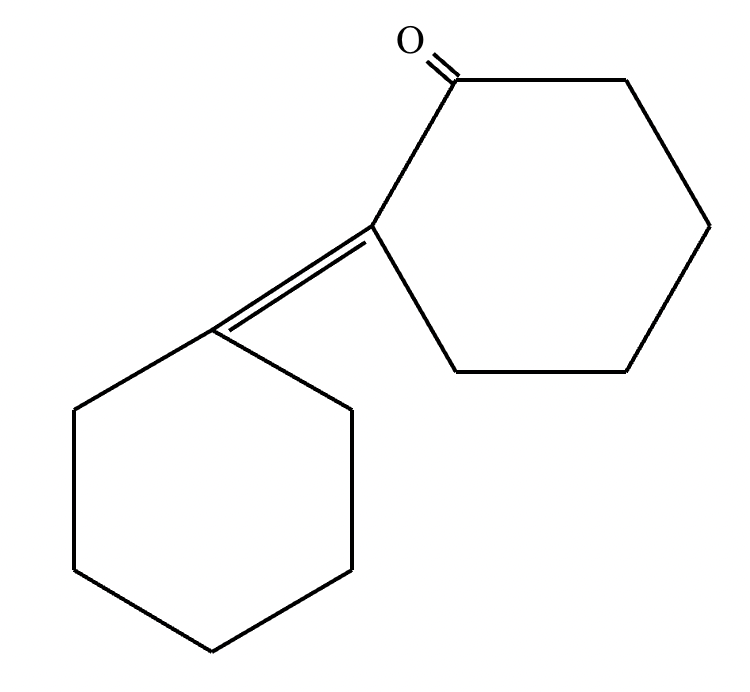
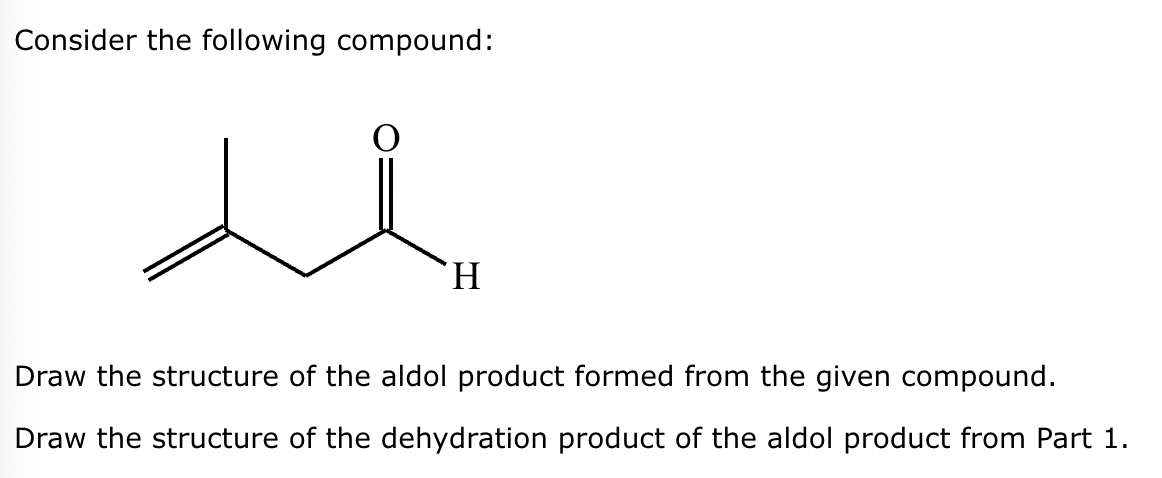
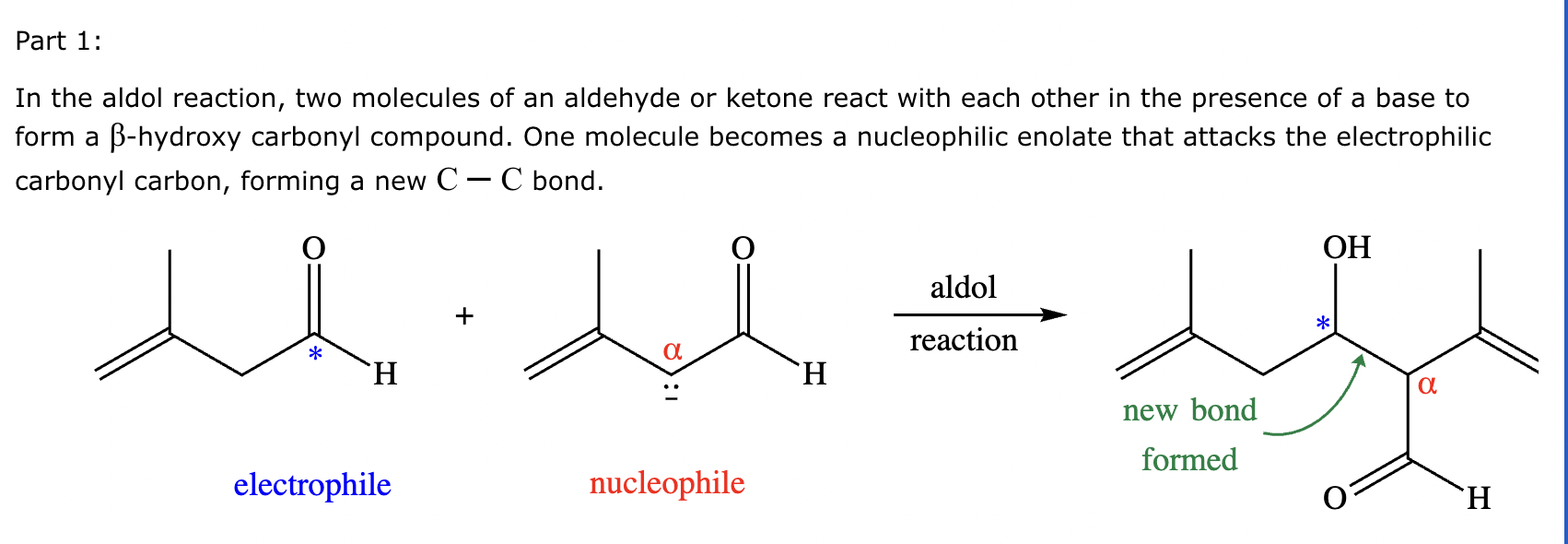
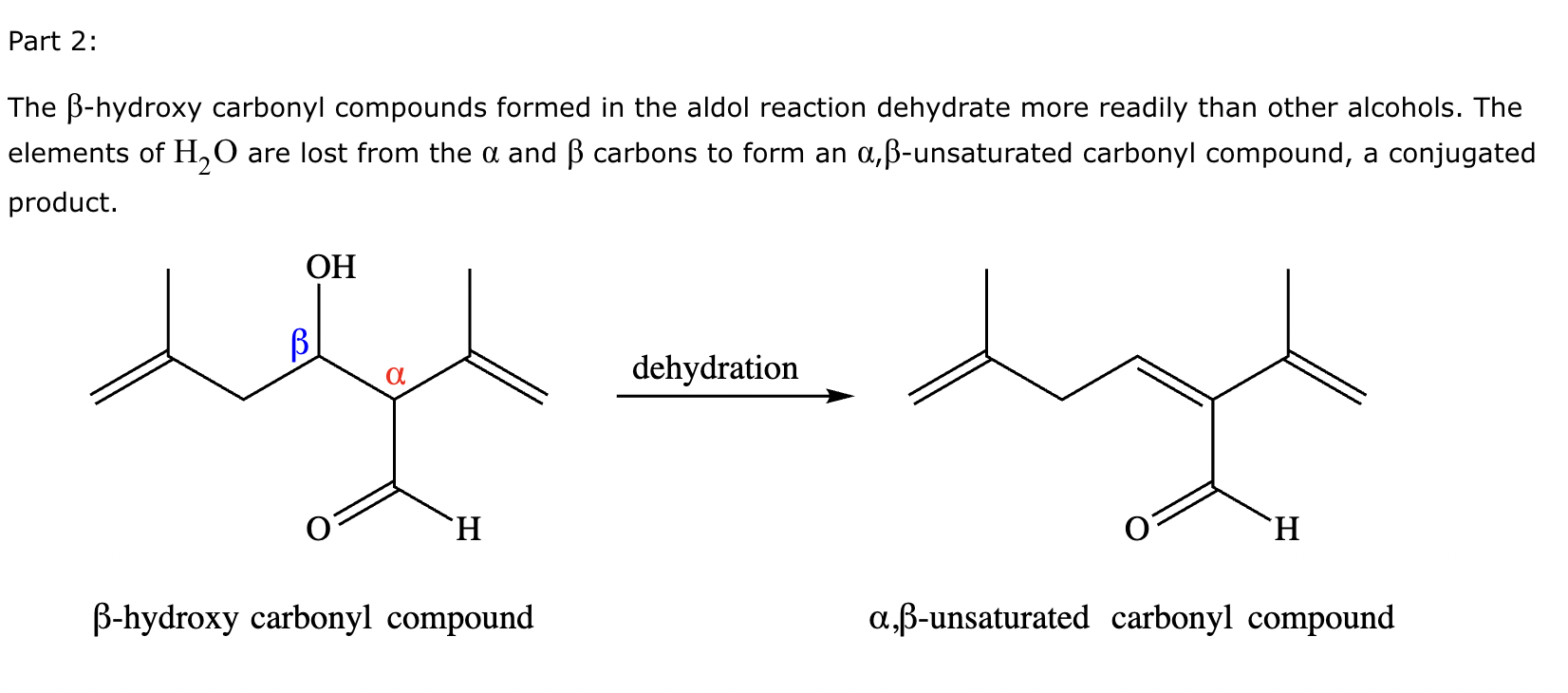
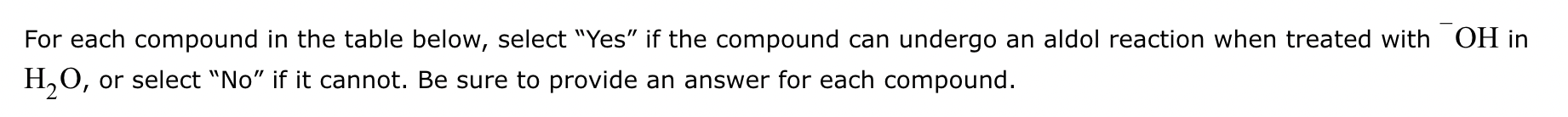
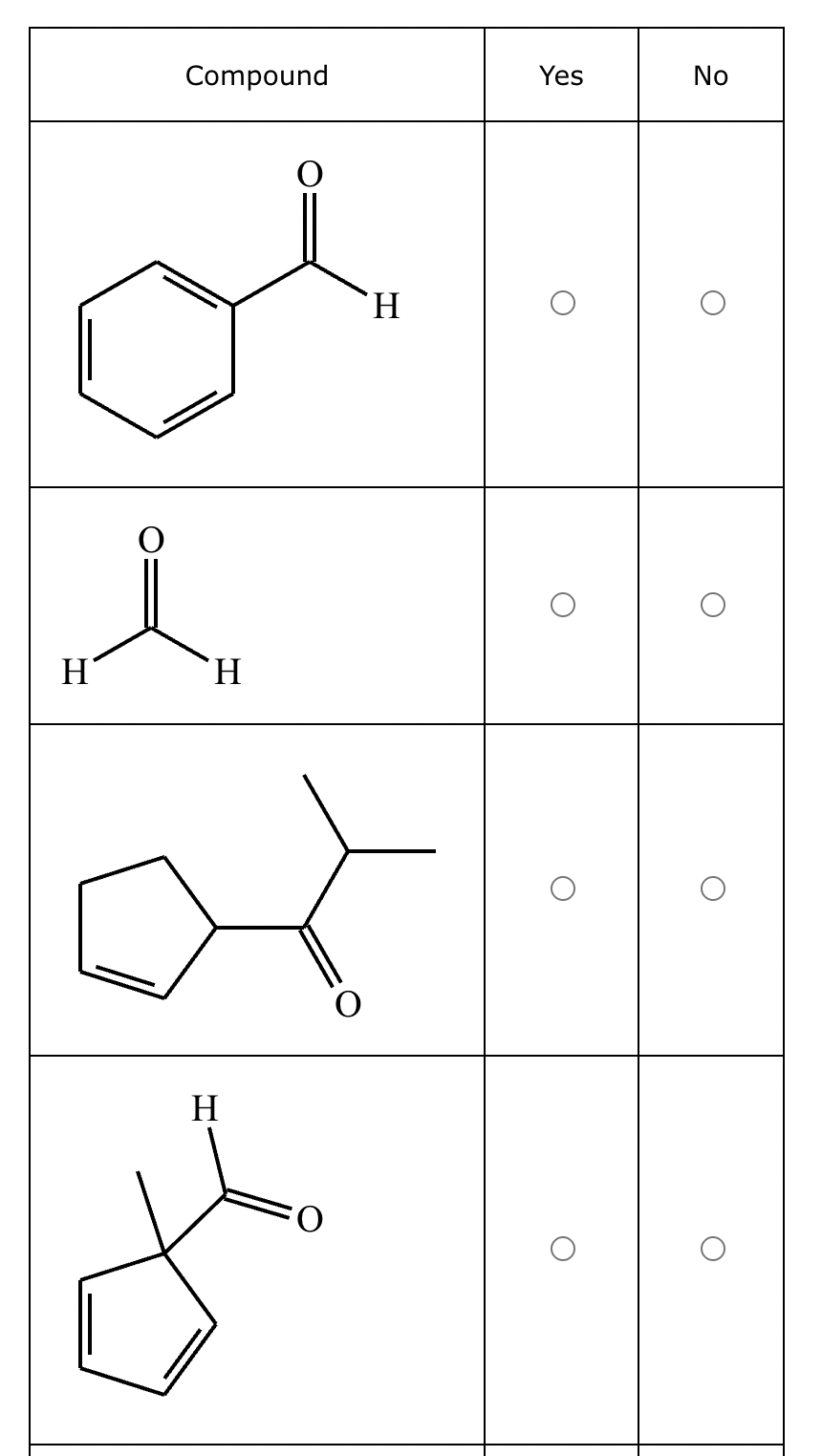
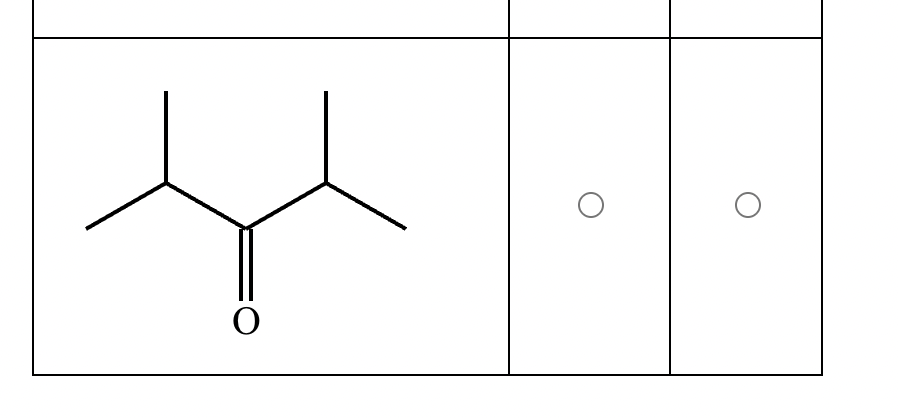
1: No
2: No
3: Yes
4: No
5: Yes
(Just count alpha carbons and hydrogens).

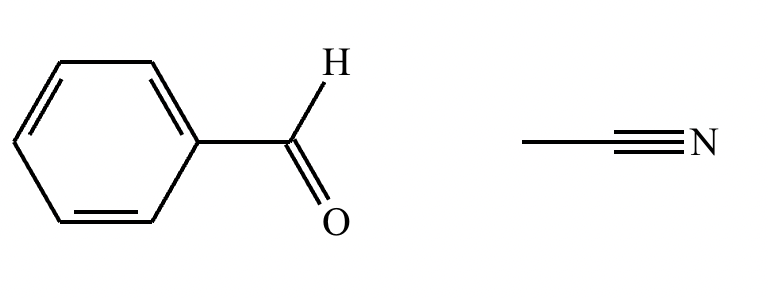
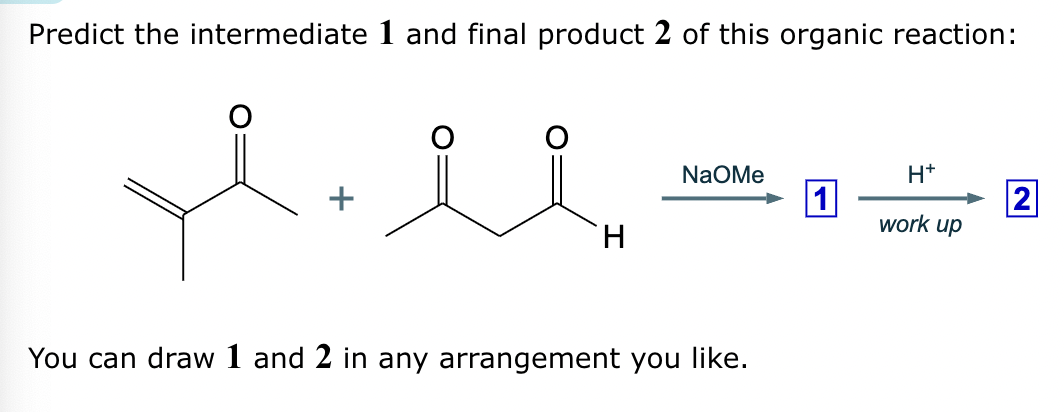
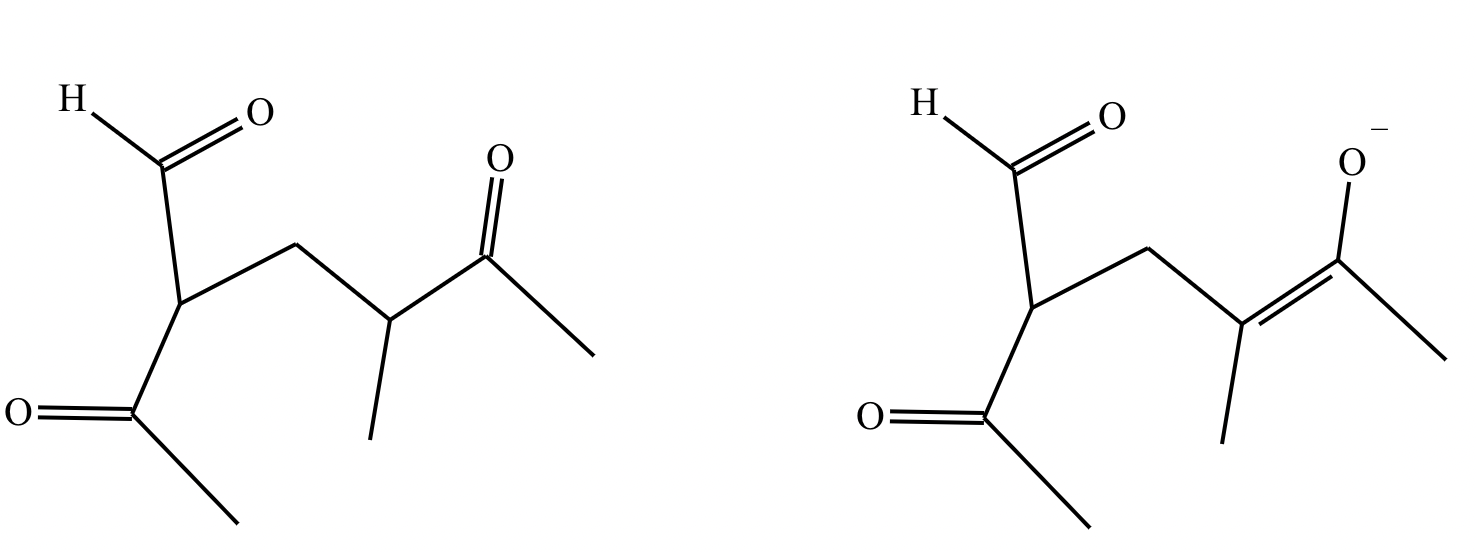
Draw the structures of the starting materials needed to synthesize the compound below using aldol or similar reactions.
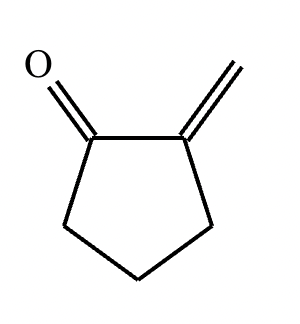
Draw the structures of the starting materials needed to synthesize the compound below using aldol or similar reactions.
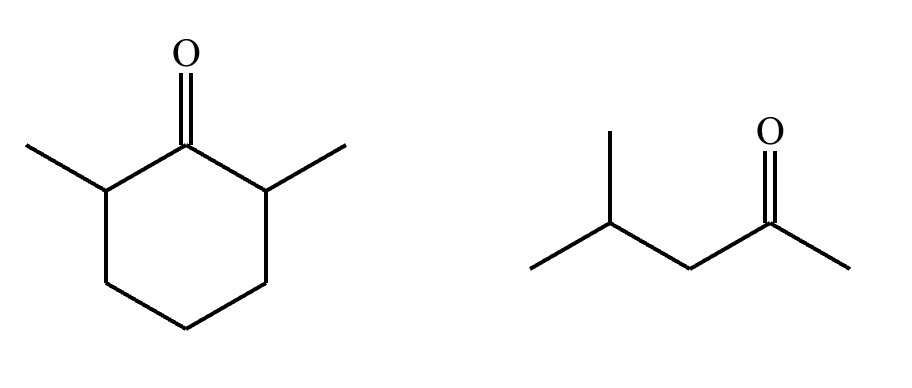
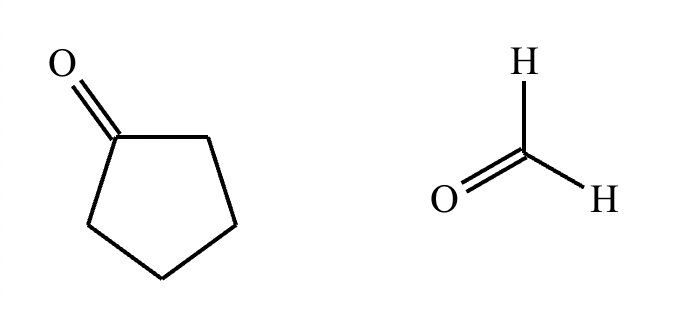
Draw the structures of the starting materials needed to synthesize the compound below using aldol or similar reactions.
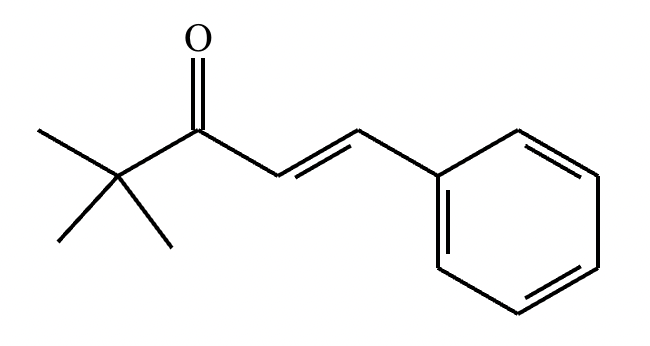
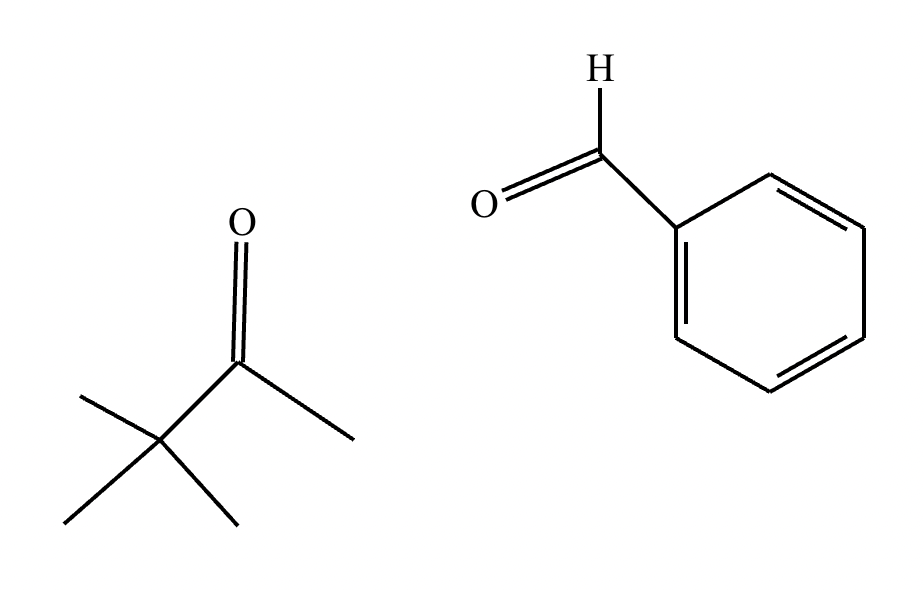
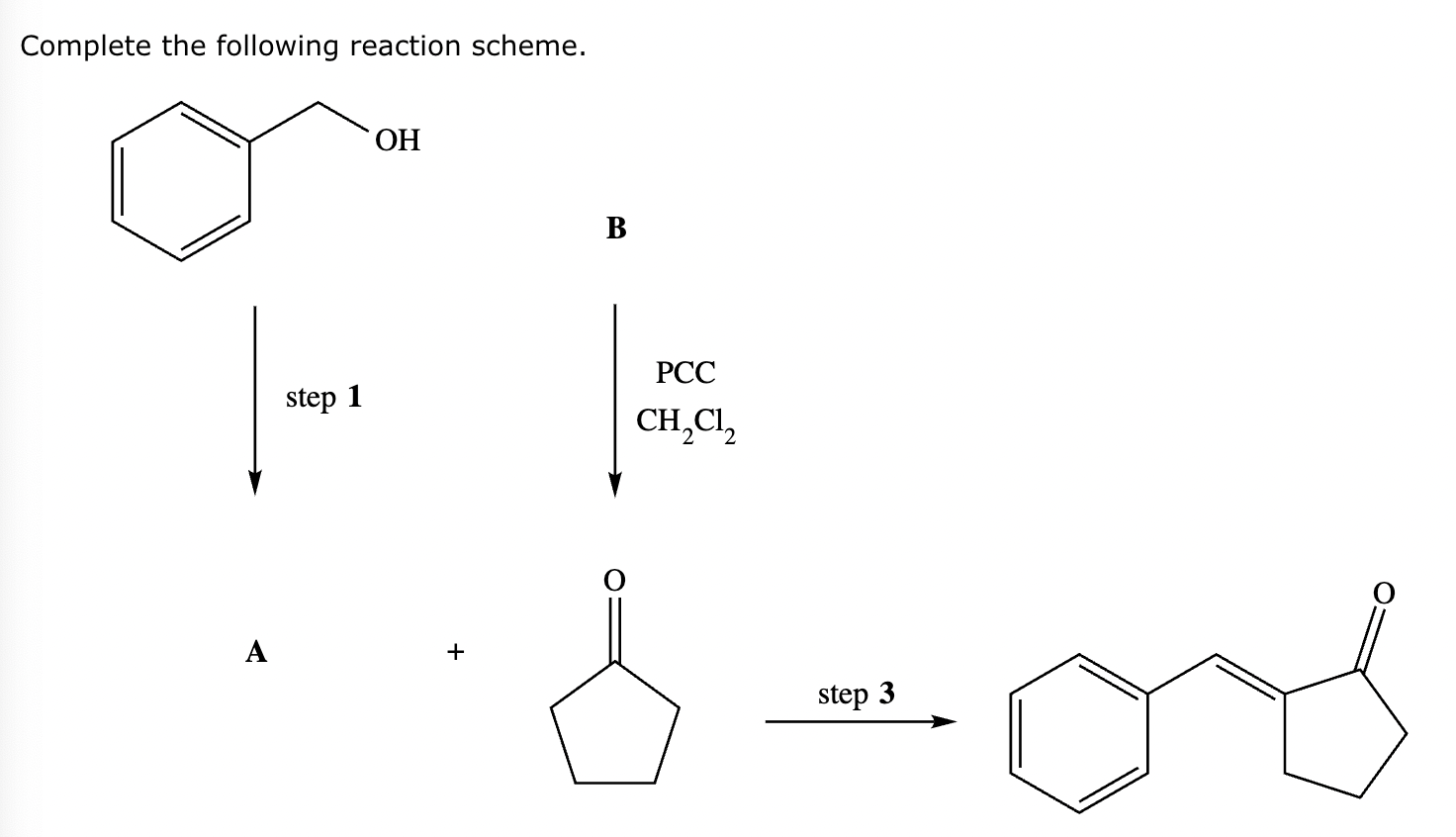

Part 2: Draw the structure for compound A.
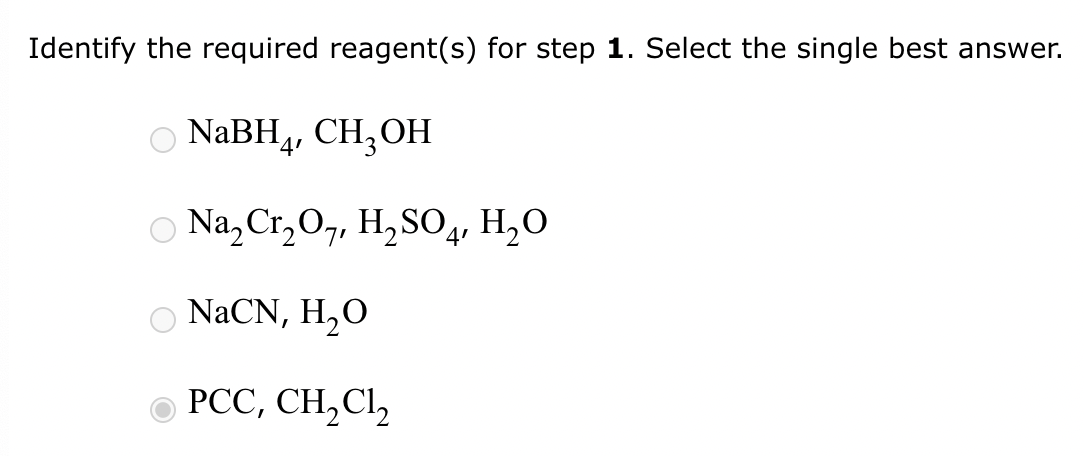
Part 3: Identify the required reagent(s) for step 3.
Part 4: Draw the structure for compound B.$
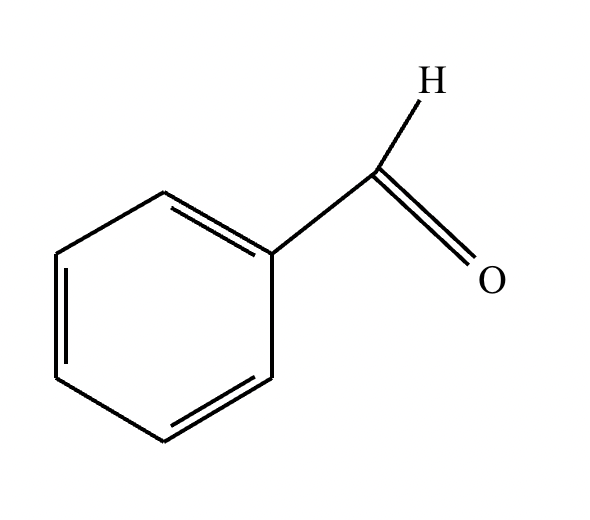

Draw the structure for the product of the following mixed aldol condensation reaction.
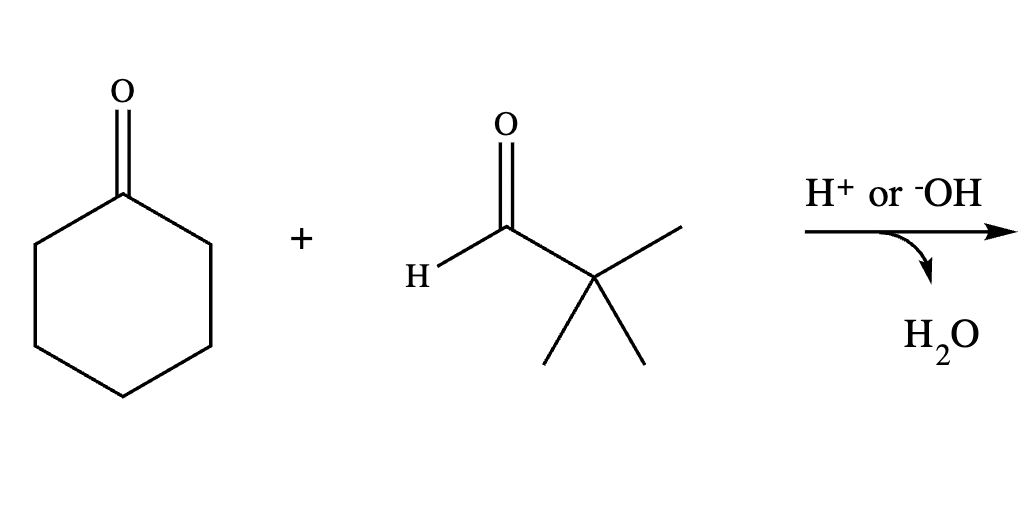
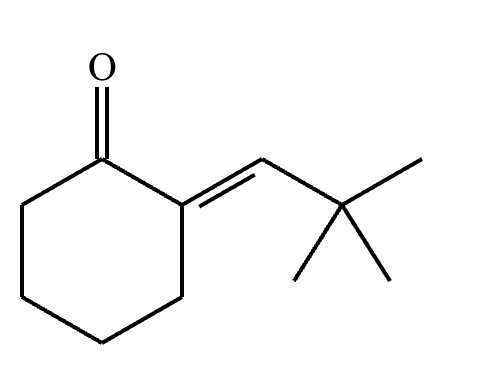
Draw the structure for the product of the following mixed aldol condensation reaction.
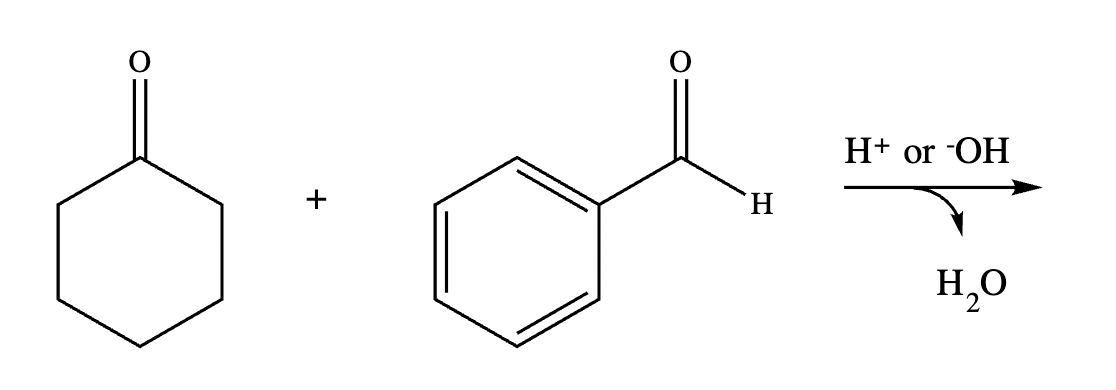
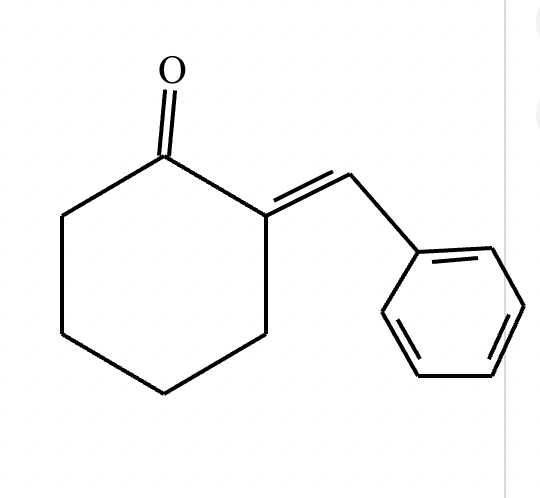
Draw the structures of the starting materials needed to synthesize the compound below using aldol or similar reactions.
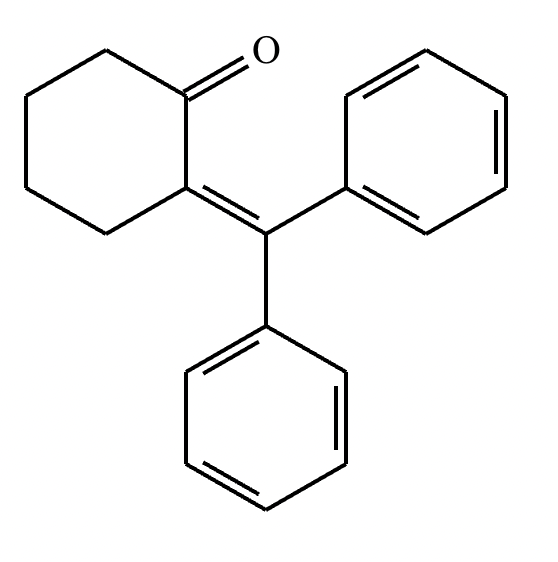
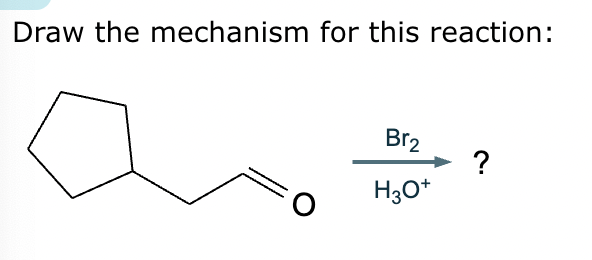
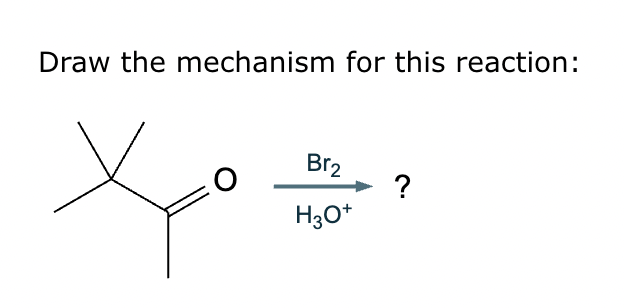
No reaction (no alpha hydrogens).
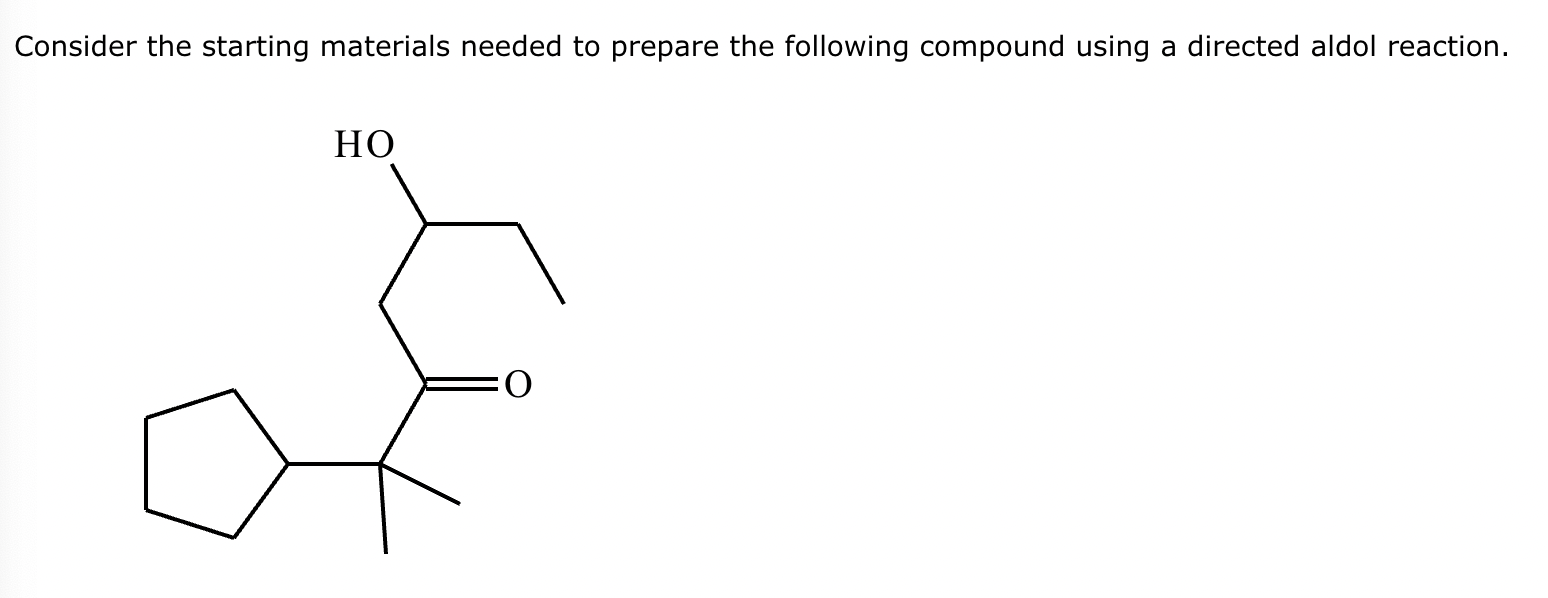
In the structure of the desired product, highlight the alpha carbon in red, the beta carbon in blue, and the bond between them in green. Then, draw the structures of the carbonyl starting materials needed to prepare the given compound.
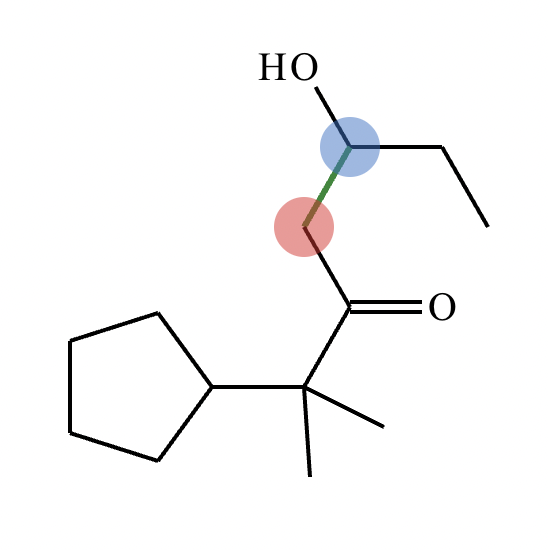
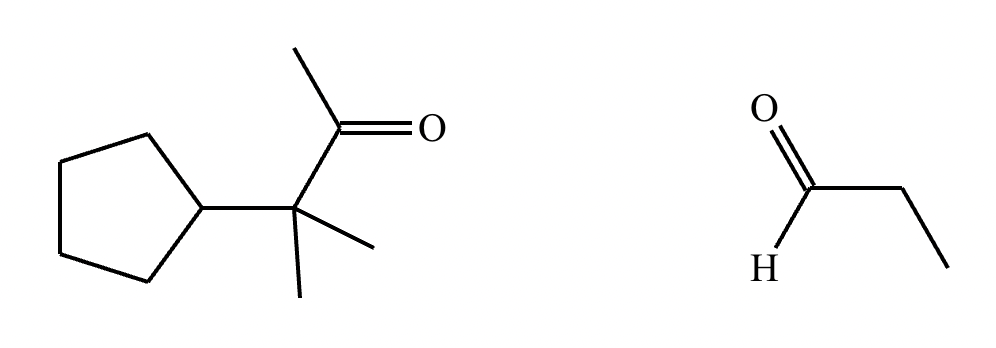

In the structure of the desired product, highlight the alpha carbon in red, the beta carbon in blue, and the bond between them in green. Then, draw the structures of the carbonyl starting materials needed to prepare the given compound.
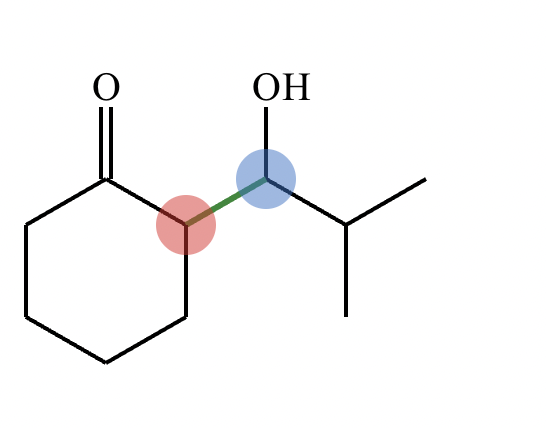
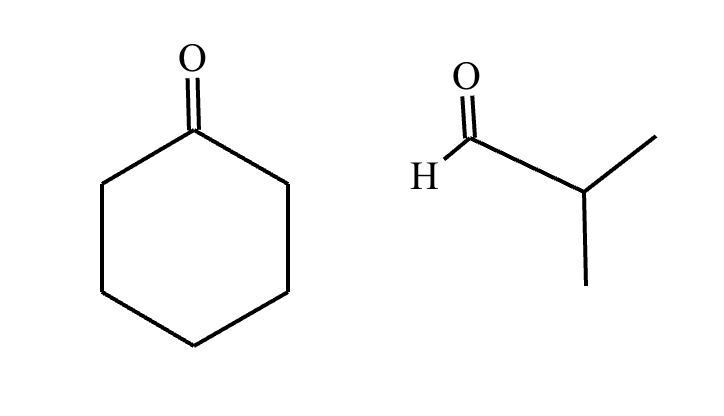
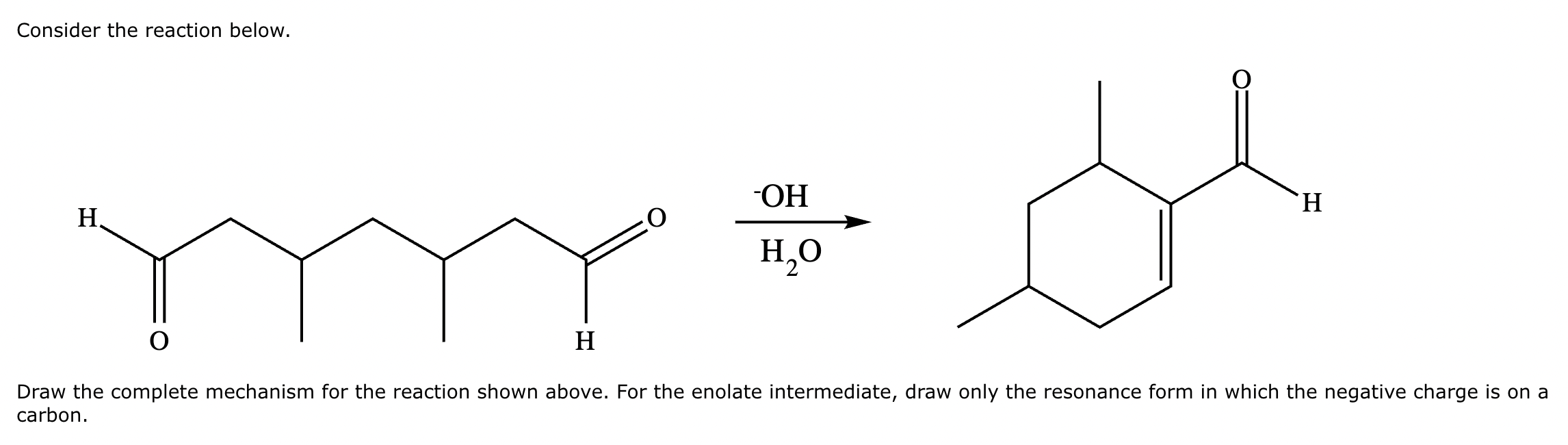
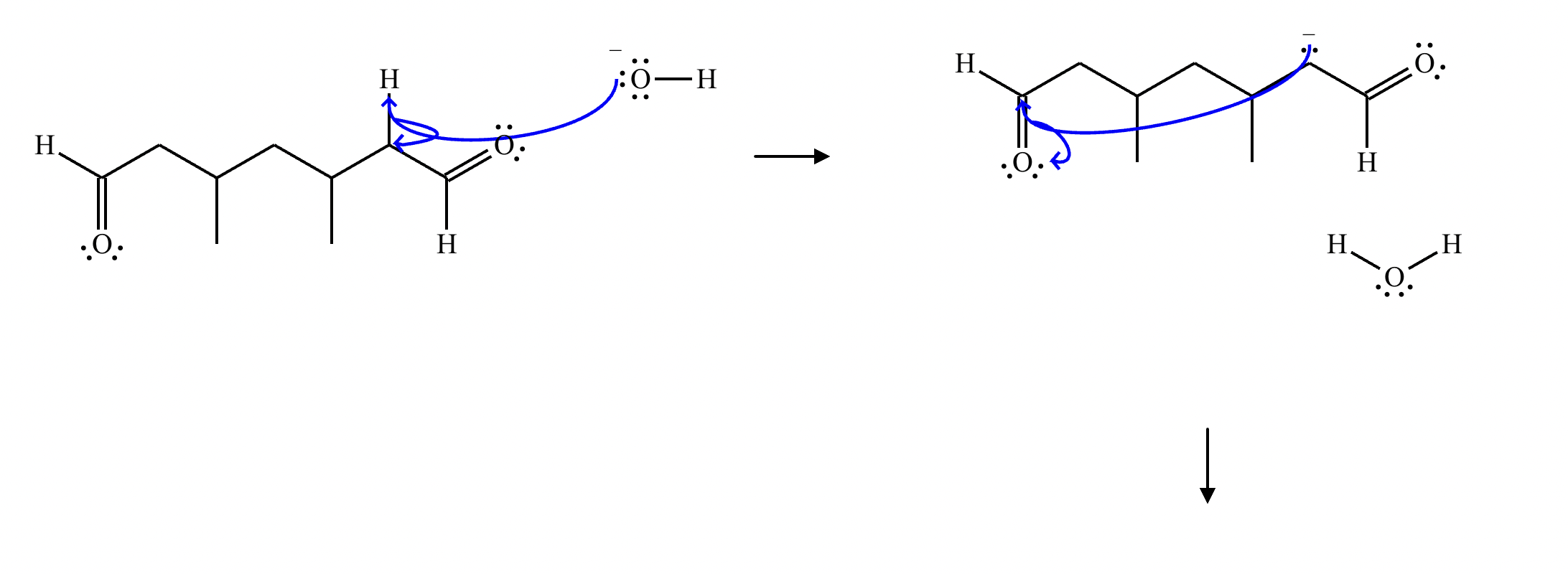
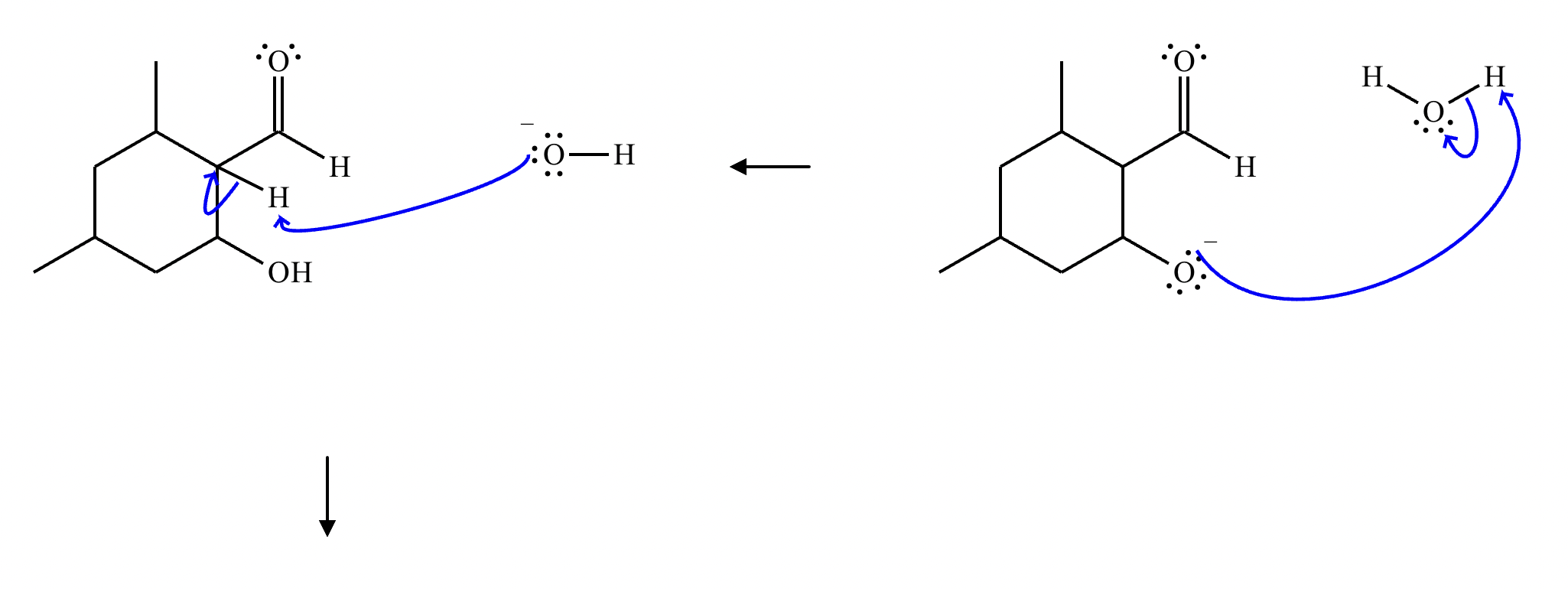
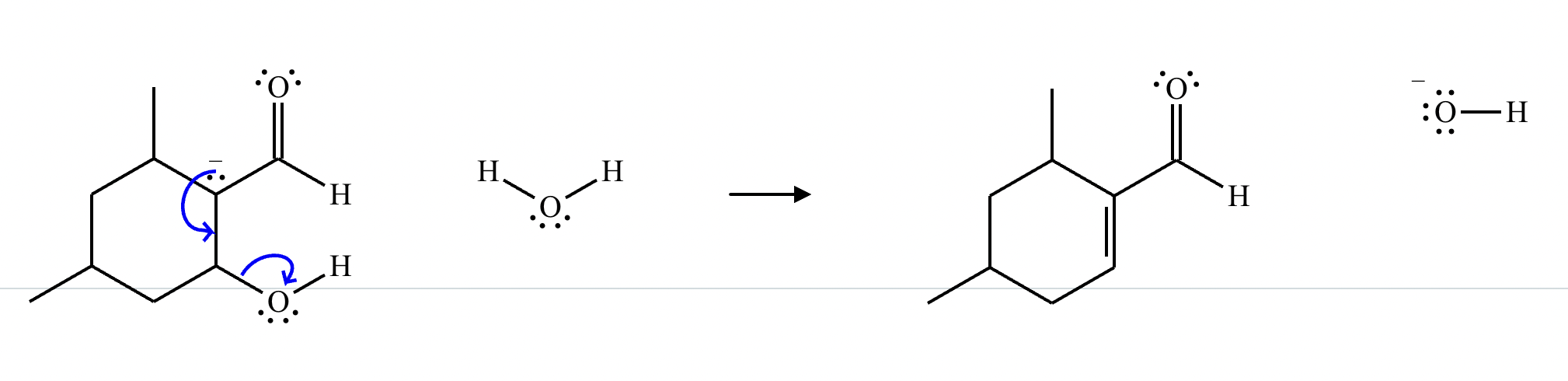
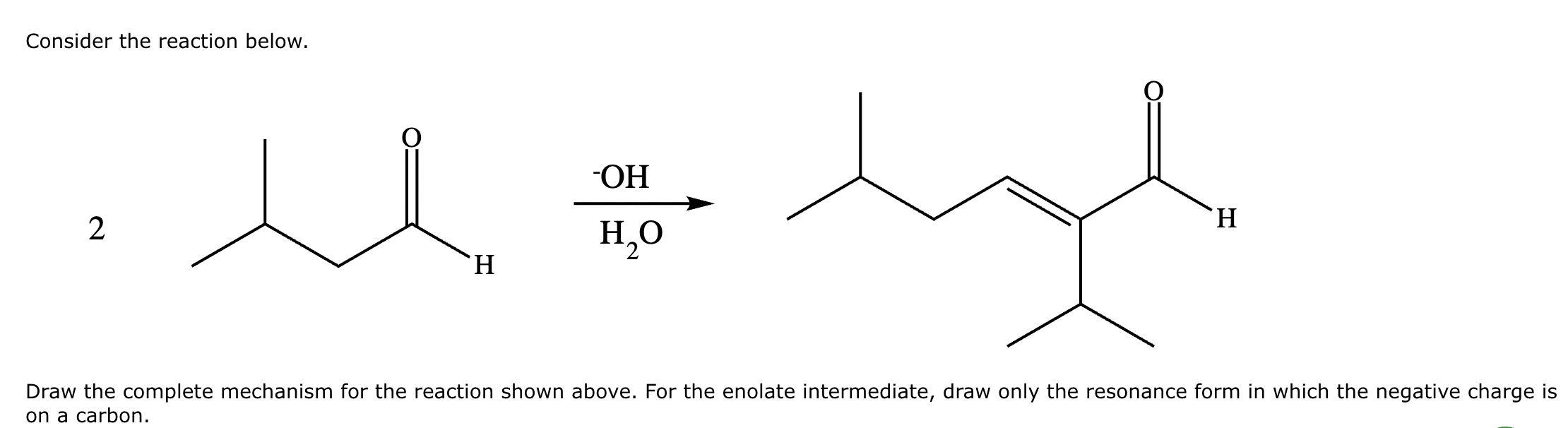
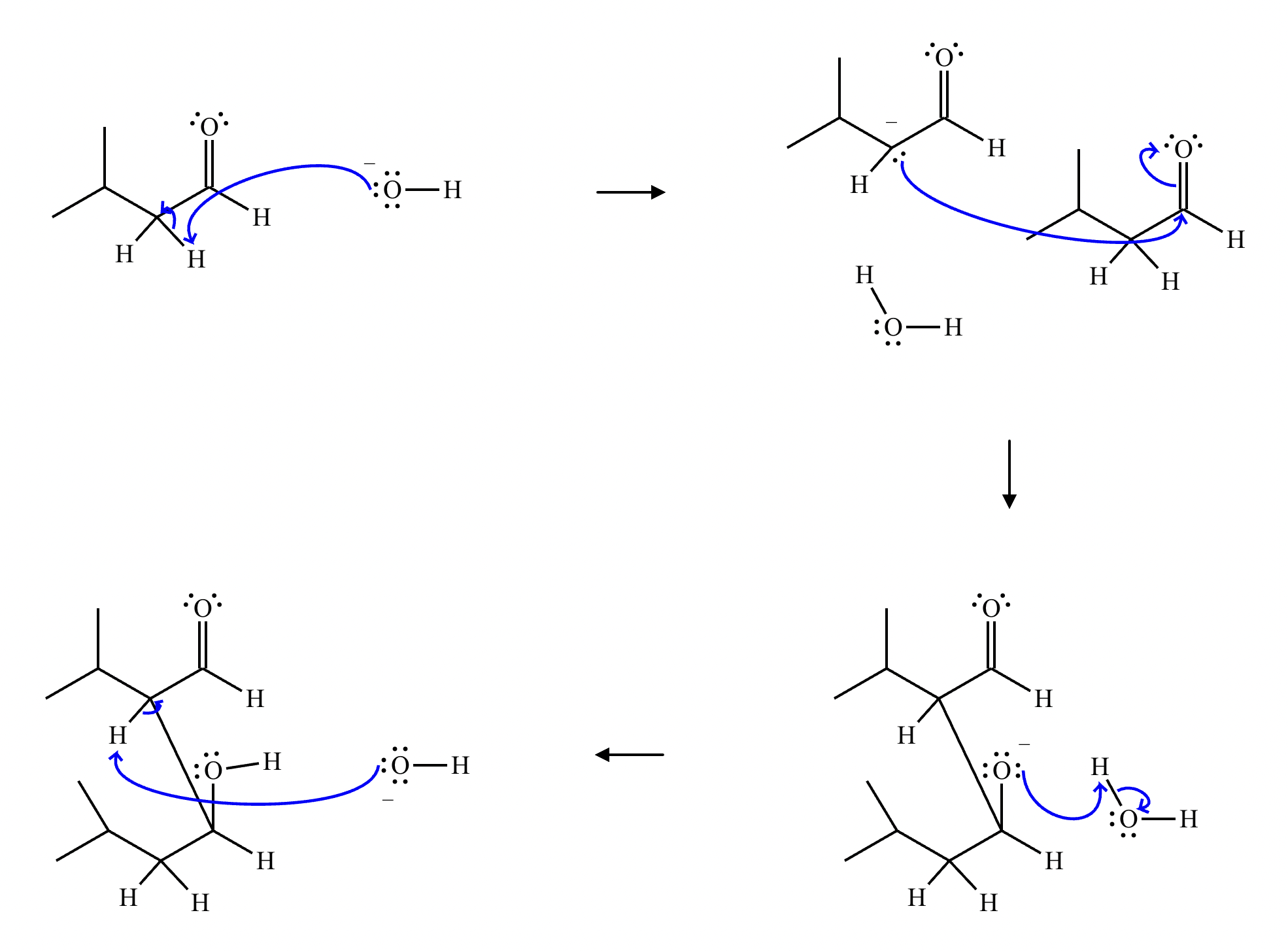
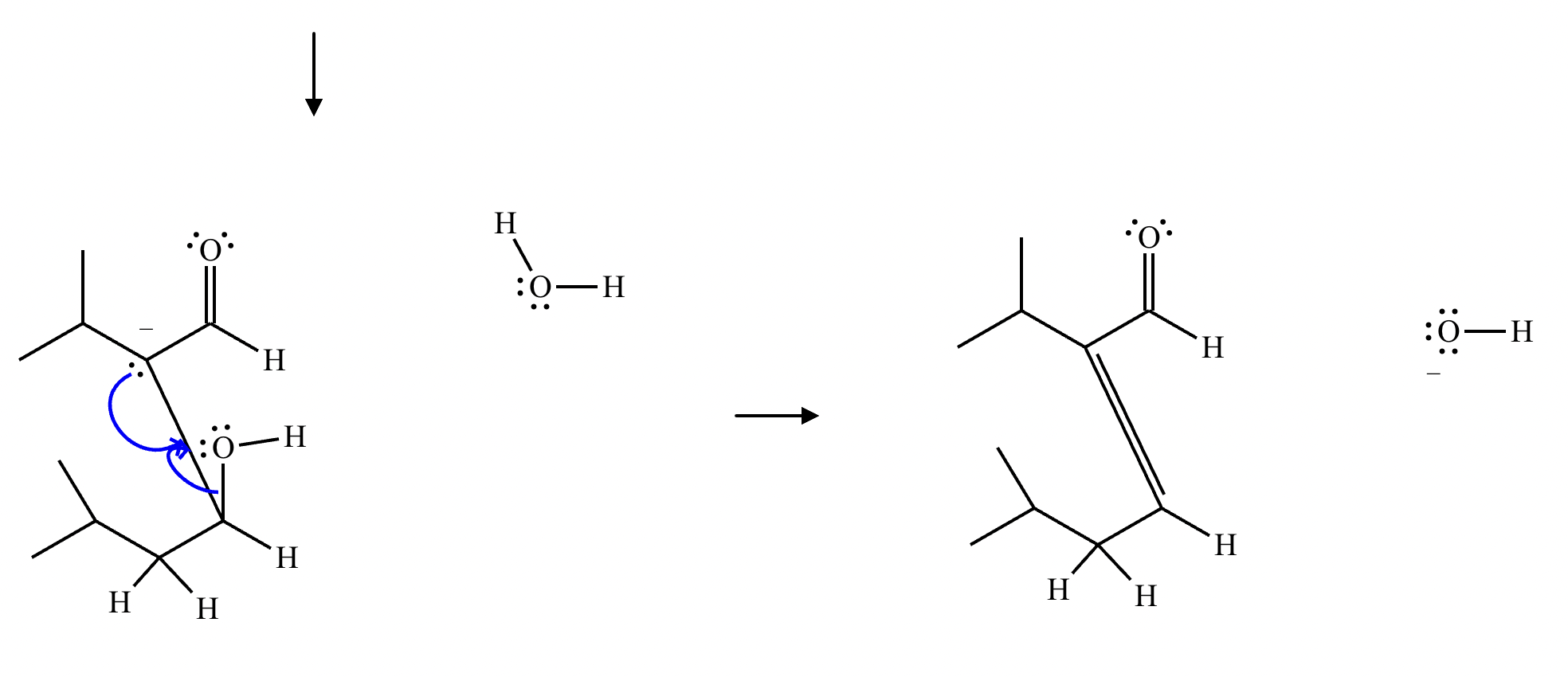
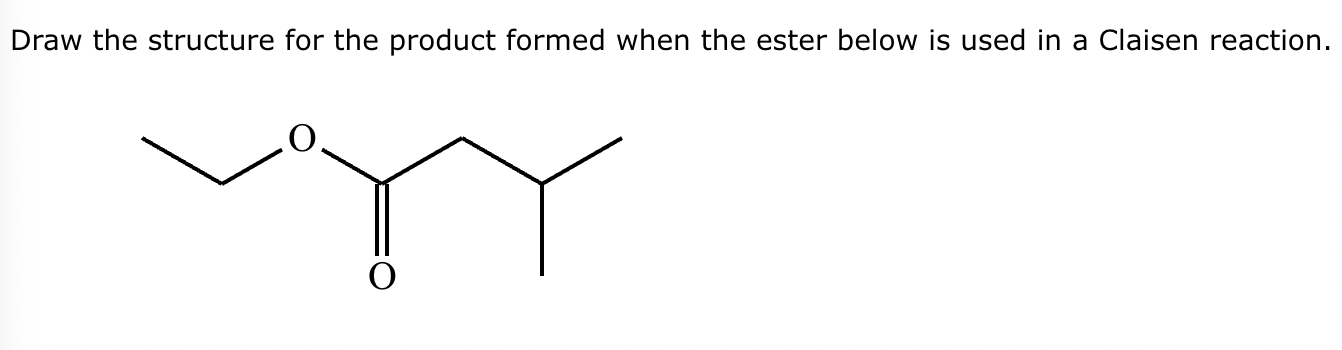
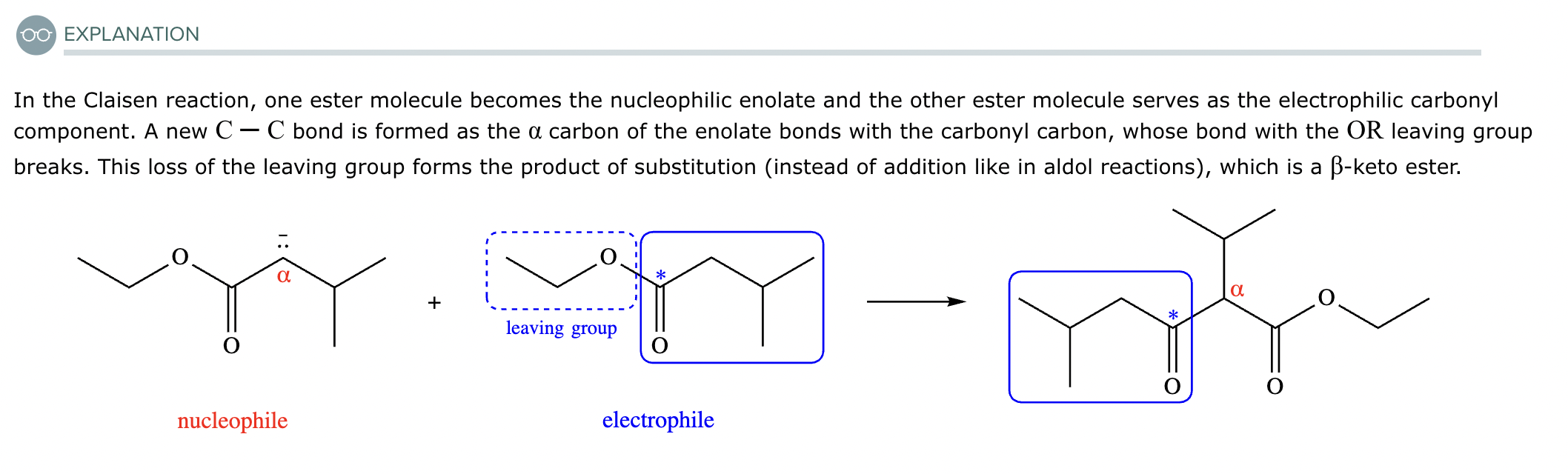
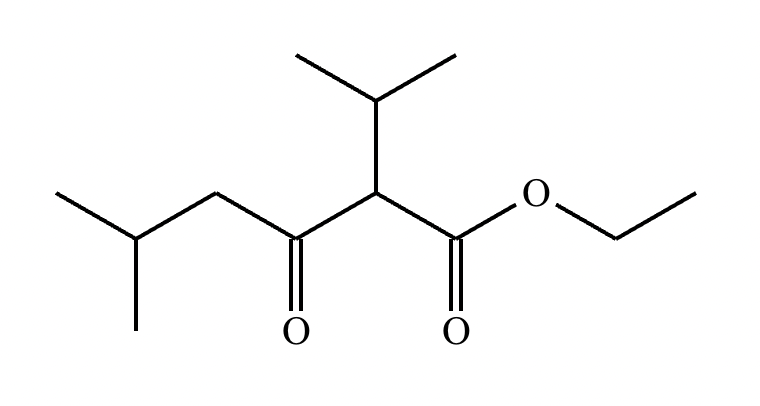
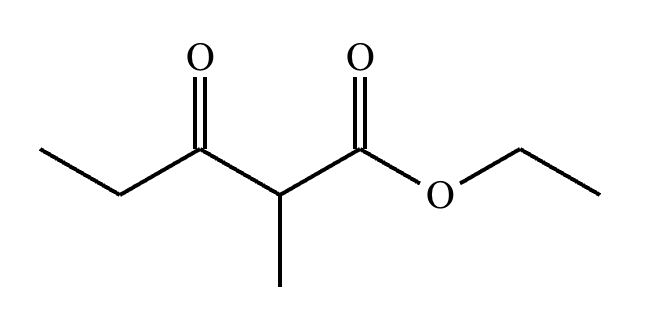
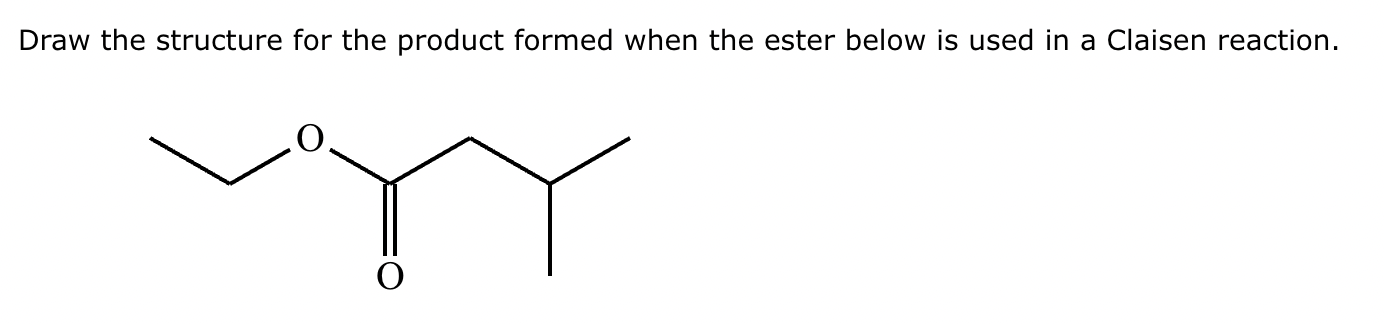
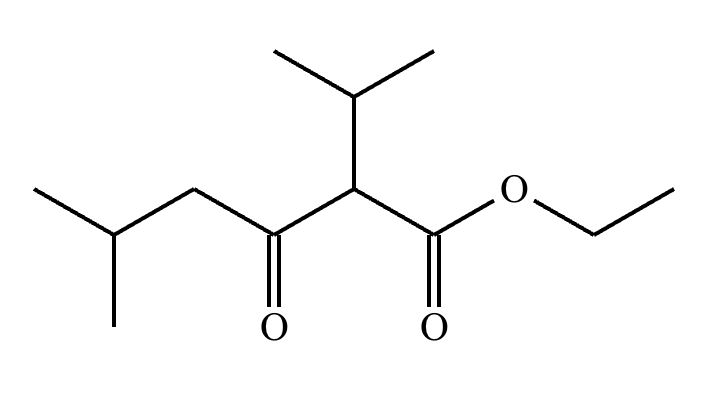
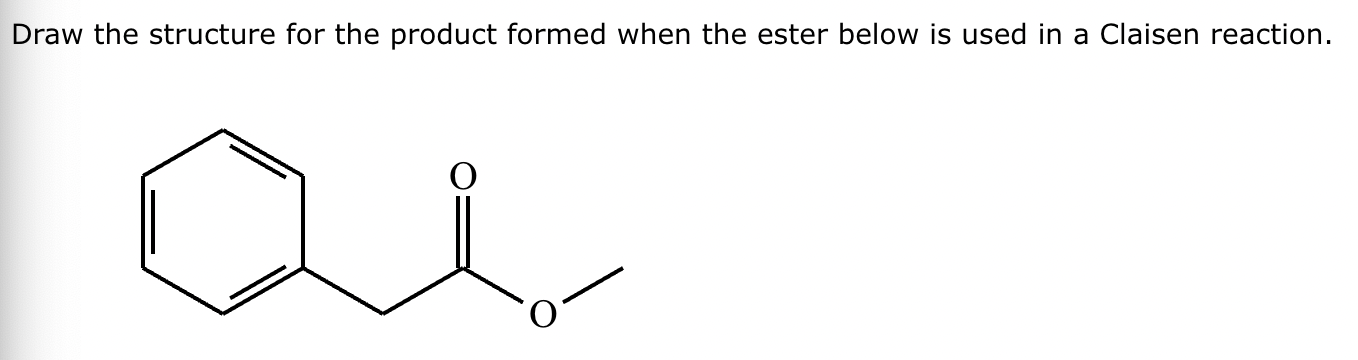
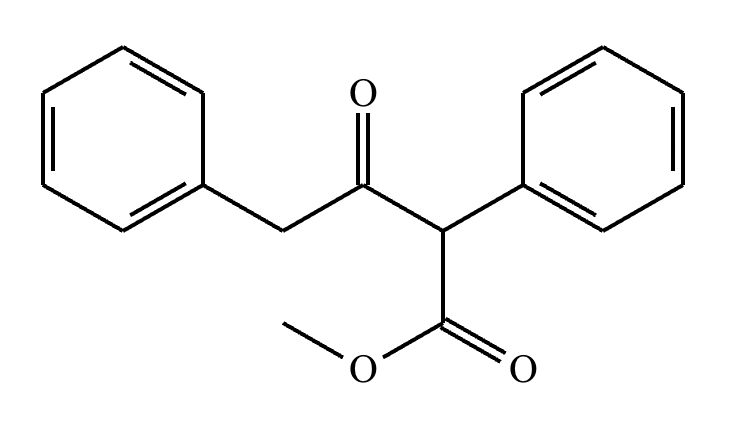
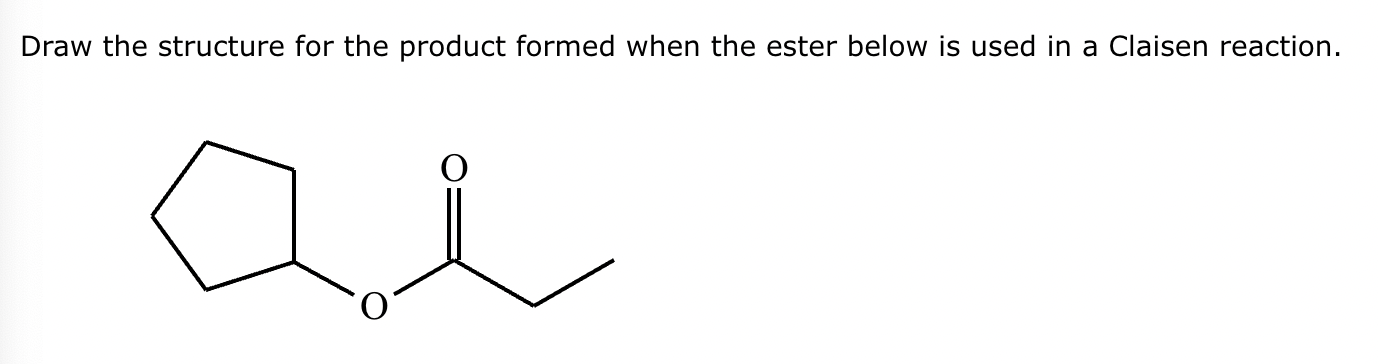
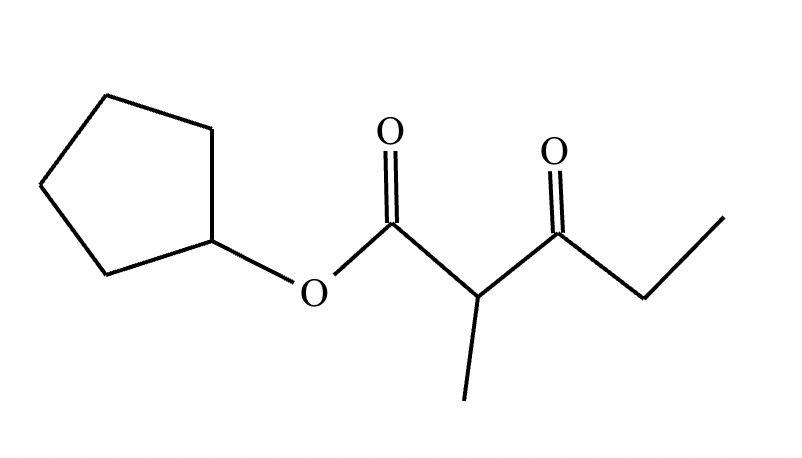
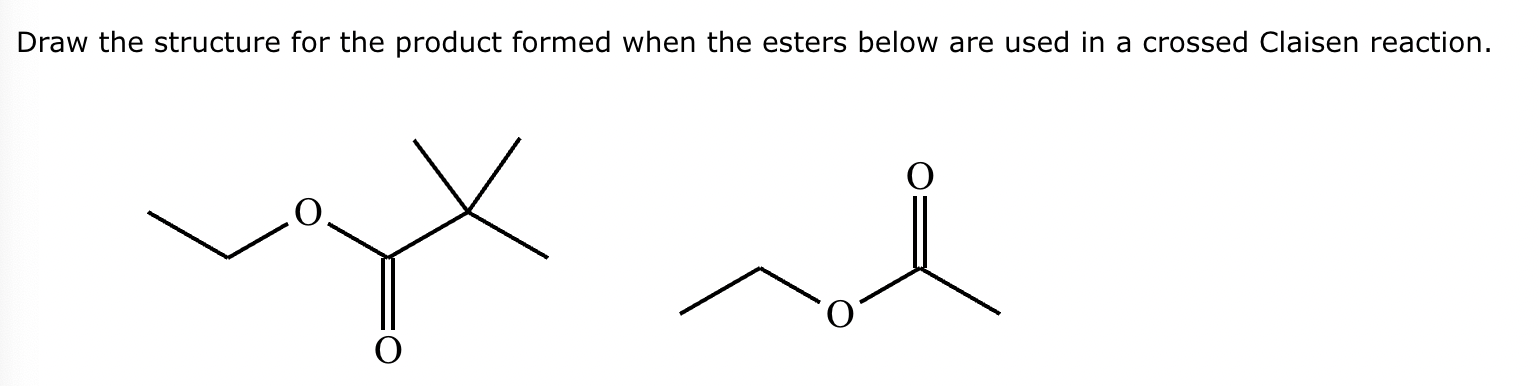
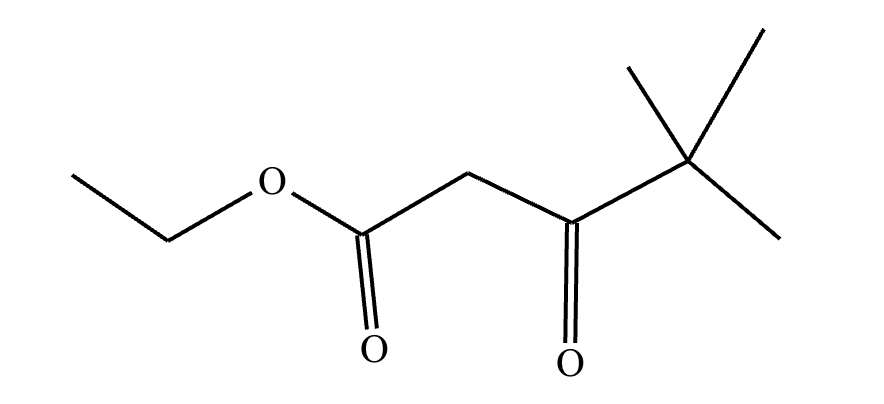
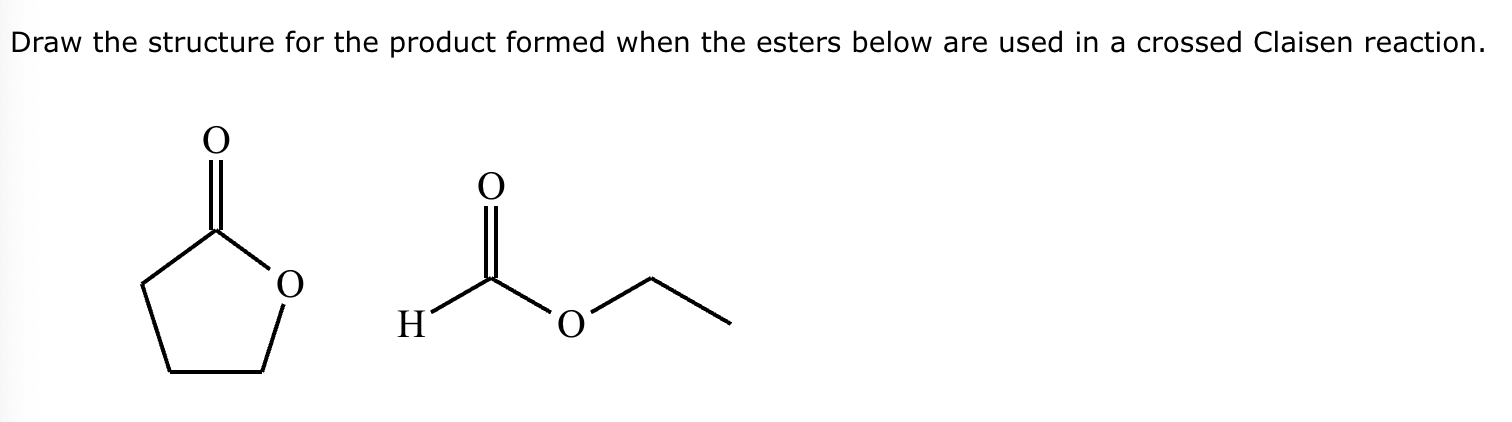
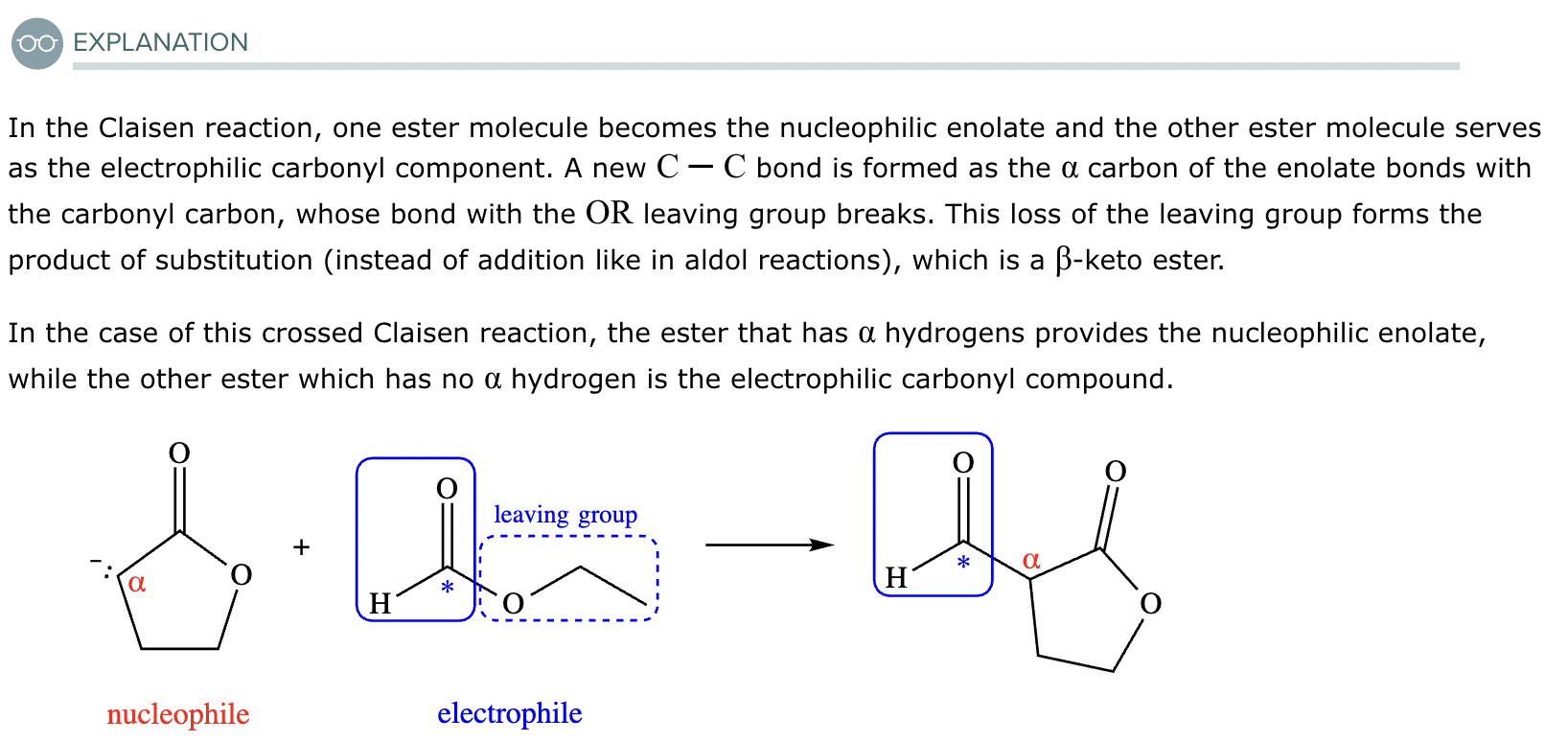
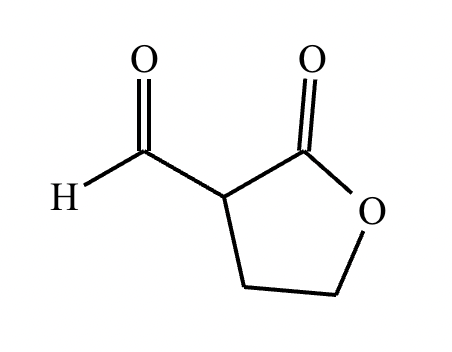
A student claims the right-hand side of the reaction in the drawing area below shows the product of a Claisen condensation. If the student is correct, complete the reaction by adding the necessary organic reactants to the left-hand side, and by adding any necessary reagents and reaction conditions above and below the arrow. If the student is incorrect, because it's not possible to obtain this product from a Claisen condensation, check the box under the drawing area instead.
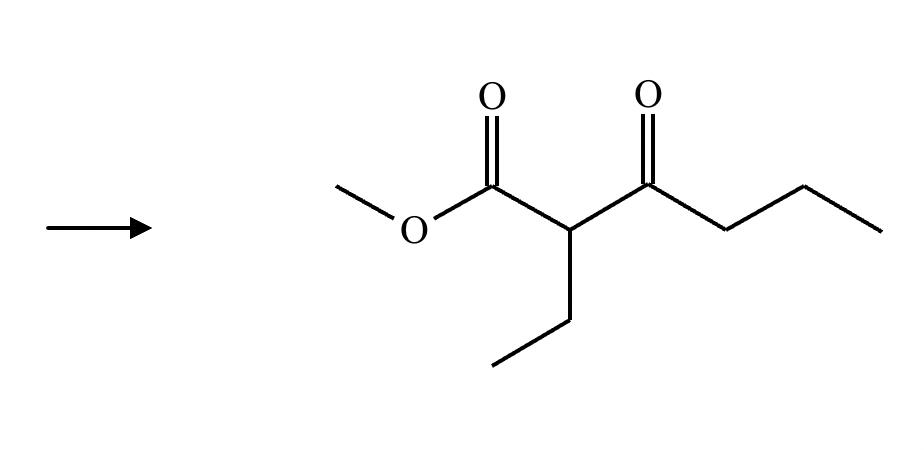
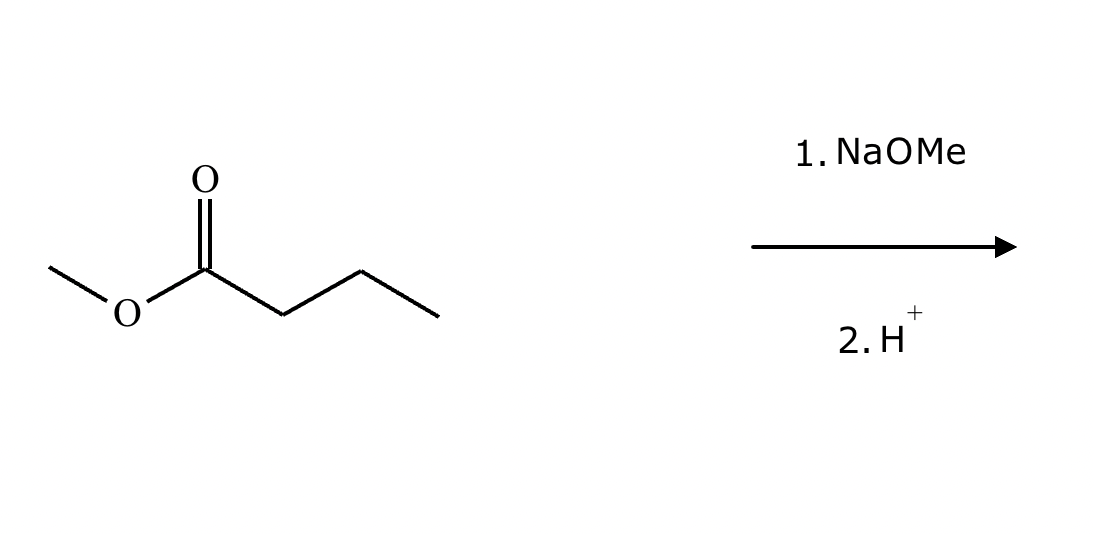
A student claims the right-hand side of the reaction in the drawing area below shows the product of a Claisen condensation. If the student is correct, complete the reaction by adding the necessary organic reactants to the left-hand side, and by adding any necessary reagents and reaction conditions above and below the arrow. If the student is incorrect, because it's not possible to obtain this product from a Claisen condensation, check the box under the drawing area instead.
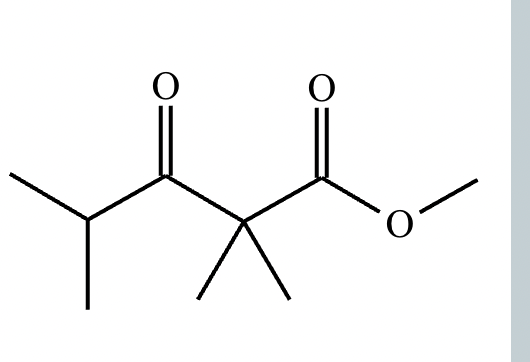
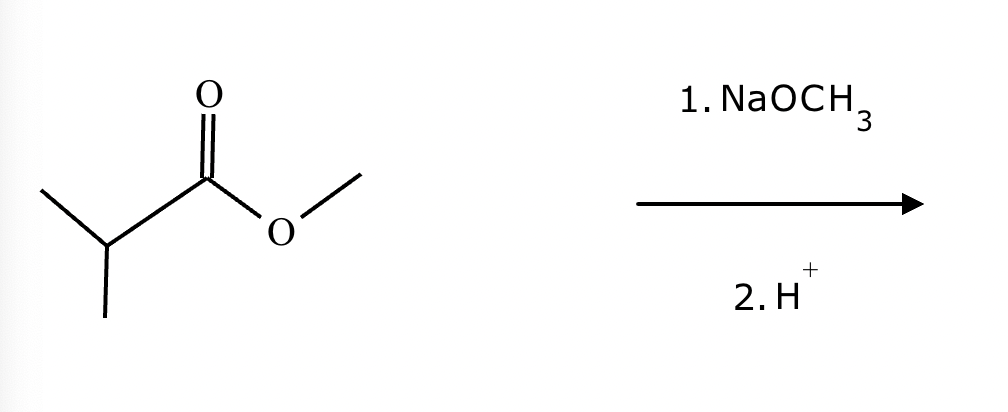
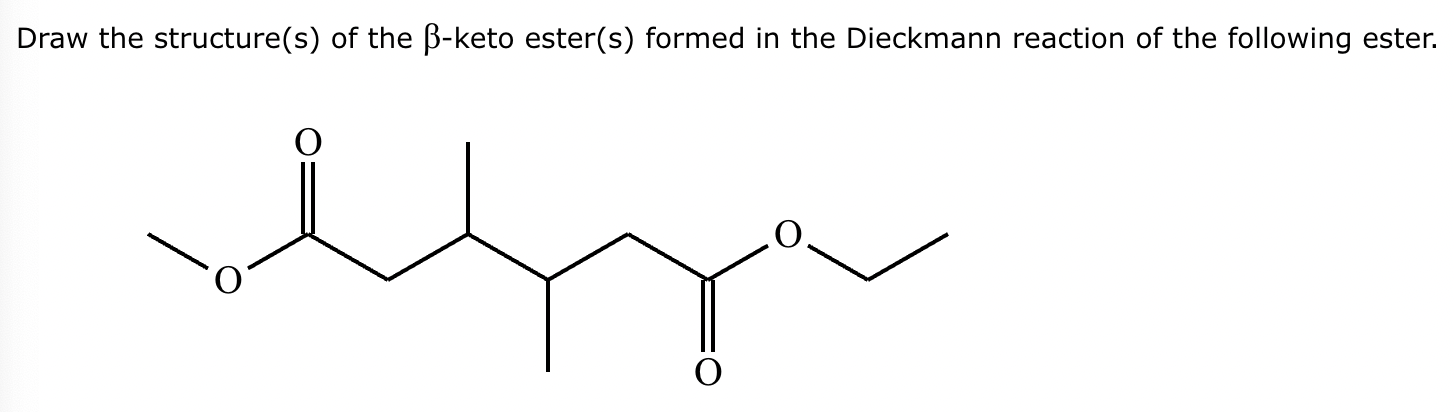
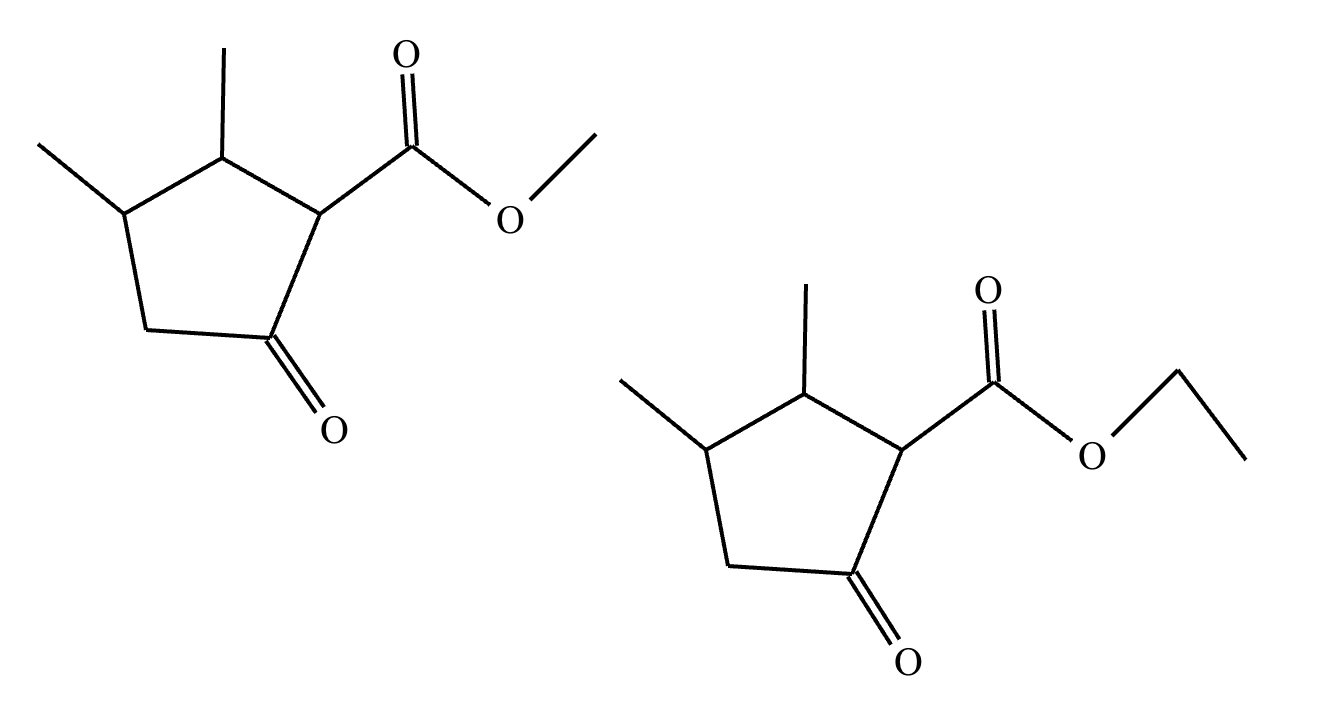
Provide the structure for the Dieckmann cyclization product for the reaction below. Stereochemistry can be ignored for this problem. If multiple products are expected, either is acceptable.
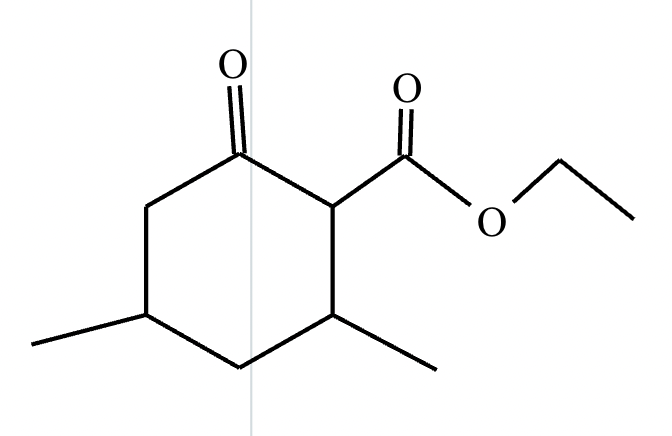
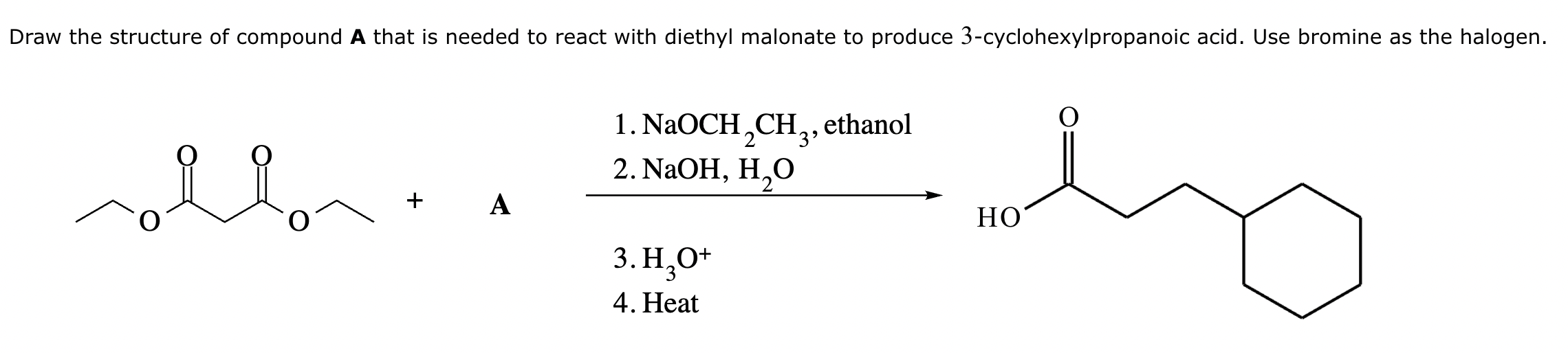
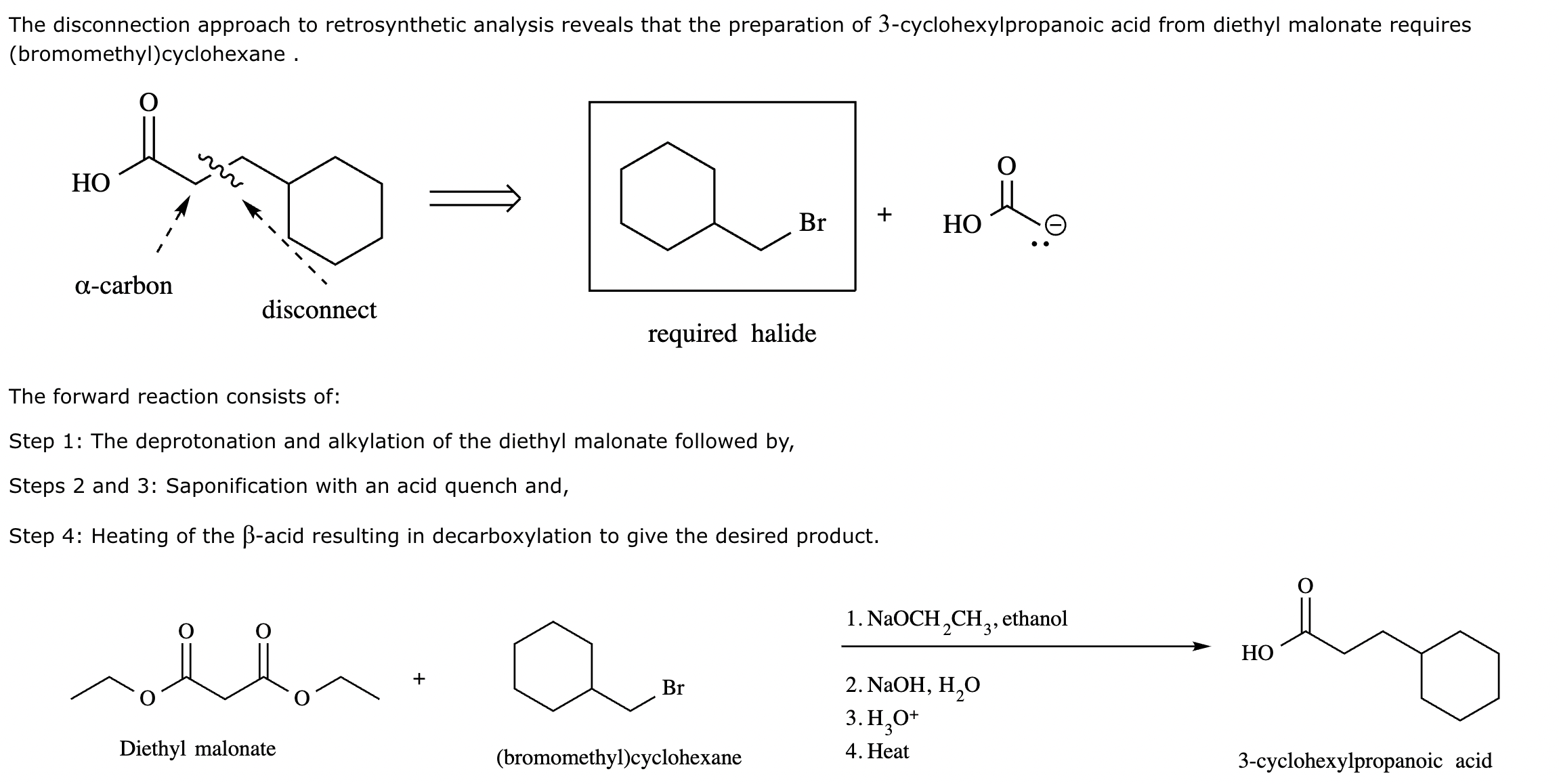
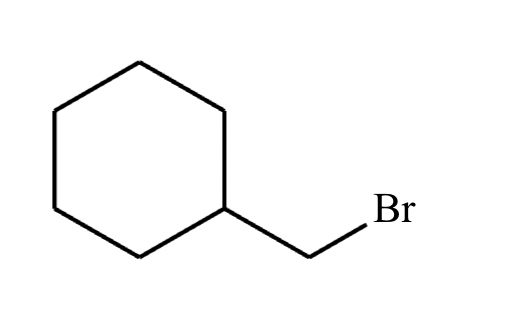
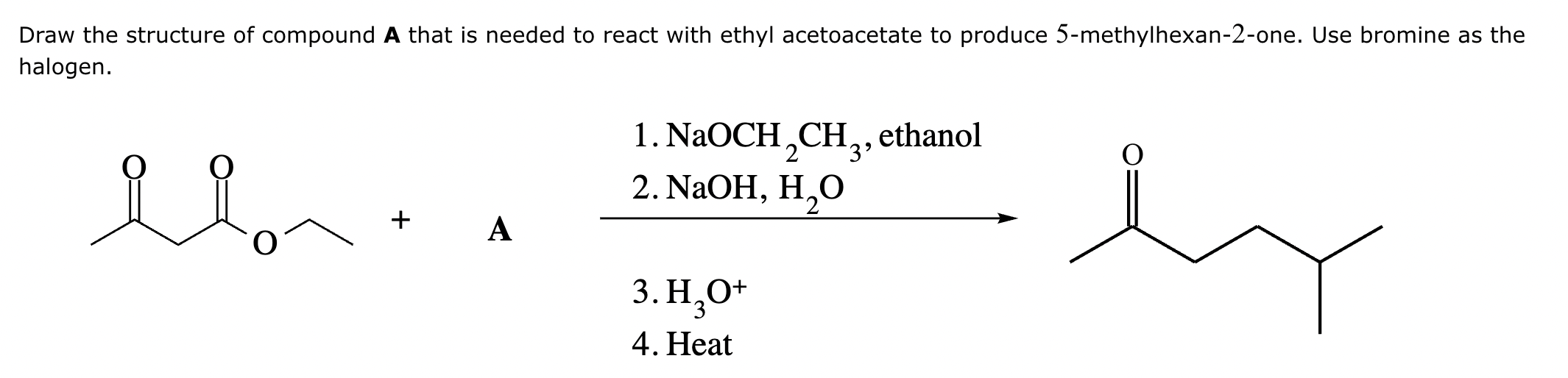
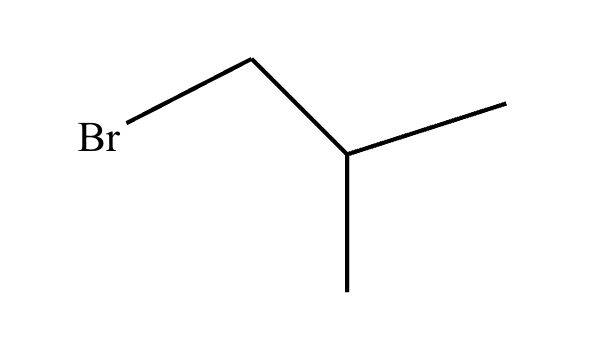

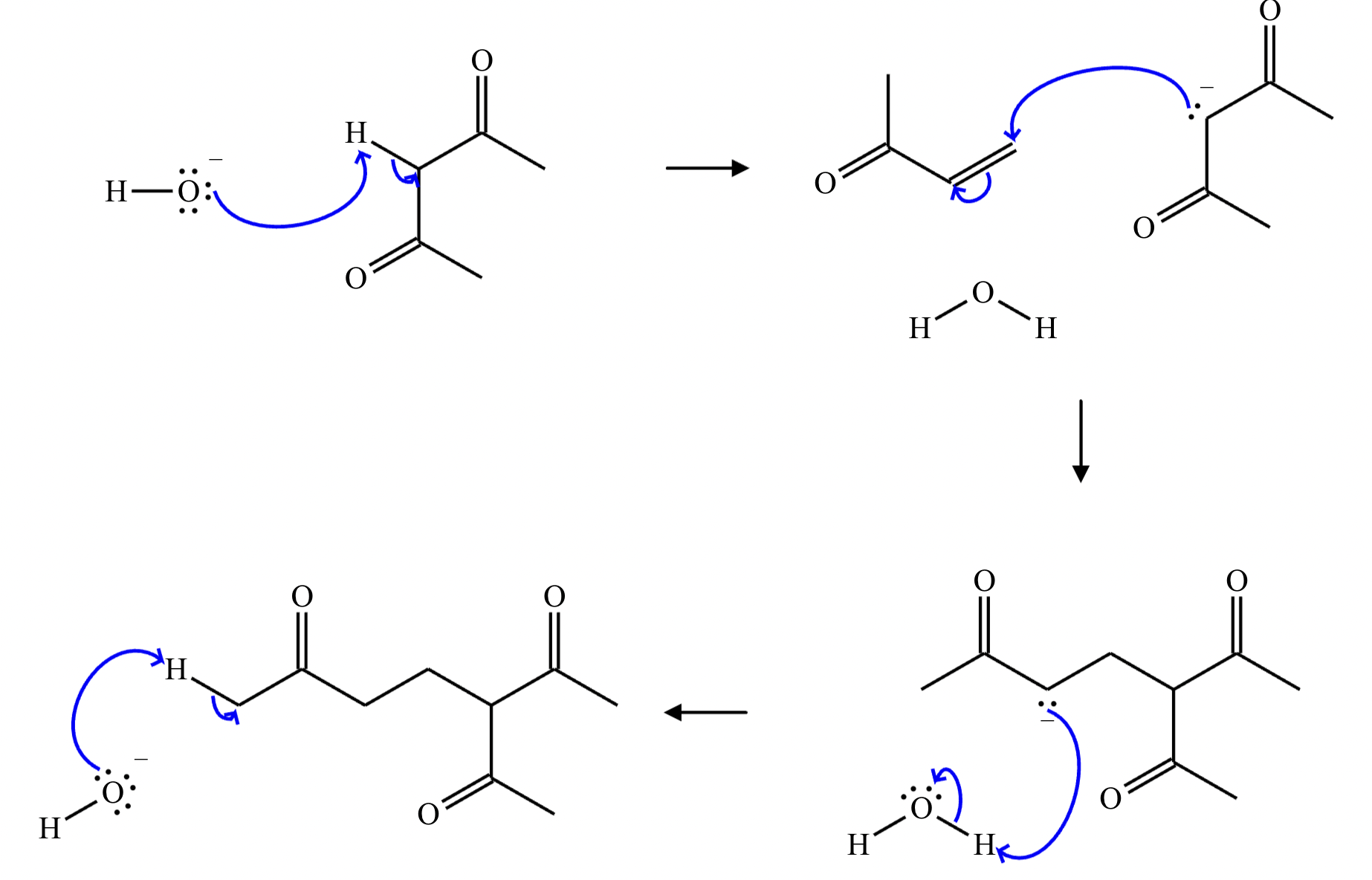
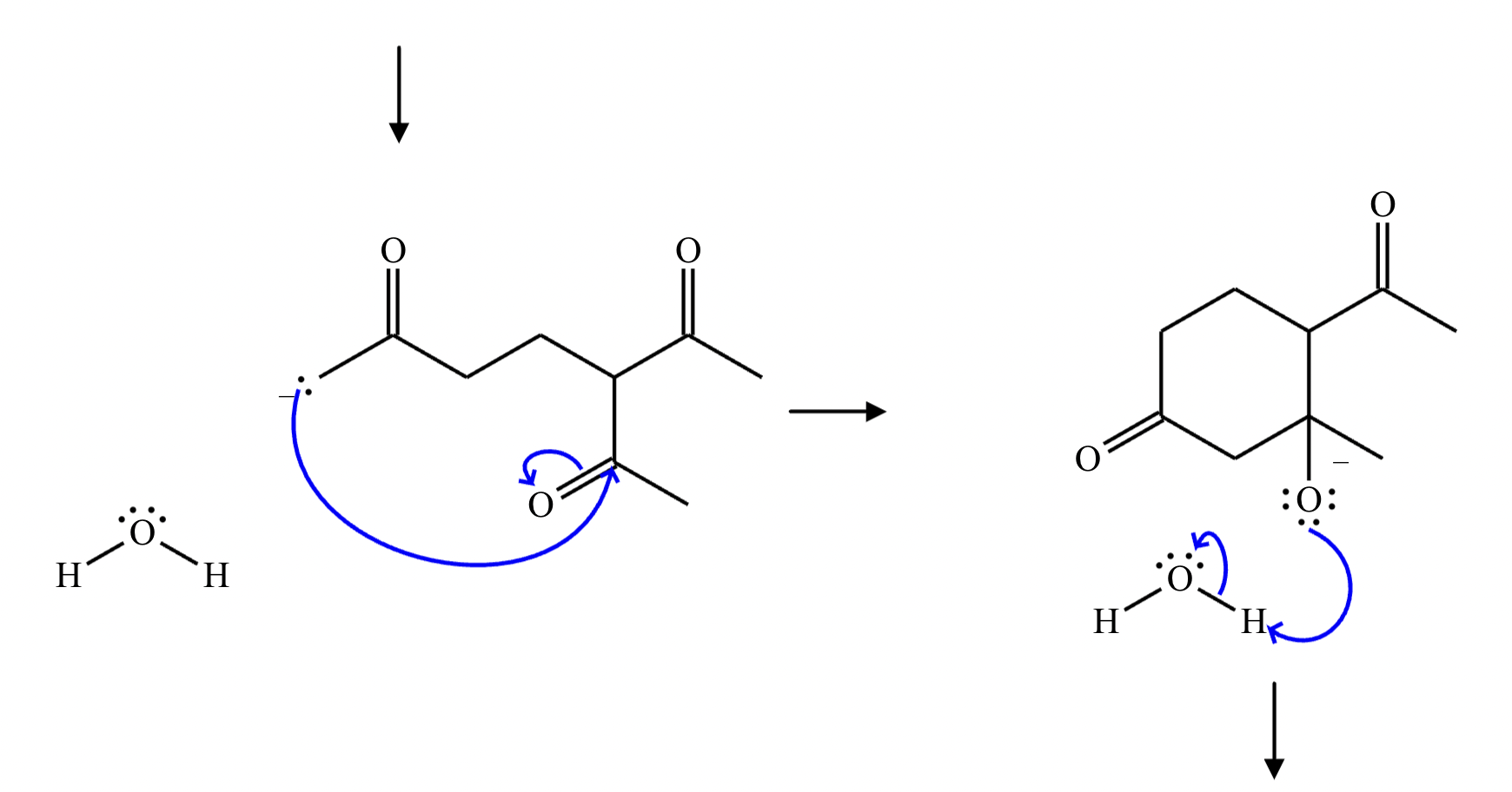
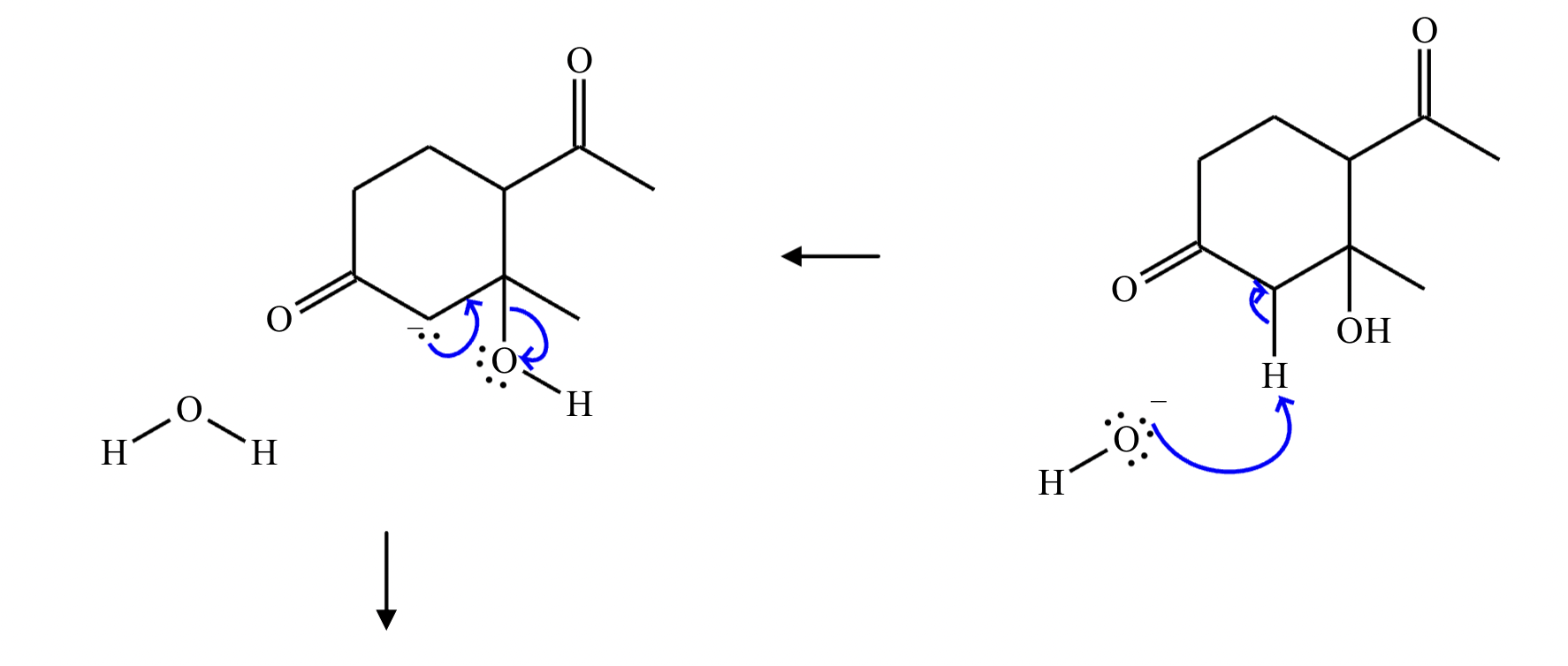
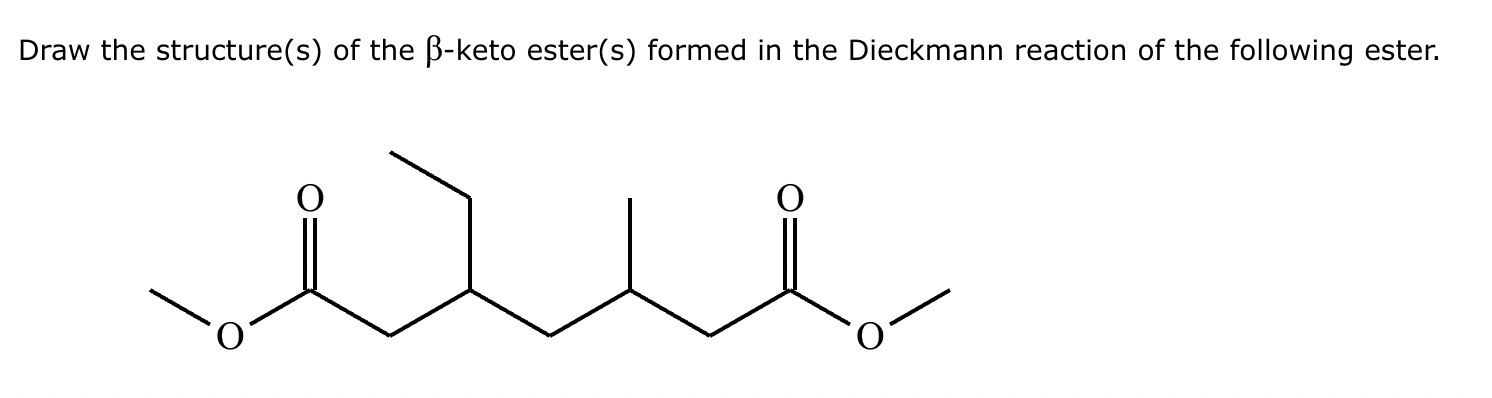
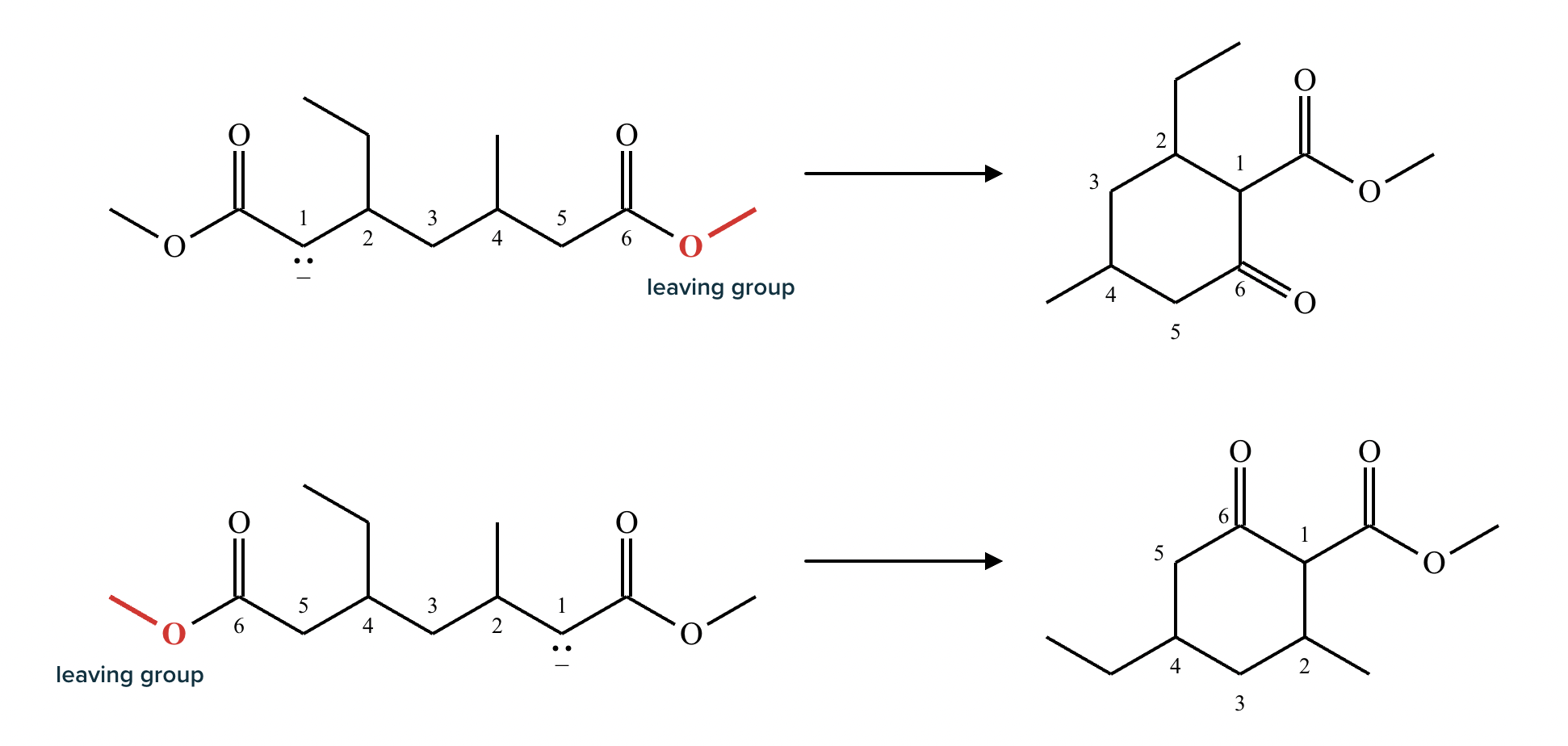
]
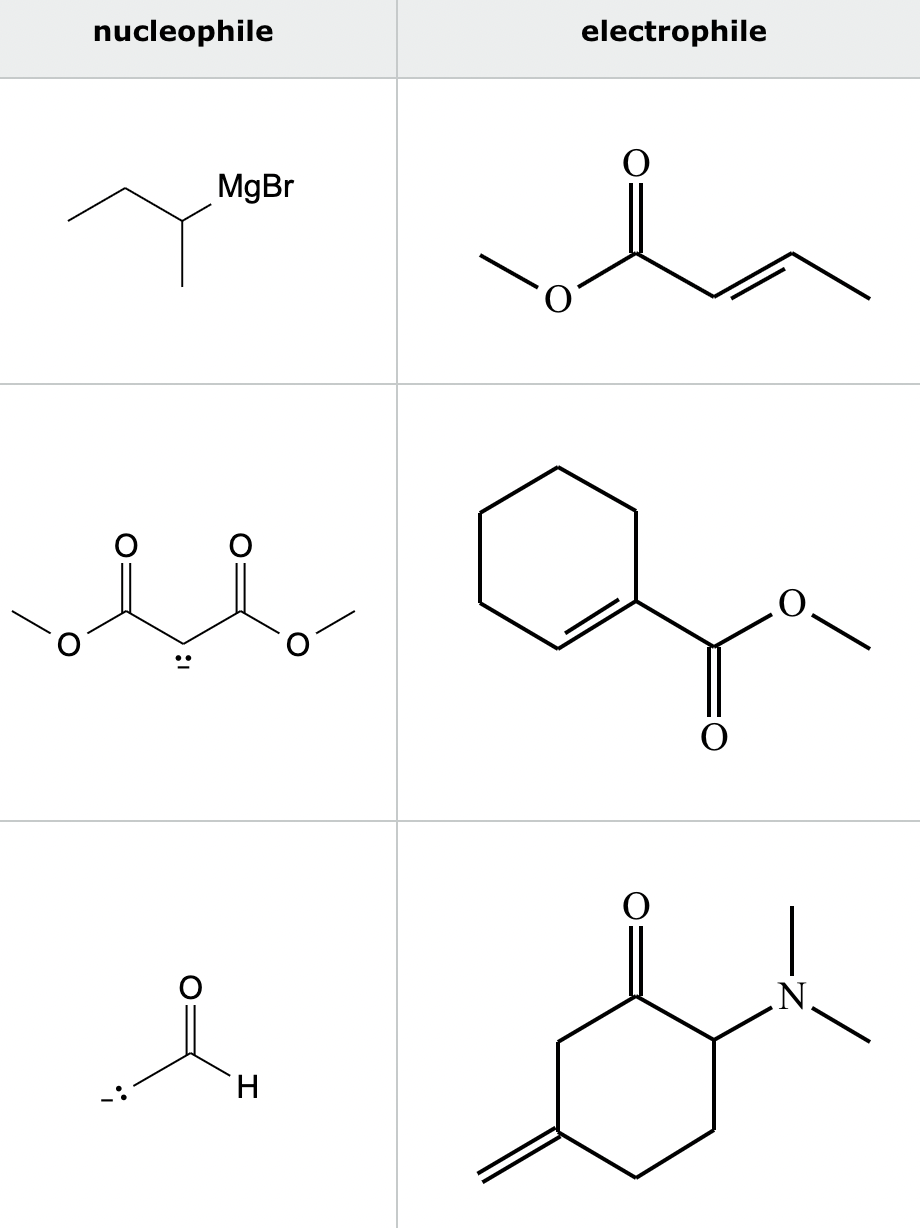
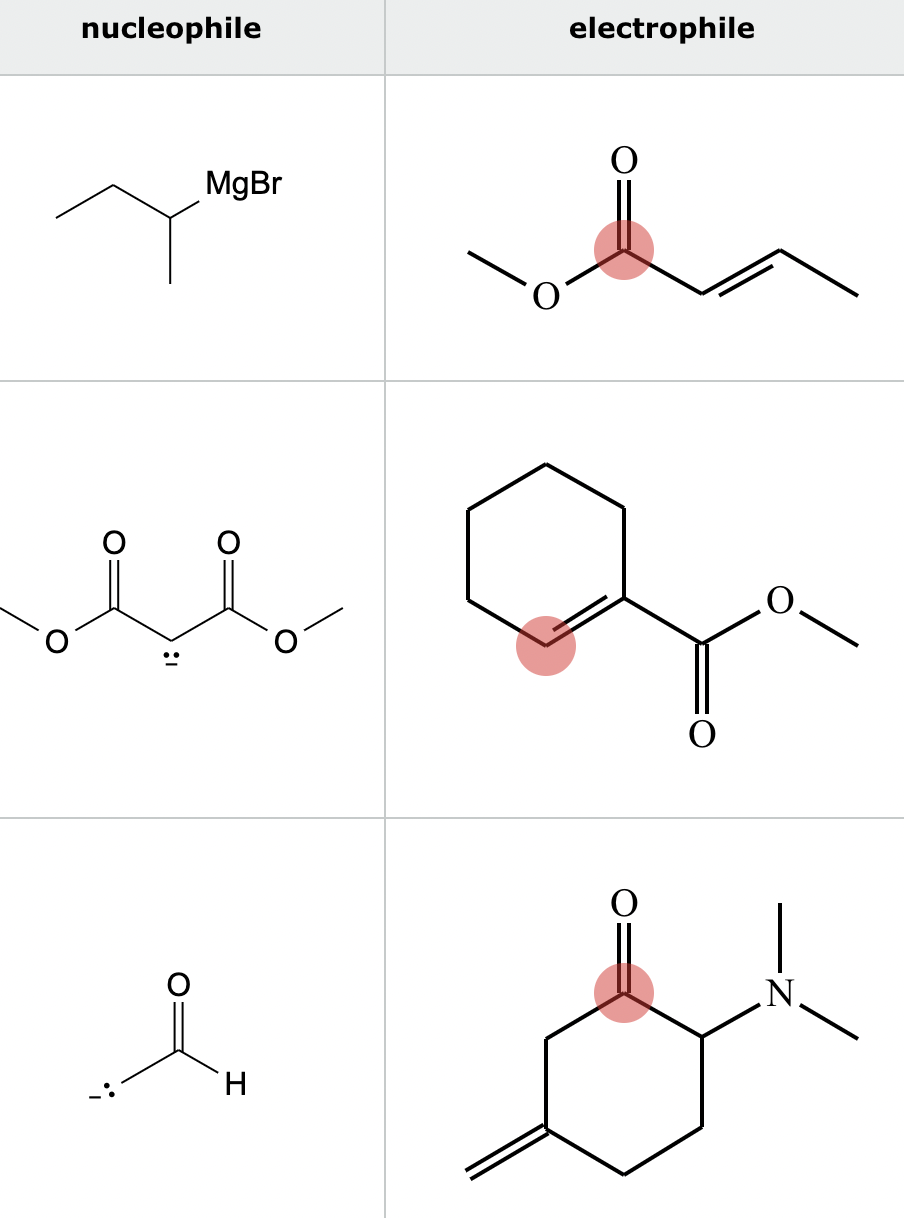
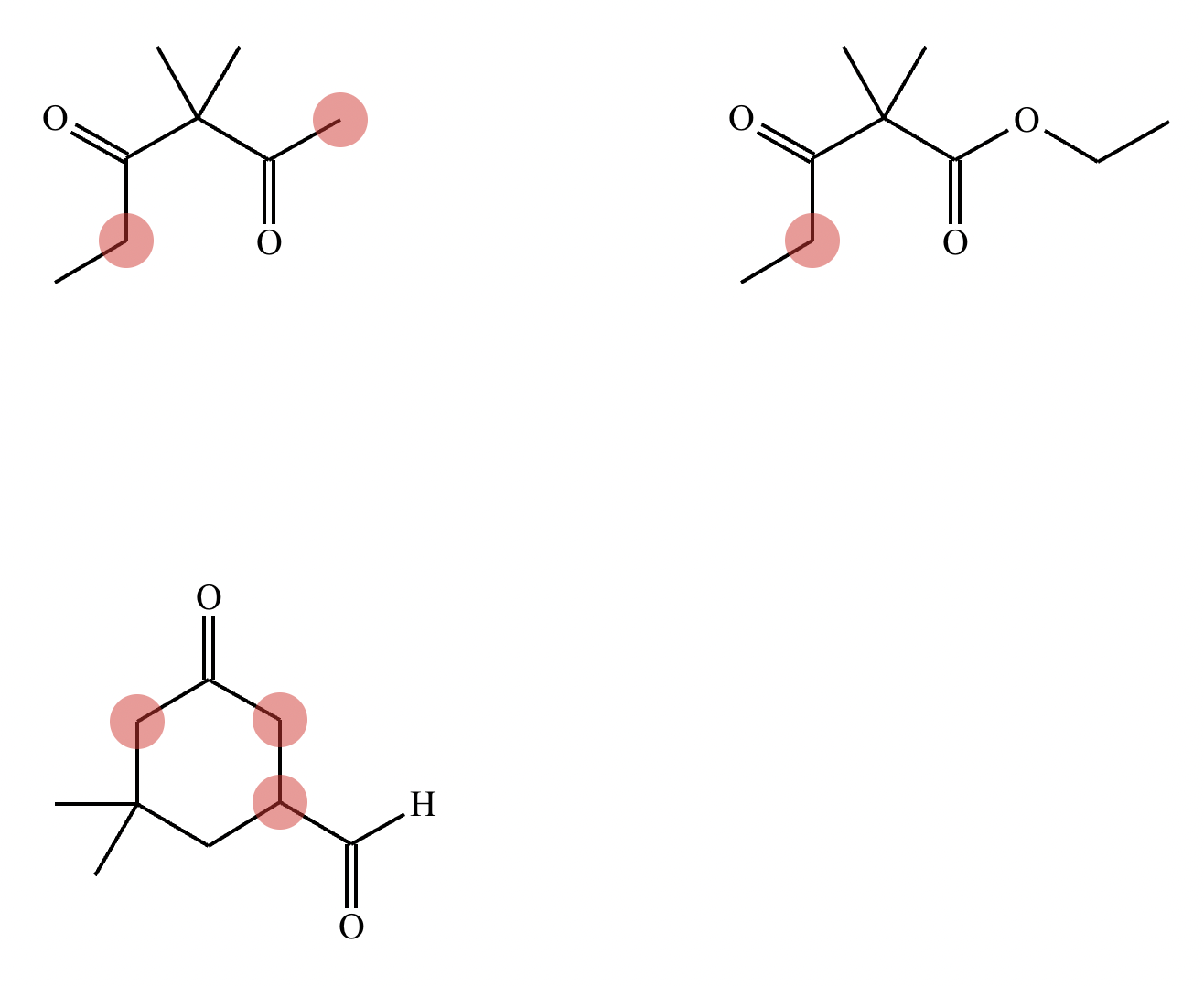
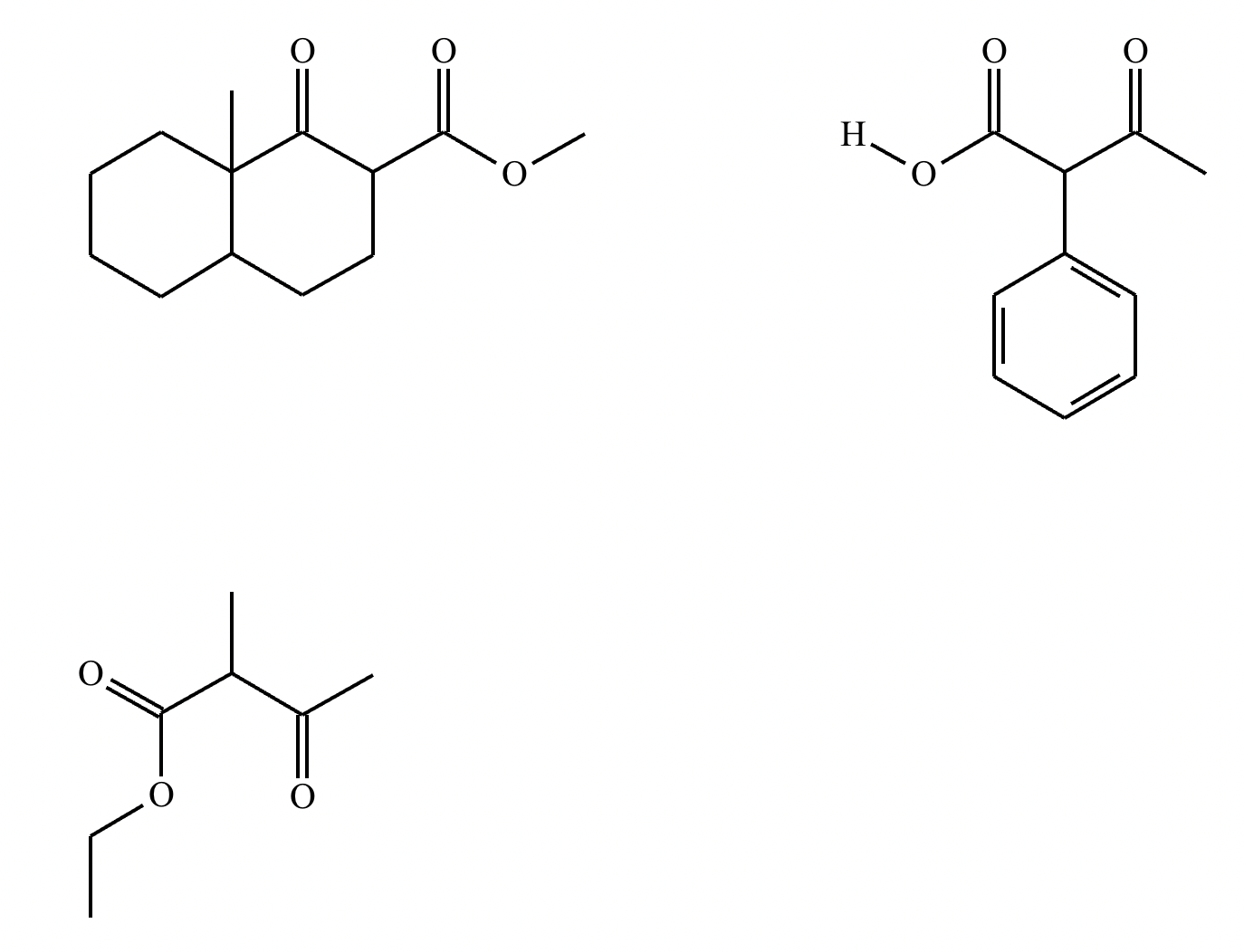
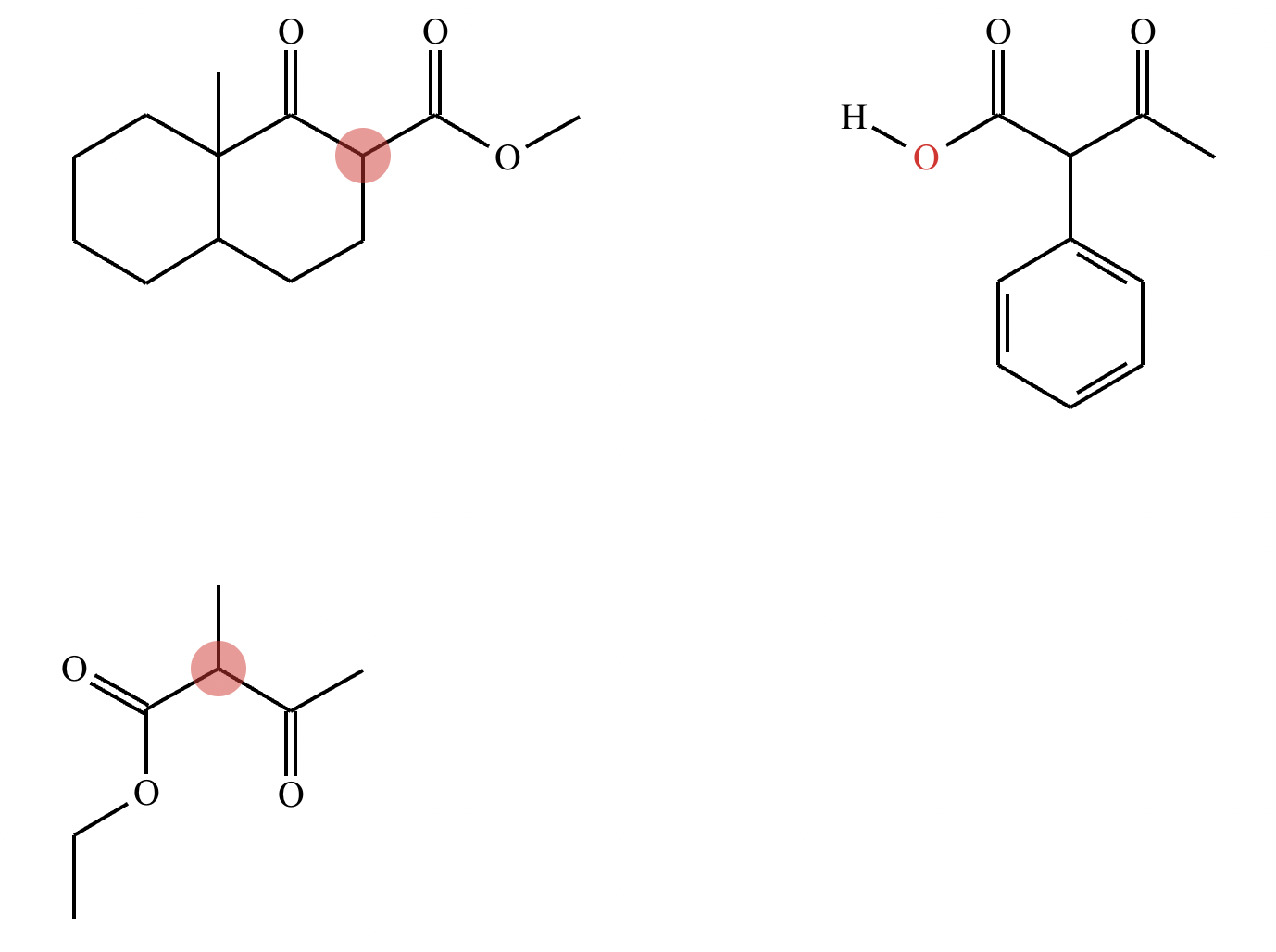
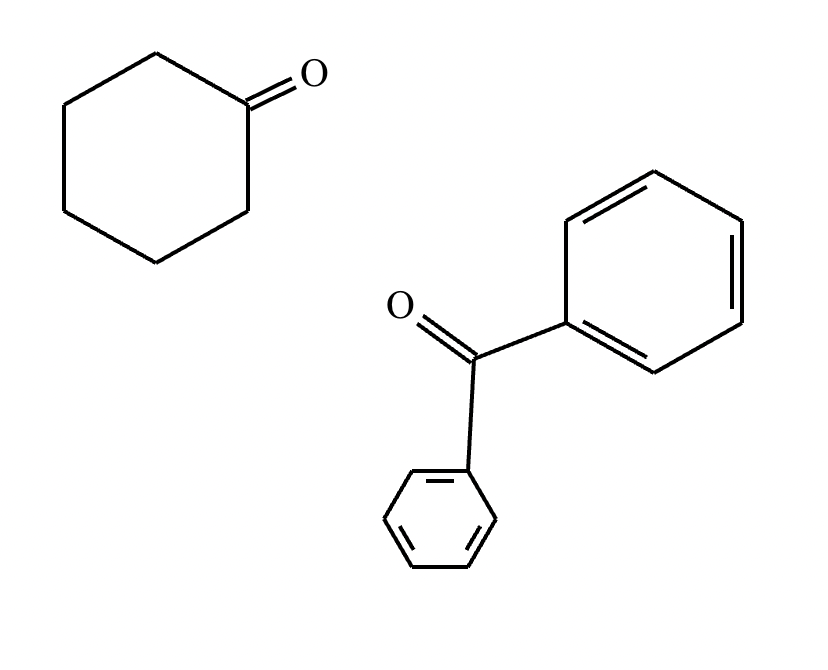
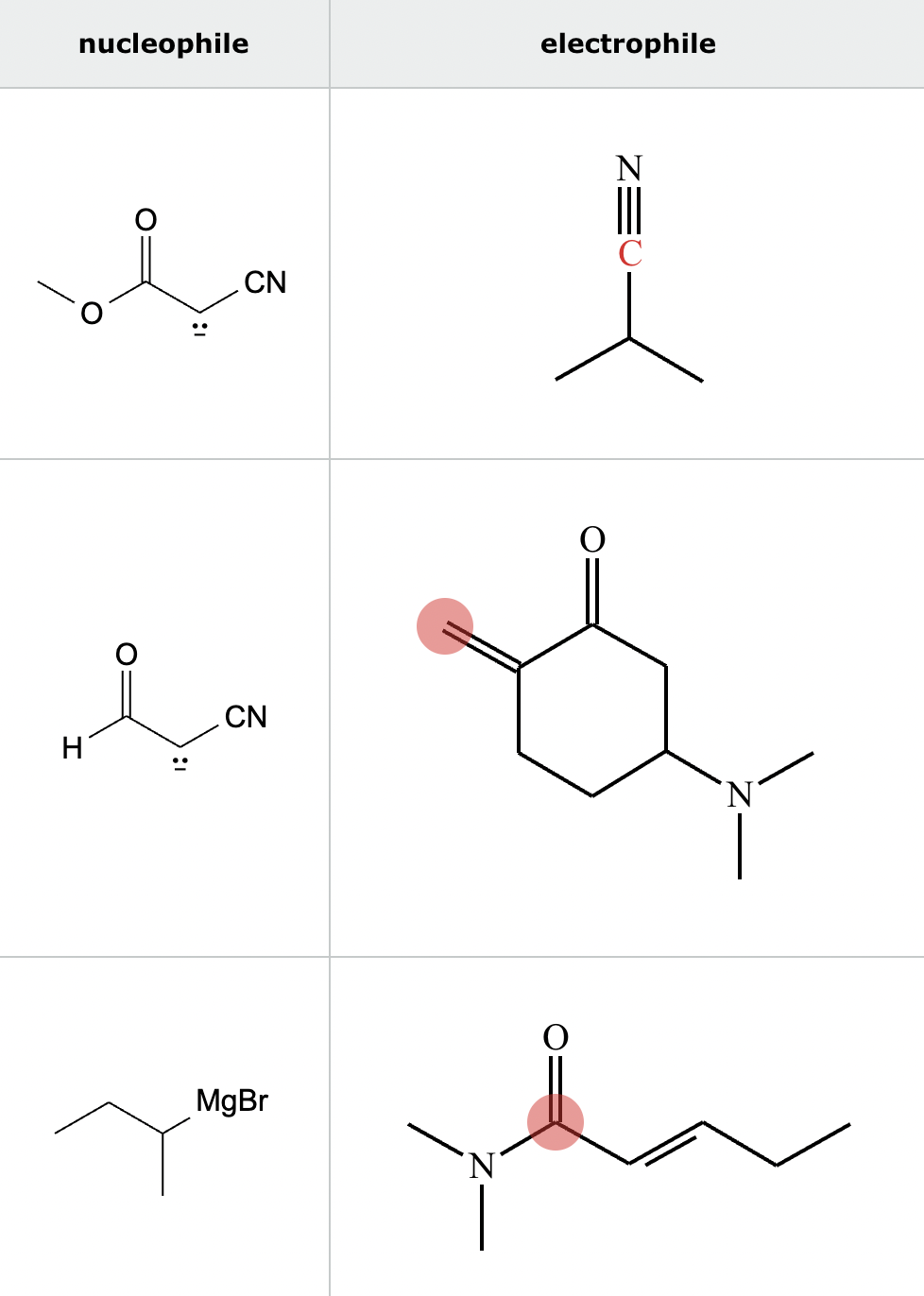
Highlight the atom in each electrophile to which the nucleophile is most likely to form a new bond.
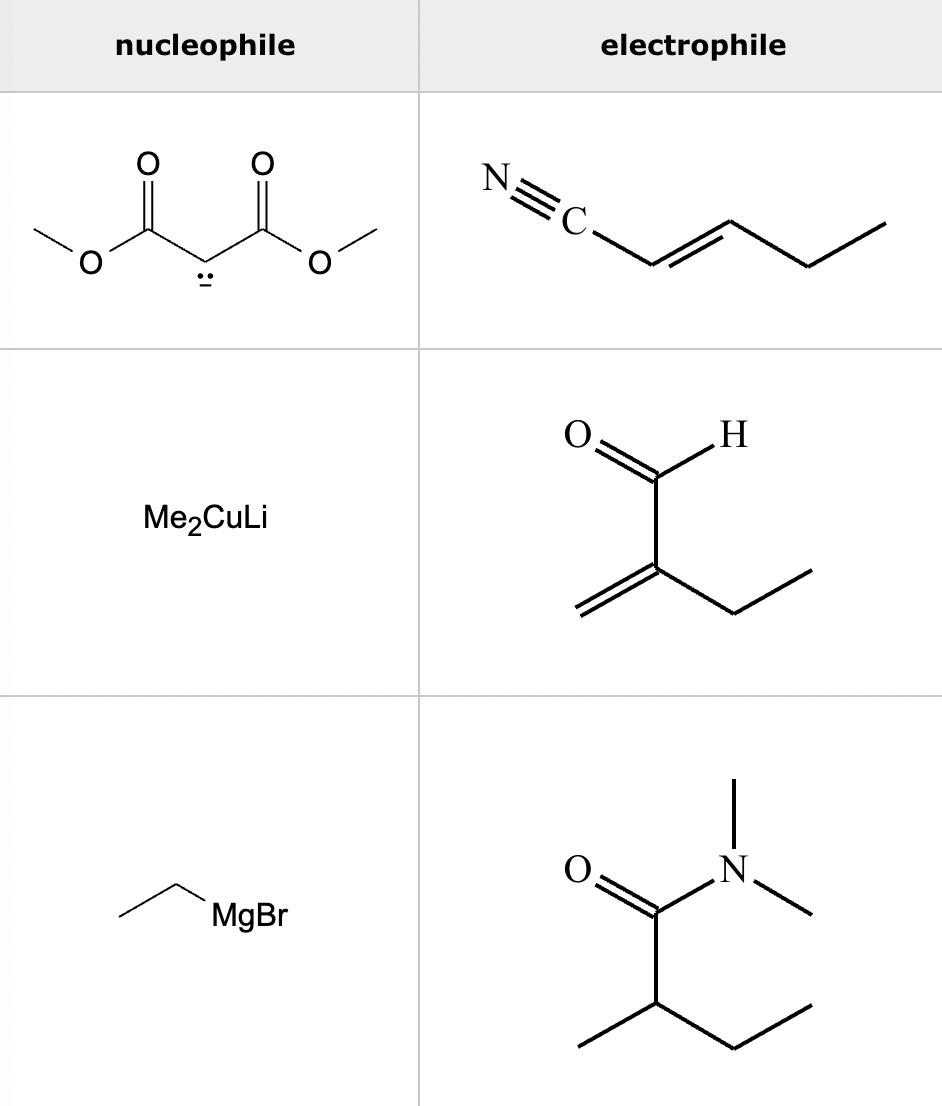
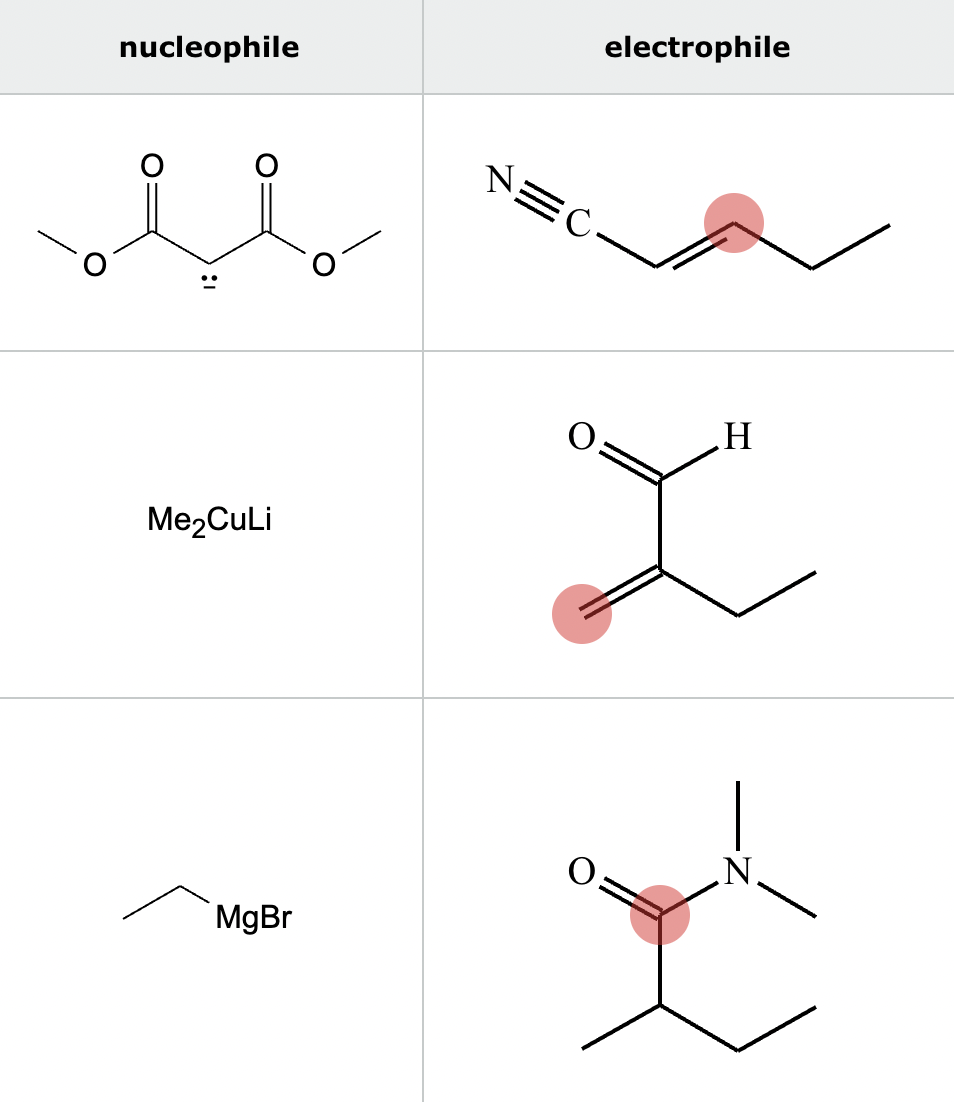
Highlight the atom in each electrophile to which the nucleophile is most likely to form a new bond.
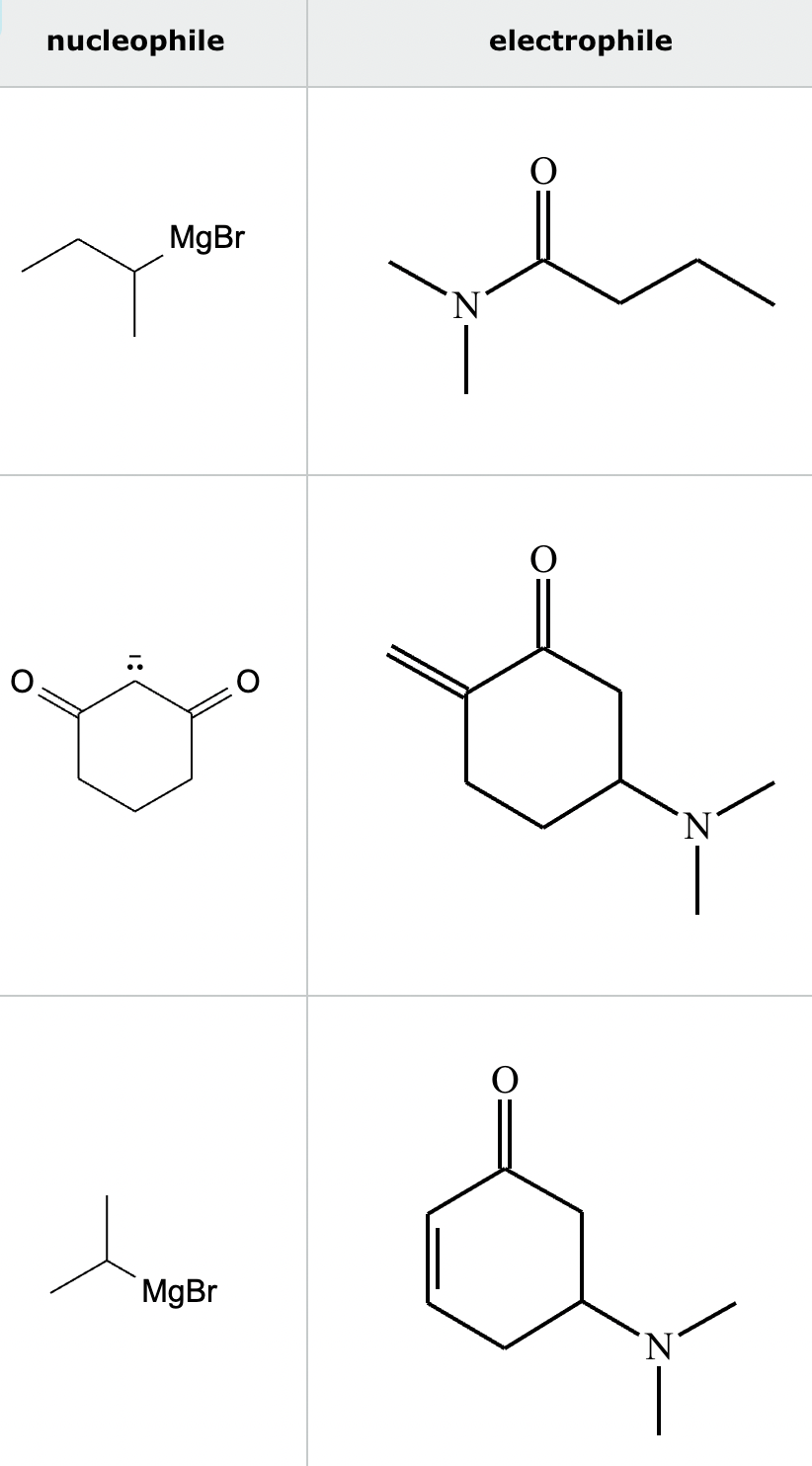
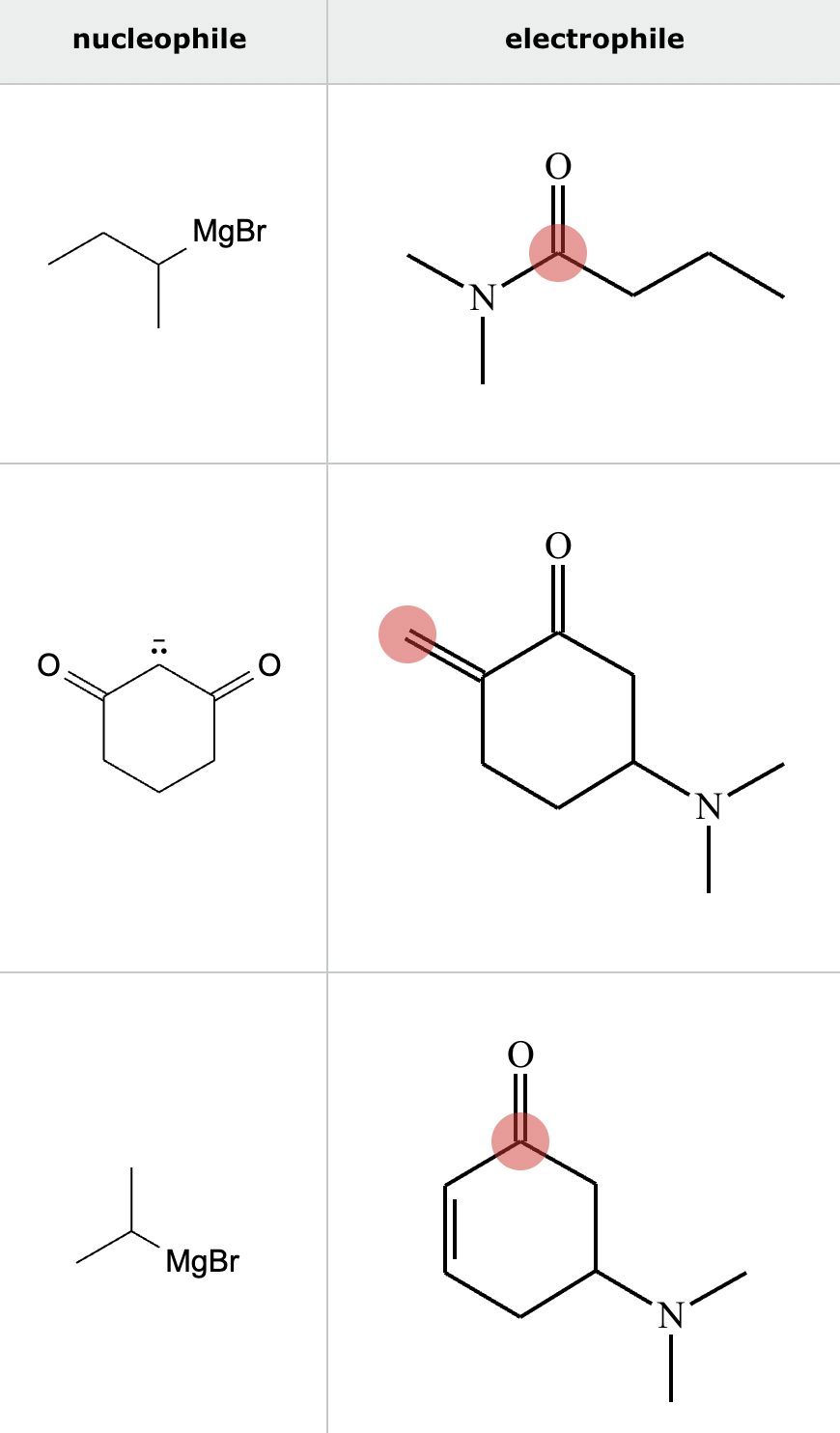
Highlight the atom in each electrophile to which the nucleophile is most likely to form a new bond.
(Answers already included).
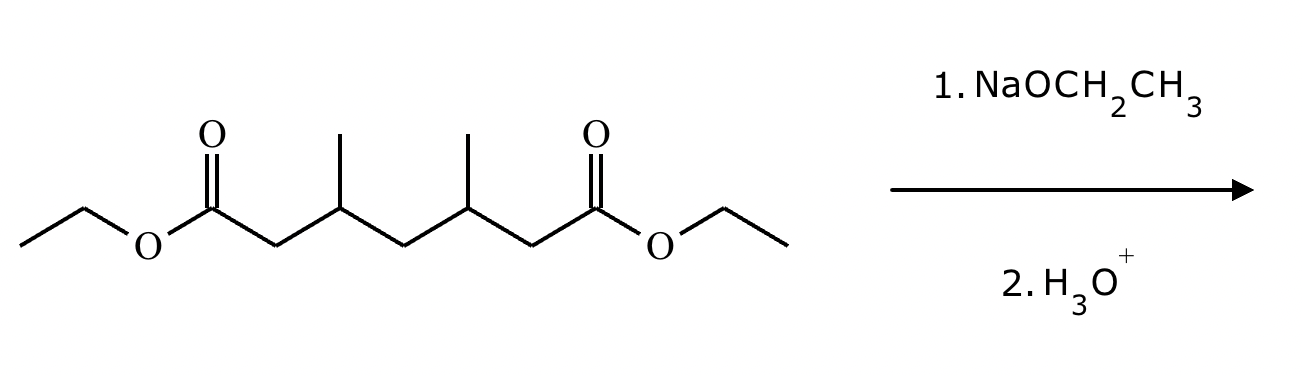
Complete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead.
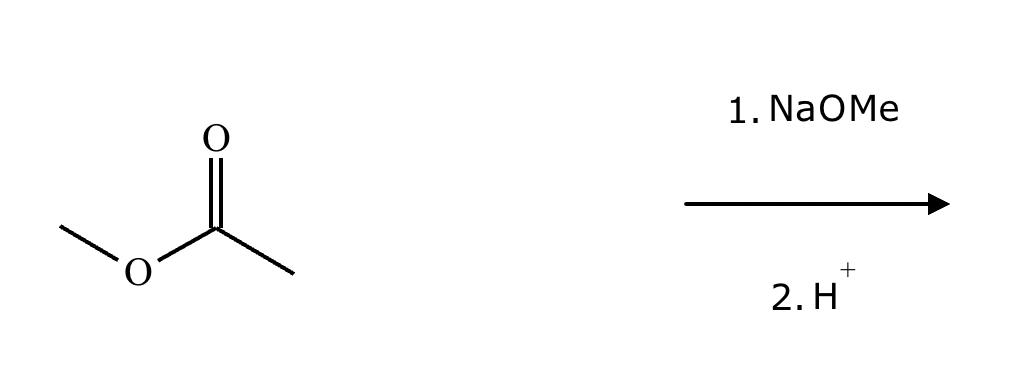
A student claims the right-hand side of the reaction in the drawing area below shows the product of a Claisen condensation. If the student is correct, complete the reaction by adding the necessary organic reactants to the left-hand side and by adding any necessary reagents and reaction conditions above and below the arrow. If the student is incorrect because it's not possible to obtain this product from a Claisen condensation, check the box under the drawing area instead.
Complete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead.
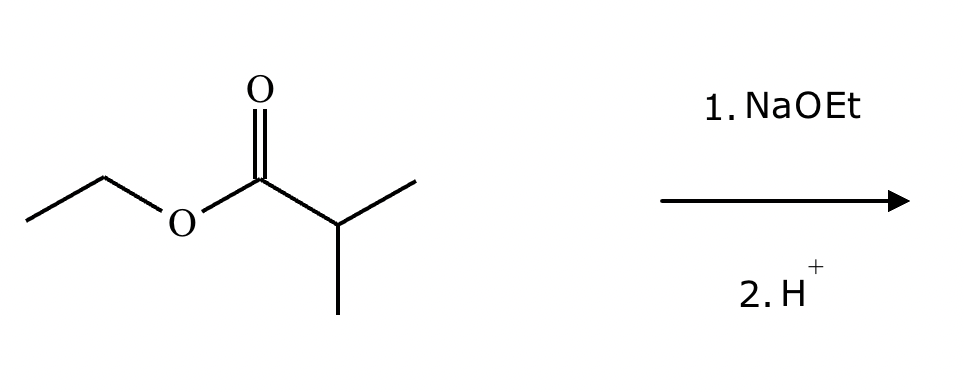
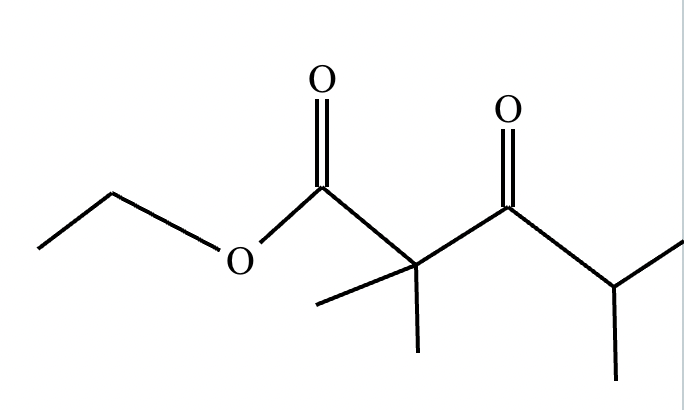
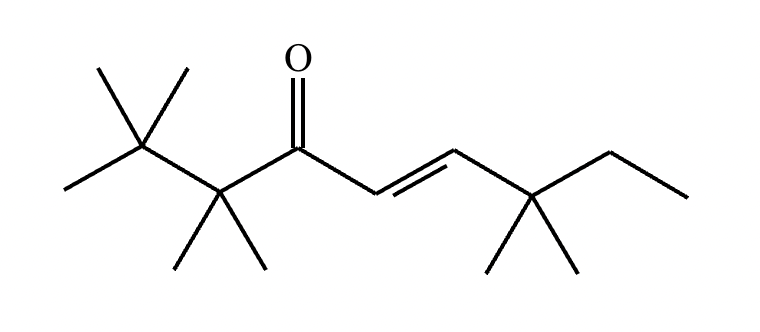
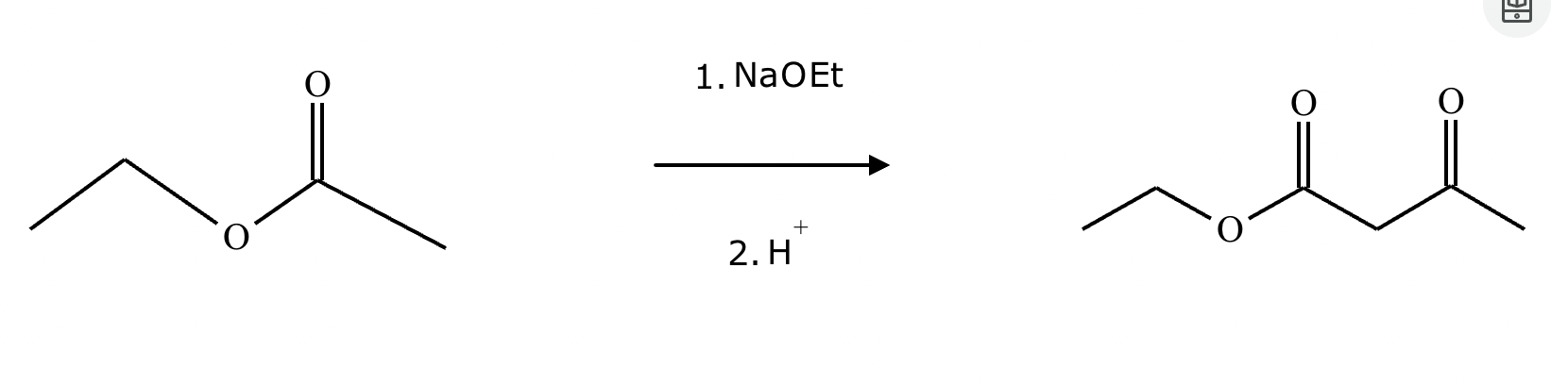
The right-hand side of this reaction shows the product of an aldol condensation. What are the reactants missing from the left-hand side? Draw them below.
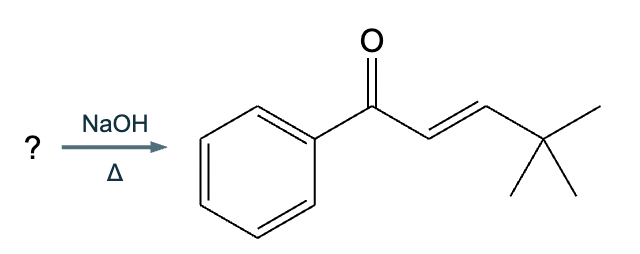
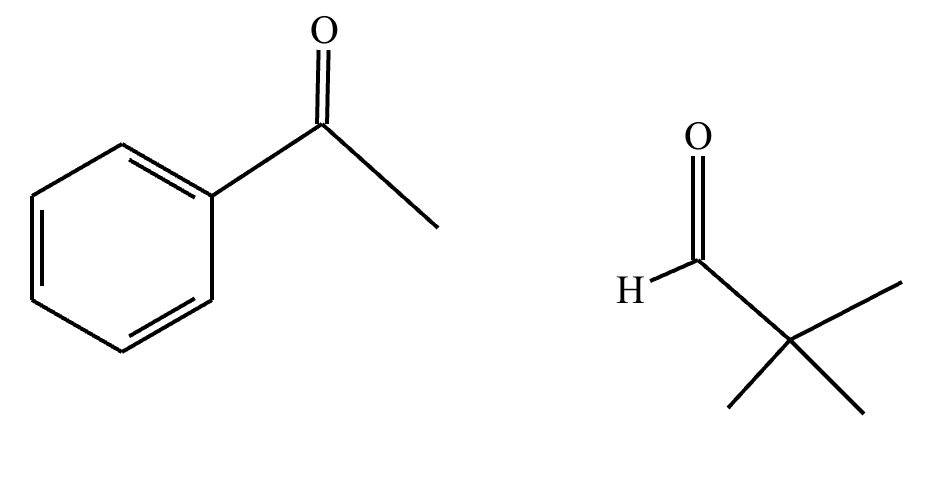
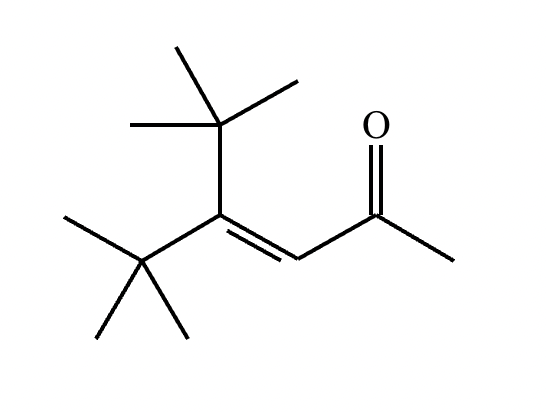
The right-hand side of this reaction shows the product of an aldol condensation. What are the reactants missing from the left-hand side? Draw them below.
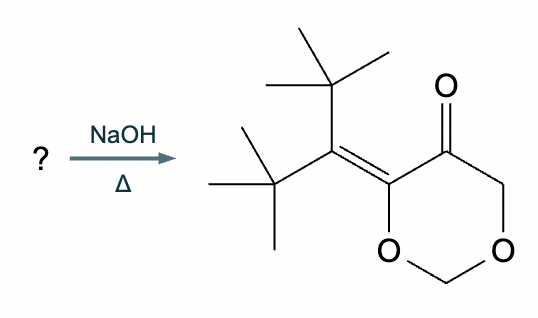
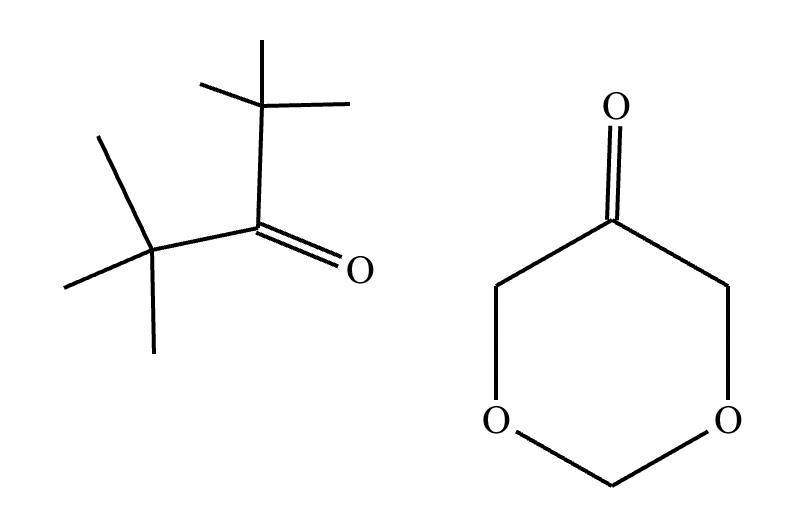
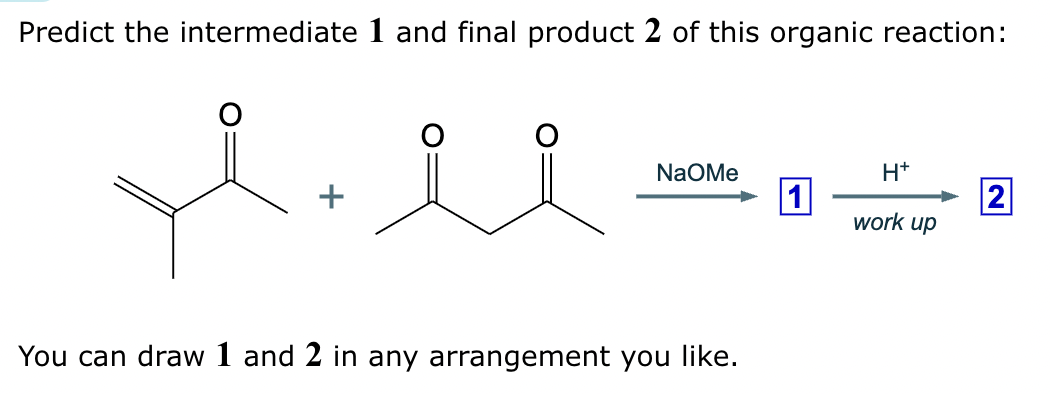
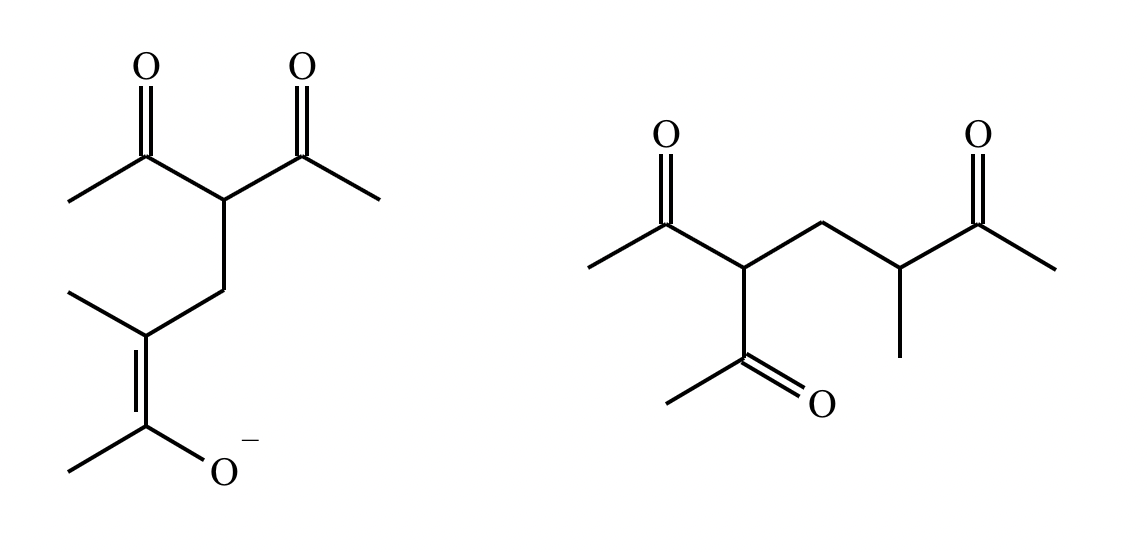
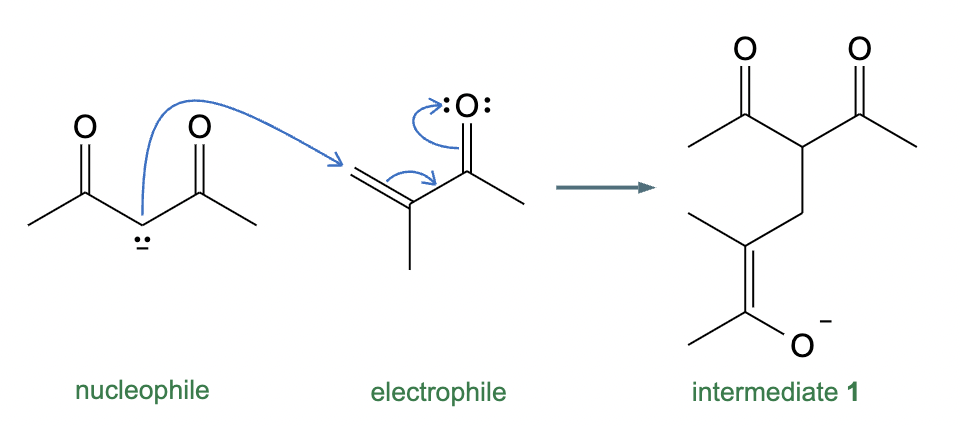
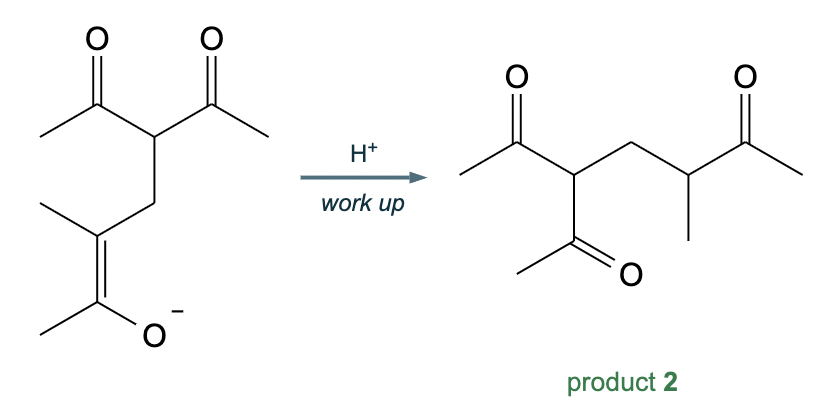
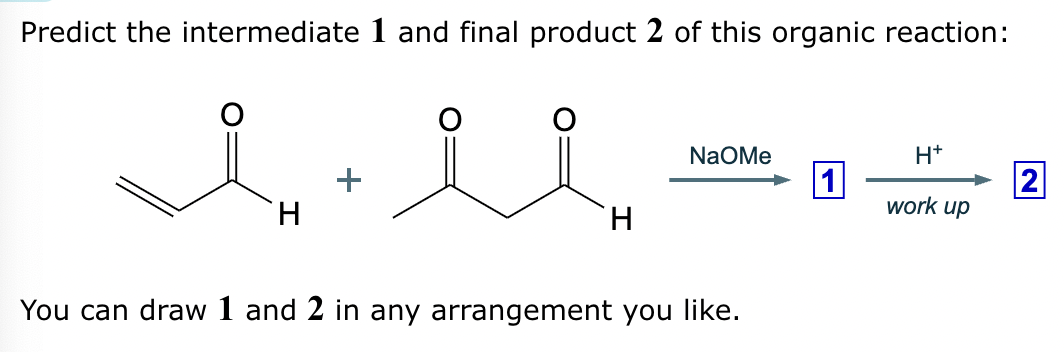
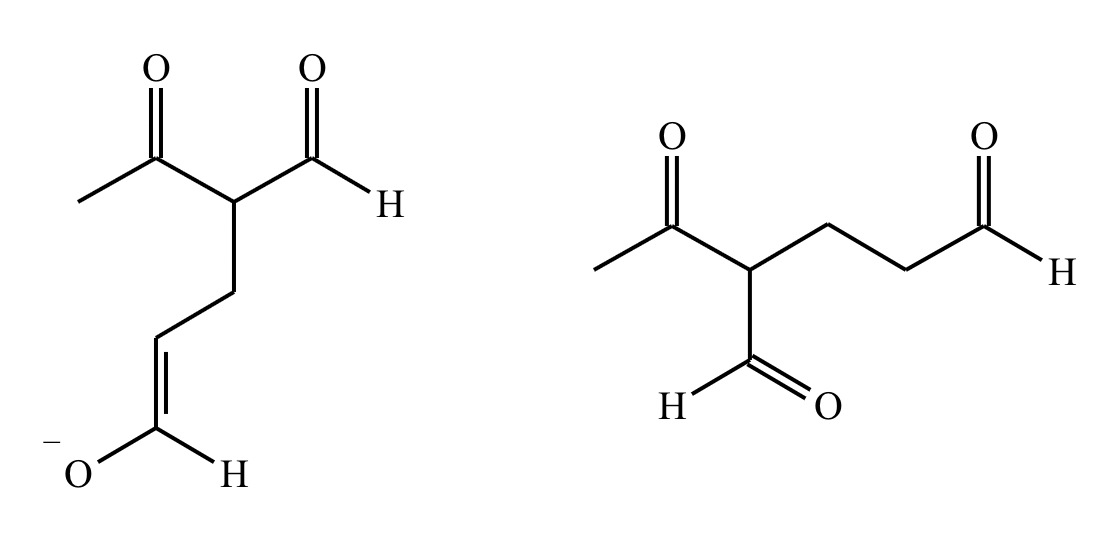
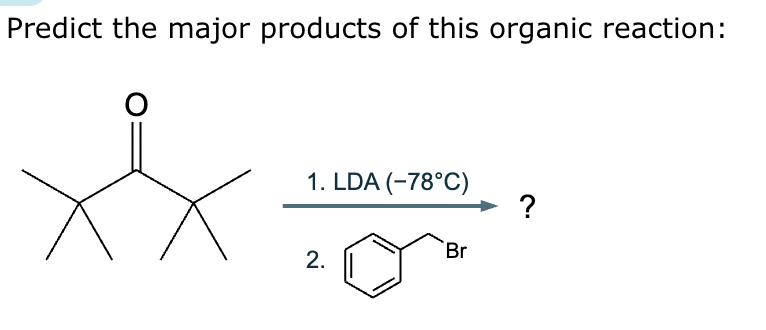
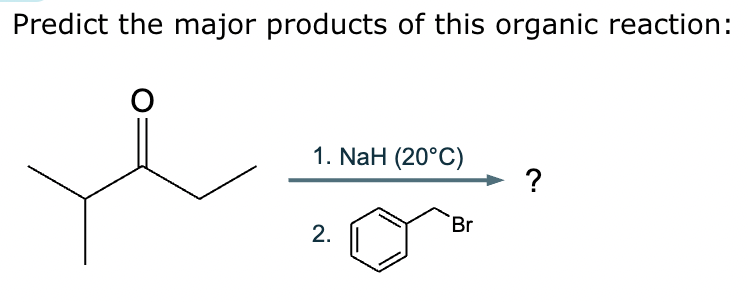
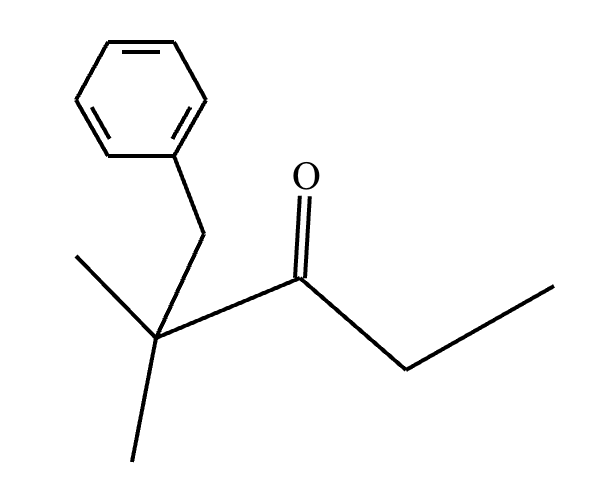
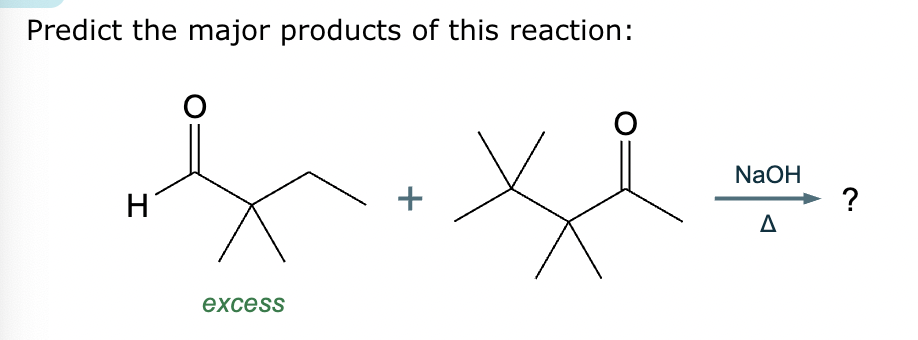
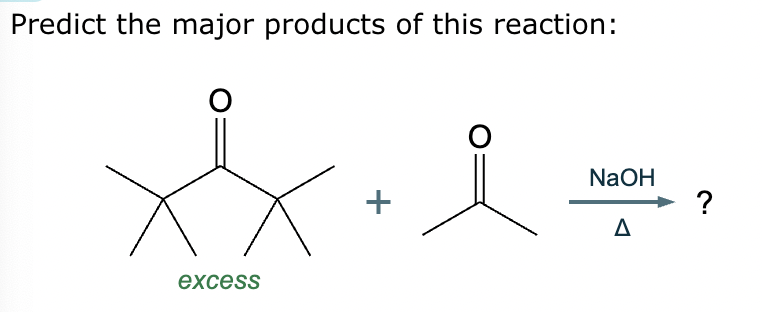
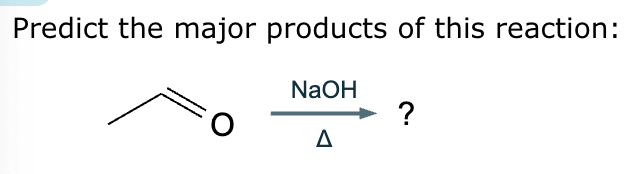
Predict the major products of this reaction:
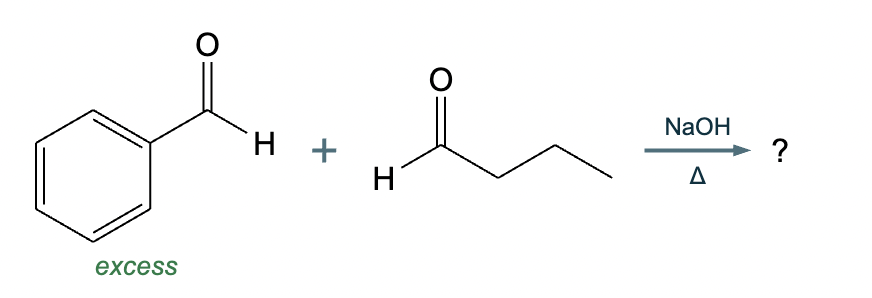
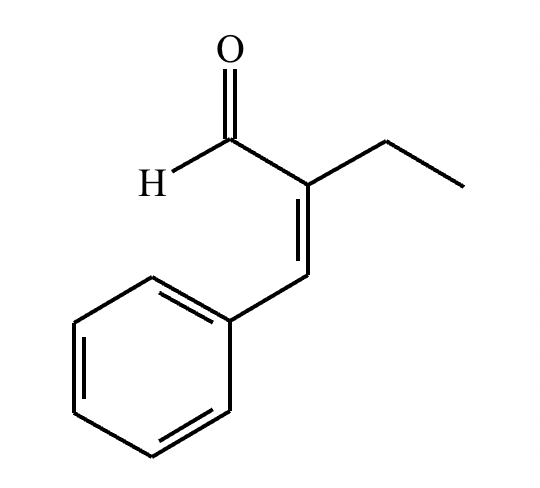
The right-hand side of this reaction shows the product of an aldol condensation. What are the reactants missing from the left-hand side? Draw them below.
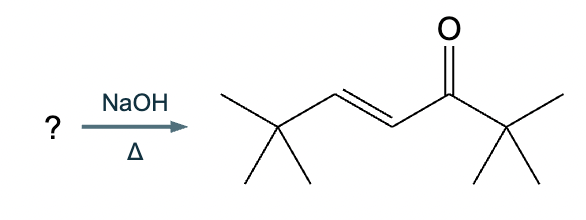
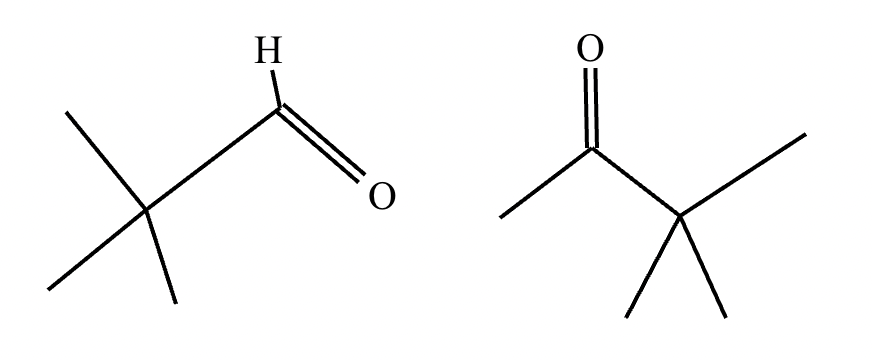
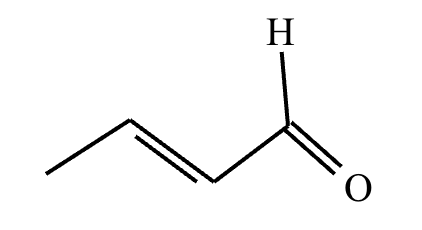
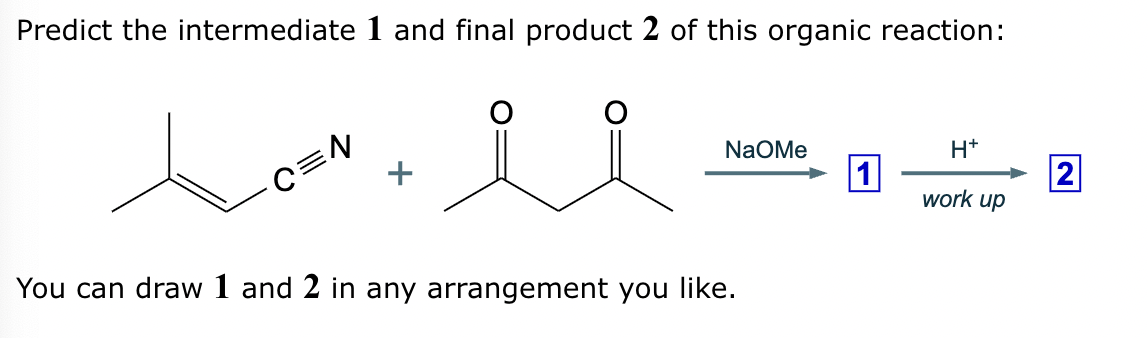
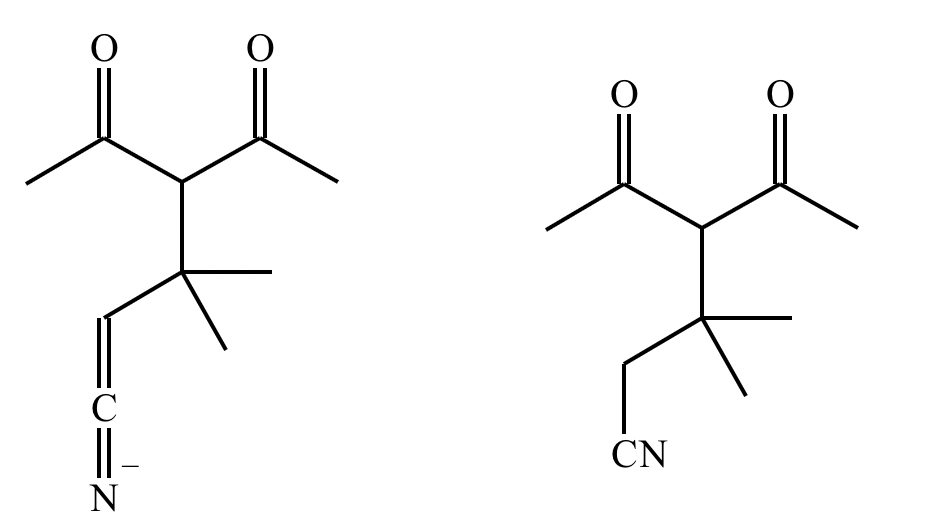
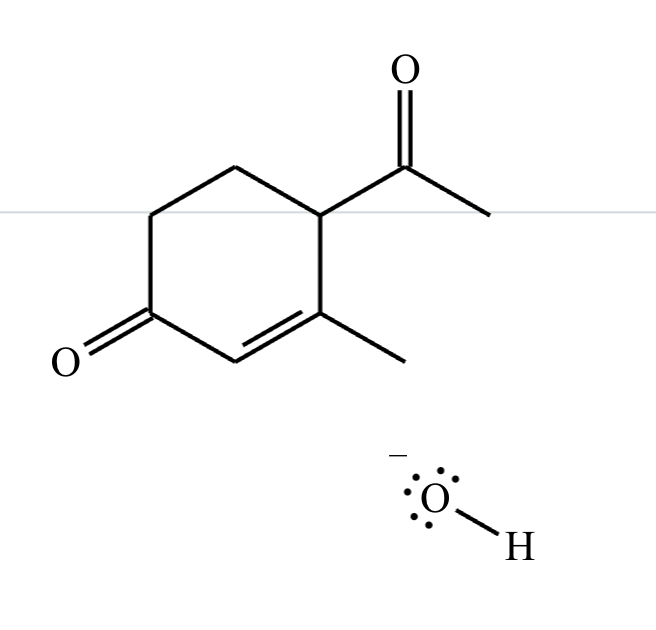
An organic chemistry teaching assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area.
The TA is wrong.
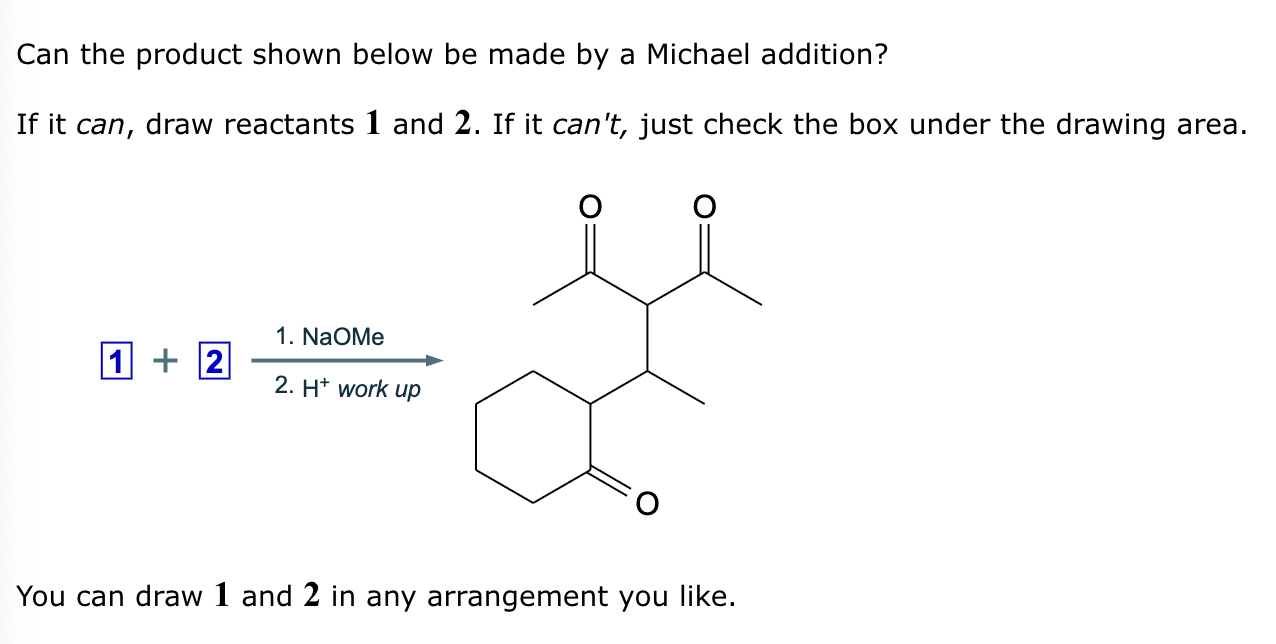
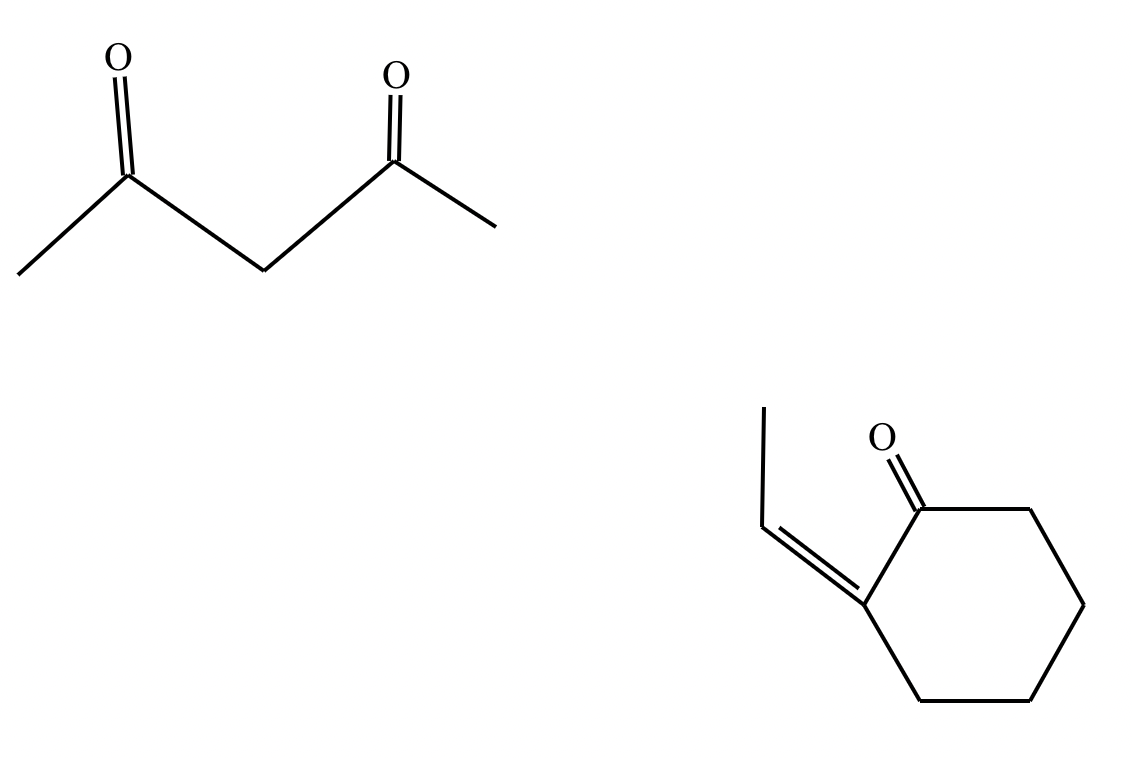
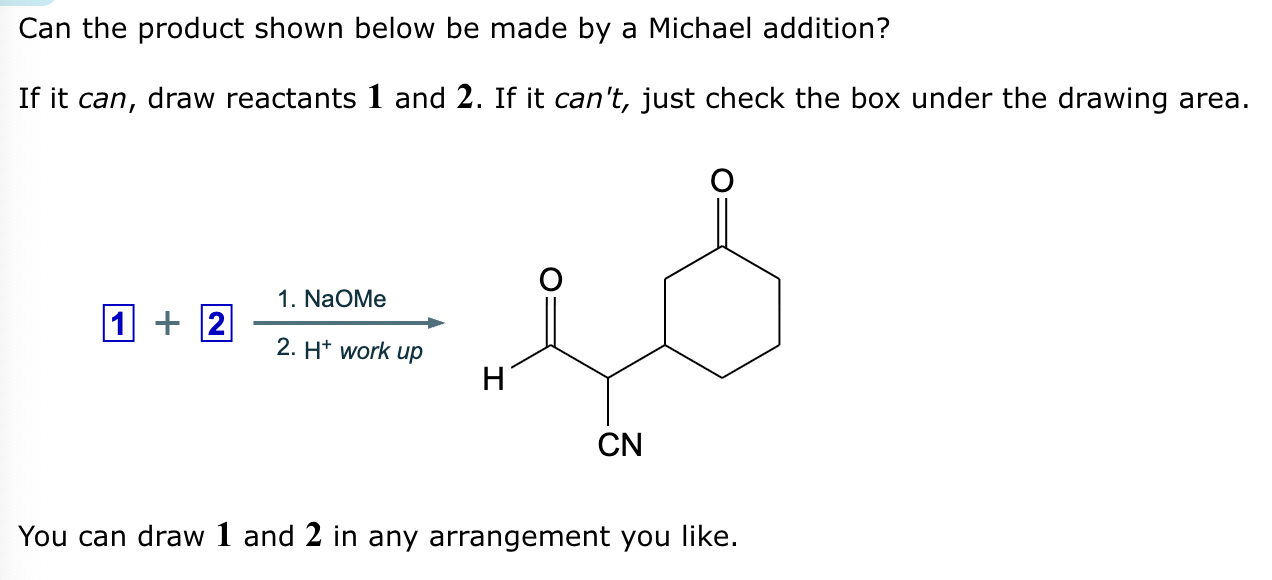
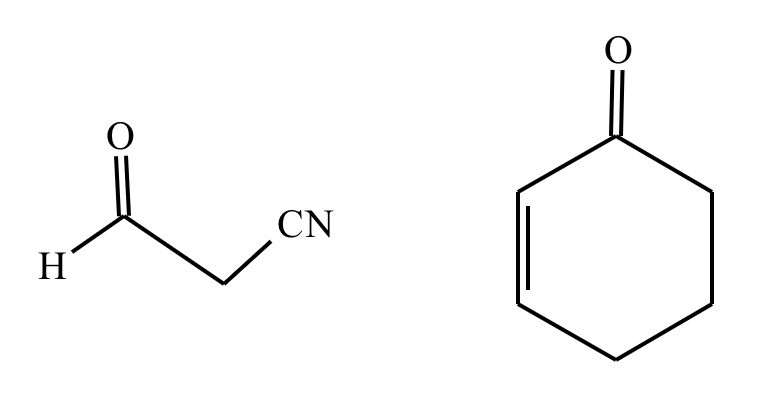
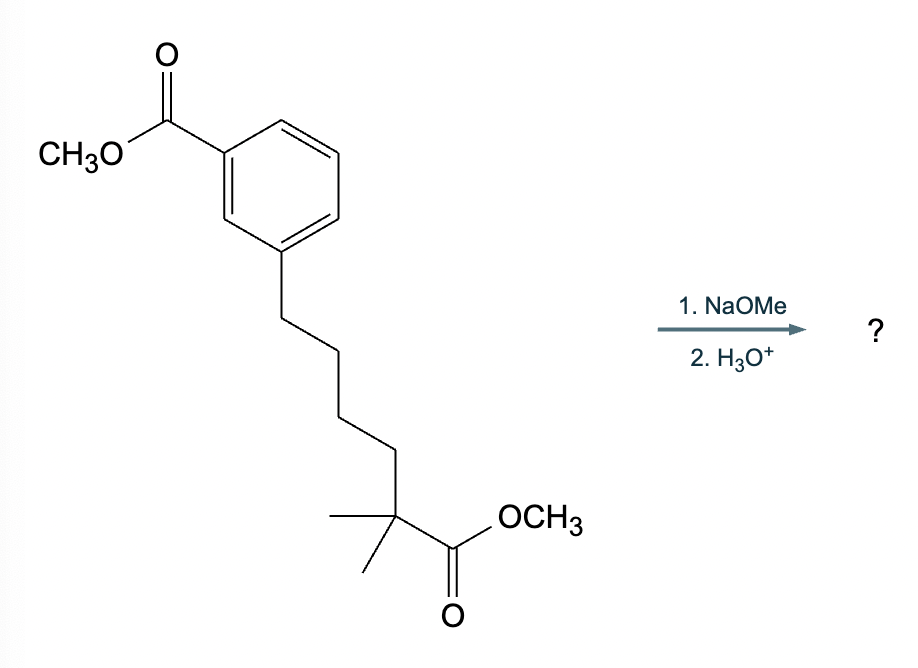
A student suggests that the molecule on the right can be made from a single starting molecule 1, under the conditions written above and below the arrow. Is the student correct? If so, draw 1 in the area below. If the student is not correct, just check the box under the drawing area.
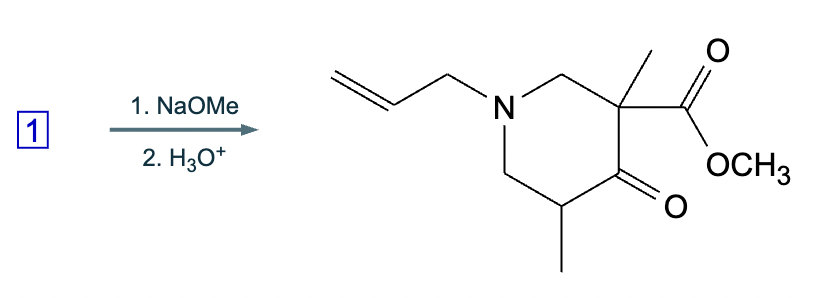
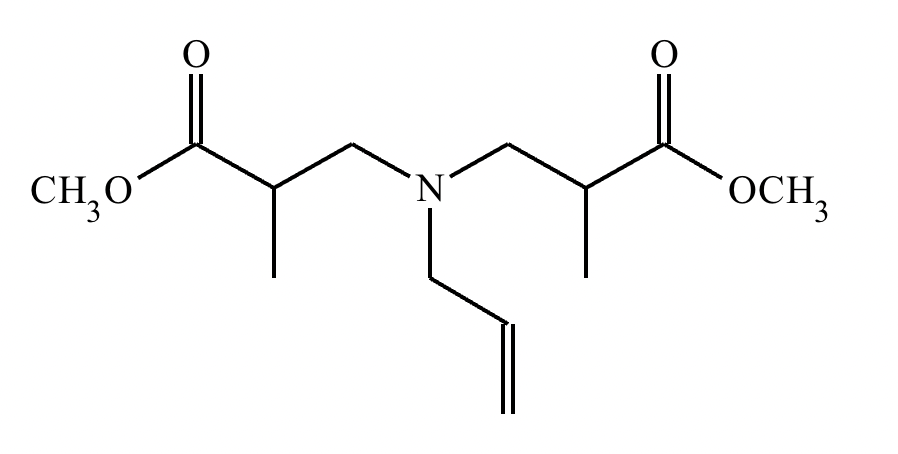
An organic chemistry teaching assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area.
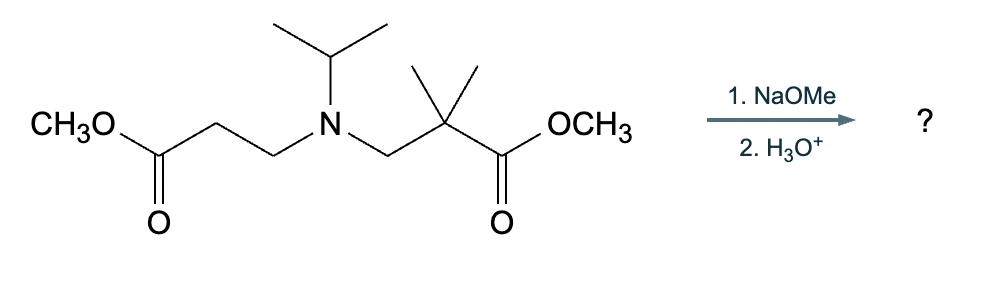

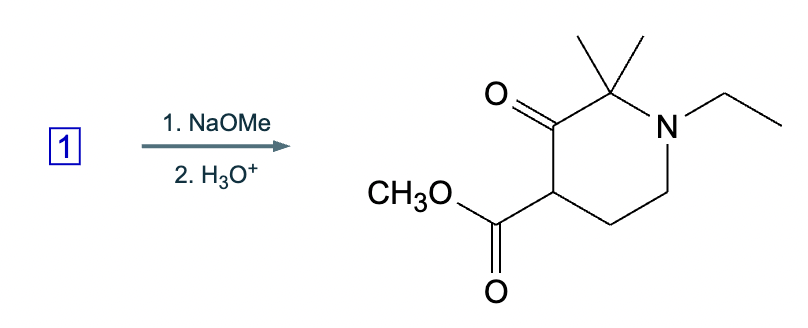
A student suggests that the molecule on the right can be made from a single starting molecule, 1, under the conditions written above and below the arrow. Is the student correct? If so, draw 1 in the area below. If the student is not correct, just check the box under the drawing area.
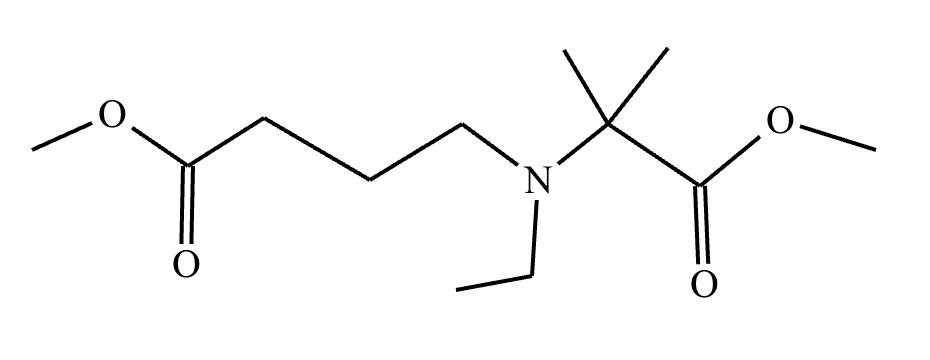
An organic chemistry teaching assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area.
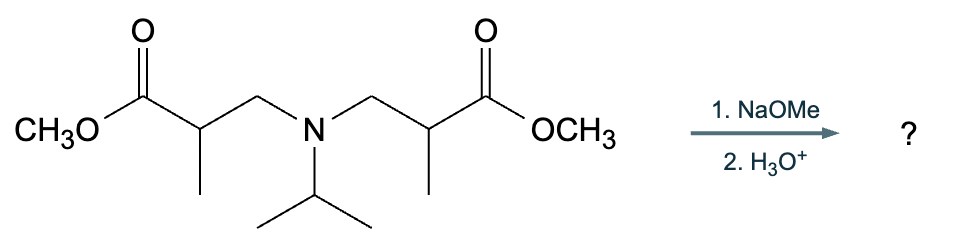
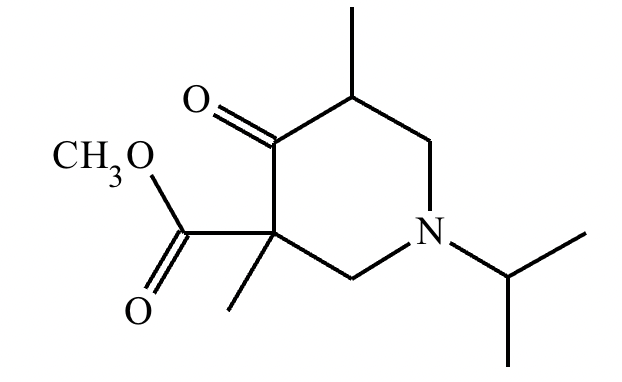
A student suggests that the molecule on the right can be made from a single starting molecule, 1, under the conditions written above and below the arrow. Is the student correct? If so, draw 1 in the area below. If the student is not correct, just check the box under the drawing area.
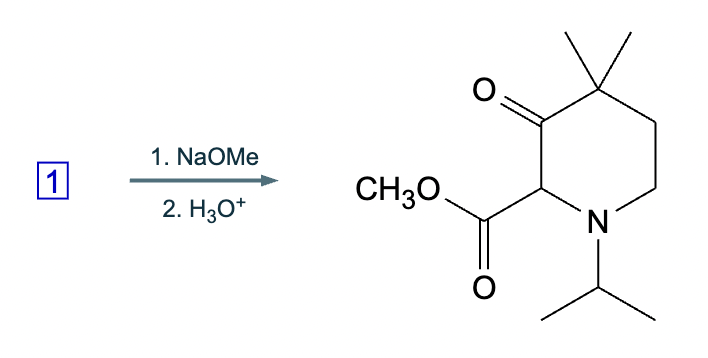
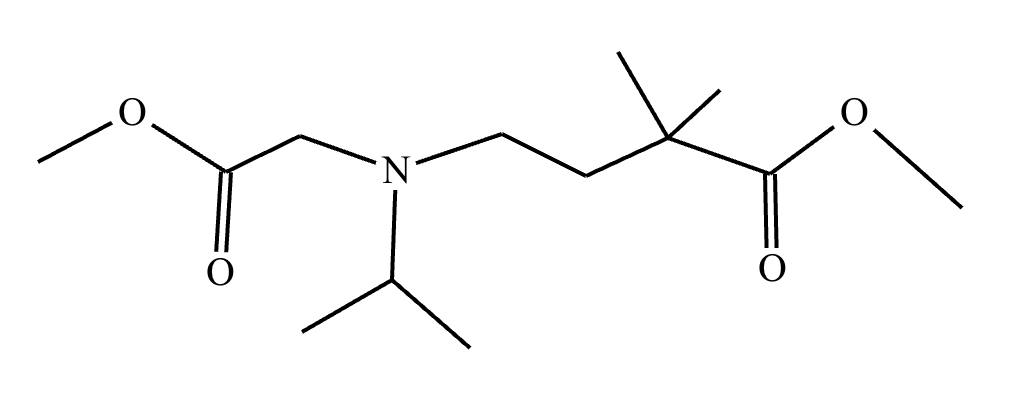
A student suggests that the molecule on the right can be made from a single starting molecule 1, under the conditions written above and below the arrow. Is the student correct? If so, draw 1 in the area below. If the student is not correct, just check the box under the drawing area.
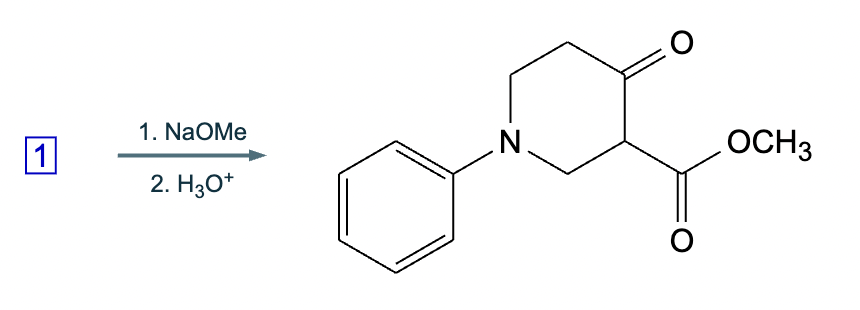
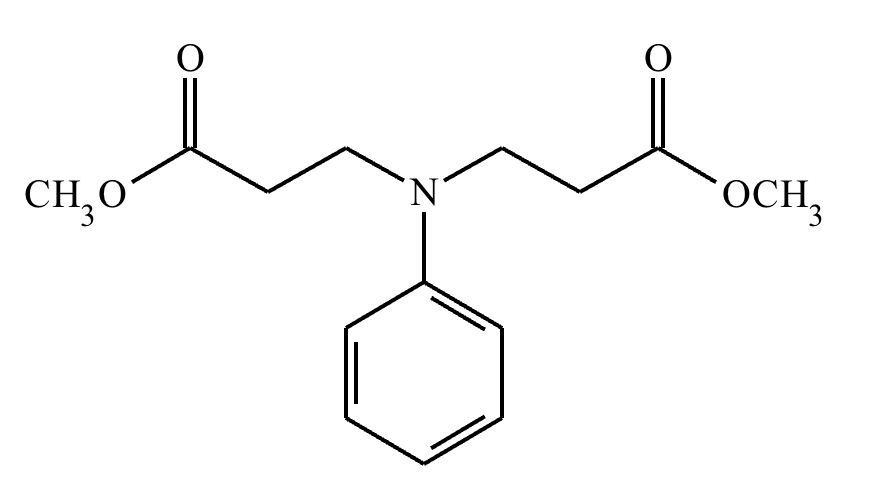
A student suggests that the molecule on the right can be made from a single starting molecule, 1, under the conditions written above and below the arrow. Is the student correct? If so, draw 1 in the area below. If the student is not correct, just check the box under the drawing area.
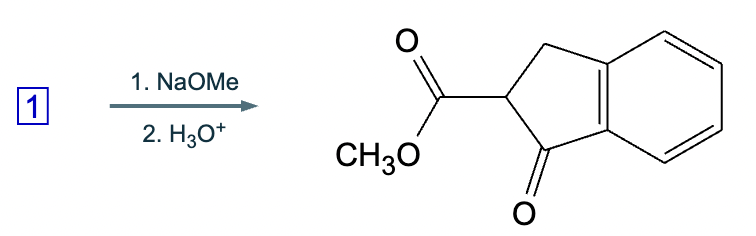
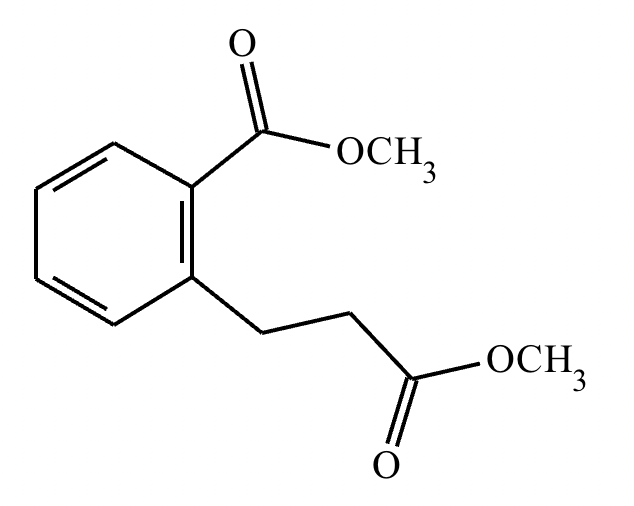
An organic chemistry Teaching Assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area.
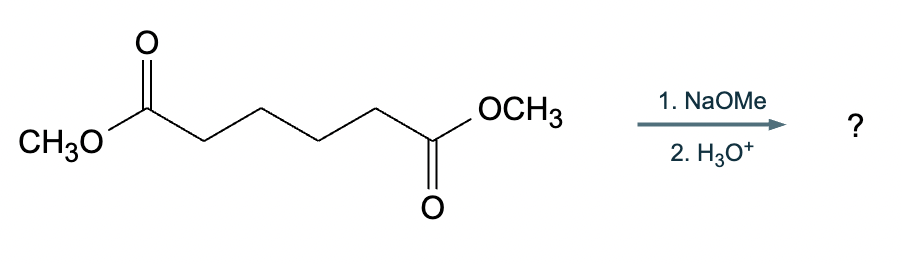
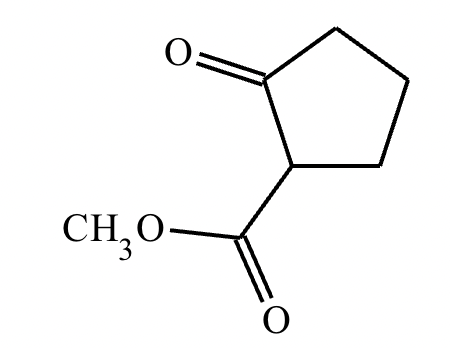
A student suggests that the molecule on the right can be made from a single starting molecule, 1, under the conditions written above and below the arrow. Is the student correct? If so, draw 1 in the area below. If the student is not correct, just check the box under the drawing area.
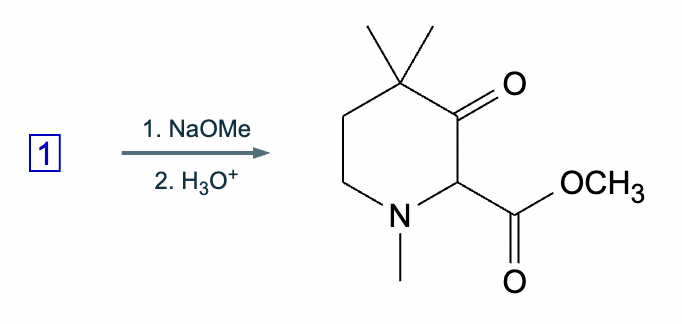
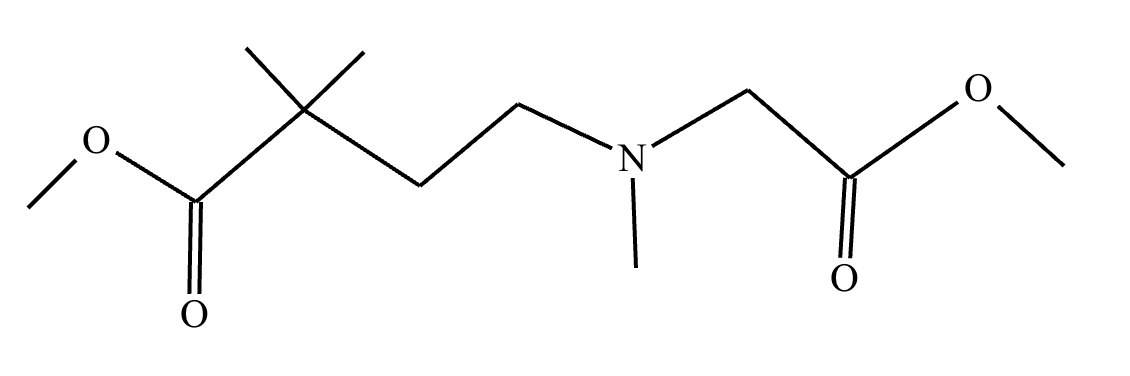
An organic chemistry teaching assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area.
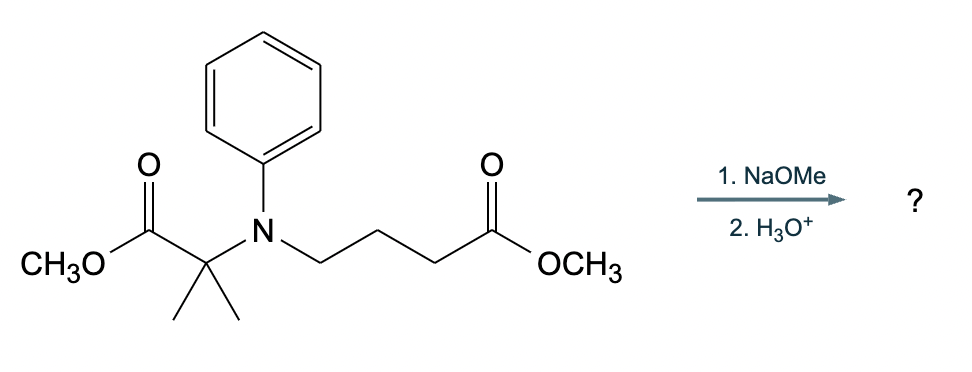
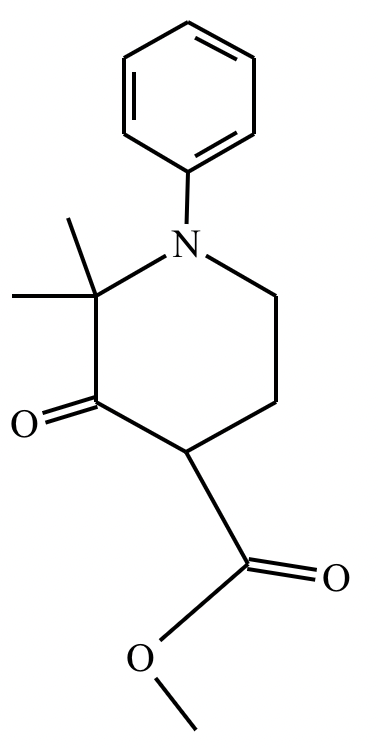
Highlight the atom in each electrophile to which the nucleophile is most likely to form a new bond.