Final Exam Ch11/Ch12 Practice Problems
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
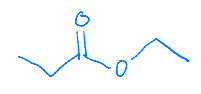

The pKa of acetic acid is 4.74. The pKa for trifluoroacetic acid is 0.23. Explain why trifluoroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
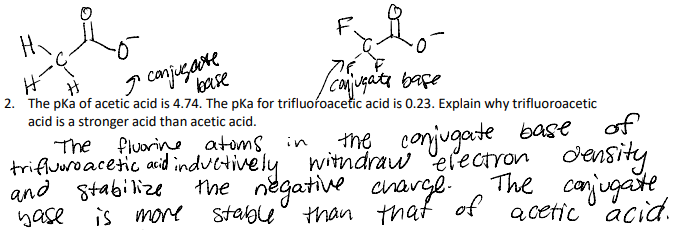
The boiling point of acetic acid and ethanol is 117.9 °C and 78.3 °C, respectively. Explain the substantially higher boiling point of acetic acid compared to ethanol.
Acetic acid forms a dimer with two molecules that have hydrogen bond IMFs. The increase in IMF strength increases the boiling point.
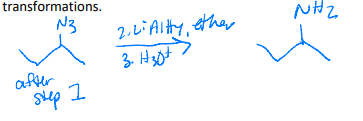
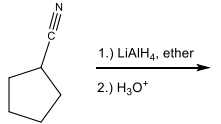

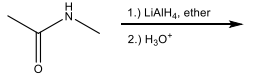

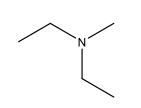
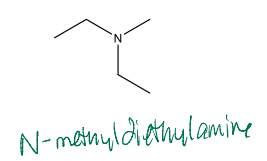
Name the following compound
N-methyldiethylamine
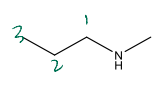
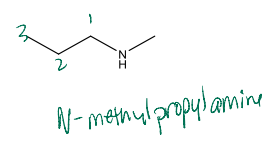
Name the following compound
N-methylpropylamine
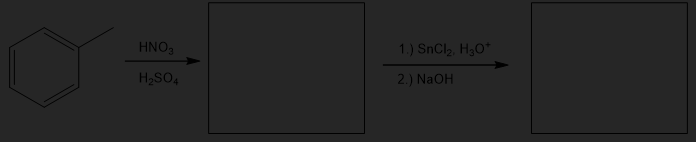
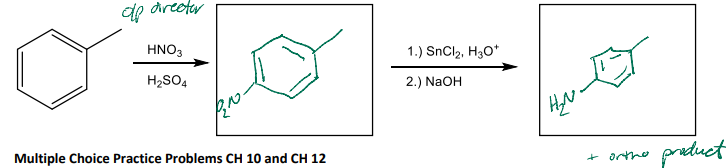
Fill in the products for the following multi-step reaction. The first reaction is nitration of benzene, followed by a reduction reaction.
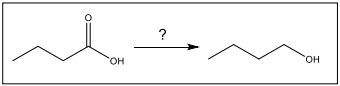
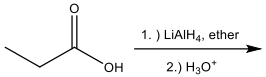
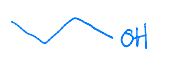
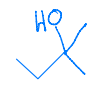
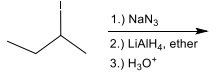
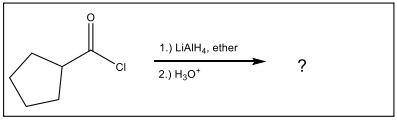
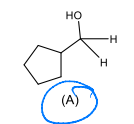
Identify the set of reagents needed to complete the following reduction reaction.
1.) LiAlH4, ether 2.) H3O+
(needs strong reductant)
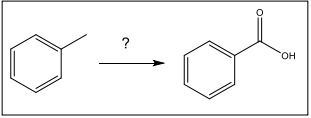
Identify the set of reagents need to oxidize toluene to benzoic acid.
KMnO4, H2O
In general, which carboxylic acid derivative has the fastest rate for nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions?
Acid halide
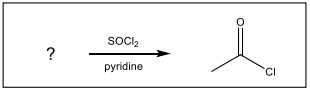
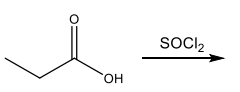
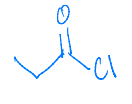
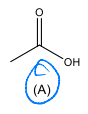
Identify the starting material needed to form the following acid chloride using thionyl chloride.
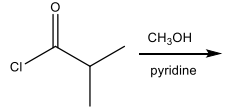
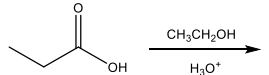
What major organic product is formed in the following reaction?
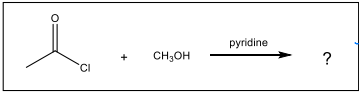
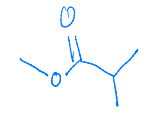
What major organic product is formed in the nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction shown?
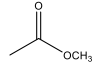
How are reactions between aldehydes/ketones and nucleophiles fundamentally different than reactions between acyl chlorides and nucleophiles?
Acyl chlorides have a leaving group, Cl- , whereas aldehydes/ketones do not.
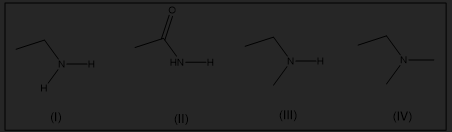
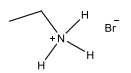
Which of the following are primary amines?
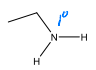
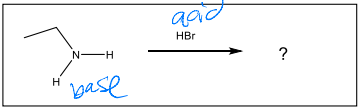
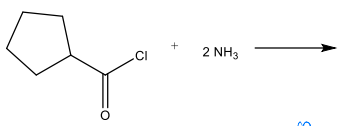
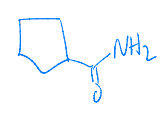
What is the major product of the following reaction?