GROUP 7
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
properties of halogens
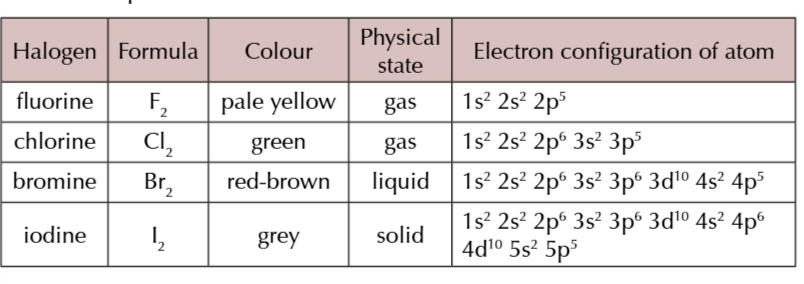
fluorine gas
pale yellow
chlorine gas
green
bromine liquid
red-brown
iodine solid
grey
boiling points INCREASE down group 7
because of increasing strength of van der waals forces as the size and relative mass of molecules increase
electronegativity DECREASES down group 7
larger atoms attracts electrons less than smaller ones because their valent electron is further from the nucleus and there’s more shielding
when halogens react they gain electrons
making them oxidising agents
going down group 7 halogens become less oxidising
because atoms get larger n distance increases
fluoride displaces
all halide ions
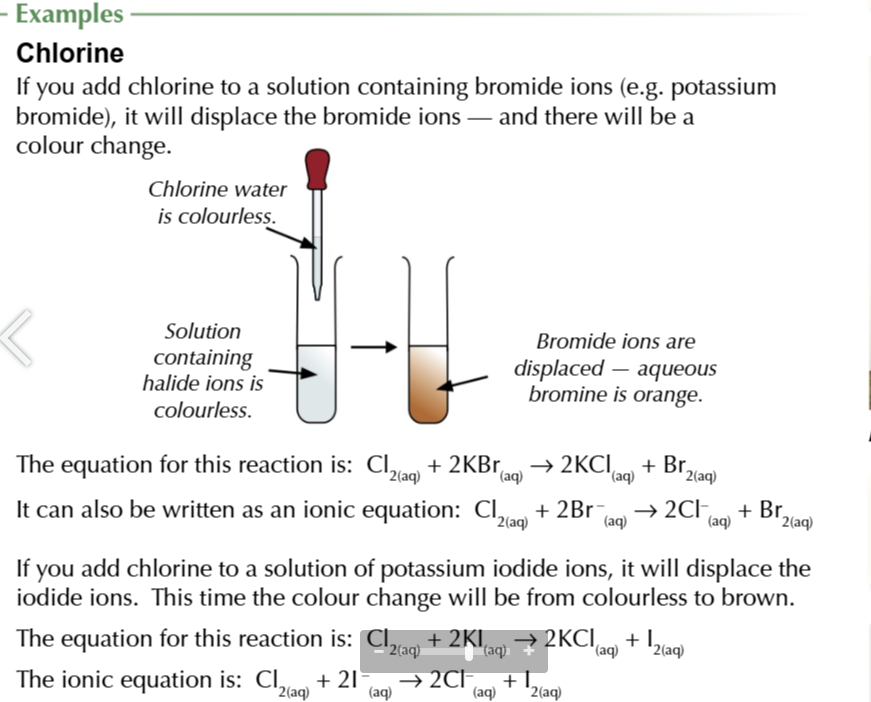
chlorine displaces
bromine (forms orange solution ) and iodine (forms brown solution)
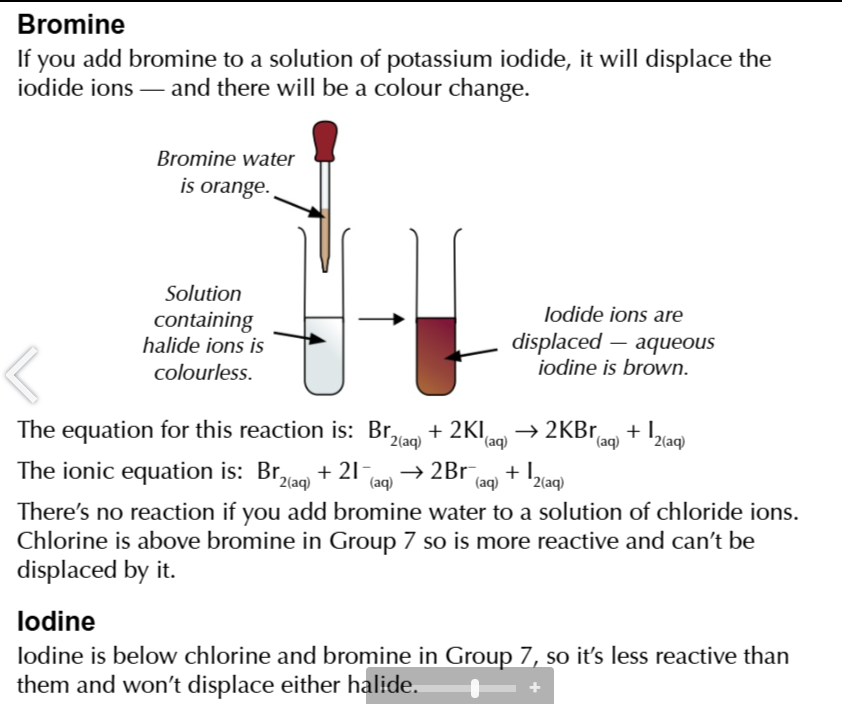
bromide displaces
iodine forms brown solution

halide ions are colourless in solutions
but when the halogen is displaced it shows a distinctive colour
MIXING CHLORINE GAS W COLD DILUTE SODIUM HYDROXIDE AT ROOM TEMP
produces sodium chlorate NaClO, aka bleach in a disproportionation reaction
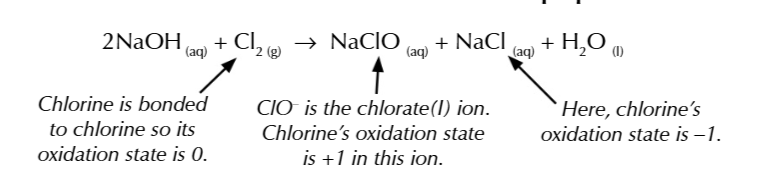
chlorine is oxidised and reduced
sodium chlorate uses
water treatment
bleach paper and textiles
good product
chlorine mixed w water undergoes disproportionation again
to ptoduce a chloride ion and chlorate ion
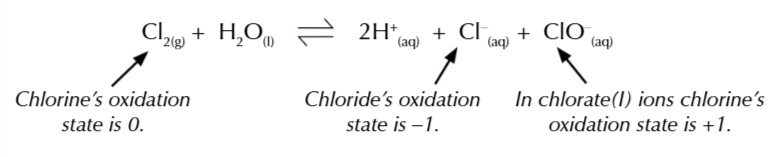
in sunlight chlorine can also decompose water to form chloride ions and oxygen
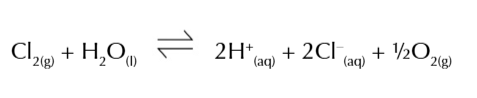
chlorate ions kill bacteria
adding chlorine to water can make it safe to drink or swim in, however chlorine is toxic
chlorine kills disease causing microorganisms and prevents reinfection
it also prevents the growth of algae eliminating bad tastes and smells and removes discolouration caused by organic compounds
chlorine has is very harmful if breathed in
it irritates the respritory system
liquid chlorine on the skin or eyes causes severe chemicla burns
accidents involving chlorine could be serious and even fatal
water contains a variety of organic compounds like decomposed plants
chlorine reacts w these compounds to form chlorinated hydrocarbons which are carcionogenic
however this increased cancer risk is small compared to the risks from untreated water and cholera epidemic
we weight the risk and benefits when making decisions ab what chemicals to add to drinking water supplies
in reactions halogens gain 1 electron
to form halide ions
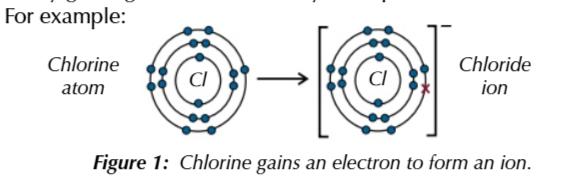
halides in reactions get oxidised (lose their extra electron)
they are reducing agents
going down group 7
reducing power of halide increases
as you go down group 7 the attraction gets weaker between valent electron and nucleus
because the ions get bigger so electrons are further away from positive nucleus with extra shells in the way
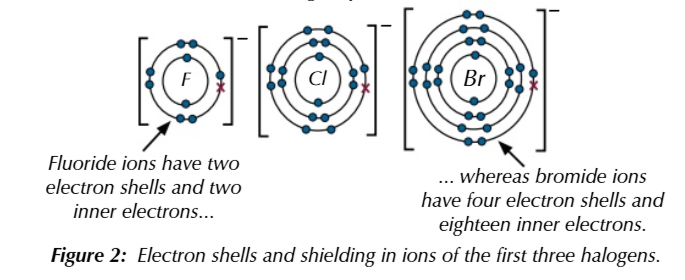
All halide react w conc sulfuric acid to give a hydrogen halide
NaX + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HX

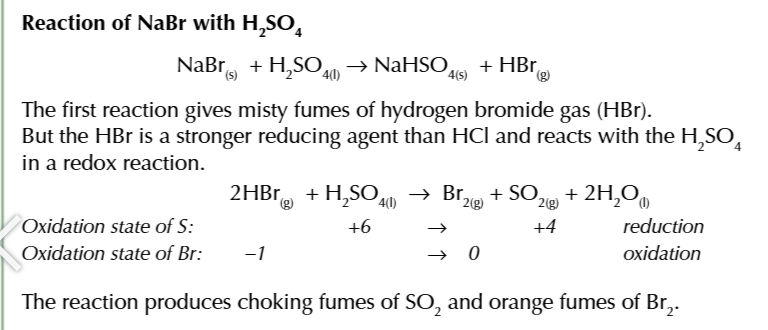
some halides are strong enough reducing agents to reduce sulfuric acid to water and sulfur dioxide
2HX + H2SO4 → X2 + SO2 + 2H2O
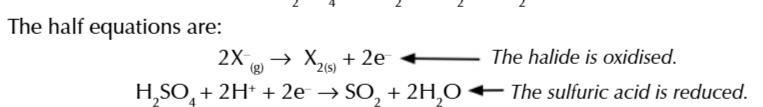
iodine is such a strong reducing agent is can reduce SO2 into H2S or S
6HI + SO2 → H2S + 3I + 2H20

halogens have very distinctive colours
halides are all colourless

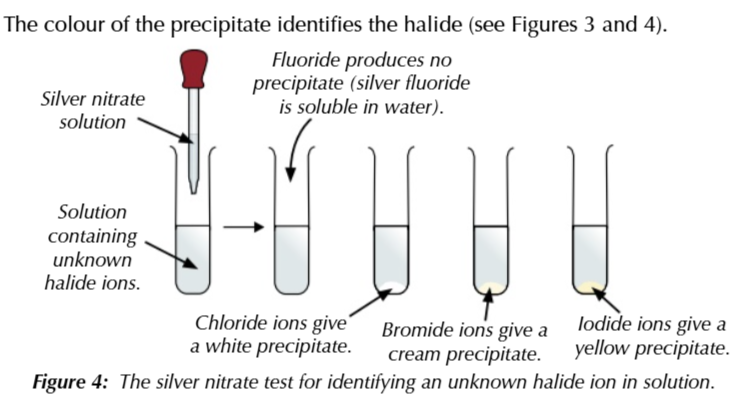
use silver nitrate to test for halides
add a few drops of dilute nitric acid to remove ions which might interfear w the test
add a few drops of silver nitrate solution (AgNO3)
a precipitate is formed or silver halide
white precipitate
chloride ion
cream precipitate
bromide ion
yellow precipitate
iodide ion
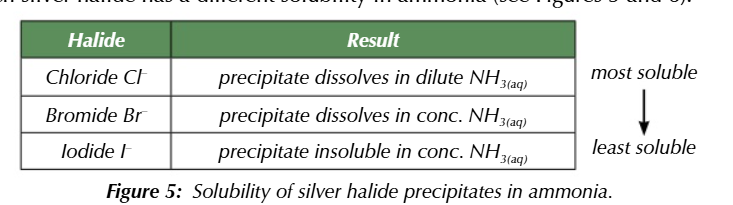
adding ammonia solution to each precipitate mixture
indicates the different solubilities of the silver halides formed
white precipitate + dilute ammonia
dissolves → chloride ion confirmed
cream precipitate + conc ammonia
dissolves → bromide ion confirmed
yellow precipitate + conc ammonia
DOESNT DISSOLVE → iodide ion confirmed
group 2 + flame
distinct colour
flame test:
dis cichrome wire loop in conc HCL to clean
then dip in unknown compound
hold loop in the clear blue part of a bunsen burner flame and observe colour change
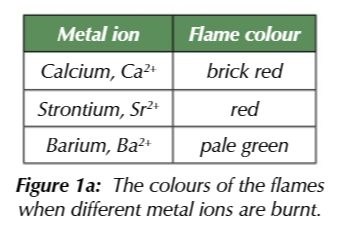
Ca 2+ flame
brick red
Sr2+ flame
red
Ba2+ flame
pale green
NaOH identifies group 2 ions
observe the rpecipitate that formes from excess NaOH + metal ion solution
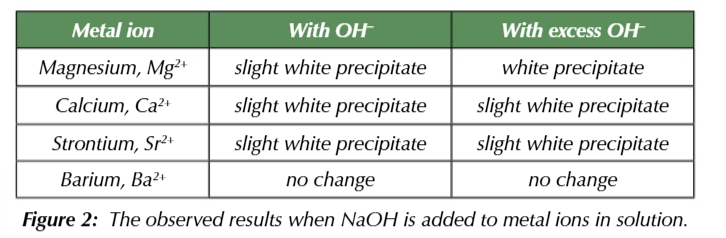
Mg 2+
OH- = slight white ppt
excess OH- = white ppt
Ca2+
OH- =slight white ppt
excess OH- = slight white ppt
Sr 2+
OH- = slight white ppt
excess OH- =slight white ppt
Ba 2+
OH- = no change
excess OH- = no change
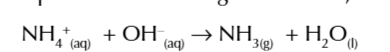
NH3 is an alkaline
using a damp red litmus so ammonia gas can dissolve will turn it blue
OH- + NH4+ → ammonia gas and water
to test for ammonia in a substance w ammonium ions:
add dilute NaOH to substance
gently heat mixture
hold a damp red litmus over test tube
if it changes to blue ammonia gas has been given off
test for sulfate ions
add dilute HCl + barium chloride (BaCl2) to substance
if white precipitate forms = barium sulfate
therefore origional compound contains sulfate
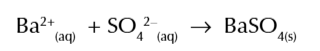
test for hydroxide ions:
hydroxide ions make a solution alkaline
add ph indicator (eg red litmus will turn blue)
test for halide ions:
add dilute nitric acid (HNO3) then silver nitrate solution AgNO3
chloride = white ppt
bromide = cream ppt
iodide = yellow ppt
to differenciate between the similar silver halide precipitate colours add ammonia solution
silver chloride + dilute ammonia = dissolves
silver bromide + conc ammonia = dissolves
silver iodide + conc ammonia = no change
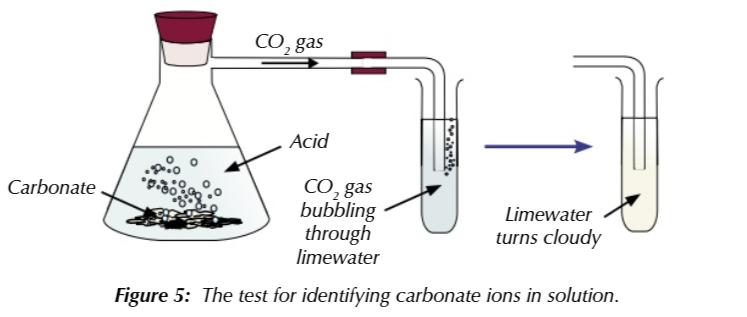
test for carbonate (CO3 2-) ion
add dilute hydrochloric acid
solution will fizz, CO2 produced
CO3 2- + 2H+ → CO2 + H2O
you can test for the CO2 using lime water, if it turns cloudy CO2 is present