Micro L25 - L29
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Principal agent + behavioural and experimental economics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Fill in the missing information
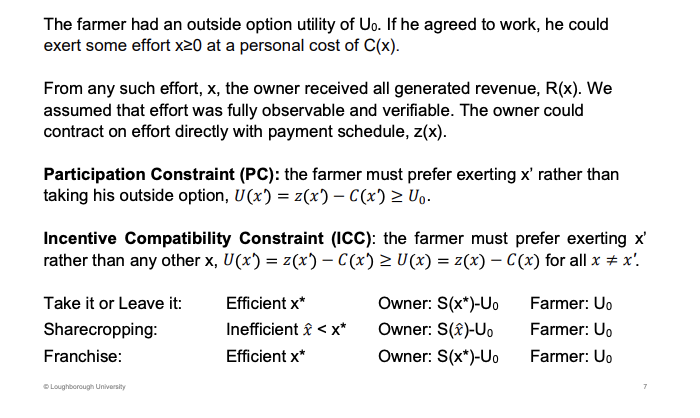
An Agent
Residual claimant
Ownership from control
In objectives
Owner want to max profits, the agent will likely want to make the job easier

Summarise the principal best design a set of incentives to influence the agent
More effort, higher revenue for the owner.
The three possible payment systems at the bottom which the owner can use.
Agent will only get a utility just above the outside option, U0
What happens if we consider asymmetric information, what can’t be observe, what will the principal make it conditional on and is the difference compared to perfect information
Cant observe what the agent is doing, not perfect information, introduces a moral hazard problem, effort is unobserved. Incentive to not work as hard as under perfect information
Bonus based on output could solve this?

How does this affect the optimal contract and the resulting equilibrium effort
How will the principal going to adapt to this new information. Some industries can still do this, like number of boxes you made.
Relationships between effort, normally has a lot of random factors. Farmers, weather, quality of the soil. Bankers, based on market conditions, lots of noise.

With moral hazard what can you farmer do with their effort? How can it be solved? How does risk attitude impact this?
Franchising solution, can work under both full and incomplete information. The fee happens none the less.
Risk adverse - not willing to pay a lot for the franchise, lots of risks with the random variables, like weather in the farmers situation.

What are the three factors simualtenous that create principal agent games?
Three factors, create the principal agent game. Random factors - stochastic outputs
Effort is no observable but output is
Offers wage, not correlated to what you do, but the bonus is. Effort is now high or low, with respective costs.

Set up the asymmetric game, what is the probability of success with High and Low effort? How does risk levels cahnge the utility curve
If the effort is high, the project might be successful. If low, no chance in succeeding at all.
U0 = 1 - outside option
Risk neutral, principal reality risk, diversify this situation. Agent is a small fish, more concerned but this one payoff

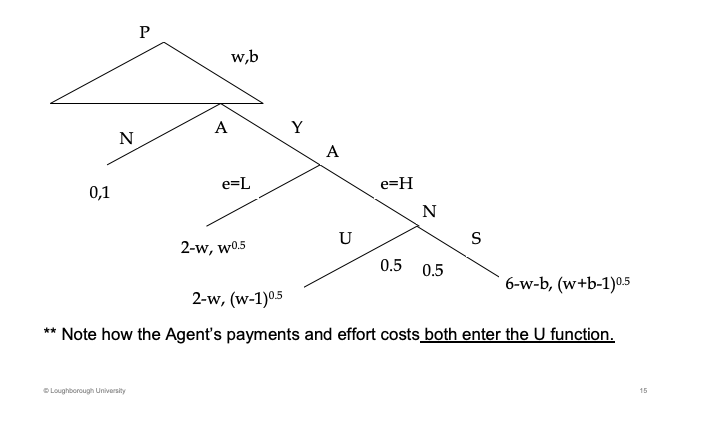
Draw the tree diagram of this situation. What components both enter the U function
Principle goes first , wage and bonus. If the agent says N, it gets one which is the outside option. Then effort, if H, nature decides with a 50/50 chance.
-w on the principal as they always have to pay the wage.
Agent get w^0.5 as it is put into the utility function.
U = unsuccessful, S = successful
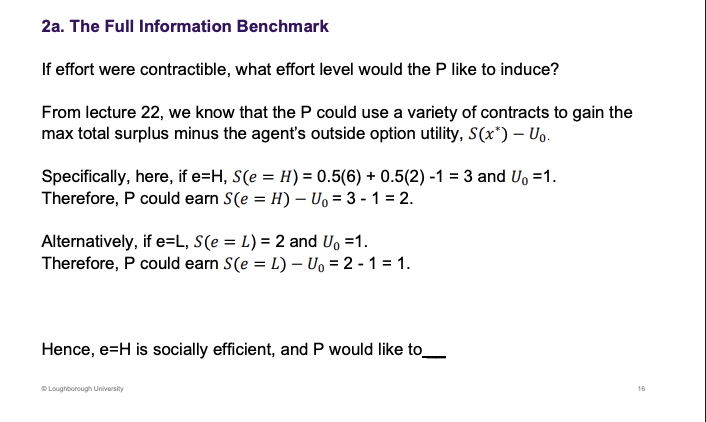
What is the full information benchmark, how is it calculated? what is the efficient outcome
Induce e=H if possible
Compared to last week - full information
If I am a principal, surplus - U0
Based on the contracts from last week, the principal could earn 2 if effort is H
Principal wants the agent to work H, rather than L. How to do that??
If we use a take it or leave it approach here what is the outcome, what is the agents utility function.
Outside option U0.

From this take it or leave it option, what happens to the risk? And what does this mean
If the P pays 2
Principal is taking the risk, the revenue is the risk, agent has a certain pay off. All of the risk is allocated to the principal. This is socially efficient as the principal isn't worried about the risk, risk neutral, big fish. The risk is allocated to the right person not the agent who doesn’t like it.

Under asymmetric information what can the principal not do, how is franchising sub optimal? What else can be used.
Draw the tree diagram for w and bonus
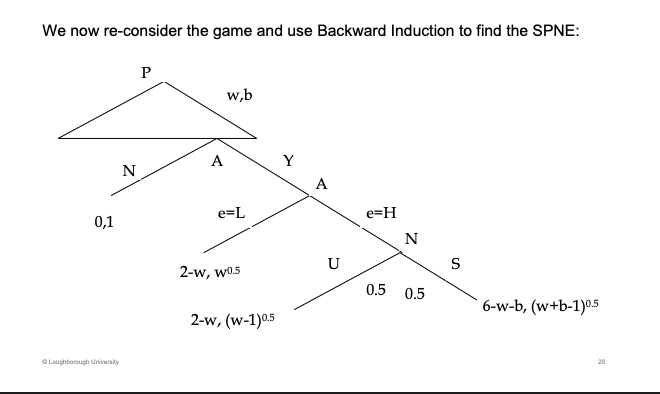
What is the expected pay off of A if e = H and how does this satisfy both conditions
Principal wants to agent to be H effort.
Agent has a 50/50 chance of S and U of the project.
ICC - better than the low effort outcome.
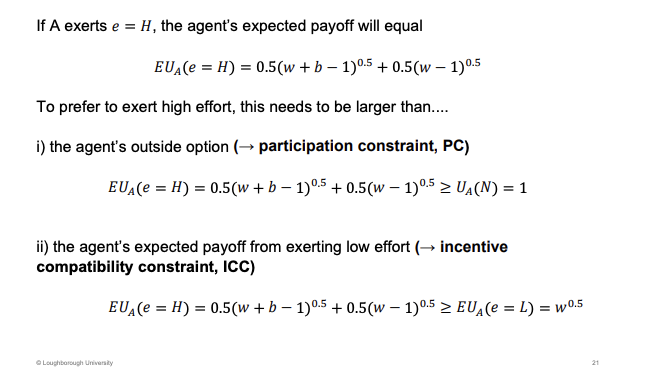
What happens if b=0. What does this tell us about banking bonuses
The bonus can't be zero. As this is a cost to H effort, no incentive to do H effort.
Bonuses can be a good thing, incentive people
Both should be equal to rather than an inequality.

How the ICC condition hold with the bonus, also what happens as the agent is risk adverse
Wage bill constant
RN - risk netrual/ RA - risk adverse
Just willing to prefer H than L. P is risk neutral, care about expected returns, what you pay on average. 50% of paying the bonus. A is risk adverse, they don’t like risk. Much prefer, through wages rather than Bonuses. If the rewards from h effort is too low, P increase W and reduce B to keep (W + 0.5B) constant, the utility will increase in the A as they are risk adverse


Solve this

From that example what is the two parties pay offs
Agent will get 1, the outside option utility
P will get the average of S/U which equals expected payoff of 1.


Solve this and add answer in
What are some features of the optimal contract, how does the principal move some risk onto the agent? What is this similar to? Why does the principal do this?
Drives up the expected payment
P is giving some risk to the agent through the payment, in the A they have a 50/50 of w or w + b. The A doesn’t like this.
Adding some risk, revenue, similar to revenue sharing. In full info it was inefficient, but here it is efficient
B has to positive, need to be some risk on the A, otherwise they have no incentive to give H effort. This is the only way the P can do this. A is compensated for taking the risk.

How is the principal’s payoff under asymmetric information and why relative to full information
Compared to full, they are worse off. A is the same, outside utility.
Social welfare has decreased, which is called agency costs

What can happen in extreme cases of asymmetric information
Too expensive
Not worth motivating you sometimes, as B is so much. If this happens social welfare falls by even more

PA2 - go through lecture 26 exam questions 25/12/25 second half
Experimental economics + Behavioural
How can we go further to test game thoery? What are traditional econometric data not good at? What do laboratory experiment good at?
Traditionally, not really tested.
Can't just directly check it, sensitive to what we assume. We use experiments instead, became popular in 90s or 80s

What are the general advantages of laboratory experiments, what does internal validity mean?
Replicate more easily
Control things very carefully, test the theory to the situation that corresponds.
Internal - clean conclusions that could be impact by the outside environment.

What are some of the disadvantages and what doe external validity mean?
Likely be observed in real markets
External validity - behaviour this way here, can we transfer it to wider settings.
Market selection - not rational, kicked out of the market quickly, whereas they can be seen in a lad settings, in the real world this will be filtered out

What other types fo experiments are there? what are the similar to?
Ran in the real world, utilise some randomisation in the real world
Natural experiment randomisation - policy effects some but not all. Some states in US increased minimum wage, some didn’t is an example

Example of natural and filed experiments
Natural experiments rely on external events outside the researcher's control (e.g., observing health outcomes after a sudden policy change or earthquake), whereas field experiments involve the researcher actively manipulating variables in a real-world setting (e.g., sending different resumes to real employers to test discrimination).
What is the ultimatum game, what is the set up, how many players, what action are they doing.

Draw the tree diagram of this ultimatum game. What is the outcome of the game
Player one and two dividing money between them, if player two accepts they get m and player one gets the reminder. If rejected 0,0. Player two should accept anything which is greater than 0, player 1 should offer something very close to 0 so they get to keep more of the pot
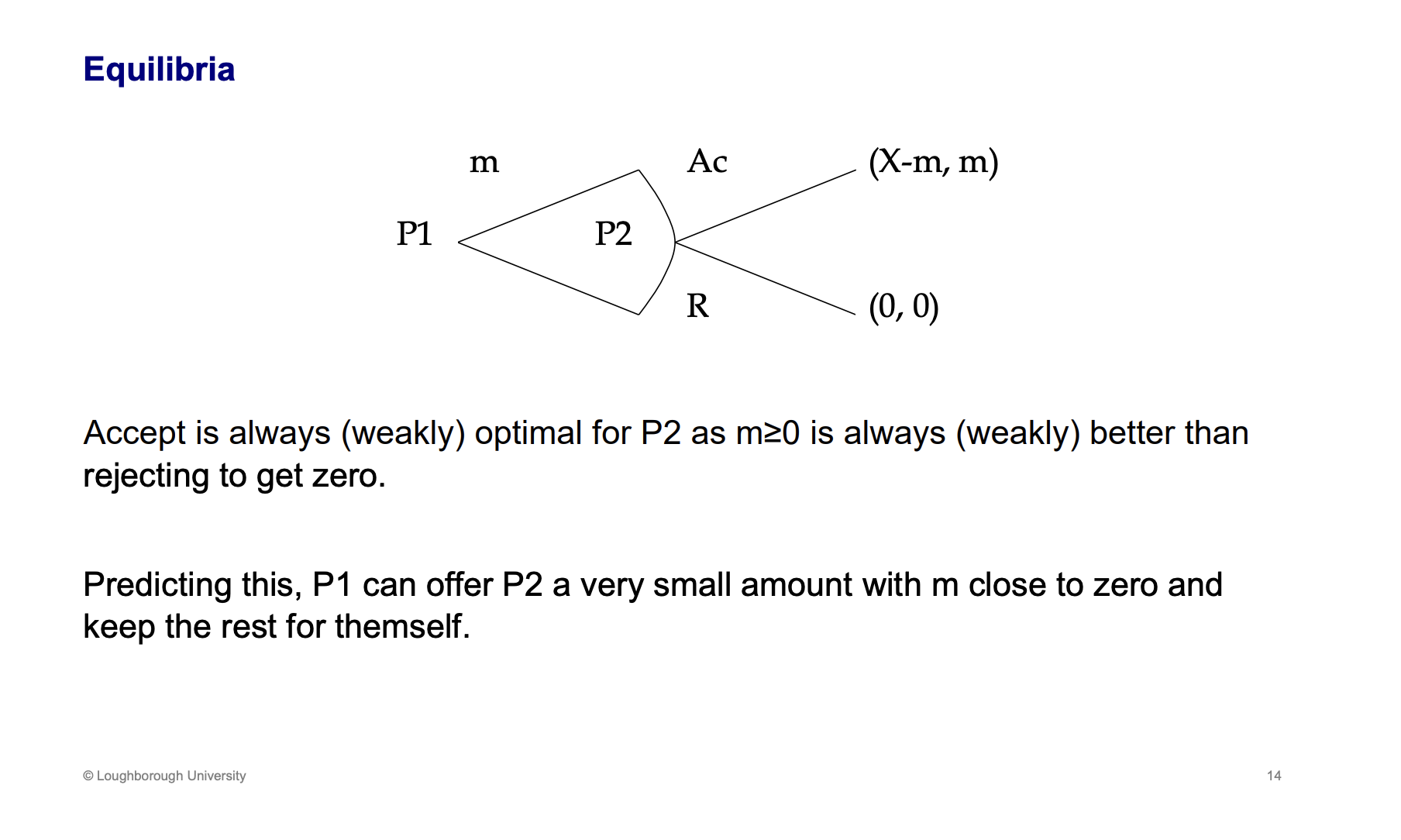
What happens to the outcome if m is in increments and what is the SPNE
P1 gets the vast majority

What are the summary results of the ultimatum game in the experiement
P1 typically offers half of the pot, theory based they shouldn't

What are the possible explaination of this
Not testing the theory properly - low internal validity
P1 might get rejected and leave with nothing, led to higher offers - risk adverse. Doesn’t explain they p2 rejects
Theory could be misleading, rational model suggests selfishness.

How can we distinguish risk aversion and fairness, what is the game called? What is the difference to the ultimatum game?
Self interest
Using a variation of the game, dictator game. Will p1 give any money across, takes the risk aversion away. Offers go down which is still not at the rational level.

Whats the purpose of the dictator game, whats it trying to show Criticism 1
Decrease slightly
Time to learn how to play things, be more accurate. The theory is only one shot. Playing different people, they can learn to play the game.

What is criticism 2 of the design
Even with a larger amount of money the results don't converge back to the theory

What is criticism three?
Maybe not perfectly anonymous.
Potential social sigma from being selfish
Able to develop reputation in the lab for rejecting low offers to induce higher offers later

How did the results vary between, gender race culuture and other characteristics

What person studied the impact of culture of the ultimatum game, what was found
Right and wrong formed from social norm may have developed differently in different places.

Who self tried to explain the culutre differences and what were his aims?
The U game - Ultimatum game

What is the difference between game m and u. What did the SPNE predict in both games
Positive winning bid
Played the u game or the m game. Same as before, divide money between two people. Rationally should be very low to p2.
Highest bid, winners. Earners 10 - bid.
Both have very unequal outcomes.

What happened before both games? What was this intended to do. What happen across countries.
The outcome of a randomly selected round.
Was a practice round, know the rules. Incentivised. Across different countries, made sure to be identical.

What were the market game results
Shrank with subject experience
Market game - very close to theory, across all countries. - converge to the equilibrium. Similar to the in class experiment

What were the ultimatum game results
Shrink with subject experience, instead they grow!
Country differences become more significant with more games

What cross country differences were observed
Countries with lower offers
Fairness may differ between cultures - they think they deserve more, therefore reject. But some countries think, it's better than nothing.

Additional comments about the cross country difference

What did the robustness of the m game suggest in the u game
Countries were different due to currency's or anything

What were the final conclusions of the roth el paper
Vary across countries.
Market game, set up as an auction, prompts people to think differently. Automation less market language, about sharing, invokes different feelings


Answer the following
Internal, External
What are the three types of experiments, and explain
Three different types of experiments. Natural - natural arising situations which carefully controls things, this isn't done on purpose

How did behavioural economics come around

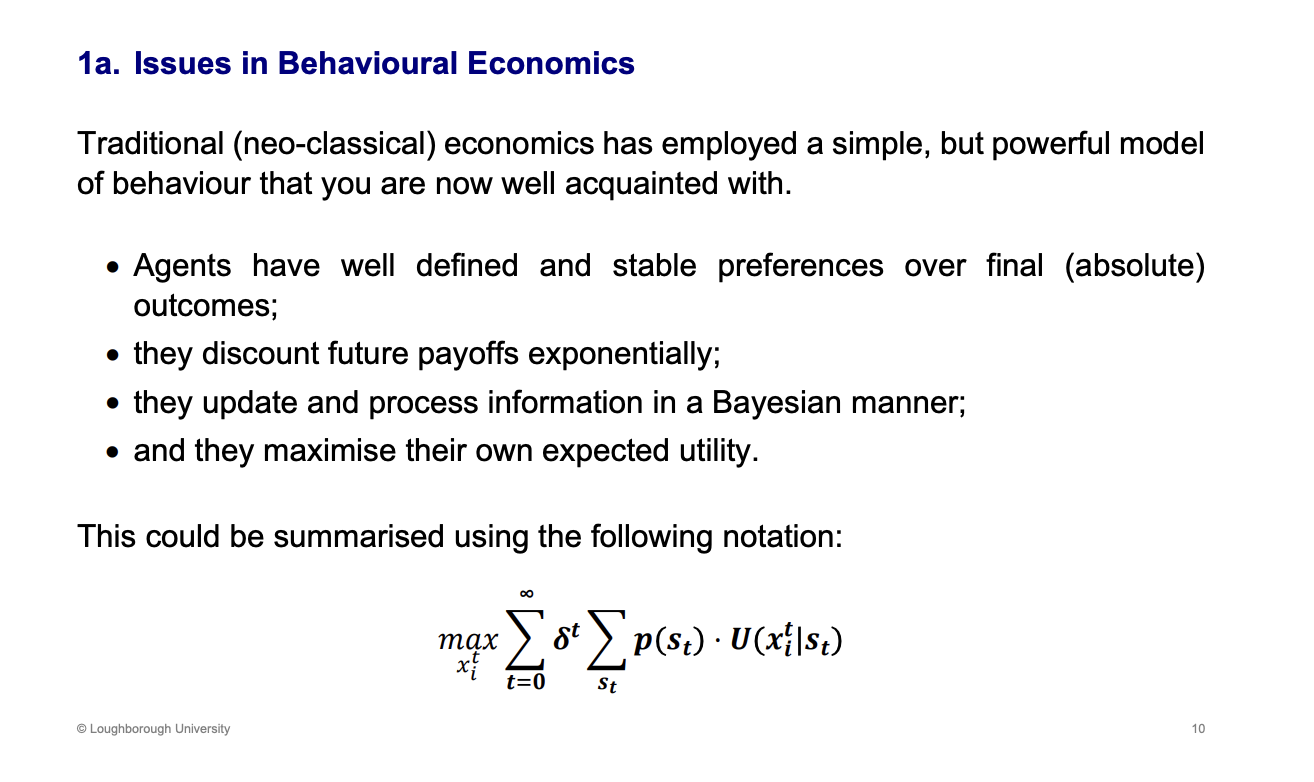
What is the model which neo classical economists have emloyed
Equation summarises the neo classical model - this model, has well defined and stable preferences.
What is good about traditional models, how does behavioural hope to use this
Better realism
Behvaioural is trying to build on it, make it more realistic

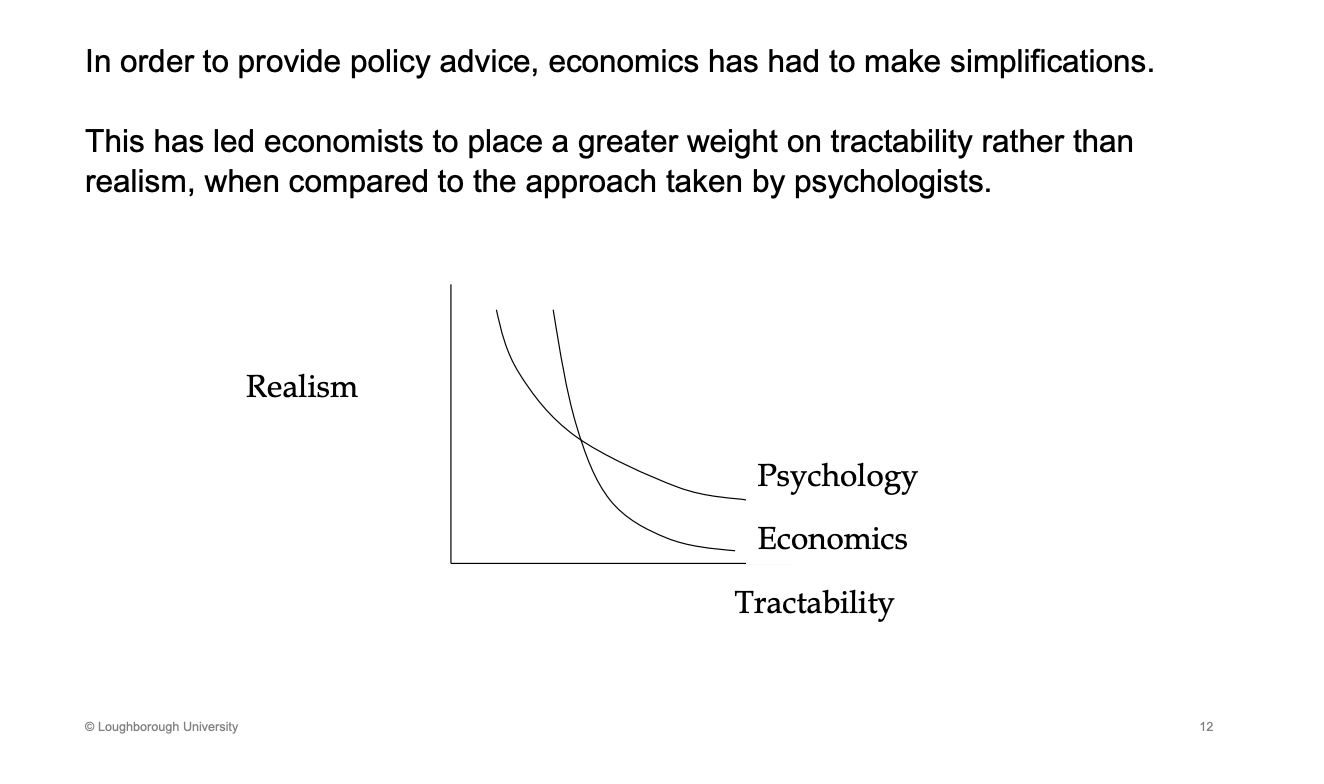
What is the diagram of realism between psychology and economics
PSc - explain behaviours really well
Econo - our first priority is to get policy advise, tractable, needs to be usable. Give up a lot of realism for another unit of tractability
What is criticisms one of behavioural economics
Marketing activity, financial bubbles
Nothing wrong with the standard neo classical model, the lab evidence doesn't co inside with theory.
Are the lab findings credible? In a market situation, not profit max, a force in the market will push them out. Market selection effect will allow the profit maxers to survive in the market - support for the standard model
Doesn’t always have the time to learn, only buy a house a couple times in life.

What is the second criticism of behavioural
General models that connect different phenomena
Too many models, only accept the model if there is a body of evidence for it. Als looking for model which can look at an loads of behaviours, rather than individual behaviours

What is the basic understanding around fairness and preferences
People care about fairness

When do people care about others payoffs - examples
Some of the situations where this fairness can occur.
Are they genuine games where people care about fairness or other reasons
Culture/expectations - US tipping
Stigma - people will think bad \
Pity/ Warm glow - when you give to charity, makes you feel good
Future production/service - same waiter, if you didn’t tip him last week, what is the service likely to be this week, worse?

What are the three possible ways people appear to be. What is a new generation of models looking at?
Equilibrium concepts
Ii) is the warm glow idea, selfish is a way, I get utility from it
Iii) really care about fairness, being treated badly

What does charness and robin look at, what year. Write out their utility functions. What does the model assume
Two people, incomes x
Utility function - weigthed avergae not just of my income but also your income. Row (P) or sigma = 0 means utility depends on just my income not yours.
The assumptions, get some positive weight from p2 utility, e.g. if they get a pay rise. The amount you care, depends if you earn more or less money.

How does Fehr and schmidt, what year, differ to charness and robin model
Similar to the model above.
Max operator is the first equation, this simply selects out of the brackets, which one of them is bigger and then it chooses that one
Get some negative utility from the difference in incomes, inequality. Preference to fairness of same incomes
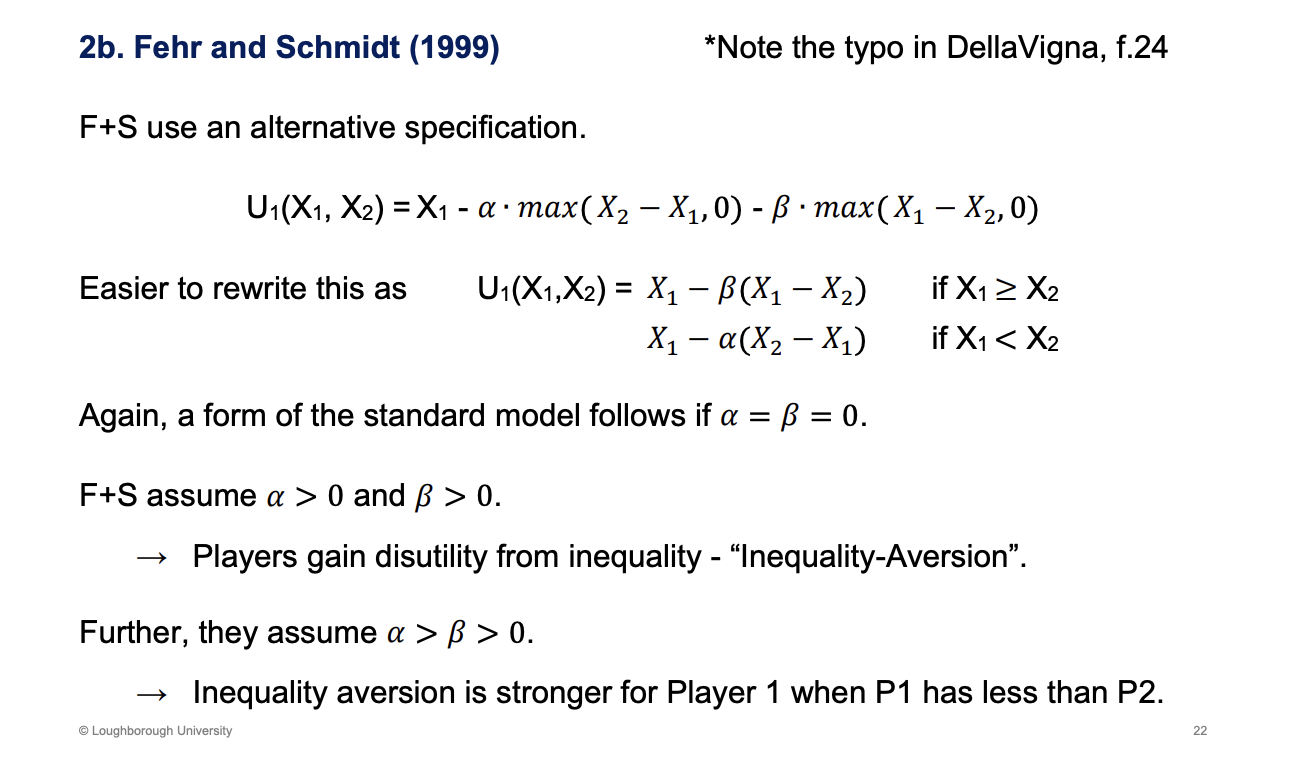
What does the model imply about utility
Increase in x2, we are more equal.
Summarises the inequality, if it gets closer to equality, the utility will get higher

What can both of these model help with. What is the dicator game again?
Dictator game - p2 has no action. Gets what p1 gives them, can't reject.


Answer this question
What are the other applications and features which could be considered?


In self control, what is the anomaly we see here
Wont wait in the short term but will in the long term

What is the model that describes this, What are preferences predicted to be? what is the evaluation of the options meant to be
Utility today isn't discounted, anything tomorrow will.
A and D choice doesn’t fit with the model.
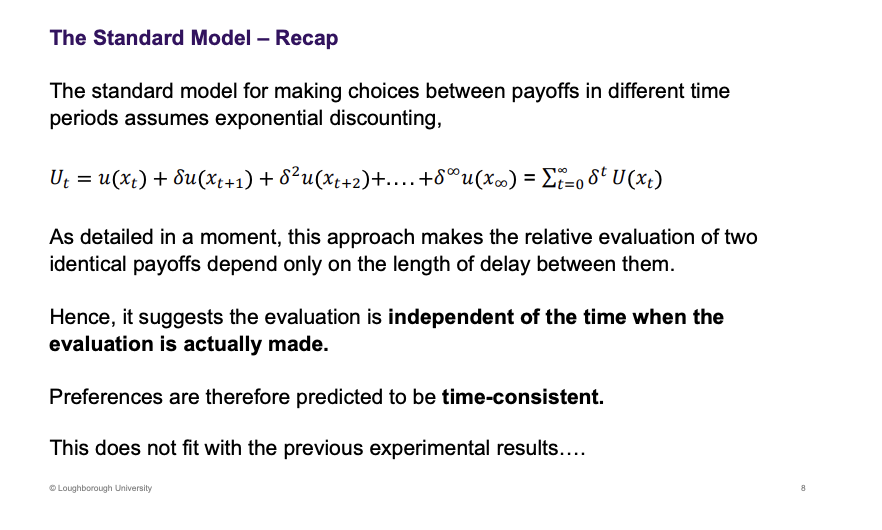
What does the model suggest should occur and what does this suggest

How can we see this formally, what do we define?
Should be consistent but it isn't.

Some evidence which describes ths in real life (OJ)
Change decisions when there is a time frame
Another example around healthy food
In the more distant future

What does the evidence suggest about the standard theory, what does it show and what type of bias is represent
Depend on when the decision is being made, time inconsistent.

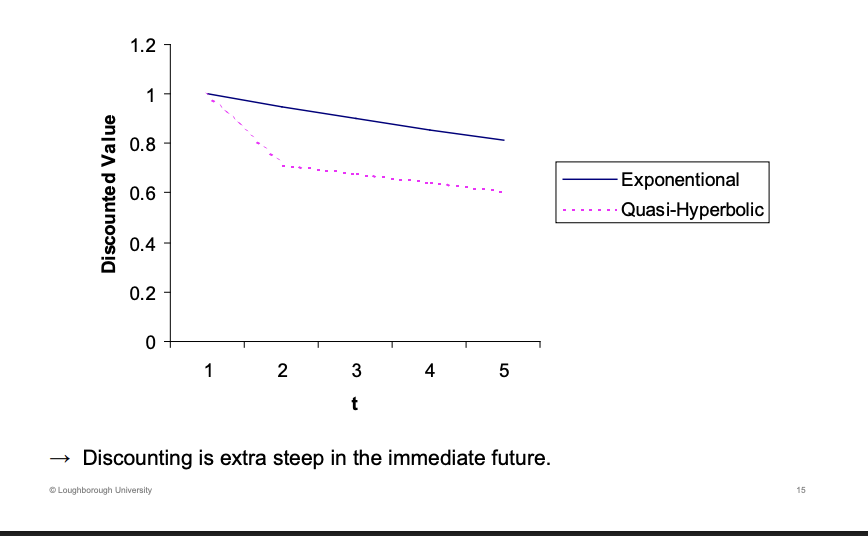
What is the name of the new for of discounting which takes this into effect? Write the equation out, what is the condition of the new term
Can be adapt the model to take into consideration of this present bias

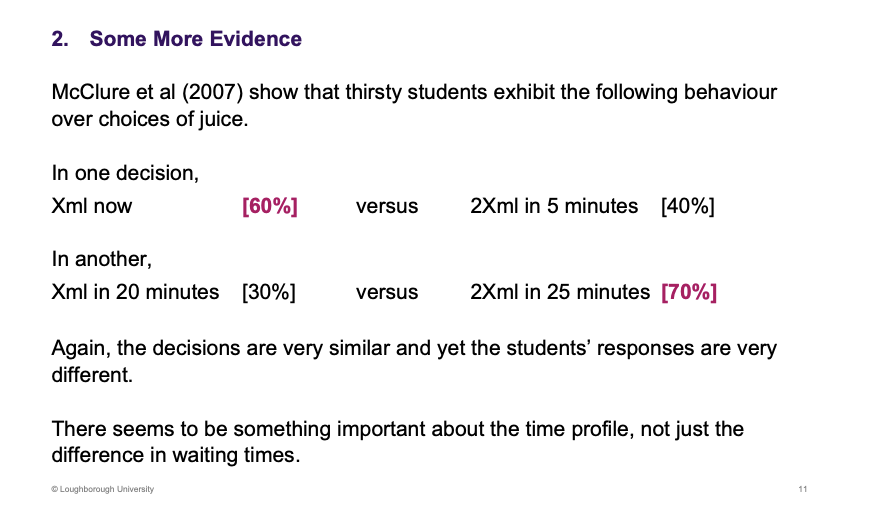
Draw the diagram of this with discount value of the y axis and t on the x
Quasi Hyperbolic (beta delta) - everything in the future is pulled downwards, the present has a greater focus on
Using this new form os discounting, how does it impact the anomalies
For this to hold, the sigma has to be large and beta has to be relatively small.

Explain the anomalies using a leisure good
The future costs
Leisure good, going for a drink tomorrow example. Hey Ewe, on Tuesday asked if you're going out tomorrow. Tomorrow will be a benefit, but its tomorrow need to discount this and Thursday it has a cost (delta squared), would go drinking if the net benefit is positive at t=o. Tomorrow, on Wednesday t=1. b - beta simga c is the criteria.
T=0 is negative but T=1 is positive as the beta parameter is reducing the negative. Happens through present bias . Explain why people do bad things often.
Behaviour differently in different time period. Beta parameter, reduces the costs

Explain the anomalies using a investment good
The future benefits, b
Revising example - immediate cost with a future benefit, sit down over Christmas - increase chances of getting a better grade

What can present bias explain. If you are self aware what might you do?
We know ourselves, self aware. Constraint future behaviour to behave in a way we want to behave. E.g. have to revise over Christmas.

Examples of commitment devices
Freezing a credit card, if you still want it after the card is no longer frozen.
What is the extended beliefs on the quasi hyperbolic model
Beta hat is how you think about yourself. Not fully aware of the problem, self control problem

Go through example of lesiure good and naive
Drinking example, now the second row is new. T=0. Do you want to go drinking, no this will be negative. T=0 second row, do you think you will in the end? Been here before you said no and then you've come drinking because you can't control yourself. It can still be negative beta hat can be bigger than beta. At t=0 row 2 don’t think you will go, tomorrow comes t=1 and now instead of beliefs and the real self comes out and you go drinking. Not aware of the problem, mis predicting yourself.
The second row is working by, today how are you going to behaviour tomorrow. What are you going to do tomorrow, forecast the decision criteria for tomorrow. DO I want to do drinking, imagining myself, immediate benefit and one period cost. When tomorrow comes the true decision criteria is there and the beta changes to the truth, rather than the belief beta.

Go through investment good exmaple with having a naive beta
Same with the revision example. Are you coming to the library tomorrow, its different this time. Row 1 and 2 is positive. T=1 comes along, I'm not going this can now be negative. People don’t understand themselves as see the pattern emerging.
The second row is working by, today how are you going to behaviour tomorrow. What are you going to do tomorrow, forecast the decision criteria for tomorrow. DO I want to do drinking, imagining myself, immediate benefit and one period cost. When tomorrow comes the true decision criteria is there and the beta changes to the truth, rather than the belief beta.


Answer this question
Investment good - gym, immediate cost and future benefit - more healthy and fit in the future.
People might want to go, but they might not actually go. What implications does this have on the pricing of the gym? Increase F and decrease P. This happens because…
If consumers are naïve, you want to raise F. They think they are going to go. Give them a special offer, fixed fee and no additional payments. When it comes to going they can't be bothered. If they relied on P, they never go and the gym would receive no revenue. Collect revenue up front.
If they are sophisticated, they know what there self control issues are. Increase F here as well, through commitment devices. I know the consumer will not make the most. If the gym lowers the P, this acts as a commitment device. Oh its free to go, my future self will be more likely to go as there is no marginal cost. More inclined to go. If I know I will go in the future my willingness to pay will increase, now the firm increases its fixed fee and by reducing p they made it more attractive to the consumer who is sophisticated.
Both situations the firm will increase F and decrease P.
They will increase F as they think they have paid for it so they need to go in another example - sunk costs

What is a policy example of this?