Animal Digestion
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Vent
Where the wastes leaves the avian's system.
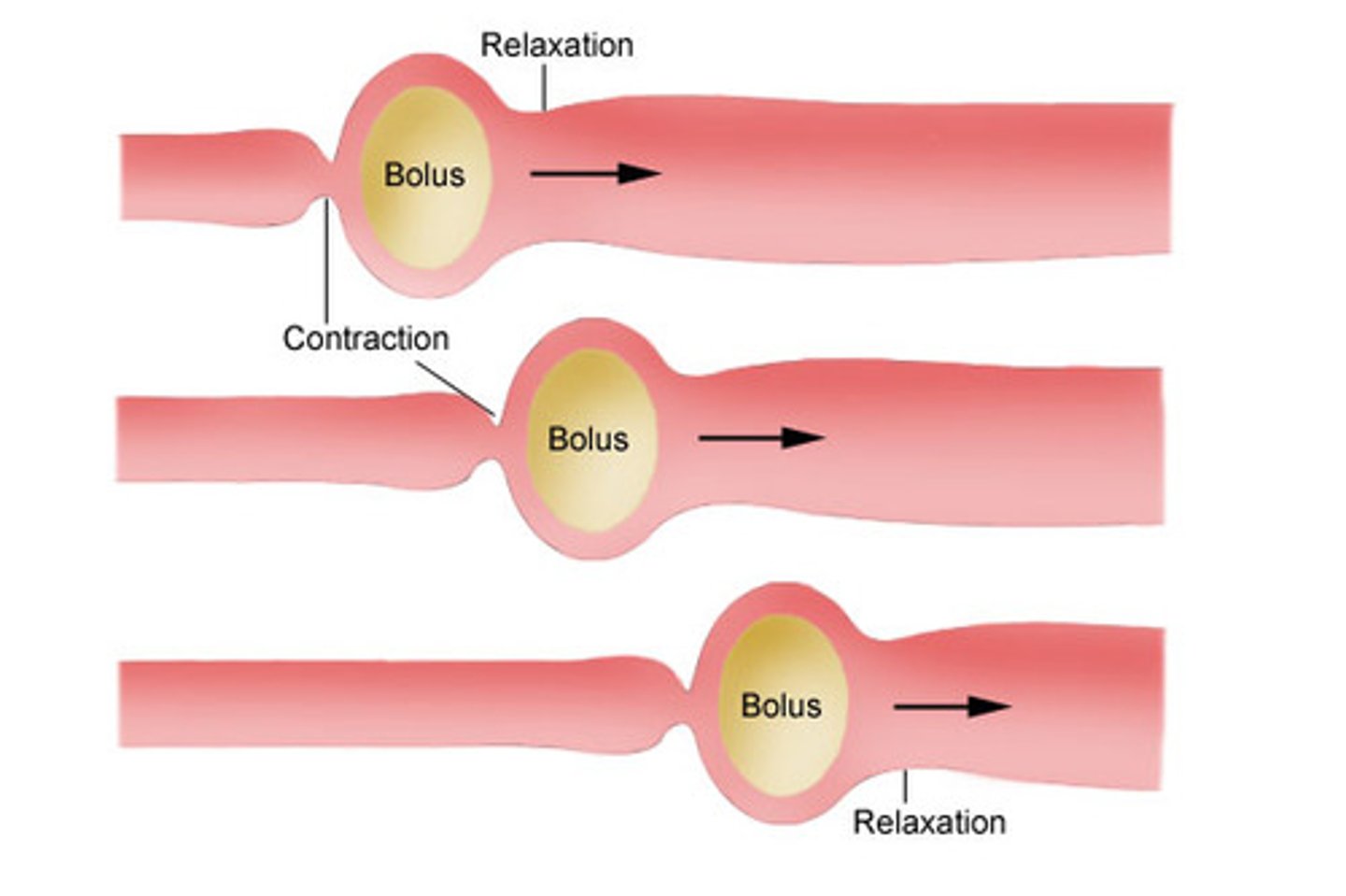
Peristalsis
Wave like movements to push food through digestion system
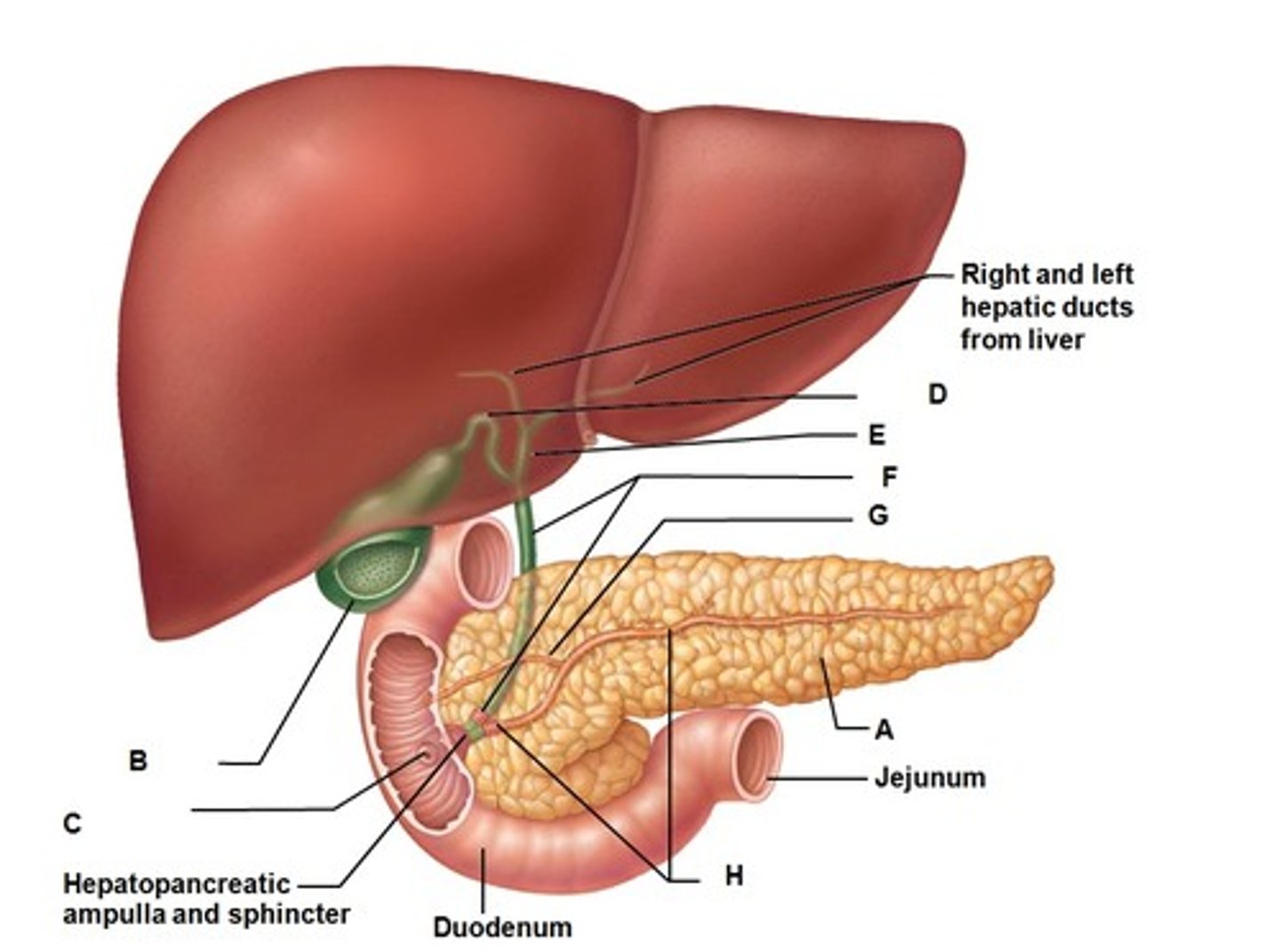
Pancreas
Organ that creates and secretes enzymes for fats, starch and protein
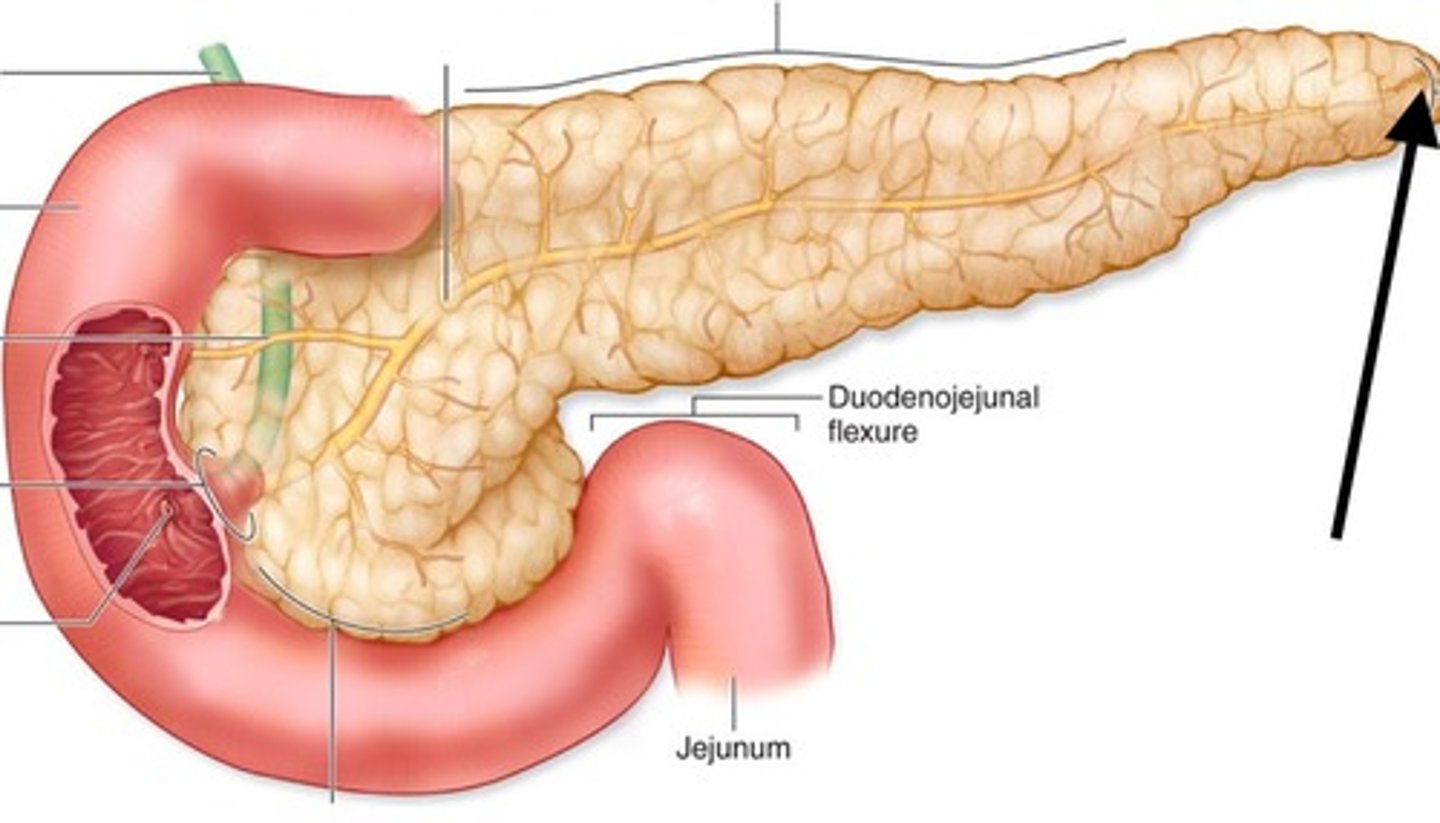
Duodenum
Beginning of small intestine where digestive enzymes are added from the gall bladder and pancreas
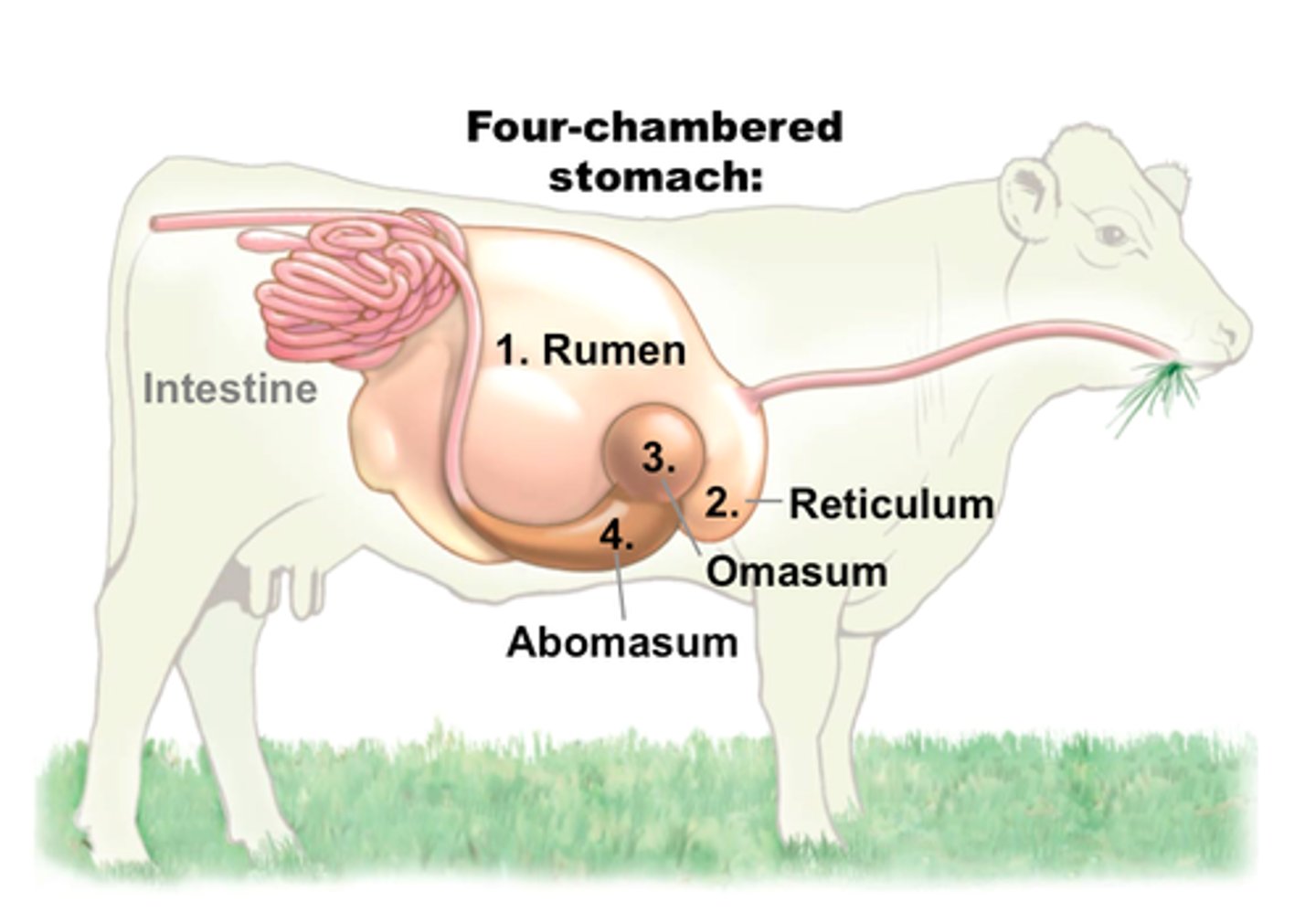
Rumen
The largest compartment of the ruminant digestive tract. It ferments hay.
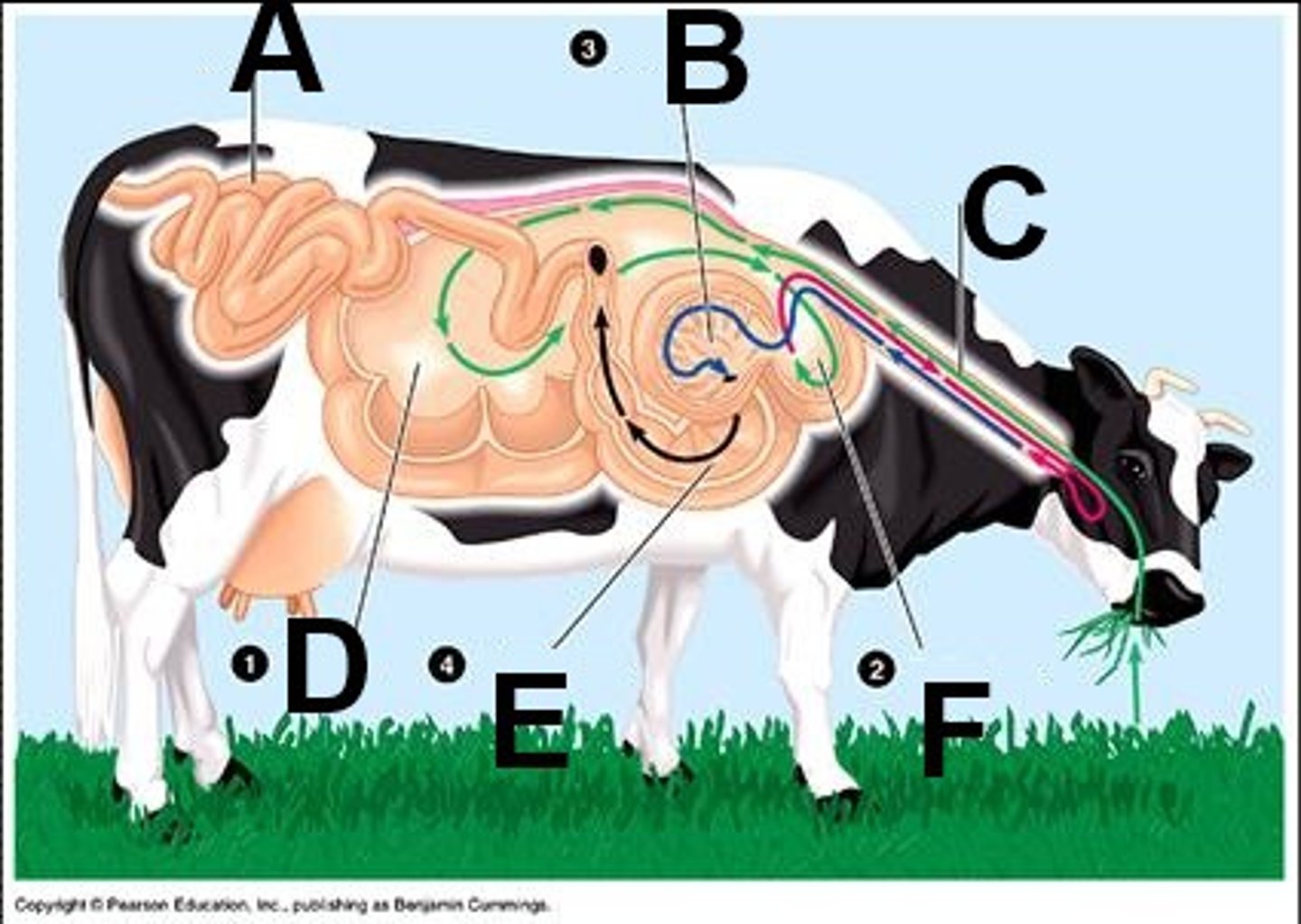
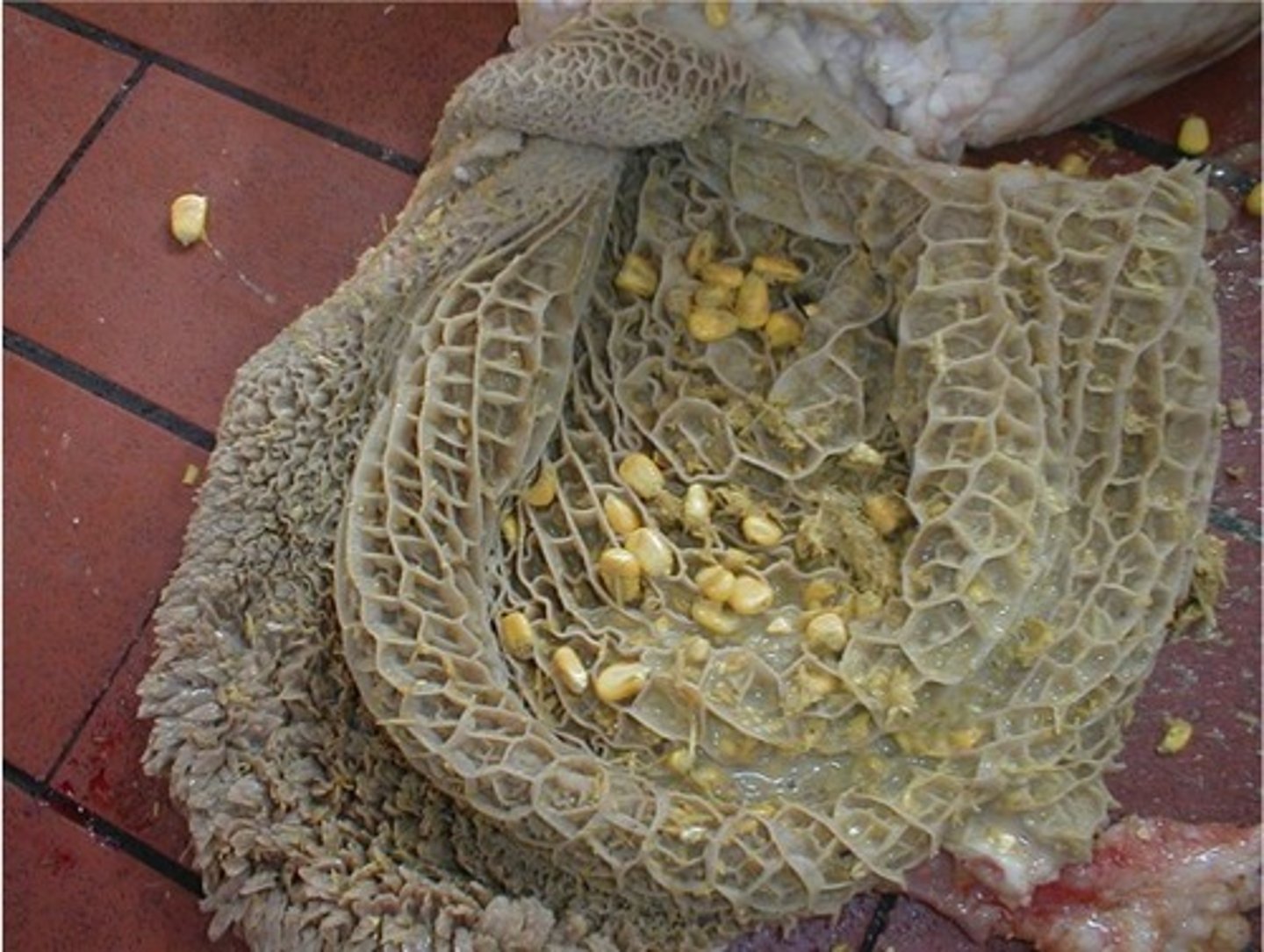
Reticulum
The compartment of the ruminant stomach. Catches foreign material. Honey Comb texture

Omasum
The third compartment of the ruminant stomach. It acts as a filter. Looks like pages of a book!
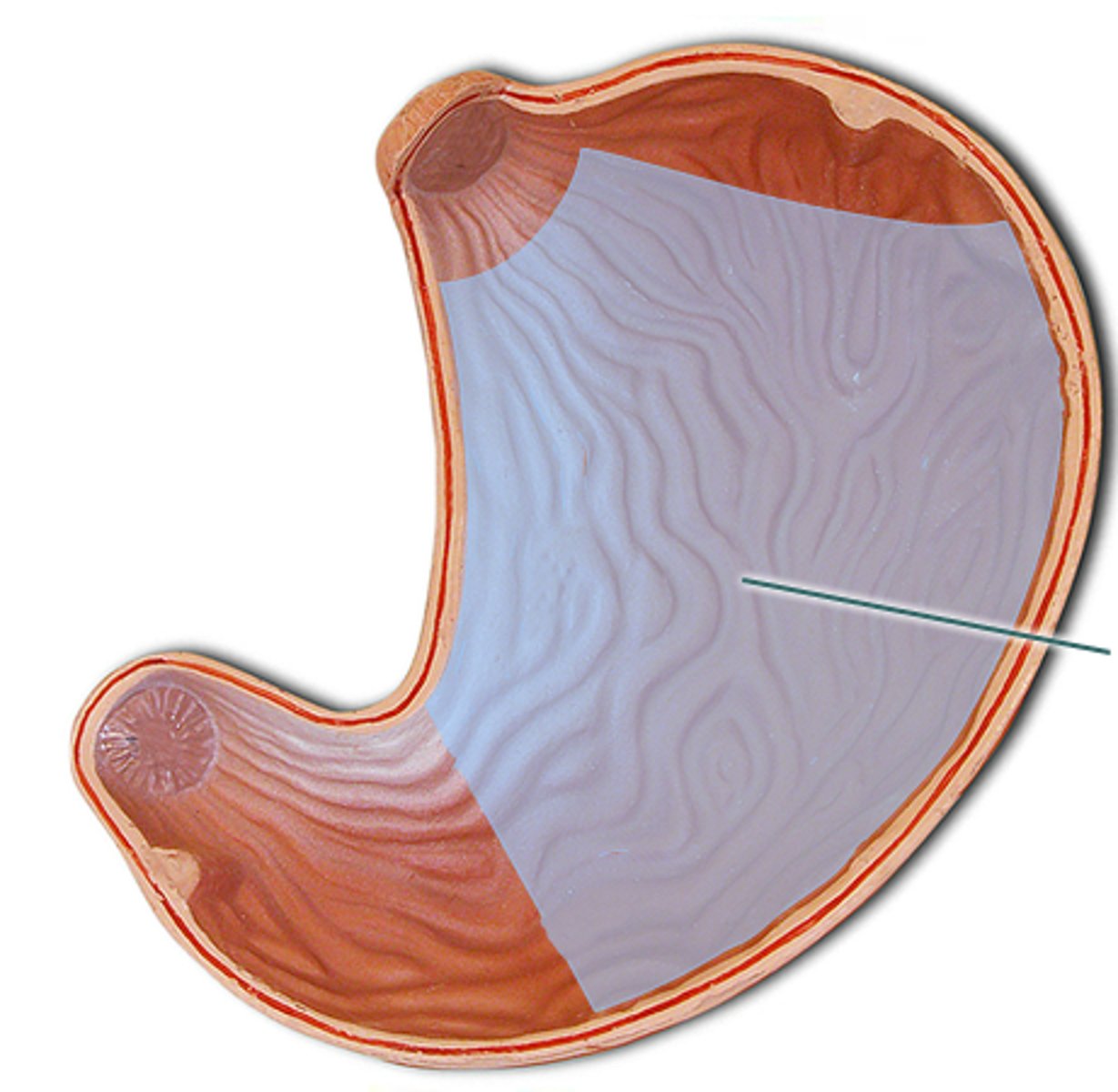
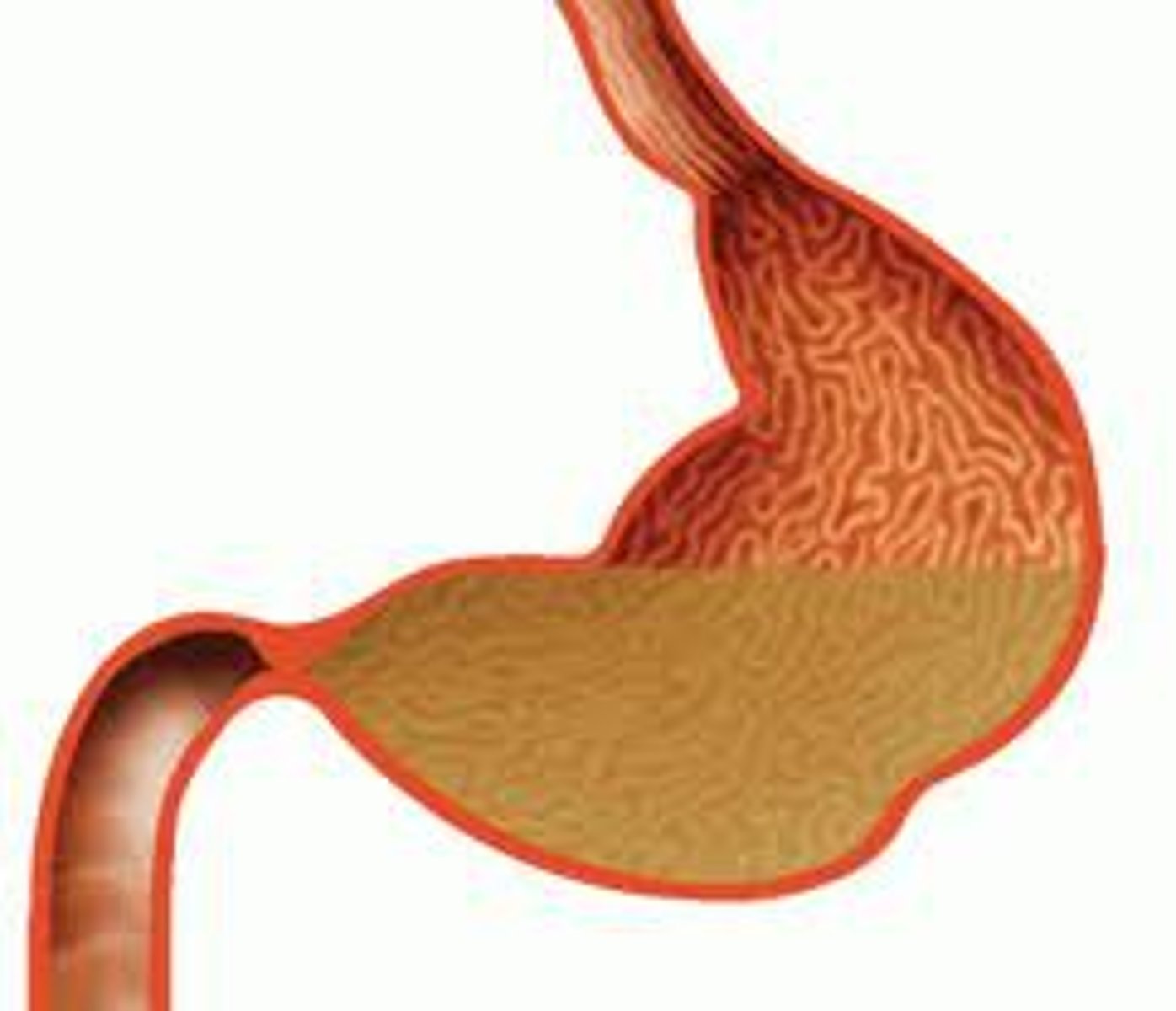
Stomach
A muscular organ secretes acids and squeezes foods.
The three parts to the small intestine
Duodenum, jejunum, ilium
Crop
Food storage in birds prior to stomach. where food is stored and soaked.
Bile
Produced in the liver, digests fatty acids and fats.
Chyme
Partially digested food
Gall bladder
Stores and releases bile from the liver
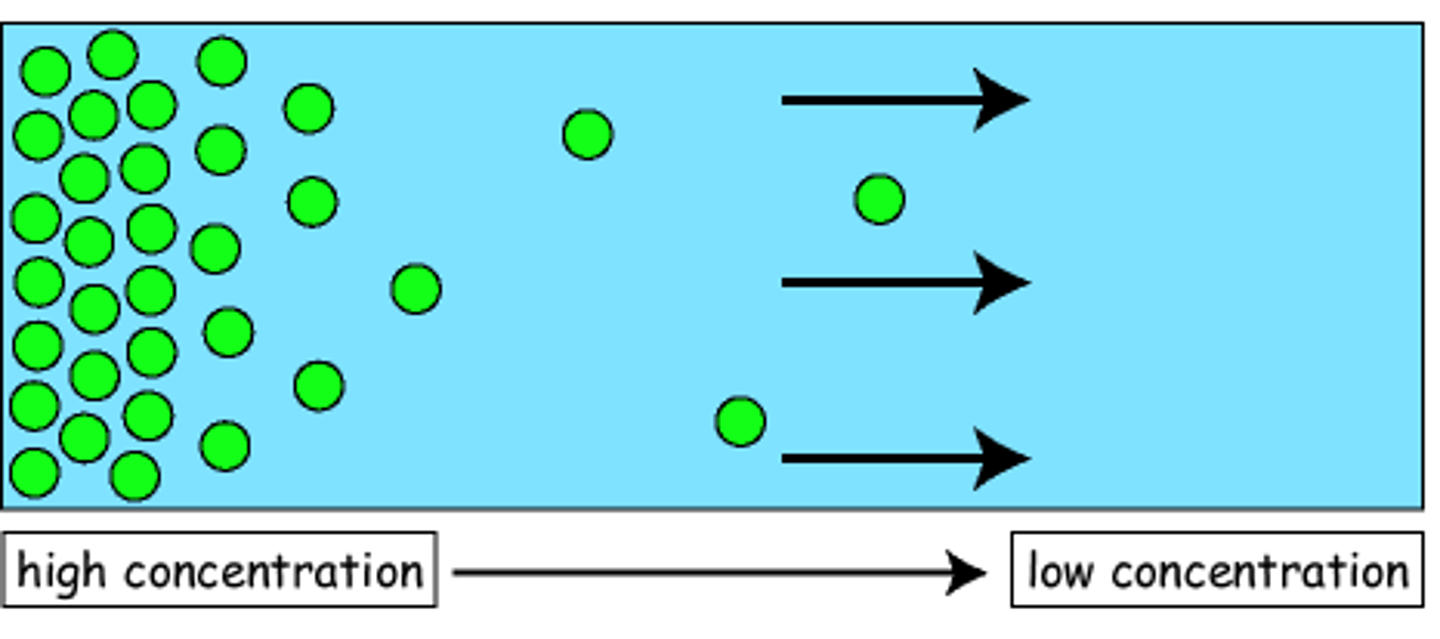
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration - how nutrients are absorbed into body
Saliva
Softens food contains amylase to digest starches
2 Organs with bacterial digestion of roughages or hay
Cecum and Rumen
Coprophagy
Eating feces to gain nutrients

Ruminant
The digestive system where an animal can easily digest roughages most have four chambers to their stomach
Monogastric
A digestive system that contains one stomach.
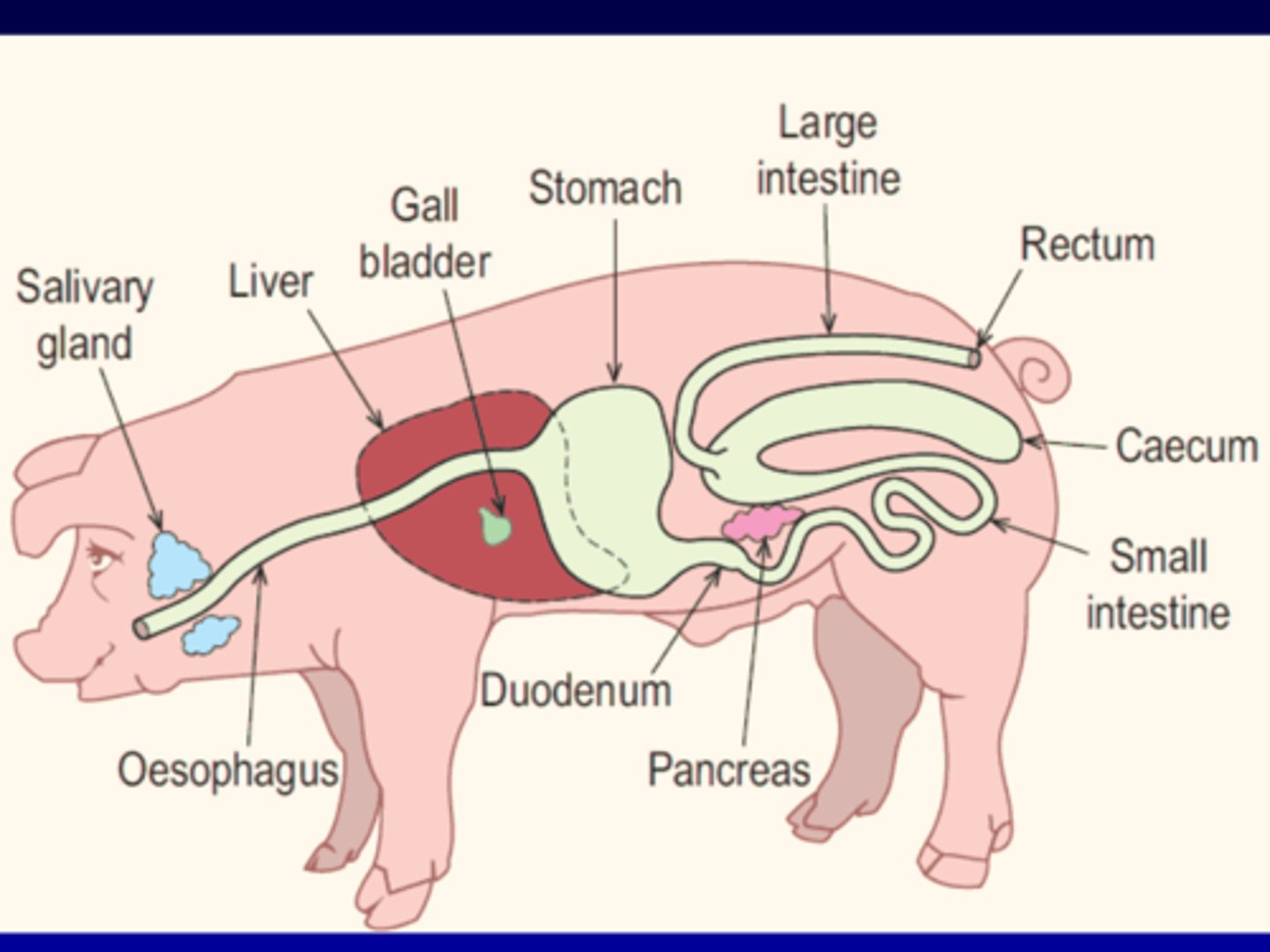
Avian
Chicken or Bird

Rumination
Chewing Cud - regurgitated food from the rumen

Abomasum
The "true stomach" of the ruminant digestive system. It secretes gastric juices consisting of hydrochloric acid.

Esophagus
A tube that connects the mouth to stomach
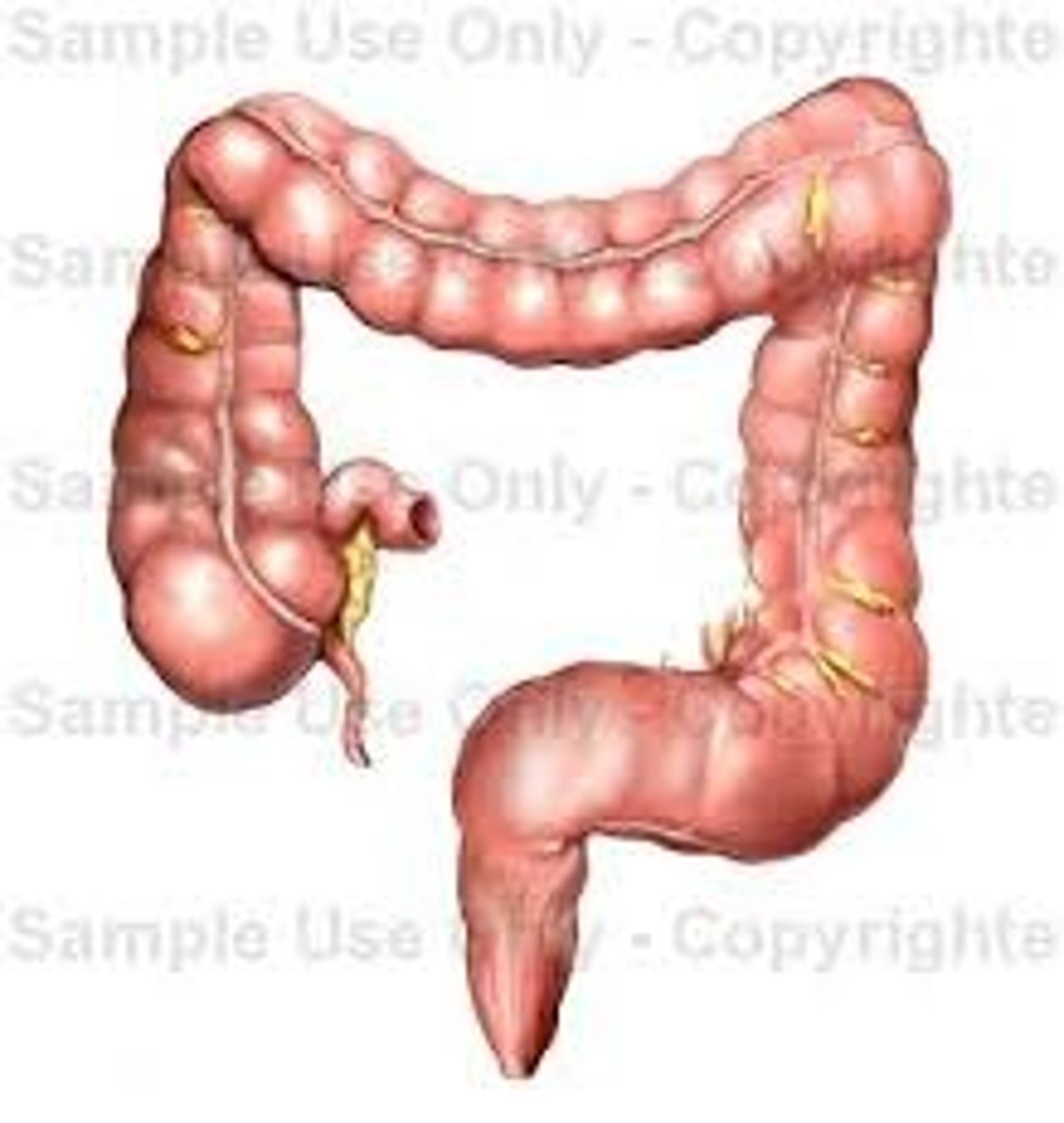
Large Intestine
The last part of the digestive system. The site where water is absorbed and the nutrients enter the bloodstream.
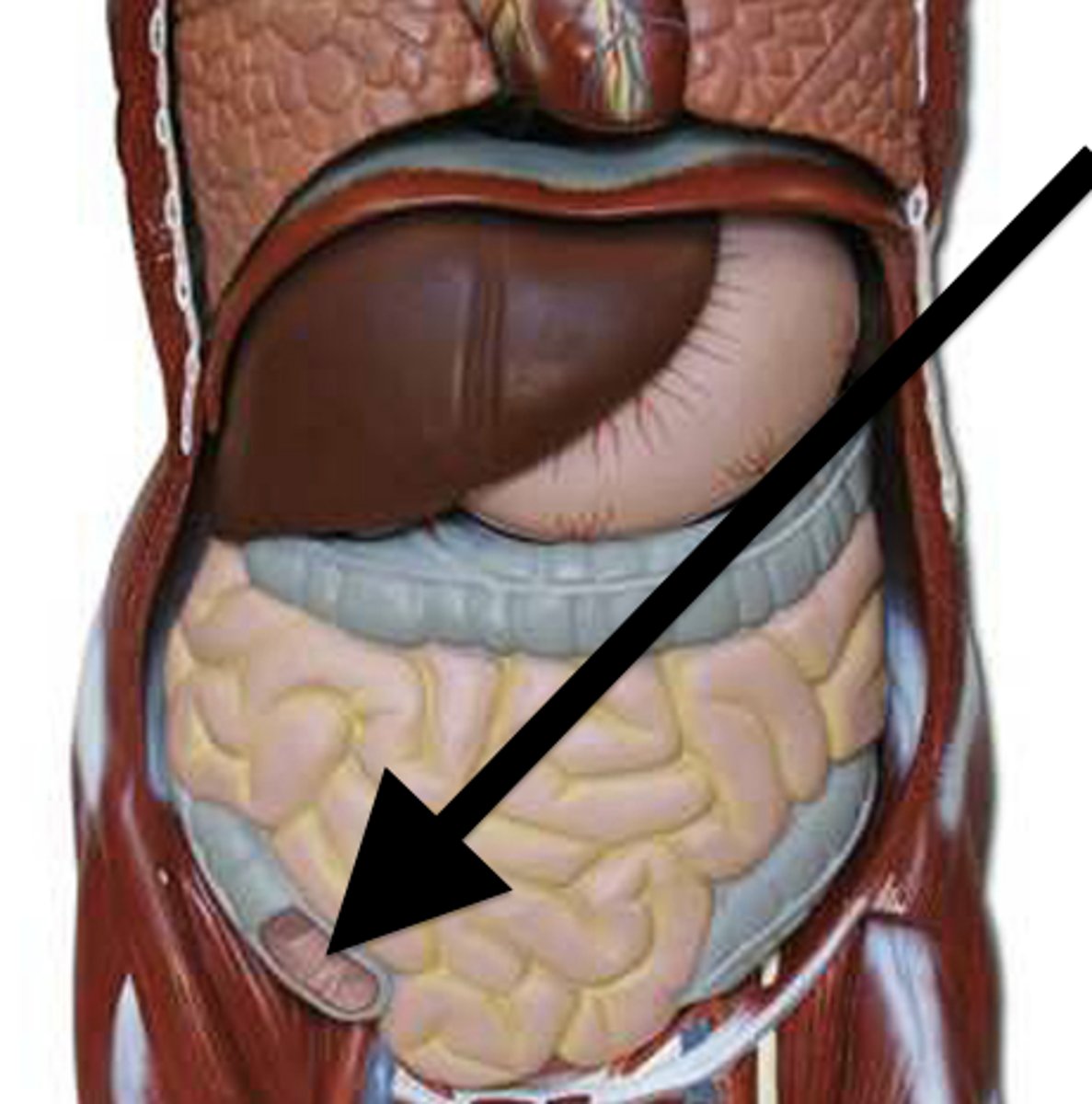
Cecum
Organ between small and large intestine. Digests hay. Horses/rabbits have large ones.
Rectum
The final section of the large intestine that ends at the anus.
Proventriculous
The stomach of a chicken.
Gizzard
Organ that Acts as the teeth for the avian digestive system and grinds up food with gravel
Ceca
Organ in hind gut digesters Located between the small and large intestine used for digestion of fiber with the help of Bacteria.
Cloaca
Where the digestive system and urinary system meet. .
Enzyme
Chemical that speeds up the digestion process.
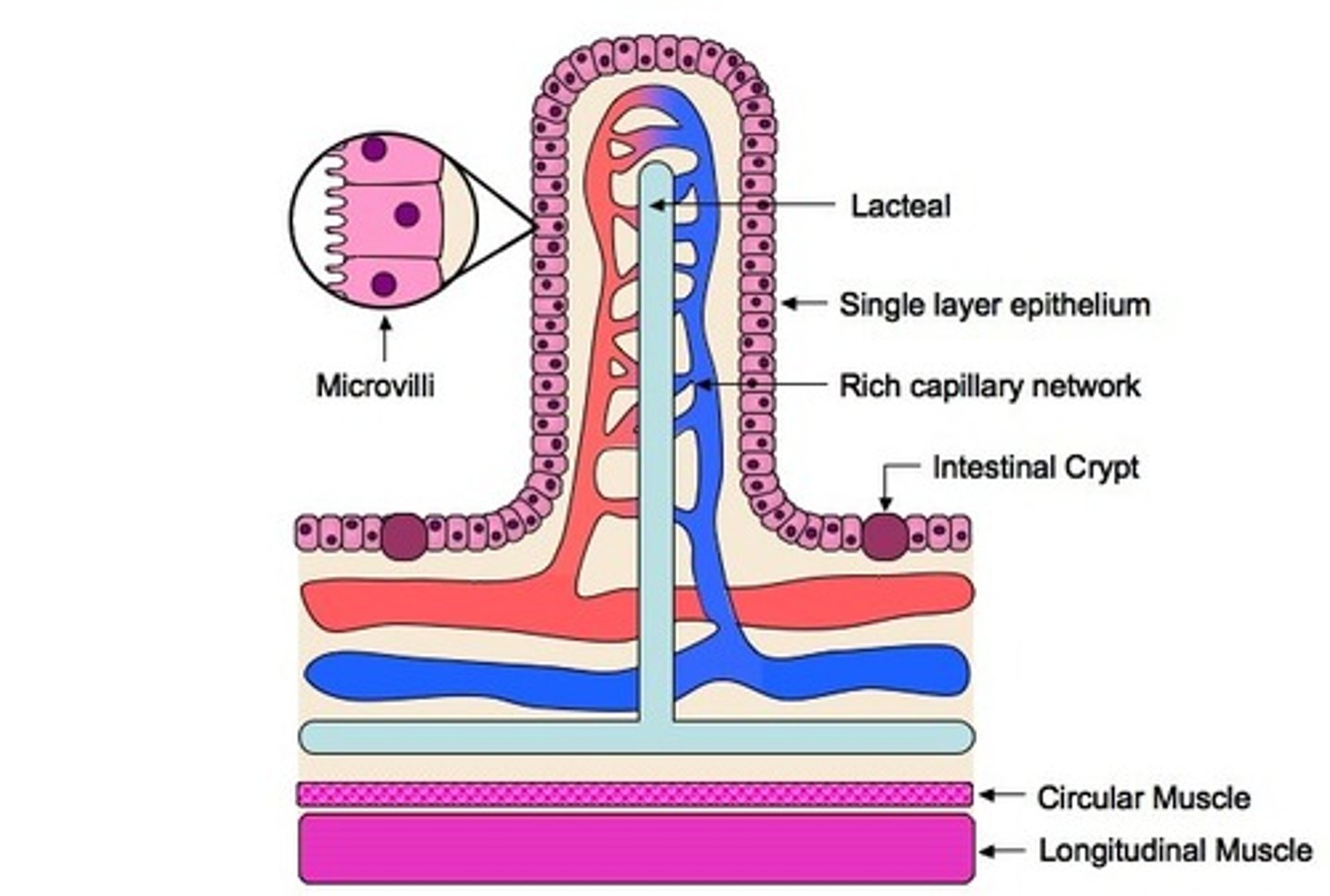
Viili
small finger-like projections on intestine wall for nutrient absorption
How many times ruminants chew cud/ day
6-8 times
Cud
Regurgitated food in ruminants

Canines
Teeth meant to eat meat in carnivores

Incisors
Front teeth meant for clipping plants
Lipase
enzyme that breaks down fat

Amylase
enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates

Lactase
Enzyme that breaks down milk sugar lactose

Hindgut digestion
-Horses, guinea pigs, rabbits
Large cecum and colon allow fermentative digestion in hindgut similar to rumen