Rat Dissection Flashcards
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on rat dissection for biology students, with a focus on anatomy and key terms.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Dorsal
Toward the back
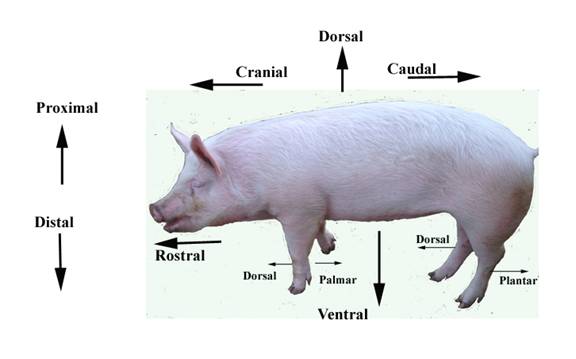
Ventral
Toward the belly
Lateral
Toward the sides
Median
Near the middle
Anterior
Toward the head
Posterior
Toward the hind end (tail)
Superficial
On or near the surface
Deep
Some distance below the surface
Sagittal
Relating to the midplane, bisects the left and right sides
Transverse
Relating to the plane separating anterior and posterior
Horizontal
Relating to the plane separating dorsal and ventral
Proximal
Near to the point of reference
Distal
Far from the point
Caudal
Toward the tail end
Pectoral
Relating to the chest and shoulder region
Pelvic
Relating to the hip region
Dermal
Relating to the skin
Longitudinal
Lengthwise
Abdominal Cavity
Related to the area below (posterior) the ribcage
Thoracic Cavity
Related to the area above (anterior) the ribcage
Cranial region
Head region
Cervical region
Neck region
Pectoral region
Area where front legs attach
Thoracic region
Chest area
Abdomen
Belly
Pelvic region
Area where the back legs attach
Vibrissae
Sensory hairs (whiskers) located on the rat's face
Nictitating membrane
Membrane that can be drawn across the eye for protection
Pinna
External part of the ear
Biceps brachii
Located on the anterior surface of the humerus
Triceps brachii
Located on the sides and back of the upper arm
Spinotrapezius
Located across the dorsal thoracic region of the rat
Latissimus dorsi
Located posterior (and partially covered) by the spinotrapezius
Biceps femoris
Located on the side of the thigh, in two bundles
Tibialis Anterior
Located on the front of the leg
Gastrocnemius
Located on lower leg, bulk of the calf muscle
External Oblique
Located on the sides of the abdomen
Gluteus Maximus
Located on the lower back and rear
Pectoralis Major/Minor
Located in chest
Salivary glands
Soft spongy tissue that secrete saliva and amylase
Lymph glands
Circular glands that lie anterior to the salivary glands
Trachea
Identifiable by its ringed cartilage which provides support
Larynx
Voice box
Diaphragm
Layer of muscle that separates the thoracic from the abdominal cavity
Pericardium
Thin membrane that covers the heart
Thymus gland
Functions in the development of the immune system
Lungs
Spongy organs that lie on either side of the heart
Coelom
Body cavity within which the viscera (internal organs) are located
Peritoneum
Thin membrane that covers the organs of the abdominal cavity
Liver
Dark colored organ suspended just under the diaphragm
Esophagus
Moves food from the mouth to the stomach
Stomach
Functions include food storage, physical breakdown of food, and the digestion of protein
Cardiac sphincter
The opening between the esophagus and the stomach
Pyloric sphincter
The opening between the stomach and the intestine
Spleen
Attached to the greater curvature of the stomach and functions in the destruction of blood cells and blood storage
Pancreas
Produces digestive enzymes that are sent to the intestine via small ducts and secretes insulin
Small intestine
Slender coiled tube that receives partially digested food from the stomach
Mesentery
Membrane that holds the coils of the small intestine together
Colon (large intestine)
Large greenish tube that extends from the small intestine and leads to the anus
Cecum
Large sac where the small and large intestine meet
Rectum
Short, terminal section of the colon that leads to the anus
Pulmonary circulation
Carries blood through the lungs for oxygenation and then back to the heart
Systemic circulation
Moves blood through the body after it has left the heart
Left and right superior vena cava
Conduct blood from the upper part of the body into the right atrium
Inferior vena cava
Carries blood from the lower part of the body to the right atrium
Excretory system
Removes wastes
Reproductive system
Produces gametes (sperm & eggs) and provides an environment for the developing embryo
Kidneys
Primary organs of the excretory system; large bean shaped structures located toward the back of the abdominal cavity
Ureters
Attach to the kidney and lead to the bladder
Urethra
Carries urine from the bladder to the urethral orifice
Adrenal glands
Small yellowish glands embedded in the fat atop the kidneys
Testes
Located in the scrotal sac
Epididymis
Coiled tube on the surface of the testis that collects and stores sperm cells
Vas deferens
Moves sperm from the epididymis to the urethra
Seminal vesicles
Lumpy brown glands located to the left and right of the urinary bladder
Prostate gland
Gland below the bladder that is partially wrapped around the penis
Vagina
Short gray tube lying dorsal to the urinary bladder
Duplex uterus
Divide into two uterine horns that extend toward the kidneys
Ovaries
Small lumpy glands at the tips of the uterine horns
Oviducts
Connect the ovaries to the uterine horns