Humanities | Australian Politics, Law and Economy
1/63
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Laws
Legal rules made by a legal authority that are enforceable.
Rules
Made by private individuals/groups in society.
Principles of justice
Fairness
Equality
Access
Fairness
Means that all people can participate in the justice system. The justice system should be impartial and open.
Equality
All people in the justice system are treated in the same way.
Access
All people should be able to participate and use the justice system.
Characteristics of an Effective Law
Reflect society’s values
Be enforceable
Be known
Be clear and understood
Be stable
Levels of Government
Federal
State
Local
Federal Government
The parliament makes laws for the whole of Australia and is based out of Canberra.
The Federal Government takes care of:
Post, telephones and the internet
Money
Immigration
Defence
State Government
Each of the leaders of the six states and two territories make laws for their state or territory.
The State Government takes care of:
Public transport
Schools
Hospitals
Public housing
Local Government
Look after the particular needs of a city or local community and make local laws.
The Local Government takes care of:
Rubbish collection and recycling
Parks, sports fields and swimming pools
Pet control
Parking
When do we get a federal election?
Every three years
How government is formed
Whoever wins 76 seats or more in the House of Representatives gets to be ‘in government’.
What does The Australian Labor Party typically focus on?
They typically focus on workers’ rights and middle-class issues.
The Labor Party care for causes such as:
Workers getting paid better wages
Workers getting paid more for working overtime and on holidays
Taxing businesses more, so they can redistribute money into roads, hospitals and schools
Generally focussed on health, education, infrastructure and Australian industry.
What does The Liberal Party of Australia typically focus on?
Freedom and traditional values.
The Liberal Party of Australia care for causes such as:
Freedom of speech
Strict law and order policies
Support for individual ownership of private property
Less rules and regulations on business
Lower taxes, to support business and personal wealth
The Australians Greens policies are based around:
Environment and climate change
actionExpanding social welfare
taxing large corporations
Indigenous rights
Reducing the cost of healthcare and education.
National Party of Australia policies are based around:
Supporting farming and agriculture
Regional infrastructure, health and education
Traditional, family values
Media bias
A democratic system relies on individuals being able to make informed decisions about who they vote for.
Is the media impartial?
the media is not impartial. Perceived bias or political leanings.
Referendums
A national vote on a question about a proposed change to the Constitution.
How old do you have to be to vote for the Referendum?
18
What does a referendum need to pass
Double majority, meaning:
It needs a national majority of voters
- I.e. over 50% of all Australians
AND
A majority of voters in a majority of the states
- I.e. over 50% of people in at least 4 of the 6 states
Classical criminology suggests that
A criminal is someone with free will
They make these choices on a cost-benefit analysis
E.g. is doing something illegal worthwhile? If I can rob a bank and make $10 million without any consequence → why wouldn’t I?
Modern criminology theory suggests that:
Criminal behaviours are learned behaviours and Behaviours are reinforced
What does Social bond theory look at?
Why don’t we do crimes?
What are the 4 elements of Social bond theory?
Attachment, Commitment, Involvement, Belief
Labelling theory suggests
assigning of labels to individuals or certain groups can have an effect on their future behaviour.
Labelling theories two key components:
Primary deviance - doing an illegal act.
Secondary deviance - where a person embodies their label as a means of defense or attack.
Feminist criminology
females were seen as ‘doubly deviant’ as they were
breaking the law and
going against their gender roles.
Can a PSO Search you?
Yes, A PSO can search you and your car for spray paint, markers and other graffiti tools if you are 14 years old or older or look over 14, they can also search you for drugs or weapons.
Do I have to give PSOs my name and address?
Yes, PSOs can ask for your name and address around train stations.
Other PSO Powers
arrest you if they think you broke the law or are drunk and disorderly
take alcohol from you if you’re under 18
tell you to move on if you’re disturbing, annoying or making other people unsafe
What is forensics?
methods and processes used to collect, analyse, and interpret evidence in order to assist in investigations and legal proceedings.
Why do we need DNA evidence?
DNA evidence can establish that a person is responsible for a serious crime if she/he leaves behind traces of DNA
What are the two main types of forensic samples?
Non-intimate - hair sample, matter from under fingernail, external body swabs.
Intimate - blood sample, sample of pubic hair, scraping from the mouth, genital swab.
What is scarcity in economics?
Needs and unlimited wants, yet only limited productive land, labor and capital resources to satisfy these needs and wants
What is ‘opportunity cost’?
The value of the next best alternative that must be given up when making a choice between two or more options.
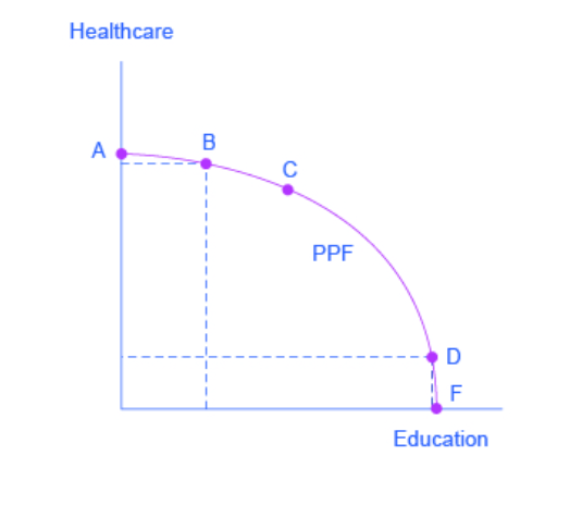
How could opportunity cost be seen in this PPF?
From Point A to C, most of our resources are going into healthcare. From Point C to D, our resources gradually shift towards education, until Point F, where all of our resources go to education.
What is economic efficiency?
It refers to the optimal use in resources in the production of goods and services, with no wastage.
What can economies do to promote economic growth?
To increase productivity, improve quality, enhanced efficiency and expand resources.
What current issues impact Australia’s economy?
Australia’s GDP is declining the reasons are: Fewer people are going into Australia. Higher housing prices and slow construction rates. We focus too much on a few key industries.
What is bounded rationality?
People have limited rationality and make a decision based on a limited set of info and cognitive abilities.
What is the anchoring bias?
People rely too heavily on the first piece of info they receive when making a decision.
What is consumer willpower?
Consumers don’t posses absolute self-control when confronted with choices
What is free trade?
The absence of government intervention of any kind in international trade
What are the benefits of free trade?
Increased competition leading to lower prices. Trade increases the flow of new ideas and tech, greater choice of consumers, and specialisation
What are the negatives of free trade??
Increased unemployment, infant industries can’t develop, predatory pricing and a loss of culture.
What are the protections against free trade?.
Using trade barriers. They are restriction that prevent foreign products of services from freely entering the nation’s territory.
What is the free market?
A free market is an economic system based of supply and demand with little to no government control
What are public goods?
Public goods are services or resources provided by the government that benefit everyone in society.
What is market failure?
A situation where the free market, doesn’t allocate resources effiently.
What is Herd behaviour?
When individuals in a group follow the decisions of others, rather than making their own choices.
What is Vividness?
Consumers may place too much weight on a small number of vivid observations.
What is Framing Effect?
People's decisions are influenced by how information is presented or "framed."
What is Sunk Cost Fallacy?
Continue to invest time, money, or other resources into a decision, even if it's no longer rational to do so, simply because they've already invested a lot of time, money, or resources in it.
What is a Absolute advantage?
Refers to the ability of one country to produce a good using fewer resources than another country.
What is a monopoly?
A market structure that consists of a single seller or producer with no close competition.
What is a duopoly?
Two competing businesses control the majority of the market for a particular product or service they provide.
What is a oligopoly?
Is when a few companies exert significant control over a given market.