APES Unit 5 Land and Water Use
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
DDT
A synthetic organic compound used as an insecticide. Like other chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons, it tends to persist in the environment and become concentrated in animals at the head of the food chain. Its use is now banned in the U.S., but is still used in other countries.
Labor-Intensive Subsistence Agriculture
Type of agriculture that requires large levels of human and animal labor to be successful
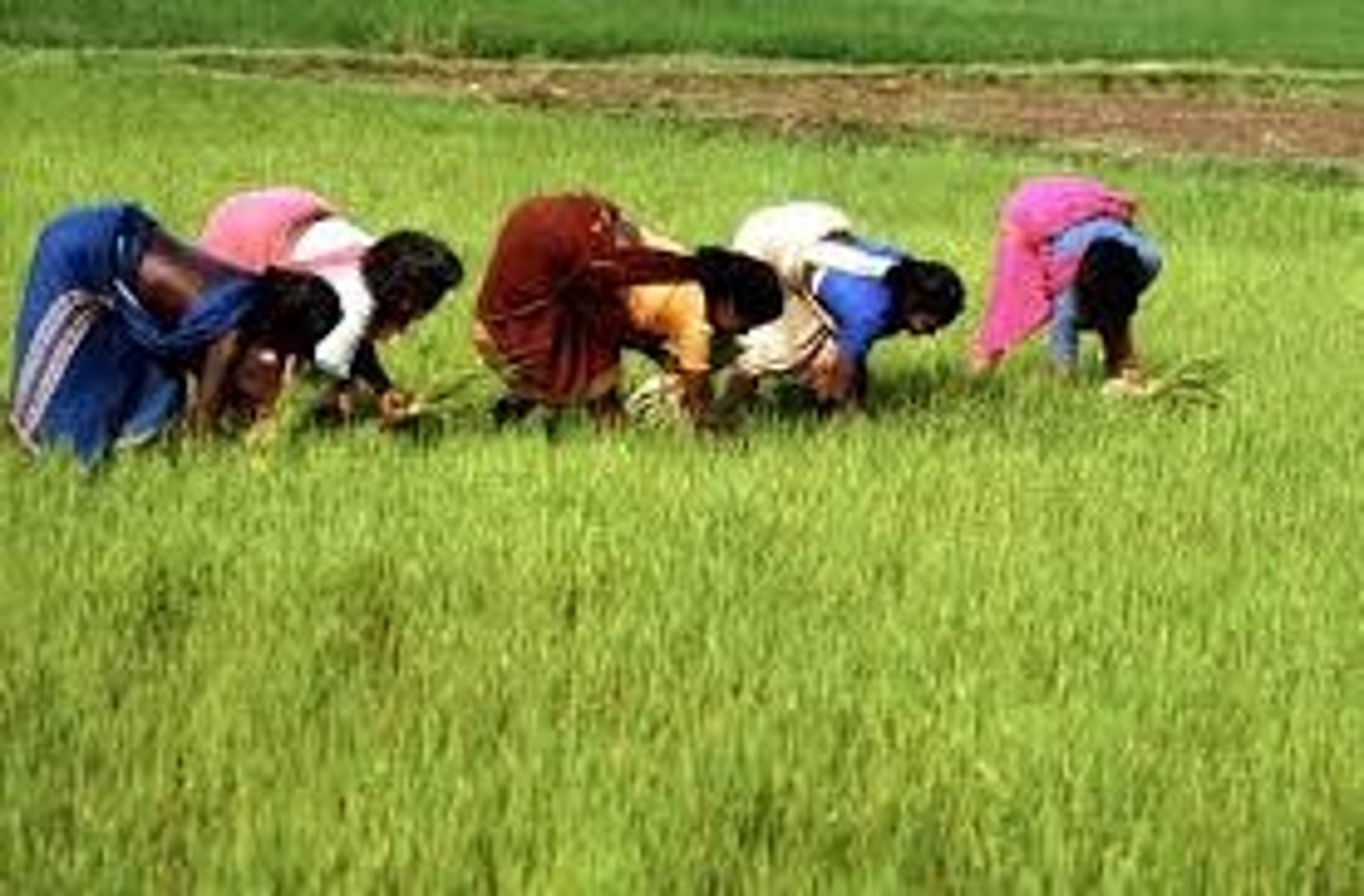

Subsistence Agriculture
Agricultural practice used mostly in developing countries. Production of food primarily for consumption by the farmer's family

Industrial Agriculture
A form of agriculture that uses large scale mechanization and fossil fuel combustion, enabling farmers to replace horses and oxen with faster and more powerful methods of farming.

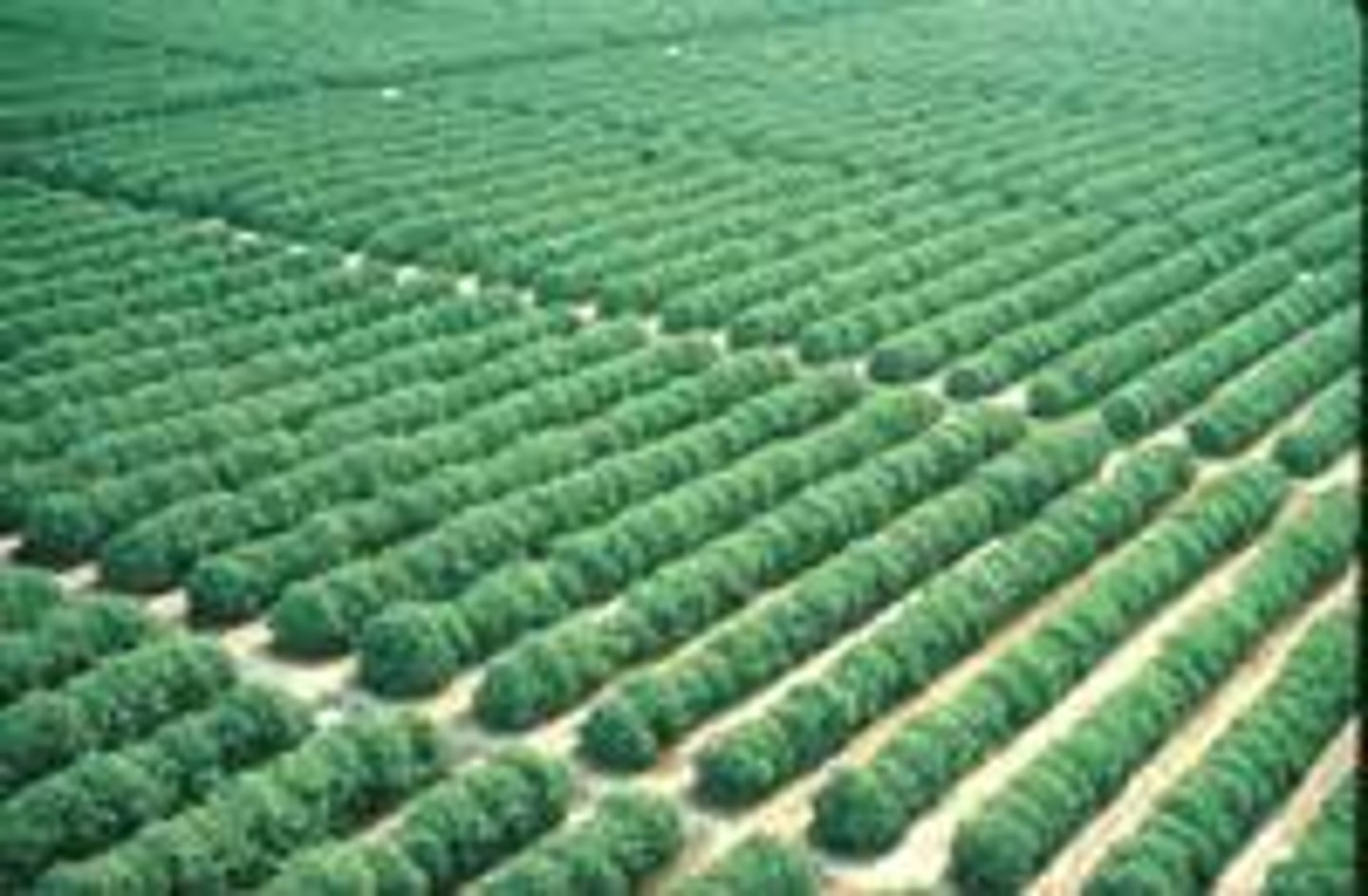
Monocropping (Monoculture)
The cultivation of a single crop on a farm or in a region or country; a single, homogeneous culture without diversity or dissension.

Intercropping (Polyculture)
Planting different types of crops in alternating bands or other spatially mixed arrangements.
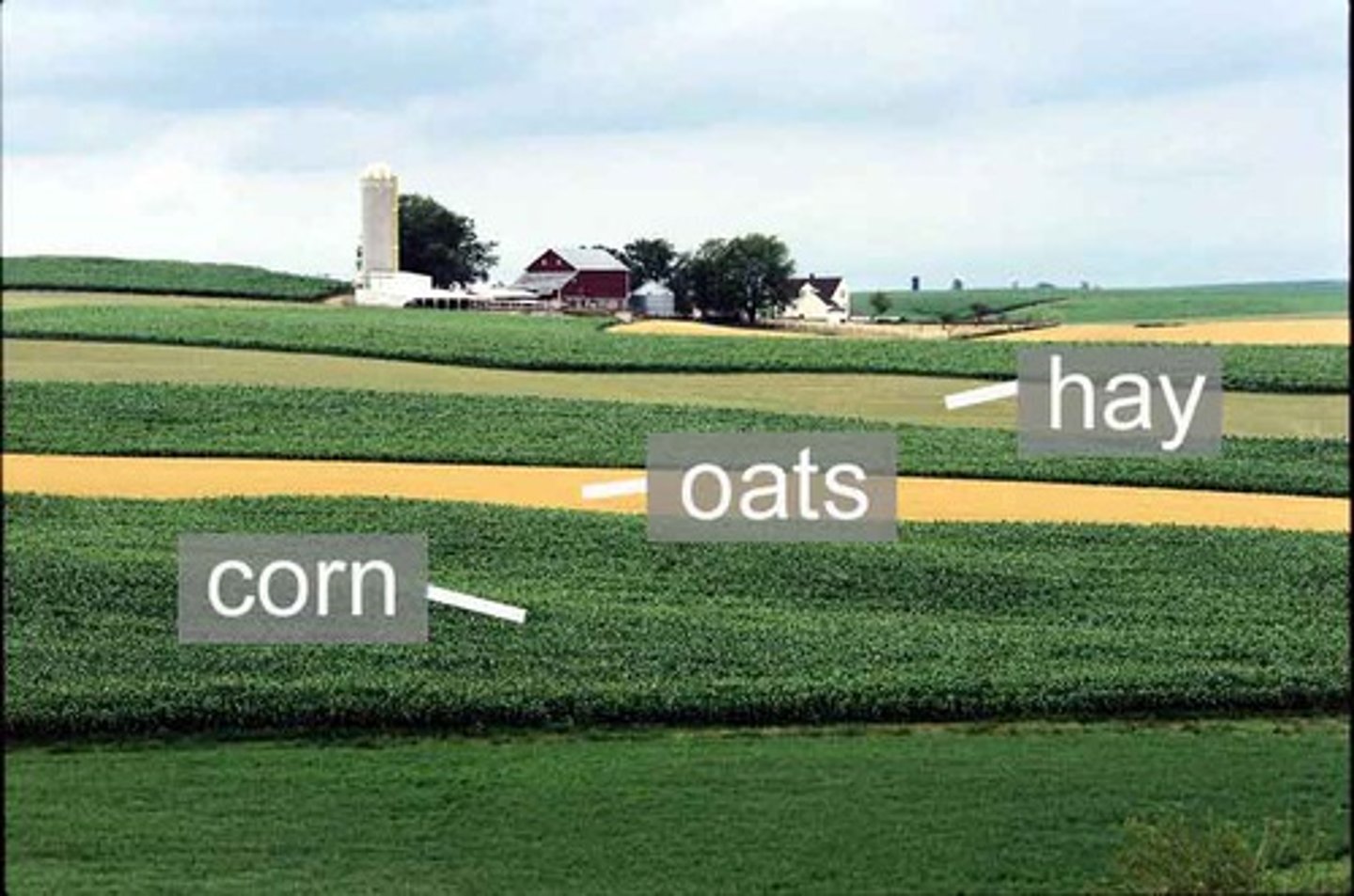

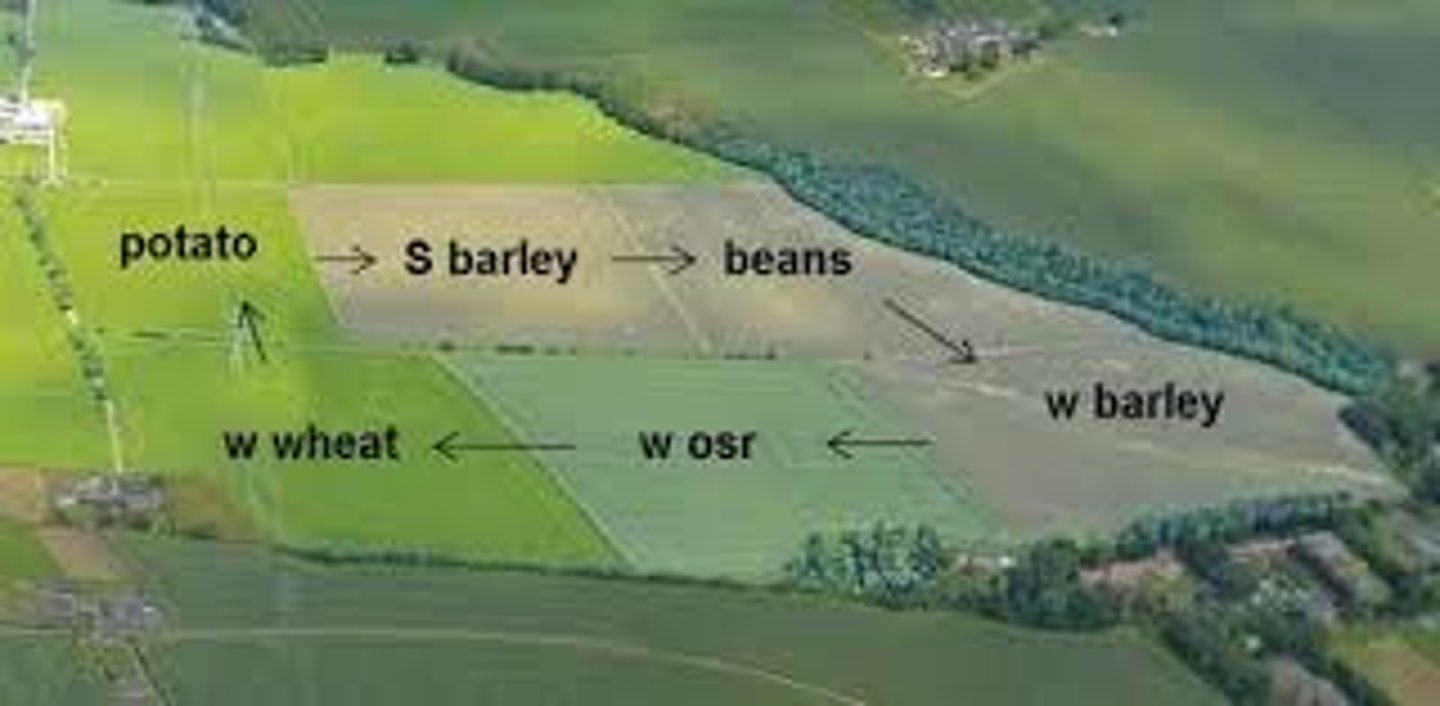
Crop Rotation (Polyculture)
The planting of different crops in a field each year to maintain the soil's fertility.
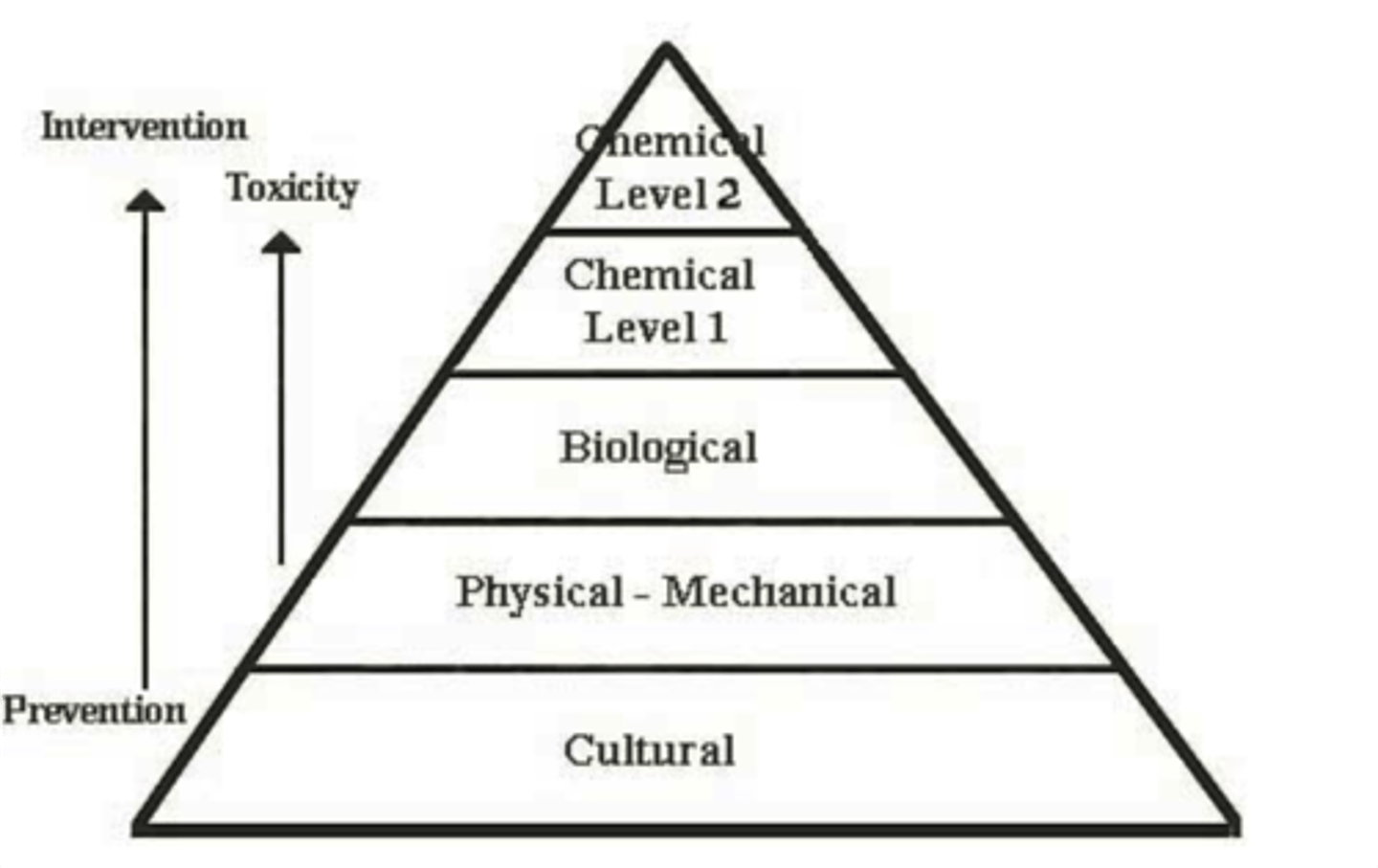
Integrated Pest Management
A combination of methods used to effectively control pest species while minimizing the disruption to the environment. These methods include biological, physical, and limited chemical methods such as biocontrol, intercropping, crop rotation, and natural predators of the pests.
Pesticide
Chemicals used on plants that do not harm the plants, but kill pests and have negative repercussions on other species who ingest the chemicals.
Persistence
Pesticides remaining in the environment for more than one growing season or for more than one year after applications
Soil Erosion
The loss of soil components, especially topsoil; usually caused by flowing water, wind, or both. This process has been greatly accelerated by modern agricultural practices.
Automobile
Form of transportation that dominates suburbs in the U.S due to poor planning. Its reliance encourages use of petroleum/gasoline and discourages the development of mass transportation.
Pesticide Resistance
Describes the decreased susceptibility of a pest population to a pesticide that was previously effective at controlling the pest. Caused by natural selection.
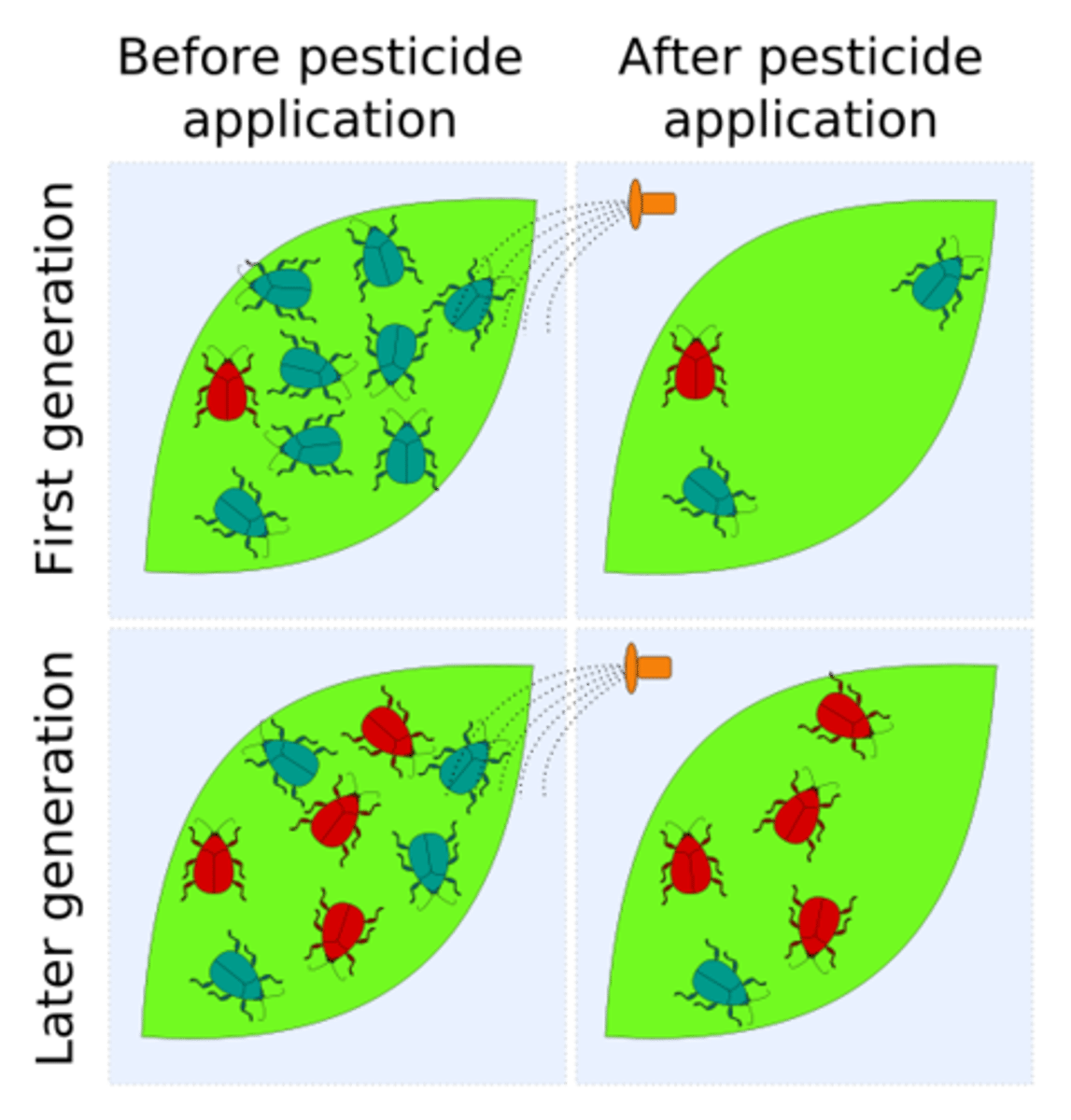
Pesticide Treadmill
Process through which a farmer uses more pesticides, with increasing costs, as the effectiveness of pesticides decreases
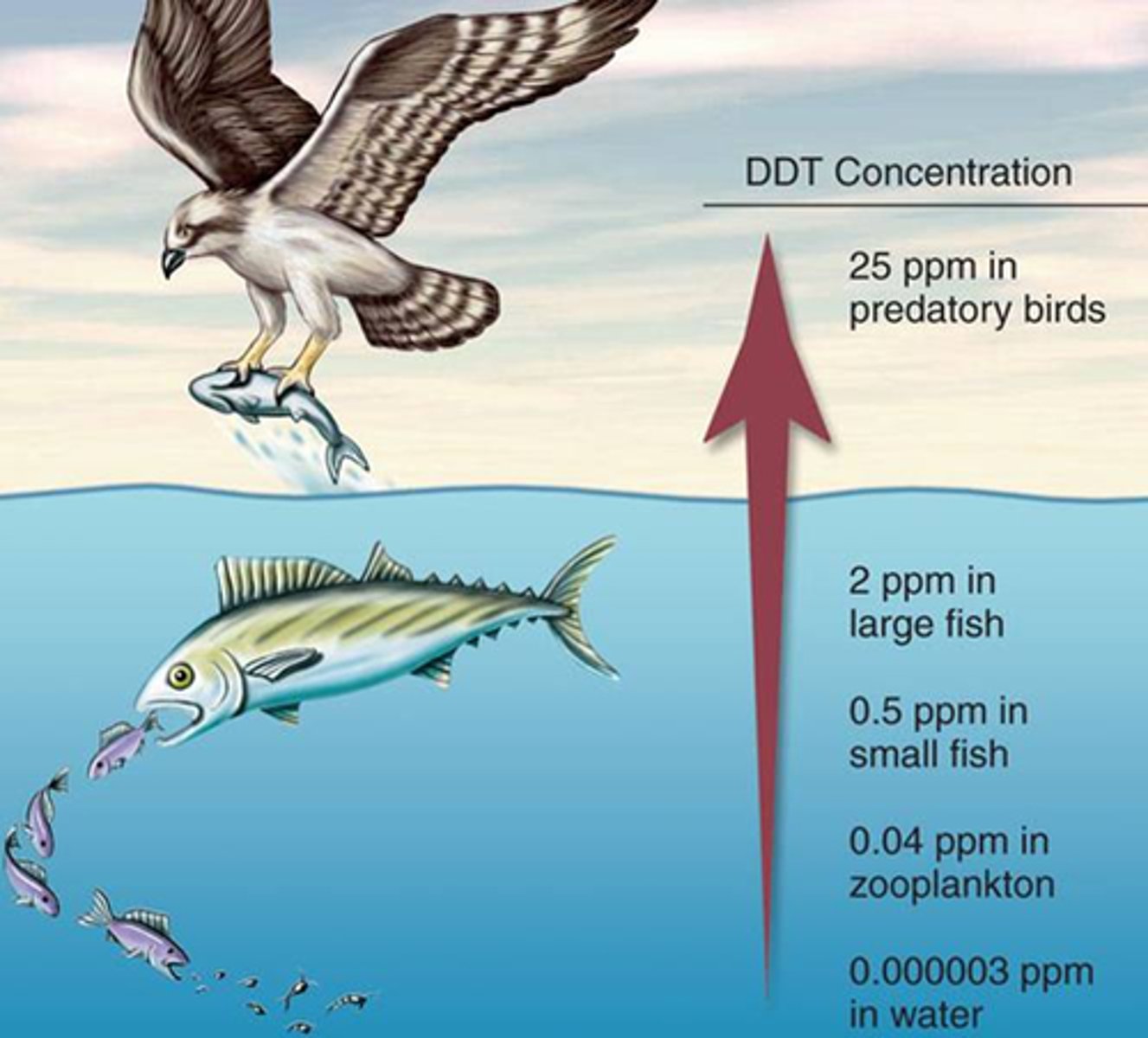
Biomagnification
Increase in concentration of certain stable chemicals (for example, heavy metals or fat-soluble pesticides) in successively higher trophic levels of a food chain or web
Organic Agriculture
The use of crop rotation, natural fertilizers such as manure, and biological pest control, as opposed to artificial fertilizers,pesticides, hormones, antibiotics, additives, and genetically modified organisms, to promote healthy vigorous crops.
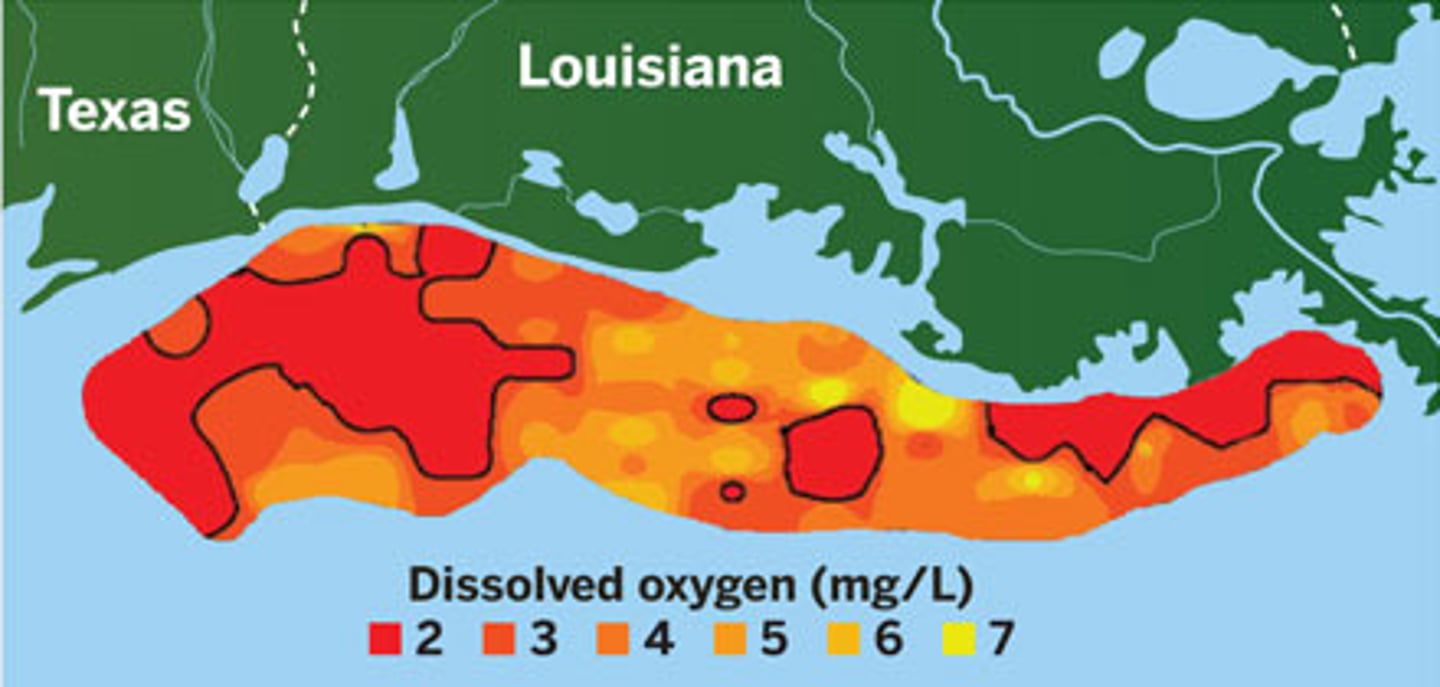
Gulf of Mexico Dead Zone
Largest hypoxic zone in the US (about the size of Connecticut). Result of excess nutrients from the Mississippi River and seasonal stratification in the Gulf. This stratification prevents the mixing of oxygen-rich surface water with oxygen-poor water on the bottom of the Gulf.
Sustainable Development
Modern movement in urban development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Smart Growth
Anti-sprawl development that is environmentally and economically smart; it includes improved land-use planning, efficient buildings, and better transportation efficiency.
Genetically Modified Crops
Foods that are mostly products or organisms that have their genes altered in a laboratory for specific purposes, such as disease resistance, increased productivity, or nutritional value allowing growers greater control, predictability, and efficiency. However, they can lead to loss of genetic diversity of that particular crop.
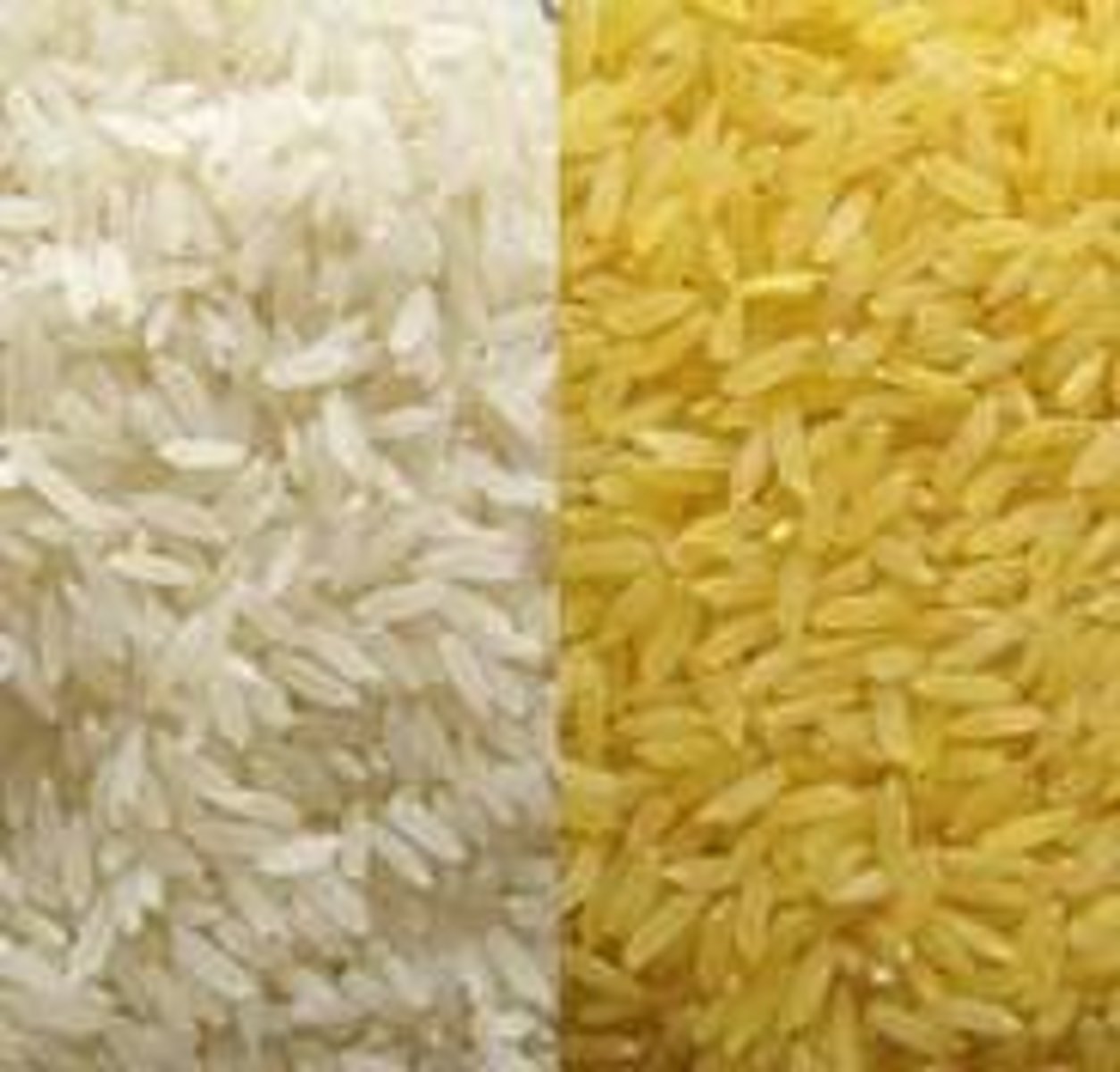

Green Revolution
The worldwide campaign to increase agricultural production from the 1940s to 60s, stimulated by new fertilizers and strains of wheat. The movement saved millions from starvation.

Fertilizers
Sprayed on crops to increase nutrients and crop yield; contain nitrates and phosphates
Colony Collapse Disorder
The disappearance of bees due to them dying far away from the hive

Old Growth Forest
Forests that have not been cut or disturbed for hundreds of years

Deforestation
The removal of trees faster than forests can replace themselves.

Clear Cutting
A method of harvesting trees that involves removing all or almost all of the trees within an area.
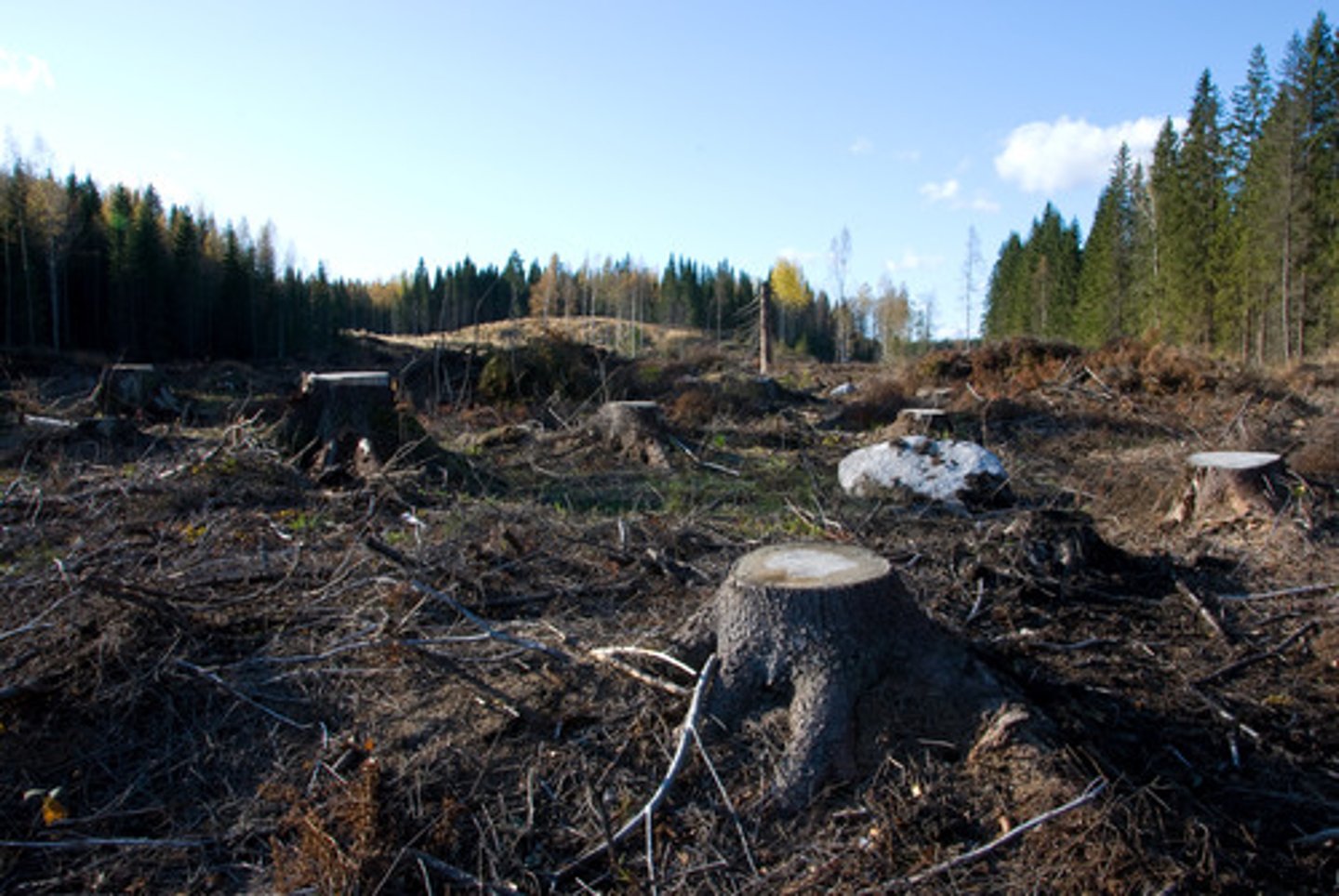

Selective Cutting
Method of forestry which you only cut trees of a certain type, size or quality
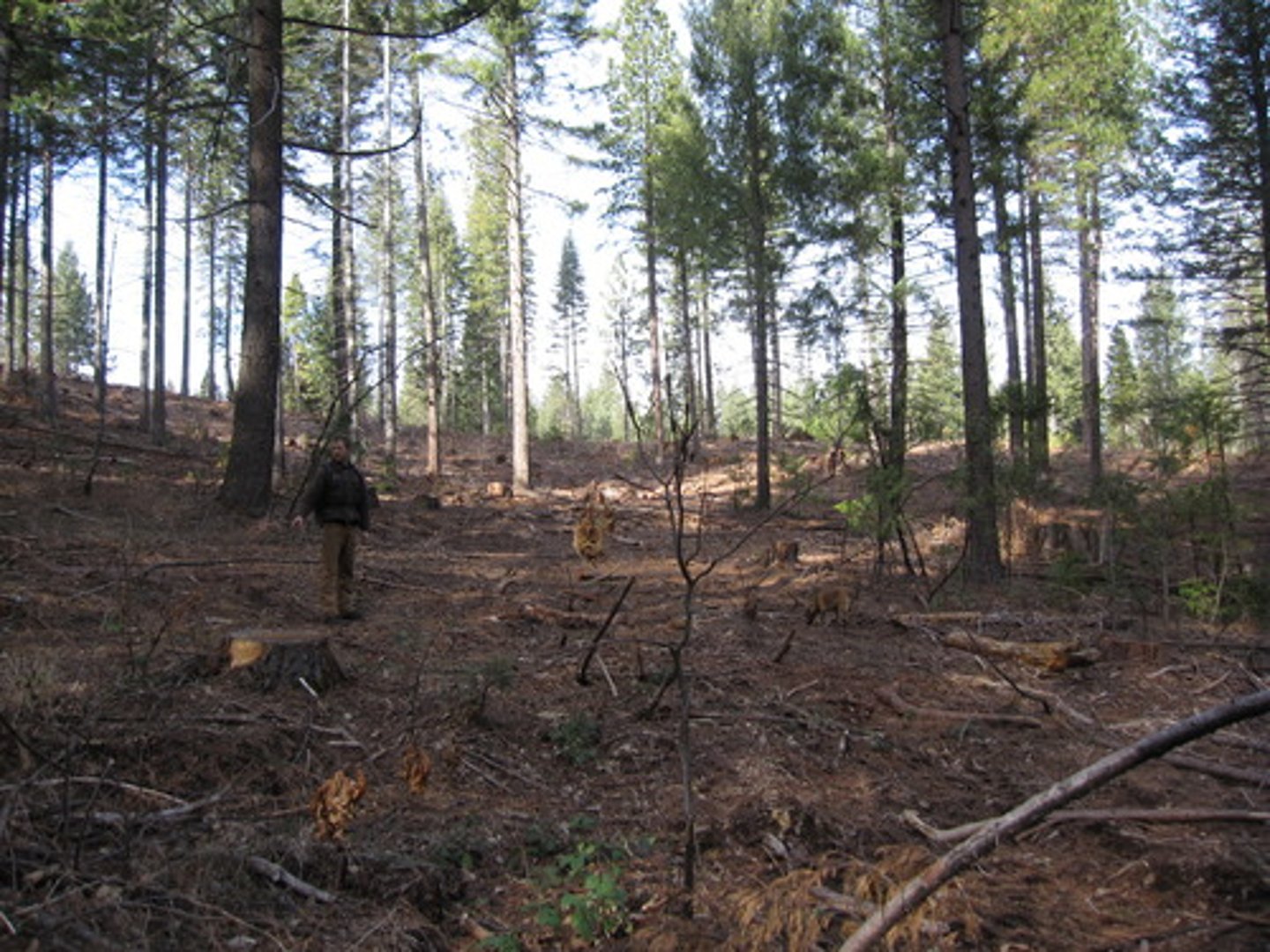

Forest Fire Suppression
Practice of reducing the occurrence of natural forest fires. Leads to over-growth of vegetation, and eventually, more severe forest fires.

Urbanization
Movement of people from rural areas to cities
Runoff
Water that moves across the land surface and into streams and rivers, rather than soaking into the ground.

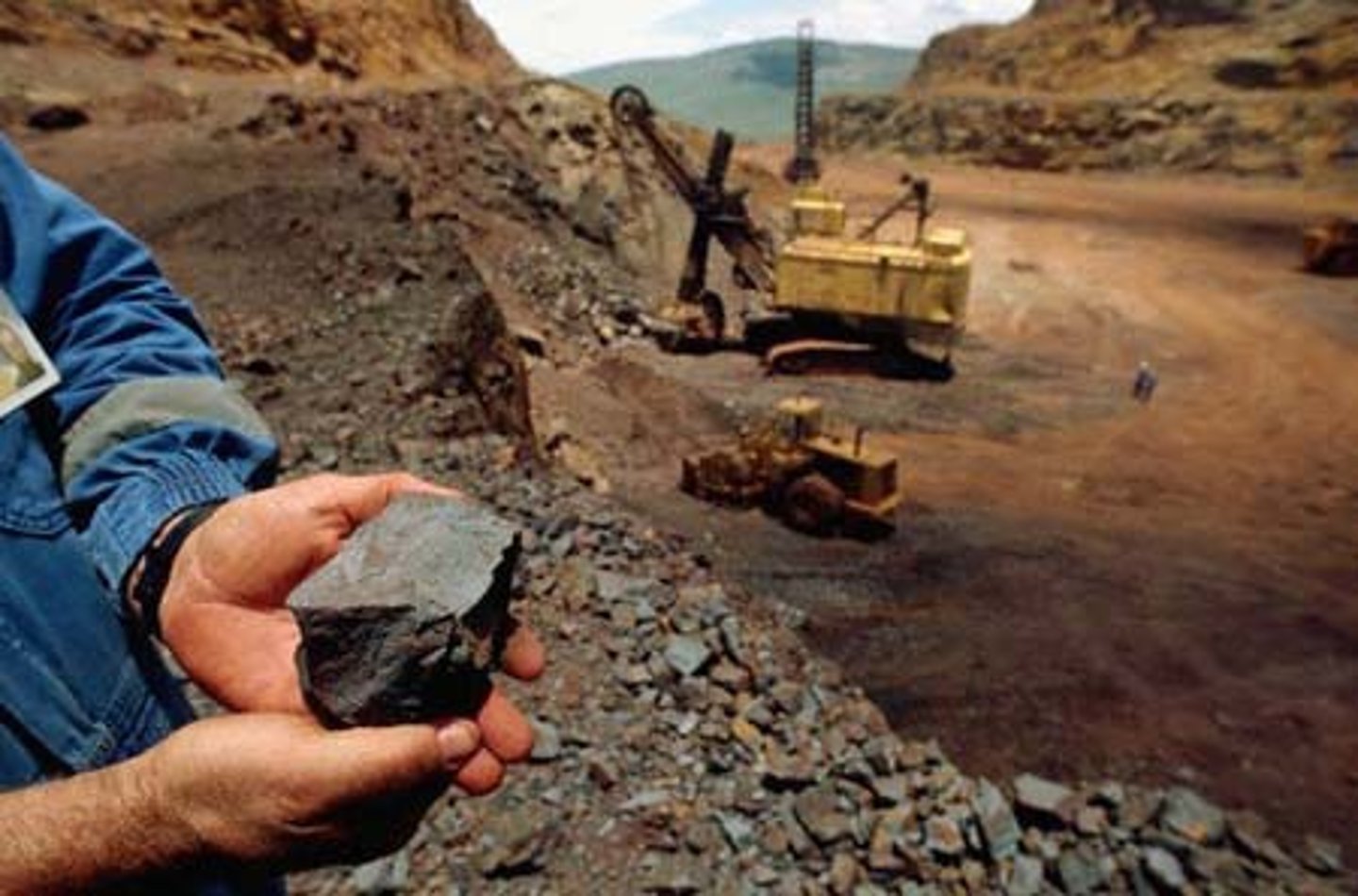
Ore
Rock that contains a metal or economically useful mineral

Overburden
Layer of soil and rock overlying a mineral deposit. Surface mining removes this layer.
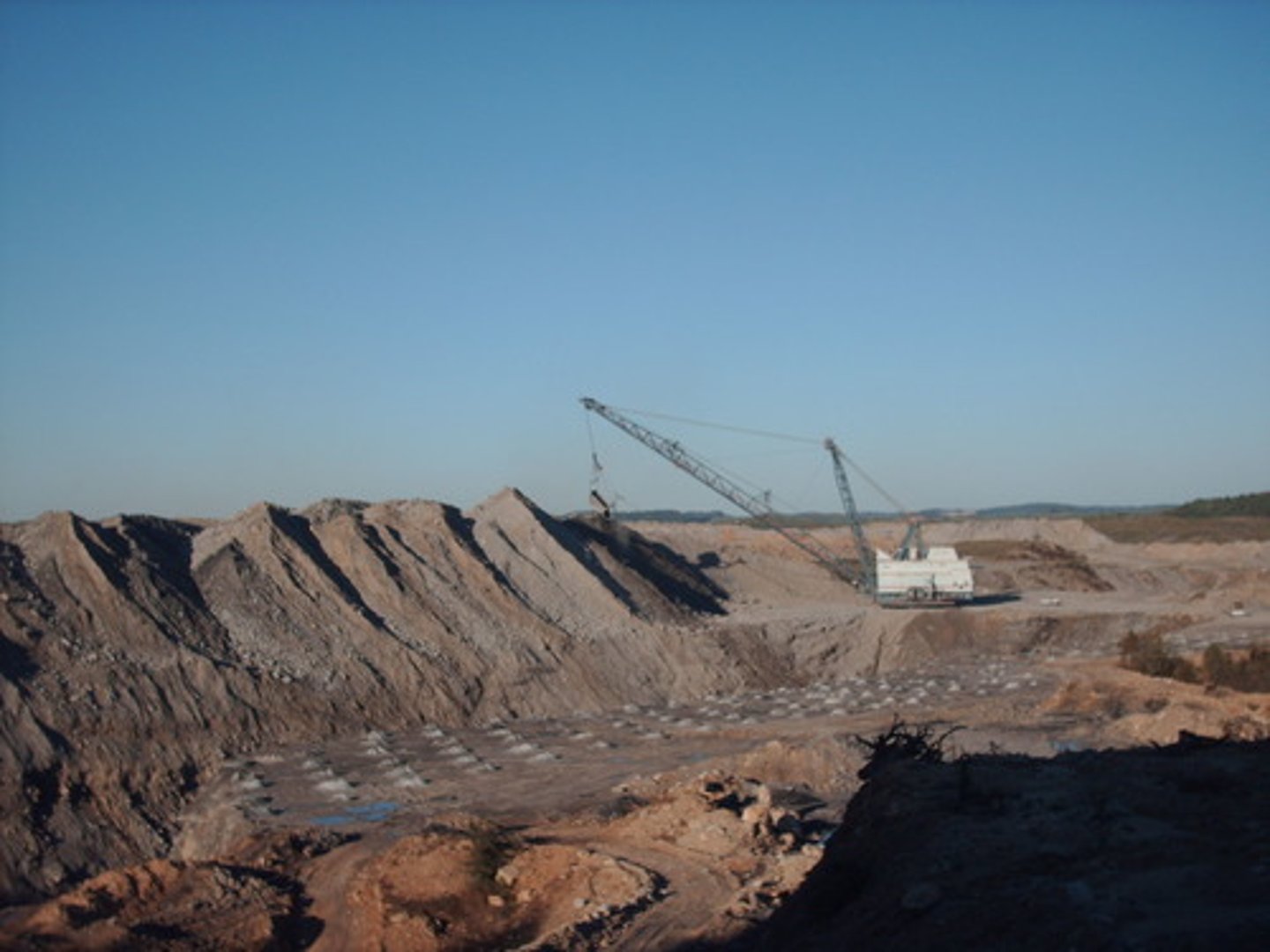

Surface Mining
The removal of large portions of soil and rock, called overburden, in order to access the ore underneath. An example is strip mining, which removes the vegetation from an area, making the area more susceptible to erosion.
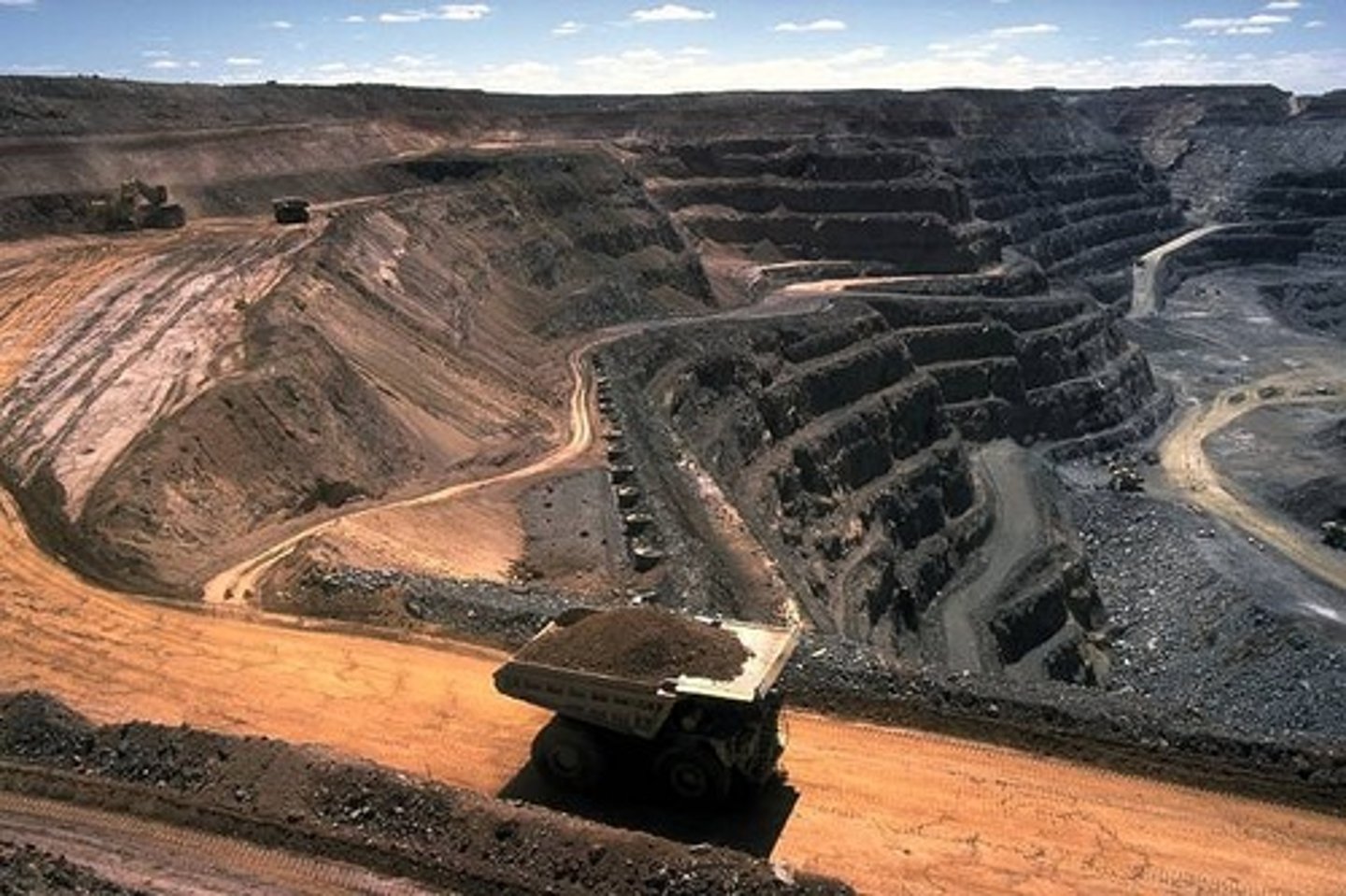

Subsurface Mining
The practice of digging shafts deep into the ground to find and remove a mineral

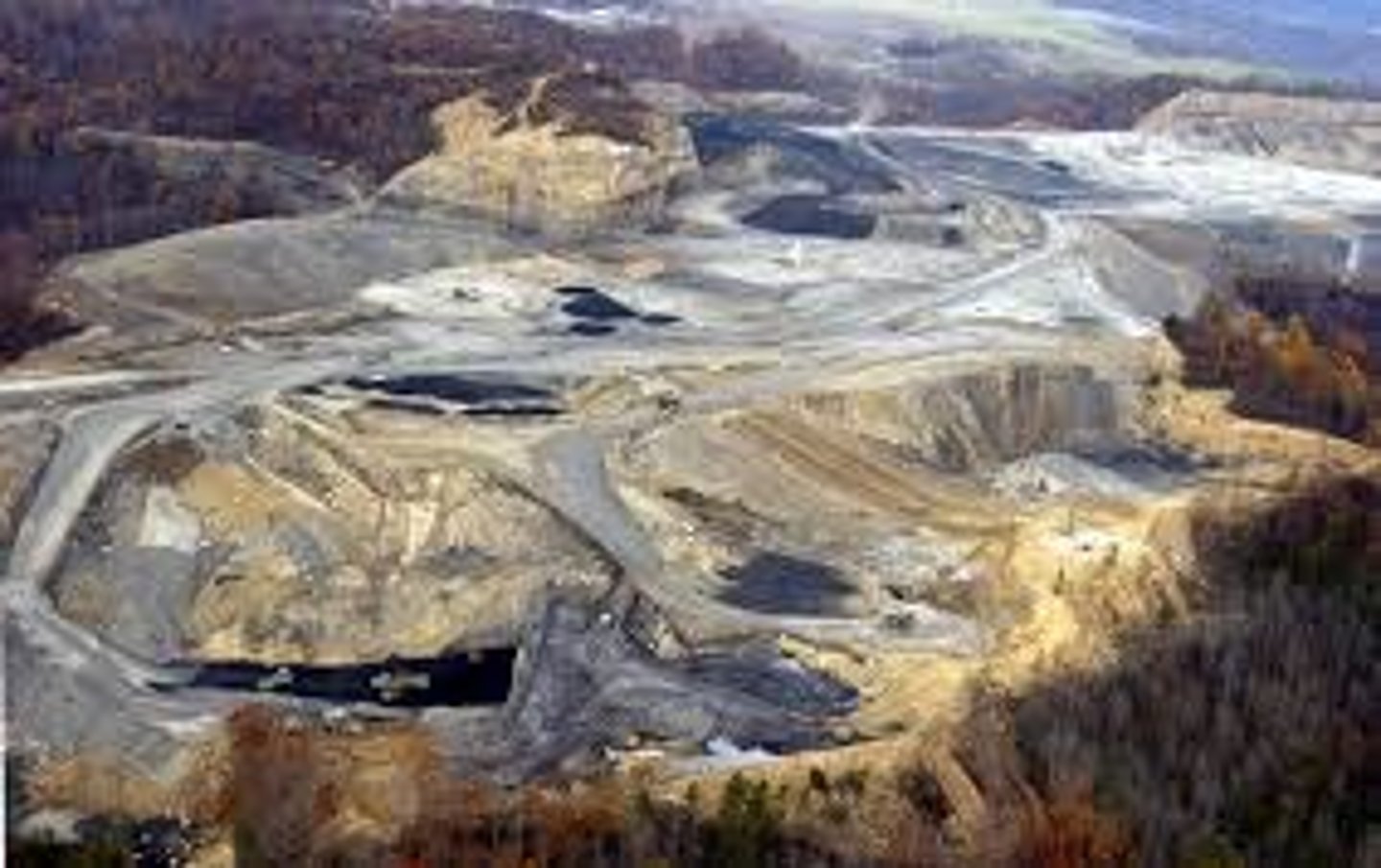
Mountaintop Removal
A mining technique in which the entire top of a mountain is removed with explosives

Black Lung Disease
Inflammation and fibrosis caused by accumulation of coal dust in the lungs or airways.
Acid Mine Drainage
Acidic leachate, normally rich in heavy metals that drains from either tailings or underground mines.
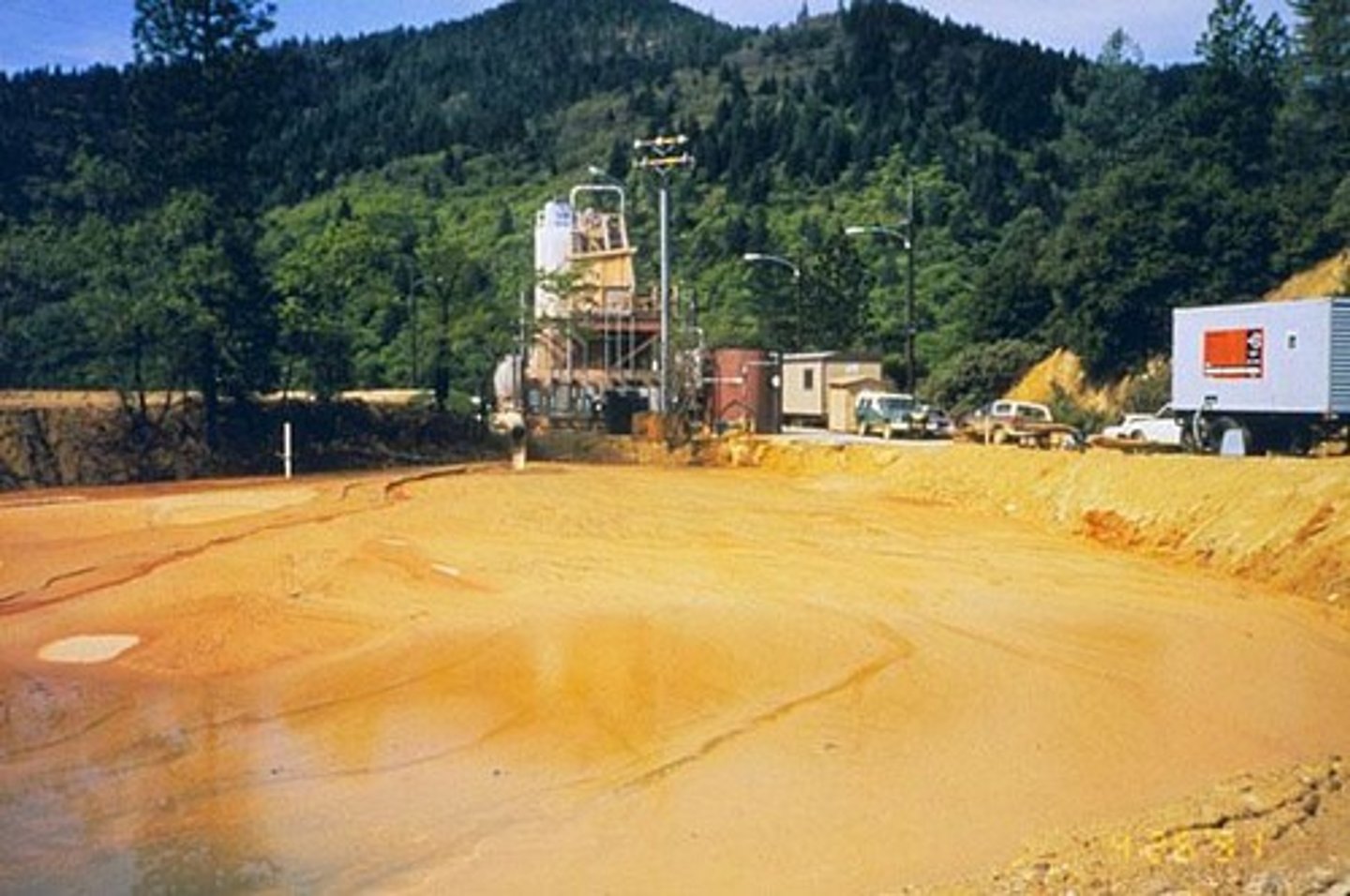

Subsidence
The gradual caving in or sinking of an area of land, potentially caused by subsurface mining.
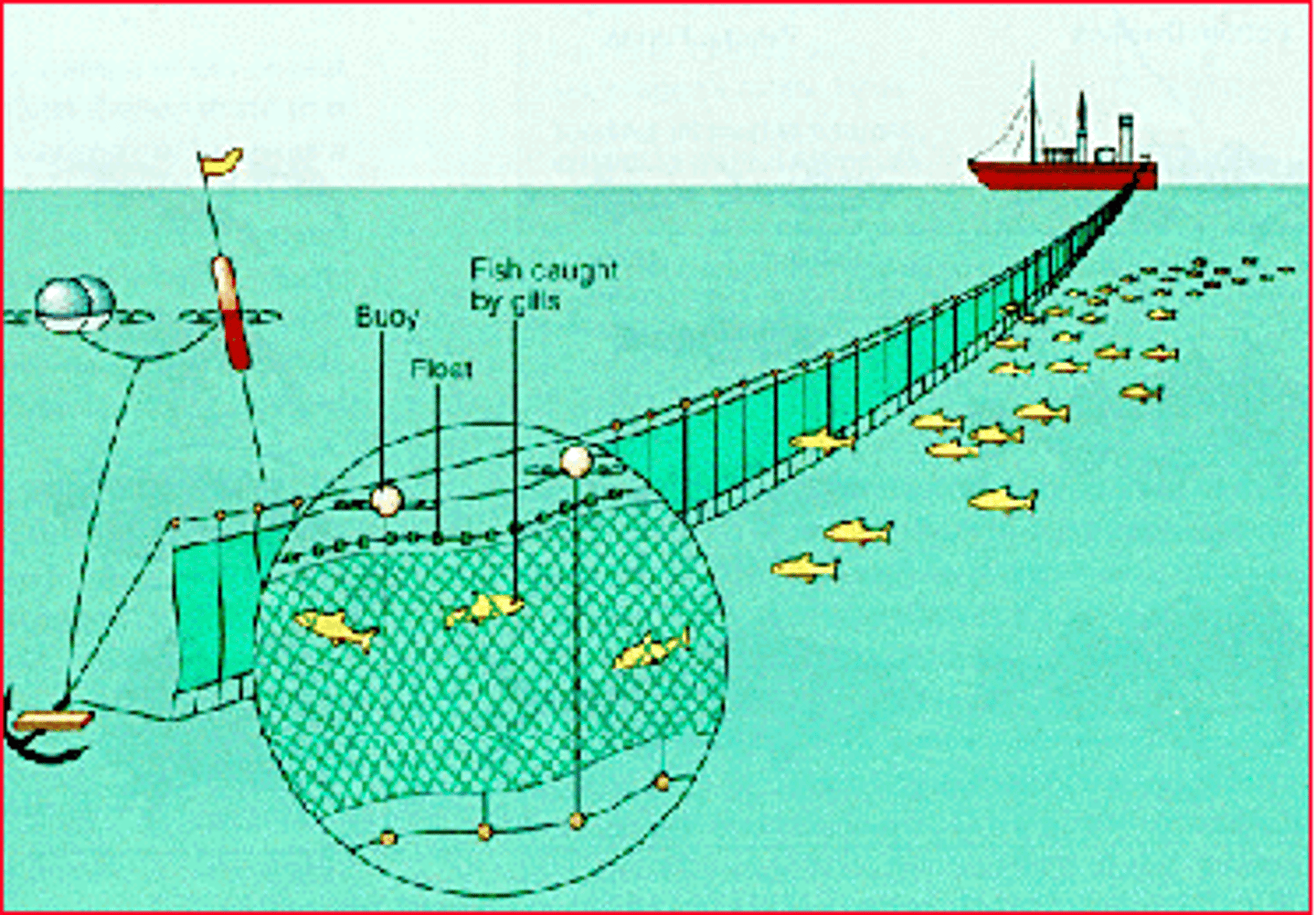
Trawling
Method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats.
Drift Net
A fishing net that is allowed to drift for a long time before it is pulled on board
Longlining
This type of fishing puts out lines up to 80 miles which have thousands of baited hooks
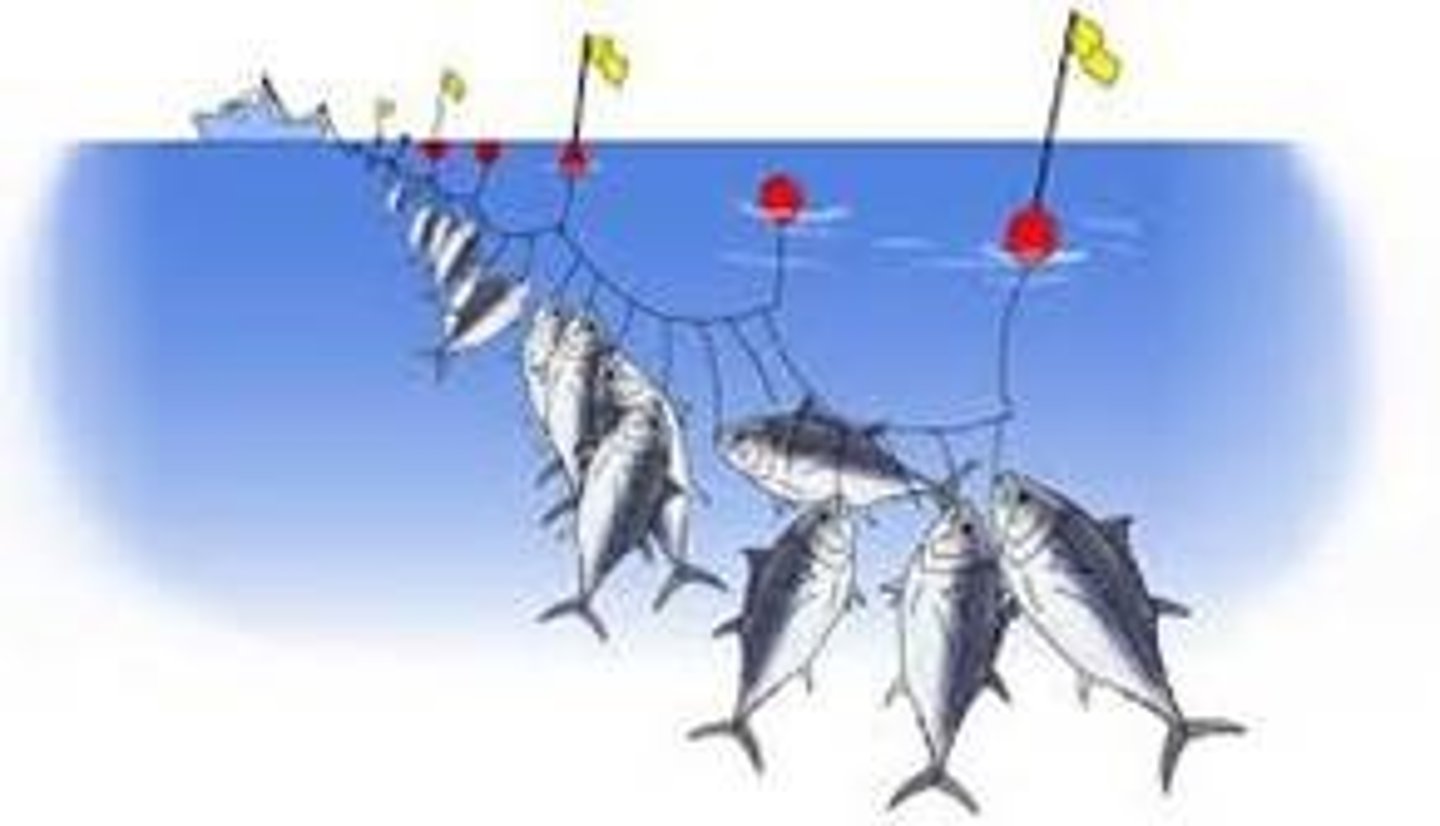

Overfishing
Harvesting fish to the point that species are depleted and the value of the fishery reduced. Has led to the extreme scarcity of some fish species, which can lessen biodiversity in aquatic systems and harm people who depend on fishing for food and commerce.
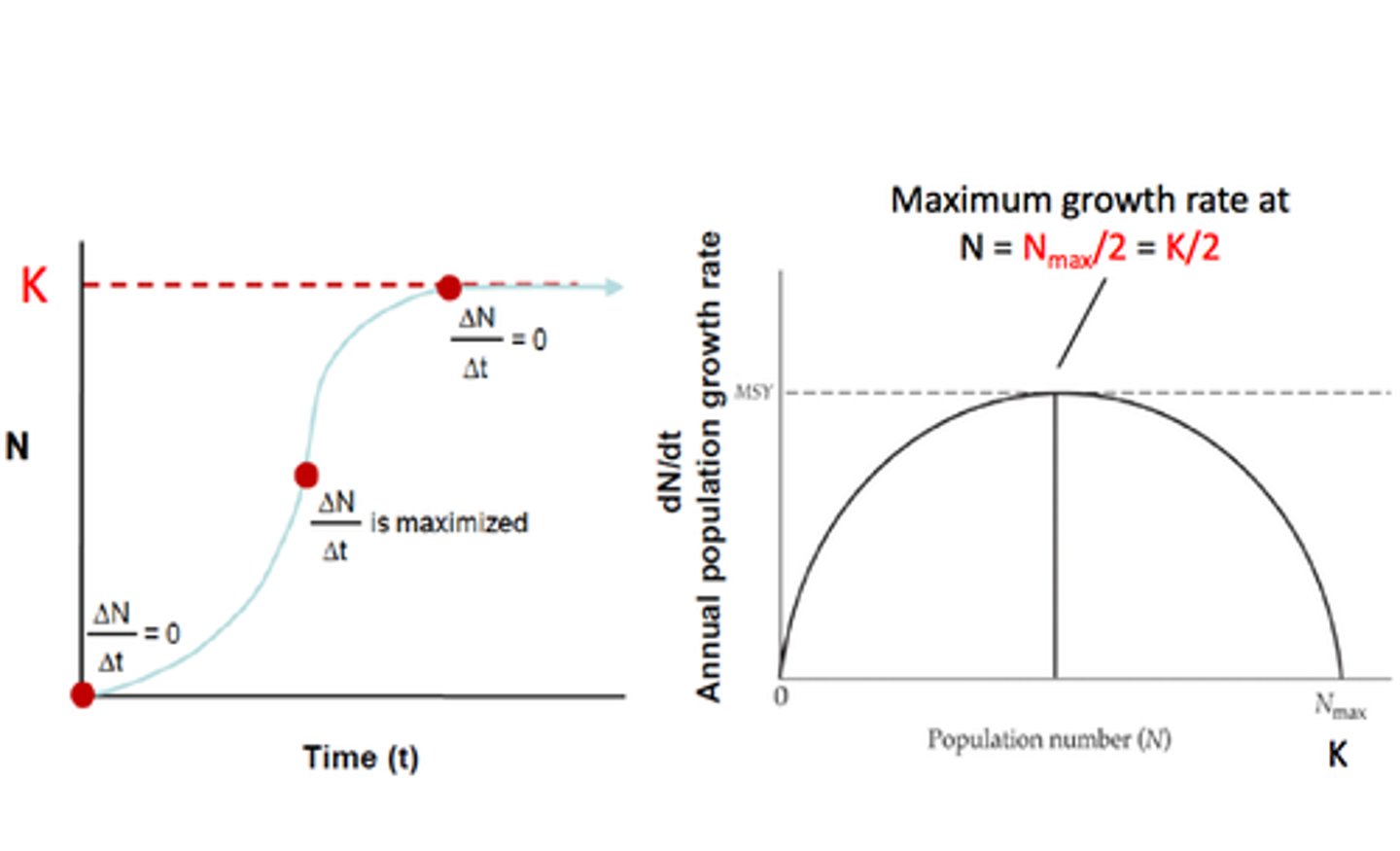
Maximum Sustainable Yield
The amount of a renewable resource that can be taken without reducing the available supply.
Bycatch
The unintentional catch of nontarget species while fishing
Tragedy of the Commons
Suggests that individuals will use shared resources in their own self-interest rather than in keeping with the common good, thereby depleting the resources.
Reduced Tillage
Farming methods that preserve soil and save energy and water through reduced cultivation.
Tilling
The turning-over of soil before planting. (i.e. plowing)

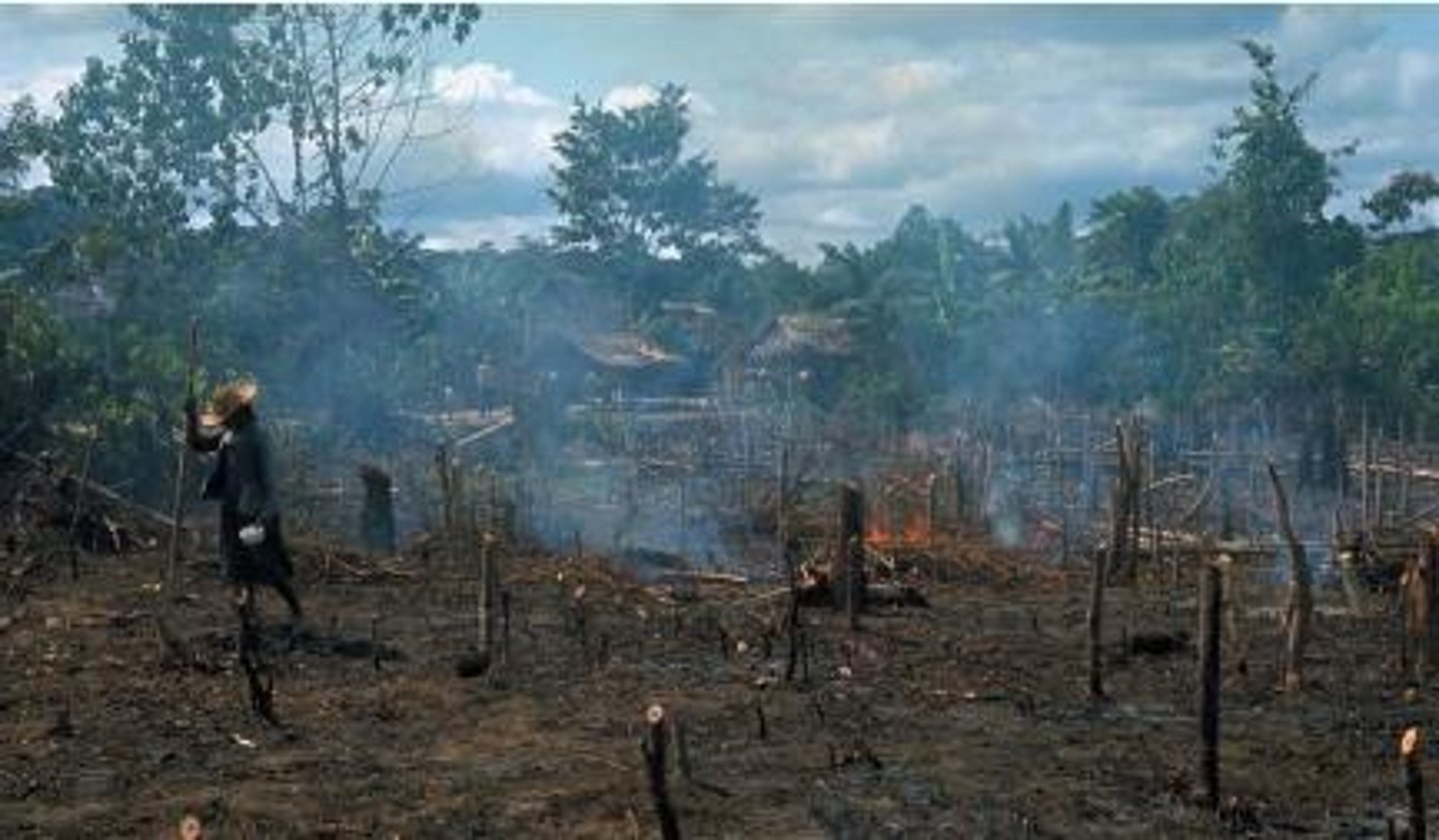
Slash and Burn Agriculture
System of cultivation that usually exists in tropical areas where vegetation is cut close to the ground and then ignited. The fire introduces nutrients into the soil, thereby making it productive for a relatively short period of time.

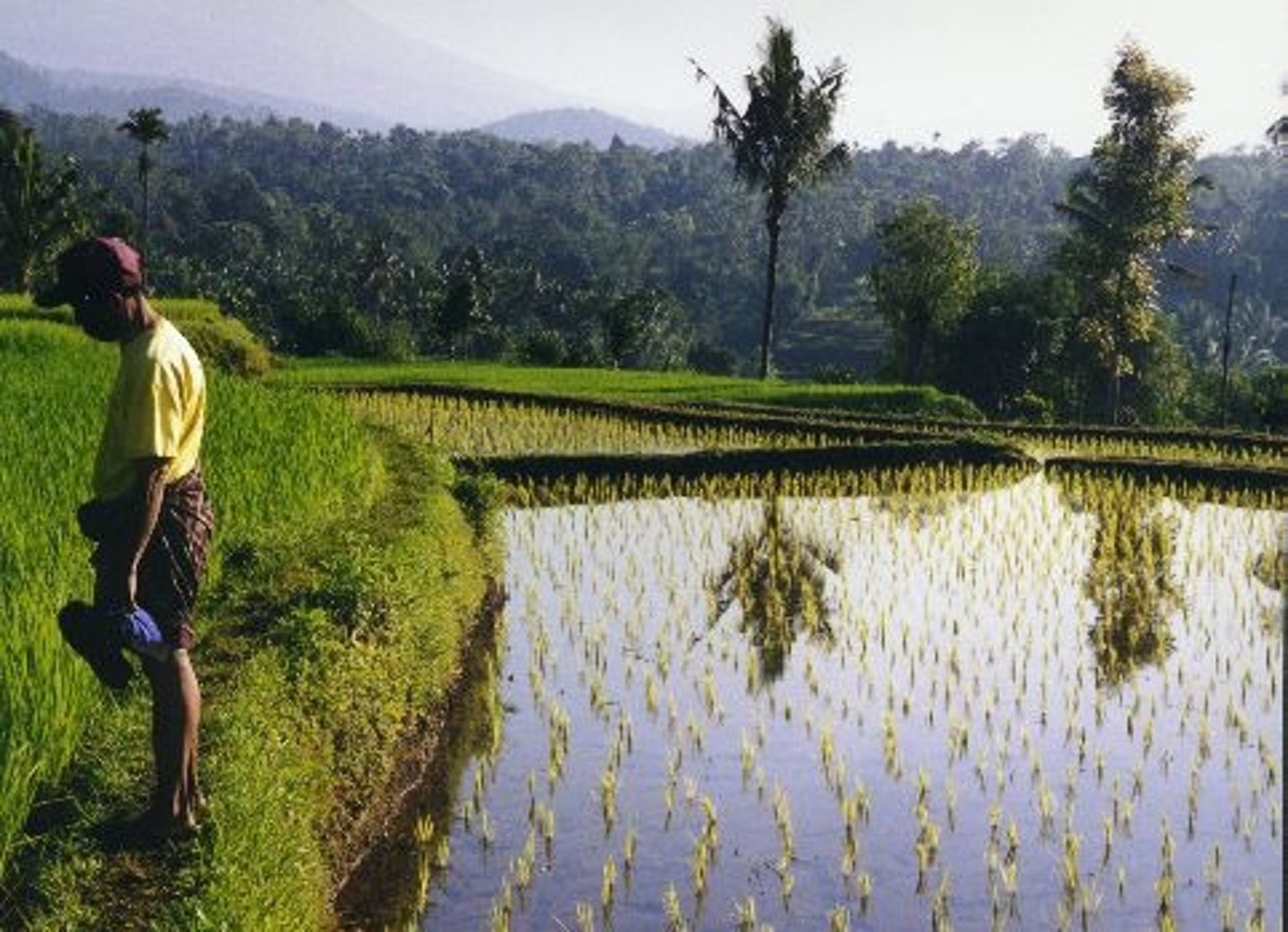
Irrigation
The process of supplying water to areas of land to make them suitable for growing crops. (70% of global water use)
Drip Irrigation
Uses perforated hoses to release small amounts of water to plant roots. This system is the most efficient, with only about 5% of water lost to evaporation and runoff. However, this system is expensive and so is not often used.
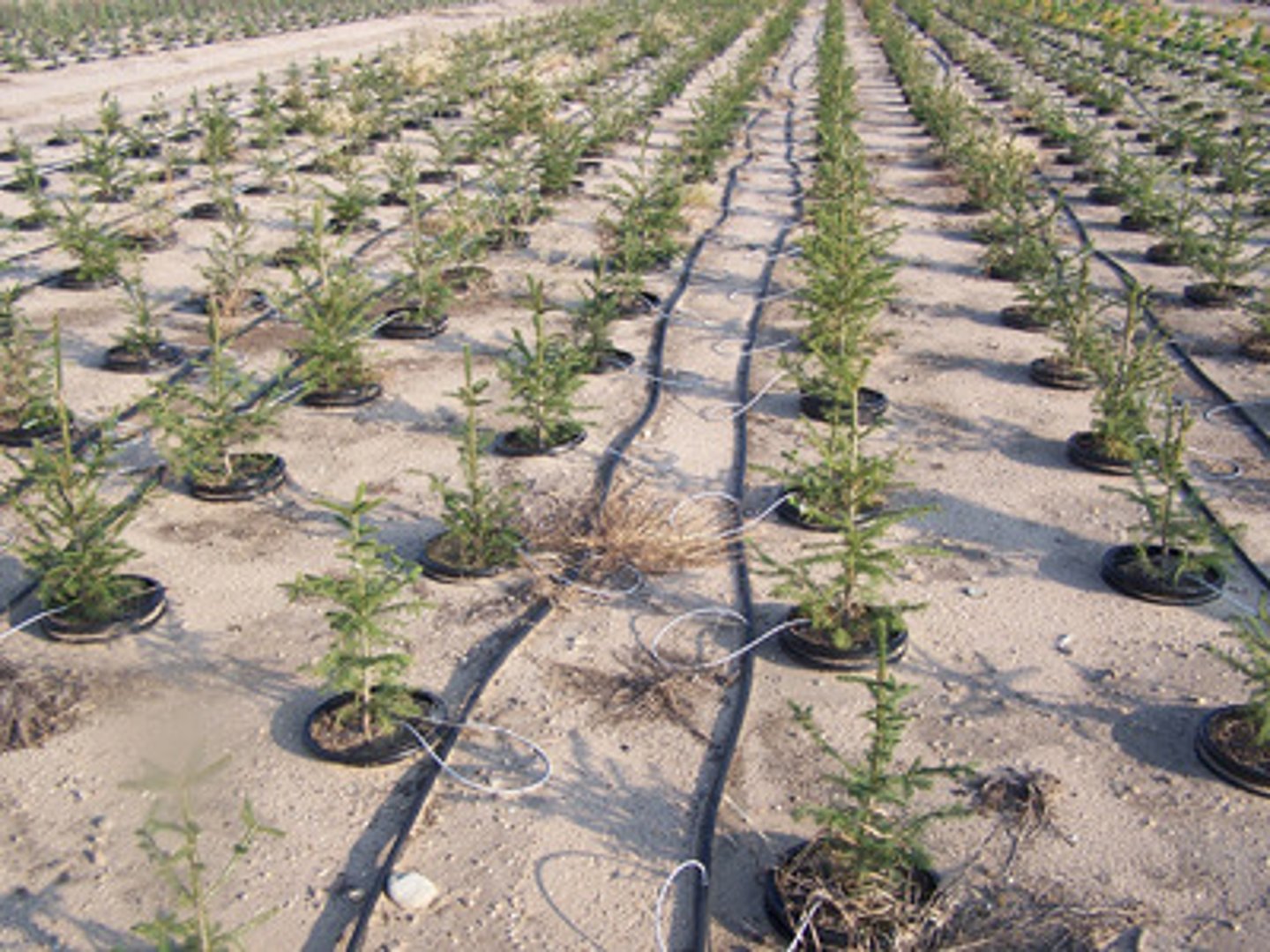

Flood Irrigation
Involves flooding an agricultural field with water. This system sees about 20% of the water lost to evaporation and runoff. This can also lead to waterlogging of the soil.

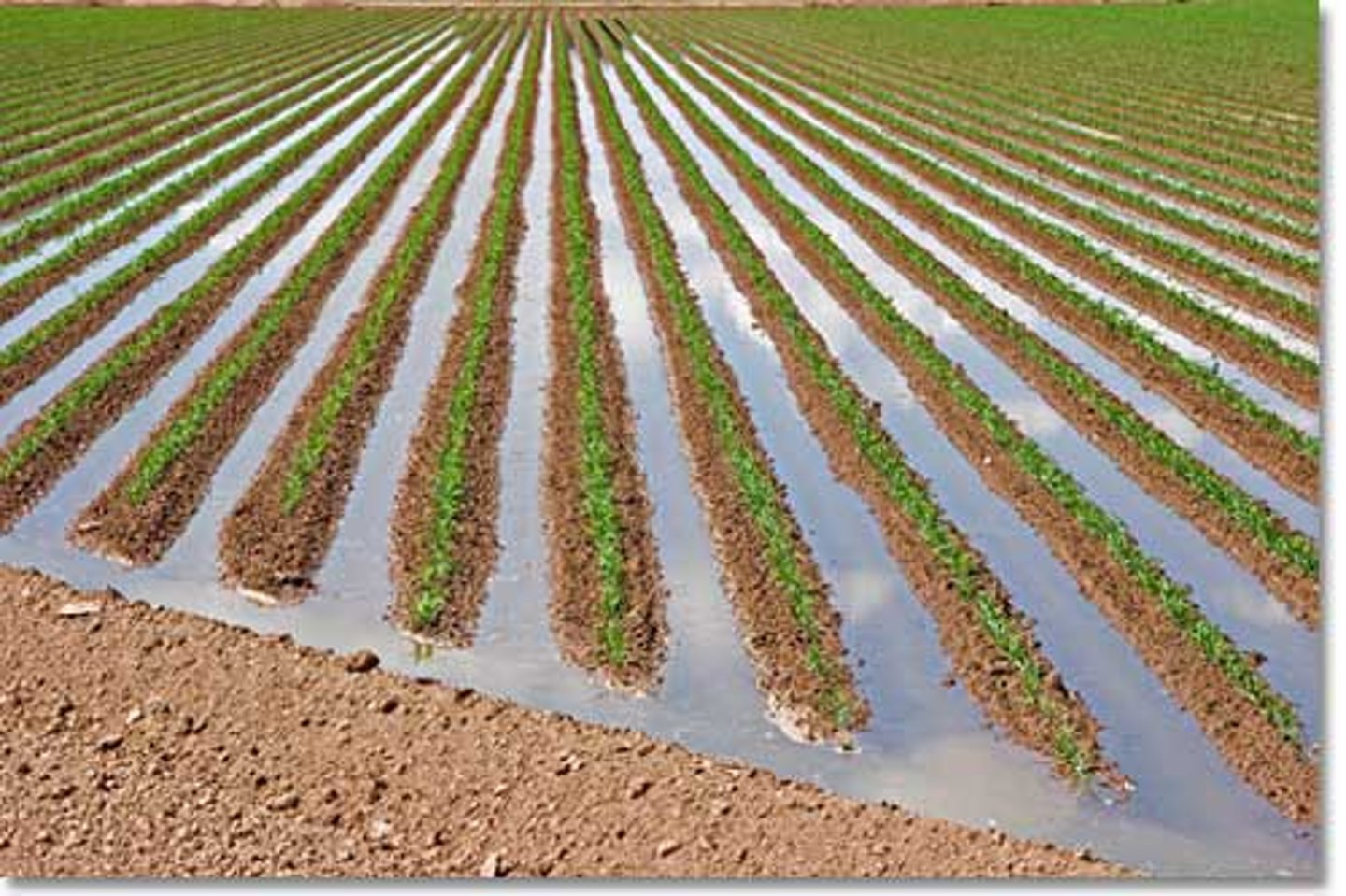
Furrow Irrigation
Involves cutting furrows between crop rows and filling them with water. This system is inexpensive, but about 1/3 of the water is lost to evaporation and runoff.

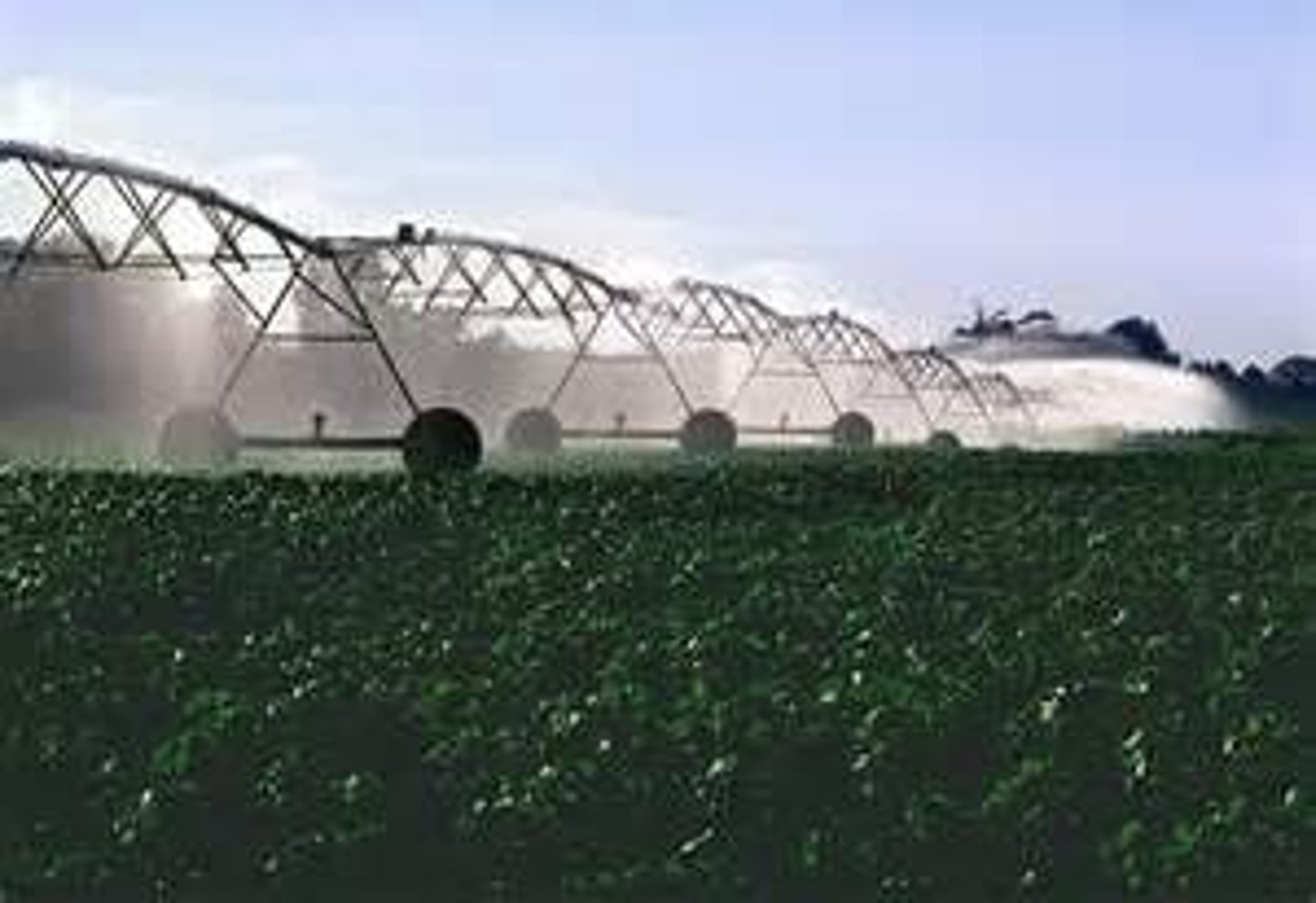
Spray Irrigation
Involves pumping ground water into spray nozzles across an agricultural field. This system is more efficient than flood and furrow irrigation, with only 1/4 or less of the water lost to evaporation or runoff. However, it is more expensive, and also requires energy to run.

Waterlogging
A form of soil degradation that occurs when soil remains under water for prolonged periods; when too much water is left to sit in the soil, which raises the water table of groundwater and inhibits plants' ability to absorb oxygen through their roots.
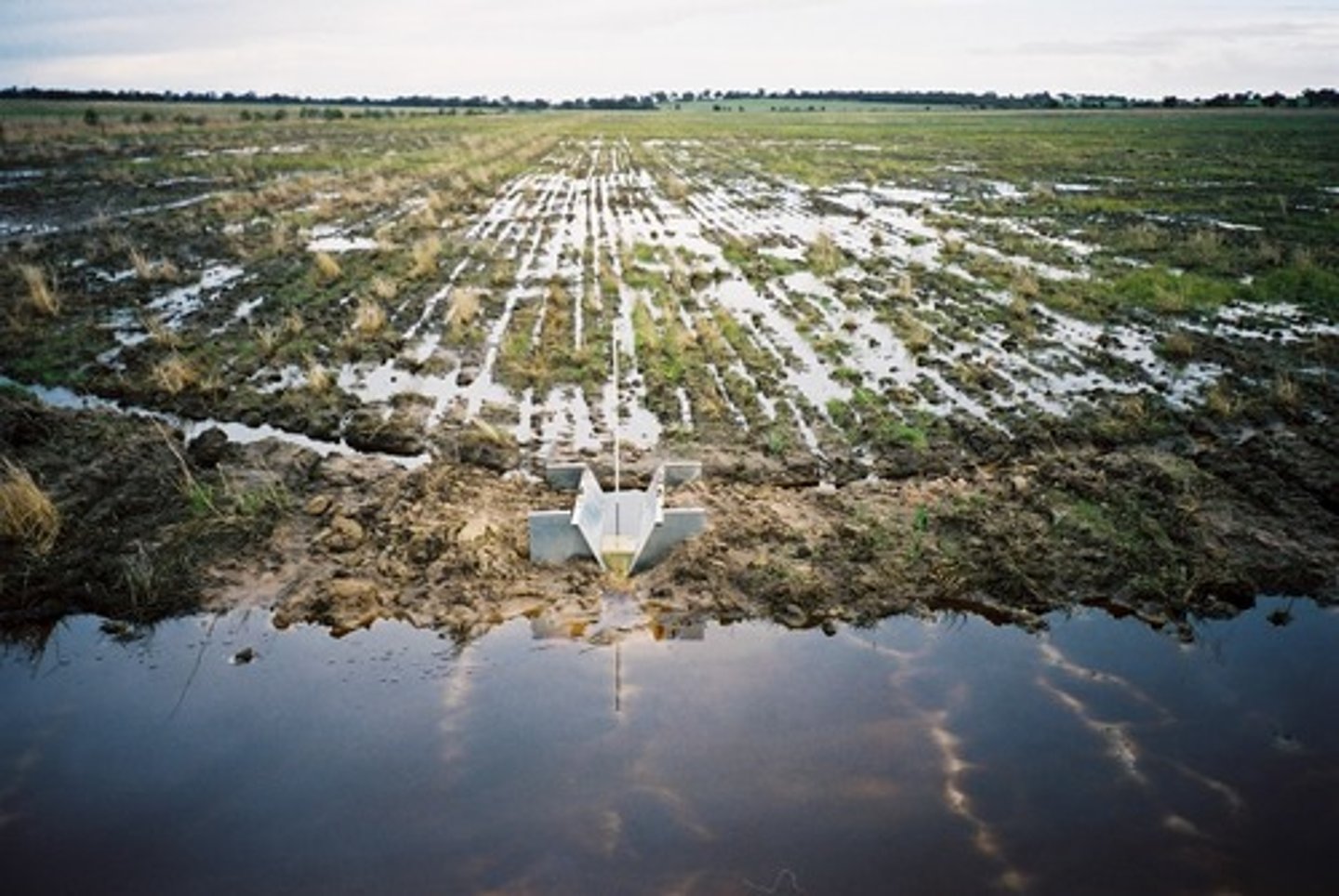

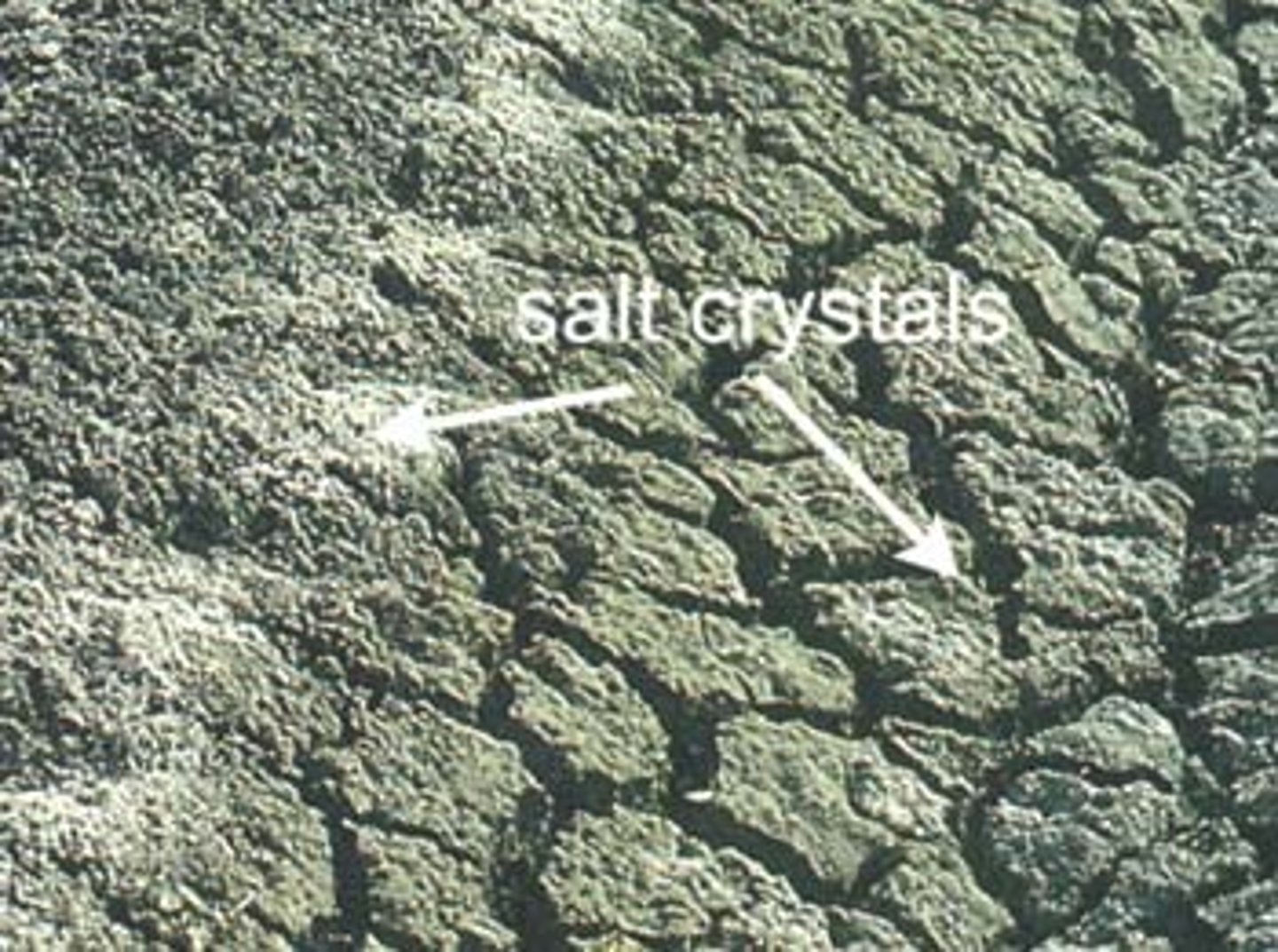
Salinization
Occurs when the salts in groundwater remain in the soil after the water evaporates. Over time, it can make soil toxic to plants.

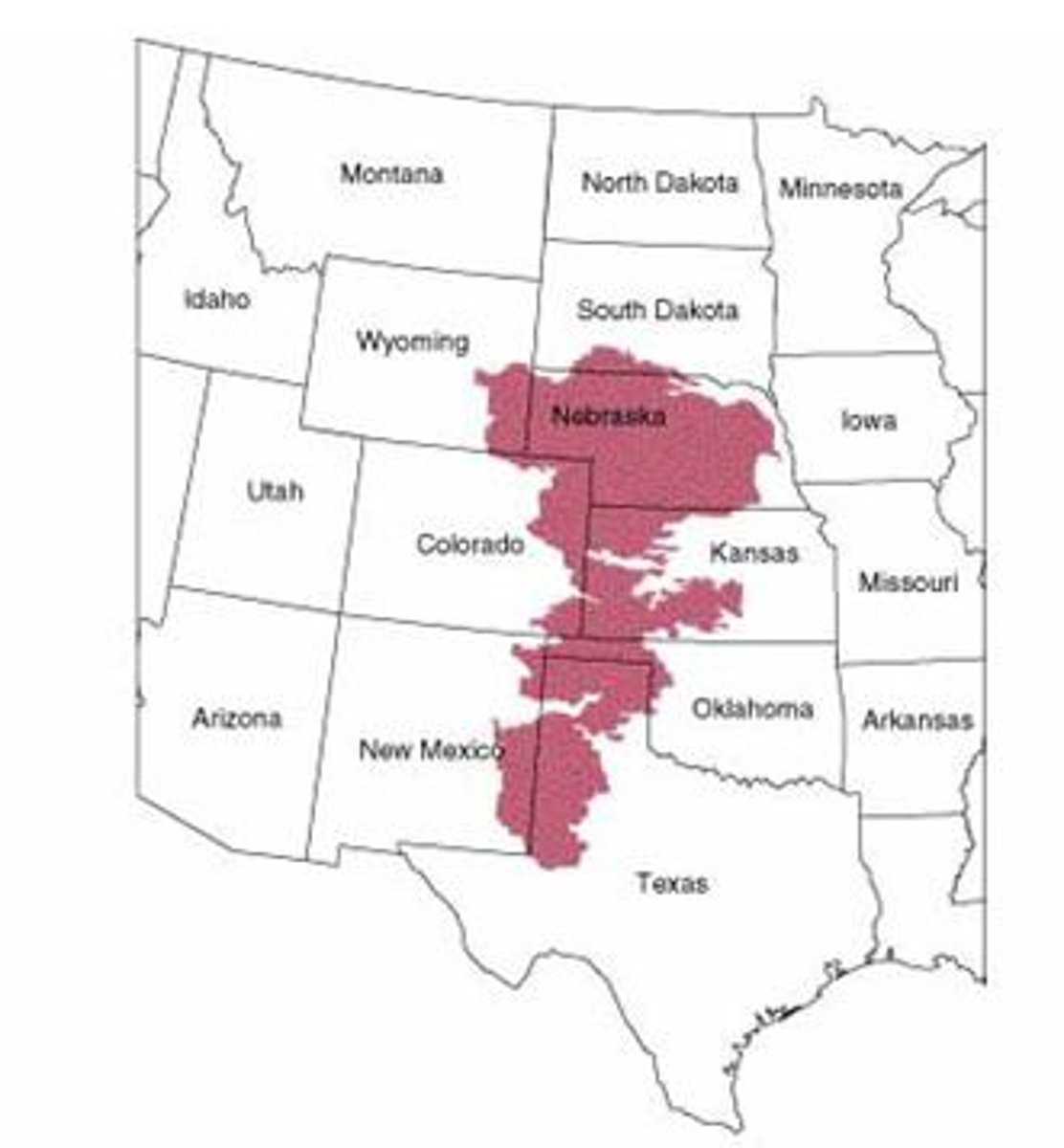
Ogallala Aquifer
World's largest aquifer; under parts of Wyoming, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, Colorado, Oklahoma, New Mexico, and Texas (the Midwest). Holds enough water to cover the U.S. with 1.5 feet of water. Being depleted for agricultural and urban use.
Artificial Selection
Breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with identical traits. Unintendedly caused by the use of pesticides on pest populations.
Feedlots (CAFOs)
Used as a way to quickly get livestock ready for slaughter. They tend to be crowded, and animals are fed grains or feed that are not as suitable as grass. Additionally, they generate a large amount of organic waste, which can contaminate ground and surface water. Their use is less expensive than other methods, which can keep costs to consumers down.
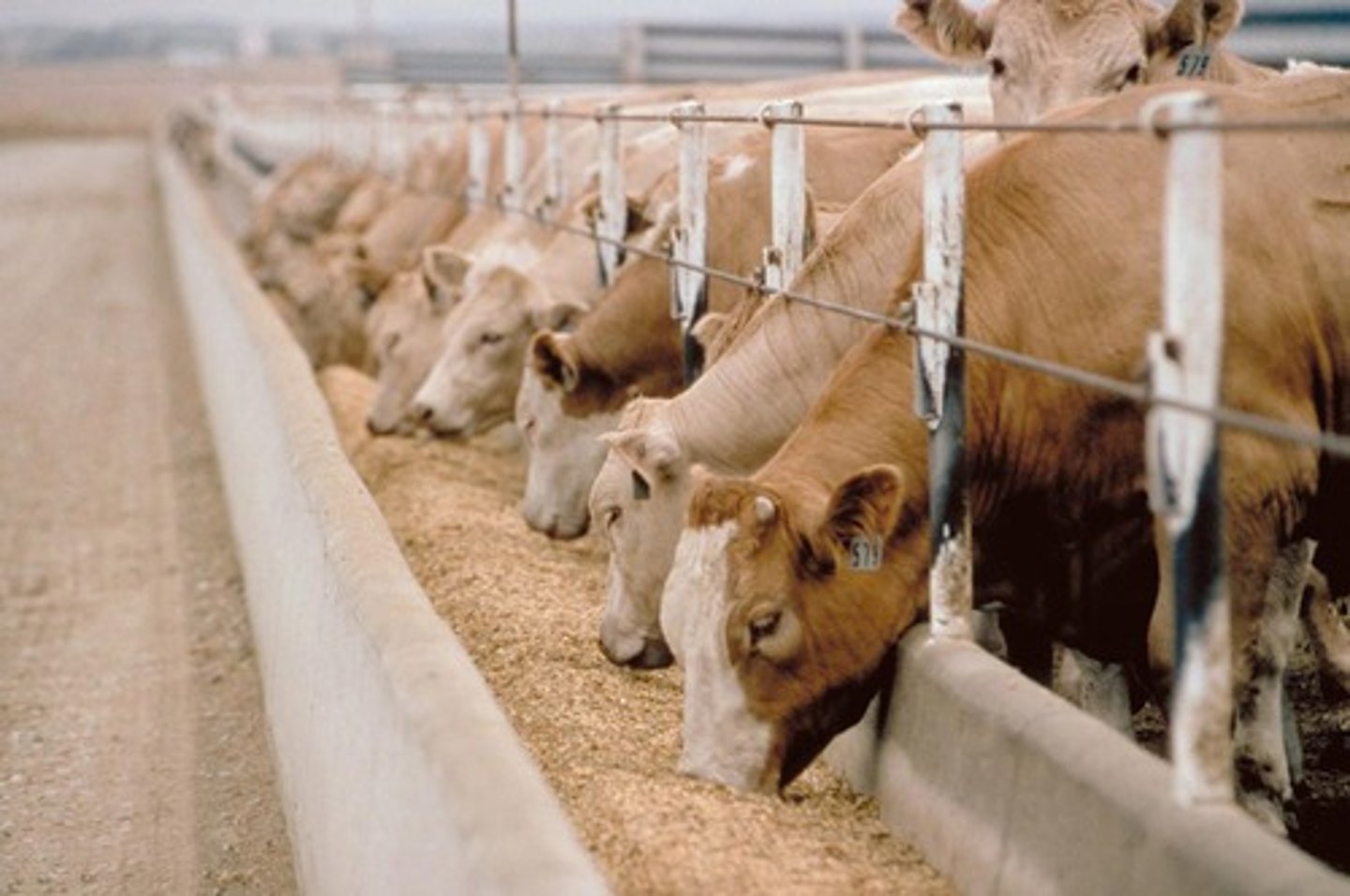

Meat production
_____ _____ is less efficient than agriculture; it takes approximately 20 times more land to produce the same amount of calories from meat as from plants.
Free range grazing
Allows animals to graze on grass during their entire lifecycle. Meat from these animals tends to be free from antibiotics and other chemicals used in feedlots. Requires large areas of land and the meat produced is more expensive for consumers.

Overgrazing
Occurs when too many animals feed on a particular area of land. It causes loss of vegetation, which leads to soil erosion.

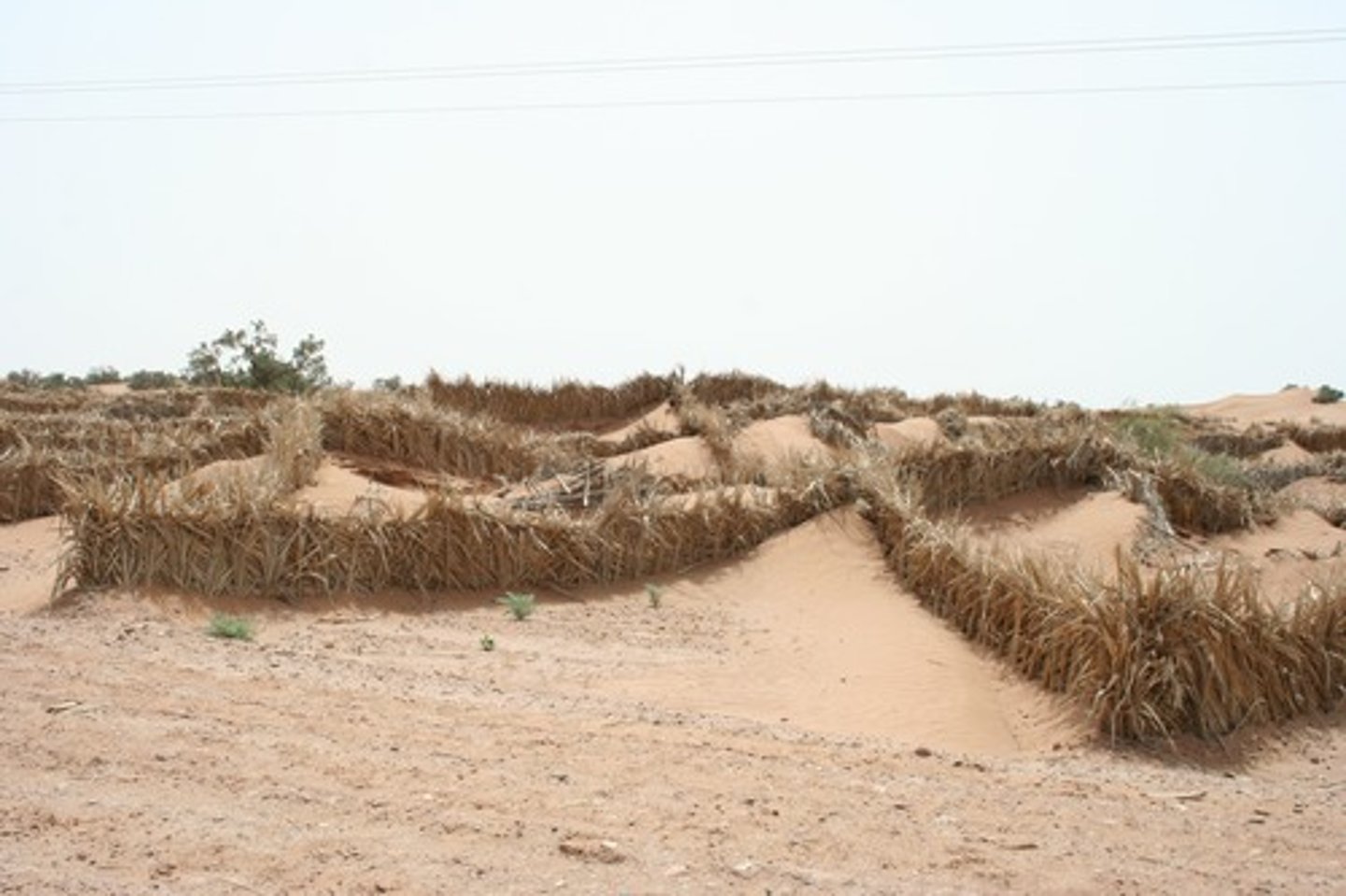
Desertification
The degradation of low precipitation regions toward being increasingly arid until they become deserts.

meat
Less consumption of _____ could reduce CO2, methane, and N2O emissions; conserve water; reduce the use of antibiotics and growth hormones; and improve topsoil.
Urban sprawl
The change in population distribution from high population density areas to low density suburbs that spread into rural lands, leading to potential environmental problems.

Ecological footprints
Compare resource demands and waste production required for an individual or a society
Sustainability
Refers to humans living on Earth and their use of resources without depletion of the resources for future generations.
Urban Forestry
Management of naturally occurring and planted trees and associated plants in urban areas.

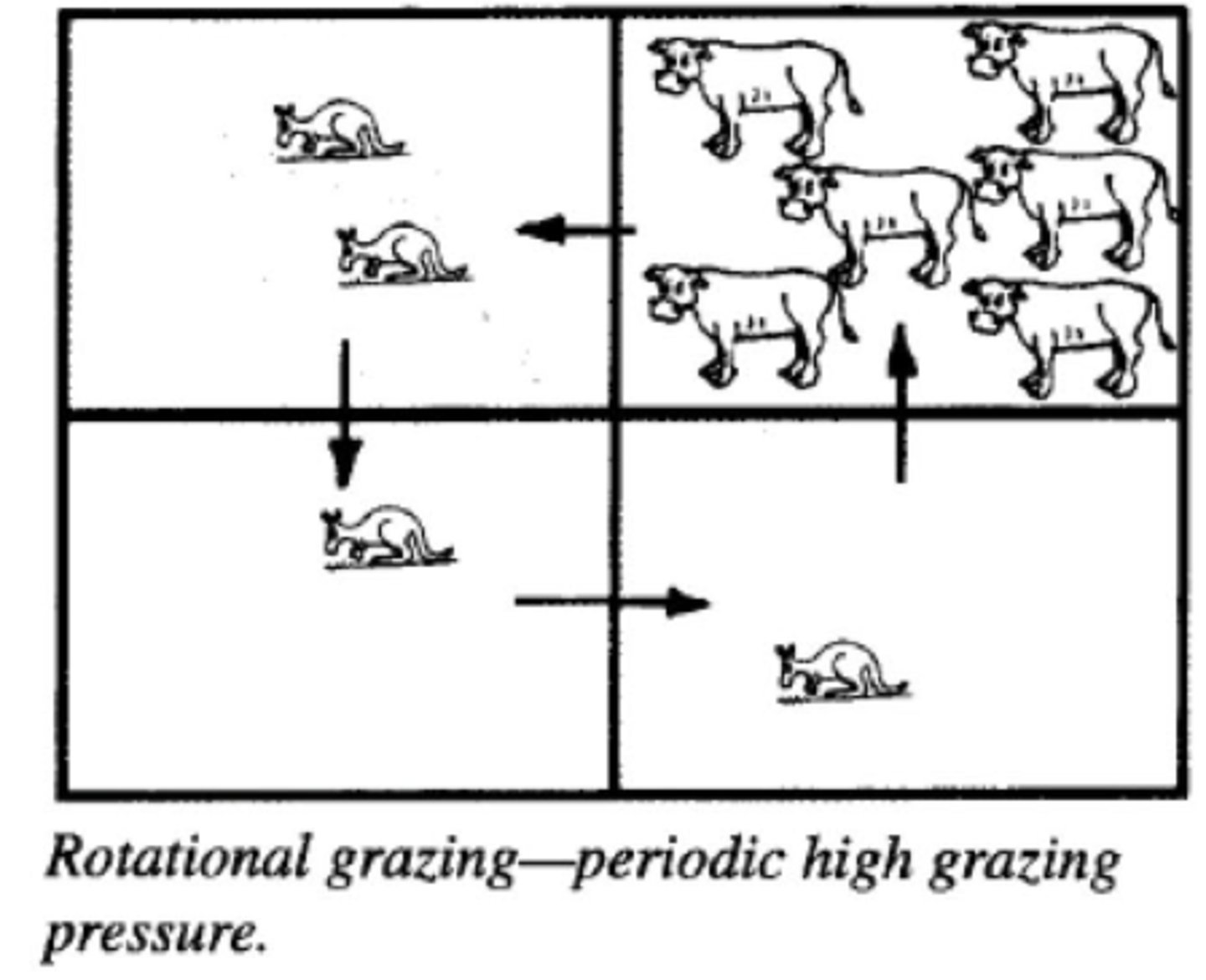
Rotational grazing
The regular rotation of livestock between different pastures in order to avoid overgrazing in a particular area.
Aquaculture
"Fish Farming" has expanded because it is highly efficient, requires only small areas of water, and requires little fuel. But it can contaminate wastewater, and increases in disease incidences, which can be transmitted to wild fish.

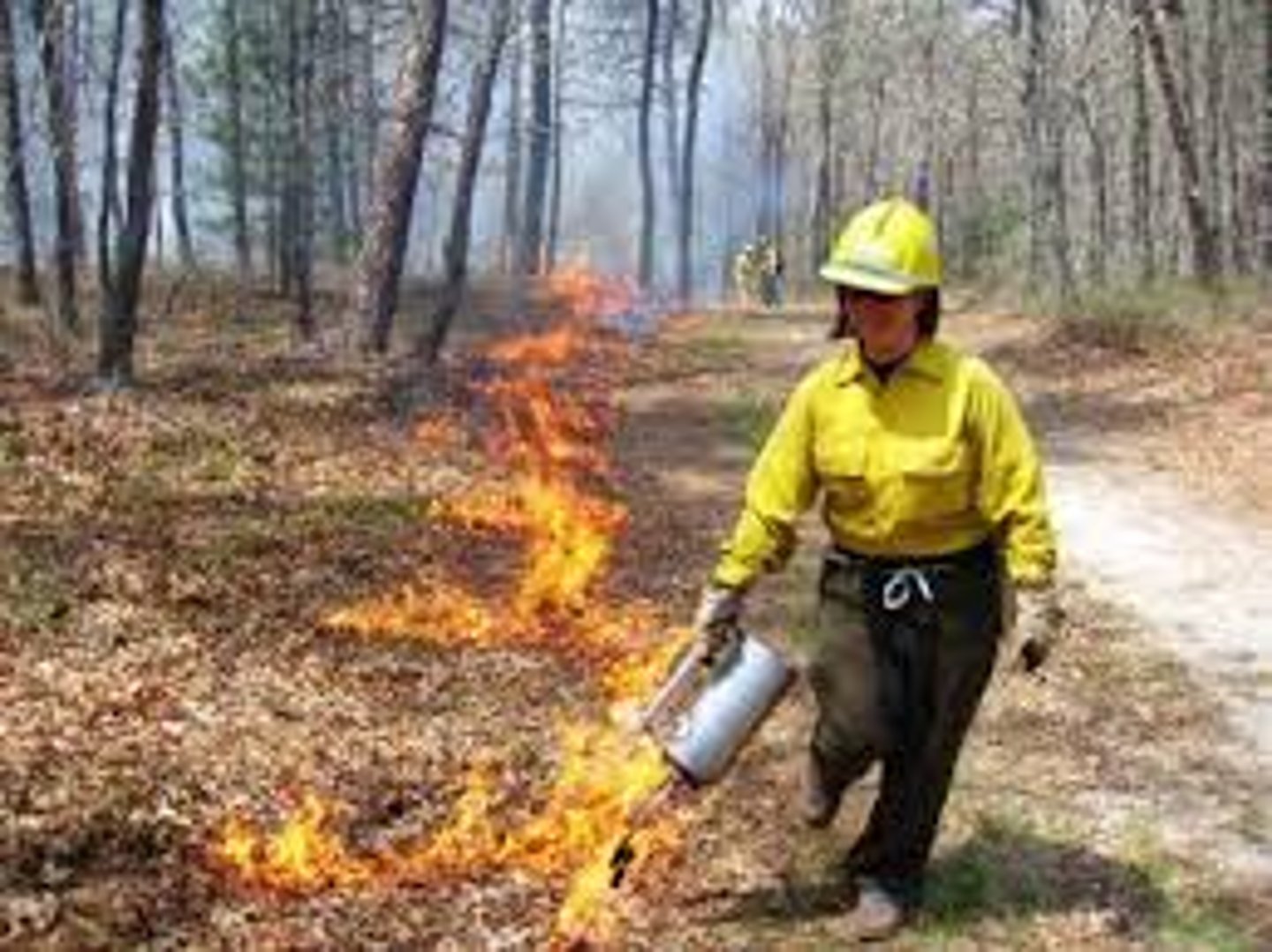
Prescribed burn
A method by which forests are set on fire under controlled conditions in order to reduce the occurrence of natural fires.

Contour Plowing
Plowing along the contours of the land in order to minimize soil erosion.

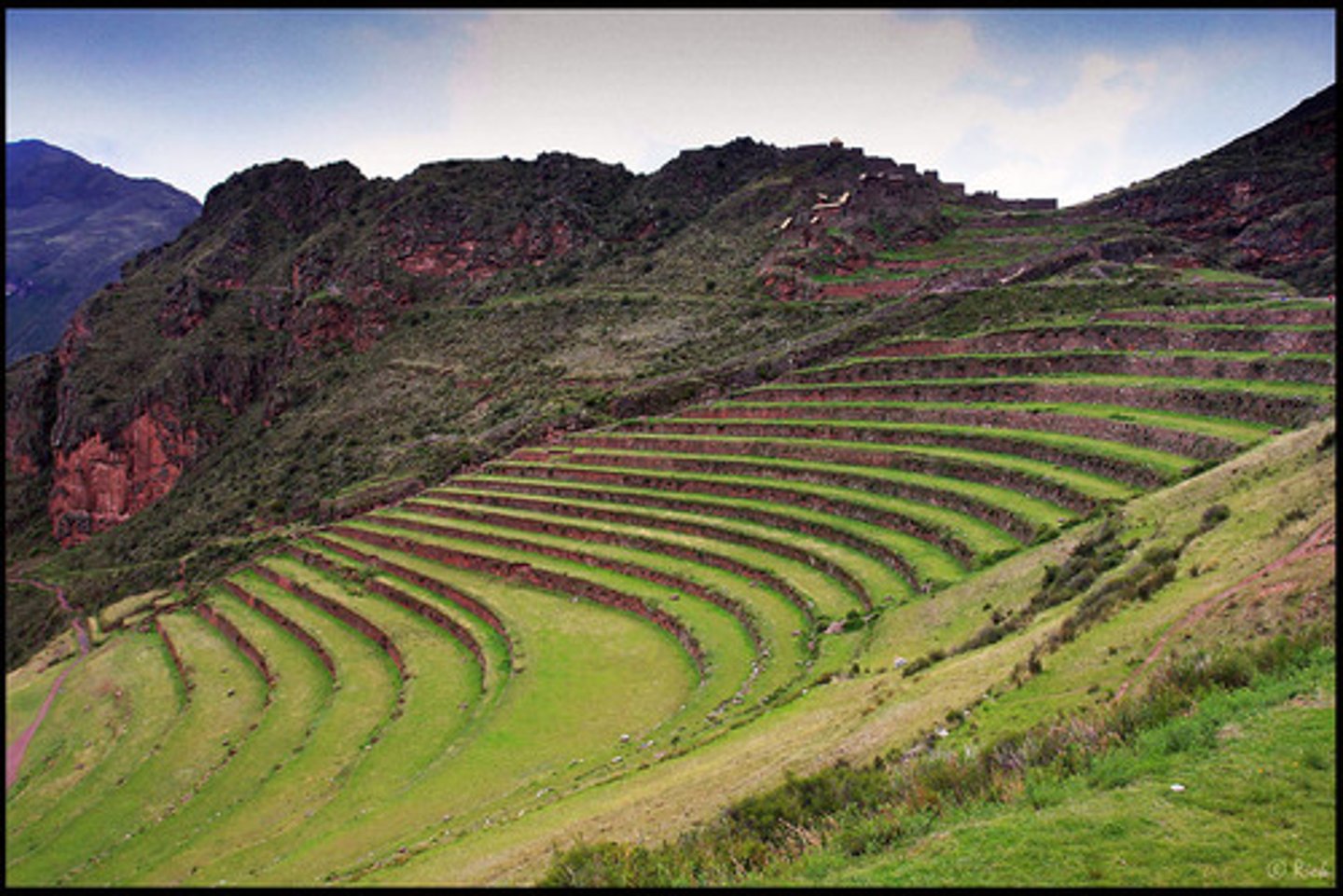
Terracing
Creating flat platforms in the hillside that provide a level planting surface, which reduces soil runoff from the slope.

No-Till Agriculture
An agricultural method in which farmers do not turn the soil between seasons, used as a means of reducing erosion
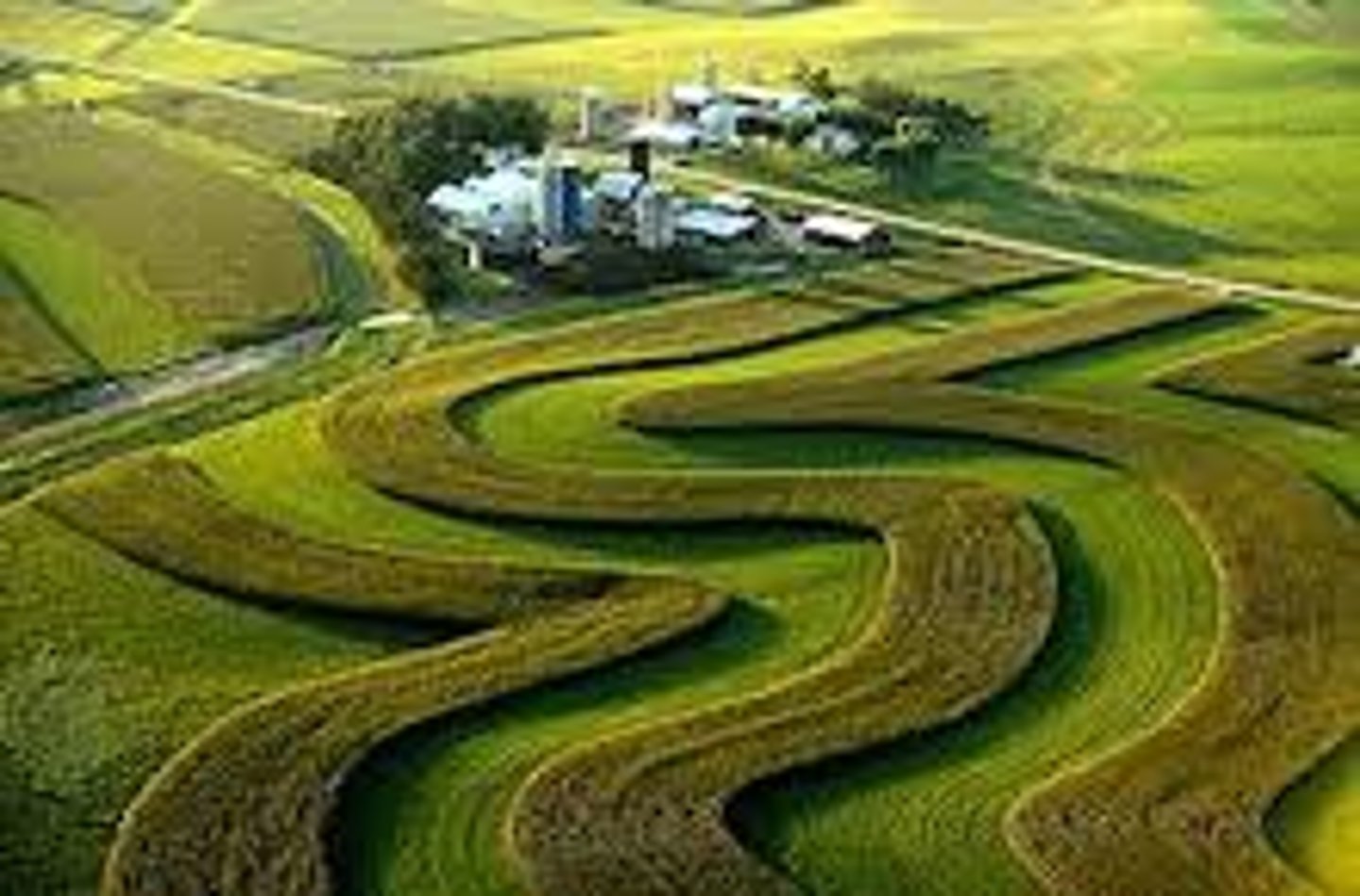
Strip Cropping
Planting regular crops and close-growing plants, such as hay or nitrogen-fixing legumes, in alternating rows or bands to help reduce depletion of soil nutrients.
