APC EXAM 1- OGDEN
1/69
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Define the term patient safety:
the prevention of harm to pts.
or
freedom of accidental or preventable injuries produced by medical care
Define the term medication-related error:
an error (of commission or omission) at any step along the pathway that begins when a clinician prescribes a medication and ends when the patient actually receives the medication
considered a type of adverse drug event (ADE)
What’s the difference between an error of commission vs. error of omission?
error of commission
an action is TAKEN
operation is performed incorrectly
error of omission
an action is NOT taken
operation is NOT performed
What are the proximal causes of med errors?
lack of drug knowledge- #1 most common
lack of pt. info- #2
rule violations- #3
slips/ memory lapses- #4/5
transcription errors- #4/5
faulty drug identity checking
fault interaction with other services
faulty dose checking
infusion pump/ parenteral delivery problems
inadequate pt. monitoring
drug stocking/ delivery problems
preparation errors
lack of standardization
What are some abbreviations that should not be used due to common misinterpretation?
U, u (write unit instead)
IU (write international unit)
Q.D., QD, q.d., qd (write daily)
Q.O.D., QOD, q.o.d., qod (write every other day)
trailing zero (ex: 4.0)
lack of leading zeros (ex: .4)
MS (write morphine sulfate)
MSO4 and MgSO4 (write magnesium sulfate)
What is 1 strategy that has been implemented to prevent med errors associated with drug labeling?
“tall man letters”
The ISMP recommends institutions develop lists of time-critical and non-time-critical medications.
time critical meds are those that are administered within ___ minutes of scheduled time.
non-time critical meds those administered within ___ hour(s) if frequency is daily or longer and ___ hour(s) if frequency more than daily.
time critical- within 30 min
non-time critical
within 2 hours if frequency is daily or longer
within 1 hour if frequency more than daily

What type of approach is best to reduce errors?
a. punitive, system-based approach
b. non-punitive, system-based approach
c. punitive, teamwork-based approach
d. non-punitive, teamwork-based approach
b.
T/F: Med errors should be attributed to human error not the system.
false—> should be attributed to system failures, NOT people
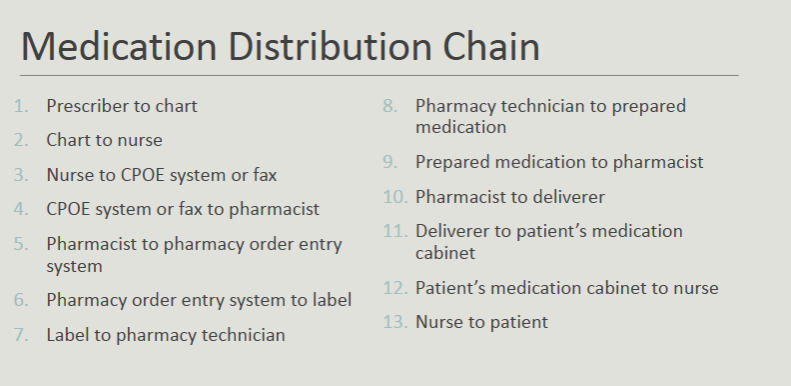
Describe the medication distribution chain:
prescriber—> chart—> nurse—> CPOE system/fax —> pharmacist —> pharmacy order entry system —> label —> pharm tech —> prepared med —> pharmacist —> deliverer—> pts. med cabinet —> nurse —> pt.
Define the term “drug-related morbidity”
failure of a therapeutic agent to produce the intended therapeutic outcome
“therapeutic malfunction”
Drug-related morbidity is typically preceded by a drug-related problem.
Define “drug-related problem”
an event or circumstance involving drug treatment that actually or potentially interferes with the pt. experiencing an optimum outcome of medical care
What are the major categories of drug related problems?
untreated indication
improper drug selection
subtherapeutic dosage
overdosage
failure to receive drug
adverse drug reaction
drug interactions
drug use without indication
Define each of the major categories of drug related problems:
untreated indication
improper drug selection
subtherapeutic dosage
overdosage
failure to receive drug
adverse drug reaction
drug interactions
drug use without indication
untreated indication: pt. is in need of drug that was not prescribed
improper drug selection: wrong drug used
subtherapeutic dosage: too little of appropriate drug is being used
overdosage: pt. receives too much of an appropriate drug
failure to receive drug: pt. does not obtain/use the drug that was prescribed
adverse drug reaction: unintended and potentially harmful effect of a drug
drug interactions: undesirable consequences of drug-drug or drug-food interactions
drug use without indication: pt. taking a drug for which they have no need to
Describe the “second-victim” phenomenon:
health care providers who are involved in an unanticipated adverse patient event, in a medical error and/or a patient related injury and become victimized in the sense the provider is traumatized by the event
basically, after med errors/ADRs clinicians turn into “second victims” bc they are effected emotionally
What is root cause analysis (RCA) used to do? May lead to what?
used to identify critical underlying reasons for the occurrence of an adverse event or close call
basically: helps to get to the root of a med error, and helps pinpoint what happened to help recurrence
ultimately—> may lead to reduced patient harm by identifying contributing factors and excluding noncontributing factors
When is a RCA Necessary?
when investigating a sentinel event
an unexpected occurrence involving death or serious physical/psychological injury or risk there of
includes loss of limb/function
NOT for non-sentinel events

Outline the RCA process:
charter the team
document/ research
identify root causes
develop actions
establish outcome measures
When identifying root causes in a RCA, you should refer to what?
5 rules of causation

What is an “aggregated root cause analysis”? how does it relate to a RCA?
same process as a RCA—> but a “batch” analysis of common events
ex: pt. falls
Define system-level vulnerabilities
weaknesses/ flaws embedded in an organization's processes, structures, or culture that increase the risk of errors or adverse events

Define human-factor engineering:
The study of how people interact with systems/tools, aiming to improve performance by designing intuitive cues (e.g., alarms, alerts) rather than relying on memory/vigilance

List obstacles to appropriate RCA conduction:
(learning objective but idk how imp really)
Skipping the chronology
Reliance on policies & procedures
Failure to conduct at-risk behavior investigations
Failure to identify deep-seated, latent failures
Failure to conduct human error/human factors investigations
Failure to seek outside knowledge
Not linking the causation to the actions
Selecting weak risk-reduction strategies
Failure to carry out the action plan & measure success
Unjust punitive action

Ogden RCA Quiz:
The primary goal of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in healthcare is to:
a. assign blame for medical errors
b. improve hospital workflow
c. increase pt. monitoring
d. identify and correct the underlying cause of adverse events
d.
Ogden RCA Quiz:
Which of the following is NOT a common tool used in RCA?
a. fishbone diagram
b. flowchart
c. SWOT analysis
d. cause-and-effect diagram
c.
Ogden RCA Quiz:
A sentinel even in healthcare is defined as:
a. an unexpected occurrence involving death/ serious injury
b. a near miss incident
c. a recurring procedural error
d. any event that causes minor patient harm
a.
Ogden RCA Quiz:
The “five whys” technique is a useful tool in RCA because it helps to:
a. determine the consequences of a medical error
b. identify contributing factors
c. investigate human error specifically
d. drill down to the root cause by repeatedly asking “why”
d.
Ogden RCA Quiz:
Human factors engineering principles in RCA emphasize:
a. increasing staff vigilance
b. designing systems to prevent errors
c. punishing staff for errors
d. improving documentation processes
b.
What is the purpose of a failure modes analysis (FMA)?
discover potential risks in a product or system by identifying all the ways in which it might fail

Define Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA):
risk assessment method based on simultaneous analysis of failure modes, their consequences, and their associated risk factors

Both FMA and FMEA have been used to reduce what?
reduce frequency and consequences of failures
Define failure:
probz fyi, not imp
when a component or a collection of components of a system behave in a way that is not included in its specified performance criteria

Healthcare failure mode and effects analysis (HFMEA) combines what 2 things?
FMEA + hazard analysis

Outline the HFMEA process:
select a topic (ex: warfarin prescribing)
assemble the team (safety officers, admin, physicians, pharms, nurses, etc.)
graphically design the process
conduct a hazard analysis
develop actions and outcome measures

A hazard analysis is done for each ________________.
a. step in the process
b. failure mode
b.

What are the components to conducting a hazard analysis?
assign a SEVERITY score
a numerical subjective estimate of how severe the pt. will perceive the EFFECT of a failure
assign a OCCURENCE score
a numerical subjective estimate of the LIKELIHOOD that the cause of a failure mode will occur
assign a DETECTION score
a numerical subjective estimate of the EFFECTIVENESS of the controls to prevent or detect the cause of failure mode before the failure reaches the pt.
calculate a Risk Priority Number (RPN)

How do you calculate a risk priority number?
severity x occurrence x detection = RPN
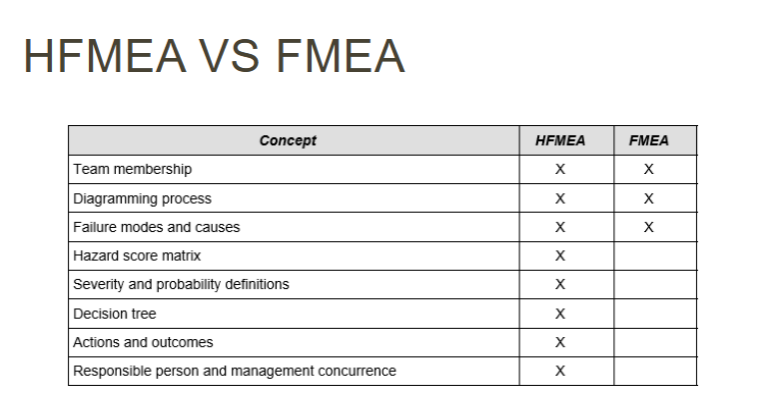
Compare and contrast FMEAs and HFMEAs
MAIN DIFFERENCE—> HFMEAs involve a hazard analysis
IDK HOW IMP, BUT HERES A LITTLE TABLE:
FMEAs | HFMEAs | |
purpose | predict/prevent failures | predict/prevent failures (related to healthcare) |
when used | design phase (proactive) | high-risk clinical processes |
focus | system/process flaws | patient safety |
Compare and contrast RCAs and HFMEAs
MAIN DIFFERENCE: RCA investigates PAST failures, while HFMEAs are used to predict/prevent failures!!!!
IDK HOW IMP, BUT HERES A LITTLE TABLE:
RCA | HFMEAs | |
purpose | investigate past failures | predict/prevent failures (related to healthcare) |
when used | after an error | high-risk clinical processes |
focus | root causes of a specific event | patient safety |
Ogden FMEA Quiz:
The primary purpose of applying FMEA to medication administration is to:
a. Assign blame for medication errors.
b. Identify and mitigate potential risks in the medication administration process.
c. Track the frequency of medication errors.
d. Simplify the medication administration process
b.
Ogden FMEA Quiz:
Which of the following is NOT a key component of a Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
(FMEA)?
a. Identifying potential failure modes (ways things can go wrong).
b. Assessing the severity of each potential failure mode.
c. Determining the likelihood of each failure mode occurring.
d. Calculating the cost of the medication
d.
Ogden FMEA Quiz:
In a FMEA for medication administration, a "severity score" reflects:
a. The likelihood of a failure mode occurring.
b. The effectiveness of controls to prevent failure.
c. The potential harm to the patient if a failure occurs.
d. The cost associated with the failure.
c.
Ogden FMEA Quiz:
The Risk Priority Number (RPN) in an FMEA is calculated by:
a. Severity only.
b. Severity x Occurrence.
c. Severity x Occurrence x Detection.
d. Occurrence x Detection
c.
Ogden FMEA Quiz:
A Healthcare Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (HFMEA) differs from a standard FMEA
primarily by:
a. Focusing solely on human error.
b. Excluding system-level analysis.
c. Incorporating a multidisciplinary team and hazard analysis.
d. Not using a risk priority number (RPN)
c.
Define each of the following terms:
Adverse Drug Event
Medication Error
Adverse Drug Reaction
Drug Misadventure
Adverse Drug Event- an injury resulting from a drug-related intervention (includes reactions/errors in prescribing, dispensing, and admin)
Medication Error- a deviation from the prescriber’s order
Adverse Drug Reaction- an injury resulting from taking a medication appropriately
Drug Misadventure- a broad term including both ADRs and med errors

T/F: error reporting should not be a routine part of practice
F—> should be
What are the 3 approaches to addressing quality problems?
not addressing them
addressing them using a linear approach
addressing them using a systems approach
Describe the “not addressing problems” approach to addressing quality problems:
(ik im sorry that is a TONGUE TWISTER)
pretty self explanatory—> you avoid, deny, think it’s unimportant, deny responsibility, or procrastinate when a problem is brought to you

Describe the “linear thinking” approach to addressing quality problems:
what is the problem associated with this thinking?
simple approach that assumes—> each problem has 1 cause and the solution will only affect the problem and nothing else
problem:
problems usually have multiple causes
makes false assumption no further action is needed or follow up after the solution
(fyi ex: a med error happens, you retrain the staff and think that’s the solution… when really you maybe should look at the deeper underlying causes to the med error or system, etc.)

Describe the “systems approach” to addressing quality problems:
basically considers interrelationships among different systems before implementing a solution
fyi ex: redesigning drug delivery system to prevent misrouting next time

What is the swiss cheese model when talking about errors?
providing multiple layers of defense may prevent an event from occurring, but occasionally the holes may line up just right for an event to occur

What is the first step in solving any problem?
What is the second step?
recognizing the existence of a problem
clearly defining the problem

What are the 2 modes of mental functioning? errors made in each mode are called what?
automatic mode: rapid, effortless thought processing
errors called slips
problem-solving mode: prolonged, intense mental activity
errors called mistakes

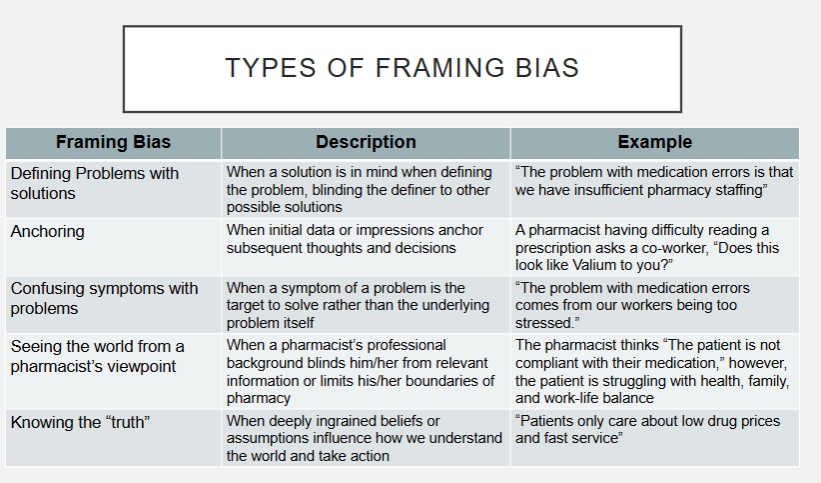
What are the 5 types of framing biases? Describe them.
defining problems with solutions- when a solution is already in mind when defining the problem, blinding the definer to other possible solutions
anchoring- when initial data or impressions anchor subsequent thoughts and decisions
confusing symptoms with problems- when a symptom of a problem is the target to solve rather than the underlying problem itself
seeing the world from a pharmacist’s viewpoint- when a pharmacist’s professional
background blinds him/her from relevant information or limits his/her boundaries of pharmacy
knowing the “truth”- When deeply ingrained beliefs or assumptions influence how we understand the world and take action
What is a problem statement?
single, short sentence that defines the broad problem to provide focus and avoid distractions to the issue

What is health?
idk how imp, but learning objective
the condition of being sound in body, mind, or spirit; especially freedom from physical disease or pain
or
state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity

What are determinants of health?
idk how imp, but learning objective
conditions that affect health, functioning, quality of life, and risks
can be social (ex: access to education), economic (ex: poverty), or physical (ex: exposure to toxic substances)
can also be broken into individual (ex: genetics), community, and state/national/global

What is public health?
what does it promote?
overall goal?
promotes and protects the health of people and the communities where they live, learn, work, and play
functions:
promotes wellness by encouraging healthy behaviors
conducts research to educate about health
work to ensure people are in healthy conditions (vaccinations, education)
set safety standards for workers
school nutrition programs
track disease outbreaks
prevent injuries
overall goal: prevent rather than treat

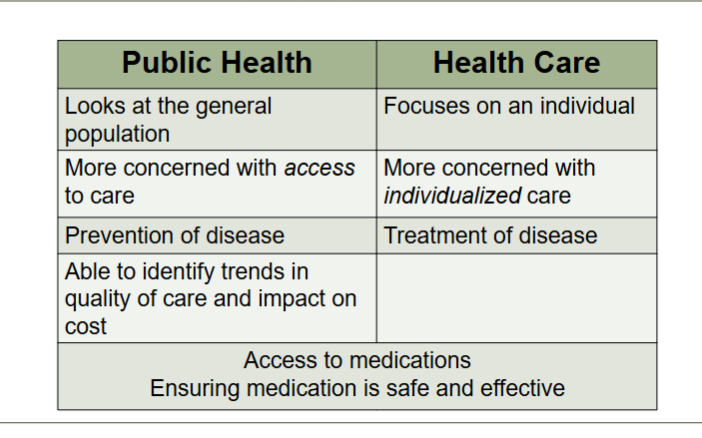
Compare public health to health care:
general vs. individual?
access vs. individualized care?
prevention vs. treatment?
public health
looks at general population
focus on ACCESS to care
prevention of disease
health care
focuses on individual
focus on INDIVIDUALIZED care
treatment of disease
What are the 2 broad population health goals? What does HRQOL mean?
increase overall/mean population health
includes mortality and health-related quality of life or HRQOL (aka a personal sense of physical and mental health and the ability to react to factors in the physical and social environments)
eliminate disparities within the population

What is the definition of health promotion?
the process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve, their health
moves beyond a focus on individual behavior towards a wide range of social and environmental interventions
What are the core features of public health?
assessment
policy development
assurance

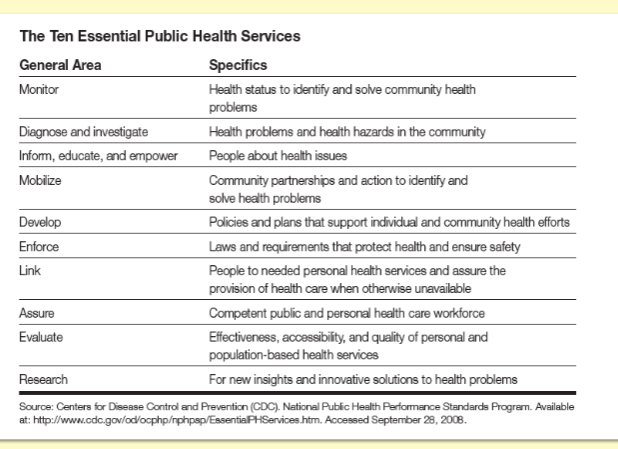
What are the essential services of public health?
idk how imp, but learning objective
monitor
diagnose/investigate
inform, educate, empower
mobilize
develop
enforce
link
assure
evaluate
research
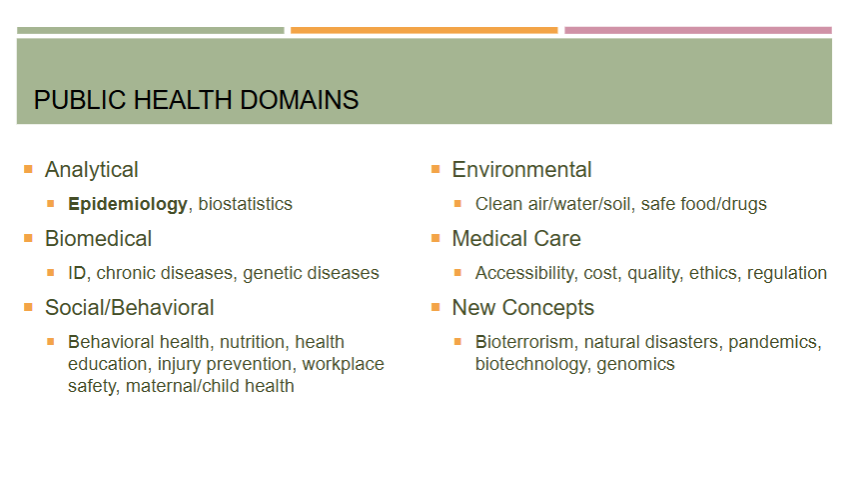
What are the domains of public health?
analytical
epidemiology, biostats
biomedical
social/behavioral
environmental
medical care
new concepts
What are the types of prevention in public health?
primary- before disease/injury happens
secondary- reduce the impact of a disease or injury that has already occurred or prevent recurrence
tertiary- soften the impact of an ongoing illness/injury that has lasting effects

What is cultural competence?
the ability of providers and organizations to effectively deliver health care services that meet the social, cultural, and linguistic needs of patients

Disease surveillance includes monitoring what?
number of new and existing cases, including incidence and prevalence

What is the name of a national public health agency that provides a system to track and report diseases as well as providing local support to communities?
CDC

What is necessary to help address pandemics? definition of pandemic?
international public health necessary to help address pandemics
the world health organization “WHO” is the primary international public health organization
pandemic—> full-blown global outbreak of a disease

What is government agency that is a source of guidance, policy, and funding, does not directly implement programs, and contains multiple agencies like the FDA?
idk how imp, not even going to remember this
US department of health and health services (HHS)
