neurology
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
The nervous system 2
Central nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
Central nervous systems
Spinal cord
Brain stem
Brain
The body’s master control unit
Peripheral Nervous System
Links brain and central nervous system to the exterior
Peripheral nervous system can be broken down to the
The autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Regulates involuntary bodily processes
Sympathetic ns
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic nervous system
Prepare the body for action and stress. This is called fight or flight. It’s going to accelerate our body
Sympathetic, nervous system catecholamines
epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Dopamine
Sympathetic nervous System catecholamines attach to what
Adrenergic receptors
Alpha 1 and 2
Beta 1,2,3
The sympathetic Nervous system also has
Antagonist, we are going to block
Example for Sympathetic nervous system
If you take a medication that blocks your alpha or your beta, then that’s gonna cause your nervous system to decrease your heart rate and your blood pressure Which is equal to activating the parasympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Calm the body and helps the body to conserve energy
Rest and digest
Parasympathetic nervous system meds
Acetylcholine neuron transmitters for the parasympathetic nervous system that attach to the cholinergic receptors
cholinergic receptors Types
Muscerinic
Nicotinic
Digestion and urination
The somatic nervous system
Voluntary movement
In the nervous system, we have two cells
neurons
Glia cell
Neurons and glia cells
The recover axon
Glia cells
Will make myelin
Myelin and axon
We will be the white matter Of the central nervous system
Myelin
Help increase speed of impulse transmission
Example, if the Milan is not intact, then our impulse transmission is going to be slower
Neuron - cell body
Will make the gray matter of the Brain and whole central nervous system
Nerve impulse
Is an action potential
The basics of Cell firing
Resting membrane potential cell
Then a stimulus comes and depolarizes because sodium channels are openSo sodium is entering the cell
Up to the point that we have a threshold and whenever you have a threshold, you’ll have an action potential
The potassium channels will open potassium will diffuse out of the cell, causing repolarization
Meniniges
The layers protecting the central nervous system
Meniniges Layers
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia Mater
Dura mater and arachnoid mater what space do you have
Subdural space
Arachnoid mater and Pia mater what space do you have b
Subarachnoid space
Dura mater
two layers of Venus sinuses between them
Venus drainage
Arachnoid mater
lies just beneath the dural matter
waterproof
Pia mater
Liz is right on the surface of the brain
Holds the cerebral arteries in place
Subarachnoid space
You have cerebral spinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid CSF
clear fluid similar to blood plasma
Cerebrospinal fluid CSF Production
600ml
Cerebrospinal fluid CSF Reabsorption
Into the Venous circulation through the arachnoid villi
Cerebrospinal fluid is located where
Inside of the 4 ventricles that’s where is circulates It goes through the central canal to go down to the spinal cord
What happened if we don’t have that communication within the ventricles?
Increase intracranial pressure because you were gonna have a buildup of fluid
Pain terms - Gate control theory
A search that non-painful input closes the gates to painful input, which prevents Pain sensation from traveling to the central nervous system
Example: You hit your elbow and then you begin to rub your elbow with your other hand and that is like preventing in sensation of pain because now your brain is feeling that comfort instead
Pain terms: Pain threshold
Lowest intensity of pain that a person can recognize
Pain terms: Pain tolerance
Greatest intensity of pain that a person can endure
Paint terms: nocieptive pain
Tissue injury, pain: visceral, somatic, or referred : Throbbing, pulsing, stabbing or aching pain
Somatic
Skin joints, and muscles pain
Visceral
Internal organs and lining of cavity pain
Referred
Perceived at a different location
Acute pain
Warning signals
Chronic pain
More than six months
Pain terms neuropathic pain
A damage nerve that can be chronic pain: Central pain or peripheral pain; Tingling, Numbing, or burning
What is the most common type of pain?
Headaches
Headache – migraine
Pain last from 4 to 72 hours in women usually - Genetics
Migraine manifestation
unilateral pain
Throbbing
Worsen by movement and noise
Nausea
Vomiting
Photophobia - fear of light
Phonophobia - fear of sound
Migraine triggers
Altered sleep patterns
Skipping meals
Over exertion
Weather changes
Hormonal changes
Excessive afferent stimulation
Chemicals- alcohol or nitrates
Migraine phases
Premonito4y - A few days before the migraine starts, you feel like it’s coming
Aura - What you feel right before the migraine comes
Headache-
Recovery
Headaches – cluster
More in males between 20 and 50
Headache last for a minute to hours
Example- You have it every day for two weeks and then it doesn’t show up again for another four months
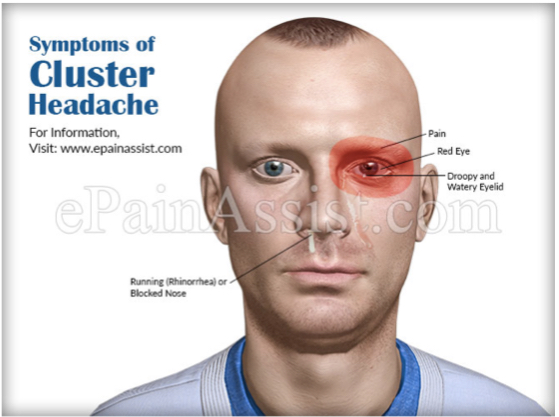
Cluster manifestation
Stabbing pain in eye
ptosis is of the ipsilateral eye - there’s a drop in your eye and it’s in the same side as the pain
Red eye
Stuffy nose
Cluster headache activation
Trigeminal
Cluster headache treatment
Oxygen therapy- But nothing really works even that doesn’t really work
Tension type headaches
Most common
Can last several days at least 15 days per month for at least three months
Tension type headaches, manifestations
Sensation of a tight band or pressure around the head with gradual onset of pain
Plegia
Stroke or paralysis
Paralysis
Loss of movement
Paresis
Weakness
Hemi
Both limbs on one side
Di or para
Both upper limbs or both lower limbs
Quadri or tetra
All four limbs
Myasthenia graves
Type two hyper sensitivity - autoimmune
Myasthenia graves receptors stuff
We have a nerve ending that releases ACH acetylcholine
Our muscles have ACH receptors
But there are antibodies to the ACH receptors, which causes the binding of the new transmitters to be inhibited or decreased
gradual destruction
Myasthenia gravis manifestation
The blockage of receptors causes no contraction in the muscle, which makes weakness
Progressive weakness
Ptosis
Diplopia - seeing double
Dysphagia - difficulty swallowing
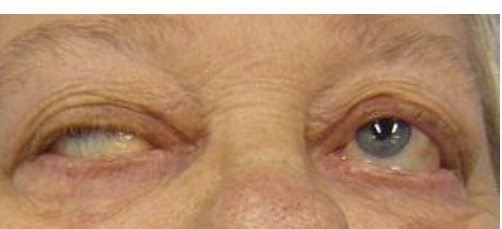
Myasthenia gravisis diaghram
due to the muscles not being able to contract, you can have diaphragmatic involvement
Creating difficulty breathing
Myasthenia gravis Evaluation
tension test
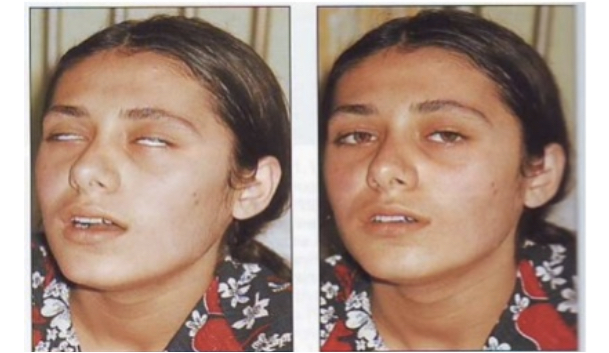
Tensilon test
Give them a medication and it improves the Tessalon very fast
anti acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Acetylocholinesterase
Nerve ending that releases acetylcholine binds the the acetylcholine receptor on the muscle or post synaptic cell
Then it gets degraded or destroyed by acetylcholinesterase
We end up with choline that gets reabsorbed into nerve terminal and acetate that degrades
anti acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
With these inhibitors were just gonna have access ACH and we will still have muscle contraction
Myasthenia gravis Treatment
anticholinesterase inhibitors
Corticosteroids
Myasthenia crisis
Tensilon improves them
Cholinergic crisis
caused by too much anticholinesterase drug toxicity- too much ACH
They will get worse with Tensilon test
Cholinergic crisis manifestations
high GI and GU
Low cardiovascular and respiratory
Extra parasympathetic response
MS is
A demyelination disorder in the central nervous system
Gillian barre syndrome
Demyelination’s disorder in peripheral nervous systems
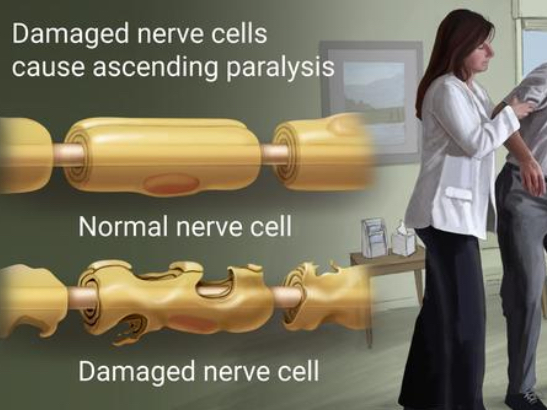
Guillain barre syndrome movement
Ascending motor paralysis
Starts from the bottom up distal extremities are first affected
Also affect our diaphragm and give us problems breathing
Guillain barre syndrome trigger
infection - respiratory or GI - campylobacter jejuni enteritis
Surgery
Vaccinations
G-B manifestations
muscle weakness
Ascending paralysis
Respiratory arrest
Symmetrical ascending
Paresthesias in the feet
The person can recover from this
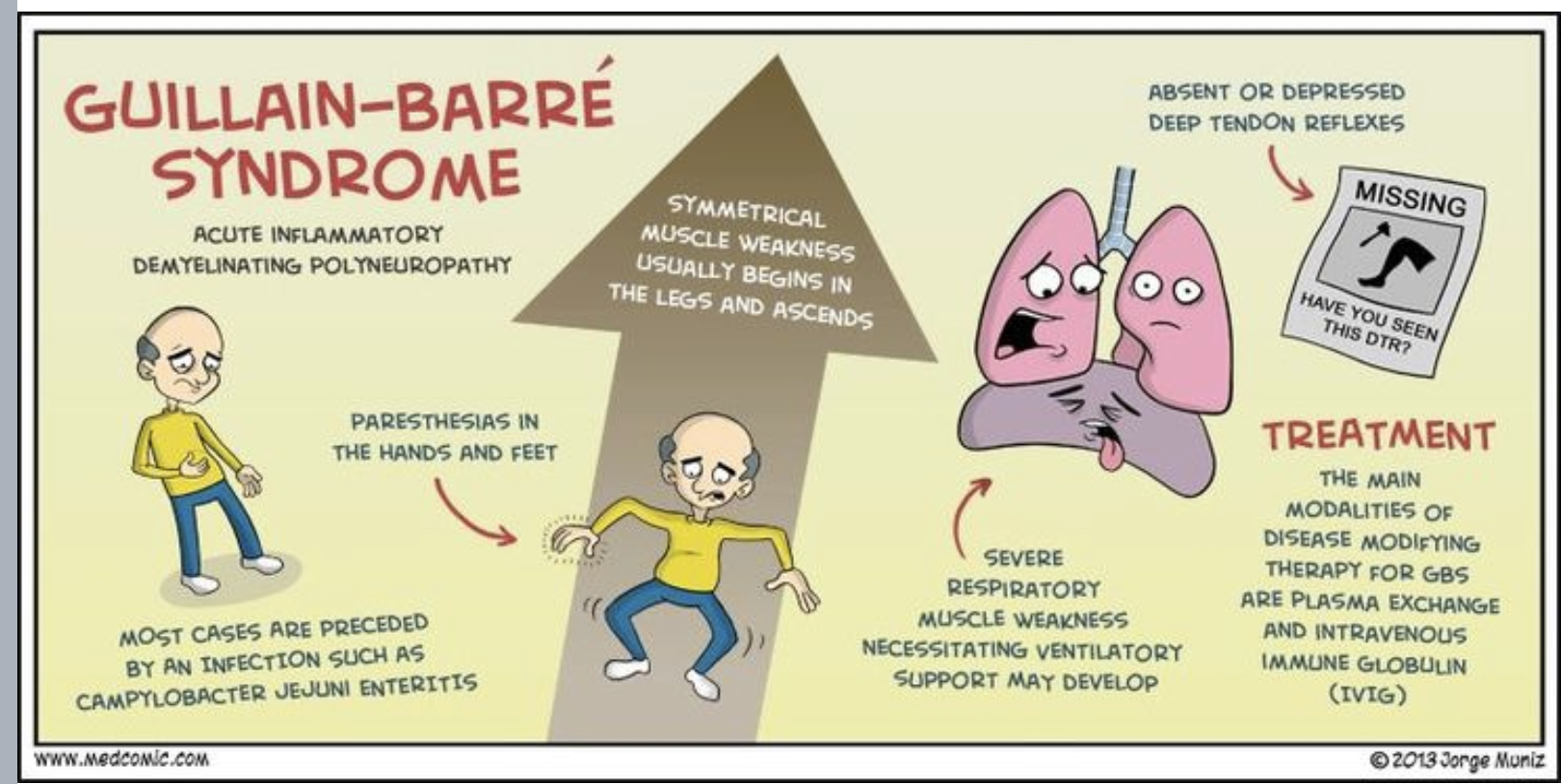
G-B treatment
supportive care
Ventilator support
Plasmapheresis
Intravenous immune global in administration
Parkinson’s disease
Chronic and progressive
Degenerative
Debilitating
Parkinson’s disease what’s happening
lack of dopamine Due to basal ganglia and substantial nigra neurological disease
More common in males
Parkinson’s disease
Normal amount of Acetylocholine and low dopamine imbalance creates all these problems
Parkinson’s has something called
Levy bodies
What happens when you have an imbalance
Impairment of extrapyramidal tracts controlling movements
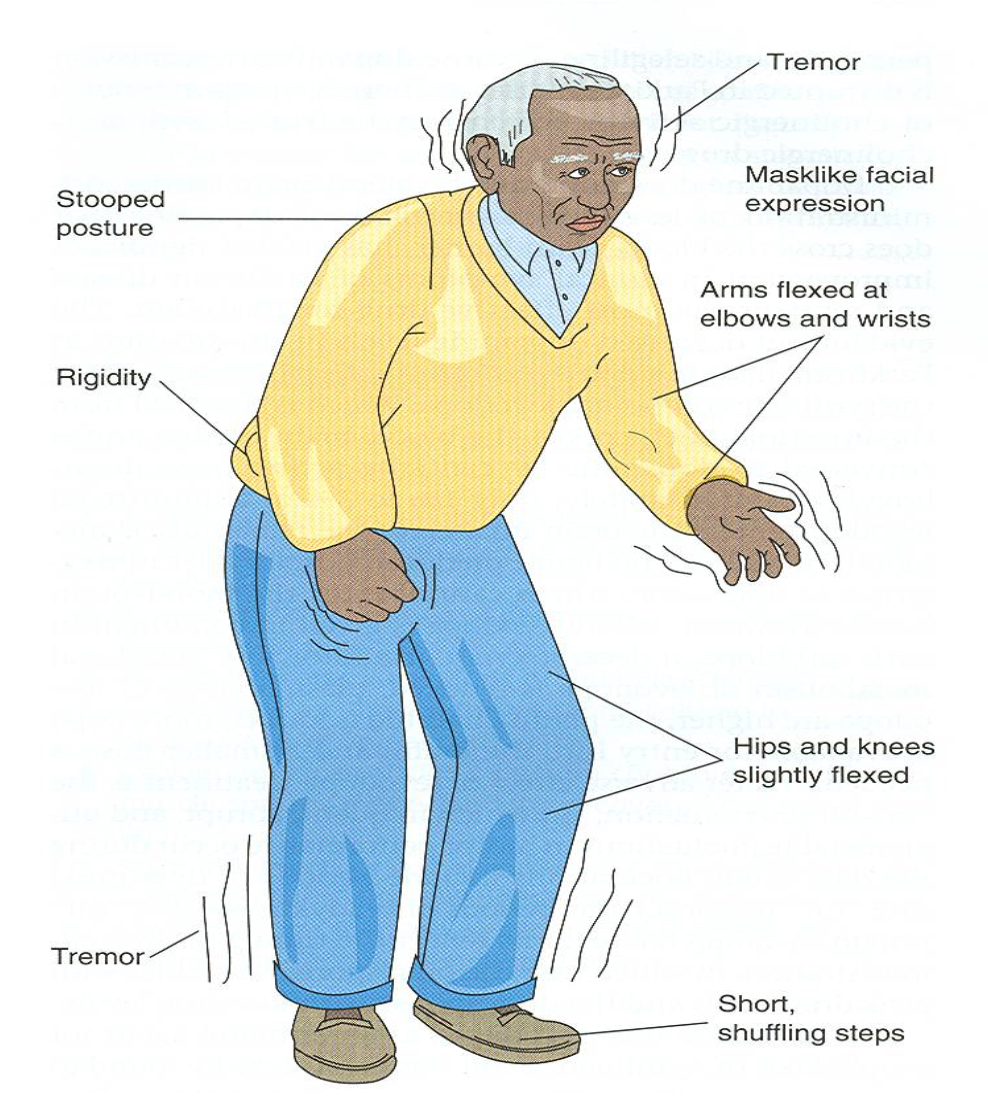
Parkinson’s manifestation
tremors at rest
Rigidity
Bradykinesia / akinesia - move slowly
Postural changes
TRAP
pill rolling
dementia
Depression
Shuffling steps
Parkinson treatment
dopamine replacement
Reduce ACH - anti cholinergic drugs
Deep brain stimulation
This treats the symptoms this is not a cure
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS - Lou Gehrig disease
neural degenerative disorder that involves upper and lower motor neurons
Not century and autonomic symptoms
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS - Lou Gehrig disease Manifestation
excessive glutamate
Muscle weakness in any or all
No inflammation
Normal intectual and sensory function
More males
Use computer to speak
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS - Lou Gehrig disease Death
2 to 5 years after onset symptoms
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS - Lou Gehrig disease Treatment
Little treatment available
Antiglutamate
Rehabilitation to prevent complications
Psychological support
Multiple sclerosis - MS
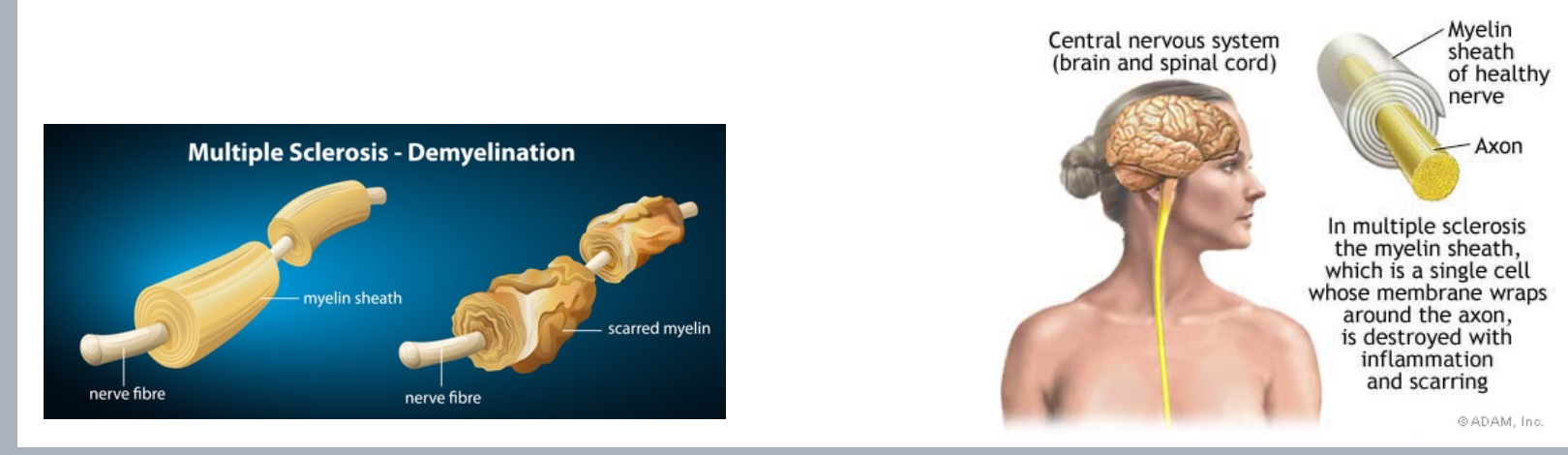
Demyelination- autoimmune - inflammatory destruction of CNS myelin
Scarred myelin Because the nervous system goes little by little it takes long
MS patho
You have a blood brain barrier
immune cell stay in theblood vessels
Sometimes the tea helper cells will leave the blood Brain barrier And go to the brain and find the myelin
They will mark the Myelin and triggered the inflammatory response. - attracting T cytotoxic cells, B cells, macrophages, and natural killer cells
B cells will make antibodies against myelin
Myelin is
White mater
MS goes through what
Destruction and recovery but another T cell will come and have neuro inflammation at the end it will stop repairing itself
MS clinical manifestations
crisis and remission
Mild symptoms to serious
Parenthesis
Weakness
Impaired gait
Numbness of extremities and difficulty walking
Optic nerve involvement
Loss of eye movement- 3,4,6 cranial nerve
Stalling difficulty
Cerebellum system - motor movement and balance
MS evaluation
lesions in white mater CNS
Ct scan
elevated IgG= CSF
MS treatment
Want them to stay in remission
immunosuppresors
Avoid extreme temperatures
Plasma exchange
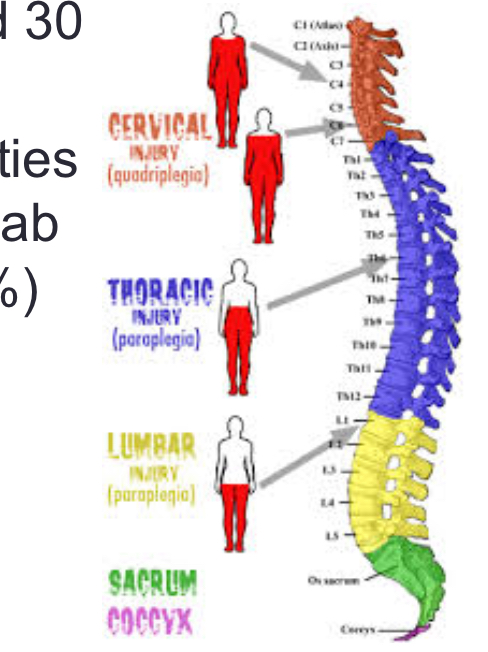
Spinal cord injury
Men are effected 16 to 30
7,800 to 10,000
Common in car accidents and motorcycle crashes, gunshots, stab wounds, and elderly falls
Spinal shock / neurogenic shock
Complete loss of all reflex, motor, sensory and automatic activity below of lesion
The muscles become paralyzed and flaccid and reflexes are absent. Loss of bladder and rectal control: bladder and bowel distention