phloem part 1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
The accumulation of nutrients into plant tissues is the source for
Almost all nutrients in humans
What elements are essential for structure or metabolism in plants
N, P, K - the limiting nutrients
What happens if plants don’t have the essential nutrients
Abnormal growth, development, or reproduction
What forces drive movement
Hydrostatic pressure
Gravity
Concentration
Electric field for ions
What sums up all of the forces that drive movement
Chemical potential
What is the driving force for a neutral molecule?
The concentration gradient
What impacts the chemical potential for ions?
Concentration gradient, and any electrical potential (Electrochemical potential)
Passive transport
Occurs spontaneously when one solute concentration is higher than the other and goes down a chemical potential gradient
Active transport
Occur against a chemical potential gradient
Membrane permeability
The extent to which a membrane permits the movement of a substance
Diffusion of salts across the membrane can produce
An electrical membrane potential
Diffusion potential
Ions crossing a membrane at different rates, causing separation of charge
When does the diffusion potential form an ion speed up or slow down?
as potassium diffuses along its concentration gradient, it slows down and the diffusion of chlorine speeds up. Ultimately, both diffuse at the same rate, but a diffusion potential exists
What if only K was passing through the membrane instead of KCl
K, would diffuse across the membrane until the membrane potential balanced the concentration gradient
Do all cells have a membrane potential?
Yes, due to selective ion movement across their plasma membranes
Equilibrium
When ions electrochemical potential is equal for an ion across a membrane- No extra energy is needed
Steady state
Active transporters to maintain equilibrium for ions- Extra energy required
What ion has the greatest concentration of any ion in plant cells and the greatest membrane permeability
Potassium
What is the predicted diffusion potential for cells?
-80 to -50 mV Because it’s close to the theoretical diffusion potential of potassium since it’s the most permeable and abundant ion in most eucaryotic cells
What is the actual resting membrane potential for plants?
-200 to -100 mV
Why is the actual membrane potential more negative than predicted?
H+ ATPase electrogenic pumps that transport protons out of the cell without an accompanying ion making the inside more negative
Plant membrane potential consist of
Diffusion potential
Active electrogenic ion transport
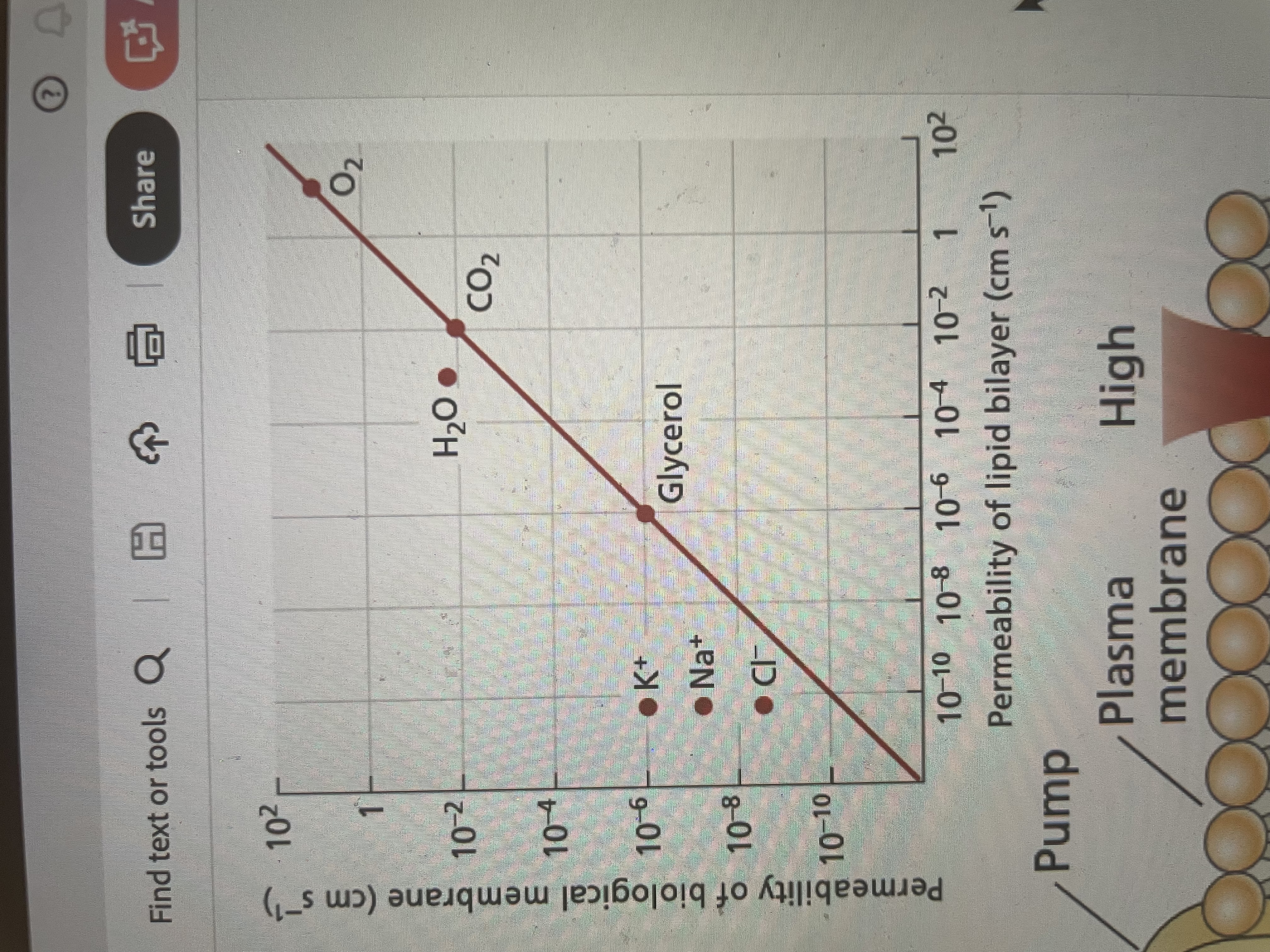
More permeability for ions and water, suggesting other things that move these in or out other than the membrane
Porsche in channel proteins can be opened or closed by gate regions in response to
Membrane potential changes, ligands, hormones, light, post translational protein modifications, mechanical stress- thigmomorphogenesis
Two types of potassium
Inwardly opening to allow inward diffusion of potassium from the apoplast
Outwardly opening to release potassium from membrane to apoplast
Carrier proteins
Bond to an organic or inorganic cell to transport it across a membrane. Slower than a channel protein
In what kind of diffusion are carrier proteins used
Passive facilitated diffusion or secondary active transport
Primary active transport- H+ ATPase
Proton binds to pump and energy is needed to change conformation and move proton across cell membrane. Pumping protons out, causes the outside to be lower in pH and inside more neutral
secondary active transport
Move solute against their concentration gradient which requires energy. Energy is delivered by protons, moving with their concentration gradient, generating proton motive force. as protons move inside it carries the solute against its concentration with it