lecture 11-GH and IGF axis
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
human growth
growth is genetically determined
nutrition, health and growth hormone determine growth
rate of growth varies with age
in utero has fastest rate of growth
rapid period of growth during infancy
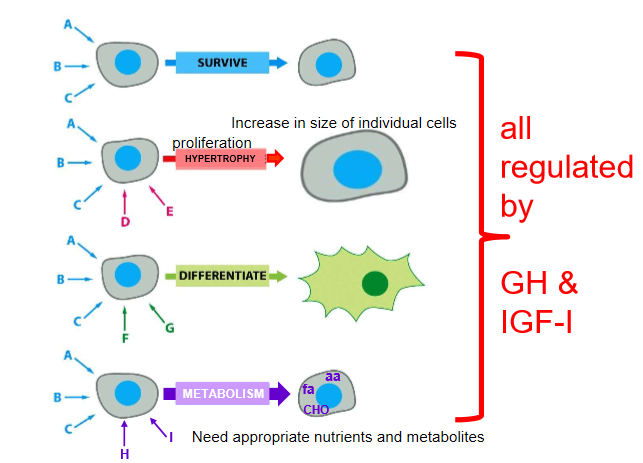
all growth depends on coordinated cellular function
cell behaviour
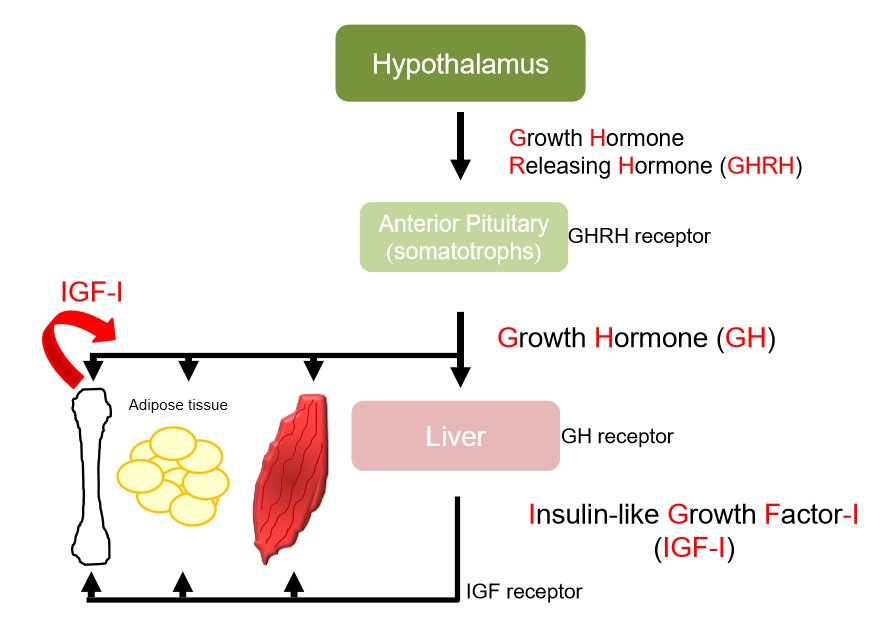
GH axis
rise in intracellular cAMP
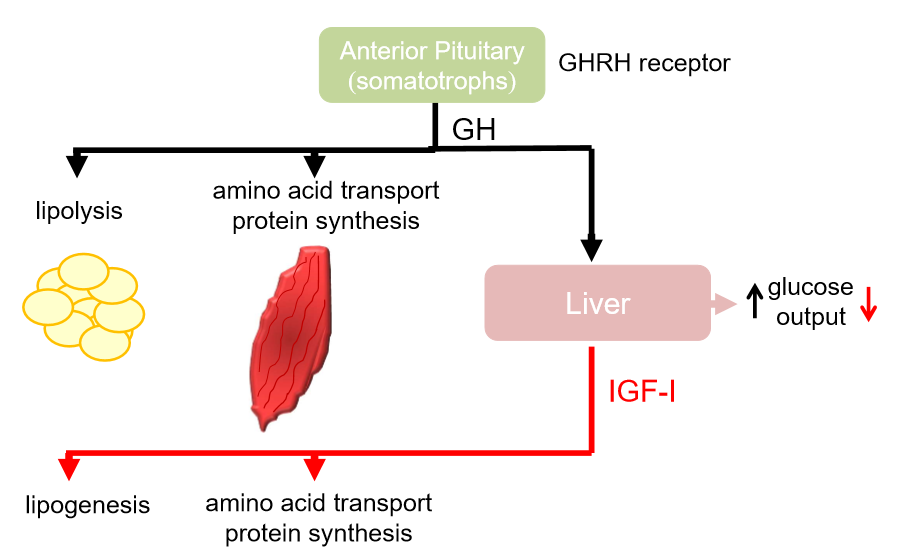
liver produces another hormone- IGF-1
growth hormone has direct and indirect effects
some IGF-1 produced locally- acts within bone
IGF-1 has endocrine, paracrine(neighbouring cells) and autocrine(same cell) effects
growth hormone
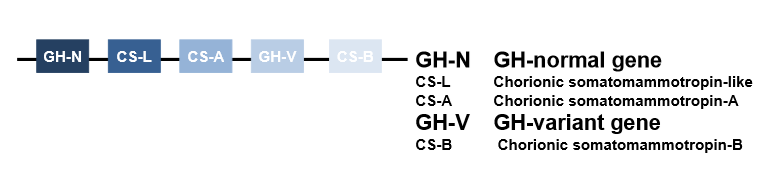
gene- part of cluster composed of 5 closely related genes
GH-N expressed in pituitary gland
GH-V expressed in placenta(important in pregnancy)
ancestral gene duplication 3.5×108 years ago
human GH~75% sequence homology with rat and bovine GH
GH normally expressed in anterior pituitary
GH-N gives rise to 22kDa(191 amino acids)-most abundant in plasma 90%, 20kDa(deletion of residues 32-46)
GH synthesised as precursor protein, N terminal signal peptide cleaved when secreted
secreted in pulses, more pronounced in males than females
not sure if shorter version(20kDa) has any specific role
predominantly produced at night
insulin-like growth factor
gene on chromosome 12
7.5kDa(70 amino acids), significant homology with insulin
GH and IGF-1 actions
promote growth in long bones, soft tissues and organs
effects on cellular proliferation, survival, differentiation, metabolism
can also bind to insulin receptor
functionally similar to insulin
good at stimulating cell mitosis
prevents apoptosis
affects storage and use
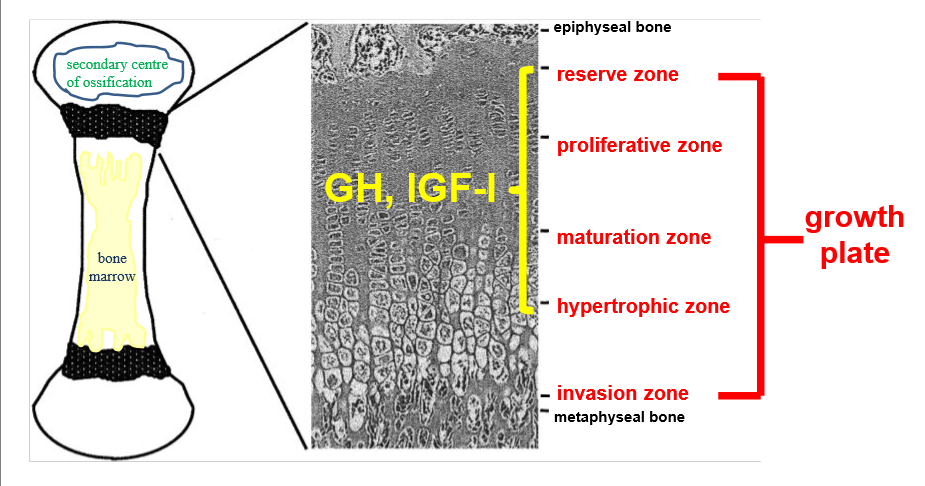
GH and IGF in bones
growth plate at both ends of long bone
reserve zone- bone in small clusters in matrix of collagen, progenitor cells
maturation zone- mature and become chondrocytes secrete matrix
matrix becomes calcified, acts as scaffold for new bone
GH and IGF in metabolism
stimulates glycolysis
stimulates muscle to take up amino acids, converts them into proteins
hyperglycaemia- increase breakdown of glycogen in liver, increase glucose output, stimulates glucogenesis
increase glucose uptake into tissue and fat
growth hormone not involved in normal state
IGF-1 has opposite actions to growth hormone
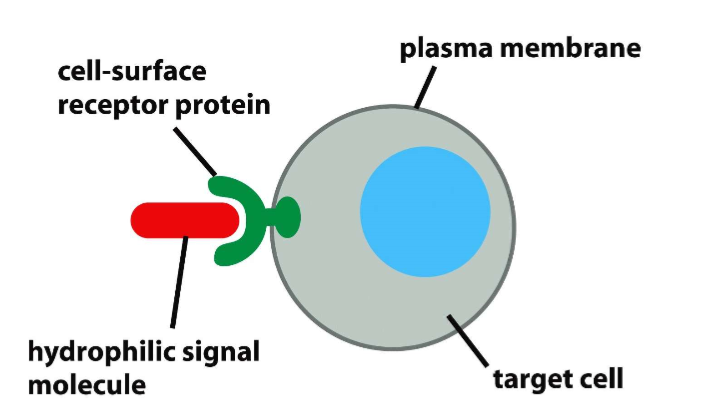
GH and IGF-1 act at cell surface receptors
both are protein hormones
can’t cross plasma membranes, hydrophilic
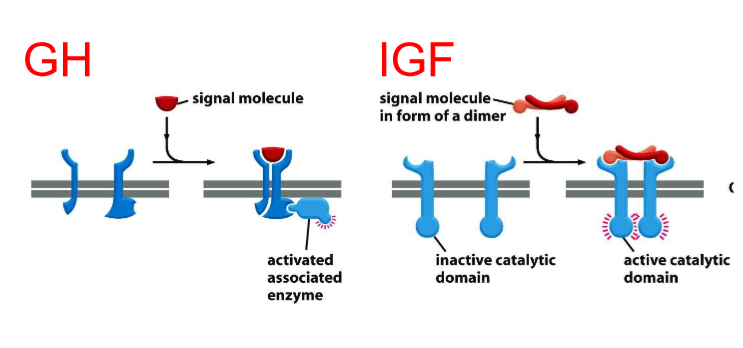
growth hormone receptor has to recruit enzyme
enzyme-coupled receptors
IGF has enzyme already built it
intrinsic enzyme is activated
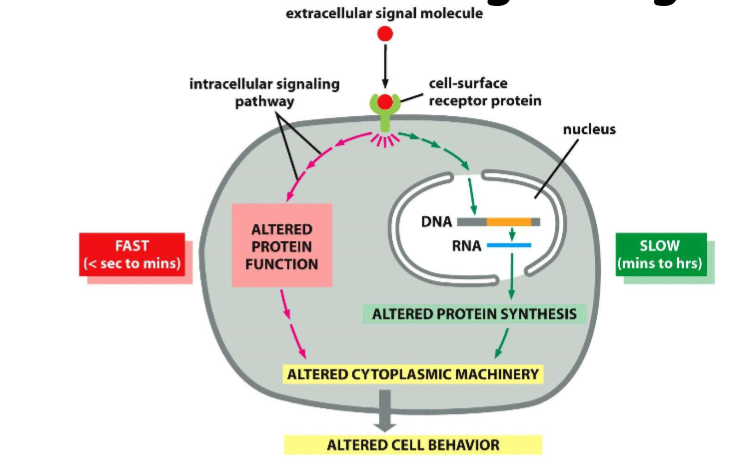
intracellular signalling
uptake of glucose
alter amino acid uptake and release
can have long term effects, alter gene expression
can have rapid and slow responses
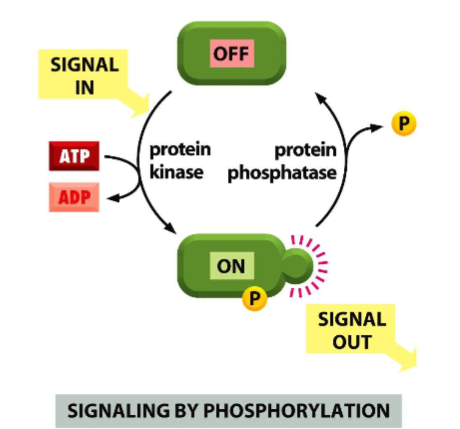
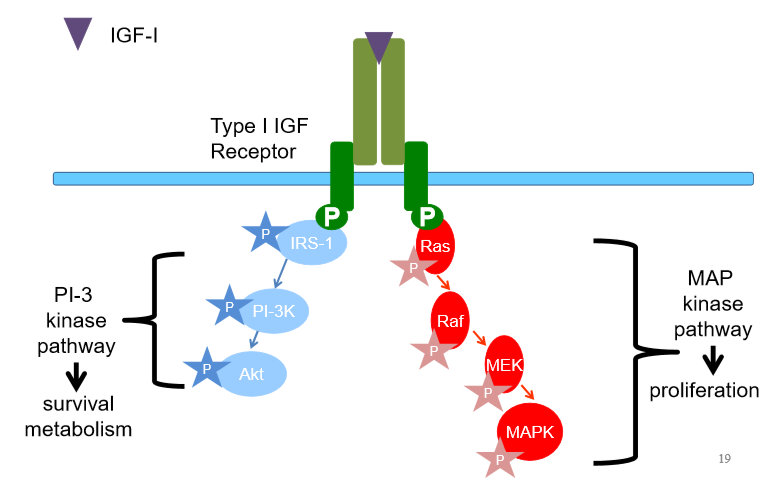
GH and IGF-1 activate kinase cascades
phosphate added to serine, threonine
switch signal one
turn signal off by phosphatase, removes phosphate
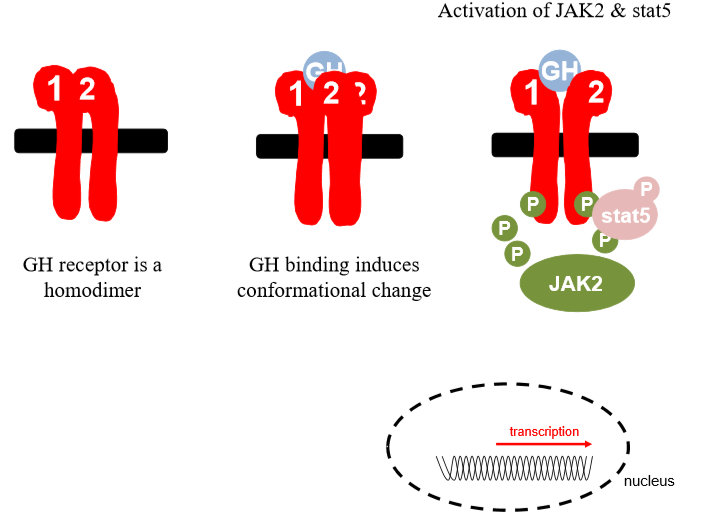
GH receptor
Exists in plasma as homodimer
Conformational change when gh binds, one subunit rotates, reveals binding site
Once enzyme recruited, jak2 phosphorylates on residue, cytoplasmic portion, transcription factor
Stat 5 gets phsophorylated and active, moves into nucleus binds to promoter regions
GH binding protein
physiological significance of GHBP poorly understood
prolong GH half life?
compete with GH receptor for GH?
intracellular portion can be cleaved off
extracellular portion is GHBP
role of GHBP is not known
TNF converting enzyme involved in cleavage of receptor
insulin like growth factor axis
Heterotetramer- 2 alpha, 2 beta subunits
Identicalsubunits
Beta subunits span membrane, alpha are extracellular
Enzyme already built into beta subunit
Beta become phosphorylated
Irs1 becomes phosphorylated, phosphocascade
Can also phosphorylate ras
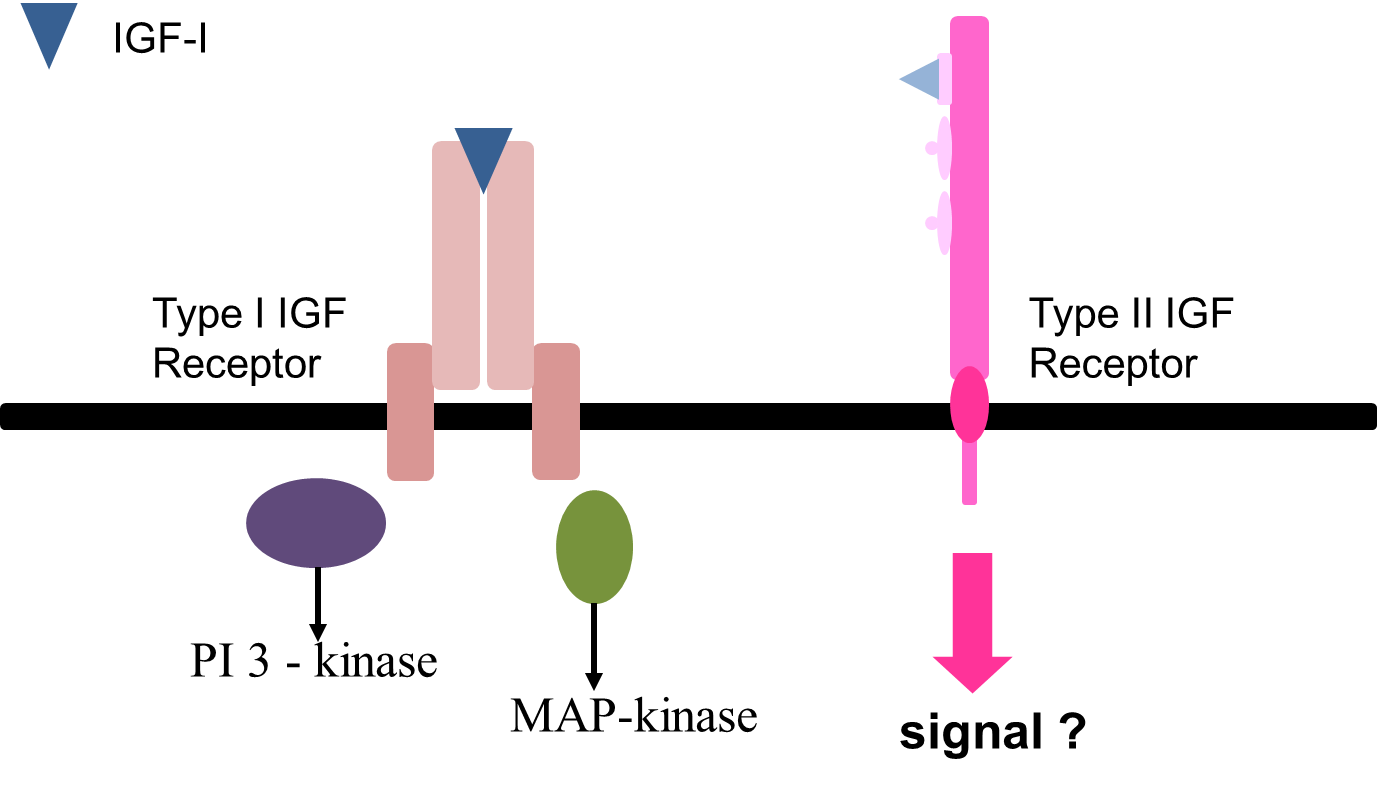
type 2 unknown if it can signal, clearance receptor than signal receptor
insulin-like growth factor axis(ii)
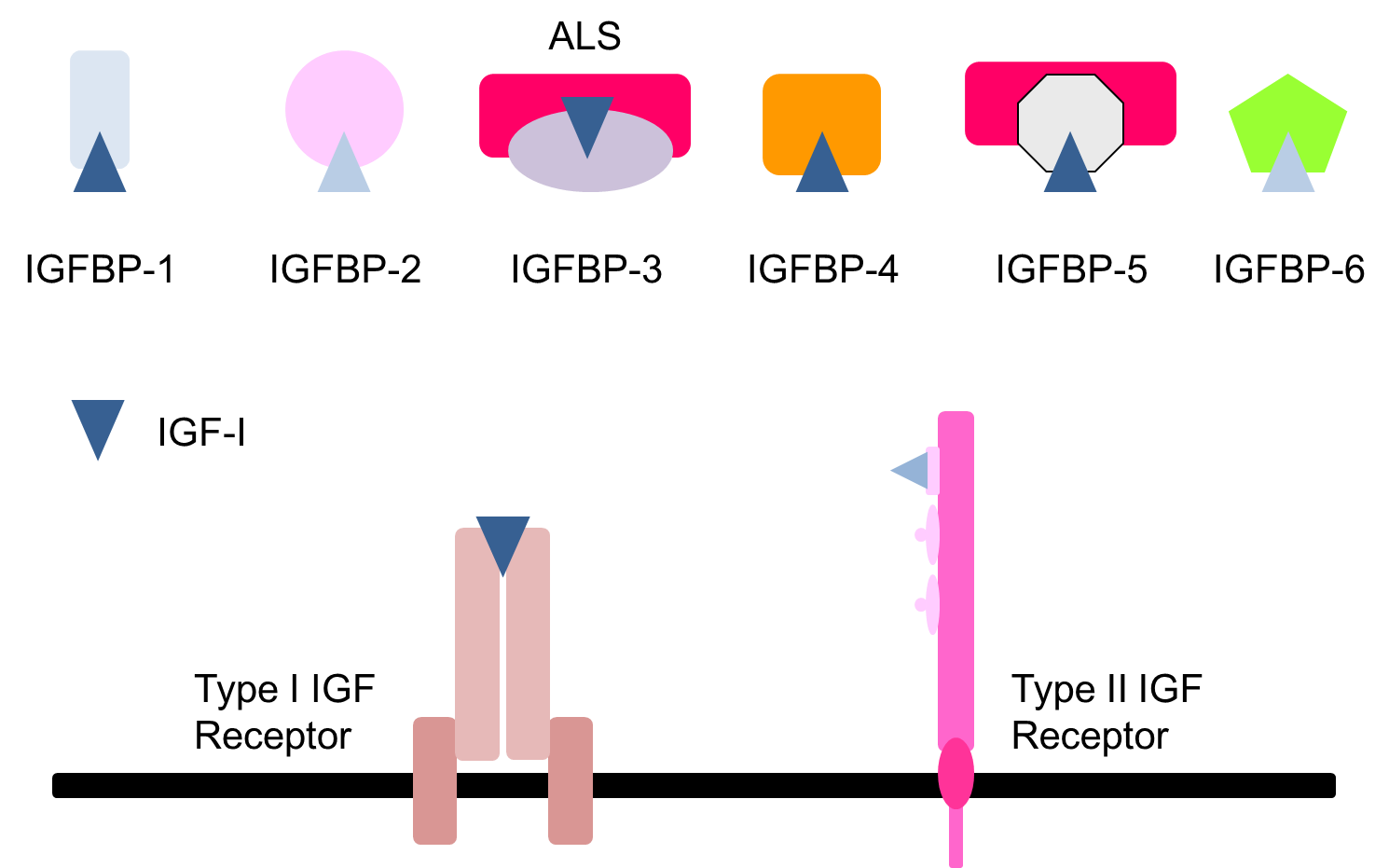
most IGF present in circulation bound to one IGFBP
less than 5% IGF free
BP3 and BP5 have tertiary complex
others are binary complexes
IGF binding proteins
majority of IGF associated with IGFBP
6 well characterised
evolutionary homology
some structural similarities
differing regulation and tissue sources
IGFBP-3 main IGFBP in circulation, storage of IGF
prolong IGF half life
transport molecules
modify IGF action
IGF levels don’t fluctuate
long half life, protected from proteolysis
complex is too big to move out of circulation
binary complexes are able to leave circulation and can reach target tissue
can regulate IGF actions
IGF binding proteins regulate IGF activity
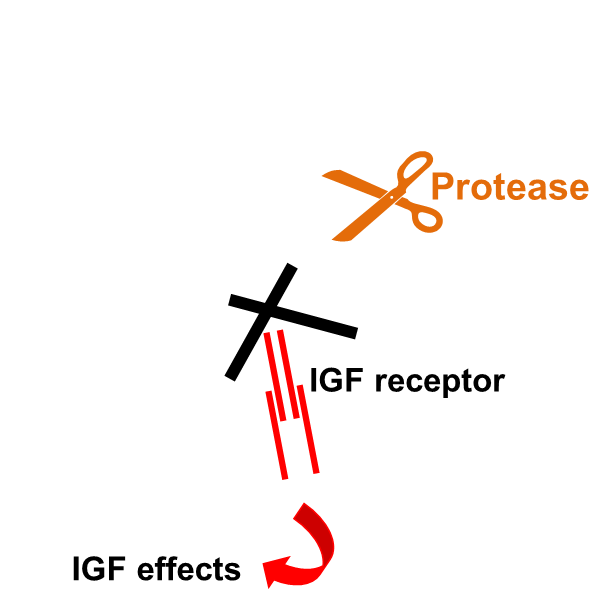
binding proteins have high affinity for IGF
blocked from acting at receptor
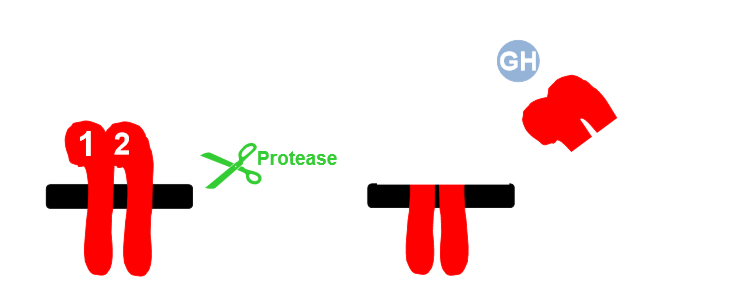
Igf needs to be released from binding proteins, cleaved by proteases
Once bp fragmented, binding site, igf can interact with receptor
Proteolysis, other post translational modification can affect affinity, glycosylation status can affect affinity
Release igf as appropriate
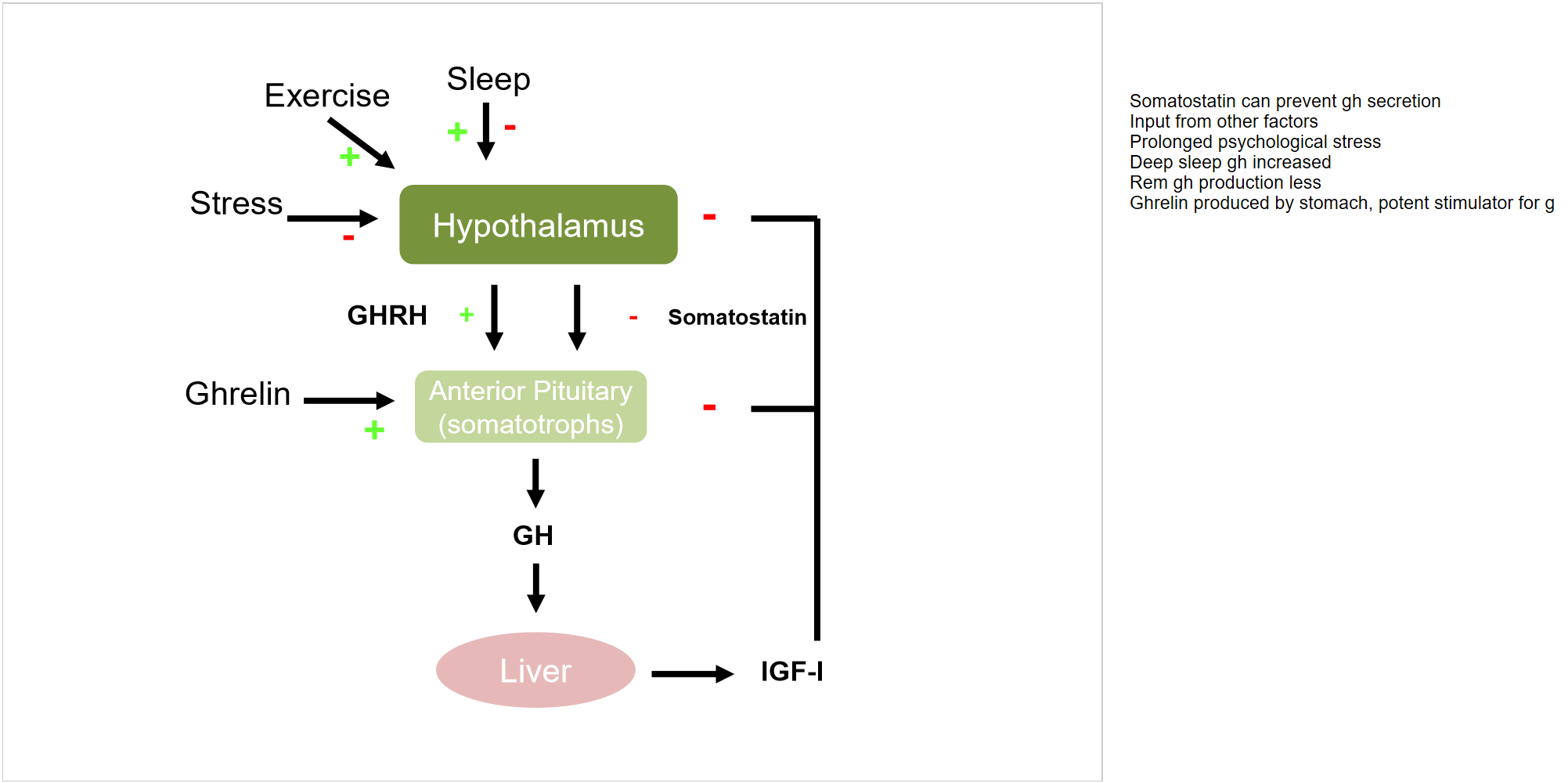
factors affecting GH and IGF axis
Somatostatin can prevent gh secretion
Input from other factors
Prolonged psychological stress
Deep sleep gh increased
Rem gh production less
Ghrelin produced by stomach, potent stimulator for g
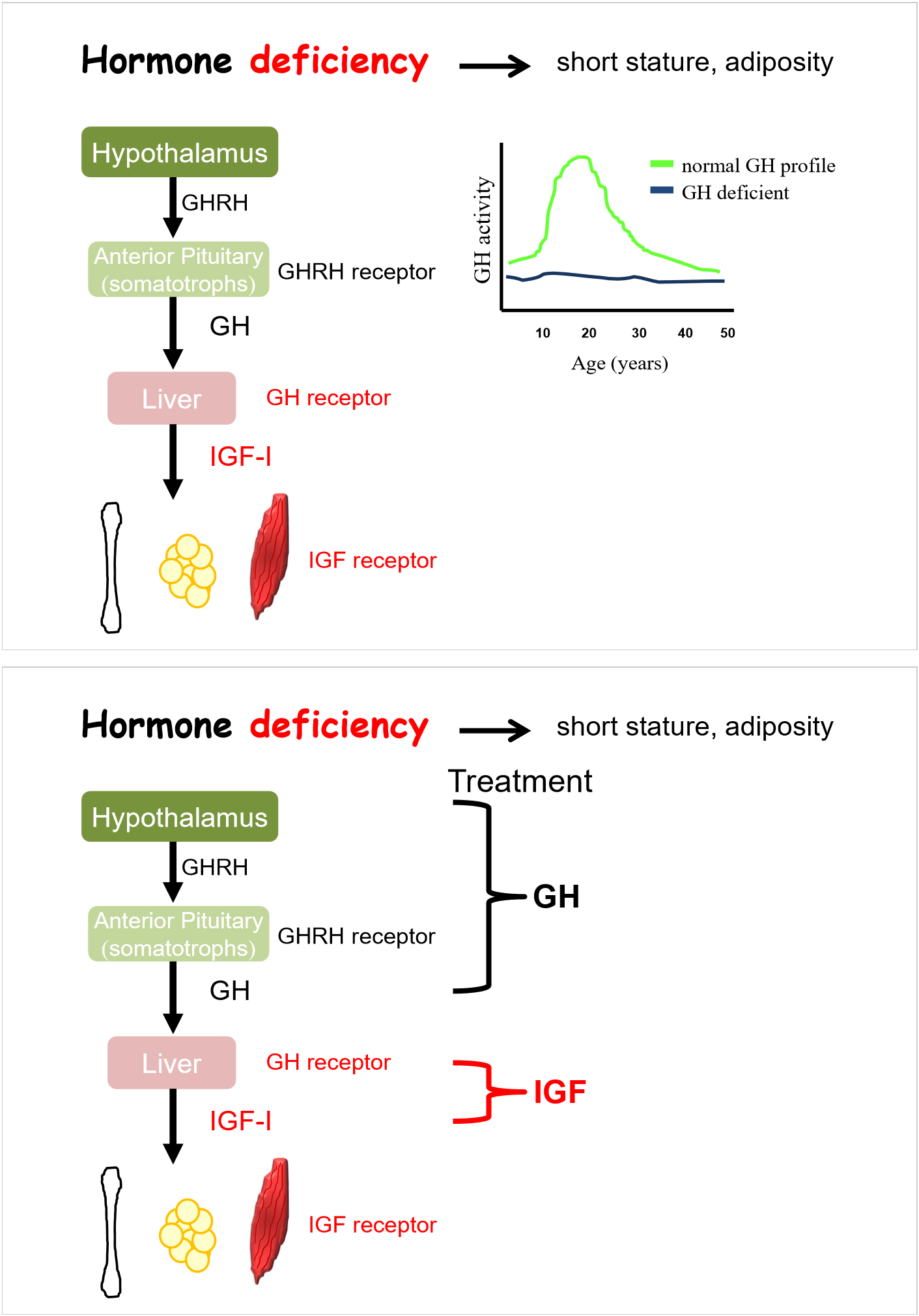
hormone deficiency- short stature, adiposity
treatment is to replace IGF
replace with daily injections of GH
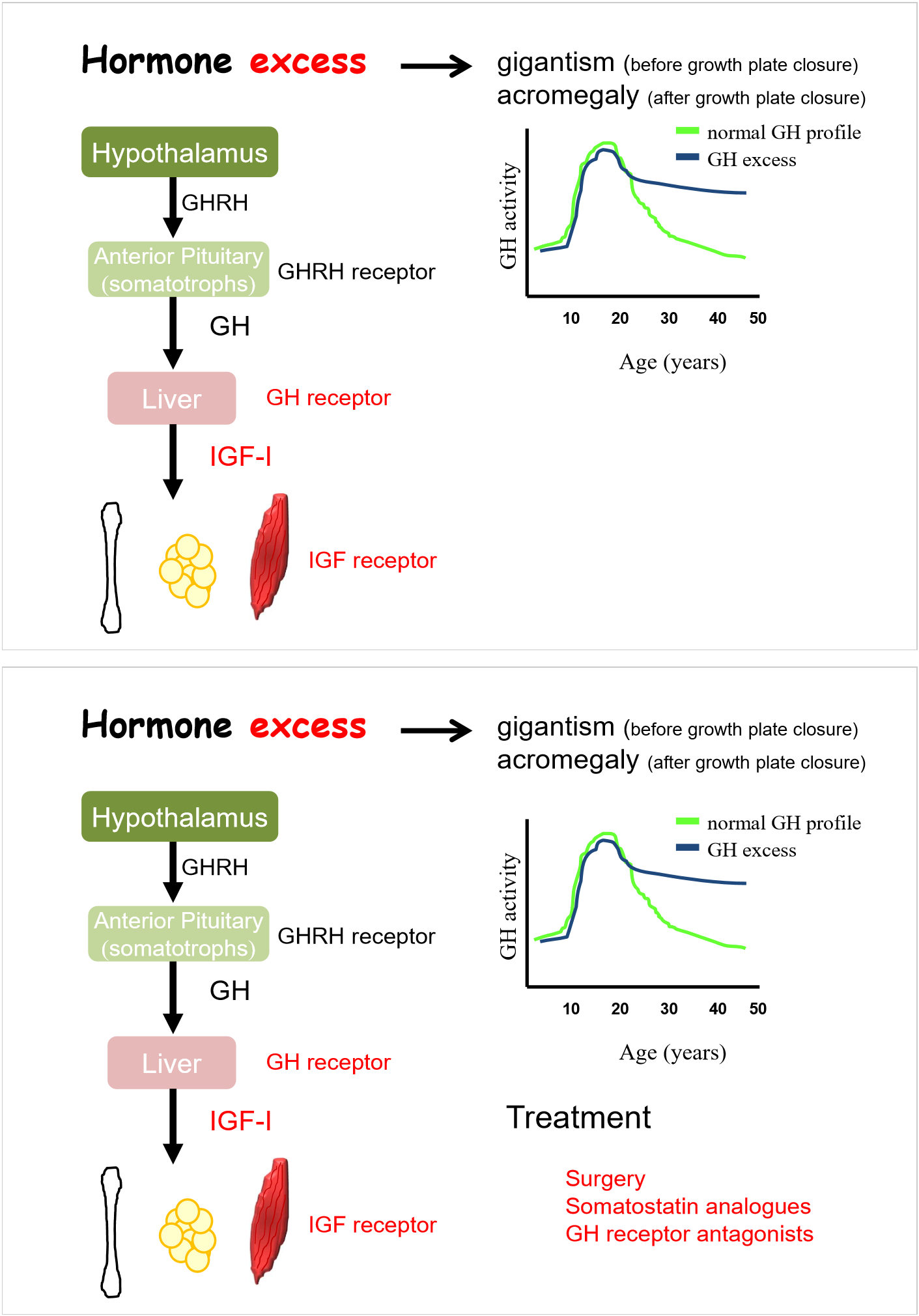
hormone excess- gigantism, acromegaly
depends on point in individual’s life
tumour in anterior pituitary
acromegaly has no increase in height, thicker bones
surgery to remove tumour
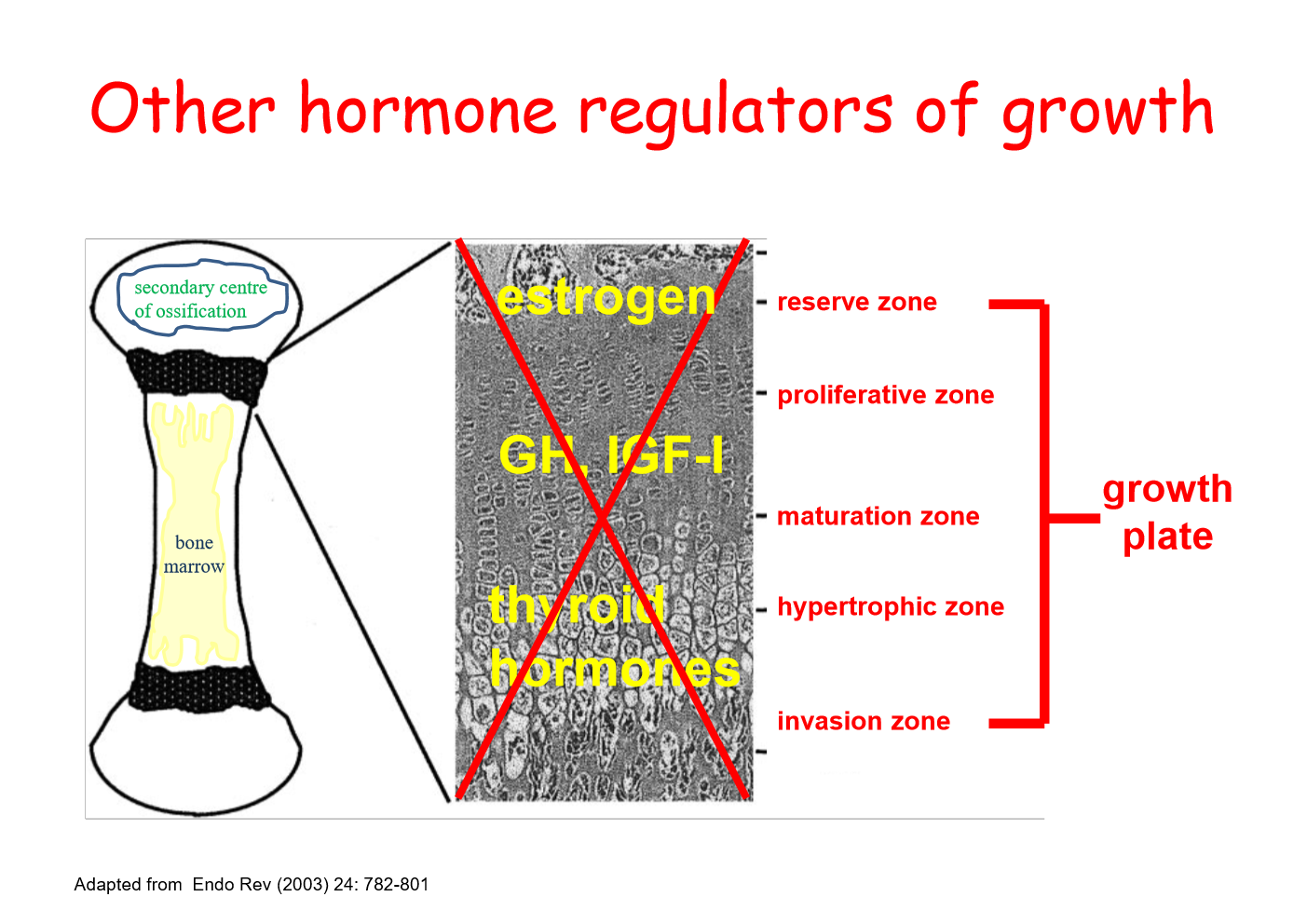
other hormone regulators of growth
oestrogen involved
levels increase through puberty, lead to apoptosis of cells in reserve zone
nothing to feed into growth plate
thyroid also contribute to long bone, act in hypertrophic zone