Lecture 5: Pelvis and Perineum
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about Pelvis and Perineum Lecture Notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Cavity that lies below and behind the abdominal cavity, communicating with the lower limbs, surrounded by the pelvic girdle from the pelvic brim to the pelvic diaphragm.
Pelvic cavity
What is the pelvic diaphragm?
Muscular "hammock" forming the inferior extent of the pelvic cavity.
related to continence and prolapsed uterus
What is the perineum?
What is it the attachment site for?
Area between the legs and the shallow compartment below the pelvic diaphragm.
place of attachment for genitalia
What are the main functions of the pelvis?
Transmit body weight to the lower limbs and support and protect pelvic viscera.
What forms the Os Coxae (hip bone)?
Fusion of ilium, ischium, and pubis.
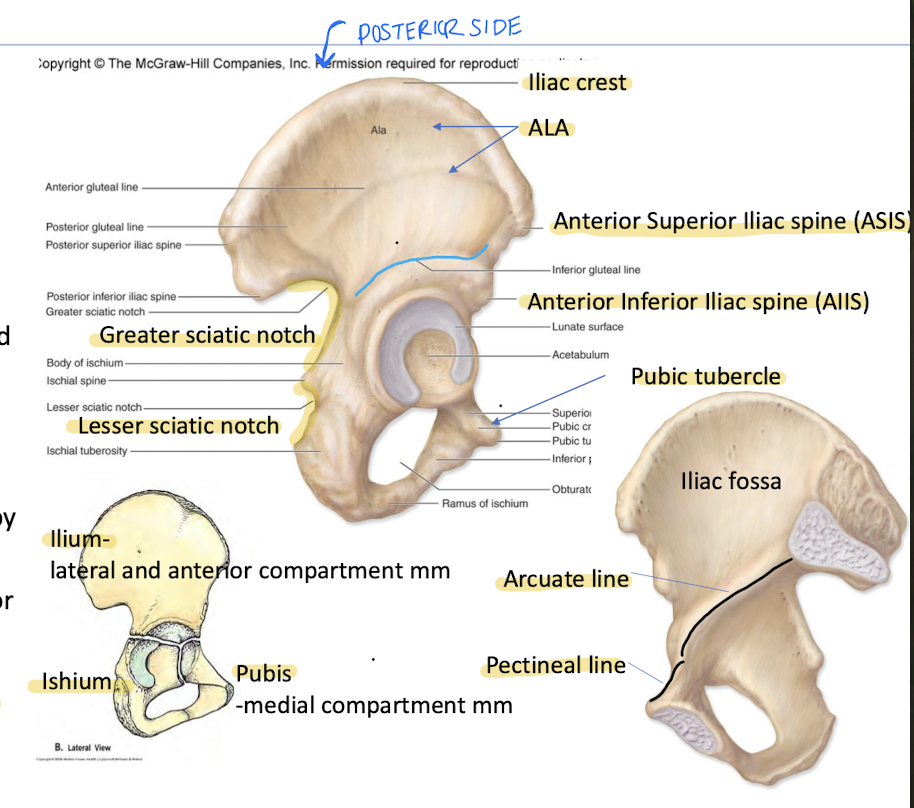
“Wing"-lateral surface of ilium is known as the
Ala of the Os Coxae
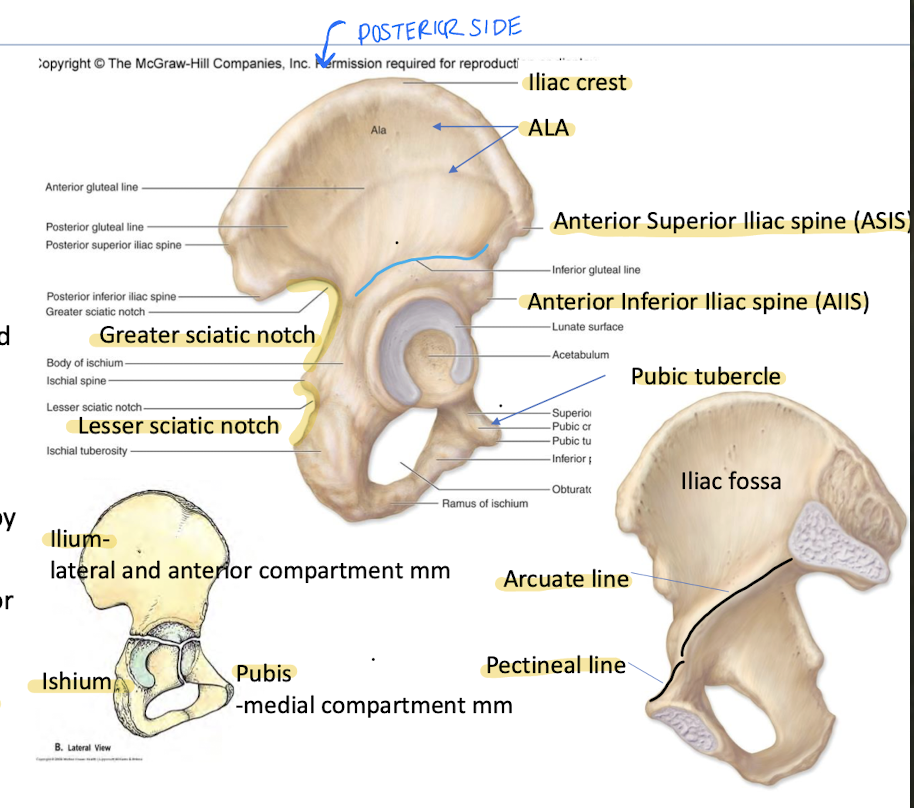
What is the Greater Sciatic Notch?
What is the lesser Sciatic Notch?
Between PIIS and ischial spine; enclosed by sacrospinous ligament to form Gr. Sciatic foramen containing piriformis + neurovascular structures.
Between ischial spine and ischial tuberosity; enclosed by sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments to form lesser sciatic foramen. Transmits tendon of obturator internus.
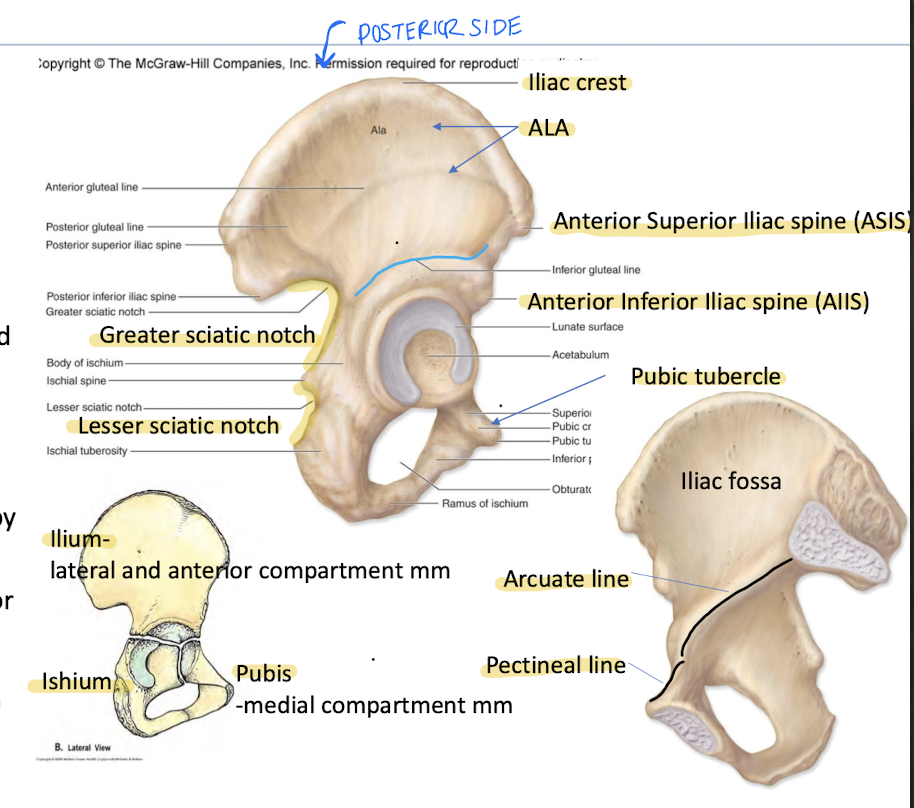
What is the Pubic Tubercle?
Raised eminence on lateral end of pubic crest; attachment of inguinal ligament.
What is the attachment site of the inguinal ligament in the pelvis?
Pubic Tubercle
_______ and ______ form the true pelvic brim
arcuate line
pectineal line
What is the function of the ligaments of the pelvis?
Stabilize the pelvis and form spaces for the passage of vessels, nerves, and muscles.
What do the Sacrotuberous and Sacrospinous ligaments do?
Transform the greater and lesser sciatic notches into the greater and lesser sciatic foramina.
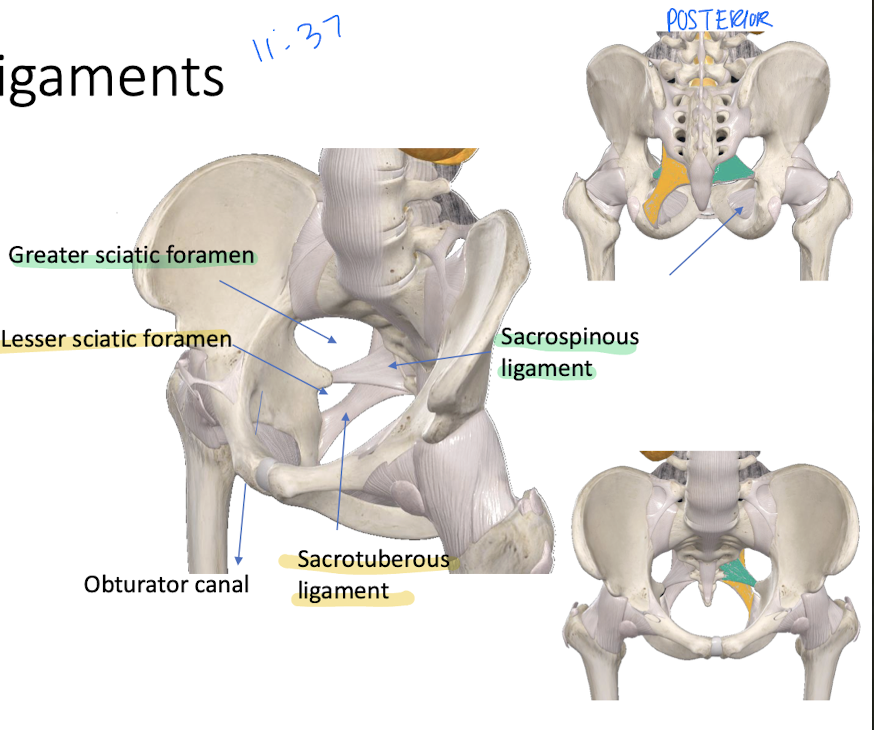
The obturator foramen is closed by the obturator membrane except for a small obturator canal allowing for passage of which nerve?
Obturator nerve.
Compare the False Pelvis to the True Pelvis
The false pelvis is superior to the pelvic brim aka pelvic inlet
True pelvis is the basin inferior to the pelvic brim holding pelvic organs
has inlet and outlet where are bony dimensions the baby’s head must pass through
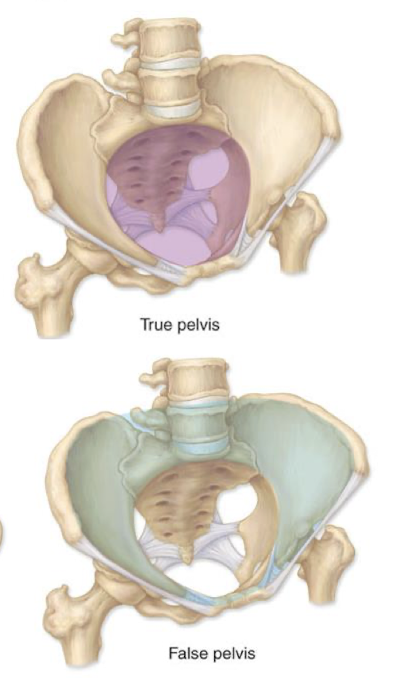
which organs are in the true pelvis basin?
bladder
terminus of GI
reproductive apparatus
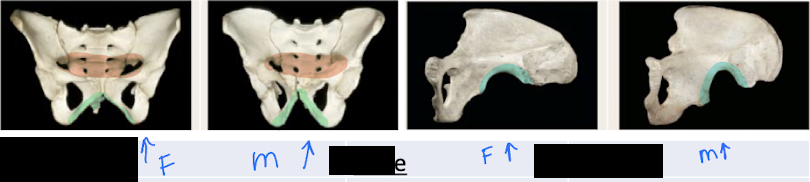
How can you differentiate a male vs female pelvis on a skeleton?
Male
Pelvic inlet is heart shaped (red)
Pubic arch and Subpubic angle is less than 80 degrees (green)
greater sciatic notch is narrow (blue)
Female
pelvic inlet is wide oval (red)
Pubic arch and subpubic angle is greater than 90 degrees (green)
greater sciatic notch is wide (blue)
Which two structures form the pelvis?
Pelvic diaphragm - Muscles and fascia that line the floor of the pelvis.
Perineal membrane (urogenital diaphragm) - gives passage to urethra in females
What are the muscles of the pelvic diaphragm?
these two are the most important for incontenece
coccygeus
levator ani muscles
What is the action of the Coccygeus muscle?
Draws pelvic diaphragm upwards; pulls coccyx forward; helps maintain fecal continence.
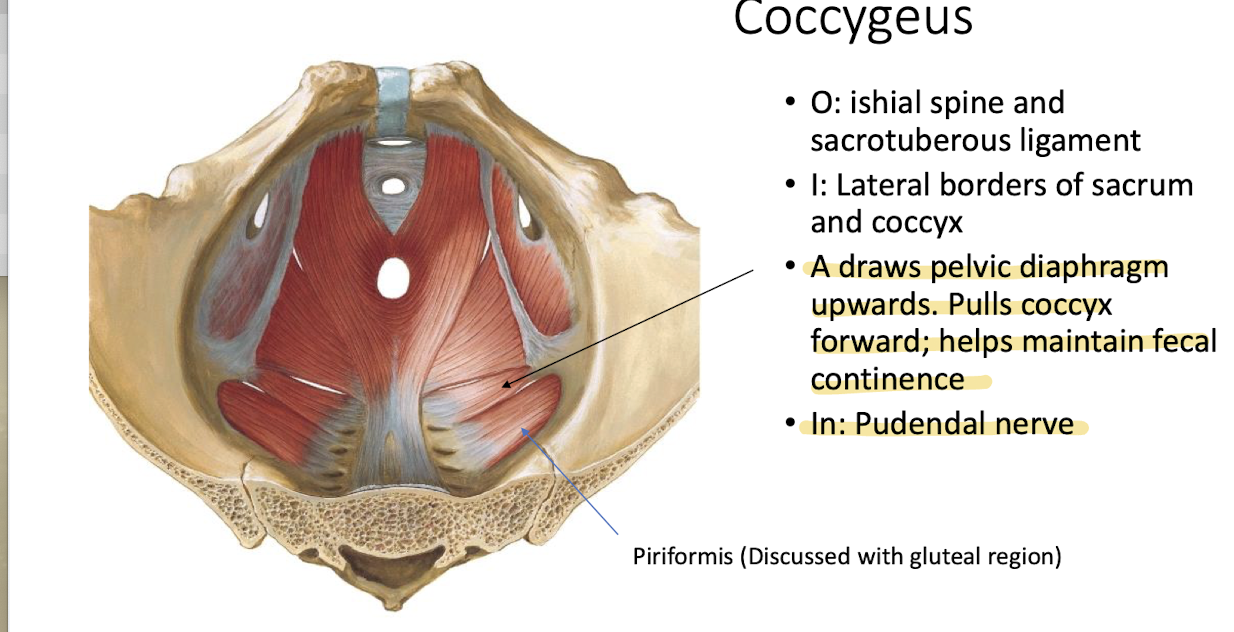
What is the innervation of the Coccygeus muscle?
Pudendal nerve.
What are the three muscles that make up the Levator ani? Name their action and innervation
Puborectalis - draws rectum upward and forward to aid anal sphincter; innervated by Pudendal nerve
Pubococcygeus - elevation of pelvic floor; inn: Pudendal
Illiococcygeus - supports pelvic viscera; innervated by sacral n
Which muscles in the pelvis are supplied by the inferior gluteal artery?
Muscles of Levator ani = puborectalis, pubococcygeus, and Illiococcygeus
Describe the viscera of the pelvis?
Holds both the Bladder and rectum in both sexes; uterus and part of the vagina in females; prostate and seminal vesicles in males.
Portions of these organs bulge into the abd cavity and covered by reflections of the peritoneum
reflections (green) are where the membrane changes direction
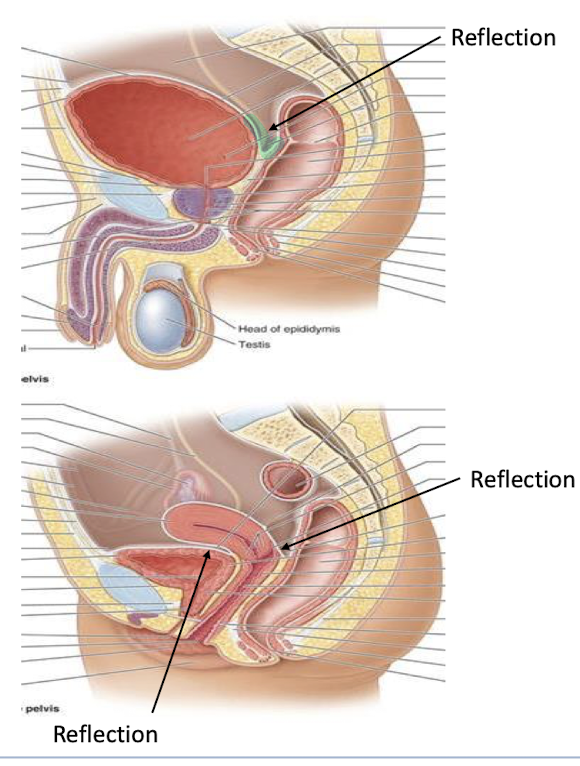
What are the peritoneal reflections/pouches responsible for?
Permit expansion and collect debris
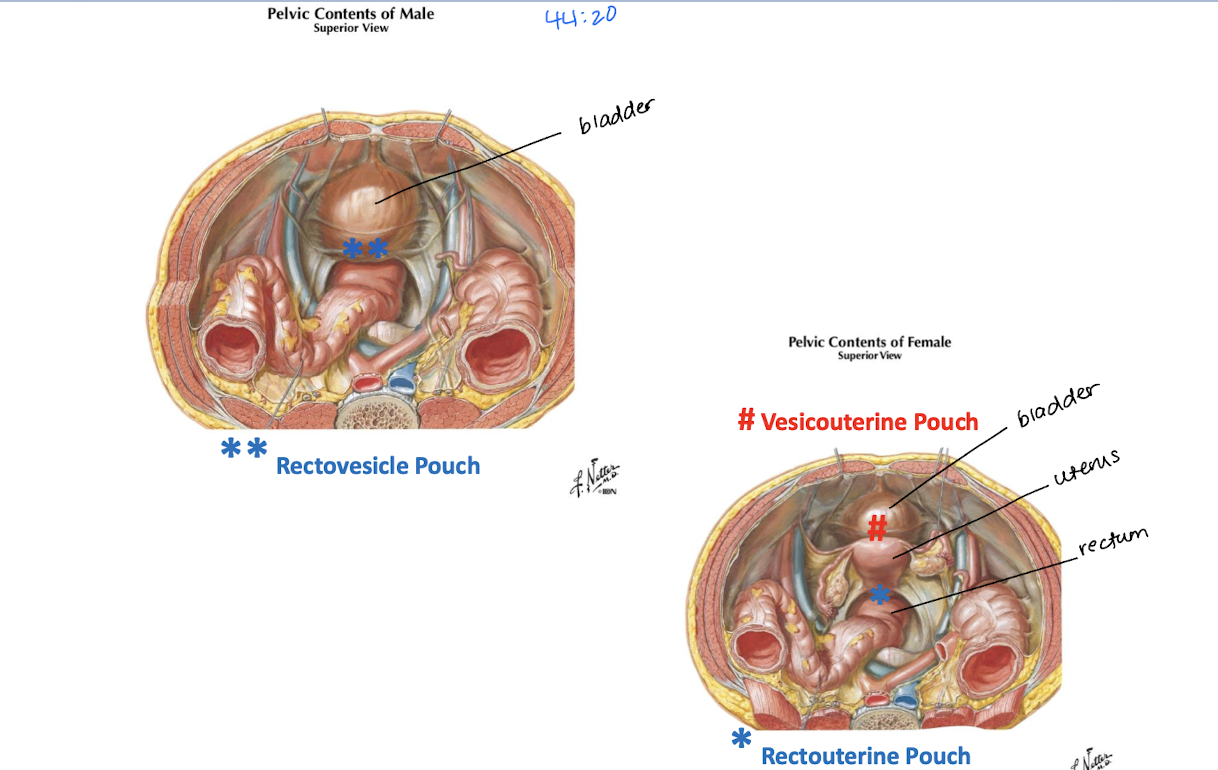
Describe the pouches found in males and females
Male
Rectovesical pouch
Female
Vesicouterine pouch
Rectouterine pouch
What are the ureters?
Muscular tubes connecting the kidney to the urinary bladder.
They conduct urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
_______ crosses over the iliac vessles and pelvic brim
Ureters
Hollow distensible organ located posterior to the pubic bone (pubic symphysis)
urinary bladder
Where does the bladder sit in males vs females
Males - upon prostate
Females - rests on the anterior wall of the vagina posteriorly
The walls of the bladder are composed of the ______ and are continuous with the ______ which guards the urethra
detrusor muscle
internal urethral sphincter
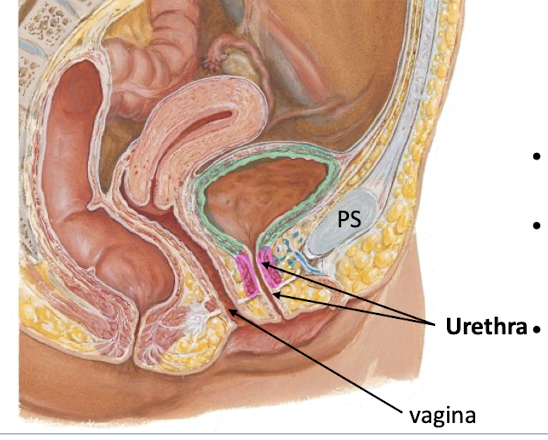
What is the trigone of the bladder?
Triangle-shaped area between urethra and 2 ureter openings.
What supplies blood to the Is Urinary Bladder?
Superior vesicle (bladder) arteries
Males: Inferior vesicle artery
Females - vaginal artereis
T/F: when the bladder is full, it ascends in the abd above the pubic symphesis
true
What do the male internal genital organs include?
Testes
epididymides
ductus deferens
ejaculatory ducts
seminal glands
prostate
bulbourethral glands.
Describe the ductus deferens
continuation of the epididymis
crosses over the ureter and ends by forming an ampulla (for sperm storage)
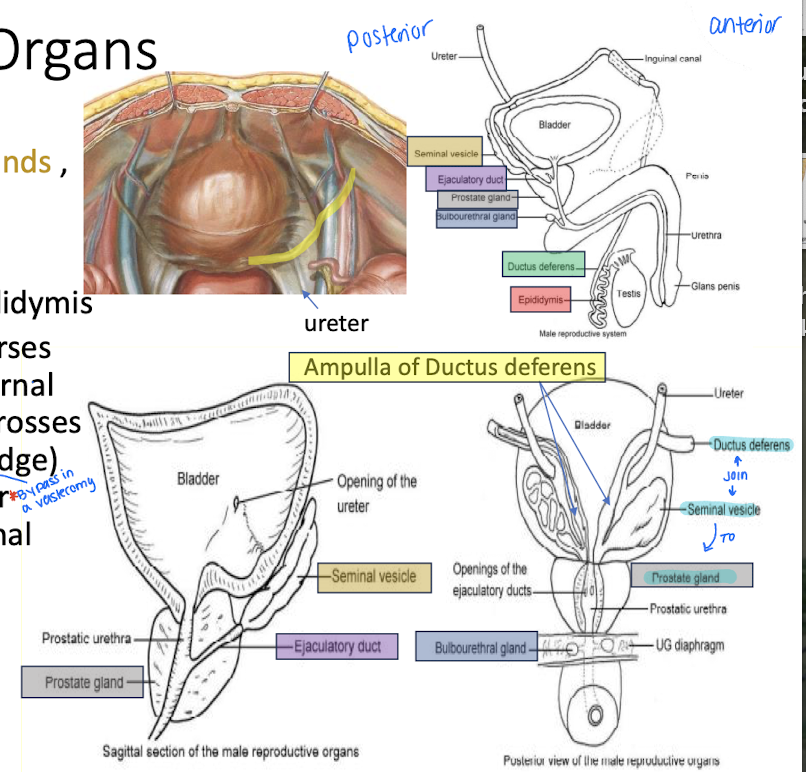
_____ and _____ in the male genitalia join to from the ejaculatory duct
ductus deferens
seminal vesicle
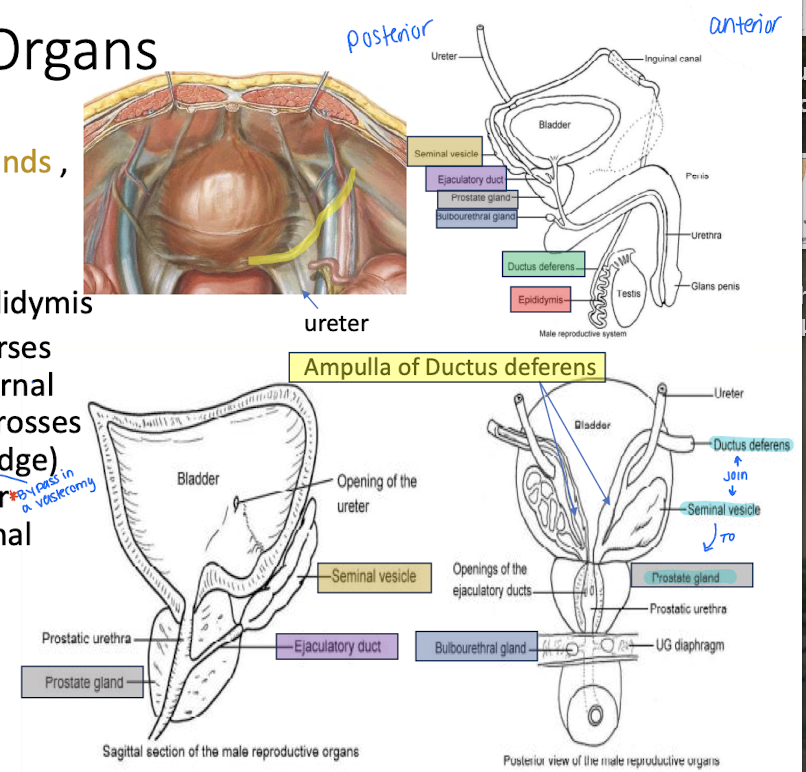
What does the prostate produce?
Largest male reproductive ACCESSORY organ
Milky fluid for activating and transporting sperm.
What does the seminal vesicle provide?
Fructose food for sperm in alkali fluid.
What is the function of the bulbourethral glands?
Lubricate urethra for passage of semen during ejaculation.
What is the ejaculatory duct?
Union of seminal vesicle and ductus deferens leading to the prostate gland and urethra
Clinical application: _____ is common in older men usually not malignant but it can cause difficulty with urination and patients tend to feel incontenence
enlarged prostate
Clinical application: _______ is described as a cancer common among men over 75 but it is not considered problematic because it spreads slowly
Prostate cancer
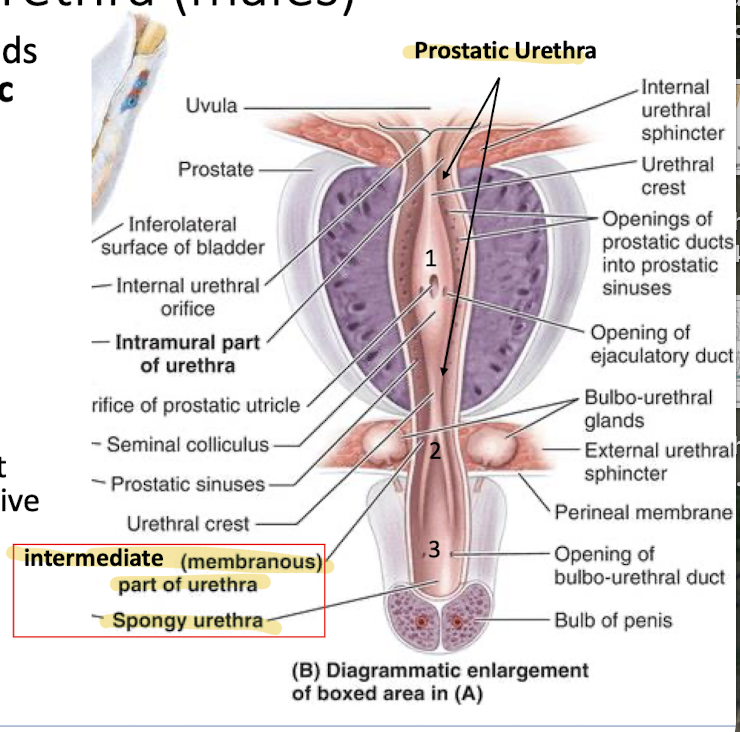
What are the three parts of the male urethra?
Anterior prostate (prostatic urethra) (1)
pelvic diaphragm (intermediate (membranous) urethra) (2)
bulb of the urethra (spongy urethra) (3)
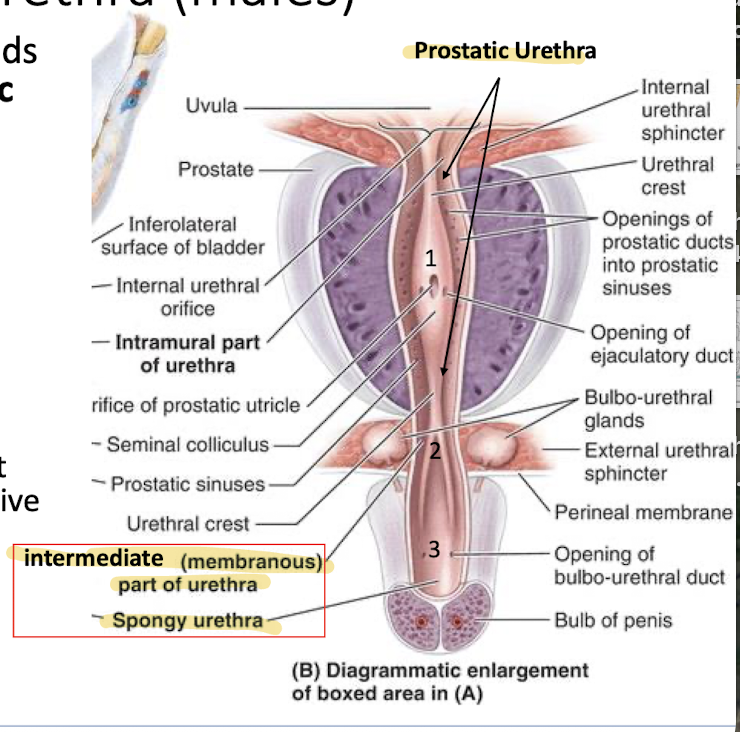
Where do the prostatic ducts in males empty into? Why is that important?
T/F: the prostate is vascularized and has nervous tissue as well
Anterior prostate (prostatic urethra) (1) - important because it adds prostatic fluid to ejeculate and support sperm
True
List the male internal genital organs of the pelvic viscera
ductus deferens
seminal vesicle
Ejaculatory duct
Prostate
Bulbourethral gland
List the female internal organs of the pelvic viscera
vagina
uterus
uterine (fallopian) tubes
Ovaries
What are the functions of the vagina?
Excretory flow during menstruation
birth canal
reproductive organ that receives the penis during intercourse.
“cup” around the cervix: analyzed during childbirth to judge cervical thinning is known as______
vaginal fornices
What is the structure of the uterus?
Contains 3 parts: fundus, body, and cervix.
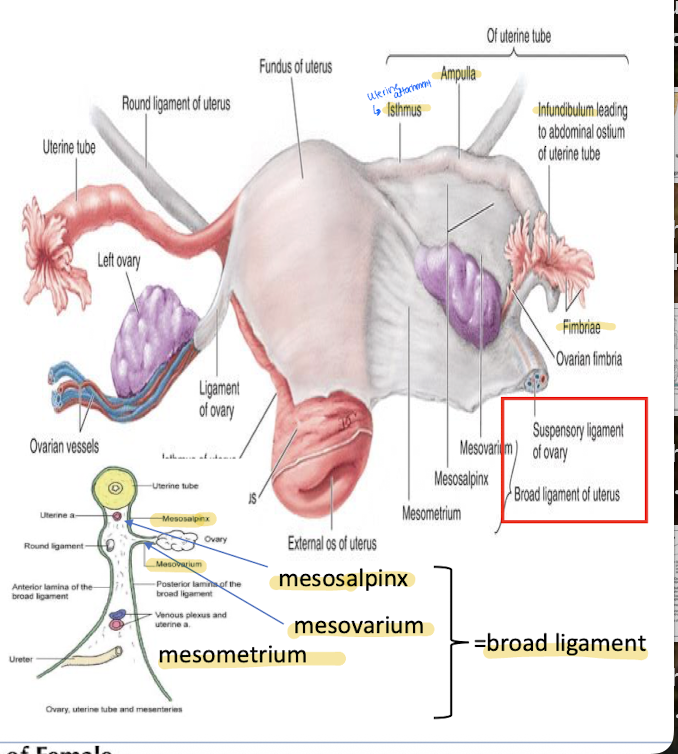
What is the broad ligament?
Fold of peritoneum that suspends the uterus.
What is the ovarian ligament vs the suspensory ligament
Both are forms of the broad ligament
OL: Remnant of gubernaculum; attaches ovary to uterus.
SP: Lymphatics, nerves, and ovarian vessels that supply the ovary.
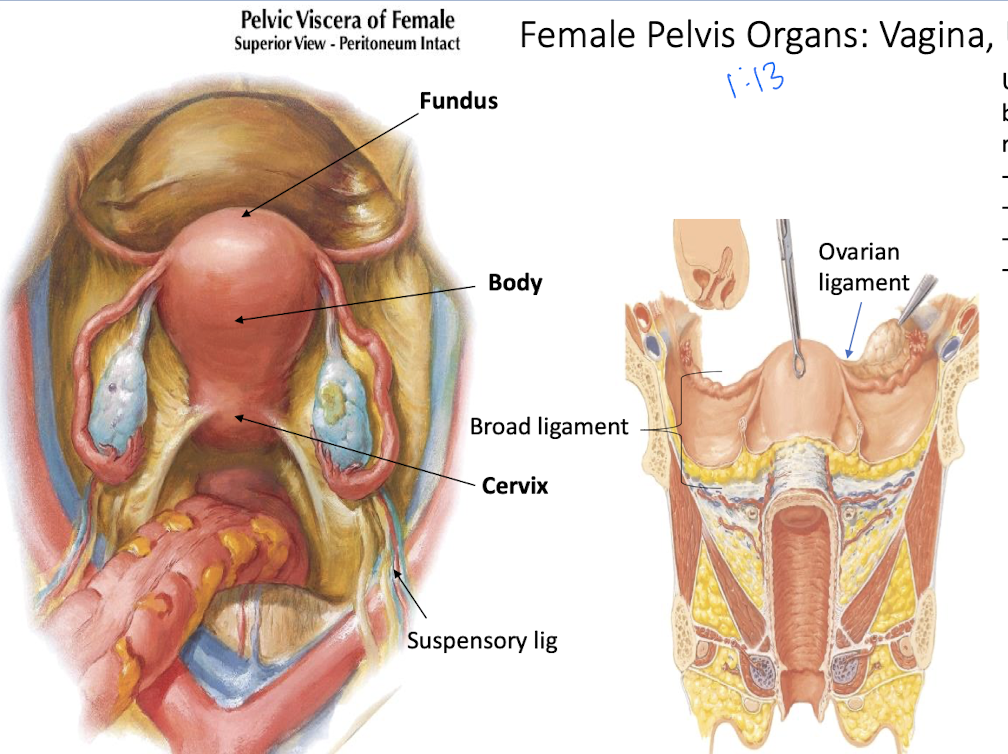
What are the ovaries? How are they suspended to the uterus?
Almond-sized; produce eggs and hormones.
By a short, mesentary fold of the broad ligament called the mesovarium.
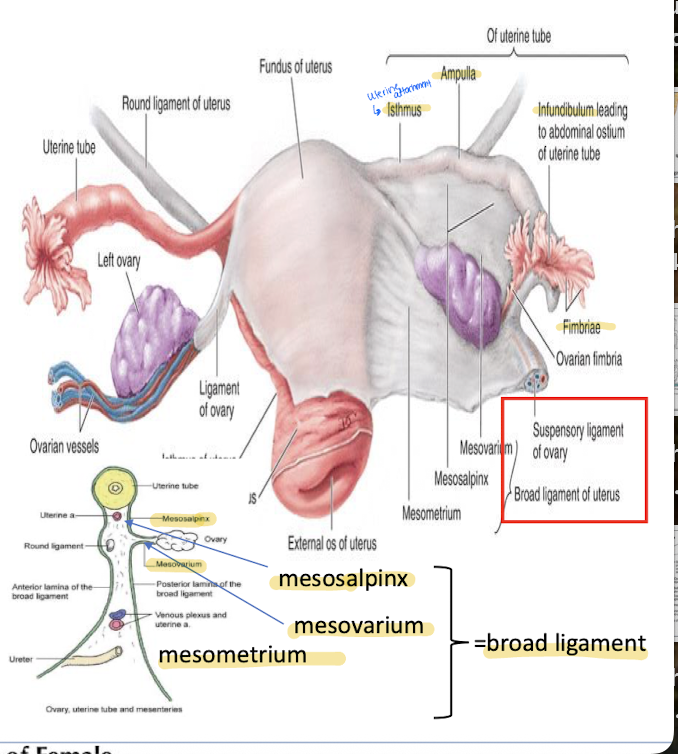
What makes of the broad ligament on the uterus?
mesovarium
mesosalpinx
mesometrium
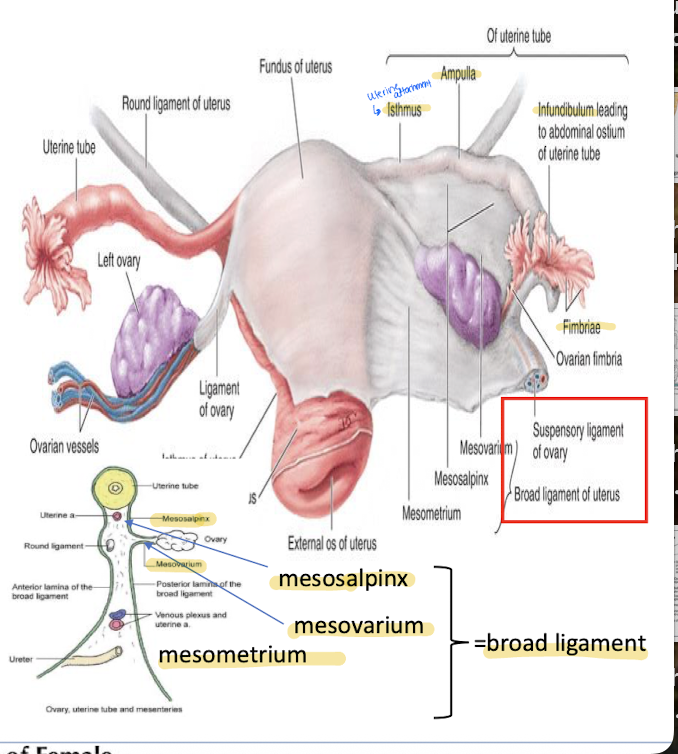
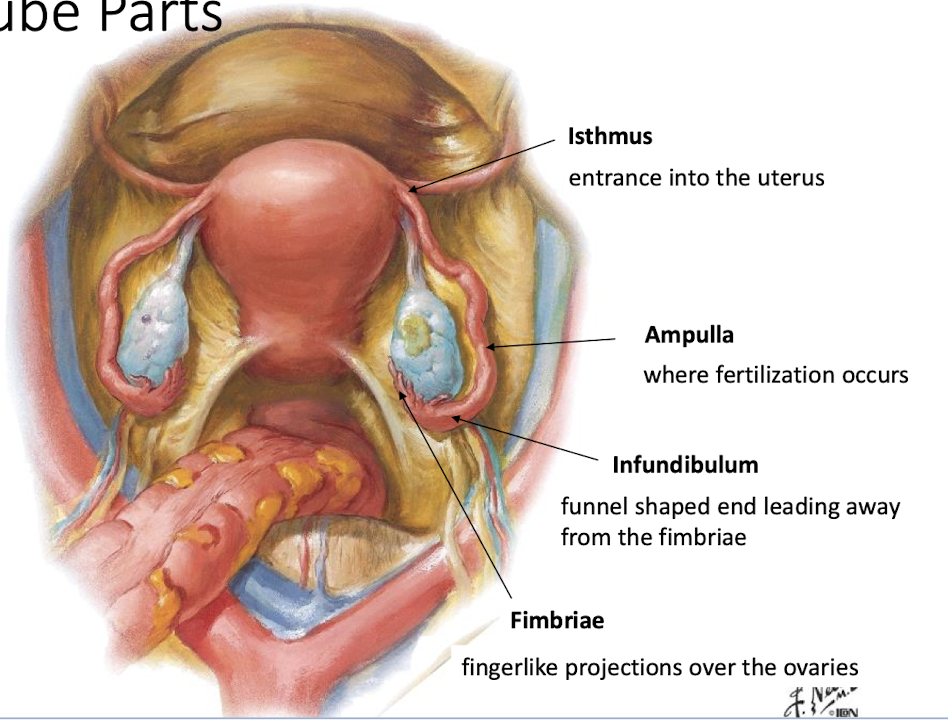
What are the four parts of the uterine tubes?
Isthmus - entrance to the uterus
Ampulla - where fertilization occurs
Infundibulum - funnel shaped end leading away from the fimbriae
Fimbriae - finger like projections over the ovaries
______ conduct oocytes to the uterine cavity
They are invested by which part of the broad ligament?
Uterine tubs
Mesosalpinx
What is the Pelvic part of the GI that is continuous with the sigmoid colon?
Rectum
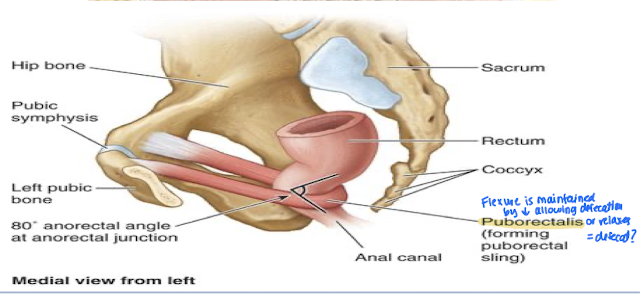
Which pelvic muscle is a “sling” around the anal canal and dictates defication and relaxation?
Puborectalis
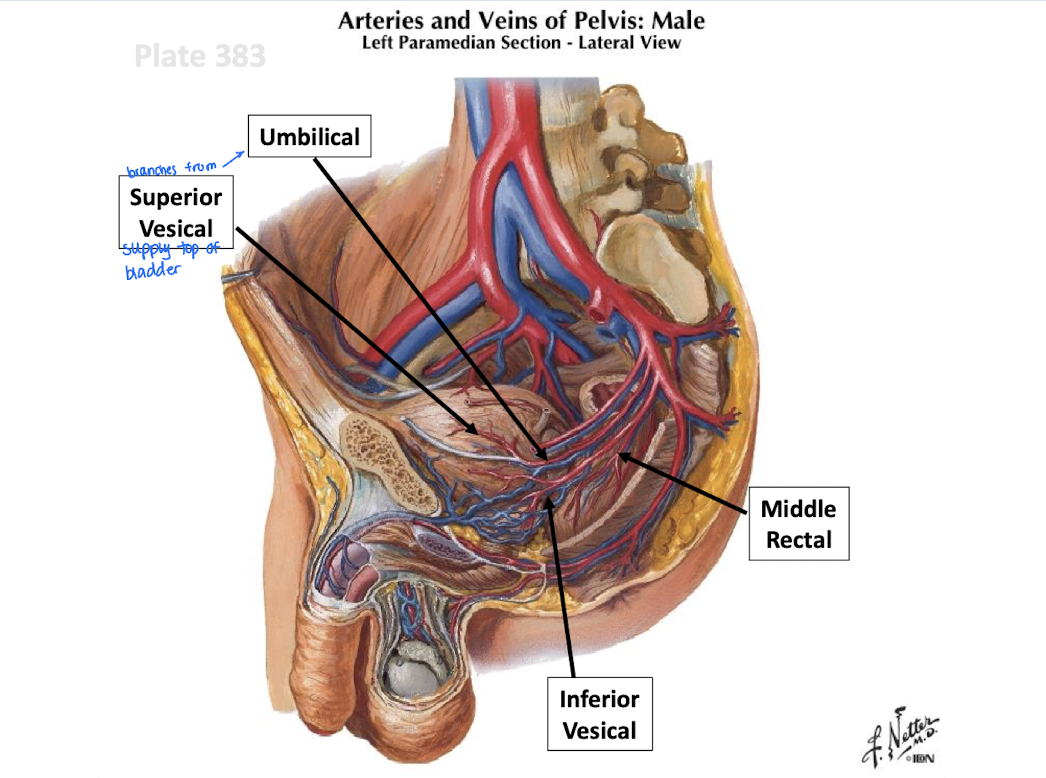
What artery primarily supplies the pelvis and perineum?
Internal iliac artery.
What does the anterior division (of the pelvis) of the internal iliac artery supply?
Supplies most pelvic viscera, perineal structures (via pudendal), and some gluteal muscles (via inferior gluteal)
What does the posterior division of the internal iliac artery (of the pelvis) supply?
Supplies posterior abdominal wall, lower back, and gluteal region.
all via superior gluteal
From the internal iliac and its branches (anterior and posterior division), where does the blood drain into that is surrounding the organs?
Where does it go to next?
Venous plexus (network around the organs)
Internal iliac vein OR portal system
What are the branches of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery?
Superior vesical (umbilical)
obturator
inferior vesical
uterine and vaginal (female)
middle rectal
internal pudendal
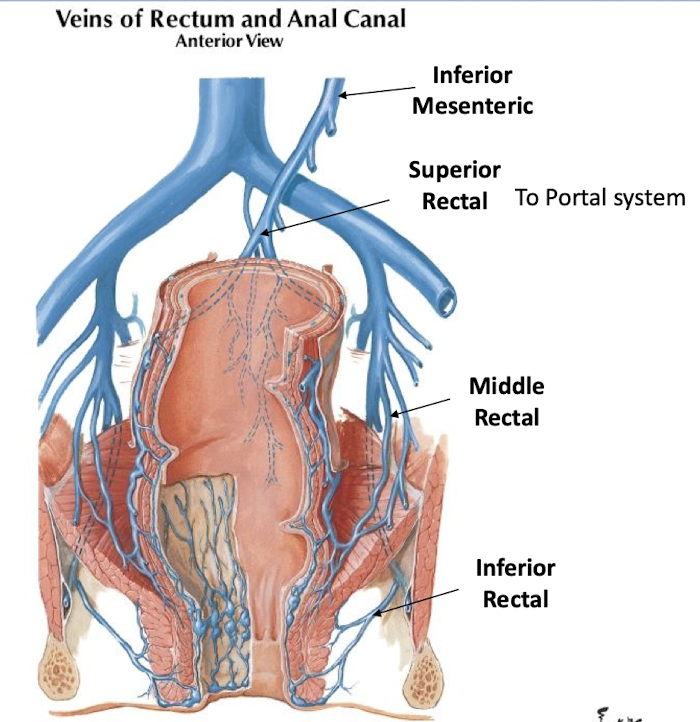
What are the branches of the posterior division of the internal iliac artery?
Iliolumbar, lateral sacral, superior gluteal, and inferior gluteal
_______ is the site for hemorrhoids - due to portal/system shunts
rectal veins
Where does the superior rectal drain into?
What about the middle and inferior rectal?
portal system
systemic venous vessels (internal iliac)
Where do the pelvic lymphatics receive drainage from?
Where do they drain into?
Receive from inguinal nodes
Drain into thoracic duct
What are the groups of lymphatic nodes in the pelvis?
Internal iliac nodes, common iliac nodes, lumbar nodes, external iliac nodes, and superficial inguinal nodes.
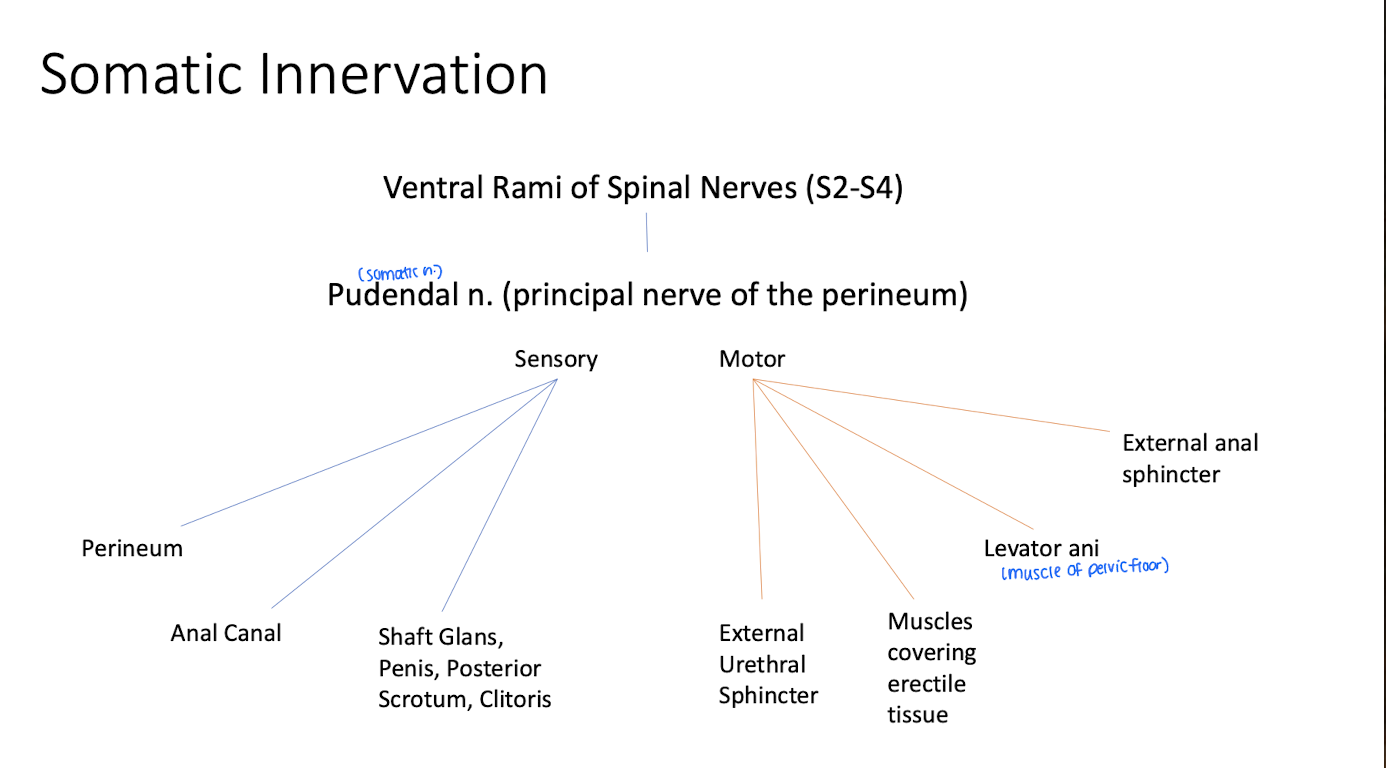
What is the difference between the somatic and autonomic nerves in the pelvis?
Somatic is supplied by pudendal nerves and innervate superficial areas
Autonomic carry sensations for reflex (urination, defecate)
Where do the branches of the somatic nerves innervate to?
What regions of the body do the somatic nerves of the sacrum innervate?
Branches from somatic nerves (lumbar and sacral plexus (L4-S4), and coccygeal plexus (S4-5).
They innervate the lower limb, perineum, and gluteal region
Important branch of the sacral plexus and is the primary nerve to the perineum.
Pudendal nerve
What is the role of the pudendal nerve on the body?
provides motor innervatoin to external anal sphincters and levator ani
Cutaneous innervation to scrotum, vulva, and perianal skin
sensory innervation to glans penis and clitoris
What are the types of autonomic innervation in the pelvis?
Sympathetic - provide sympathetic fibers for the pelvis/lower limb via sacral plexus
parasympathetic - nerves originate in the sacral cord and join with the hypogastric nerves to form the inferior hypogastric plexus
Which nerve of the anterior division supplies skin and muscles of the perineum?
Pudendal nerve
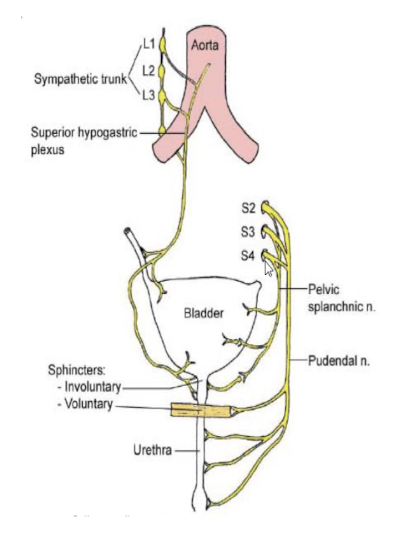
What are the Pelvic splanchnic nerves?
Originate in sacral cord (S2-4) and join with the hypogastric nerves forming the inferior hypogastric plexus.
PNS innervation to descending, sigmoid colon + pelvis (hindgut)
Which nerve plexus regulates erection, urination, and defection?
Inferior hypogratric plexus (part of PNS)
What ganglia provides sympathetic input to the bladder?
Sacral ganglia.
Sensation from the pelvis are carried by _____ to different regions of the cord depending on the relation to the peritoneum
afferent
Explain the pain sensation from the pelvis
sensations above the pain line follow sympathetic nerves. They terminate T10-T12 and refer to anterior thigh up to suprapubic region
Sensations below the pain line pass through the pelvic plexi (PNS fibers) and terminate at S2-S4. Refer to buttocks and posterior thigh
Sensations from the skin are carried by pudendal n
What is the perineum?
Shallow space below the pelvic diaphragm; diamond-shaped.
subdivided into the anal triangle and urogenital triangle
Levator ani is the muscle covering the triangles
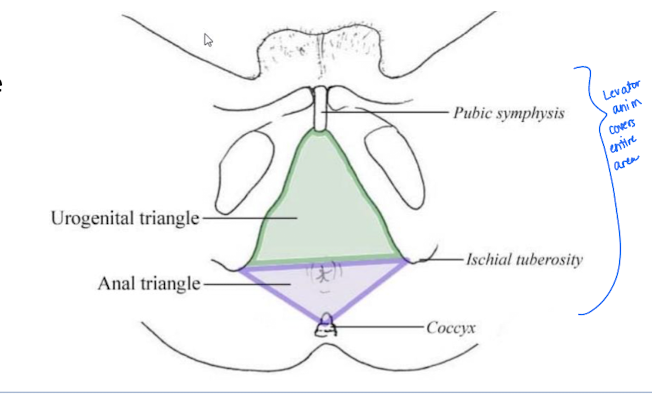
What are the boundaries of the perineum?
Pubic symphysis, ischial tuberosities, and coccyx.
What are the contents of the anal triangle?
Levator ani muscle
ischioanal fat pad
perineal body
pudendal canal (space the pudendal n goes through)
anal canal and anus
which triangle subdivision of the perineum surrounds the anus?
anal triangle
Convergence of muscles including posterior margin of the UG diaphragm, transverse perineal muscles, pelvic diaphragm, and external anal sphincter.
Perineal body
What is the role of the perineal body?
supports the abd viscera
Applied clinical: tearing during childbirth can lead to urinary incontinence and prolapse of the pelvic viscera here
perineal body
What is the pudendal nerve?
Main nerve of the perineum, formed from 3 branches from S2-4.
What muscles do the pudendal nerve pass between?
piriformis and coccygeus to enter the obturator canal with internal pudendal vesseles
Describe the Pudendal nerve branching and course
In the Pudendal canal, the pudendal nerve branches into the inferior rectal nerve and artery - supplies the external sphincter and perianal skin
As it continues through the canal it bifurcates into the perineal nerve and the dorsal nerve of the penis/clitoris
perineal nerve supplies scrotum and labia
DNP/C supplies glans penis with the shaft and the clitoris
What nerve supplies the scrotum and labia?
The perineal nerve
Which nerve supplies glans penis with the shaft and the clitoris?
The dorsal nerve of the penis/clitoris
What is the Anal Canal?
Terminal part of GI, extends from pelvic diaphragm to anus.
Consists of the internal and external anal sphincters
What artery supplies the internal sphincter
Sympathetic -hypogastric plexus (and superior rectal a) - promote contraction
PNS- pelvic splanchnic - inhibits contraction
What nerve supplies the external sphincter
Pudendal-inferior rectal nerve
Describe sensation of the anus
the pectinate line separates the sensitive and insensitive areas; above the line is visceral sensation, while below is somatic sensation.
insensitive to pain is elicited by stretching
sensitive areas detect pain, touch, and temp
What is the Innervation for the anus below the pectinate line?
Above?
Pudendal nerve
Inferior hypogastric plexus
Applied Clincal: explain hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are painless because they are above the pectinate line
external hemorrhoids are below the pectinate line and are very sensitive to pain and usually require treatment
What is the Urogenital Triangle?
Anterior portion of the perineum.
function: attachment site for genitalia in both genders
Pierced by the urethra in both genders and the vagina in females, it provides a stable base for attachment of external genitalia and associated muscles
Perineal membrane
What are the two spaces that the Perineal membrane divides the UT into?
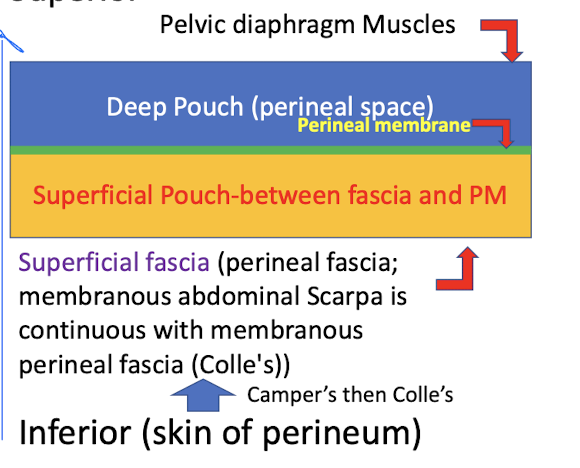
Deep perineal space or pouch (superior) and superficial perineal space or pouch (inferior).
Give the layers of the fascia layers of the perineum from deep to superficial
Pelvic diaphragm muscles
Deep pouch (perineal space)
Perineal membrane
superficial pouch
superficial faccia
Skin of perineum