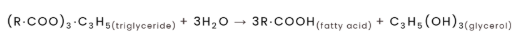CPL 1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Chemical Technology
It takes into account principles of ChE and applies at industrial
scale to produce chemicals
• Based on nature of chemicals produced, it can be grouped as:
• Organic Chemical Technology
• Inorganic Chemical Technology
Edible oils
Compounds based on long chain fatty acids and esters such as
glycerides
• Derivatives such as glycerin, long chain fatty alcohols, sulfates and
sulfonates
• Products of these compounds are used for food, sanitation,
polymers and in paint industry
Soap
Compounds of type R∙COO∙M where R∙COO∙ is fatty acid radical
representing oleic, stearic, palmitic, lauric and myristic
Detergents
These are synthetic organic chemicals; however, discussed under
natural products industries because of competitive position with soaps
• Promote better surface tension, lowering than soaps
• Types: anionic, cationic, non-ionic and detergent builders
Carbohydrates
Naturally occurring organics having combinations of C, H, and O,
with H and O ratio same as H2O
• Sucrose, dextrose, starch and cellulose are common products
Fermentation
• In this industry, specific microorganism acts on substrate to
produce desired chemical compound
India
First country to use bamboo as basic raw material for making paper
is
True rubber
• It must elongate at least 200% and return to its original dimensions
rapidly and forcibly
Petroleum
• It is formed millions of years ago from organic matter of marine deposits
in anaerobic conditions, i.e., in the absence of oxygen
• Selective bacterial attack destroyed proteins and carbohydrates of
organic matters and leaving fats to accumulate as oil reserves; thus,
known as fossil fuel
Petrochemicals
These are chemical compounds or elements recovered or derived
partially or entirely from petroleum or natural gas HCS
Polymers
are composed of molecules of MW from 103-107
are made up of repeated basic units produced from
monomers
Alkylation
Addition of alkyl radical (-CH3
) with side chain final product
Carbonylation
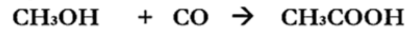
Condensation
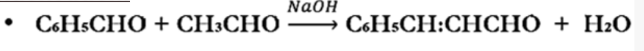
Cracking / Pyrolysis
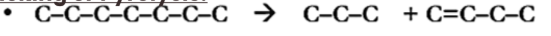
Cyanation
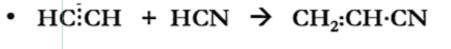
Dehydration
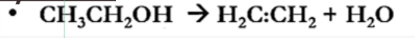
Dehydrogenation
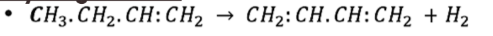
Hydration
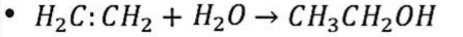
Hydrogenation
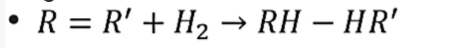
Hydrolysis
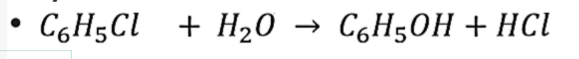
Sulfonation
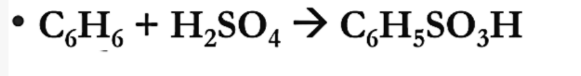
Oxidation

Thionation
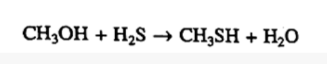
Isomerization
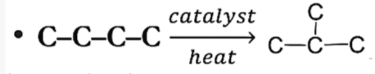
Halogenation
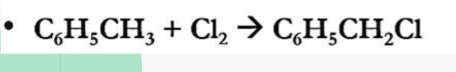
Esterification
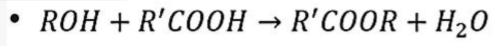
saponification
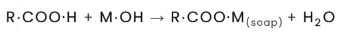
fat splitting reaction