Direct Cell-Cell Signalling and Gap Junctions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
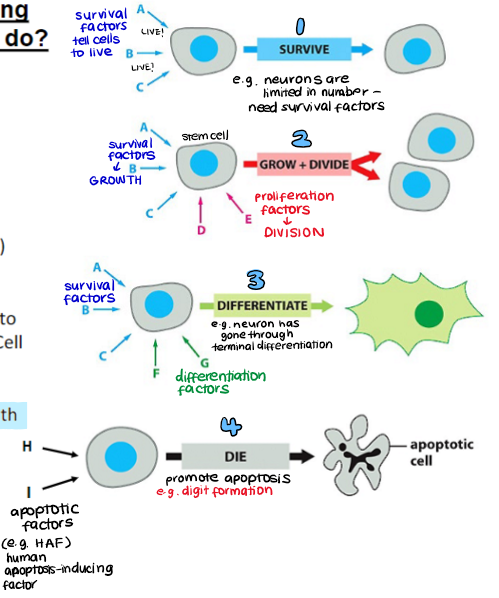
What can signalling influence cells to do?
cell survival and cell division
cell differentiation
morphogenesis
apoptosis
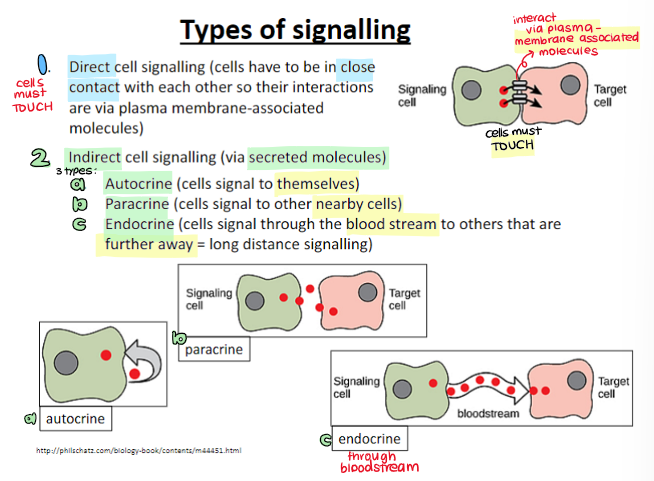
two main types of signalling
direct cell signalling
indirect cell signalling
autocrine
paracrine
ion channel coupled receptors
enzyme coupled receptors
G-protein coupled receptors
endocrine
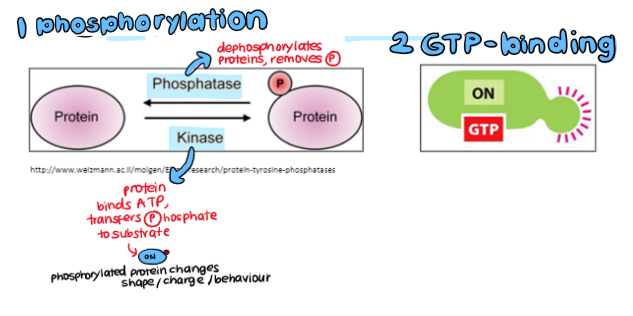
molecular switches
intracellular signalling proteins
switch on (ACTIVE) and off (INACTIVE)
length of time they are switched on determines how long cell is responding
for every activation step there is an inactivation step
types of molecular switches
proteins that influence phosphorylation status
kinase → PHOSPHORYLATES
phosphatase → DEPHOSPHORYLATES
GTP-binding proteins
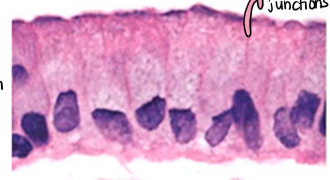
direct cell-cell signalling
signalling by plasma-membrane attached proteins
cells must be touching
bidirectional signalling via gap junctions
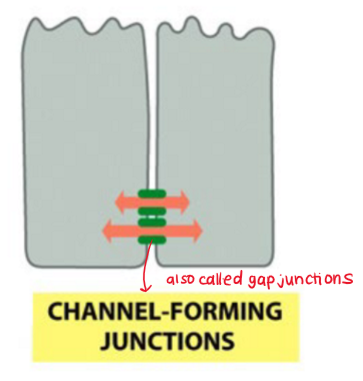
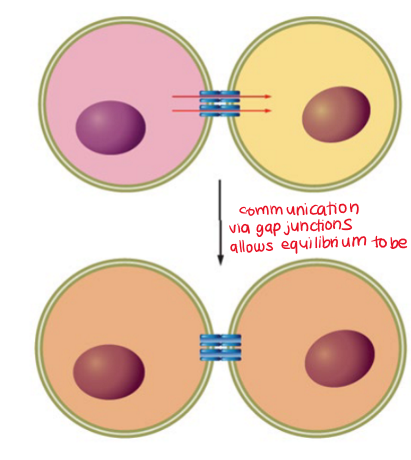
gap junctions equilibrium
communication via gap junctions allows equilibrium to be reached
electrochemical gradients direct the transfer of small molecules through gap junctions until an equilibrium is reached
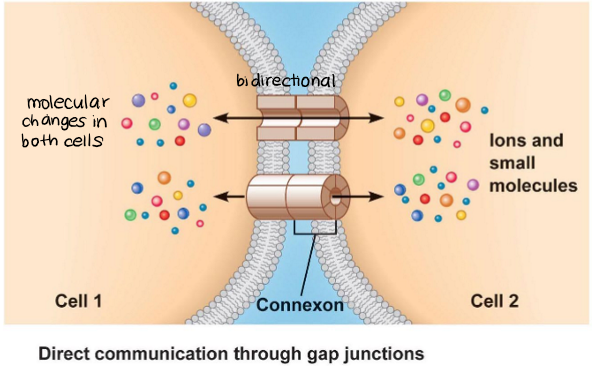
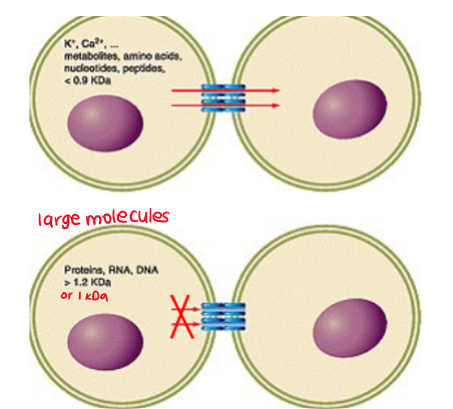
gap junctions size restriction- what molecules can pass through?
only small molecules can pass through (<1kDa)
amino acids
nucleotides
ions
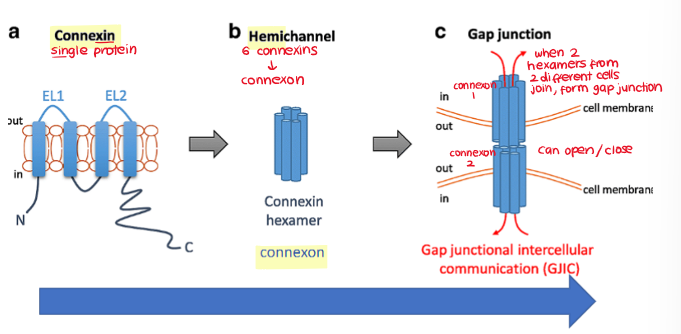
structure of gap junctions
4 transmembrane proteins → CONNEXIN
6 connexins → CONNEXON (hemi junction)
2 connexons → GAP JUNCTION
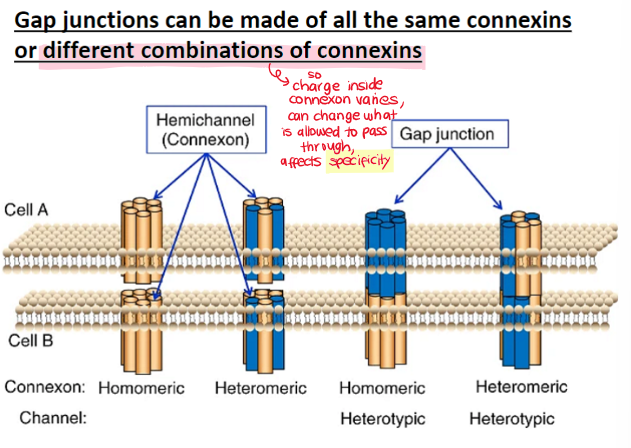
selectivity of gap junctions
21 different connexin genes identified
gap junctions made of same connexins or different combinations of connexins
selectivity due to differences between amino acids that face the internal channel
can be selective for different charged molecules
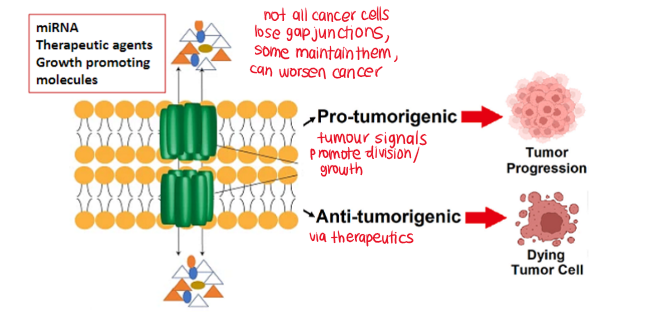
What happens to gap junctions in most cancer cells?
gap junctions are lost
no longer undergo coordinated, regulated growth

two possible effects of gap junction communication on tumour spread and pathology
progression
suppression
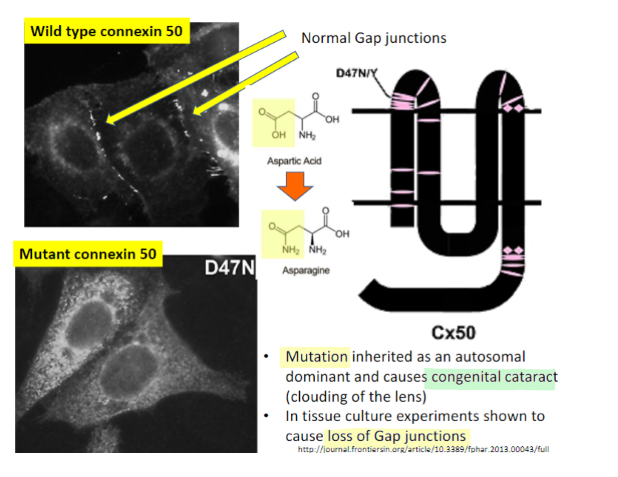
example of pathology caused by loss of specific gap junctions
congenital cataracts
lens relies on gap junctions for delivery of nutrients
mutations cause loss of function of connexin-46 and connexin-50