Exercise Science General Terminology
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Circular Muscles
Muscles form a circle, arranged to from concentric rings, contract to close
Convergent Muscles
Broad Origin, converge towards single tendon
Parallel Muscles
Strap-like, flat bands, spindle-shaped, parallel fascicles to muscle axis
Fusiform Muscles
Muscles who’s Belly Widens
Pennate Muscles
Fibres start and attach at certain angle to central tendon. Short, high force, small ROM
Motional Pennate Muscles
Unipennate - insert into 1 side of tendon
Bipennate - insert into opposite sides of tendon
Multipennate - Central tendon branches into multiple muscles (eg, deltoid, pec)
Isotonic
Maintain constant tension throughout eccentric and concentric movements
Isometric
Contracts a force with no further movement or stretching of the muscle
Recruitment
Nervous system under pressure enters process of recruitment to use as many muscle fibres as possible to generate strength
Origin of a muscle
Site where the muscle is attached to stable bone which it pulls against
Insertion
Occurs where muscle attaches to a bone that is pulled by the action of the muscle
Belly of the muscle
Fleshy part of the muscle when it contracts
Agonist
Prime Mover
Antagonist
Opposing mover
Stabiliser Muscles
Extra muscles to control a movement
Fixator muscles
Stabiliser muscles that reduce unwanted movement within an action
Voluntary Muscles
Skeletal Muscles
Involuntary Muscles
Smooth Muscle, Cardiac Muscle
Epimysium
Surrounding muscle membrane
Perimysium
Around fascicles (filler tissue)
Fascicles
Muscle tissues that run side by side (look like spaghetti)
Slow twitch
Long distance, continual, aerobic activity. Cannot produce quick bursts of power easily
Fast twitch
High intensity, anaerobic activity, short bursts of power, unable to continue long bursts of power.
Flexion
Decreasing angle at point
Extension
Increasing angle at point
Abduction
Movement away from an imaginary midline
Adduction
Movement towards the body
Tendons
Connect muscles to bones
Ligaments
Tough, elastic fibres that link bone material to bones themselves
Cartillage
Prevents the ends of bones from rubbing together. Synovial fluid helps to lubricate joint
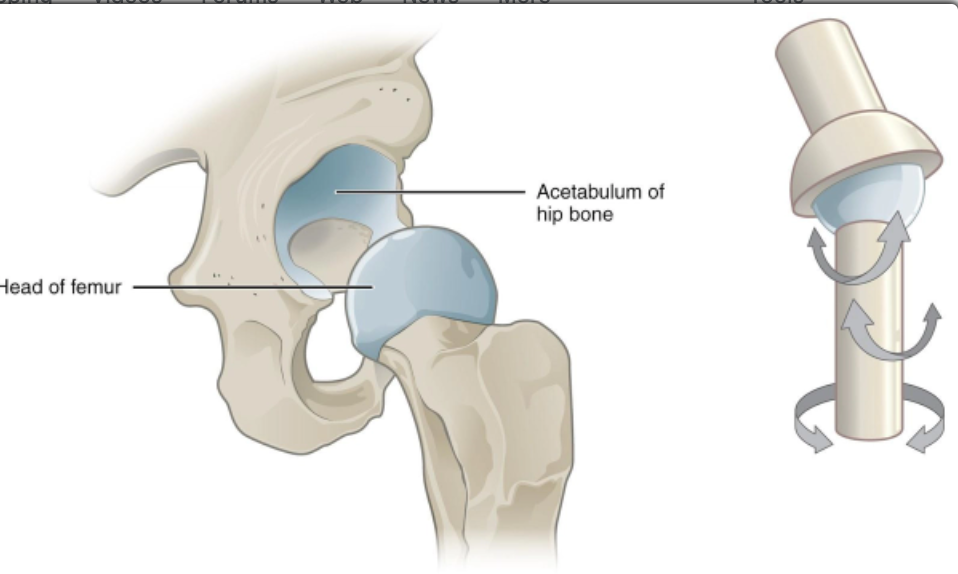
Ball-socket joint
Horizontal Flexion
Moving arms forward in horizontal plane
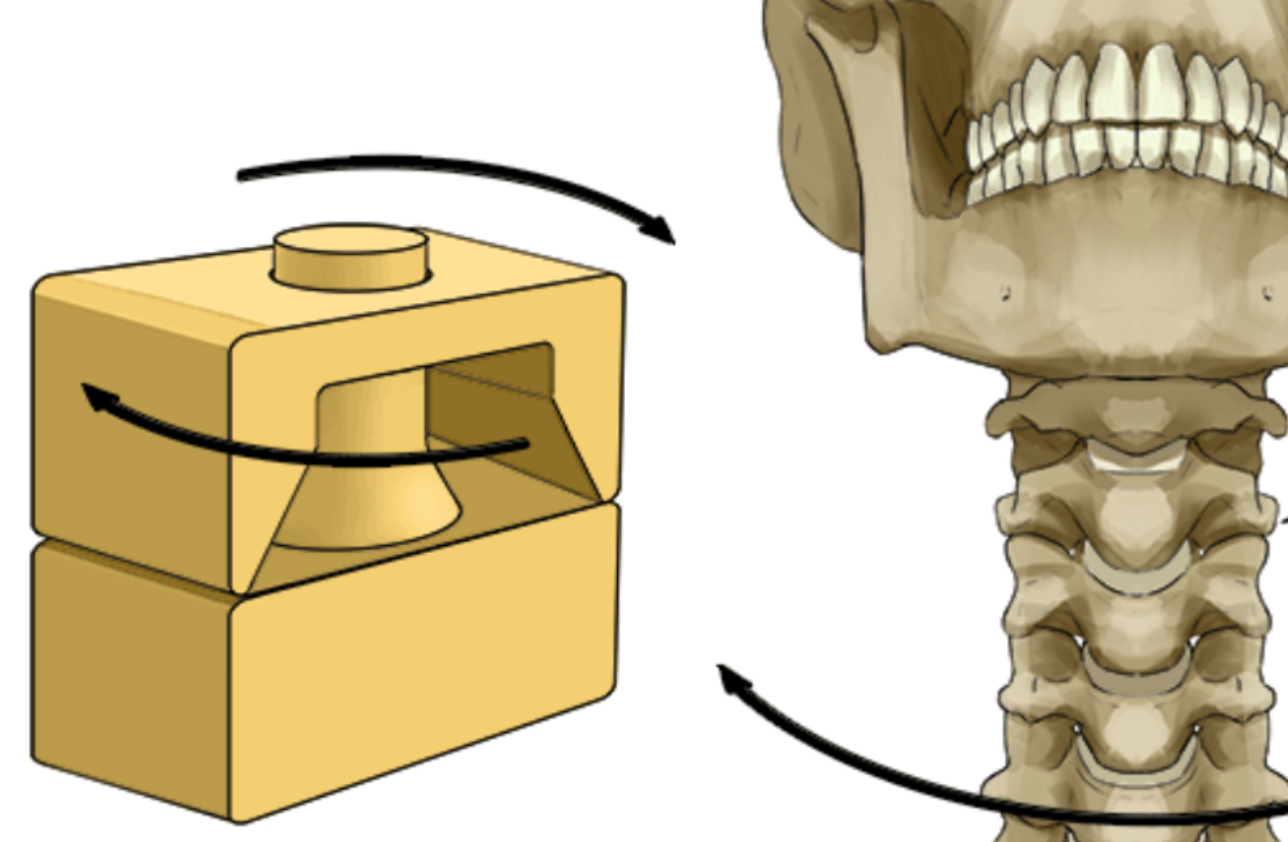
Pivot joint
Horizontal extension
Returning arm to abducted position
Rotation
Moving a limb in a circular motion in either direction
Circumduction
Combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
Hyper flexion
The flexion of a limb beyond its natural limit (eg large jumping movements)
Hyper extension
The excessive joint movement in which the angle is straightened beyond its normal range.
Pronation
Movement of palm facing downwards
Supination
Movement of palm facing upwards
Plantar flexion
Extension of ankle, pointing of foot and toes
Dorsiflexion
Flexion of the foot in an upward direction
Elevation
Movement in superior direction (shoulder shrug- up)
Depression
Movement in anterior direction (shoulder shrug- down)
Protraction
Movement forward in anterior direction
Retraction
Movement backwards in posterior direction
Inversion
Toe- up
Eversion
Ankle- leaned inwards

Saddle joint- up, down, left, right
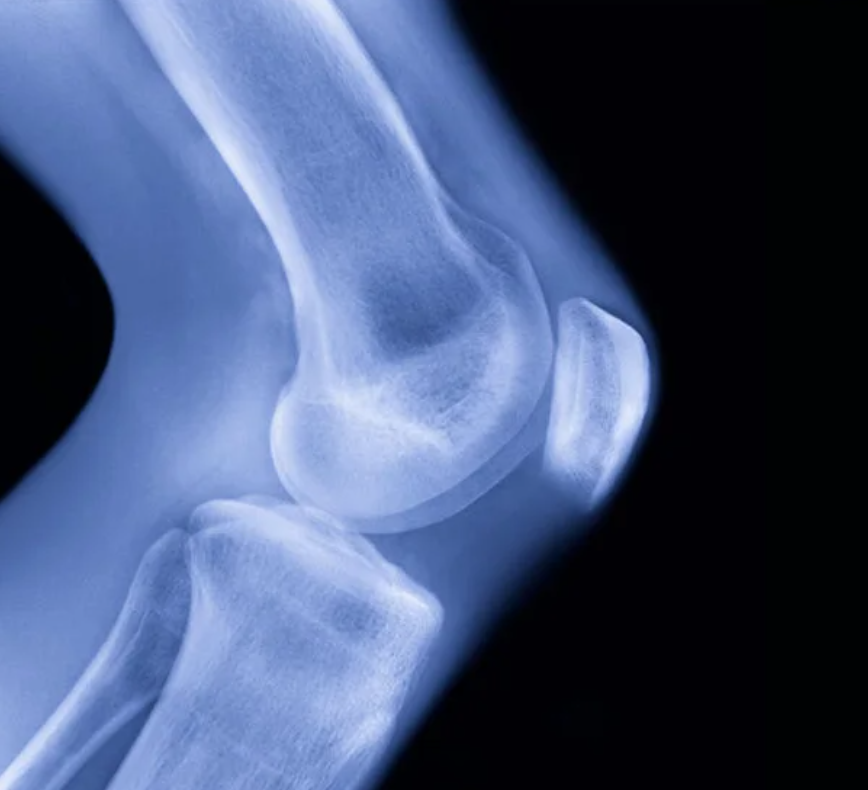
Hinge joint
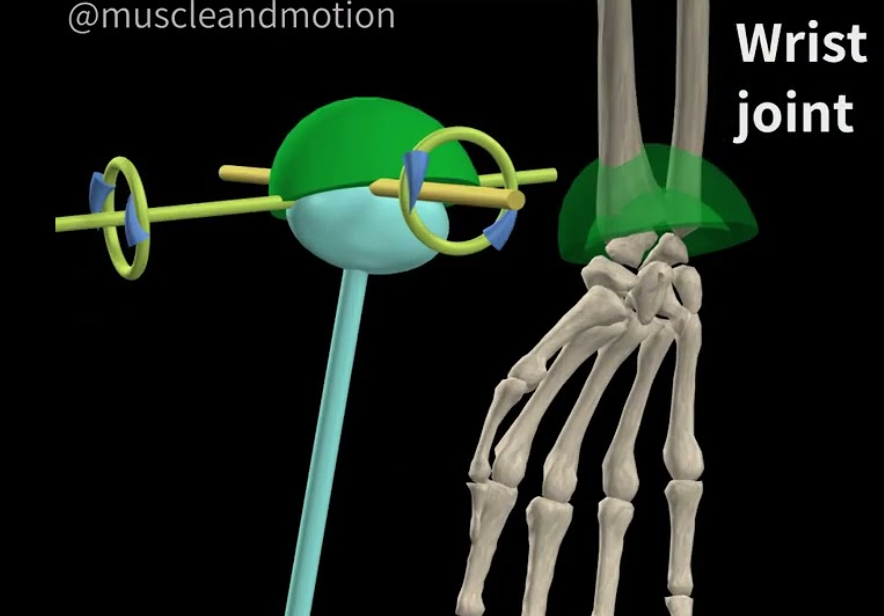
Condyloid joint
% of Synovial joints in the body
90%
Articular system
The name for the system of joints around which our bones move and articulate
Ossification
The process in which cartilage becomes bone
Cartilage components
Chondroblasts, Chondrocytes
Chondroblasts
Active growing cell in cartillage
Chondrocytes
Mature cell-form of cartilage
Intramembranous ossification
Bone develops directly from mesenchyme
Mesenchyme
Connective tissue found in the embryo
Endochondral Ossification
Cartilage serves as a precursor to bone
Epiphyseal plates
Growth plates located on the upper-head of the bone
Periosteum
Outer membrane of the bone
Diaphyseal plates
Osteoblasts underneath the periosteum deposit layers of bone
Epiphysis, Diaphysis
Top bone, middle bone
Compact bone
Located in the diaphysis of a long bone, hard, strong, yellow bone marrow nearby
Spongey bone
Pockets of air, contains red bone marrow, shock absorber (miniscus)
Sesamoid bones
Bones that form within tendons and are located around joints
Irregular bones
Bones that are shaped or made to perform one specific function (eg, patella, vertabrae)
Short bones
Light, strong bones that are composed of spongey bone surrounded by a thin layer of compact bone
Flat bones
Bones that serve as areas for muscle attachment.
Long bones
(fairly self-explanatory), generates a lever for mechanical force to be exerted.
Axial skeleton
Skull, vertebral column, ribcage (vertical).
Appendicular Skeleton
Providing support for apendages, eg limb bones and girdles.
Functions of skeleton and bones:
Movement
Structure
Protection
Size
Shape
Mineral resource deposit