AQA GCSE Physics - PARTICLE MODEL OF MATTER (HT)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
The equation that relates Density, ρ, Mass, m, and Volume, V, is...
Density = Mass/Volume (ρ=m/V)
Unit of Mass, m
kilogram, kg
Unit of Volume, V
Metres cubed, m^3
Unit of Density, ρ
kilograms per metre cubed, kg/m^3
In a solid, particles are...
closely packed in a regular arrangement. The particles vibrate about a fixed position.
In a liquid, particles are...
closely packed in a irregular arrangement. The particles can move through the liquid.
In a gas, particles are
Far apart, moving fast and randomly.
Melting involves heating a...
Solid to a liquid state.
Boiling and evaporating involves heating a...
Liquid to a gas state.
Sublimating involves heating a...
Solid to a gas state.
Condensing involves cooling a...
Gas to a liquid state.
Freezing involves cooling a...
Liquid to a solid state.
When a substance changes state, it's mass and the number of particles...
Is conserved.
The total energy stored by the particles in a system is called the...
Internal Energy.
The internal energy of a system is the sum of the particles'...
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy.
Heating a system changes the energy stored in it, by increasing the energy of...
The particles within.
Heating a system either...
Raises the temperature or changes the state
The amount by which the temperature of a system increases depends on...
The mass, the type of material, and the amount of energy added to the system.
The equation that relates Change in Thermal Energy, ΔE, Mass, m, Specific Heat Capacity, c, and Change in Temperature, ΔT, is...
Change in Thermal Energy = Mass x Specific Heat Capacity x Change in Temperature (ΔE=mcΔT)
Units of Change in Temperature, ΔT
Degrees Celsius, °C
Definition of Specific Heat Capacity, c
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of substance by 1°C
The energy needed for a substance to change state is called...
Specific Latent heat
When a change of state occurs, the Heat energy supplied changes the internal energy of the system. The temperature...
Remains constant.
Definition of Specific Latent Heat, L
The amount of energy required to change the state of 1kg of a substance with no change in temperature.
The equation that relates Specific Latent Heat, L, Mass, m, and Energy for a Change of State, E, is...
Energy for a Change of State = Mass x Specific Latent Heat (E=mL)
Units of Specific Latent Heat, L
Joules per kilogram, J/kg
Unit of Energy, E
Joules, J
Specific Latent Heat of Fusion is used when a change of state occurs from...
Solid ⇌ liquid
Specific Latent Heat of Vaporisation is used when a change of state occurs from...
Liquid ⇌ vapour (gas)
The difference between Specific Latent Heat (SLH) and Specific Heat Capacity (SHC) is...
SHC involves a change in temperature, and the state of a substance remaining the same. SLH involves temperature remaining the same, but a change in the state of a substance.
The molecules of a gas are in constant...
Random motion
Increasing the temperature of the gas increases the...
Kinetic Energy of the Molecules
Gas molecules with increased kinetic energy collide with the walls of their container...
Harder and more often.
Changing the temperature of a gas, HELD AT CONSTANT VOLUME, changes the...
Pressure of the gas.
Increasing the pressure of a gas increases the...
Volume of a gas.
Pressure of a gas is determined by the ______ ______ at right angles to the walls of the container.
Net Force
How are Pressure, p, and Volume, V, related for a fixed mass of gas held at CONSTANT TEMPERATURE.
Pressure x Volume = constant (pV=constant)
Unit of Pressure, p
Pascal, Pa
The equation used to find initial or final Pressure or Volume of a gas, HELD AT CONSTANT TEMPERATURE, after a change to the system is...
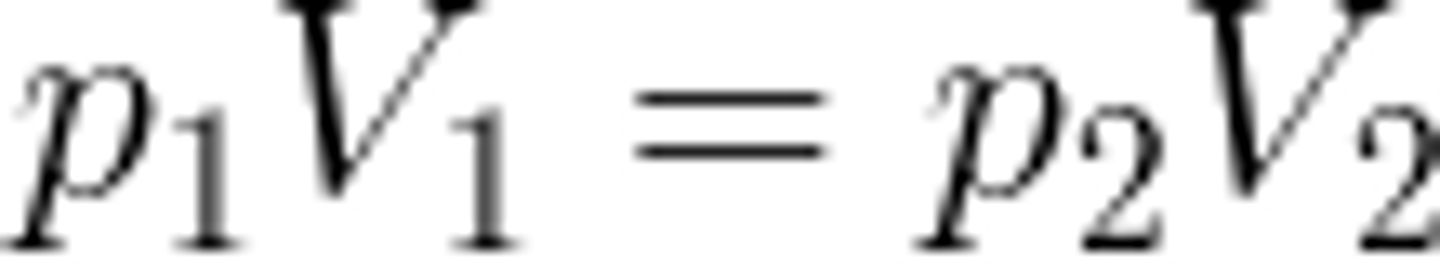
Work is the transfer of energy by a...
Force
Doing work on a gas increases the internal energy of the gas, and can cause an increase in the gas'...
Temperature.
Applying a FORCE on a bicycle pump, for example, compresses the enclosed gas, doing WORK on it. This leads to an increase in the TEMPERATURE of the gas, because the...
Internal energy increases.
Unit of Specific Latent Heat, L
Joules per kilogram, J/kg
Unit of Specific Heat Capacity, c
Joules per kilogram per degree Celsius, J/kg°C