animal husbandry
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
cat eats 300g fish per day with 20% DM and 20MJ/kgDM gross energy
excretes 100g faeces per day with 10% DM and 12 MJ/kgDM gross energy
how much DM does cat eat each day
2. how much gross energy does cat eat each day
what is apparent digestibility of dry matter and of gross energy
60
0.06kg x 20 = 1.2
10/60 = 16.66% lost so 100-16.66 = 83.8% digested
eats 1.2MJ, excretes 0.12MJ - 0.12/1.2 = 10% lost

star
stripe
blaze
snip
white face

ermine marks - black spots on white coronet
what age does deciduos incisors erupt
01s - 6 days
02s - 6 weeks
03s - 6 months
age at which permanent incisors erupt
01s - 2.5 yrs
02s - 3.5yrs
03s - 4.5yrs
at what age do the cups in teeth leave
6,7,8 yrs
age at which cheek teeth erupt
06s - 2.5yrs
07s - 3yrs
08s - 4yrs
09s - 1yr
10s - 2yrs
11s - 3.5yrs
straw bedding
comfortable
relatively absorbent
easy disposable
cheap
cons = edible - could impact colic, potentially allergenic = dust and fungal spores
wood shavings bedding
comfortable
very absorbent
less allergenic dust
cons = expensive, disposable difficult, accidental ingestion
common bedding for horses
shredded paper
sand
hemp/flax
wood pellets
rubber matting
horse bedding systems
mucked out once/ twice a day
deep litter system - empty at least once or twice over winter - only remove faeces daily and add fresh bedding
horse vaccinations
equine influenza
tetnus
equine herpes virus
equine viral arteritis
water intake of horse
50/ml/kgBW/day
approx 25L/day
water intake of lacating mares
70-100ml fluid/kgBW
averga DM intake of horse
2-2.5% BW/day
min 1% BW/day
constituents of food for horse
forage
concentrates
protein
macrominerals
microminerals
supplements
energy required for light work horse
M + 25%
energy required for moderate work
M + 50%
energy required for intensive work
M + 100%
energy for breeding
Early gestattion = M only
Late gestattion = step-wise increase to M + 20% at term
Ealy lactation = M x 2
Late lactation = M + 25%
Stallion in breeding season = M + 25%
causative factors for negative energy balance
Competition for Nutrients – intestinal parasites
Lactation
Pregnancy
Workload
Owner factors – ignorance, neglect, cruelty, poverty
Herd hierarchy – bullying, competition for food
Access to adequate pasture – overstocking, overgrazing paddocks, soiled/weed infested
Decreased ability to- swallow food, absorb food, utilise food
e.g. Cushing's, GI tract condition (hepatic disease), dental disorders(quidding is indicator), energy losses
Environmental conditions
Growth
typical body composition of a horse
water = 60%
protein = 20%
fat = 12%
minerals = 7%
carbohydrate and stored carbohydrate = 1% and <1% stored
most variable component of body composition of horse
fat
minimium amount of dietary fibre for horse
1% of body mass as daily DMI
2 forms of starvation
Simple
Small reduction in intake
Adaptive response = decreased BMR, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, lipolysis increases
Most horses can survive 2-3 days of acute starvation
Fat ponies and donkeys, pregnant mare = susceptible to hyperlipaemia
Rare
Stressed
Die to systemic illness or injury
Increased BMR
Early glycogneolysis rapidly depletes glycogen stores
Organ dysfunction, immuno-compromise, poor tissue repair
Difficult to halt weight loss
re-feeding a thing horse
start low and go slow
25-75% of maintanence energy for 1st 2-5days then increase to 125%maintanence over next few days
avoid high carbohydrate foods
causative factors for excess body condition
overfeeding
lack of exercise
yr round access to good quality food in excesss
rugs, stables and winter feed
major consequences of equine obesity
osteoarthirits
respiratory dysfunction
equine metabolic syndrome
laminitis
safe rate of weightloss for horses
0.5-1% BW/ week
what to feed to encourage weightloss in horses
High level of fibre
Feed more bulk – 1.5-2% Bwt DMI with lower NSC, soaked hay to reduce sugar
Caloric restriction for medium term plan not long term
Long term strategies should be favourable to horses well being and welfare
Control food intake – grass muzzles( can cause rubs on face or damage to incisors or very small pasture/ bare pasture, easy if stabled
Feed 1.5% of body weight as daily DMI- achieves gradual decline in body weight
Soak hay for at least 6hrs
Feed Little and often
Monitor the weight loss – weight tape, BCS after 2-3 months of weight loss
Make sure owner is on board with decision making
kennel club dogs
gun dogs
hounds
toy
terriers
utility
pastoral
working
core dog vaccinations
canine distemper virus
canine parovirus
canine adenovirus/ infectios canine hepatitis
leptospirosis
vaccination schedule for dog and cats
primary course - 2 vaccinations - 2-4weeks apart, from 6-10weeks of age
secondary vaccinations not before 12 weeks
black and tan breeds - 3rd parovirus vaccination around 16 weeks
annual boosters
non-core vaccination for dog and cat
kennel cough
canine herpevirus
leishmania
rabies virus
band breeds in UK
pit bull terrier
japenes tosa
fila brasileiro
xl bully
dogo argentino
how can owners keep there banned breed dogs
if on index of exempt dogs
Provided with certificate of exemption and dog must be – neutered and microchipped, muzzled and kept on lead in public, kept safe place so can't escape, unsured
Mustn't be sold, given away or abandoned
Index of exempt dogs must be informed if owner changes address or dog dies
Section 3
Against law to let dog be dangerously out of control anywhere – in public, private place or owners home
Applies to all dogs
Out of control - dangerously out of control if injures someone, make someone worried it might injure them, injures an assistance dog
Court could decide that your dog is dangerously out of control – injures someone's animal, owner of animal thinks they could be injured if someone tries to stop your dog attacking their animal

cat wrap
cat muzzle - can upset some cats
cat restraint bag - can be stressful getting them into bag

crush cage
sexing cats
males - toms
penile opening circular
testes if not castrated
gretaer anogenital distance than in female
females - queens
shorter anogenital distance
vulva appears as vertical slit
cat gestation
20-25% increase BW after 28 days
litter weight = 13.5%
feed increase energy after 4 weeks
130-160% of MER
weaning puppies
start at 3-4 weeks of age
fully wean at 6-8 weeks
offer food for voluntary intake
when do puppies reach half mature weight
6 months
when do puppies reach mature weight
12-24 months
what to feed pregnant queen
140-150% of MER throughout
what to feed lactating queen
2.5 x MER if greater than 2 kittens
when do kittens reach 75% of mature weight
6 months
what food do young kittens need - 12 weeks
3 x MER
feeding times for orphans
0-2 weeks = 10 feeds in 24hrs at 2-2.5hr intervals
2-4 weeks = 7 feeds in 24 hrs at 2.5-3.5hr intervals
4-5 weeks = 5 feeds in 24hrs at 3.5-5hr intervals
essential amino acids for dogs
Arginine, histidine, isoleucine, methionine, cystine, leucine, lysine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, threonine, tryptophan, valine
essential fatty acids for dogs
Linoleic acid
Alpha linolenic acid
Arachadonic acid
EPA/DHA
essential minerals for dogs
Ca, P, Mg, Na, K, Cl
Fe, Cu, Zn, Se, I
essential vitamins for dogs
A,D, E, K, B group
feline idiosyncrasies
Strict carnivores – vegan diets not recommended
Require taurine – can't synthesis from precursors
Need both linoleic and arachadonic acid in diet
Vitamin A from meat – can't convert β- carotene from veg
More B vitamins e.g. thiamine and niacin
proprietary food
Legislation/ guidelines
Complete and balanced
Quality assurance and safeguards
Free from toxins/ contamination
Easier
Cost
Risks if food plant contamination
B.A.R.F
More natural, enjoyable
Teeth cleaning
Health claims
Unbalanced
Bacterial contamination
Tooth damage
Foreign bodies
Cost
food options for dogs and cats
home prepared food
proprietary cooked
proprietary raw
home prepared raw
grain free
vegetarian/ vegan
components of responsible pet feeding
Make sure its safe
Make sure its complete and balanced
Make sure don’t feed too much
Measure food portions accurately with scales
Make sure its sustainable
how often should adult cat be fed
Solitary hunters, small prey species
Typically small meals 12-20/day
Feed small frequent meals
Avoid group feeding
how often should adult dog be fed
Cope with periods of fast-famine
Up to 17% BW in single setting
Optimal pattern not known
Most do 1-3 meals/day
purpose of beef cattle
young animals for slaughter
high carcass quality
maximium growth rates or maximium utilisation of cheap feed
traditional british breeds
small mature size = low maintanence costs
early maturing
hardy - climate and environment, feed = suited to forage system
good suckler cow
continental breeds
large mature size
late maturing
higher demands
more carcass
good terminal sires
average breeding herd size
28 cows
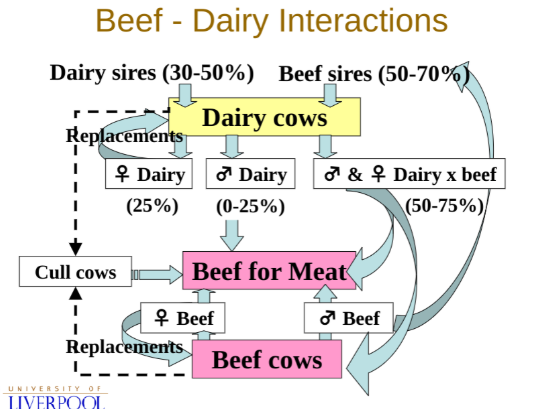
Some females from beef will be kept back for replacement the rest and males are reared for meat
Some female dairy cows are kept back for replacement
suckler herd
cow = extensive - low input low output
forage based
weightloss expected - sensible
BCS for calving
2.5 for mature cows
3 for 1st and 2nd calvers
spring calvers BCS
may gain 0.5-1 BCS over summer
1 unit BCS= 13% of BW
what makes a good suckler cow
Docile temperament giving easy management
Milky dams with good maternal qualities
Longevity
Fast growth and early sexual maturity
Excellent grass conversion ability
Hardiness and adaptability
essential components for profitable suckler herd
Low feed costs
Longevity
Tight calving pattern
1x calf every 365 days
Low calf mortality
Solid replacement policy
pro and cons of spring calving
Pro
Summer grass – good conception rates, good milk = good calf growth
Con
Supervision more difficult as calved outside
Winter feeding = maintenance – cow may lose body condition, weaned calf – compensatory growth later
pro and con of autumn calving
Pro
Cow in good condition
Easy supervision as calving inside
Weaned calves = higher price
Con
Winter feeding = higher – breeding in winter and nursing calf
weaning beef cows
Typically when 6-8 months old
Use weaning to control BCS – wean earlier if cow poor BCS or later if high BCS
Wean abruptly – gradual weaning leads to delayed stress response
Decrease stress if concentrates beforehand
Separate cows and calves by good distance
fattening stock - veal
Dairy-bred males
Milk throughout, plus hard feed and straw
1.2-1.4kg DLWG
Slaughter 6-7 months
Crates band – group housing>8 wo
Minimium dietary iron and fibre
fattening stock rose
Reared in approval system
Wean off milk at 6-12wo
Starchy feed and straw
slaughter at 8-12mo
selling calves
<7 days illegal
no resale within 28 days
transport calves
illegal <10 days
or <14 days if journey >8 hrs
navel must be healed
creep feed
Start min 6-12 weeks prior to weaning
Preserves cows BCS
Primes rumen for post-weaning diet
Avg 25kg heavier calves
14-16% CP
% weight-gain from dams milk
Month 1 of life = 100%
Month 3 of life = 66%
Month 6 of life = 33%
options after weaning
Intensive – barley/silage/bull beef, finish at 12-14 mo
Extensive – 18/24/30 - month beef
Sell as store cattle = not taken through to slaughter on farm where born but sold at 6-12mo
Flattening/ growing cattle= weaned, reared for meat
Finishing cattle = last few weeks prior to slaughter -> max. Weight gain, kept clean
barley/silage beef
Bulls> steer, heifers
Late maturing breeds
Housed
Target weight – 250kg
DLWG >1.2kg
Feed conversion 5:1
Diet options – silage and 3kg barley, ad-lib barley and straw = both protein supply
buller - steer problem
Pain, exhaustion, death
Bruising – remove ridden
Space = 4 m^2
Trough 10cm/hd
clinical problems - barley beef
Carbohydrate overload – bloat, rumen acidosis, liver abscessation
Hypervitaminosis A
Lameness
Pneumonia
common finishing weights
18 months = heifers 360-450kg, steers 530kg
22-24 mo = steer 560kg
feed conservation ratio and how to calculate it
how many kg feed required for 1kg weight-gain

critical aspects of housing
ventilation
cleanliness
space allowances
killing out percentage

factors affecting killing out percentage
Nutrition = high roughage diets = lower KO%
Gender = bull<steers = heavier skull and skin, heifers>steers = greater fat content
Age = older>young = greater fat content
Breed = traditional> continental > dairy x beef> dairy
queen excluder
prevents queen getting into honey supers to lay eggs so honey can be collected without destroying the hive
bee life cycle
Starts as an egg born by the queen placed at bottom of one of the wells, develops into larva, pupa and adult
21d cycle for workers and drones
16d cycle for queens
the queen bee
Egg-laying machine
Mates with drones at specific site sway from hive – stores sperm
Can lay up to 2000 eggs/day
Secretes pheromones
Can live up to 5 yrs but usually replaced after 1-2
Hatch yr is marked with a spot of colour by beekeeper
Can sting multiple times – often reserved for rival queens
Can buy and be sent by post
drones
Hundreds of drones in summer months, all male
Don’t work in hive or forage
Sole purpose is to mate with queen
Die after mating and others die/ cast out in winter
No sting
Drone larvae more likely to have/ produce more varroa mite
workers
Sterile females
35-60,000 per hive
Do all work
Nurse, feed young and queen, cleam and tidy hive, collect and use propolis to seal hive, collect water, nectar and pollen, make wax and honey, guard hive entrance
Produce 1 teaspoon of honey in entire life
Life span – 6 weeks in summer or 6 months over winter
life of worker bee
0-6 days = cell and hive cleaning
3-9 days = feeding the brood
3-15 days = attending the queen
6-18 days = honey processing
12-20 days = wax production and comb building
15-25 days = hive ventilation
18-35 days = guard duty
20 - death = nectar collection and pollen collection
25 - death = water and propolis collection
honey bees husbandry
Hives active only between spring and autumn when food is available
Nectar = sugar solution = carbohydrate = energy now and honey to store for energy over winter
Pollen = protein, particularly to feed brood
Nectar is reward plants give to insects to attract them to spread pollen between plants to fertilise them
Over winter queen and workers reduce their metabolic activity and survive on honey reserves they produce during summer
Cluster with queen in middle to make sure she survives
Beehive smoker = used to calm bees during inspection
what triggers swarming
Dilution of/ not enough of queen pheromone
Overcrowding
Bees determine that they have a chance to multiply and produce another colony that can survive next winter
Enough bees to split colony
Enough food stored in current colony
Enough food in environment to set up another colony
Weather
other factors to bee husbandry
Registering bees
Regular inspections
Keeping records
Controlling swarming
Controlling disease, infestation and predators
Harvest honey
Preparing hives/ bees to over-winter and feeding as necessary
bee inspections
Weekly in summer
Look for eggs/ healthy brood
Confirm presence of queen
Remove unwanted queen cells
Manipulate hive/ bees to prevent swarming
Look for diseases/ pests
Best carried out in good weather as many bees flying so fewer at home to sting
pollen
Food source – protein
Collected into pollen baskets
In honey – oral dose to reduce allergy to local pollen
Harvested from hive to be eaten
nectar → honey
Honey is bees winter food reserve
Leave enough for hive to eat over winter and or replace with sugar syrup or fondant
honey harvesting
Manual
Cut comb
Mashing
Centrifuge