TOPIC 2- 23. The afferent and efferent pathways of the cerebellum. The functions of the cerebellum
The cerebellum is responsible for unconscious coordination, and fine control of muscle actions
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Related to the motor system
- extrapyramidal system
What is the cerebellum related to?
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
The cerebellum is responsible for unconscious coordination, and fine control of muscle actions
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Related to the motor system
- extrapyramidal system
What is the cerebellum related to?
Anterior spinocerebellar tract
Which of the afferent tracts enter the cerebellum through the superior cerebellar peduncle?
Pontocerebellar tracts:
- Türk
- Arnold
Which of the afferent tracts enter the cerebellum through the middle cerebellar peduncle?
- Posterior spinocerebellar tract
- Vestibulocerebellar tract
- Reticulocerebellar tract
- Trigeminocerebellar tract
- Olivocerebellar tract
Which of the afferent tracts enter the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle?
- Cerebellothalamic tract
- Cerebellorubral tract
Which of the efferent tracts exit the cerebellum through the superior cerebellar peduncle?
None
Which of the efferent tracts exit the cerebellum through the middle cerebellar peduncle?
- Cerebelloreticular tract
- Cerebellovestibular tract
- Cerebelloolivary tract
Which of the efferent tracts exit the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle?
- Anterior lobe
- Posterior lobe
- Flocconodular lobe
Which are the lobes of the cerebellum?
Anterior lobe
1
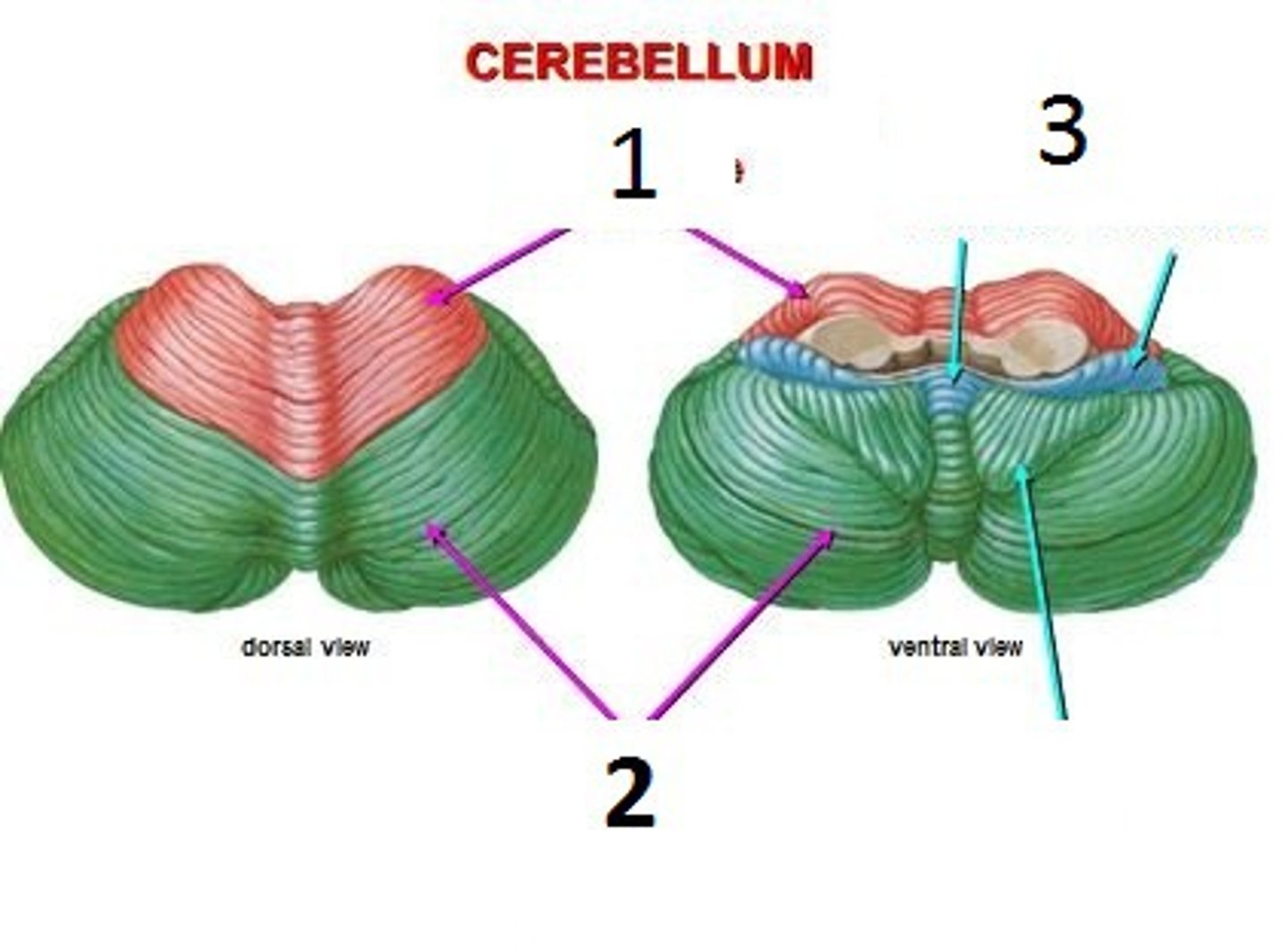
Posterior lobe
2
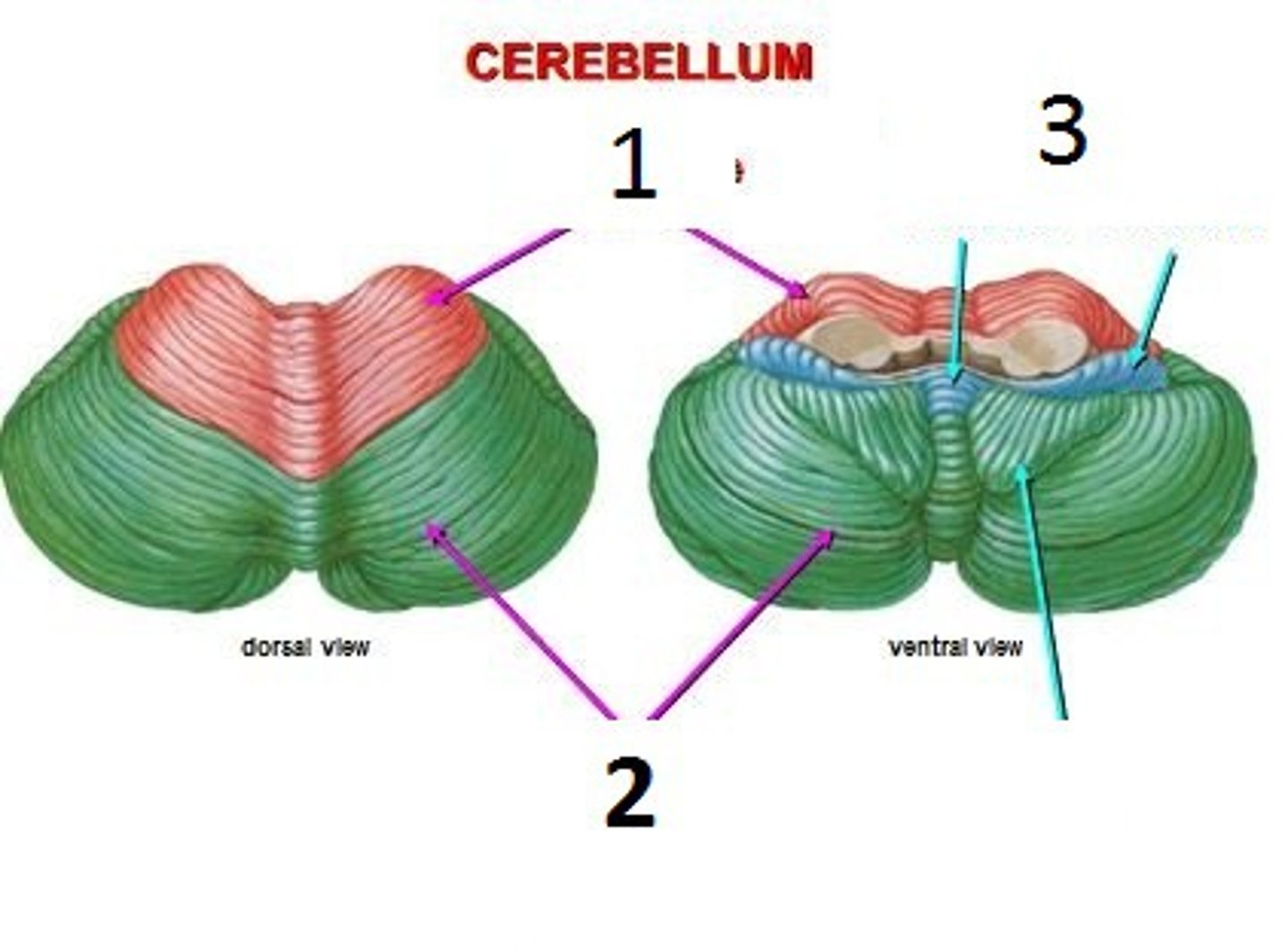
Flocconodular lobe
3
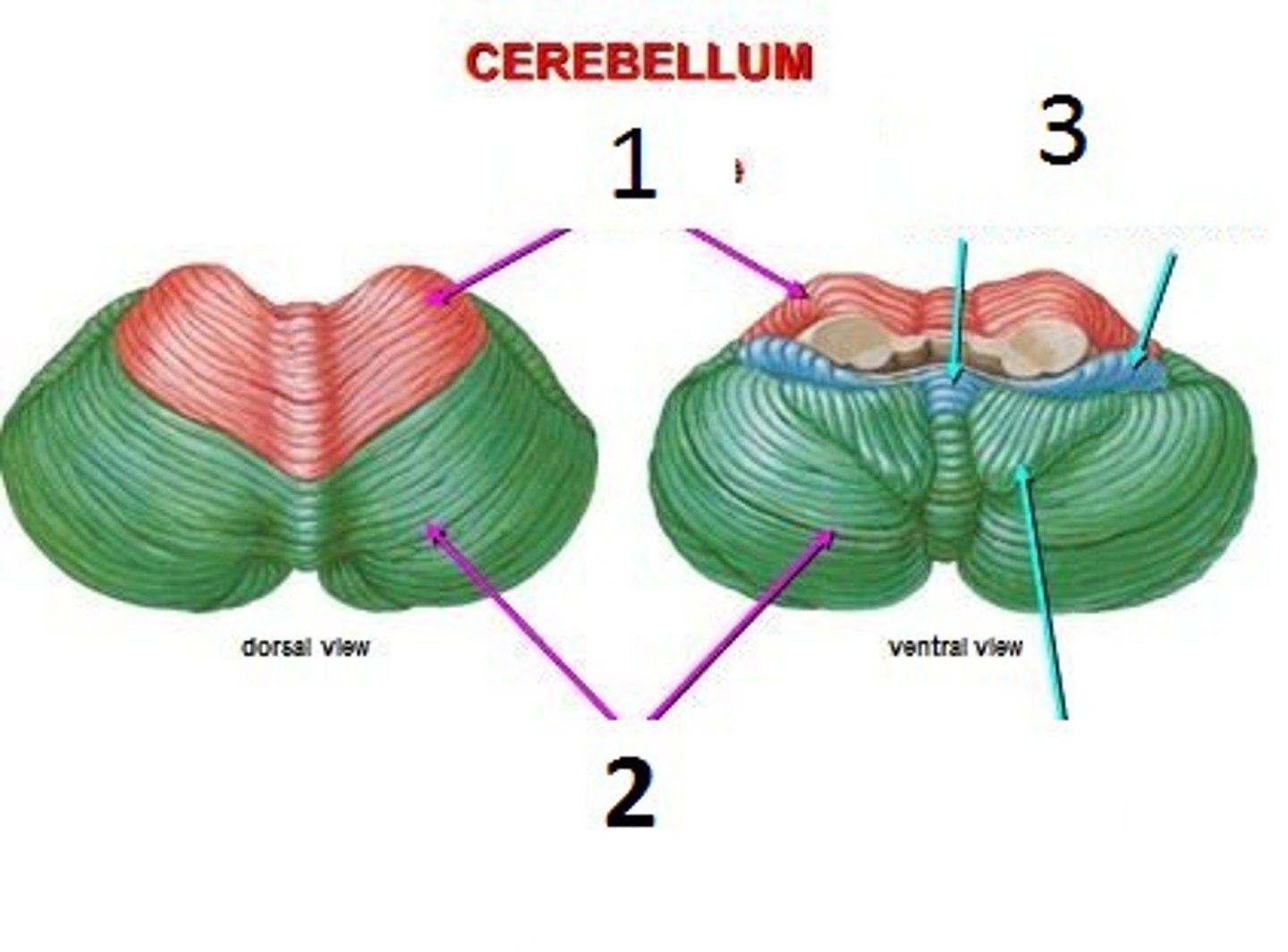
- Vestibulocerebellum = Archicerebellum
- Spinocerebellum = Paleocerebellum
- Pontocerebellum = Neocerebellum
How can we functionally divide the cerebellum?
No direct contact with the lower motor neurons
- but exerts control through cerebral cortex and brainstem
How does the cerebellum have contact with the lower motor neurons?
Ipsilateral
Does the cerebellar hemispheres control the muscles on the ipsilateral or contralateral side?
Balance
What is the vestibulocerebellum mostly related to?
Vestibulocerebellar tract
Which are the afferent pathways of the vestibulocerebellum?
Position and movements of the head
What kind of information does the vestibulocerebellum recieve through its afferent connections?
From the medial, superior and inferior vestibular nuclei
From which vestibular nuclei does the vestibulocerebellar tract go from?
Cerebellovestibular tract
Which are the efferent pathways of vestibulocerebellum?
To the lateral vestibular nuclei
- vestibulospinal tract
To which vestibular nuclei does the cerebellovestibular tract go? how is the continuation?
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
Through which peduncle does the connections of vestibulocerebellum reach the cerebellum?
- Vestibular nuclei -> vestibulospinal tract
How is the vestibulocerebellum in contact with the lower motor neurons?
Crosses and terminates in the red nucleus
- rubrospinal tract
- some fibers go to the inferior olivary nucleus
Where does the cerebellorubral tract go? and how is its continuation?
Crosses and terminates in the contralateral thalamus in ventrolateral nucleus
- from the thalamus the fibers are projected to the cortex, through superior/middle thalamic radiation
Where does the cerebellothalamic tract go? and how is its continuation?
Control of execution of fine movements
What is the function of the cerebellothalamic tract?
Terminate in the reticular formation
- reticulospinal tract
Where does the cerebelloreticular tract go? and how is its continuation?
- Frontopontine tract (Arnold)
- Temporo-parieto-occipito pontine tract (Türk)
What are the two pontocerebellar tracts?
- Fibers from cerebral cortex descend through the internal capsule, then through the cerebral crus - to the pons
- Transverse fibers of pons, cross the midline and enter contralateral cerebral hemisphere through middle cerebellar peduncle
Explain the pontocerebellar tracts?
Middle cerebellar peduncle
Through which peduncle does the pontocerebellar tract reach the cerebellum?
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
Through which peduncle does the olivocerebellar tract reach the cerebellum?
Medulla oblongata
Where is the inferior olivary nucleus located?
Originates mostly from dentate nucleus, and a small part from interposed nucleus
Which nucleus does the cerebellothalamic tract originate from?
Originates mostly from interposed nuclei, and a small part from dentate nucleus
Which nucleus does the cerebellorubral tract originate from?
Originates form fastigal nucleus
Which nucleus does the cerebelloreticular tract originate from?
Originates from fastigial nucleus
Which nucleus does the cerebellovestibular tract originate from?
Originates from dentate nucleus and interposed nuclei
Which nucleus does the cerebelloolivary tract originate from?