Molecular interactions and reactions
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
When energy is released from the system
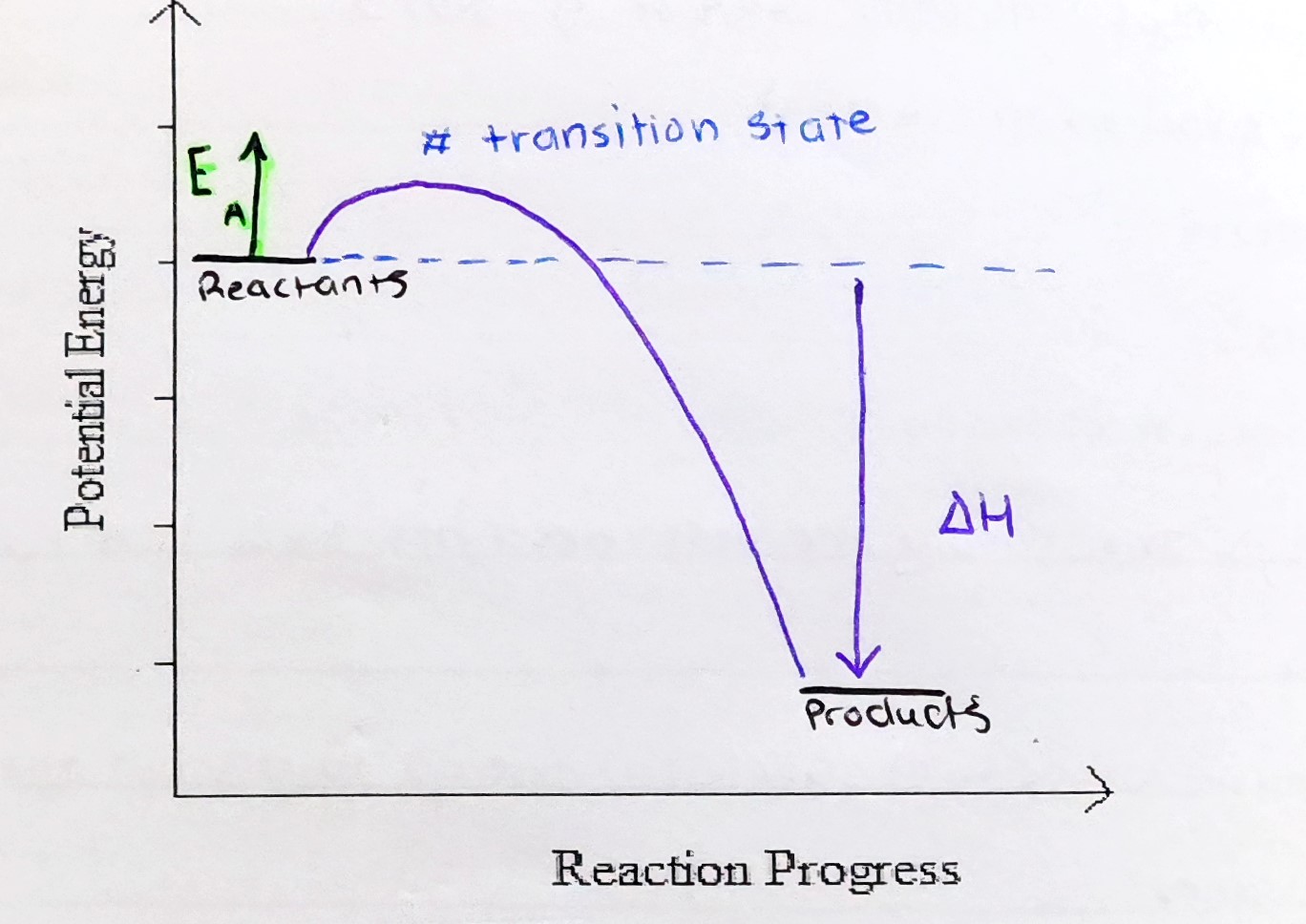
When the reactants have more potential energy than the products and the excess is released via heat or light (exothermic)
System of a chemical reaction
The collection of atoms or molecules involved in change. Usually a chemical reaction
Surroundings
Anything that is present around the atoms and molecules
Exothermic reactions
A change where energy is released from the system to the surroundings. Enthalpy of the system is reduced
Endothermic reactions
A change where energy is absorbed into the system from the surroundings. Enthalpy of the system is increased
Enthalpy
Stored chemical potential energy within a substance
Effect of endothermic reactions on surroundings
Temp OFTEN increases
Effect of endothermic reactions on surroundings
Temp OFTEN decreases
Exothermic changes of state
Condensation, freezing, deposition
Endothermic changes of state
Evaporation, melting, sublimation
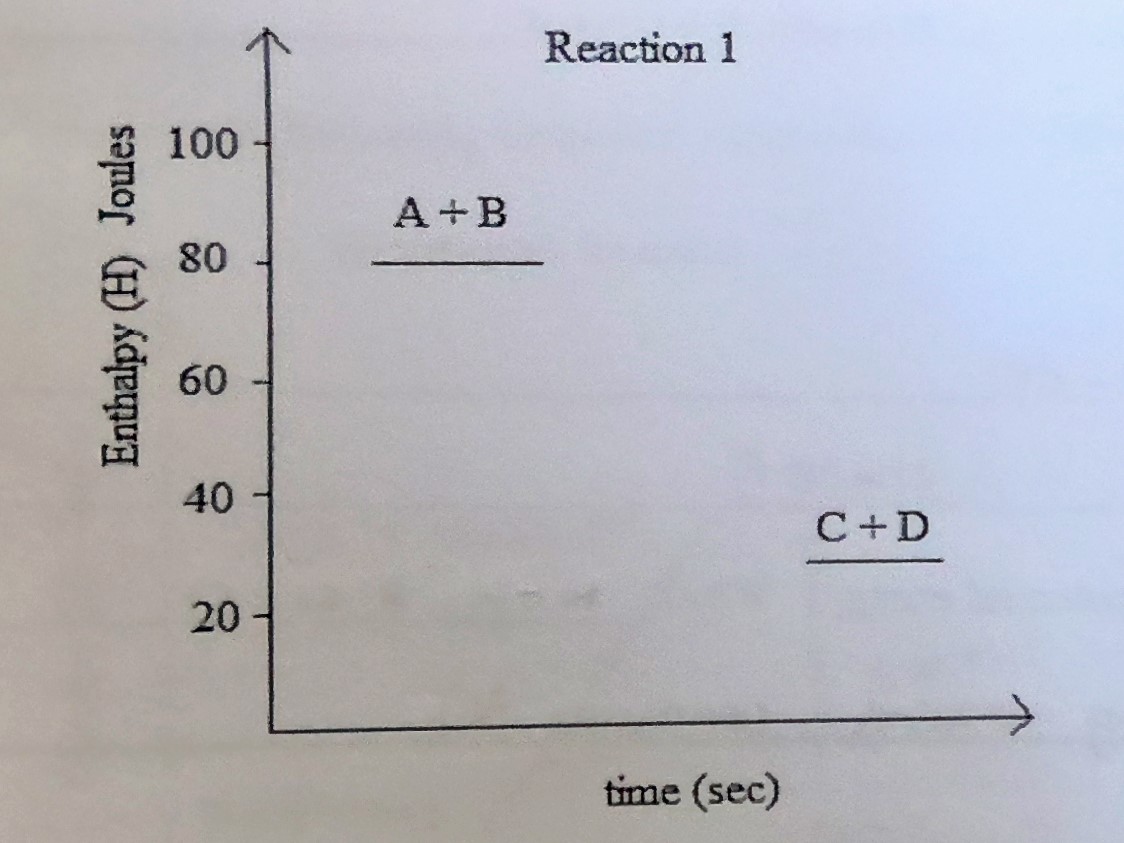
Energy equation
A+B —> C + D + E (50J)
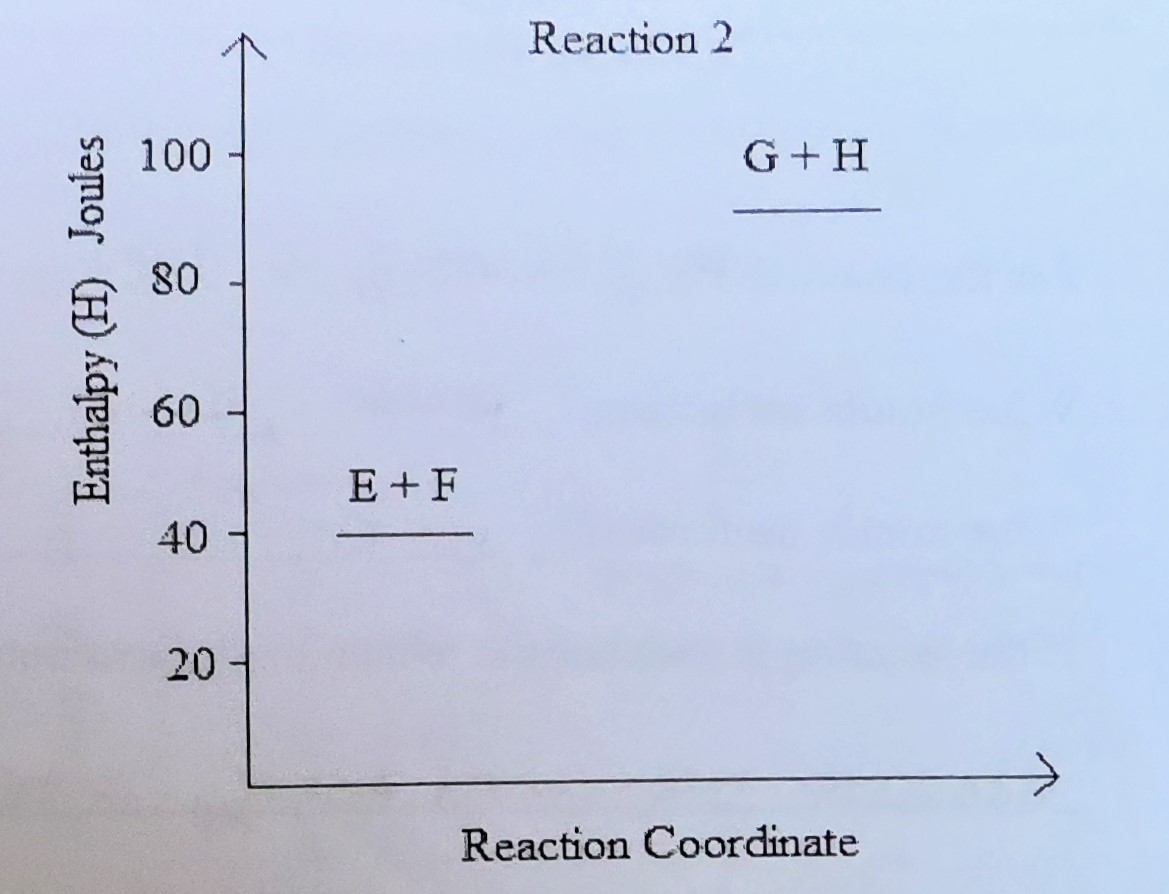
Energy equation
E (50J) + E + F —> G + H
Exothermic enthalpy association
Decrease of enthalpy in a system
Endothermic enthalpy association
Increase of enthalpy in a system
Stored potential energy dependance
The number and strength of the bonds in a substance
Exothermic reactions greater potential energy
Reactants
Exothermic reactions lesser potential energy
Products
Endothermic reactions greater potential energy
Products
Exothermic reactions lesser potential energy
Reactants
Delta H formula
Products - reactants
Endothermic reactions H value
Positive
Exothermic reactions H value
Negative
Baking a cake
Endothermic (BAC)
Making Jelly
Endothermic (MJ)
Cellular respiration
Exothermic
Methods of determining reaction rate
Rate which reactants disappear, rate at which products appear.
Reaction between CaCO3 and HCl (Products CaCl2, CO2, H2O)
Mass of CaCO3 will decrease, the concentratio of H+ ions will decrease, The volume of CO2 gas will increase, The concentration of Ca2+ ions will increase
Rate of reaction formula
Amount of substance used or produced/time taken
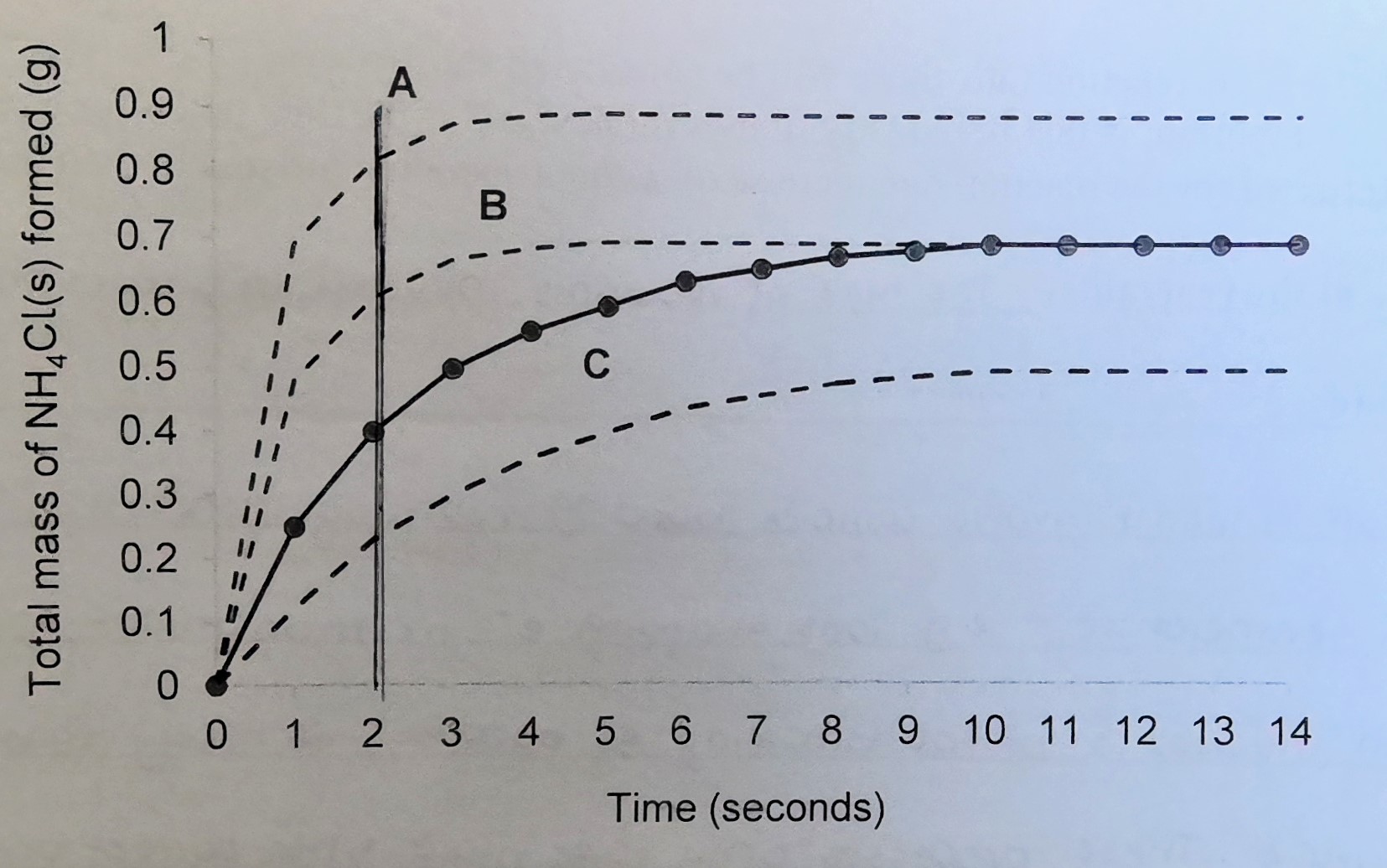
Slowest reaction rate
C
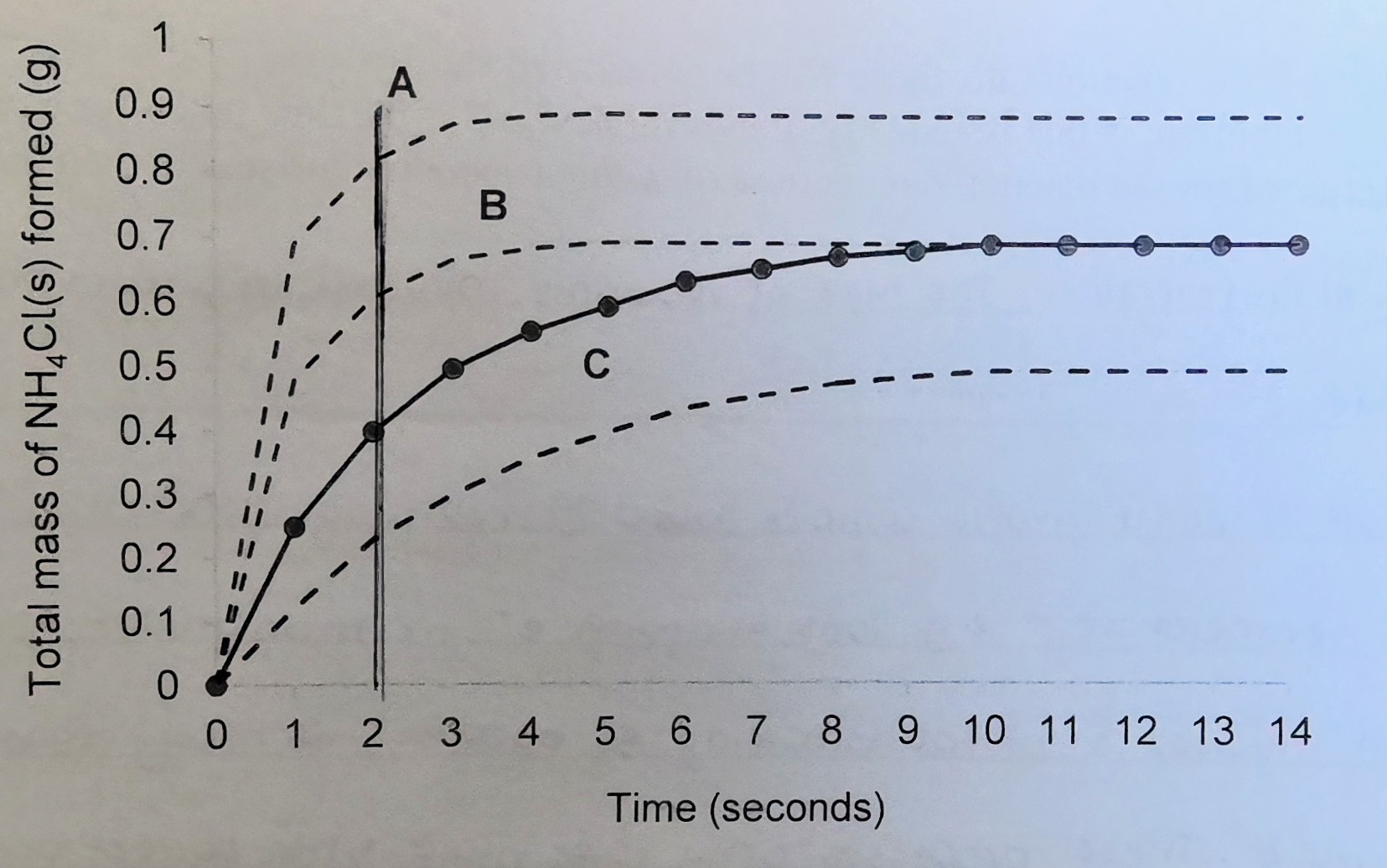
Fastest reaction rate
A
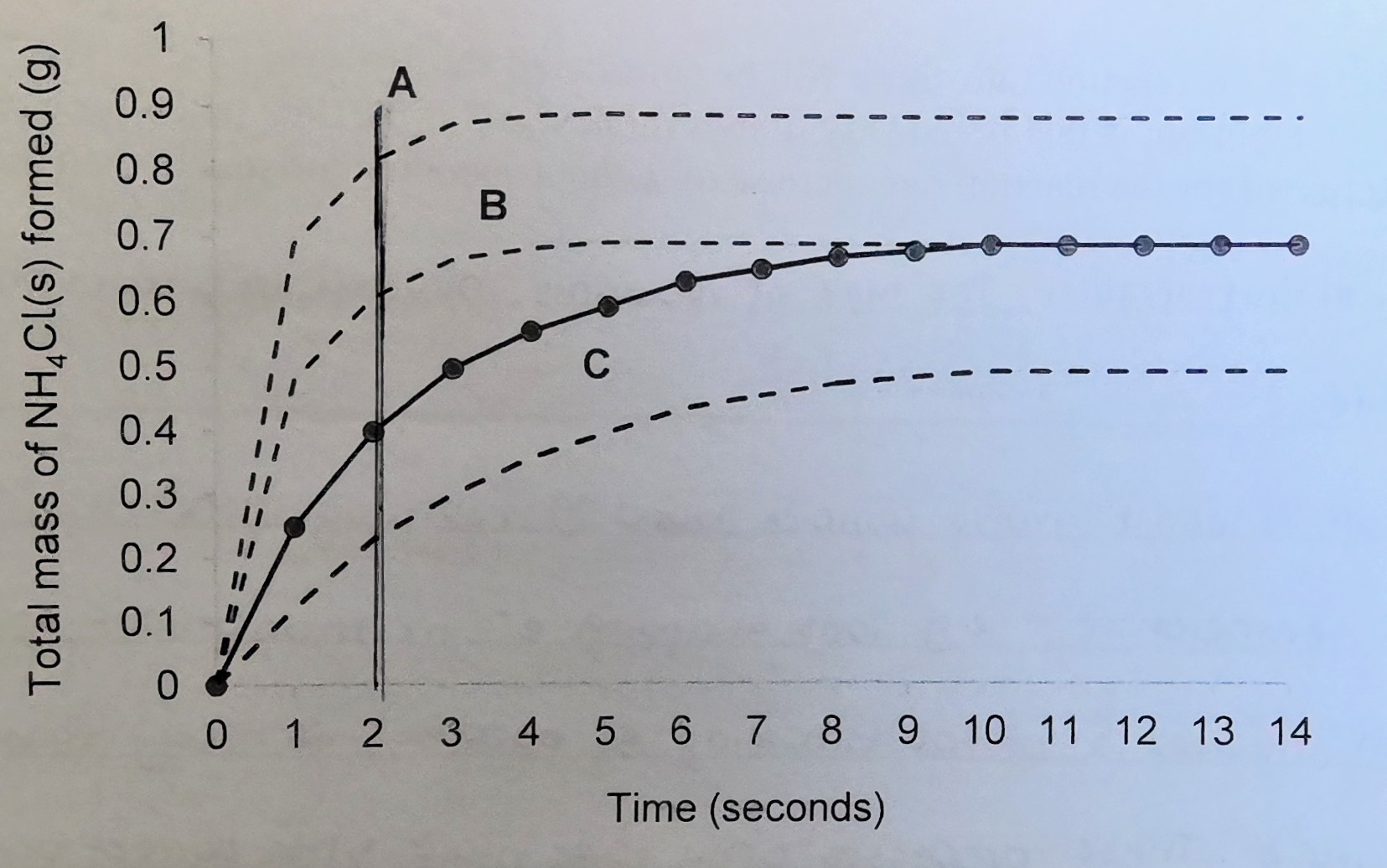
Most product formed
A
Nature of reactants
No complex bonding - fast, complex bonding - slow
Concentration of reactants
Gases or aqueous solutions - more particles per unit volume, more collisions
State of subdivision
Solids or liquids - Particles get smaller, SA increases, more likely to contact other reactants.
Temperature
All reactions - Particles move faster and with more kinetic energy. Collision is more likely to occur with enough energy to disrupt bonds.
Catalysts
Increases RR without permanent consumption - Alternative pathway with lower activation energy.
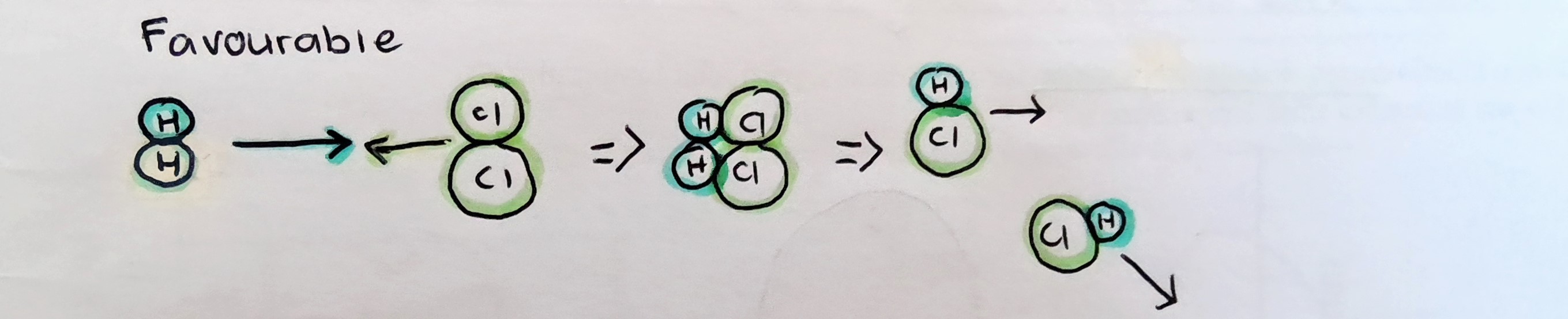
Collision theory
The theory that best describes how the RR can be affected by different factors.
Molecules must collide with enough energy to disrupt bonds
Molecules must collide with a suitable orientation for bond formation and breaking
Favourable orientation
.
Unfavourable orientation
.
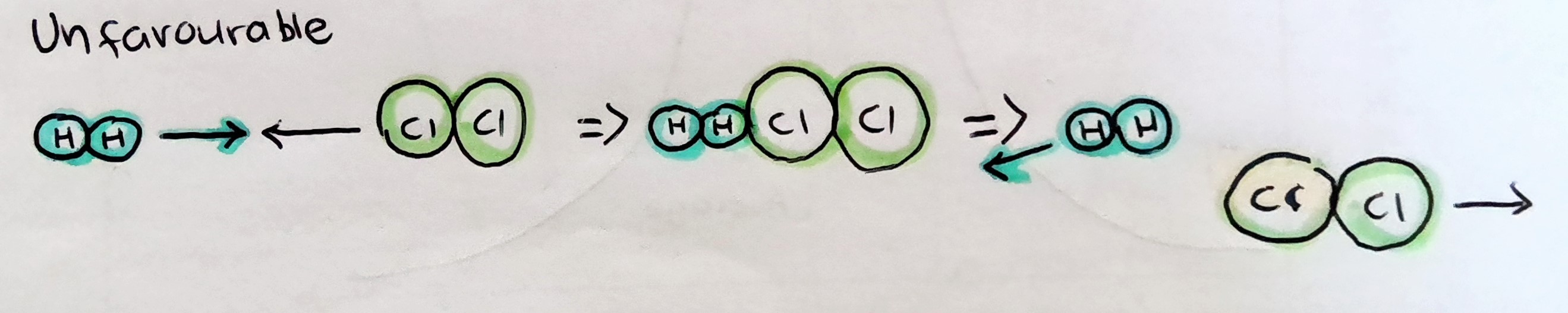
Energy profile diagram
Energy distribution diagram
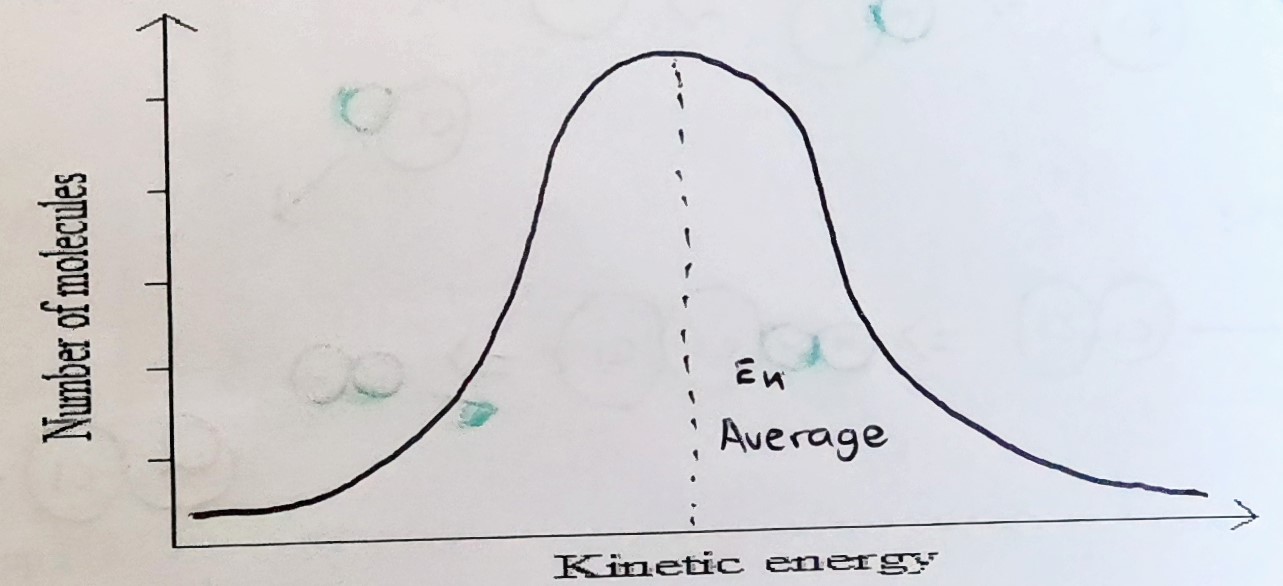
Equal factors
Slower reactions will have higher Ea than faster reactions
Kinetic theory
Increase in temp means an increase in the average kinetic energy of the particles
Haber-Bosch process
Process to produce Ammonia with the catalysts Fe/FeO
Contact process
Process to produce Sulphuric acid with the catalysts V2O5
Margarine process
Process to produce margarine with the catalysts Pt/Ni