Astrophysics Final Exam
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
how do the Balmer and Lyman line series form?
Balmer series, electrons fall to first excited state. Lyman series, electrons fall to the ground state.
What is the Doppler effect? Give one example for its use in astronomy
Change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. Can be used to determine radial velocity of celestial objects.
How do we measure stellar masses?
Using Kepler’s third law as well as Newton’s laws from orbital periods that are observed.
What is an ellipse?
Oval shape, the sum of the distances from any point on the curve to two fixed points, foci, is always constant.
What is stellar parallax and what is it used for?
Apparent shift of position of nearby stars against the background of other stars. Used to determine distance to the star.
What is apparent magnitude? How much brighter is a star with magnitude 6 compared to a star with magnitude 1
The measured brightness of a celestial object as observed from earth. 100 times brighter.
What is absolute magnitude
The measured intrinsic brightness of a celestial object, calculated as if it were at a standard distance of 10 parsecs from Earth.
Kepler’s First Law
Planets move in elliptical paths with the Sun at one focus
Kepler’s Second Law
A line from the sun to a planet sweeps equal areas, meaning planets speed up near the sun and slow down farther away.
Kepler’s Third Law
P² is proportional to a³
What is the main use of Newton’s version of Kepler’s 3rd law
To determine the masses of distant celestial objects.
For an elliptical orbit what happens when the planet is closest vs farthest from the star
When the planet is closest to the star it speeds up, when the planet is farthest from the star it slows down
What trajectories arise from negative and positive values of E?
There are not negative values of e, if e is less than 1 it is an elliptical orbit, greater than one yields a parabolic trajectory.
Black body radiation
The electromagnetic radiation emitted by an idealized object that absorbs all incident radiation and radiates energy across a spectrum of wavelengths
How does the total energy radiated per unit area depend on the temperature?
Stefan-Bolztmann Law, energy per area is proportional to T^4
How does the peak of the emitted energy depend on the temperature
The peak of emitted energy shifts to shorter wavelengths as an object’s temperature rises, Wien’s law
The angular resolution of a telescope depends on what variables and in what way?
The wavelength of light, and the diameter of its primary mirror or lens. Smaller angles (better resolution) comes from shorter wavelengths and larger diameters.
The four fundamental stellar equations, what is the physical meaning of each side in each equation?
What is the Boltzmann equation?
Determines the population of atomic/ionic energy levels
What is the Saha equation?
Describes the ionization state of a gas in thermal equilibrium. Relates temperature, pressure, and energy needed for ionization.
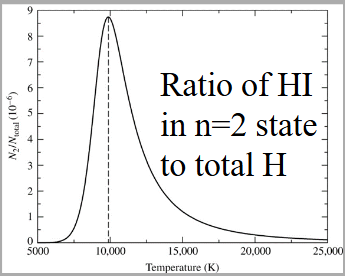
How do they together explain this plot?
Combined they determine the strength of an absorption line

Why is the temperature at the peak similar to the surface temperature of A stars?
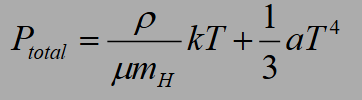
What are the two terms in the following equation?
Why does a photon emitted at the sun’s center take many thousands of years to get out of the sun?
Photons are constantly absorbed and re-emitted as the sun is very dense, causing a photon to take a random path, which takes a long time.
Why does a neutrino emitted at the sun’s center takes only 2.3 seconds to get out of the sun?
It travels at nearly the speed of light and does not interact with the sun’s dense matter as often as photons do
What is Thomson scattering and what is the Thomson cross section?
The scattering of low energy photons by electrons, mainly changing direction. Cross section is a measurement of the probability of the interaction.
How does the sun produce its luminosity
Nuclear fusion
What is the Gamow peak?
It represents the narrow energy range where most nuclear fusion reactions occur in stars
In the main thermonuclear reaction in the sun one element is converted to another element, what are these elements? How many nuclei of the first element are converted into one nucleus of the 2nd?
Four hydrogen nuclei fuse to form a helium nucleus
What is the eddington luminosity?
Theoretical maximum brightness a celestial object can achieve while staying stable. Hydrostatic equilibrium.
What causes the interstellar extinction (dimming of light) in our galaxy
Interstellar dust and gas absorb and scatter light as it travels from distant stars to earth.
What is the jeans mass?
critical mass a gas cloud must exceed to overcome its internal thermal pressure and begin gravitational collapse
What is an eclipsing binary?
two star system where the orbit is nearly edge on from earth’s perspective, one star will pass in front of the other and block its light
What is electron degeneracy pressure?
Comes from Pauli exclusion principle, electrons cannot occupy same state, forcing them into higher energy levels, generating outward pressure
Does temperature play a role in electron degeneracy pressure? Why or why not
No, this effect occurs regardless of temperature
What are the sizes of typical white dwarf and neutron stars?
White dwarfs are earth sized, neutron stars are smaller and dense about 20-40 km in diameter
What is the doppler method for finding exoplanets?
Detects the “wobble” stars make as an orbiting planet’s gravity tugs on it. This is revealed by shifts in the star’s light spectrum (redshift or blueshift)
What is the transit method for finding an exoplanet?
Detecting the slight dip in a star’s brightness as a planet passes in front of it
How does the combination of the doppler and transit methods yields the density of the exoplanet?
Transit method gives the planet’s radius, doppler method gives the mass.