The Respiratory System
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Contains all the key terms, definitions and information about the respiratory system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
The respiratory system (Function)
It’s responsible for supplying the body cells with oxygen and disposes the body of carbon dioxide
it is responsible for gas exchange
It purifies, warms and humidifies incoming air so when it reaches to the lungs it is warm, damp and there is less irritants E.g., dust and bacteria.
Upper respiratory tract
Allows air to move down the lower respiratory tract and eventually to the alveoli. It also warms, filters and moistens the air. How air travel:
Mouth and nose
Oral and nasal cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Oesophagus
Trachea
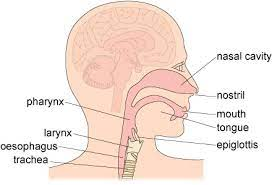
Pharynx
It’s a muscular chamber shared by the respiratory and digestive tract. It's is a pathway for both air and food. It is divided into 3 regions: the nasopharynx, the oropharynx and the laryngopharynx.
The nasopharynx
It's the top part of the throat, a muscular box-shaped passageway the nose. It allows air to pass From the nose into the windpipe and eventually into the lungs.
The oropharynx
It's the middle part of the throat, it contains the tonsils. It allows the air, food and fluids pass through.
The laryngopharynx
Its the most caudal part of the pharynx, its a vital connection point for food, water and air to pass.
Larynx
It’s a voice box which contains the vocal cords. When swallowing, it moves up and forwards so its opening is covered by the epiglottis to divert food and/or liquid to the oesophagus. If anything other than air goes into the larynx it generates a cough reflex to expel the substance.
Epiglottis
Its located in the larynx. A small, leaf-shaped cartilage that protects the larynx and helps with swallowing. Epiglottis blocks food and liquids from entering the larynx and going into the lungs.
Trachea
Has a C-shaped cartilage for protection, It is lined with goblet cells which secrete mucus and it is also lined with cilia. Cilia are small hair-like projection which constantly remove microbes and debris upwards where they can be spat out or swallowed.
Lower respiratory tract
They pull in air from the upper respiratory system, absorb the oxygen and release carbon dioxide in gas exchange.
How air travel:
Right and left bronchus
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
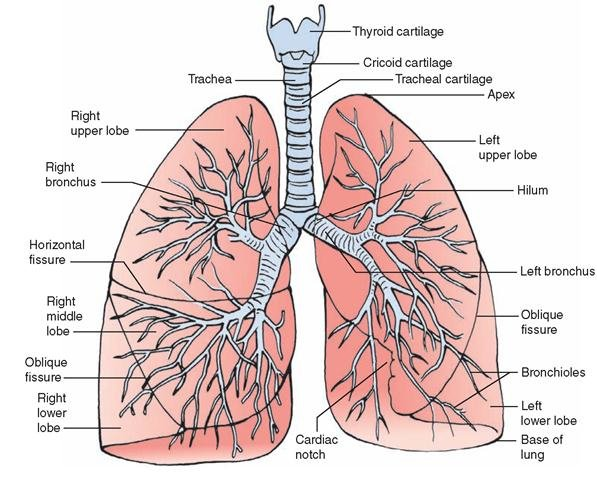
Bronchus
They carry air from and to the lungs. The right main bronchus is wider, shorter and straighter then the left. The air at this stage is warm, humidified and cleaned of most impurities.
Alveoli
Are situated at the terminal of the bronchioles. They are tiny air sacks surrounded by a network of capillaries carrying blood. This is the site of gas exchange, it takes place in the alveoli and surrounding capillaries
They are clustered together in groups which resembles grapes. They make up the bulk of the lungs, so lungs are mostly made up of air space.
what is the estimate amount of alveoli?
It’s estimated 300-500 million alveoli in our lungs so there is a very large surface area.
Gas exchange
It is taking oxygen from the external environment and transporting it to the blood. Gas exchange only takes place on the alveoli. It has a very thin membrane so gas can move easily between the alveoli and the blood.
Lungs
They are two large organs within the thorax on either side of the heart. they are and spongy because they are made up of alveoli (air).
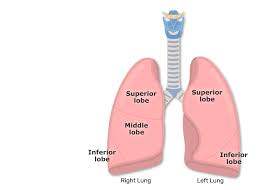
Two lobes of the lungs
Lungs are divided into two lobes:
The left lung has 2 lobes: superior and inferior lobe.
The right lung has 3 lobes: superior, middle and inferior lobe
External respiration
Gas exchange occurs from the blood to the external environment. An example of external respiration is gas exchange in the alveoli.
Internal respiration
Gas exchange from the blood to the tissue.
What percentage of oxygen we breath in?
when we breath in air , the air contains 21% of oxygen.
what is the concentration like in the alveoli and in the blood capillaries?
The concentration breathed into the alveoli is higher then the concentration of oxygen in the blood capillaries that surrounds the alveoli. Therefore the oxygen diffuses across into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide diffuses across from the capillaries.
Lung conditions
Lung conditions such as pulmonary edema and pneumonia make it for gas exchange to occur. In these conditions fluid accumulates the lungs and the alveoli.
Gas exchange (process)
when we inhale all 300 million alveoli expand and fill with air.
oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood.
At the same time, carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli.
after oxygen is diffused is transported by haemoglobin molecules which are found within red blood cells. The blood is then moved by the cardiovascular system.
Alveoli (characteristics)
Large surface area - many alveoli are present in the lungs with a shape that further increases surface area.
Thin walls - alveolar walls are one cell thick providing gases with a short diffusion distance.
Permeable walls - allow gases to pass through.
Pleura
A membrane that surrounds each of the lungs. It is made up of two layers: Parietal pleura and the visceral pleura.
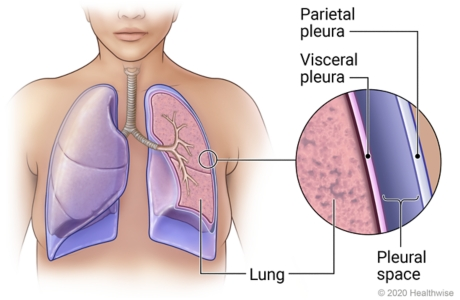
Visceral pleural
It is attached to the outside of the lung
Parietal pleural
Layers the inside of the chest wall and covers the diaphragm
Pleural space
It is the space between the parietal and visceral pleura. It contains a thin film of lubricating fluid called pleural fluid.
The pressure in the pleural space is lower than atmospheric pressure, which holds the pleura together so when the muscle and chest move , the lungs are pulled with it.
Pleural fluid
It reduces friction of the layers allowing them to slide one another when we breath.
It helps the pleura to adhere to one another
Illnesses related to the pleural space
pneumothorax- It is when air gets into the pleura space, which makes it difficult to breath.
pleural effusion- additional fluid in the pleural space
Inspirition
The main muscles used are the diaphragm and intercolestal muscles which contract. This means chest walls and ribs will move out and the diaphragm down bringing the lungs with them. This increases the volume of the lungs and decreases the pressure of the lungs.
Diaphragm
Skeletal muscle which sits underneath the lungs, when its relaxed it is dome shaped and attached to the lung tissue.
Expiration
The diaphragm and rib cage relax back down to their original position, with the ribs moving in and diagphragm moving back up. The volume of the lungs is reduced and pressure is increased.
Control of respiration
Respiration is controlled by the medulla oblagata, in the brain stem. The respiratory centre receives information about the carbon dioxide and oxygen levels within the blood which are monitored by chemoreceptors